Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (8): 1682-1696.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.08.13
Previous Articles Next Articles
Siyuan MA1,2( ), Bochao ZHANG3, Chun PU2(
), Bochao ZHANG3, Chun PU2( )
)
Received:2024-11-28
Online:2025-08-20
Published:2025-09-05
Contact:
Chun PU
E-mail:823545914@qq.com;philipcpu@163.com
Siyuan MA, Bochao ZHANG, Chun PU. Circ_0000437 promotes proliferation, invasion, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells by targeting the let-7b-5p/CTPS1 axis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1682-1696.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.08.13
| Gene name | Primer sequence (s) |
|---|---|
| Circ_0000437 | F:5'-AATCCCCGTACGTCCACTAC-3' |
| R:5'-AGGGTCATAGAAAGGCAGCA-3' | |
| CORO1C | F:5'-ATGAGGCGGCACATATAC-3' |
| R:5'-ATCCCAGGTCACACGAGAAAC-3' | |
| CTPS1 | F:5'-CAGTGTGGGCACAATACTCAA-3' |
| R:5'-CGCTCATAGTTACCCAGGTCA-3' | |
| Notch1 | F:5'-CGAACCCGTGCCAGAA-3' |
| R:5'-CAGATGCCCAGTGAAGC-3' | |
| Hes1 | F:5'-CAGTGCCTTTGAGAAGCAGG-3' |
| R:5'-CAGATAACGGGCAACTTCGG-3' | |
| Numb | F:5'-CACAACTGCCACTGAGCAAG-3' |
| R:5'-GTTGCCAGGAGCCACTGAT-3' | |
| GAPDH | F:5'-CATCAAGAAGGTGGTGAAGCAG-3' |
| R:5'-GTGTCGCTGTTGAAGTCAGAG-3' | |
| let-7b-5p | 5'-GCTGAGGTAGTAGGTTGTGTGGG-3' |
| U6 | 5'-CGCTTCGGCACATATAC-3' |
Tab.1 Primer sequences for qRT-PCR
| Gene name | Primer sequence (s) |
|---|---|
| Circ_0000437 | F:5'-AATCCCCGTACGTCCACTAC-3' |
