Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (9): 1967-1979.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.16
Ying WANG1( ), Jing LI1, Yidi WANG2, Mingyu HUA1, Weibin HU1, Xiaozhi ZHANG1(
), Jing LI1, Yidi WANG2, Mingyu HUA1, Weibin HU1, Xiaozhi ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2025-02-19
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Xiaozhi ZHANG
E-mail:wangying123456@stu.xjtu.edu.cn;zhangxiaozhi@xjtu.edu.cn
Ying WANG, Jing LI, Yidi WANG, Mingyu HUA, Weibin HU, Xiaozhi ZHANG. Construction and verification of a prognostic model combining anoikis and immune prognostic signatures for primary liver cancer[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1967-1979.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.16
| Clinical | Total (n=576) | TCGA (n=351) | GEO (n=225) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender [n (%)] | |||
| Female | 149 (25.87) | 119 (33.90) | 30 (13.33) |
| Male | 427 (74.13) | 232 (66.10) | 195 (86.67) |
| Age (mean year) | 55.78 | 59.06 | 50.66 |
| Age (median year) | 56 (16-82) | 61 (16-82) | 50 (21-77) |
| Stage [n (%)] | |||
| I | 273 (47.40) | 177 (50.43) | 96 (42.67) |
| II | 163 (28.30) | 85 (24.22) | 78 (34.67) |
| III | 7 (1.22) | 4 (1.14) | 3 (1.33) |
| IIIA | 89 (15.45) | 60 (17.09) | 29 (12.89) |
