Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (9): 1653-1661.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.09.04
Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaohua CHEN1( ), Hui LU1, Ziliang WANG1, Lian WANG1, Yongsheng XIA1, Zhijun GENG2,4, Xiaofeng ZHANG2,4, Xue SONG2,4, Yueyue WANG3,4, Jing LI3,4, Jianguo HU3,4, Lugen ZUO1,4(
), Hui LU1, Ziliang WANG1, Lian WANG1, Yongsheng XIA1, Zhijun GENG2,4, Xiaofeng ZHANG2,4, Xue SONG2,4, Yueyue WANG3,4, Jing LI3,4, Jianguo HU3,4, Lugen ZUO1,4( )
)
Received:2024-04-22
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-09-30
Contact:
Lugen ZUO
E-mail:chenxiaohua9116@163.com;zuolugen@126.com
Xiaohua CHEN, Hui LU, Ziliang WANG, Lian WANG, Yongsheng XIA, Zhijun GENG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Xue SONG, Yueyue WANG, Jing LI, Jianguo HU, Lugen ZUO. Role of Abelson interactor 2 in progression and prognosis of gastric cancer and its regulatory mechanisms[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1653-1661.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.09.04
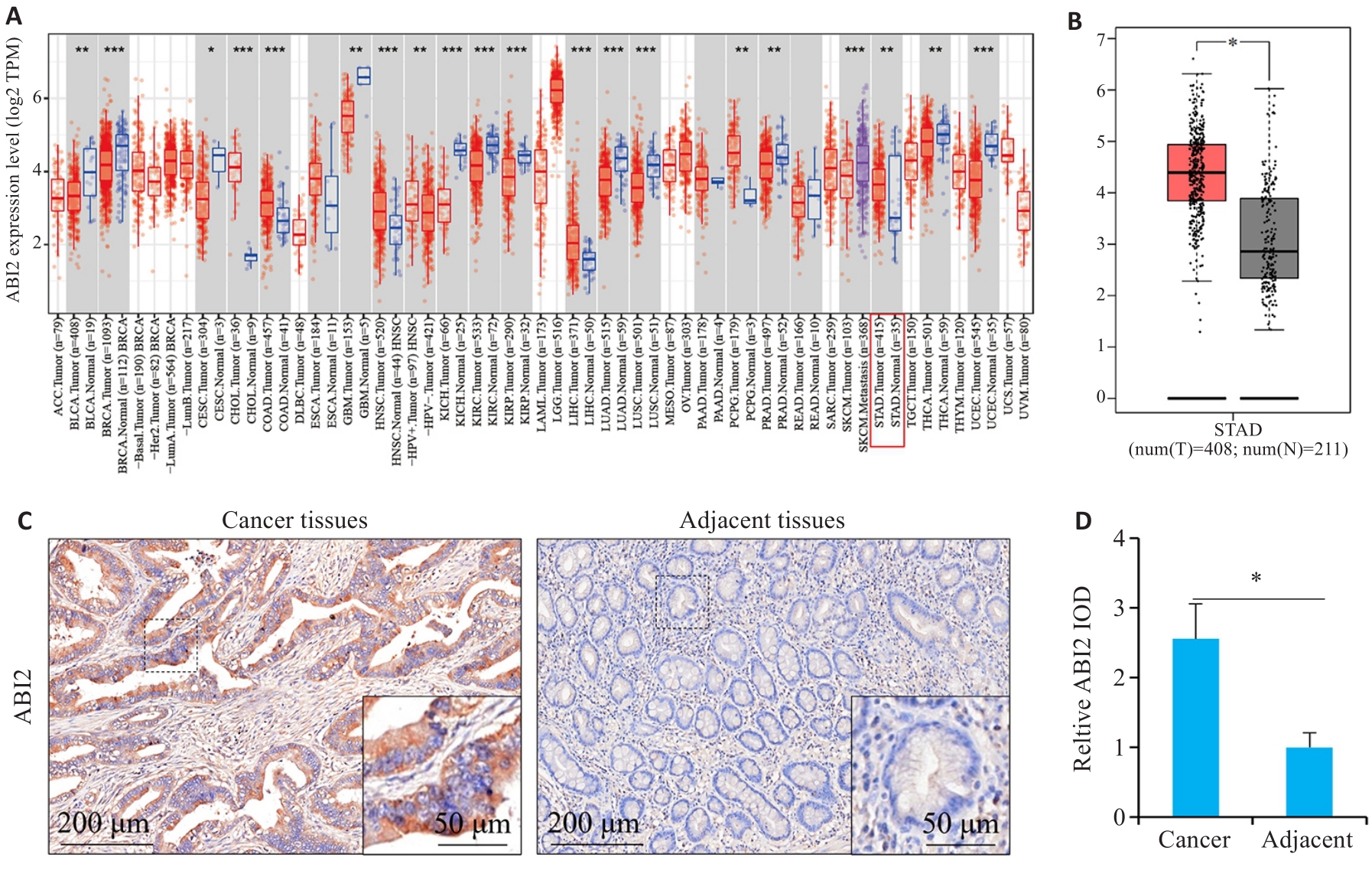
Fig.1 ABI2 is highly expressed in gastric cancer. A: Pan-cancer expression analysis. B: Expression of ABI2 in gastric and adjacent tissues. C, D: Immunohistochemical staining of ABI2 in gastric and adjacent tissues. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
| Factors | n | ABI2 expression (n, %) | χ2 | Ρ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n=60) | High (n=60) | |||||
| Gender | Male | 95 | 47 (49.47%) | 48 (50.53%) | 0.051 | 0.822 |
| Female | 25 | 13 (52.00%) | 12 (48.00%) | |||
| Age (year) | <60 | 49 | 27 (55.10%) | 22 (44.90%) | 0.862 | 0.353 |
| ≥60 | 71 | 33 (46.48%) | 38 (53.52%) | |||
| CEA (μg/L) | <5 | 57 | 35 (61.40%) | 22 (38.60%) | 5.647 | 0.017 |
| ≥5 | 63 | 25 (39.68%) | 38 (60.32%) | |||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | <37 | 67 | 44 (65.67%) | 23 (34.33%) | 14.903 | <0.001 |
| ≥37 | 53 | 16 (30.19%) | 37 (69.81%) | |||
| Tumor size (cm) | <5 | 64 | 33 (51.56%) | 31 (48.44%) | 0.134 | 0.714 |
| ≥5 | 56 | 27 (48.21%) | 29 (51.79%) | |||
