Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (12): 2421-2433.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.12.19
Fuxing ZHANG1( ), Guoqing LIU1, Rui DONG1, Lei GAO1, Weichen LU1, Lianxia GAO1, Zhongkuo ZHAO2, Fei LU2(
), Guoqing LIU1, Rui DONG1, Lei GAO1, Weichen LU1, Lianxia GAO1, Zhongkuo ZHAO2, Fei LU2( ), Mulin LIU1(
), Mulin LIU1( )
)
Received:2024-07-31
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2024-12-26
Contact:
Fei LU, Mulin LIU
E-mail:1430078329@qq.com;8022038@zju.edu.cn;liumulin66@aliyun.com
Fuxing ZHANG, Guoqing LIU, Rui DONG, Lei GAO, Weichen LU, Lianxia GAO, Zhongkuo ZHAO, Fei LU, Mulin LIU. High expression of CRTAC1 promotes proliferation, migration and immune cell infiltration of gastric cancer by regulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2421-2433.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.12.19
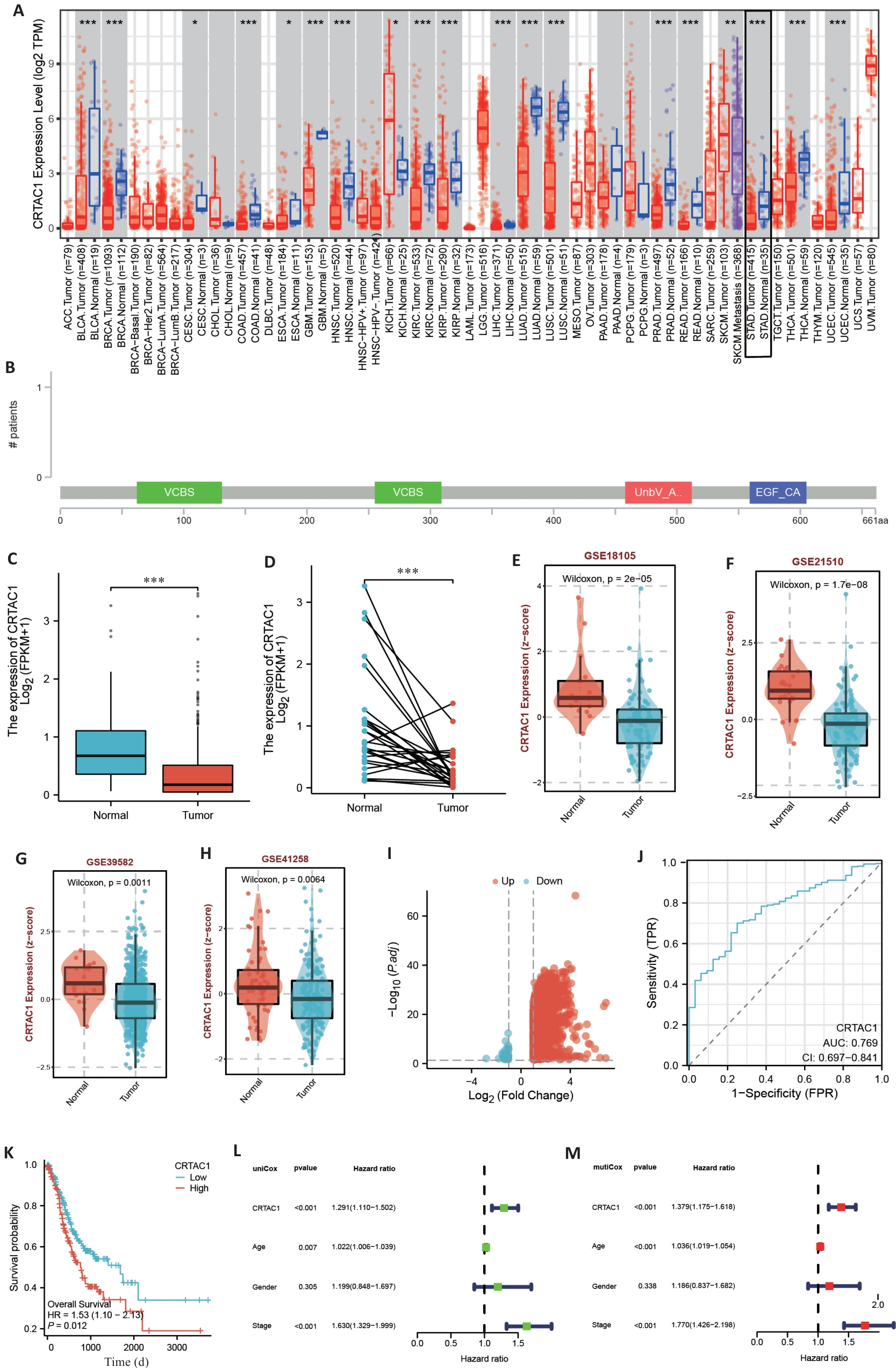
Fig.1 CRTAC1 expression level in gastric cancer is significantly correlated with the patients' prognosis. A: Pan-cancer analysis of TIMER2.0 database. B: Mutation location of CRTAC1 in gastric cancer transcriptome data of cBioPortal database. C, D: Differential analysis of CRTAC1 expression in unpaired and paired gastric cancer transcriptome data of TCGA database. E-H: Differential analysis of CRTAC1 expression in transcriptome data of BEST website of GSE18105, GSE21510, GSE39582 and GSE41258 transcriptome data in BEST website. I: Differentially expressed genes between high and low CRTAC1 expression groups in TCGA database gastric cancer transcriptome data and plotting of volcano plots. J: Expression level of CRTAC1 in TCGA database gastric cancer transcriptome data for ROC curves plotting. K: Relationship between CRTAC1 expression level and gastric cancer patients' overall survival (OS). L, M: One-way Cox and multifactorial Cox analysis of CRTAC1 in gastric cancer patients. *P<0.05,**P<0. 01, ***P<0. 001.