| IIIB | 23 (3.99) | 8 (2.28) | 15 (6.67) |
| IIIC | 13 (2.26) | 9 (2.56) | 4 (1.78) |
| IV | 2 (0.35) | 2 (0.57) | 0 (0.00) |
| IVA | 2 (0.35) | 2 (0.57) | 0 (0.00) |
| IVB | 4 (0.69) | 4 (1.14) | 0 (0.00) |
Tab.1 Clinical data of liver cancer patients in TCGA and GEO databases
| Clinical | Total (n=576) | TCGA (n=351) | GEO (n=225) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender [n (%)] | |||
| Female | 149 (25.87) | 119 (33.90) | 30 (13.33) |
| Male | 427 (74.13) | 232 (66.10) | 195 (86.67) |
| Age (mean year) | 55.78 | 59.06 | 50.66 |
| Age (median year) | 56 (16-82) | 61 (16-82) | 50 (21-77) |
| Stage [n (%)] | |||
| I | 273 (47.40) | 177 (50.43) | 96 (42.67) |
| II | 163 (28.30) | 85 (24.22) | 78 (34.67) |
| III | 7 (1.22) | 4 (1.14) | 3 (1.33) |
| IIIA | 89 (15.45) | 60 (17.09) | 29 (12.89) |
| IIIB | 23 (3.99) | 8 (2.28) | 15 (6.67) |
| IIIC | 13 (2.26) | 9 (2.56) | 4 (1.78) |
| IV | 2 (0.35) | 2 (0.57) | 0 (0.00) |
| IVA | 2 (0.35) | 2 (0.57) | 0 (0.00) |
| IVB | 4 (0.69) | 4 (1.14) | 0 (0.00) |
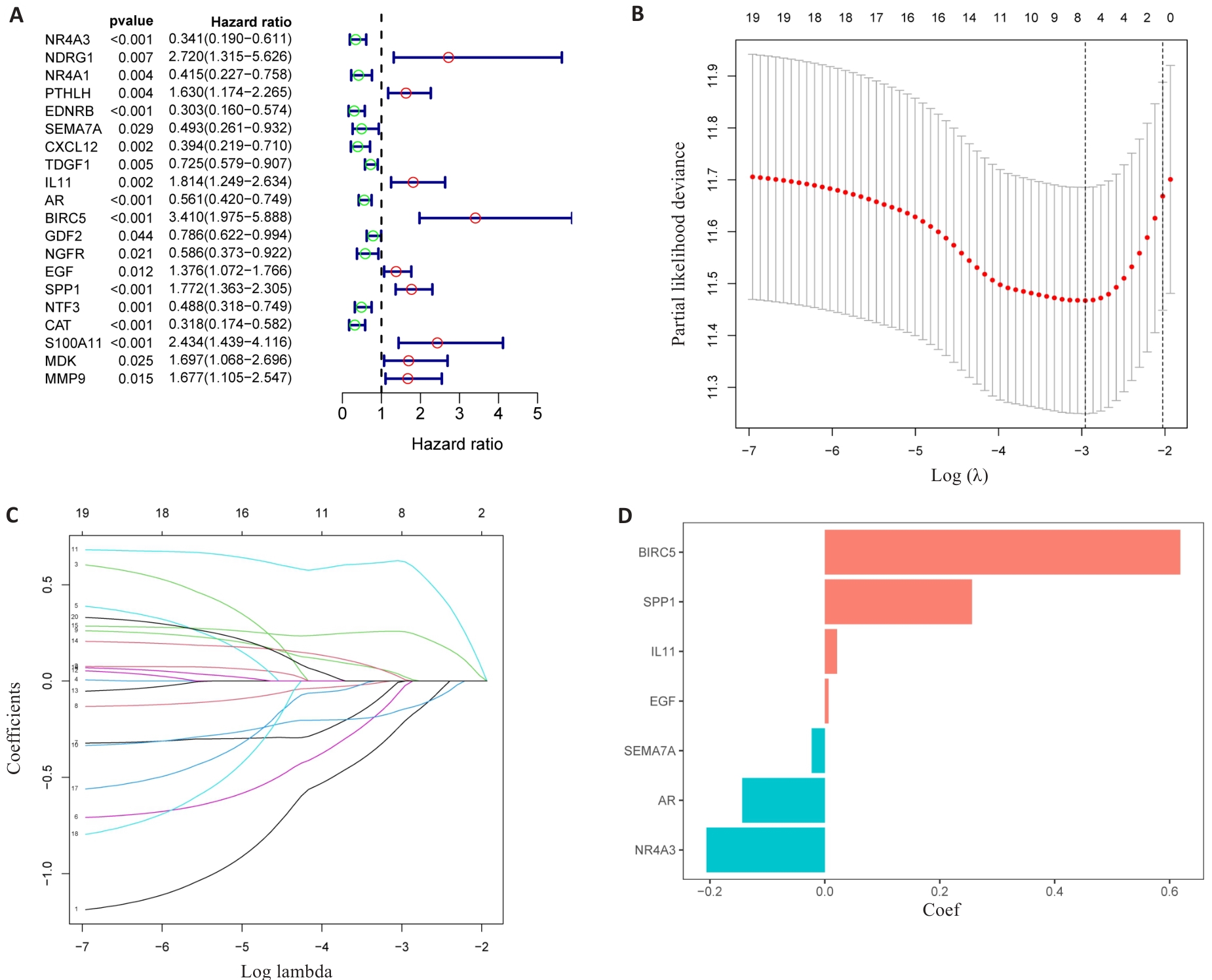
Fig.3 Identification of the DAIs. A: Forest maps of the predictive power of 20 characteristic genes. B: LASSO regression analysis based on DAIs. C: LASSO coefficient of DAIs gene in PLC. D: LASSO gene coefficient histogram.