| Cancer cell type | Adenocarcinoma | 89 | 46 (51.69%) | 43 (48.31%) | 0.391 | 0.532 |
| Other | 31 | 14 (45.16%) | 17 (54.84%) | |||
| Pathological grading | G1-G2 | 66 | 41 (62.12%) | 25 (37.88%) | 8.620 | 0.003 |
| G3-G4 | 54 | 19 (35.19%) | 35 (64.81%) | |||
| T stage | T1-T2 | 51 | 33 (64.71%) | 18 (35.29%) | 7.673 | 0.006 |
| T3-T4 | 69 | 27 (39.13%) | 42 (60.87%) | |||
| N stage | N0-N1 | 60 | 36 (60.00%) | 24 (40.00%) | 4.800 | 0.028 |
| N2-N3 | 60 | 24 (40.00%) | 36 (60.00%) | |||
Tab.1 Correlation of ABI2 expression level with clinicopathological parameters of gastric cancer patients
| Factors | n | ABI2 expression (n, %) | χ2 | Ρ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n=60) | High (n=60) | |||||
| Gender | Male | 95 | 47 (49.47%) | 48 (50.53%) | 0.051 | 0.822 |
| Female | 25 | 13 (52.00%) | 12 (48.00%) | |||
| Age (year) | <60 | 49 | 27 (55.10%) | 22 (44.90%) | 0.862 | 0.353 |
| ≥60 | 71 | 33 (46.48%) | 38 (53.52%) | |||
| CEA (μg/L) | <5 | 57 | 35 (61.40%) | 22 (38.60%) | 5.647 | 0.017 |