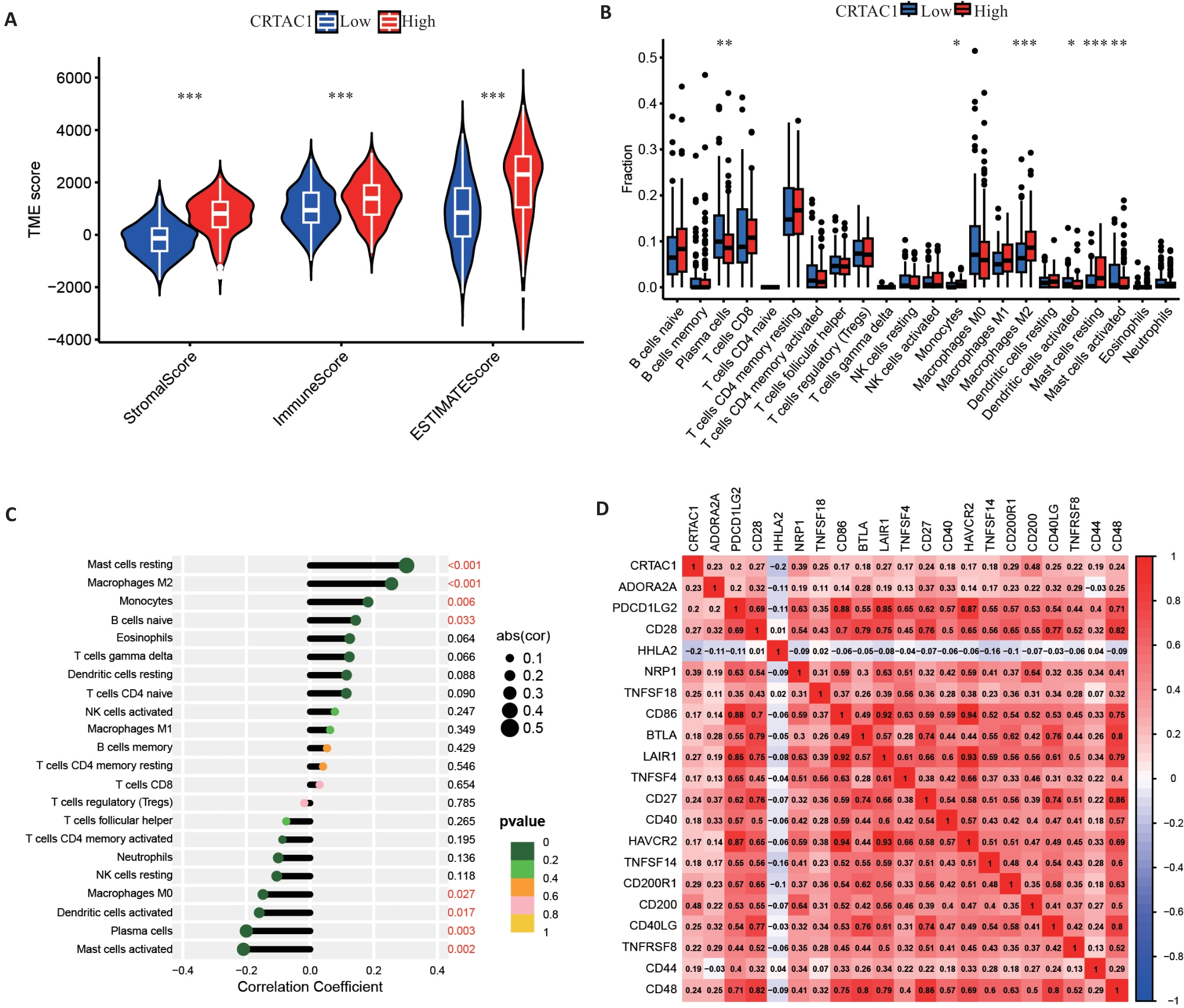
Fig.2 CRTAC1 expression affects tumor microenvironment in gastric cancer. A: Stromal cell scores, immune cell scores and tumor microenvironment scores of patients in the high and low CRTAC1 expression groups. B, C: Differential and correlation analyses of immune cells in patients in high and low CRTAC1 expression groups. D: Correlation analysis of immune checkpoints in patients in high and low CRTAC1 expression groups. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
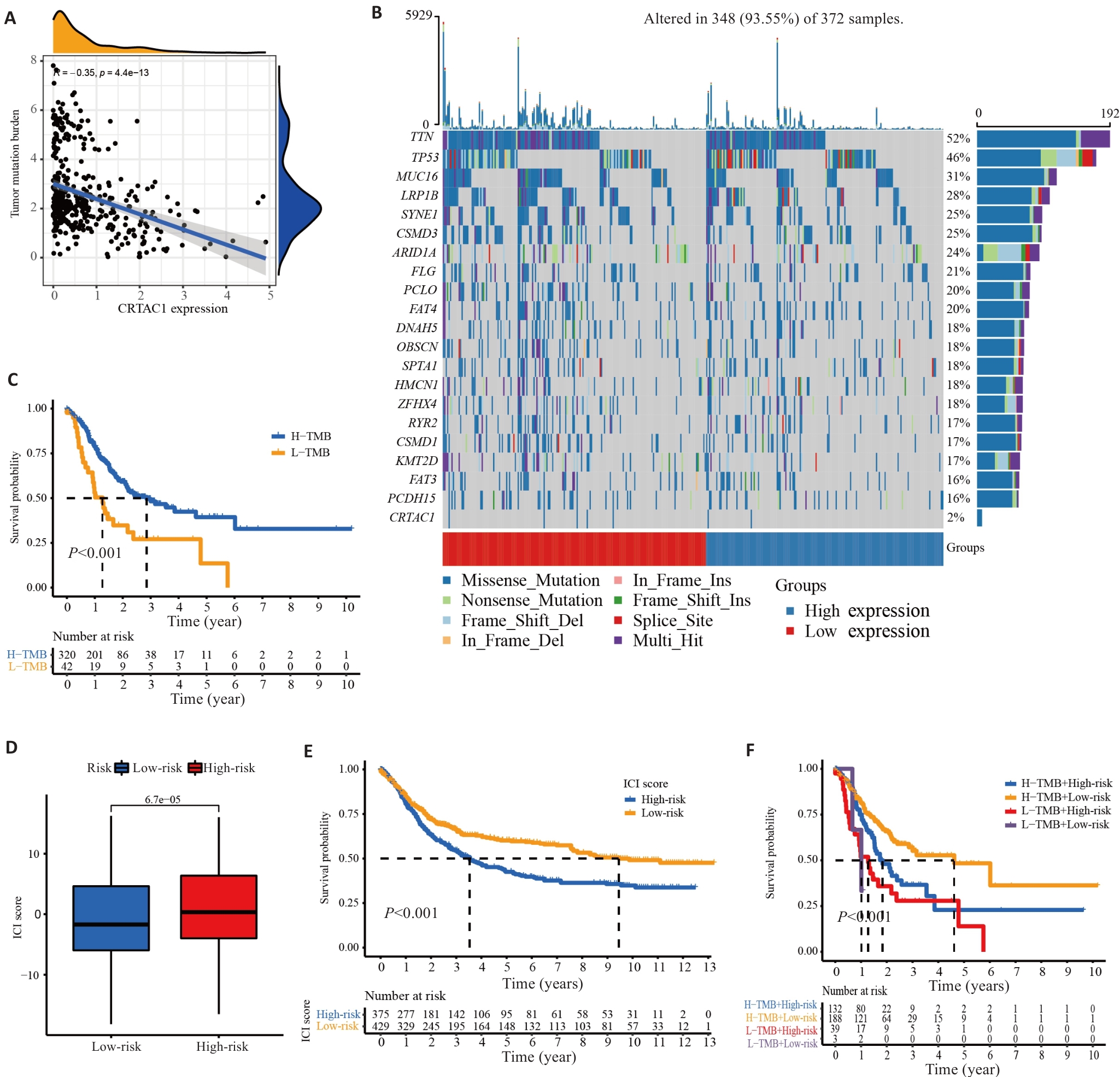
Fig.3 CRTAC1 expression level in gastric cancer affects tumor mutation load and prognosis. A: Scatter plot of correlation between CRTAC1 expression and TMB. B: Waterfall plot of the top 20 genes with mutation frequency in samples