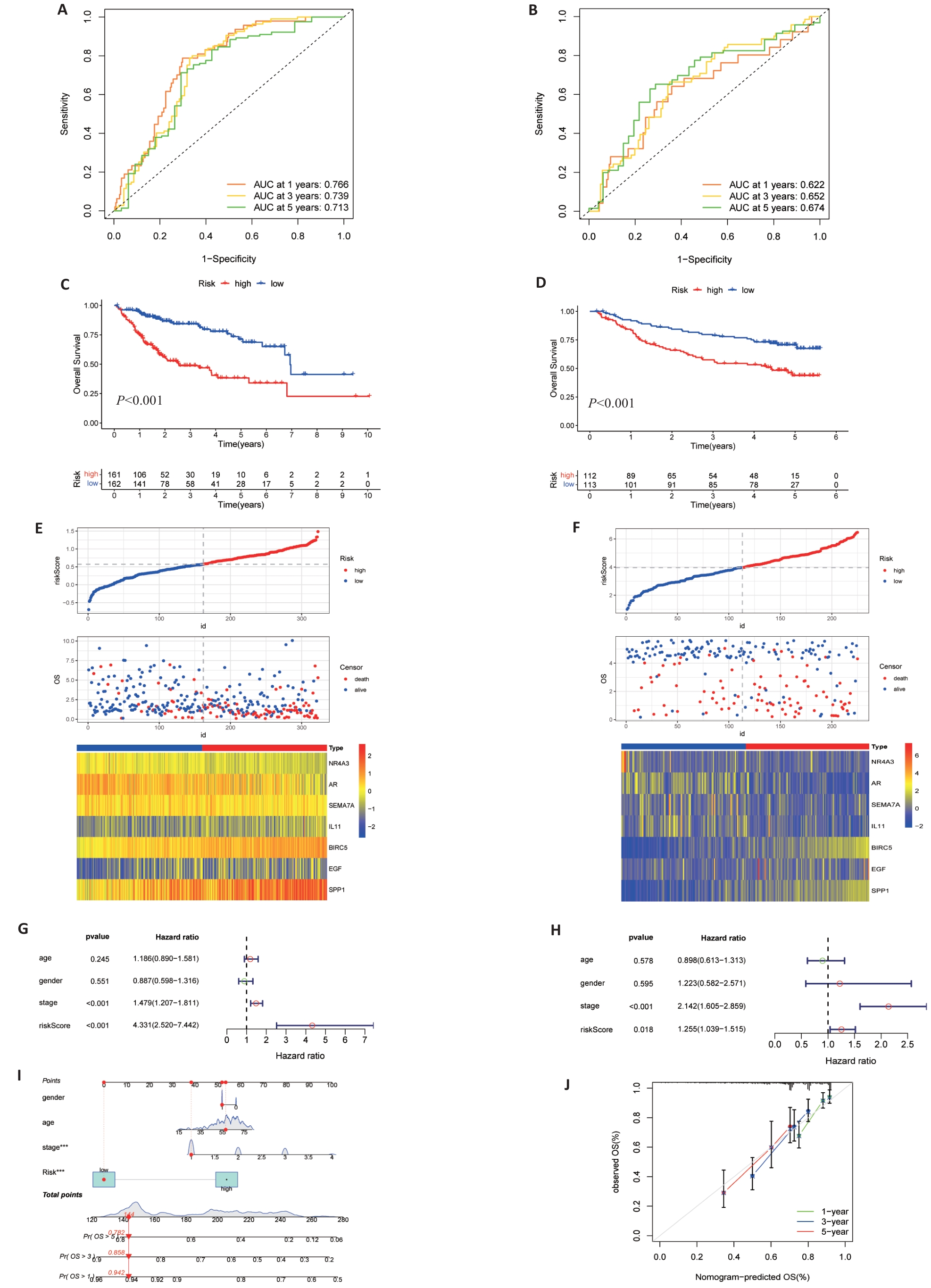
Fig.4 Validation of risk signature. A, B: Prediction of time-dependent ROC for 1, 3, and 5-year OS in TCGA cohort and GEO cohort. C, D: Kaplan-Meier survival curves showed that there were differences in OS between high and low TCGA and GEO groups. E, F: Risk scores, survival status and heat maps of 7 DAIs between high and low groups of TCGA (E) and GSE14520 (F). G, H: Multivariate cox regression analysis of TCGA (G) and GEO (H) risk scores and clinical data. I: Nomogram of clinical data and risk groups of TCGA. J: Standard curves showing good nomogram accuracy.