| ≥5 | 63 | 25 (39.68%) | 38 (60.32%) | |||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | <37 | 67 | 44 (65.67%) | 23 (34.33%) | 14.903 | <0.001 |
| ≥37 | 53 | 16 (30.19%) | 37 (69.81%) | |||
| Tumor size (cm) | <5 | 64 | 33 (51.56%) | 31 (48.44%) | 0.134 | 0.714 |
| ≥5 | 56 | 27 (48.21%) | 29 (51.79%) | |||
| Cancer cell type | Adenocarcinoma | 89 | 46 (51.69%) | 43 (48.31%) | 0.391 | 0.532 |
| Other | 31 | 14 (45.16%) | 17 (54.84%) | |||
| Pathological grading | G1-G2 | 66 | 41 (62.12%) | 25 (37.88%) | 8.620 | 0.003 |
| G3-G4 | 54 | 19 (35.19%) | 35 (64.81%) | |||
| T stage | T1-T2 | 51 | 33 (64.71%) | 18 (35.29%) | 7.673 | 0.006 |
| T3-T4 | 69 | 27 (39.13%) | 42 (60.87%) | |||
| N stage | N0-N1 | 60 | 36 (60.00%) | 24 (40.00%) | 4.800 | 0.028 |
| N2-N3 | 60 | 24 (40.00%) | 36 (60.00%) | |||
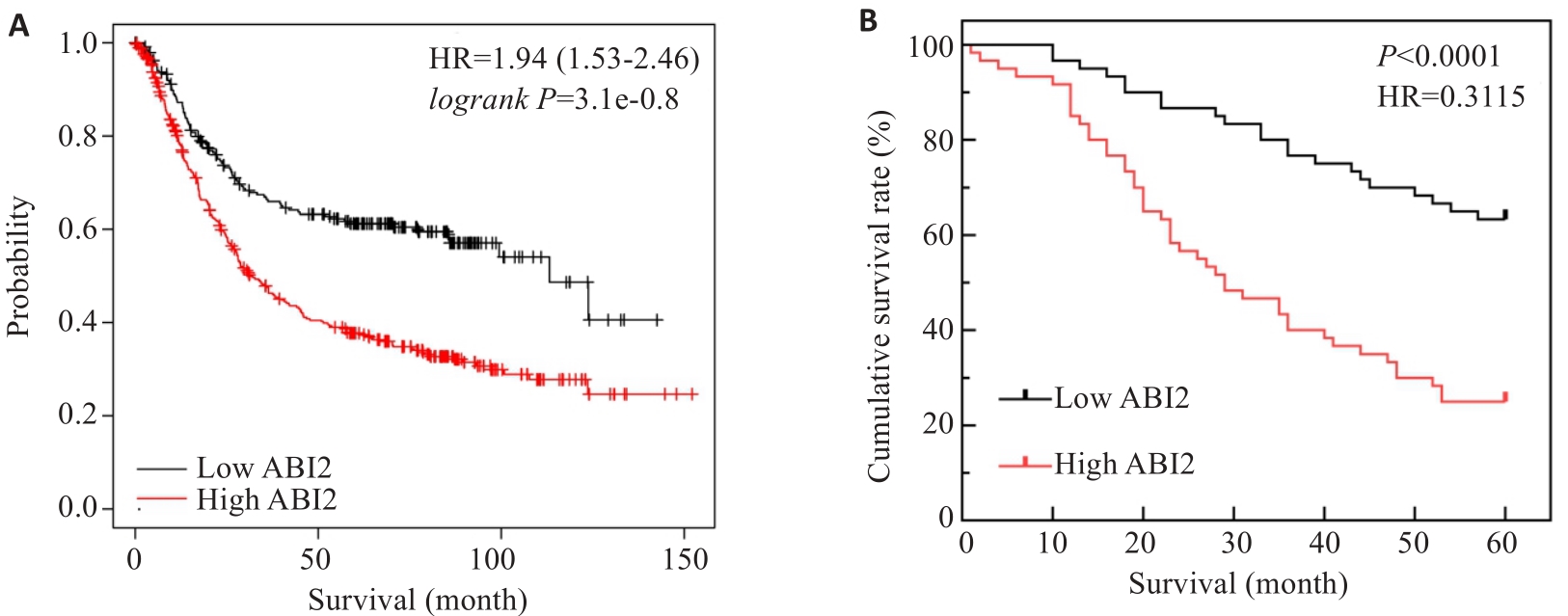
Fig.3 ABI2 expression level in gastric cancer tissues affects prognosis of the patients. A: ABI2 expression level affects overall survival of gastric cancer patients. B: Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of 5-year survival rate of the patients after radical gastrectomy.