from high and low CRTAC1 expression groups. C: Kaplan-Meier curve of TMB affecting the overall survival of gastric cancer patients. D: Box line plot of TMB combined affecting the risk scores of gastric cancer patients. E: Kaplan-Meier curves of TMB affecting the risk scores of gastric cancer patients' overall survival. F: Kaplan-Meier curves of the effect of TMB combined with CRTAC1 expression on overall survival of gastric cancer patients. *P<0.05, **P<0. 01, ***P<0. 001.
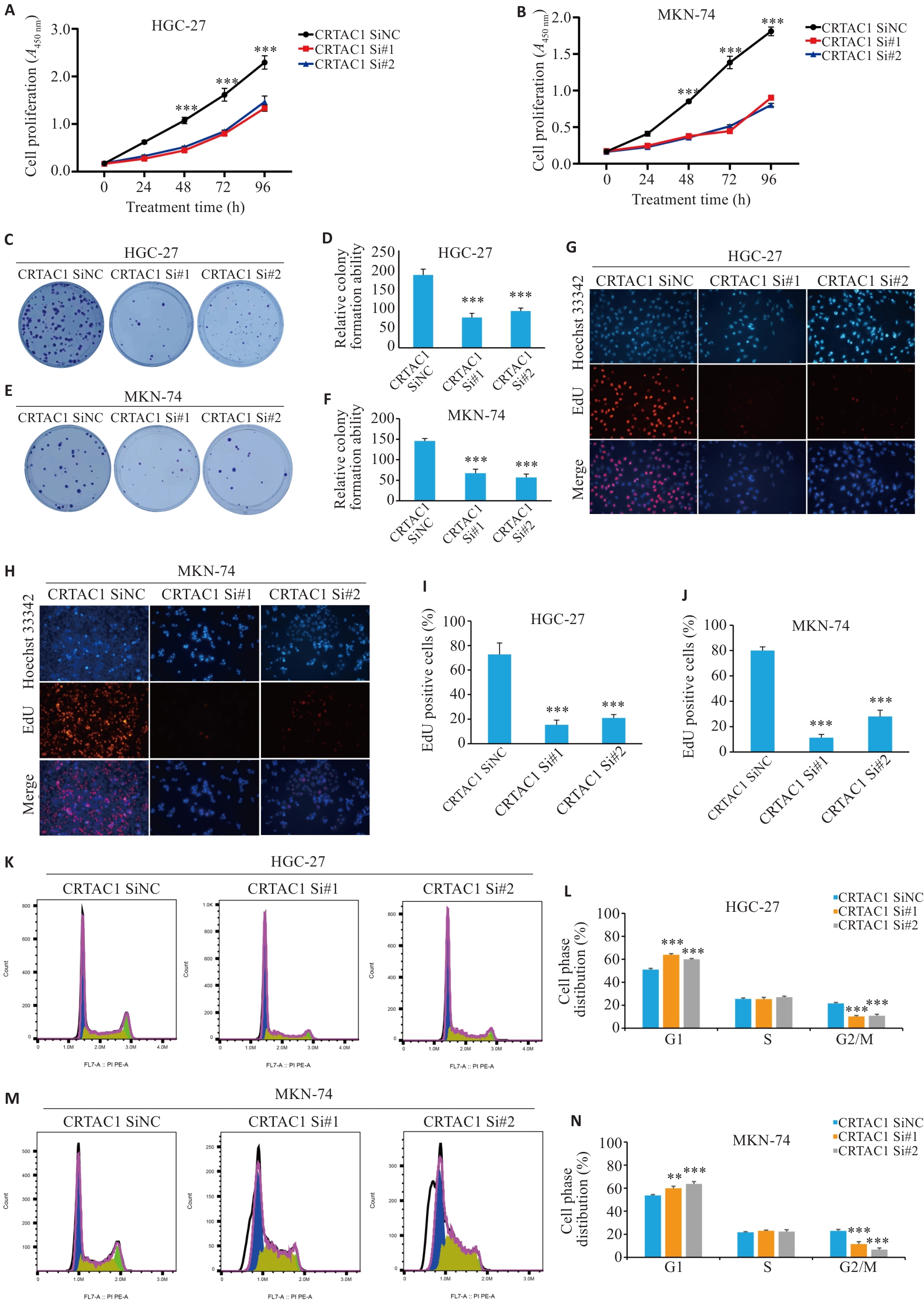
Fig. 4 High expression of CRTAC1 promotes proliferation of gastric cancer cells. A, B: Detection of proliferative capacity of the cells with CRTAC1 knockdown using CCK8 assay. C-F: Colony formation assay of the cells with CRTAC1 knockdown. G-J: EdU assay for assessing