| R:5'-AGGGTCATAGAAAGGCAGCA-3' | |
| CORO1C | F:5'-ATGAGGCGGCACATATAC-3' |
| R:5'-ATCCCAGGTCACACGAGAAAC-3' | |
| CTPS1 | F:5'-CAGTGTGGGCACAATACTCAA-3' |
| R:5'-CGCTCATAGTTACCCAGGTCA-3' | |
| Notch1 | F:5'-CGAACCCGTGCCAGAA-3' |
| R:5'-CAGATGCCCAGTGAAGC-3' | |
| Hes1 | F:5'-CAGTGCCTTTGAGAAGCAGG-3' |
| R:5'-CAGATAACGGGCAACTTCGG-3' | |
| Numb | F:5'-CACAACTGCCACTGAGCAAG-3' |
| R:5'-GTTGCCAGGAGCCACTGAT-3' | |
| GAPDH | F:5'-CATCAAGAAGGTGGTGAAGCAG-3' |
| R:5'-GTGTCGCTGTTGAAGTCAGAG-3' | |
| let-7b-5p | 5'-GCTGAGGTAGTAGGTTGTGTGGG-3' |
| U6 | 5'-CGCTTCGGCACATATAC-3' |
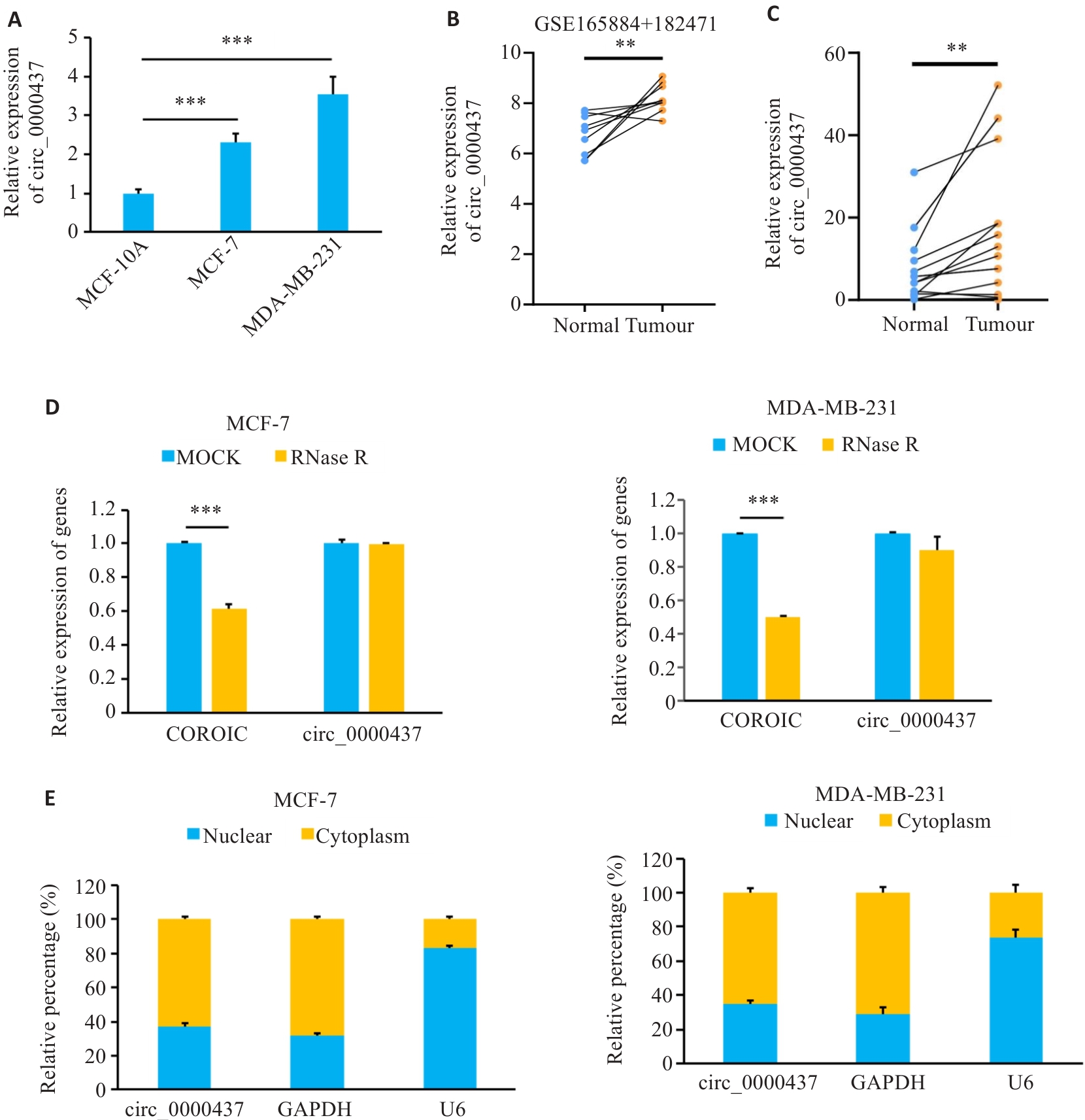
Fig.1 Expression levels of circ_0000437 in breast cancer cells and tissues. A: Expression of circ_0000437 in breast cancer cell line. B: Expression of circ_0000437 in datasets GSE165884 and 182471. C: Expression of circ_0000437 in breast cancer tissues. D: Expression of circ_0000437 and linear CORO1C in two breast cancer cell lines treated with RNase R. E: Subcellular localization of circ_0000437 in breast cancer cells. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.

Fig.2 Effects of circ_0000437 knockdown on proliferation, invasion, migration and EMT of breast cancer cells. A, B: Gene knockout efficiency and fluorescence staining of the cells after lentivirus transfection (Original magnification: ×100). C: CCK-8 assay for assessing the effect of circ_0000437 on cell