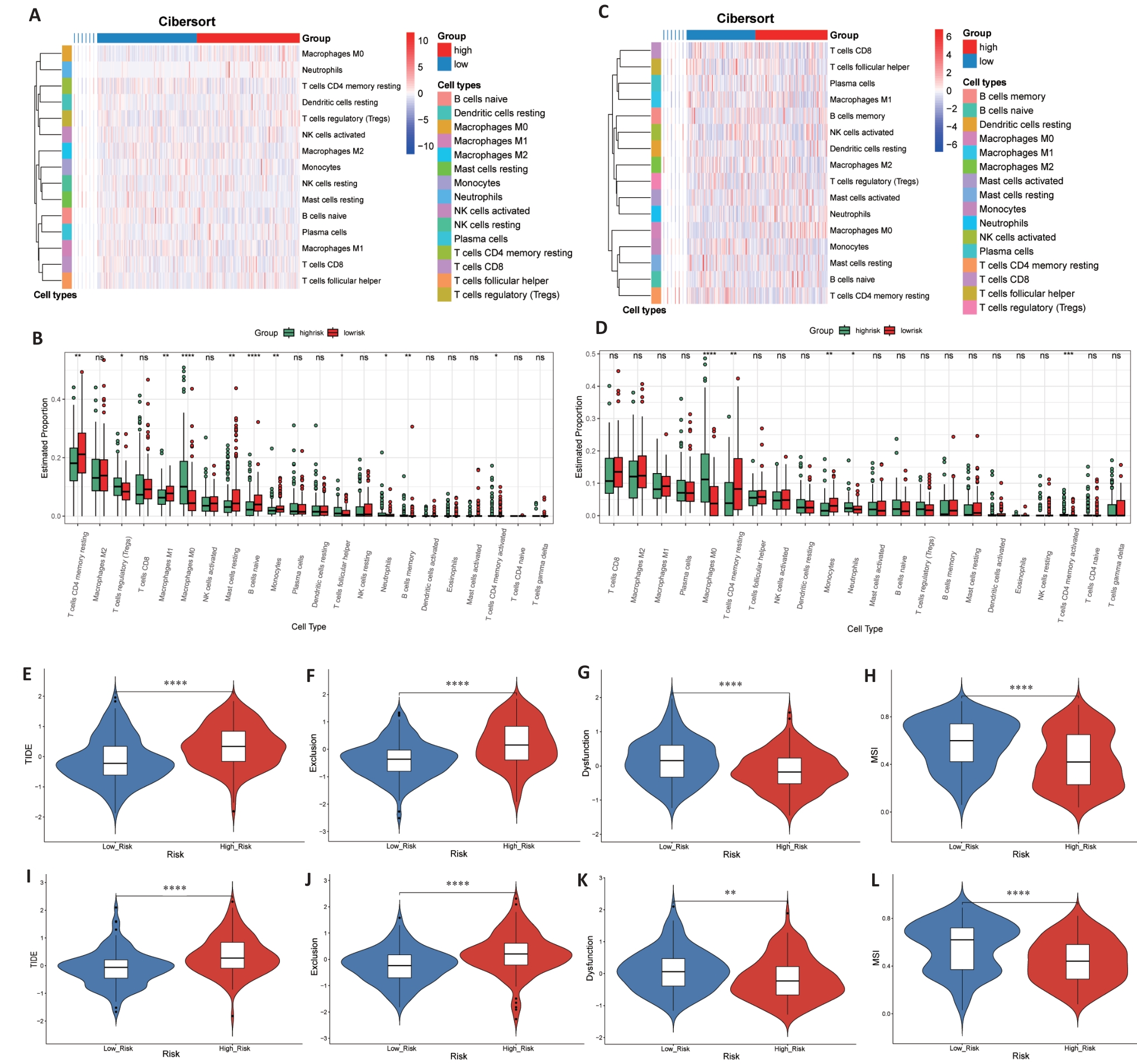
Fig. 6 Immune status and prediction of response to immunotherapy. A-D: Heatmaps and enrichment scores of 22 immune cells in TCGA (A, B) and GEO (C, D) high-risk and low-risk groups. E-L: TIDE score, rejection score, dysfunction score and MSI score between TCGA (E-H) and GEO (I-L) groups. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001).