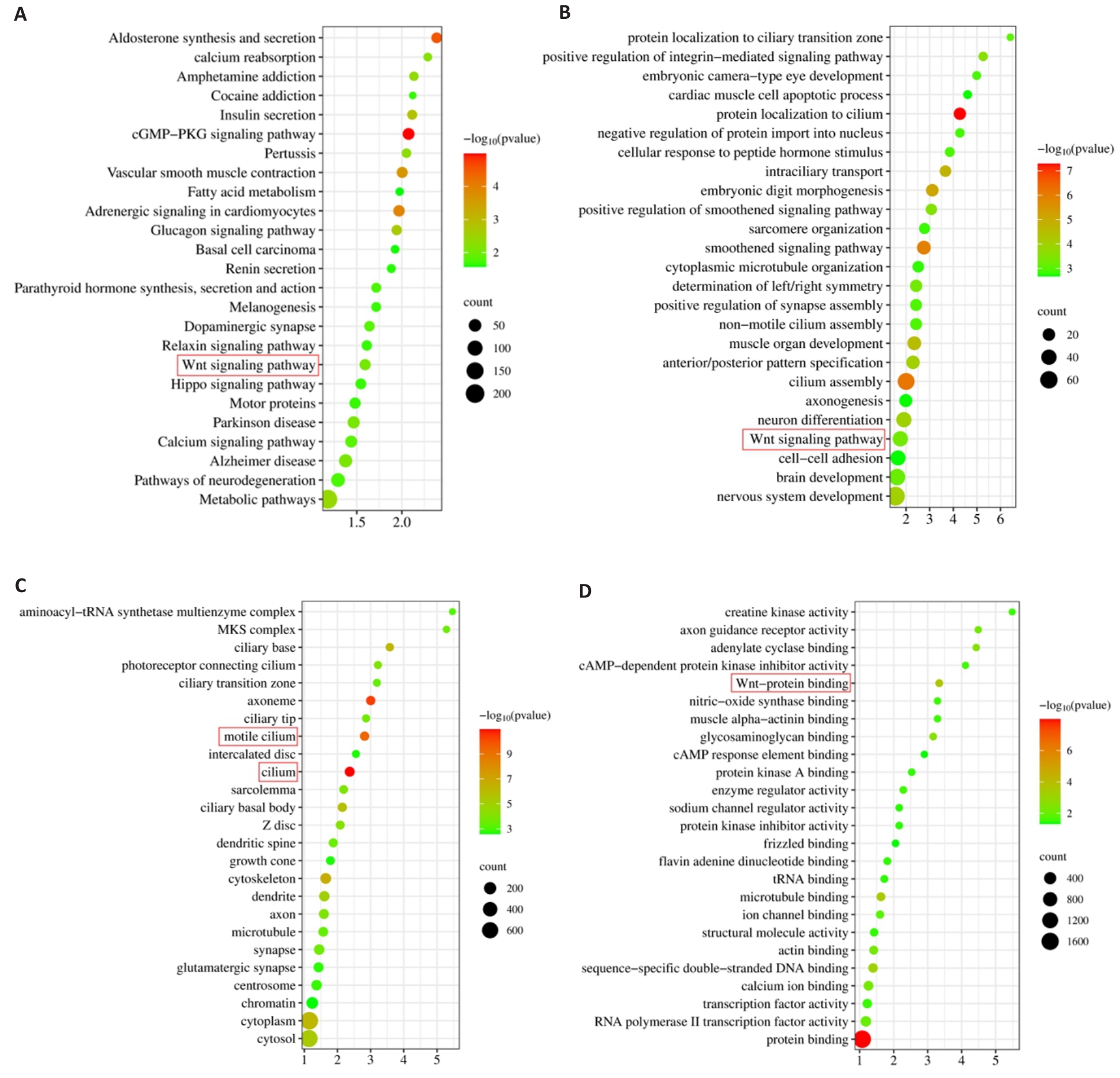
Fig.5 Results of KEGG and GO enrichment analysis. A: KEGG enrichment analysis. B-D: Biological processes, cellular component and molecular function in GO enrichment analysis.
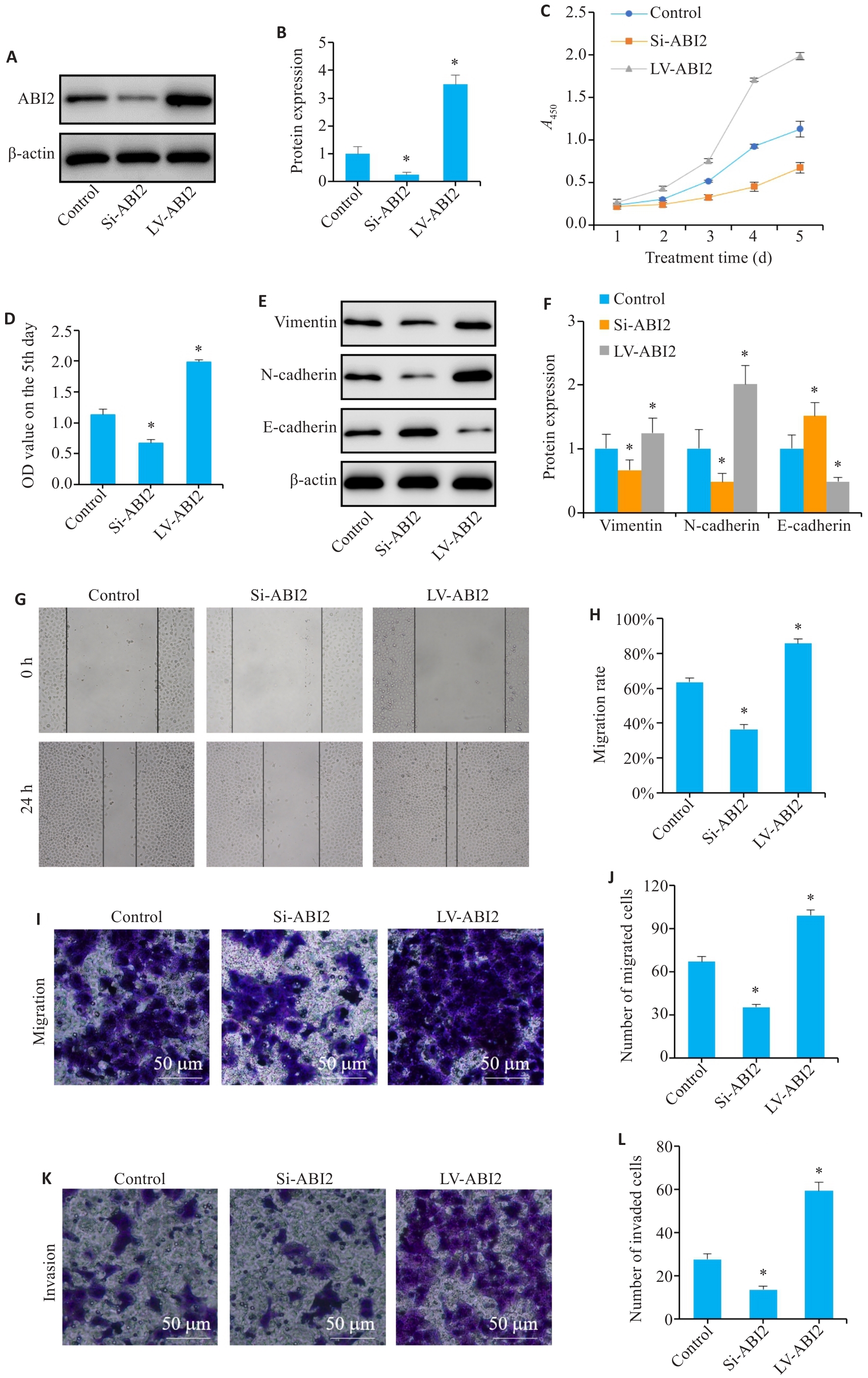
Fig.6 ABI2 overexpression promotes proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of gastric cancer cells in vitro. A, B: Lentiviral transfection efficiency. C, D: Results of CCK-8 assay (presented as A values) from day 1 to day 5. E, F: Expression of EMT markers in MGC803 cells. G, H: Wound-healing assay of the cells. I-L: Migration and invasion of MGC803 cells. Si: siRNA; LV: overexpression. *P<0.05 vs Control (n=3).
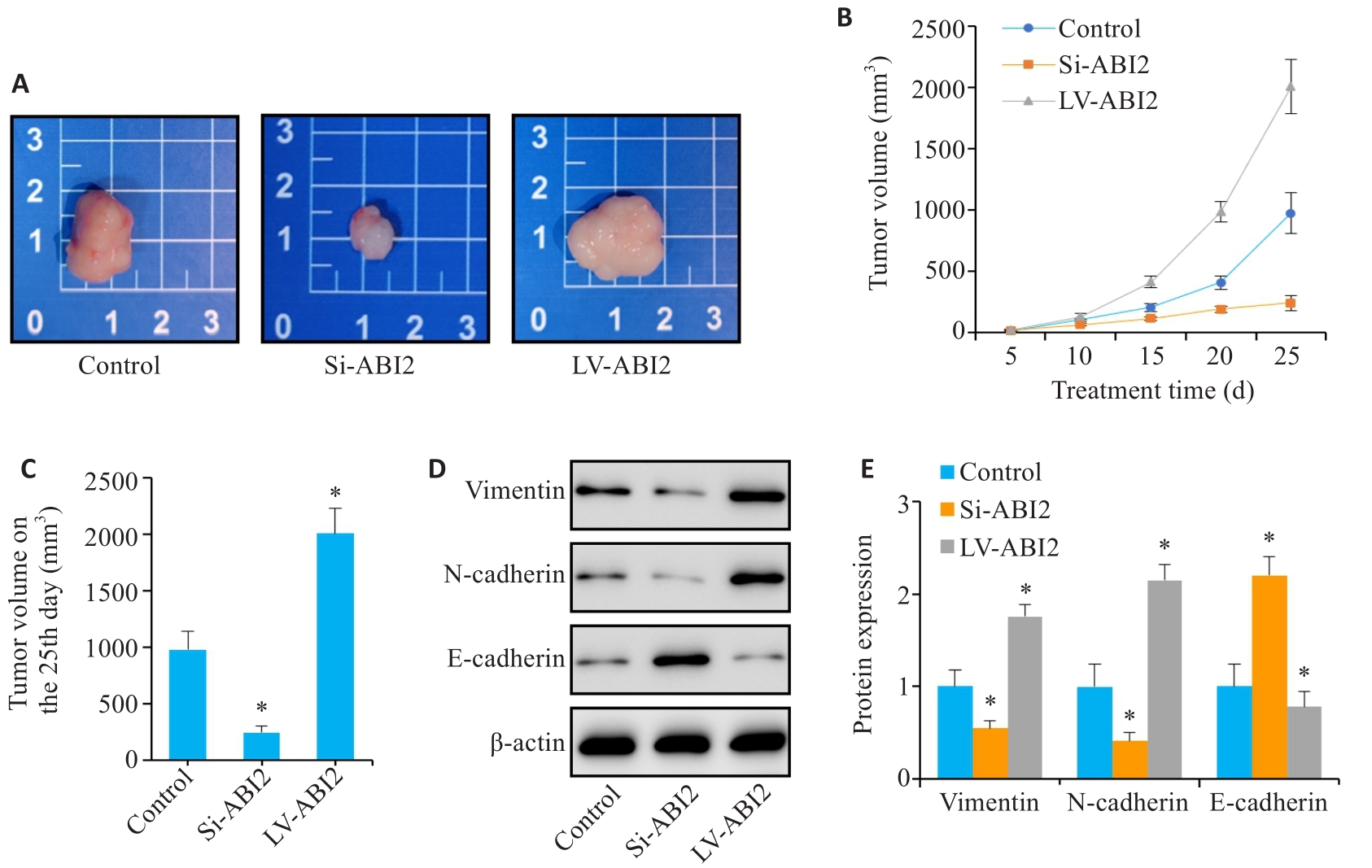
Fig.7 ABI2 overexpression promotes proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of gastric cancer cells in nude mice. A: Representative image of the transplanted tumors. B, C: Transplanted tumor volume from day 5 to day 25. D, E: Expression of EMT markers in the transplanted tumor. *P<0.05 vs Control (n=3).