proliferation. D: Transwell assay for assessing the effect of circ_0000437 on cell invasion (×400). E: Scratch assay for assessing the effect of circ_0000437 on cell migration (×100). F: Western blotting for assessing the effect of circ_0000437 on EMT in breast cancer cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
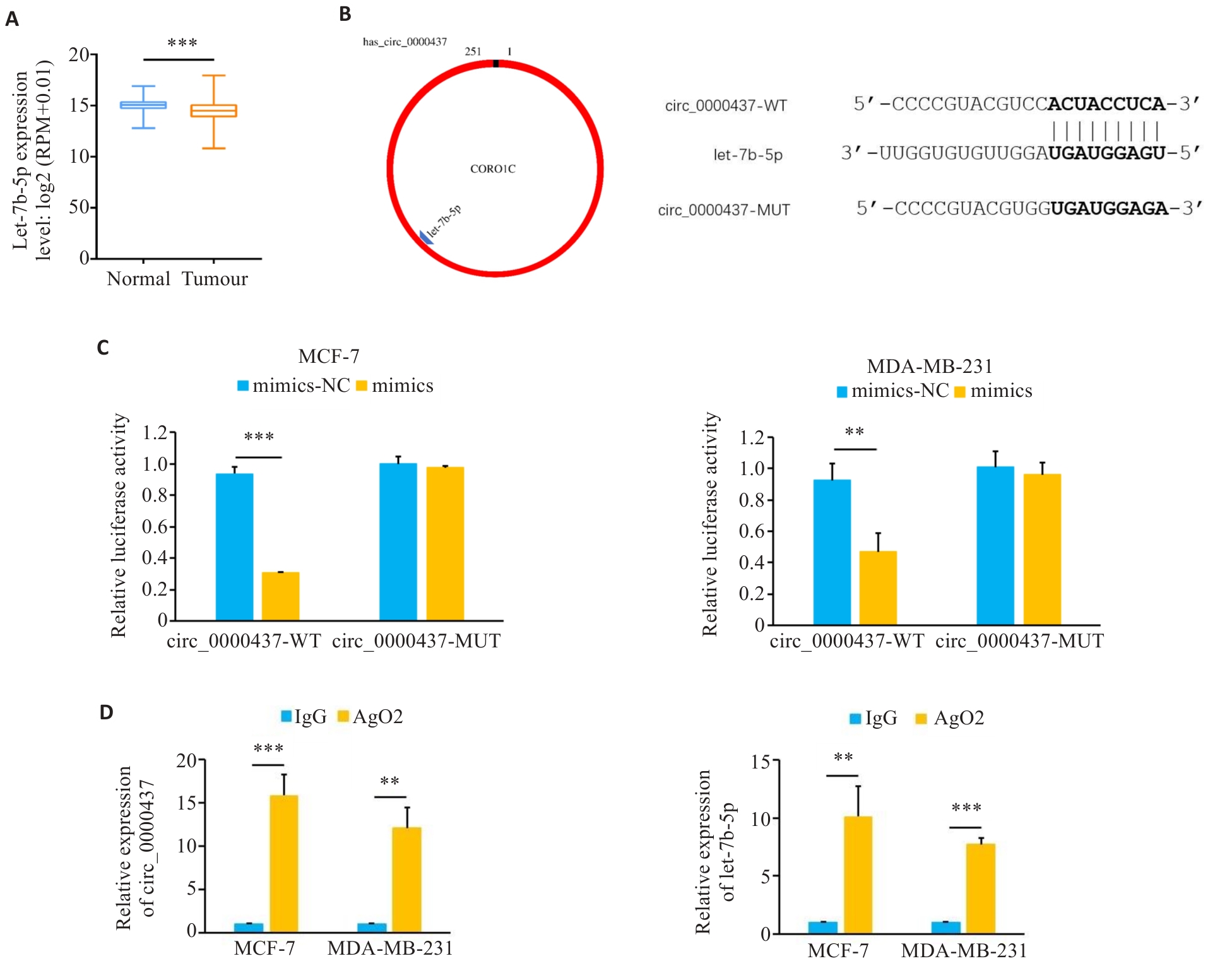
Fig.3 Circ_0000437 has a binding site with let-7b-5p. A: Expression of let-7b-5p in breast cancer in TCGA database. B: The predicted binding diagram and binding sequence of let-7b-5p and circ_0000437. C: Luciferase activity in the cells co-transfected with mimics or mimics-NC and circ_0000437 WT plasmid or MUT plasmid. D: RIP analysis showing enrichment of circ_0000437 and let-7b-5p in the AGO2 part. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
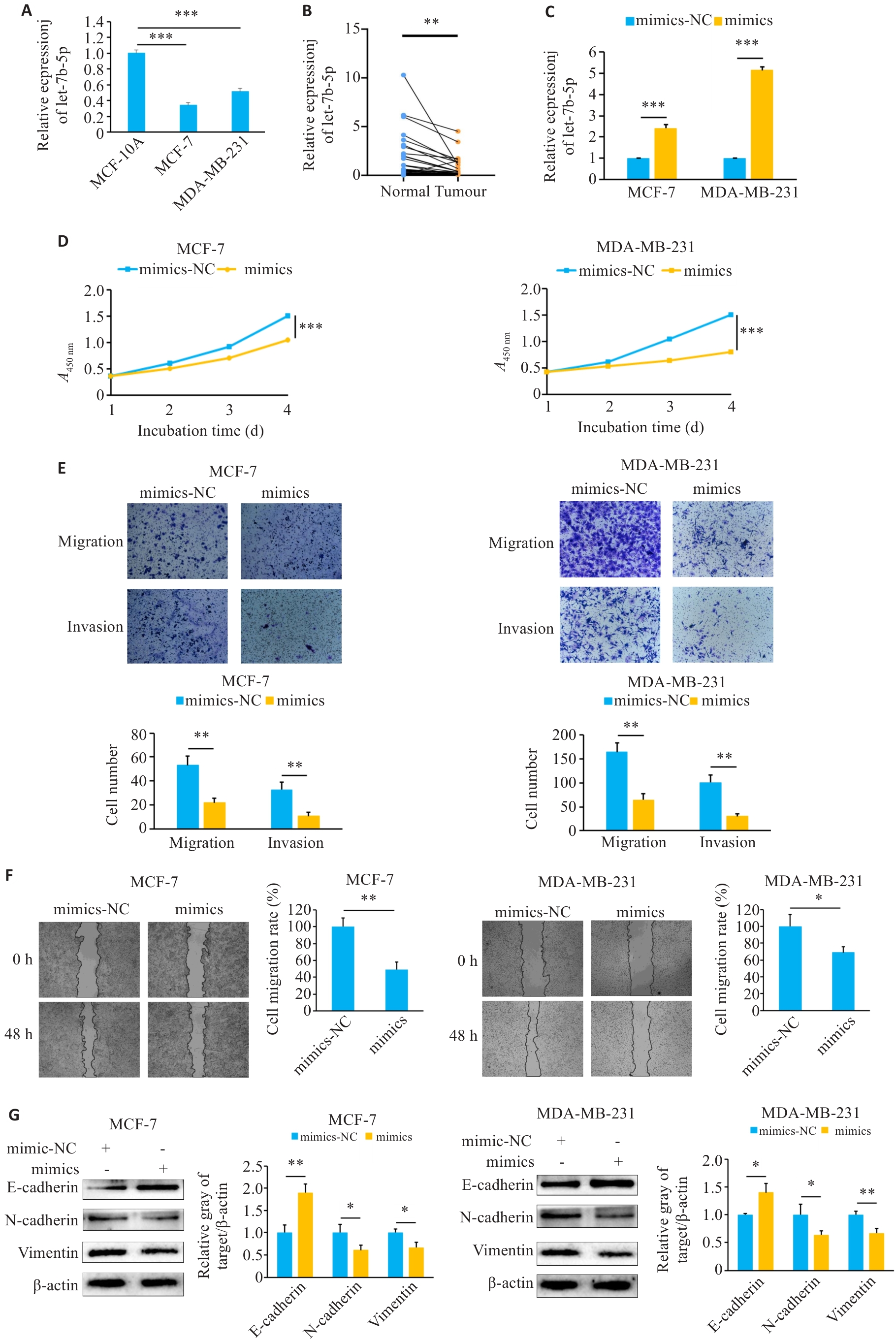
Fig.4 Overexpression of let-7b-5p inhibits proliferation, invasion, migration and EMT of breast cancer cells. A, B: Expression of let-7b-5p in breast cancer tissues and cell lines. C: Transfection efficiency of let-7b-5p mimics. D: CCK-8 analysis to evaluate the effects of mimics on cell proliferation. E: Transwell assay to verify the effect of mimics on cell invasion (×400). F: Effect of mimics on cell migration determined using scratch assay (×100). G: Effect of mimics on EMT in breast cancer cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.