proliferation of the cells with CRTAC1 knockdown (Original magnification: ×20). K-N: Flow cytometry for assessing cell cycle changes in the cells with CRTAC1 knockdown. **P<0. 01, ***P<0. 001 vs CRTAC1 SiNC group.
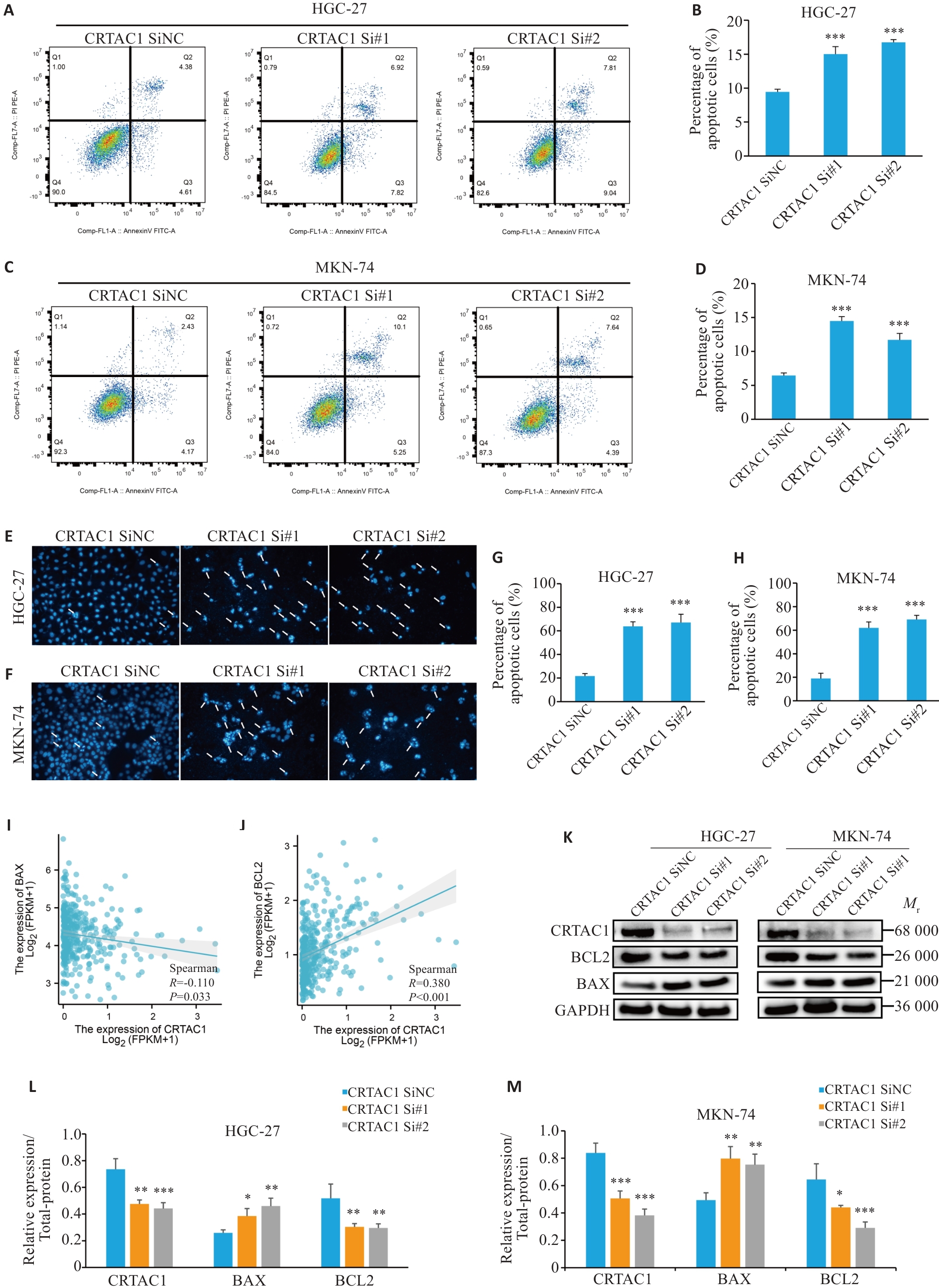
Fig.5 High expression of CRTAC1 significantly inhibits apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. A-H: Flow apoptosis assay and Hoechst assay showing that CRTAC1 knockdown promotes apoptosis of gastric cancer cells. I-J: Spearman's statistical analysis of the changes in BAX and BCL-2 expressions following CRTAC1 knockdown using the R language (×20). K-M: Changes in BAX and BCL-2 expressions in GC cells with CRTAC1 knockdown detected by Western blotting. *P<0.05, **P<0. 01, ***P<0. 001 vs CRTAC1 SiNC group.