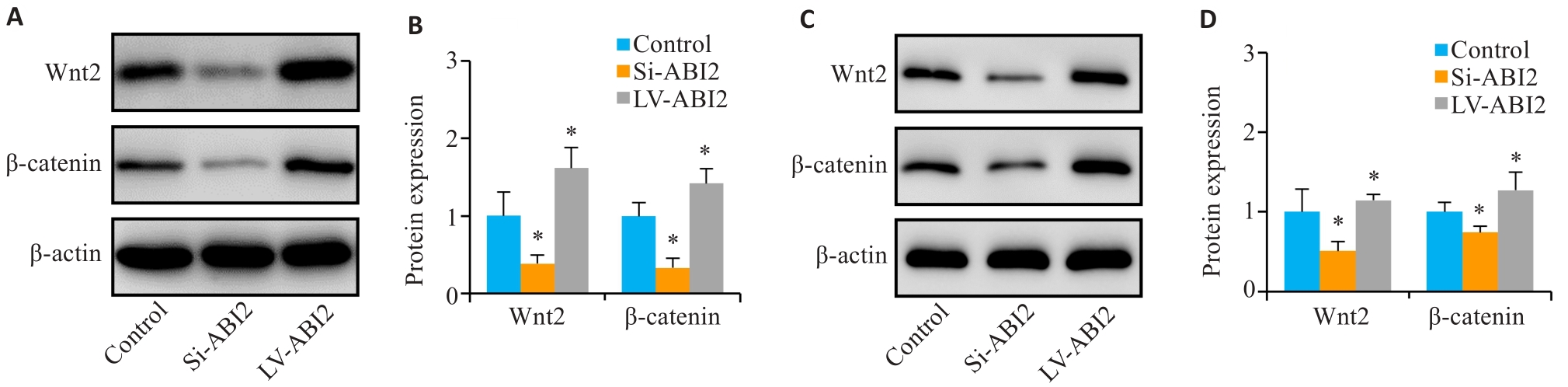
Fig.8 The effect of ABI2 on malignant biological behaviors of gastric cancer cells is related to the Wnt signaling pathway. A, B: Expression of Wnt2 and β-catenin in MGC803 cells. C, D: Expression of Wnt2 and β-catenin in the transplanted tumors. *P<0.05 vs Control (n=3).
| 1 | Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, et al. Gastric cancer[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10251): 635-48. |
| 2 | 郑荣寿, 张思维, 孙可欣, 等. 2016年中国恶性肿瘤流行情况分析[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2023, 45(3): 212-20. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20220922-00647 |
| 3 | Thrift AP, El-Serag HB. Burden of gastric cancer[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 18(3): 534-42. |
| 4 | Chia NY, Tan P. Molecular classification of gastric cancer[J]. Ann Oncol, 2016, 27(5): 763-9. |
| 5 | Jiang PX, Tang SN, Hudgins H, et al. The Abl/Abi signaling links WAVE regulatory complex to Cbl E3 ubiquitin ligase and is essential for breast cancer cell metastasis[J]. Neoplasia, 2022, 32: 100819. |
| 6 | Ichigotani Y, Fujii K, Hamaguchi M, et al. In search of a function for the E3B1/Abi2/Argbp1/NESH family (Review)[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2002, 9(6): 591-5. |
| 7 | Zipfel PA, Bunnell SC, Witherow DS, et al. Role for the Abi/wave protein complex in T cell receptor-mediated proliferation and cytoskeletal remodeling[J]. Curr Biol, 2006, 16(1): 35-46. |
| 8 | Courtney KD, Grove M, Vandongen H, et al. Localization and phosphorylation of Abl-interactor proteins, Abi-1 and Abi-2, in the developing nervous system[J]. Mol Cell Neurosci, 2000, 16(3): 244-57. |
| 9 | Hirao N, Sato S, Gotoh T, et al. NESH (Abi-3) is present in the Abi/WAVE complex but does not promote c-Abl-mediated phosphorylation[J]. FEBS Lett, 2006, 580(27): 6464-70. |
| 10 | Li YZ, Clough N, Sun XL, et al. Bcr-Abl induces abnormal cytoskeleton remodeling, beta1 integrin clustering and increased cell adhesion to fibronectin through the Abl interactor 1 pathway[J]. J Cell Sci, 2007, 120(Pt 8): 1436-46. |
| 11 | Ryu JR, Echarri A, Li R, et al. Regulation of cell-cell adhesion by Abi/Diaphanous complexes[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2009, 29(7): 1735-48. |
| 12 | Stradal T, Courtney KD, Rottner K, et al. The Abl interactor proteins localize to sites of actin polymerization at the tips of lamellipodia and filopodia[J]. Curr Biol, 2001, 11(11): 891-5. |
| 13 | Jensen CC, Clements AN, Liou H, et al. PIM1 phosphorylates ABI2 to enhance actin dynamics and promote tumor invasion[J]. J Cell Biol, 2023, 222(6): e202208136. |
| 14 | Chen JD, Li HZ, Zhang B, et al. ABI2-mediated MEOX2/KLF4-NANOG axis promotes liver cancer stem cell and drives tumour recurrence[J]. Liver Int, 2022, 42(11): 2562-76. |
| 15 | Guan WL, He Y, Xu RH. Gastric cancer treatment: recent progress and future perspectives[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2023, 16(1): 57. |
| 16 | Wang B, Mysliwiec T, Krainc D, et al. Identification of ArgBP1, an Arg protein tyrosine kinase binding protein that is the human homologue of a CNS-specific Xenopus gene[J]. Oncogene, 1996, 12(9): 1921-9. |
| 17 | Dai Z, Pendergast AM. Abi-2, a novel SH3-containing protein interacts with the c-Abl tyrosine kinase and modulates c-Abl transforming activity[J]. Genes Dev, 1995, 9(21): 2569-82. |
| 18 | Grove M, Demyanenko G, Echarri A, et al. ABI2-deficient mice exhibit defective cell migration, aberrant dendritic spine morphogenesis, and deficits in learning and memory[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2004, 24(24): 10905-22. |