Fig.5 Inhibition of let-7b-5p suppresses proliferation, invasion, migration and EMT of breast cancer cells. A: Transfection efficiency of let-7b-5p inhibitor. B: CCK-8 analysis to evaluate the effects of inhibitor on cell proliferation. C: Transwell assay to verify the effect of inhibitor on cell invasion ability (×400). D: Effect of the inhibitor on cell migration determined using scratch assay (×100). E: Effect of the inhibitor on EMT in breast cancer cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
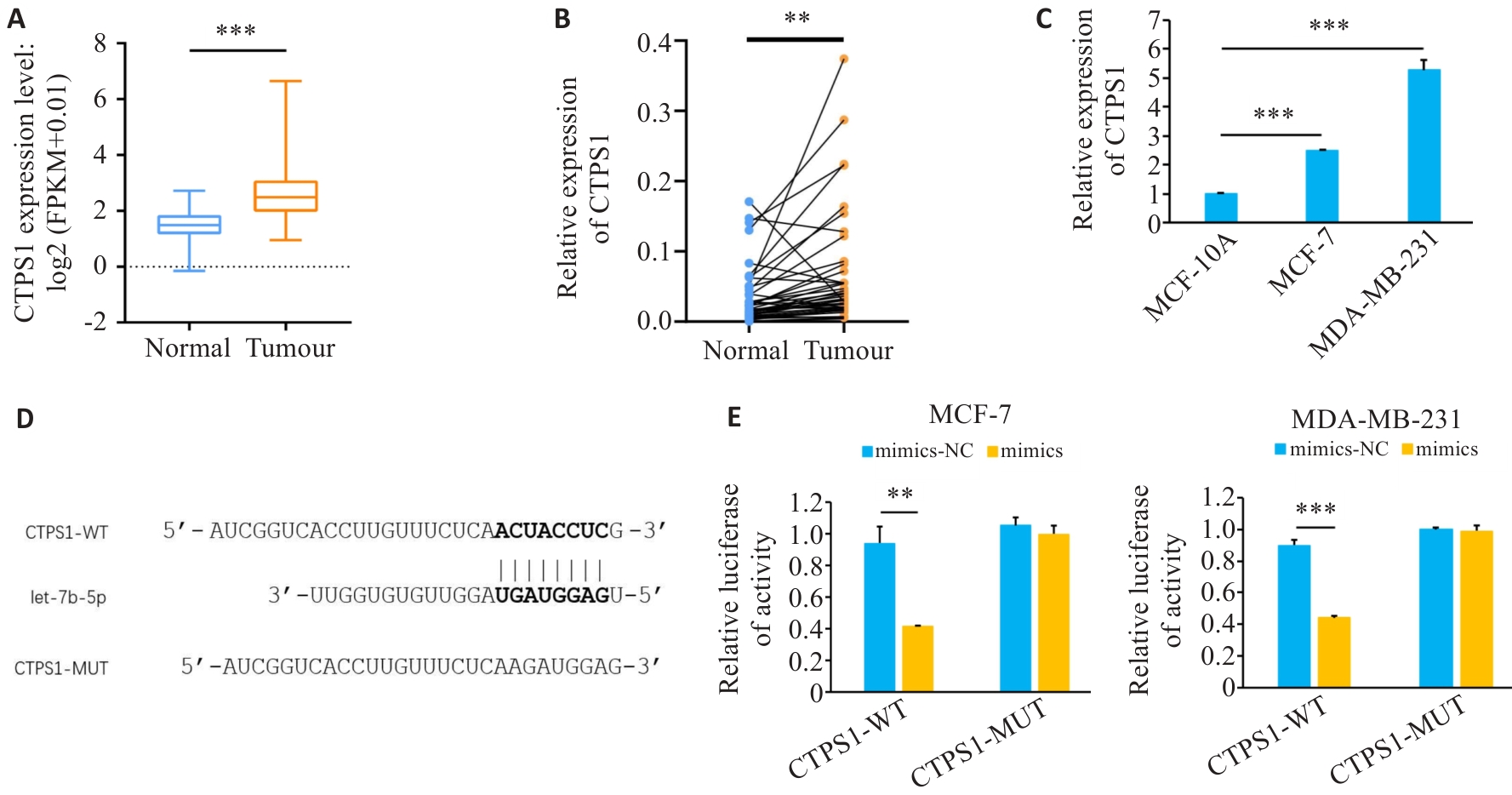
Fig.6 Expression of CTPS1 up-regulated in breast cancer. A: Expression of CTPS1 in breast cancer in TCGA database. B, C: Expression of CTPS1 in breast cancer tissues and cell lines. D: Predicted CTPS1 and let-7b-5p binding sites. E: Mimics or mimics-NC were co-transfected with CTPS1 WT plasmid or MUT plasmid, respectively, and luciferase activity was measured in each group. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
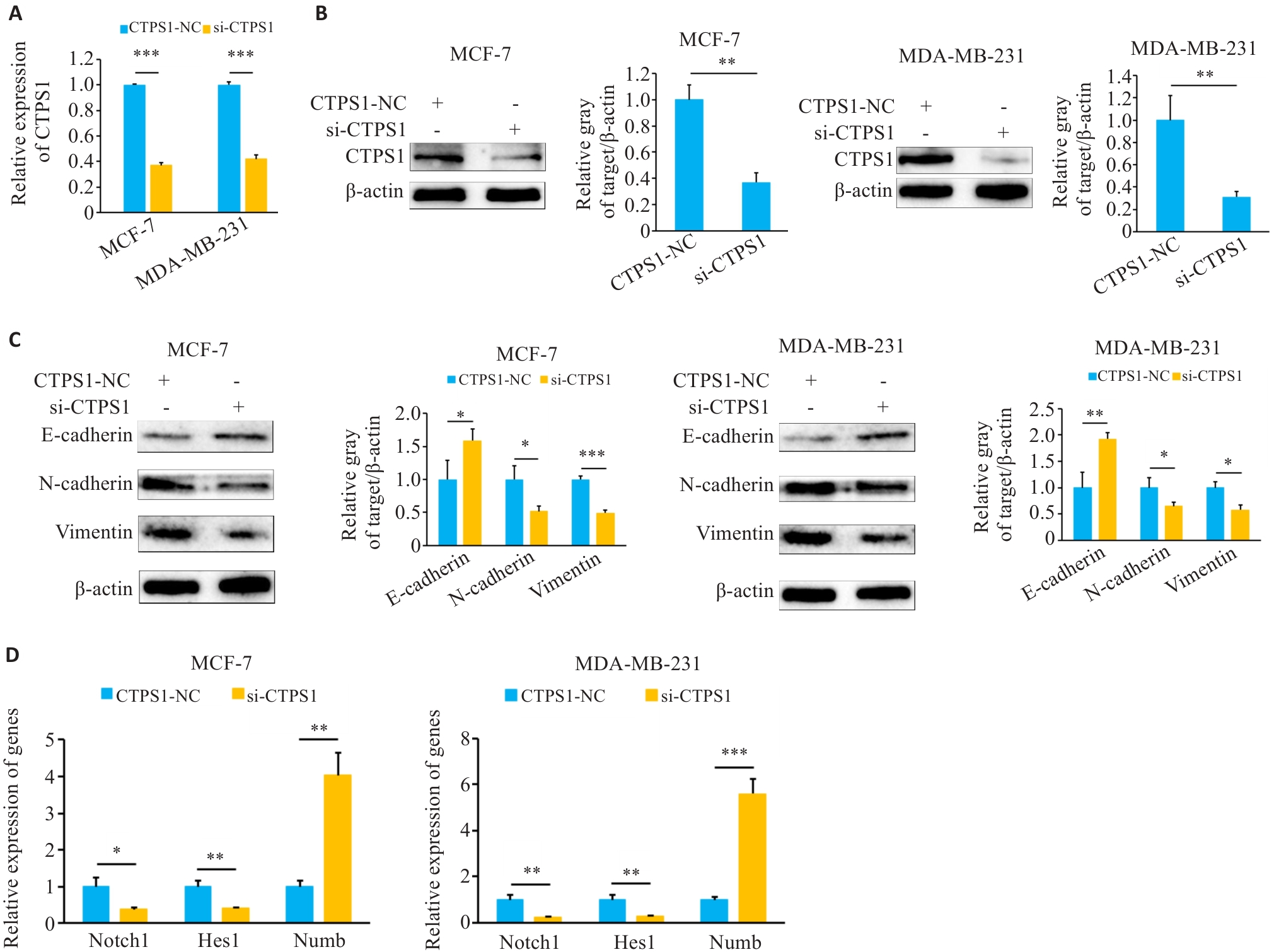
Fig.7 CTPS1 knockdown inhibits EMT and regulates the Notch signaling pathway in breast cancer cells. A: Knockdown efficiency after transfection with si-CTPS1. B: Western blotting for assessing the effect of si-CTPS1 on expression of CTPS1 protein in breast cancer cells. C: Western blotting for assessing the effect of CTPS1 on EMT of breast cancer cells. D: qRT-PCR for assessing the effect of si-CTPS1 on the expression of genes related to the Notch signaling pathway. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.

Fig.8 CTPS1 knockdown inhibits proliferation, invasion and migration of breast cancer cells. A: CCK-8 assay for evaluating the effect of transfection with si-CTPS1 on cell proliferation. B: Transwell assay for assessing the effect of transfection with si-CTPS1 on cell invasion ability (×400). C: Effect of transfection with si-CTPS1 on cell migration determined using scratch assay (×100). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
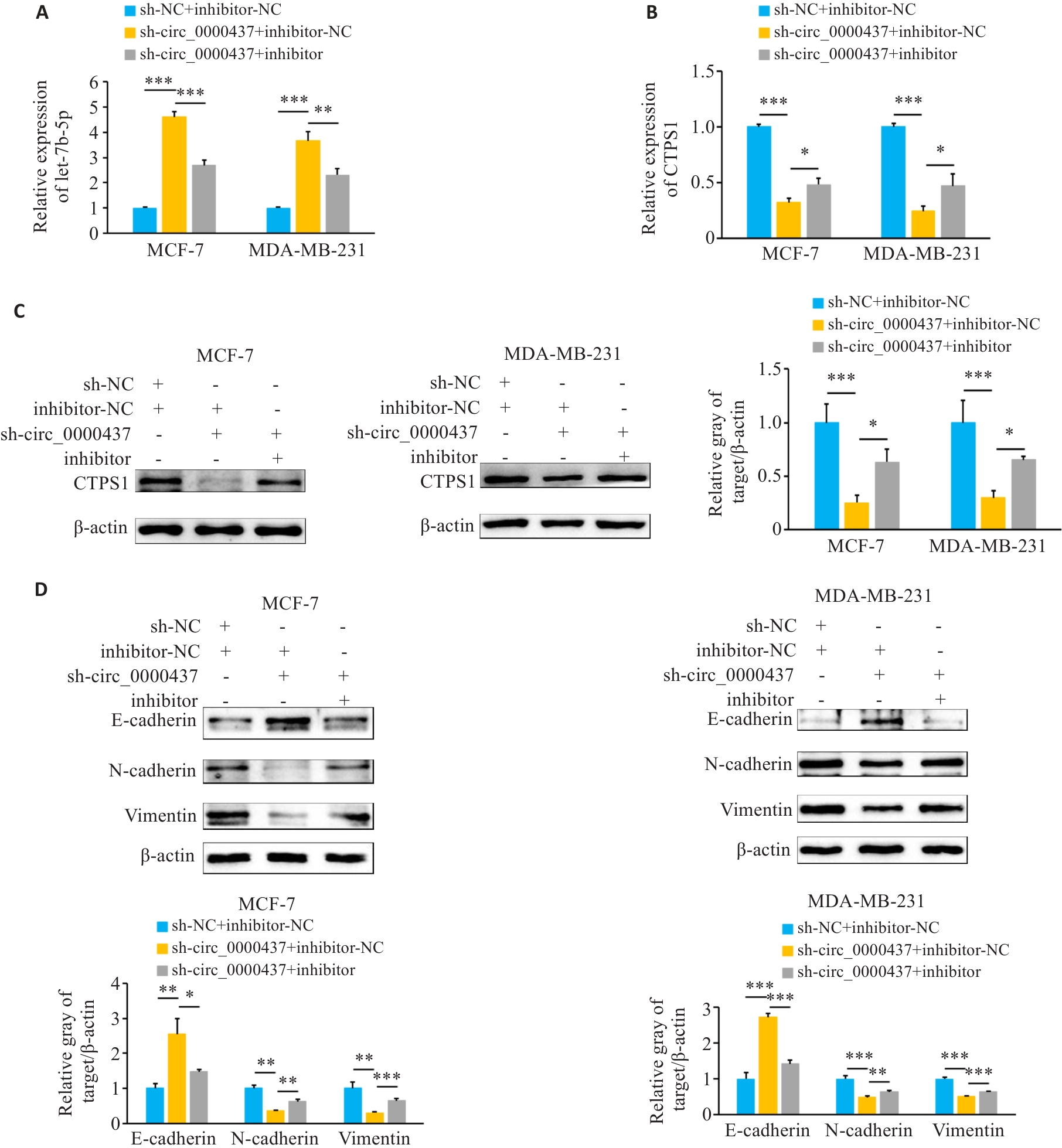
Fig.10 Circ_0000437 promotes EMT in breast cancer cells by regulating the let-7b-5p/CTPS1 axis. A: Expression of let-7b-5p in each group (sh-NC+inhibitor-NC, sh-circ_0000437+inhibitor-NC, and sh-circ_0000437+inhibitor) detected by qRT-PCR. B: qRT-PCR for detecting CTPS1 mRNA expression in breast cancer cells in each group. C: Western blotting for detecting the expression of CTPS1 protein in breast cancer cells in each group. D: Western blotting for detecting the expression of EMT-related proteins in breast cancer cells in each group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.