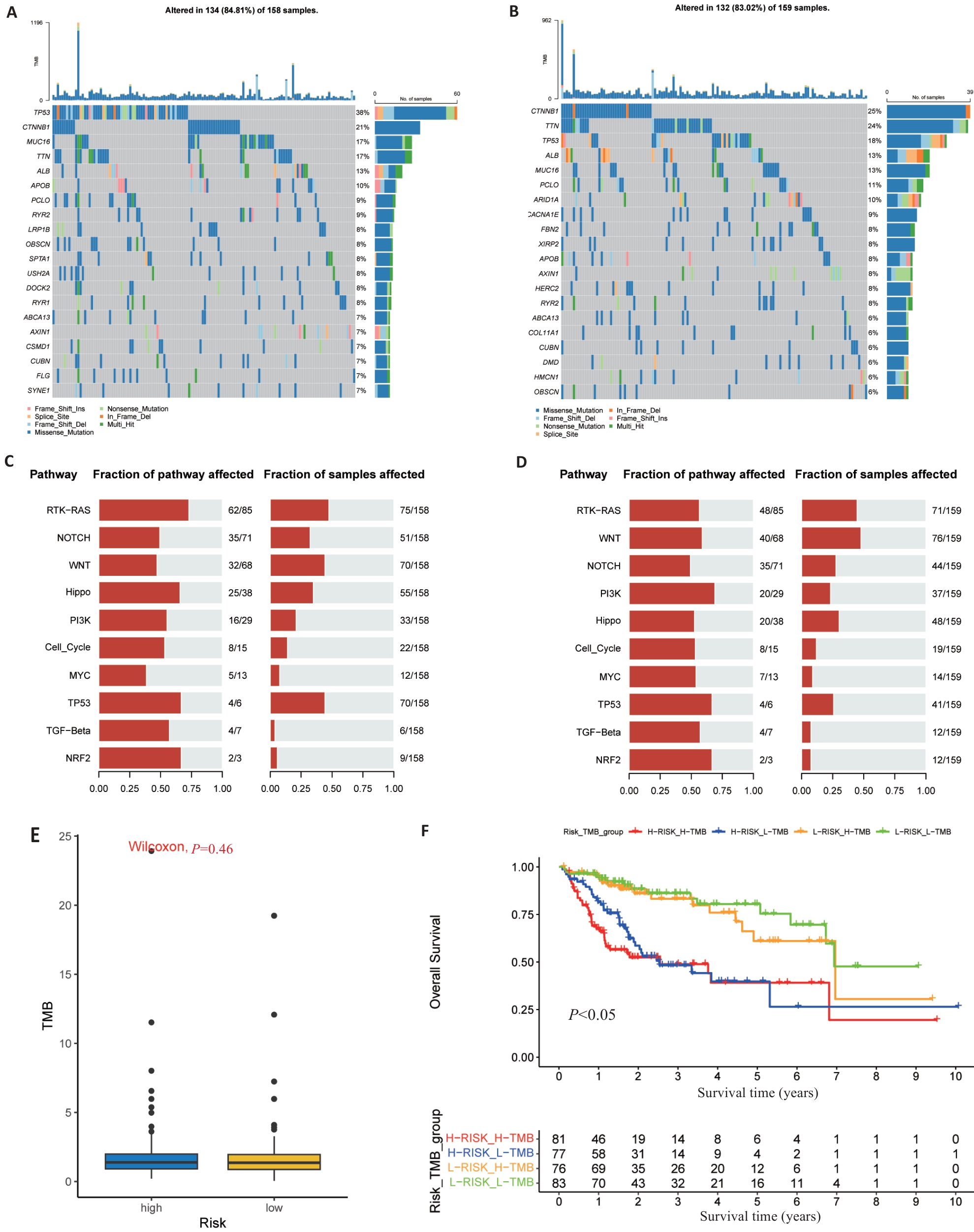
Fig.7 Somatic mutations and TMB in risk signature. A, B: The waterfall map shows the top 20 genes with the highest mutation frequency in the high-risk group (A) and low-risk group (B) of TCGA. C, D: The bar chart shows the top 10 high mutation pathways in the high-risk (C) and low-risk (D) TCGA groups. E: Box chart showing TMB score comparison between high- and low-risk groups. F: Kaplan-Meier survival curves show OS differences between groups classified according to TMB and TCGA risk.