| 19 | Chen ZC, Borek D, Padrick SB, et al. Structure and control of the actin regulatory WAVE complex[J]. Nature, 2010, 468(7323): 533-8. |
| 20 | Shami Shah A, Batrouni AG, Kim D, et al. PLEKHA4/kramer attenuates dishevelled ubiquitination to modulate Wnt and planar cell polarity signaling[J]. Cell Rep, 2019, 27(7): 2157-70. e8. |
| 21 | Nusse R, Clevers H. Wnt/β-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities[J]. Cell, 2017, 169(6): 985-99. |
| 22 | Zhao H, Ming TQ, Tang S, et al. Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer: pathogenic role and therapeutic target[J]. Mol Cancer, 2022, 21(1): 144. |
| 23 | Li HJ, Ke FY, Lin CC, et al. ENO1 promotes lung cancer metastasis via HGFR and WNT signaling-driven epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition[J]. Cancer Res, 2021, 81(15): 4094-109. |
| 24 | Hiremath IS, Goel A, Warrier S, et al. The multidimensional role of the Wnt/β‑catenin signaling pathway in human malignancies[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2022, 237(1): 199-238. |
| 25 | Rim EY, Clevers H, Nusse R. The Wnt pathway: from signaling mechanisms to synthetic modulators[J]. Annu Rev Biochem, 2022, 91: 571-98. |
| 26 | Albrecht LV, Tejeda-Muñoz N, de Robertis EM. Cell biology of canonical Wnt signaling[J]. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 37: 369-89. |
| 27 | Cheng XX, Wang ZC, Chen XY, et al. Frequent loss of membranous E-cadherin in gastric cancers: a cross-talk with Wnt in determining the fate of beta-catenin[J]. Clin Exp Metastasis, 2005, 22(1): 85-93. |
| 28 | Guo Q, Xu J, Huang Z, et al. ADMA mediates gastric cancer cell migration and invasion via Wnt/β‑catenin signaling pathway[J]. Clin Transl Oncol, 2021, 23(2): 325-34. |
| 29 | Wang J, Cai H, Liu QL, et al. Cinobufacini inhibits colon cancer invasion and metastasis via suppressing Wnt/β‑catenin signaling pathway and EMT[J]. Am J Chin Med, 2020, 48(3): 703-18. |
| 30 | Park JK, Song JH, He TC, et al. Overexpression of Wnt-2 in colorectal cancers[J]. Neoplasma, 2009, 56(2): 119-23. |
| 31 | Shi YH, He B, Kuchenbecker KM, et al. Inhibition of Wnt-2 and galectin-3 synergistically destabilizes beta-catenin and induces apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells[J]. Int J Cancer, 2007, 121(6): 1175-81. |
| 32 | Vider BZ, Zimber A, Chastre E, et al. Evidence for the involvement of the Wnt 2 gene in human colorectal cancer[J]. Oncogene, 1996, 12(1): 153-8. |
| 33 | Katoh M. WNT2 and human gastrointestinal cancer (review)[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2003, 12(5): 811-6. |
| 34 | Kramer N, Schmöllerl J, Unger C, et al. Autocrine WNT2 signaling in fibroblasts promotes colorectal cancer progression[J]. Oncogene, 2017, 36(39): 5460-72. |
| 35 | Lei L, Wang Y, Li ZH, et al. PHLDA3 promotes lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation and invasion via activation of the Wnt signaling pathway[J]. Lab Invest, 2021, 101(9): 1130-41. |
| 36 | Pu P, Zhang Z, Kang C, et al. Downregulation of Wnt2 and beta-catenin by siRNA suppresses malignant glioma cell growth[J]. Cancer Gene Ther, 2009, 16(4): 351-61. |
| [1] | Liangjun XUE, Qiuyu TAN, Jingwen XU, Lu FENG, Wenjin LI, Liang YAN, Yulei LI. MiR-6838-5p overexpression inhibits proliferation of breast cancer MCF-7 cells by downregulating DDR1 expression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1677-1684. |
| [2] | Mengnan YE, Hongmei WU, Yan MEI, Qingling ZHANG. High expression of CREM is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1776-1782. |