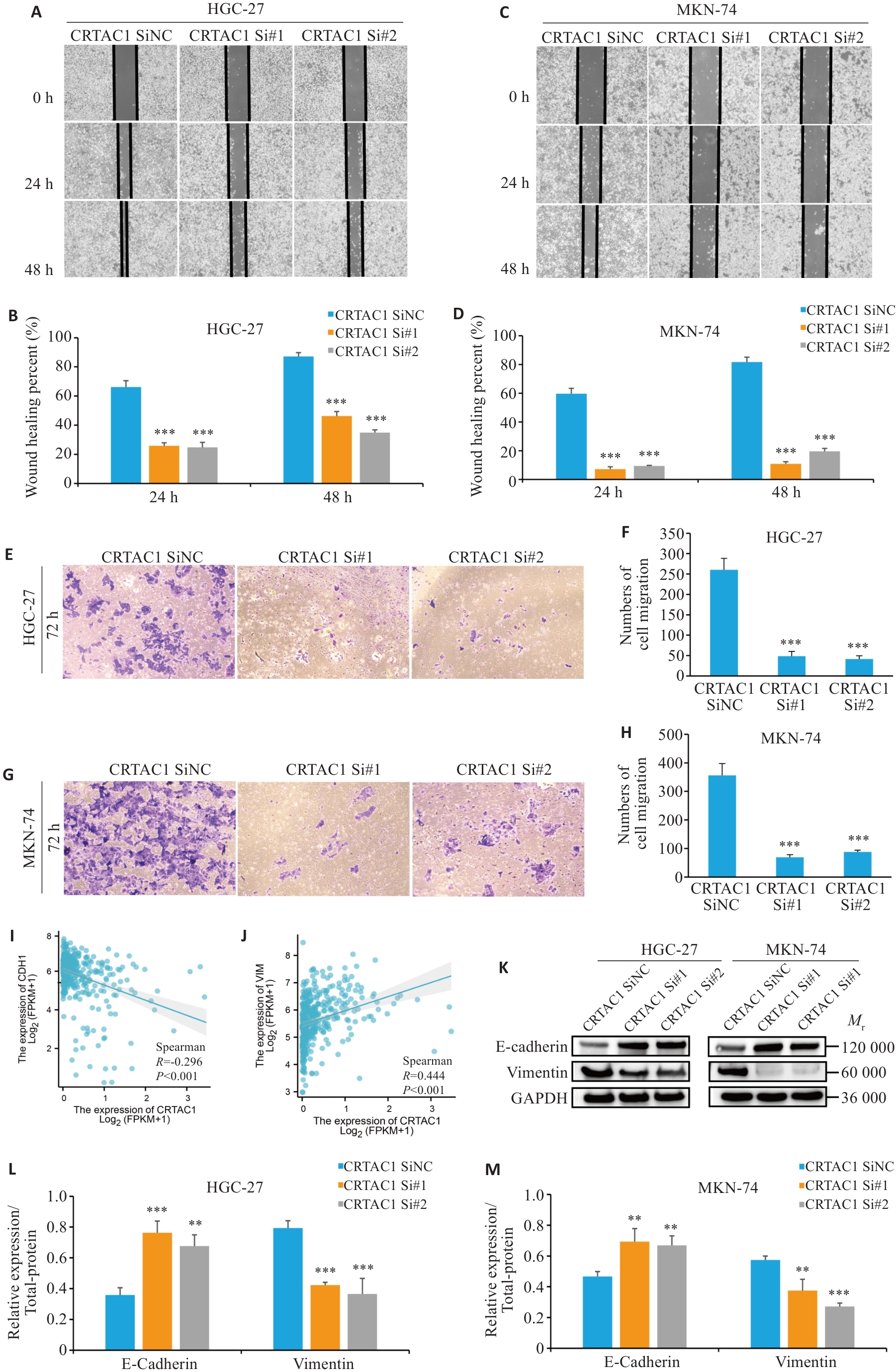
Fig.6 High expression of CRTAC1 promotes proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells. A-H: Scratch wound healing assay and Transwell assay for assessing migration ability of the cells with CRTAC1 knockdown (×20). I-J: Spearman's statistical analysis of the correlation between E-cadherin (CDH1) and Vimentin (VIM) expression using R language. K-M: Western blotting of E-cadherin and vimentin protein expressions in the cells with CRTAC1 knockdown. **P<0. 01, ***P<0. 001 vs CRTAC1 SiNC group.