Fig.11 Circ_0000437 promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration of breast cancer cells as a molecular sponge for let-7b-5p. A: CCK-8 assay of the breast cancer cells. B: Transwell assay of the breast cancer cells (×400). C: Scratch assay of the breast cancer cells (×100). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
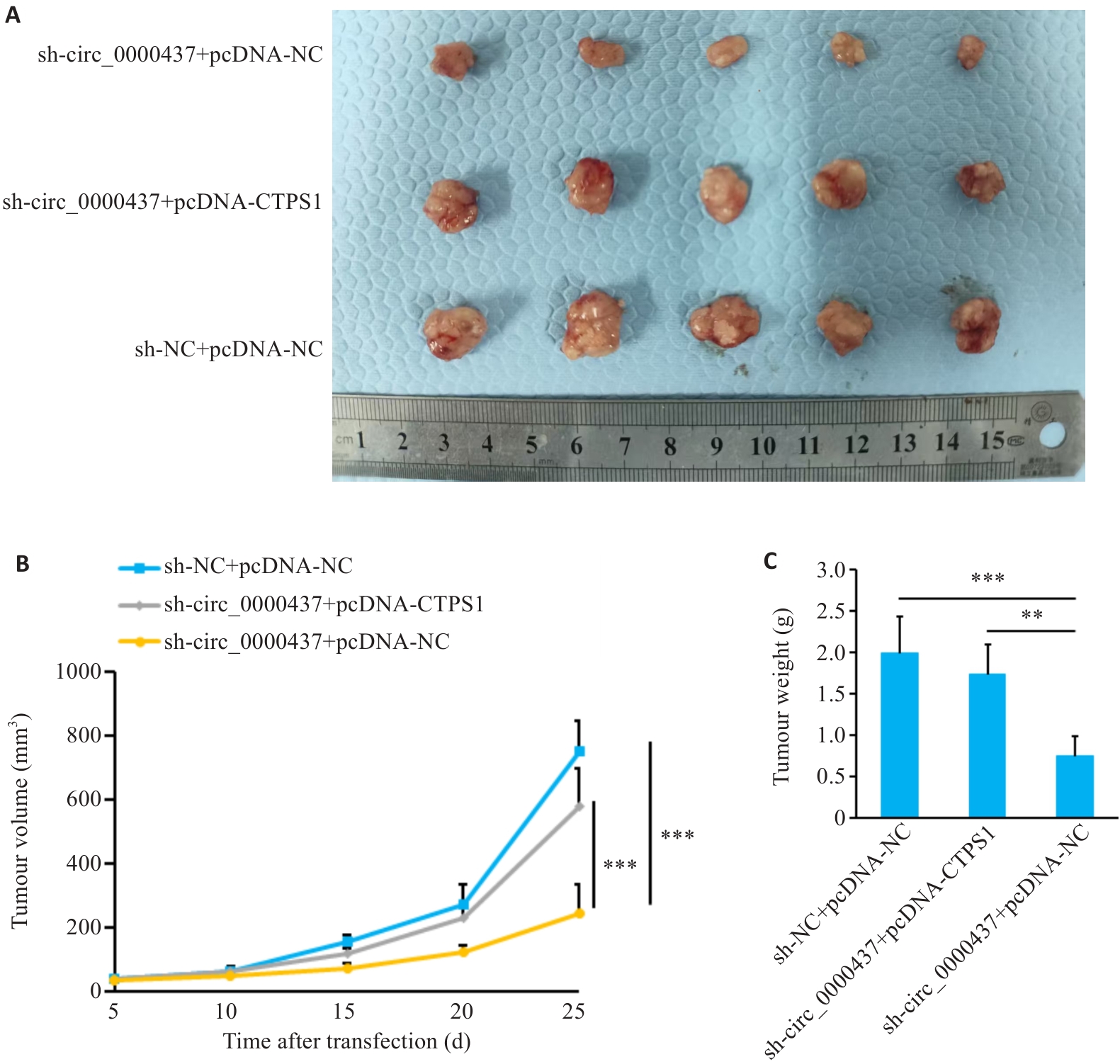
Fig.12 Construction of the tumor-bearing model in mice. A: Comparison of tumor volume 25 days after cell inoculation. B: Tumor growth curve in the mice. C: Comparison of tumor weight. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
| [1] | Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, et al. Cancer statistics[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2023, 73(1): 17-48. doi:10.3322/caac.21763 |
| [2] | Waks AG, Winer EP. Breast cancer treatment: a review[J]. JAMA, 2019, 321(3): 288-300. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.19323 |
| [3] | He X, Xu T, Hu WJ, et al. Circular RNAs: their role in the pathogenesis and orchestration of breast cancer[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 647736. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.647736 |
| [4] | DeSantis CE, Bray F, Ferlay J, et al. International variation in female breast cancer incidence and mortality rates[J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2015, 24(10): 1495-506. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.epi-15-0535 |
| [5] | Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, et al. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs[J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2019, 20(11): 675-91. doi:10.1038/s41576-019-0158-7 |
| [6] | Sharma AR, Bhattacharya M, Bhakta S, et al. Recent research progress on circular RNAs: biogenesis, properties, functions, and therapeutic potential[J]. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2021, 25: 355-71. doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2021.05.022 |
| [7] | Qu SB, Liu ZC, Yang XS, et al. The emerging functions and roles of circular RNAs in cancer[J]. Cancer Lett, 2018, 414: 301-9. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2017.11.022 |
| [8] | Ruan Y, Li Z, Shen YJ, et al. Functions of circular RNAs and their potential applications in gastric cancer[J]. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 14(2): 85-92. doi:10.1080/17474124.2020.1715211 |
| [9] | Lei B, Tian ZQ, Fan WP, et al. Circular RNA: a novel biomarker and therapeutic target for human cancers[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2019, 16(2): 292-301. doi:10.7150/ijms.28047 |
| [10] | Zhang ML, Bai X, Zeng XM, et al. circRNA-miRNA-mRNA in breast cancer[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2021, 523: 120-30. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2021.09.013 |
| [11] | Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, et al. A CeRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language?[J]. Cell, 2011, 146(3): 353-8. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.014 |
| [12] | Pastushenko I, Blanpain C. EMT transition states during tumor progression and metastasis[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2019, 29(3): 212-26. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2018.12.001 |
| [13] | Liu SY, Li LY, Ren DM. Anti-cancer potential of phytochemicals: the regulation of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(13): 5069. doi:10.3390/molecules28135069 |
| [14] | Cao ZQ, Wang Z, Leng P. Aberrant N-cadherin expression in cancer[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 118: 109320. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109320 |
| [15] | Péglion F, Etienne-Manneville S. N-cadherin expression level as a critical indicator of invasion in non-epithelial tumors[J]. Cell Adh Migr, 2012, 6(4): 327-32. doi:10.4161/cam.20855 |
| [16] | Onder TT, Gupta PB, Mani SA, et al. Loss of E-cadherin promotes metastasis via multiple downstream transcriptional pathways[J]. Cancer Res, 2008, 68(10): 3645-54. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-07-2938 |