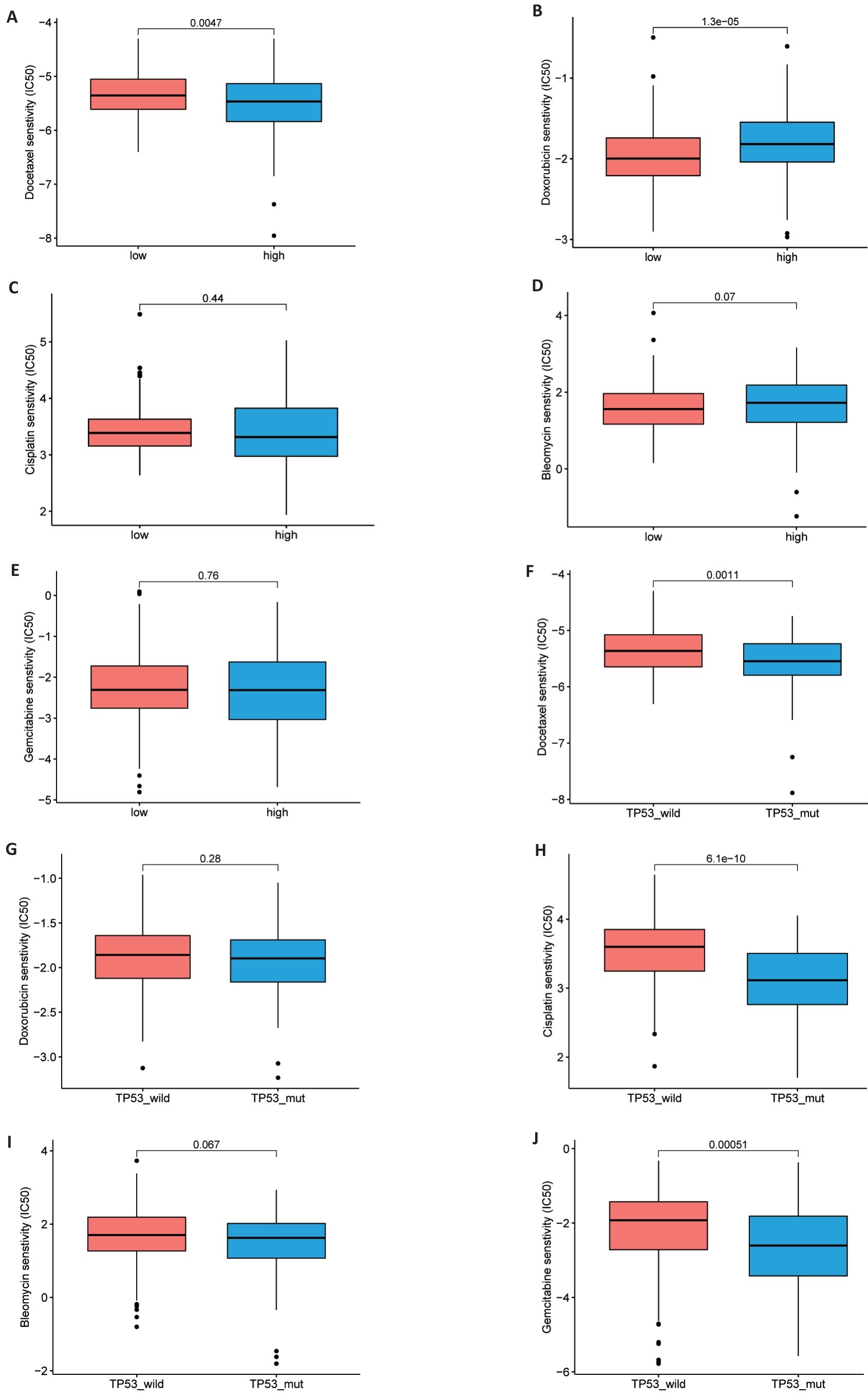
Fig. 8 Drug sensitivity analysis. A-J: Comparison of half maximum inhibitory concentrations (IC50) of docetaxel, adriamycin, cisplatin and bleomycin in high and low risk TCGA groups (A-E) and TP53 mutant and non-mutant groups (F-J).