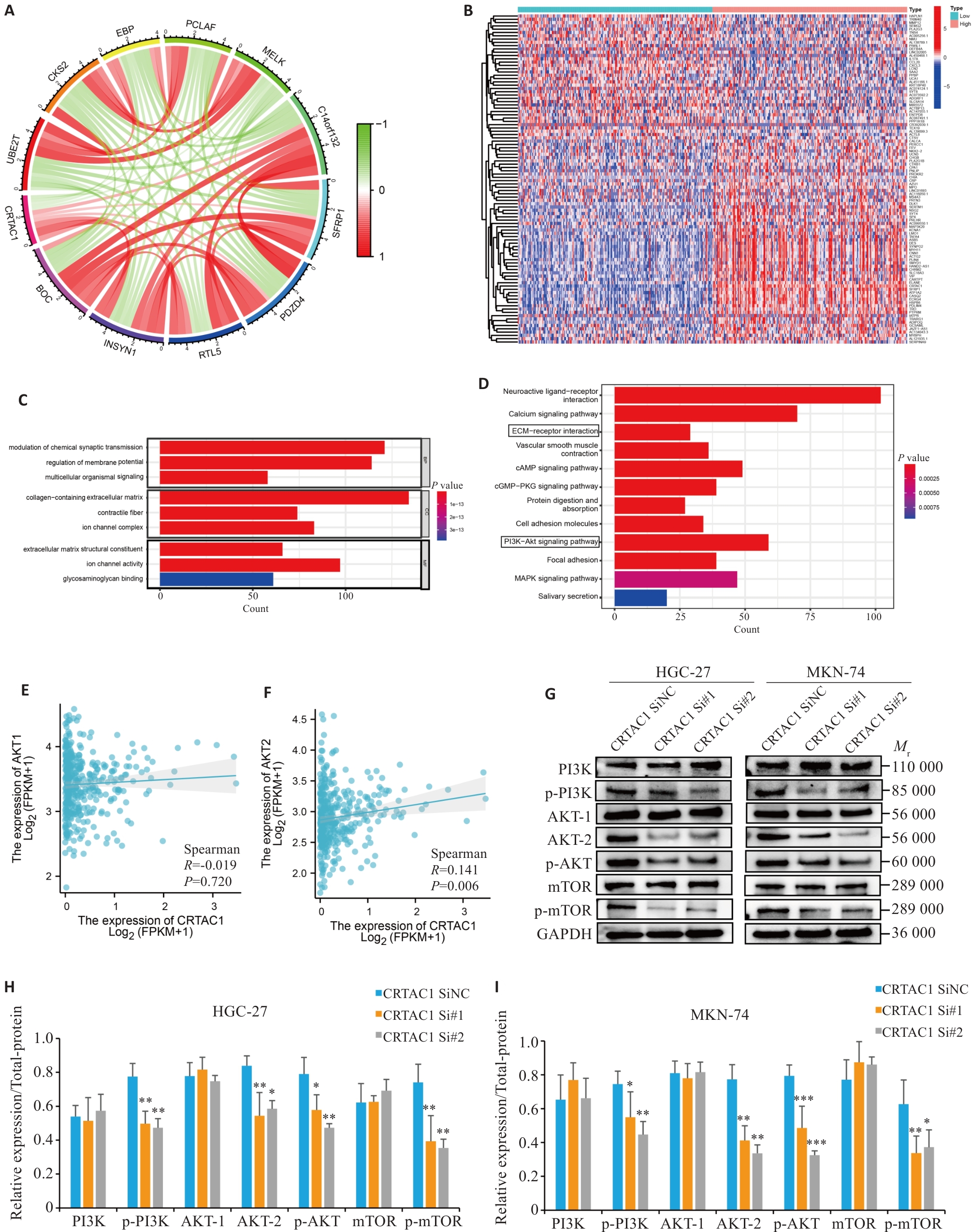
Fig. 7 High expression of CRTAC1 promotes proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells through the PI3K signaling pathway. A: Circle plot of co-expression analysis of CRTAC1 performed in gastric cancer genome (red, white, and green scatters are positively, non-significantly, and negatively correlated genes, respectively, with CRTAC1 expression). B: Heat map of differential genes between high and low CRTAC1 expression groups in gastric cancer (red, gray, and blue scatters are positively, non-significantly, and negatively correlated genes, respectively, with CRTAC1 expression). C, D: Histograms of GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of CRTAC1 differential genes, FDR<0.05. E, F: Spearman's statistical analysis of the correlation between AKT2 expressions using R language. G-I: Western blotting of the PI3K signaling pathway protein expressions in cells with CRTAC1 knockdown. *P<0.05, **P<0. 01, ***P<0. 001 vs CRTAC1 SiNC group.
| 1 | Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-49. |
| 2 | Thrift AP, El-Serag HB. Burden of gastric cancer[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 18(3): 534-42. |
| 3 | Hartgrink HH, Jansen EP, van Grieken NC, et al. Gastric cancer[J]. Lancet, 2009, 374(9688): 477-90. |
| 4 | Kanda M. Preoperative predictors of postoperative complications after gastric cancer resection[J]. Surg Today, 2020, 50(1): 3-11. |
| 5 | Zhang KC, Chen L. Chinese consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of gastric cancer with liver metastases[J]. Ther Adv Med Oncol, 2020, 12: 1758835920904803. |
| 6 | Lei YH, Lin L, Cheng SY, et al. Acute inflammatory reaction during anti-angiogenesis therapy combined with immunotherapy as a possible indicator of the therapeutic effect: three case reports and literature review[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1072480. |
| 7 | Anjos L, Morgado I, Guerreiro M, et al. Cartilage acidic protein 1, a new member of the beta-propeller protein family with amyloid propensity[J]. Proteins, 2017, 85(2): 242-55. |
| 8 | Jin ZH, Zhao LL, Chang YX, et al. CRTAC1 enhances the chemosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer to cisplatin by eliciting RyR-mediated calcium release and inhibiting Akt1 expression[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(8): 563. |
| 9 | Chemaly ER, Troncone L, Lebeche D. SERCA control of cell death and survival[J]. Cell Calcium, 2018, 69: 46-61. |
| 10 | Yang JH, Fan L, Liao XX, et al. CRTAC1 (Cartilage acidic protein 1) inhibits cell proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process in bladder cancer by downregulating Yin Yang 1 (YY1) to inactivate the TGF-β pathway[J]. Bioengineered, 2021, 12(2): 9377-89. |
| 11 | Li WM, Chan TC, Wei YC, et al. Downregulation of CRTAC1 in urothelial carcinoma promotes tumor aggressiveness and confers poor prognosis[J]. Front Biosci, 2023, 28(9): 217. |
| 12 | Shen YP, Chen K, Gu CJ. Identification of a chemotherapy-associated gene signature for a risk model of prognosis in gastric adenocarcinoma through bioinformatics analysis[J]. J Gastrointest Oncol, 2022, 13(5): 2219-33. |
| 13 | Zeng DQ, Li MY, Zhou R, et al. Tumor microenvironment characterization in gastric cancer identifies prognostic and immunotherapeutically relevant gene signatures[J]. Cancer Immunol Res, 2019, 7(5): 737-50. |
| 14 | Kushnir A, Wajsberg B, Marks AR. Ryanodine receptor dysfunction in human disorders[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res, 2018, 1865(11 Pt B): 1687-97. |
| 15 | Krishnamurthy N, Kurzrock R. Targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in cancer: update on effectors and inhibitors[J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2018, 62: 50-60. |
| 16 | Genovese I, Carinci M, Modesti L, et al. Mitochondria: insights into crucial features to overcome cancer chemoresistance[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(9): 4770. |
| 17 | Roderick HL, Cook SJ. Ca2+ signalling checkpoints in cancer: remodelling Ca2+ for cancer cell proliferation and survival[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2008, 8(5): 361-75. |
| 18 | Li J, Qi FZ, Su HS, et al. GRP75-faciliated Mitochondria-associated ER Membrane (MAM) Integrity controls Cisplatin-resistance in Ovarian Cancer Patients[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2022, 18(7): 2914-31. |
| 19 | Bruce JIE, James AD. Targeting the calcium signalling machinery in cancer[J]. Cancers, 2020, 12(9): 2351. |
| 20 | Wei CL, Wang XH, Chen M, et al. Calcium flickers steer cell migration[J]. Nature, 2009, 457(7231): 901-5. |