| [17] | Liu P, Wang ZH, Ou XQ, et al. The FUS/circEZH2/KLF5/feedback loop contributes to CXCR4-induced liver metastasis of breast cancer by enhancing epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. Mol Cancer, 2022, 21(1): 198. doi:10.1186/s12943-022-01653-2 |
| [18] | Tian XL, Yang H, Fang Q, et al. Circ_ZFR affects FABP7 expression to regulate breast cancer progression by acting as a sponge for miR-223-3p[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2022, 13(9): 1369-80. doi:10.1111/1759-7714.14401 |
| [19] | Yang L, Chen YX. Circ_0008717 sponges miR-326 to elevate GATA6 expression to promote breast cancer tumorigenicity[J]. Biochem Genet, 2023, 61(2): 578-96. doi:10.1007/s10528-022-10270-z |
| [20] | Wu F, Sun GQ, Zheng WB, et al. circCORO1C promotes the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by enhancing the expression of PD-L1 through NF-κB pathway[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2021, 35(12): e24003. doi:10.1002/jcla.24003 |
| [21] | Shen XJ, Kong S, Ma S, et al. Hsa_circ_0000437 promotes pathogenesis of gastric cancer and lymph node metastasis[J]. Oncogene, 2022, 41(42): 4724-35. doi:10.1038/s41388-022-02449-w |
| [22] | Zhu LW, Wang ZF, Sun LB, et al. Hsa_circ_0000437 upregulates and promotes disease progression in rheumatic valvular heart disease[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2022, 36(2): e24197. doi:10.1002/jcla.24197 |
| [23] | Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, et al. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats[J]. RNA, 2013, 19(2): 141-57. doi:10.1261/rna.035667.112 |
| [24] | Holdt LM, Kohlmaier A, Teupser D. Molecular roles and function of circular RNAs in eukaryotic cells[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2018, 75(6): 1071-98. doi:10.1007/s00018-017-2688-5 |
| [25] | Huang XJ, Dong HX, Liu Y, et al. Silencing of let-7b-5p inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation and stemness characteristics by Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp-box helicase 19A[J]. Bioengineered, 2021, 12(1): 7666-77. doi:10.1080/21655979.2021.1982276 |
| [26] | Dai YY, Liu JS, Li XY, et al. Let-7b-5p inhibits colon cancer progression by prohibiting APC ubiquitination degradation and the Wnt pathway by targeting NKD1[J]. Cancer Sci, 2023, 114(5): 1882-97. doi:10.1111/cas.15678 |
| [27] | Zheng ST, Liu Q, Ma R, et al. Let-7b-5p inhibits proliferation and motility in squamous cell carcinoma cells through negative modulation of KIAA1377[J]. Cell Biol Int, 2019, 43(6): 634-41. doi:10.1002/cbin.11136 |
| [28] | Sun Z, Zhang ZH, Wang QQ, et al. Combined inactivation of CTPS1 and ATR is synthetically lethal to MYC-overexpressing cancer cells[J]. Cancer Res, 2022, 82(6): 1013-24. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-21-1707 |
| [29] | Traut TW. Physiological concentrations of purines and pyrimidines[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 1994, 140(1): 1-22. doi:10.1007/bf00928361 |
| [30] | Williams JC, Kizaki H, Weber G, et al. Increased CTP synthetase activity in cancer cells[J]. Nature, 1978, 271(5640): 71-3. doi:10.1038/271071a0 |
| [31] | Chitrakar I, Kim-Holzapfel DM, Zhou WJ, et al. Higher order structures in purine and pyrimidine metabolism[J]. J Struct Biol, 2017, 197(3): 354-64. doi:10.1016/j.jsb.2017.01.003 |
| [32] | Wu FH, Mao YD, Ma T, et al. CTPS1 inhibition suppresses proliferation and migration in colorectal cancer cells[J]. Cell Cycle, 2022, 21(24): 2563-74. doi:10.1080/15384101.2022.2105084 |
| [33] | Ohmine K, Kawaguchi K, Ohtsuki S, et al. Quantitative targeted proteomics of pancreatic cancer: deoxycytidine kinase protein level correlates to progression-free survival of patients receiving gemcitabine treatment[J]. Mol Pharm, 2015, 12(9): 3282-91. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00282 |
| [34] | Zhang C, Tian CX, Zhu RZ, et al. CircSATB1 promotes colorectal cancer liver metastasis through facilitating FKBP8 degradation via RNF25-mediated ubiquitination[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2025, 12(13): e2406962. doi:10.1002/advs.202406962 |