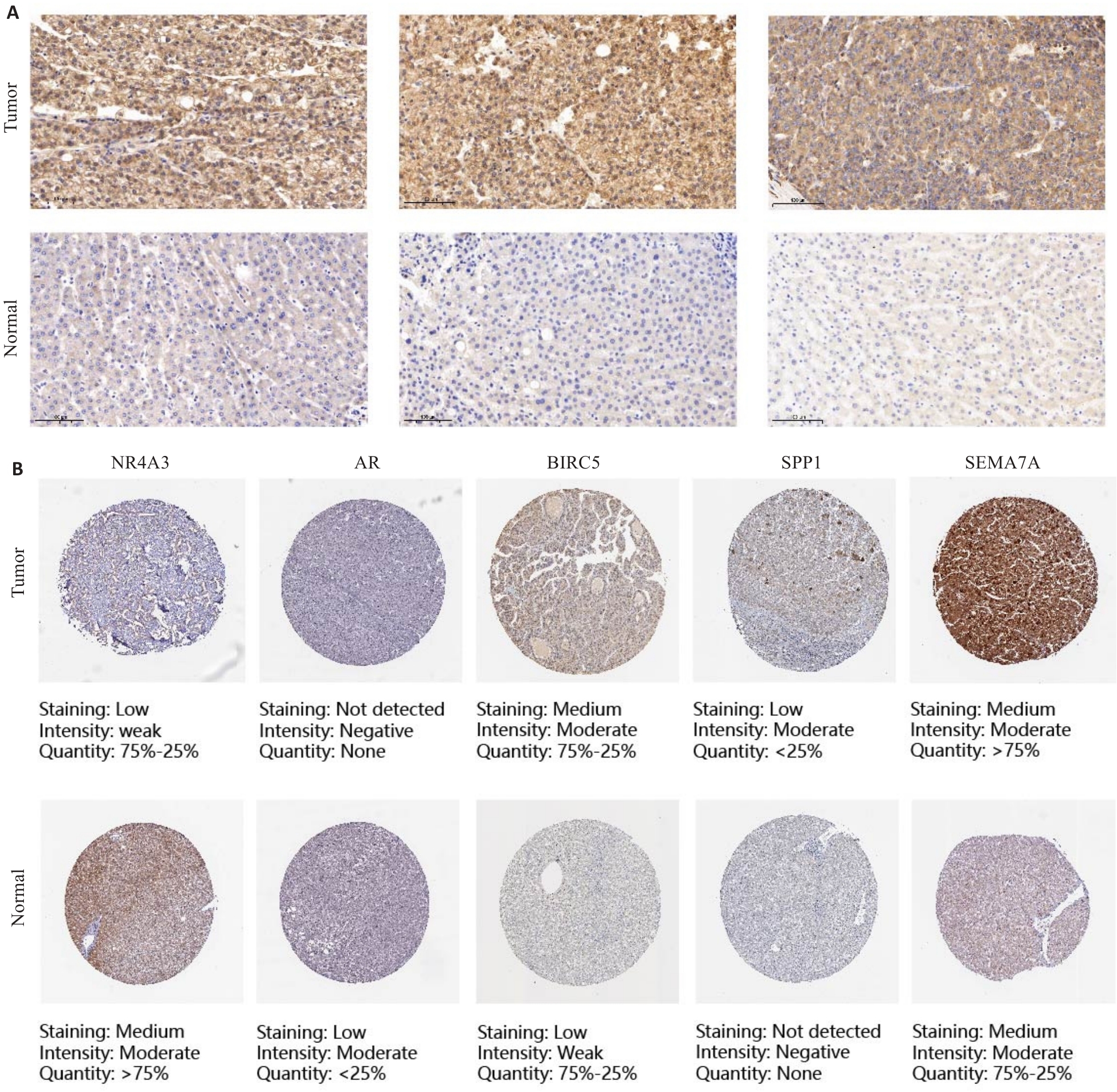
Fig.9 Immunohistochemistry and HPA website for verifying the expression of DAIs in primary liver cancer and adjacent tissues (Original magnification: ×100). A: Representative immunohistochemical images of SEMA7A in PLC tissues and adjacent tissues. B: Representative immunohistochemical images of NR4A3, AR, BIRC5, SPP1 and SEMA7A in PLC tissues and normal tissues on the HPA website.