| 21 | Neophytou CM, Kyriakou TC, Papageorgis P. Mechanisms of metastatic tumor dormancy and implications for cancer therapy[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(24): 6158. |
| 22 | Massagué J, Obenauf AC. Metastatic colonization by circulating tumour cells[J]. Nature, 2016, 529(7586): 298-306. |
| 23 | Wang C, Yang Z, Xu E, et al. Apolipoprotein C-II induces EMT to promote gastric cancer peritoneal metastasis via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway[J]. Clin Transl Med, 2021, 11(8): e522. |
| 24 | Duan SY, Huang WQ, Liu XT, et al. IMPDH2 promotes colorectal cancer progression through activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathways[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 37(1): 304. |
| 25 | Tian LY, Smit DJ, Jücker M. The role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma metabolism[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(3): 2652. |
| 26 | Xu H, Wang J, Al-Nusaif M, et al. CCL2 promotes metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of non-small cell lung cancer via PI3K/Akt/mTOR and autophagy pathways[J]. Cell Prolif, 2024, 57(3): e13560. |
| 27 | Wang Q, Chen XY, Hay N. Akt as a target for cancer therapy: more is not always better (lessons from studies in mice)[J]. Br J Cancer, 2017, 117(2): 159-63. |
| 28 | Degan SE, Gelman IH. Emerging roles for AKT isoform preference in cancer progression pathways[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2021, 19(8): 1251-7. |
| 29 | Zhang HK, Cheng Y, Jia CW, et al. MicroRNA-29s could target AKT2 to inhibit gastric cancer cells invasion ability[J]. Med Oncol, 2015, 32(1): 342. |
| 30 | Cheng ZY, Liu GY, Huang CJ, et al. KLF5 activates lncRNA DANCR and inhibits cancer cell autophagy accelerating gastric cancer progression[J]. NPJ Genom Med, 2021, 6(1): 75. |
| 31 | Ganesh K, Massagué J. Targeting metastatic cancer[J]. Nat Med, 2021, 27(1): 34-44. |
| 32 | Lüönd F, Sugiyama N, Bill R, et al. Distinct contributions of partial and full EMT to breast cancer malignancy[J]. Dev Cell, 2021, 56(23): 3203-21.e11. |
| 33 | Aiello NM, Kang YB. Context-dependent EMT programs in cancer metastasis[J]. J Exp Med, 2019, 216(5): 1016-26. |
| 34 | Akhmetkaliyev A, Alibrahim N, Shafiee D, et al. EMT/MET plasticity in cancer and Go-or-Grow decisions in quiescence: the two sides of the same coin[J]? Mol Cancer, 2023, 22(1): 90. |
| 35 | Wu N, Jiang MZ, Liu HM, et al. LINC00941 promotes CRC metastasis through preventing SMAD4 protein degradation and activating the TGF-β/SMAD2/3 signaling pathway[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2021, 28(1): 219-32. |
| 36 | Tan ZM, Sun WY, Li Y, et al. Current progress of EMT: a new direction of targeted therapy for colorectal cancer with invasion and metastasis[J]. Biomolecules, 2022, 12(12): 1723. |
| 37 | Li XC, Sun Z, Peng GX, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals a pro-invasive cancer-associated fibroblast subgroup associated with poor clinical outcomes in patients with gastric cancer[J]. Theranostics, 2022, 12(2): 620-38. |
| 38 | Matsueda S, Graham DY. Immunotherapy in gastric cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(7): 1657-66. |
| 39 | Wang JQ, Du LY, Chen XJ. Adenosine signaling: optimal target for gastric cancer immunotherapy[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 1027838. |
| 40 | Li W, Zhang X, Wu FL, et al. Gastric cancer-derived mesenchymal stromal cells trigger M2 macrophage polarization that promotes metastasis and EMT in gastric cancer[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10(12): 918. |
| 41 | Kono K, Nakajima S, Mimura K. Current status of immune checkpoint inhibitors for gastric cancer[J]. Gastric Cancer, 2020, 23(4): 565-78. |
| 42 | Yarchoan M, Hopkins A, Jaffee EM. Tumor mutational burden and response rate to PD-1 inhibition[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 377(25): 2500-1. |
| 43 | McGrail DJ, Pilié PG, Rashid NU, et al. High tumor mutation burden fails to predict immune checkpoint blockade response across all cancer types[J]. Ann Oncol, 2021, 32(5): 661-72. |
| 44 | Zhao ZD, Mak TK, Shi YT, et al. The DNA damage repair-related lncRNAs signature predicts the prognosis and immunotherapy response in gastric cancer[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1117255. |
| 45 | Li XC, Pasche B, Zhang W, et al. Association of MUC16 mutation with tumor mutation load and outcomes in patients with gastric cancer[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2018, 4(12): 1691-8. |