| [3] | Zhijun GENG, Jingjing YANG, Minzhu NIU, Xinyue LIU, Jinran SHI, Yike LIU, Xinyu YAO, Yulu ZHANG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Jianguo HU. Kuwanon G inhibits growth, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1476-1484. |
| [4] | Yidan PANG, Ya LIU, Siai CHEN, Jinglei ZHANG, Jin ZENG, Yuanming PAN, Juan AN. Biological role of SPAG5 in the malignant proliferation of gastric cancer cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1497-1507. |
| [5] | Xiaofan CONG, Teng CHEN, Shuo LI, Yuanyuan WANG, Longyun ZHOU, Xiaolong LI, Pei ZHANG, Xiaojin SUN, Surong ZHAO. Dihydroartemisinin enhances sensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma HNE1/DDP cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by promoting ROS production [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1553-1560. |
| [6] | Mengdong ZHENG, Yan LIU, Jiaojiao LIU, Qiaozhen KANG, Ting WANG. Effect of deletion of protein 4.1R on proliferation, apoptosis and glycolysis of hepatocyte HL-7702 cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1355-1360. |
| [7] | Huaxing HE, Lulin LIU, Yingyin LIU, Nachuan CHEN, Suxia SUN. Sodium butyrate and sorafenib synergistically inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma cells possibly by inducing ferroptosis through inhibiting YAP [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1425-1430. |
| [8] | Jincun FANG, Liwei LIU, Junhao LIN, Fengsheng CHEN. Overexpression of CDHR2 inhibits proliferation of breast cancer cells by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1117-1125. |
| [9] | Zhi CUI, Cuijiao MA, Qianru WANG, Jinhao CHEN, Ziyang YAN, Jianlin YANG, Yafeng LÜ, Chunyu CAO. A recombinant adeno-associated virus expressing secretory TGF‑β type II receptor inhibits triple-negative murine breast cancer 4T1 cell proliferation and lung metastasis in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 818-826. |
| [10] | Yongsheng XIA, Lian WANG, Xiaohua CHEN, Yulu ZHANG, Aofei SUN, Deli CHEN. TSR2 overexpression inhibits proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells by downregulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 913-919. |
| [11] | Jingjing YANG, Lixia YIN, Ting DUAN, Minzhu NIU, Zhendong HE, Xinrui CHEN, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Jing LI, Zhijun GENG, Lugen ZUO. High expression of ATP5A1 in gastric carcinoma is correlated with a poor prognosis and enhanced glucose metabolism in tumor cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 974-980. |
| [12] | HUANG Qiuhu, ZHOU Jian, WANG Zizhen, YANG Kun, CHEN Zhenggang. MiR-26-3p regulates proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of glioma cells by targeting CREB1 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 578-584. |
| [13] | LIANG Yihao, LAI Yingjun, YUAN Yanwen, YUAN Wei, ZHANG Xibo, ZHANG Bashan, LU Zhifeng. Screening of differentially expressed genes in gastric cancer based on GEO database and function and pathway enrichment analysis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 605-616. |
| [14] | ZHU Jin, OUYANG Xin, LIU Yu, QIAN Yemei, XIA Bin, SHI Yanan, YU Lifu. MiR-132-3p negatively regulates CAMTA1 to promote Schwann cell proliferation and migration and alleviates I-125 seeds-induced exacerbation of facial nerve injury in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 571-577. |
| [15] | SHEN Mengdi, ZHAO Na, DENG Xiaojing, DENG Min. High expression of COX6B2 in gastric cancer is associated with poor long-term prognosis and promotes cell proliferation and cell cycle progression by inhibiting p53 signaling [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 289-297. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||