| [1] | Zhaojun ZHANG, Qiong WU, Miaomiao XIE, Ruyin YE, Chenchen GENG, Jiwen SHI, Qingling YANG, Wenrui WANG, Yurong SHI. Layered double hydroxide-loaded si-NEAT1 regulates paclitaxel resistance and tumor-associated macrophage polarization in breast cancer by targeting miR-133b/PD-L1 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1718-1731. |
| [2] | Ziliang WANG, Xiaohua CHEN, Jingjing YANG, Chen YAN, Zhizhi ZHANG, Bingyi HUANG, Meng ZHAO, Song LIU, Sitang GE, Lugen ZUO, Deli CHEN. High expression of SURF4 promotes migration, invasion and proliferation of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting tight junction proteins [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1732-1742. |
| [3] | Jiahao LI, Ruiting XIAN, Rong LI. Down-regulation of ACADM-mediated lipotoxicity inhibits invasion and metastasis of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1163-1173. |
| [4] | Zhennan MA, Fuquan LIU, Xuefeng ZHAO, Xiaowei ZHANG. High expression of DTX2 promotes proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of oxaliplatin-resistant colorectal cancer cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 829-836. |
| [5] | Lu TAO, Zhuoli WEI, Yueyue WANG, Ping XIANG. CEACAM6 inhibits proliferation and migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 566-576. |
| [6] | Rui CAI, Zhuo HUANG, Wenxia HE, Tianhong AI, Xiaowei SONG, Shuting HU. The splicing factor HNRNPH1 regulates Circ-MYOCD back-splicing to modulate the course of cardiac hypertrophy [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 587-594. |
| [7] | Di CHEN, Ying LÜ, Yixin GUO, Yirong ZHANG, Ruixuan WANG, Xiaoruo ZHOU, Yuxin CHEN, Xiaohui WU. Dihydroartemisinin enhances doxorubicin-induced apoptosis of triple negative breast cancer cells by negatively regulating the STAT3/HIF-1α pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 254-260. |
| [8] | Qiao CHU, Xiaona WANG, Jiaying XU, Huilin PENG, Yulin ZHAO, Jing ZHANG, Guoyu LU, Kai WANG. Pulsatilla saponin D inhibits invasion and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer cells through multiple targets and pathways [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [9] | Mingzi OUYANG, Jiaqi CUI, Hui WANG, Zheng LIANG, Dajin PI, Liguo CHEN, Qianjun CHEN, Yingchao WU. Kaixinsan alleviates adriamycin-induced depression-like behaviors in mice by reducing ferroptosis in the prefrontal cortex [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1441-1449. |
| [10] | Jincun FANG, Liwei LIU, Junhao LIN, Fengsheng CHEN. Overexpression of CDHR2 inhibits proliferation of breast cancer cells by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1117-1125. |
| [11] | Zhi CUI, Cuijiao MA, Qianru WANG, Jinhao CHEN, Ziyang YAN, Jianlin YANG, Yafeng LÜ, Chunyu CAO. A recombinant adeno-associated virus expressing secretory TGF‑β type II receptor inhibits triple-negative murine breast cancer 4T1 cell proliferation and lung metastasis in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 818-826. |
| [12] | ZHANG Wenjing, ZHANG Nuo, YANG Zi, ZHANG Xiaofeng, SUN Aofei, WANG Lian, SONG Xue, GENG Zhijun, LI Jing, HU Jianguo. Overexpression of BZW1 promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling and promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 354-362. |
| [13] | Fuxing ZHANG, Guoqing LIU, Rui DONG, Lei GAO, Weichen LU, Lianxia GAO, Zhongkuo ZHAO, Fei LU, Mulin LIU. High expression of CRTAC1 promotes proliferation, migration and immune cell infiltration of gastric cancer by regulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2421-2433. |
| [14] | Youqin ZENG, Siyu CHEN, Yan LIU, Yitong LIU, Ling ZHANG, Jiao XIA, Xinyu WU, Changyou WEI, Ping LENG. AKBA combined with doxorubicin inhibits proliferation and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and xenograft growth in nude mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2449-2460. |
| [15] | XU Mengqi, SHI Yutong, LIU Junping, WU Minmin, ZHANG Fengmei, HE Zhiqiang, TANG Min. JAG1 affects monocytes-macrophages to reshape the pre-metastatic niche of triple-negative breast cancer through LncRNA MALAT1 in exosomes [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(9): 1525-1535. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||