| 46 | Yang Y, Zhang JY, Chen YX, et al. MUC4, MUC16, and TTN genes mutation correlated with prognosis, and predicted tumor mutation burden and immunotherapy efficacy in gastric cancer and pan-cancer[J]. Clin Transl Med, 2020, 10(4): e155. |
| 47 | Cao JL, Yang X, Chen SY, et al. The predictive efficacy of tumor mutation burden in immunotherapy across multiple cancer types: a meta-analysis and bioinformatics analysis[J]. Transl Oncol, 2022, 20: 101375. |
| [1] | Xiaohua CHEN, Hui LU, Ziliang WANG, Lian WANG, Yongsheng XIA, Zhijun GENG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Xue SONG, Yueyue WANG, Jing LI, Jianguo HU, Lugen ZUO. Role of Abelson interactor 2 in progression and prognosis of gastric cancer and its regulatory mechanisms [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1653-1661. |
| [2] | Mengnan YE, Hongmei WU, Yan MEI, Qingling ZHANG. High expression of CREM is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1776-1782. |
| [3] | Zhijun GENG, Jingjing YANG, Minzhu NIU, Xinyue LIU, Jinran SHI, Yike LIU, Xinyu YAO, Yulu ZHANG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Jianguo HU. Kuwanon G inhibits growth, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1476-1484. |
| [4] | Yidan PANG, Ya LIU, Siai CHEN, Jinglei ZHANG, Jin ZENG, Yuanming PAN, Juan AN. Biological role of SPAG5 in the malignant proliferation of gastric cancer cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1497-1507. |
| [5] | Yongsheng XIA, Lian WANG, Xiaohua CHEN, Yulu ZHANG, Aofei SUN, Deli CHEN. TSR2 overexpression inhibits proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells by downregulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 913-919. |
| [6] | Qinzhi WANG, Bing SONG, Shirui HAO, Zhiyuan XIAO, Lianhui JIN, Tong ZHENG, Fang CHAI. Bioinformatic analysis of CCND2 expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma and its impact on immune infiltration [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 981-988. |
| [7] | LIANG Yihao, LAI Yingjun, YUAN Yanwen, YUAN Wei, ZHANG Xibo, ZHANG Bashan, LU Zhifeng. Screening of differentially expressed genes in gastric cancer based on GEO database and function and pathway enrichment analysis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 605-616. |
| [8] | SHEN Mengdi, ZHAO Na, DENG Xiaojing, DENG Min. High expression of COX6B2 in gastric cancer is associated with poor long-term prognosis and promotes cell proliferation and cell cycle progression by inhibiting p53 signaling [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 289-297. |
| [9] | ZHANG Nuo, ZHANG Zhen, ZHANG Yulu, SONG Xue, ZHANG Xiaofeng, LI Jing, ZUO Lugen, HU Jianguo. PCID2 is highly expressed in gastric cancer and affects the prognosis by regulating cancer cell cycle and proliferation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 324-332. |
| [10] | ZHANG Wenjing, ZHANG Nuo, YANG Zi, ZHANG Xiaofeng, SUN Aofei, WANG Lian, SONG Xue, GENG Zhijun, LI Jing, HU Jianguo. Overexpression of BZW1 promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling and promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 354-362. |
| [11] | Zhen ZHANG, Hui LU, Xiaohua CHEN, Lian WANG, Ziliang WANG, Yueyue WANG, Sitang GE, Lugen ZUO. CEP192 overexpression is correlated with poor prognosis of gastric cancer and promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation by regulating PLK1/CDK1/Cyclin B1 signaling [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2137-2145. |
| [12] | Qianlong LING, Kai JI, Jinye CHEN, Jiajia GUAN, Ruipeng WANG, Wenjiang MAN, Bing ZHU. Sphingosine kinase-1 regulates migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells via targeting the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2163-2171. |
| [13] | DUAN Ting, ZHANG Zhen, SHI Jinran, XIAO Linyu, YANG Jingjing, YIN Lixia, ZHANG Xiaofeng, GENG Zhijun, LU Guoyu. High expression of CPNE3 correlates with poor long-term prognosis of gastric cancer by inhibiting cell apoptosis via activating PI3K/AKT signaling [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 129-137. |
| [14] | FENG Wen, LAI Yuexing, WANG Jing, XU Ping. Long non-coding RNA ABHD11-AS1 promotes glycolysis in gastric cancer cells to accelerate tumor progression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(9): 1485-1492. |
| [15] | WANG Lian, XIA Yongsheng, ZHANG Zhen, LIU Xinyue, SHI Jinran, WANG Yueyue, LI Jing, ZHNAG Xiaofeng, GENG Zhijun, SONG Xue, ZUO Lugen. High expression of MRPL13 promotes cell cycle progression and proliferation of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting p53 signaling to affect long-term prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(9): 1558-1566. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||