| Gene | Expression level | Tissue | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cancer | Normal | ||||
| SEMA7A | High expression | 28 | 7 | 7.72 | <0.01 |
| Low expression | 6 | 9 | |||
Tab.2 Expression of SEMA7A in liver cancer tissues and adjacent normal liver tissues (n)
| Gene | Expression level | Tissue | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cancer | Normal | ||||
| SEMA7A | High expression | 28 | 7 | 7.72 | <0.01 |
| Low expression | 6 | 9 | |||
| [1] | Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74(3): 229-63. doi:10.3322/caac.21834 |
| [2] | Gilmore AP. Anoikis[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2005, 12(S2): 1473-7. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401723 |
| [3] | Janiszewska M, Primi MC, Izard T. Cell adhesion in cancer: Beyond the migration of single cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2020, 295(8): 2495-505. doi:10.1074/jbc.rev119.007759 |
| [4] | Paoli P, Giannoni E, Chiarugi P. Anoikis molecular pathways and its role in cancer progression[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2013, 1833(12): 3481-98. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.06.026 |
| [5] | Kakavandi E, Shahbahrami R, Goudarzi H, et al. Anoikis resistance and oncoviruses[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2018, 119(3): 2484-91. doi:10.1002/jcb.26363 |
| [6] | Adeshakin FO, Adeshakin AO, Afolabi LO, et al. Mechanisms for modulating anoikis resistance in cancer and the relevance of metabolic reprogramming[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 626577. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.626577 |
| [7] | Guadamillas MC, Cerezo A, Del Pozo MA. Overcoming anoikis: pathways to anchorage-independent growth in cancer[J]. J Cell Sci, 2011, 124(Pt 19): 3189-97. doi:10.1242/jcs.072165 |
| [8] | Angell H, Galon J. From the immune contexture to the immunoscore: the role of prognostic and predictive immune markers in cancer[J]. Curr Opin Immunol, 2013, 25(2): 261-7. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2013.03.004 |
| [9] | Chen DS, Mellman I. Elements of cancer immunity and the cancer-immune set point[J]. Nature, 2017, 541(7637): 321-30. doi:10.1038/nature21349 |
| [10] | El-Khoueiry AB, Sangro B, Yau T, et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): an open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial[J]. Lancet, 2017, 389(10088): 2492-502. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(17)31046-2 |
| [11] | Zhao ZH, Li C, Peng Y, et al. Construction of an original anoikis-related prognostic model closely related to immune infiltration in gastric cancer[J]. Front Genet, 2023, 13: 1087201. doi:10.3389/fgene.2022.1087201 |
| [12] | Chen Z, Liu X, Zhu ZJ, et al. A novel anoikis-related prognostic signature associated with prognosis and immune infiltration landscape in clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Front Genet, 2022, 13: 1039465. doi:10.3389/fgene.2022.1039465 |
| [13] | Chen S, Gu JM, Zhang QF, et al. Development of biomarker signatures associated with anoikis to predict prognosis in endometrial carcinoma patients[J]. J Oncol, 2021, 2021: 3375297. doi:10.1155/2021/3375297 |
| [14] | Sun ZZ, Zhao YQ, Wei Y, et al. Identification and validation of an anoikis-associated gene signature to predict clinical character, stemness, IDH mutation, and immune filtration in glioblastoma[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 939523. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.939523 |
| [15] | Moujalled D, Strasser A, Liddell JR. Molecular mechanisms of cell death in neurological diseases[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2021, 28(7): 2029-44. doi:10.1038/s41418-021-00814-y |
| [16] | Chen YT, Huang WR, Ouyang J, et al. Identification of anoikis-related subgroups and prognosis model in liver hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(3): 2862. doi:10.3390/ijms24032862 |
| [17] | Chi H, Jiang PY, Xu K, et al. A novel anoikis-related gene signature predicts prognosis in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and reveals immune infiltration[J]. Front Genet, 2022, 13: 984273. doi:10.3389/fgene.2022.984273 |
| [18] | Pan Q, Luo G, Qu JQ, et al. A homozygous R148W mutation in Semaphorin 7A causes progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis[J]. EMBO Mol Med, 2021, 13(11): e14563. doi:10.15252/emmm.202114563 |
| [19] | Li X, Xie WL, Pan Q, et al. Semaphorin 7A interacts with nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 via integrin β1 and mediates inflammation[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2023, 21(1): 24. doi:10.1186/s12964-022-01024-w |
| [20] | Yeh CM, Chang LY, Lin SH, et al. Epigenetic silencing of the NR4A3 tumor suppressor, by aberrant JAK/STAT signaling, predicts prognosis in gastric cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 31690. doi:10.1038/srep31690 |
| [21] | Fedorova O, Petukhov A, Daks A, et al. Orphan receptor NR4A3 is a novel target of p53 that contributes to apoptosis[J]. Oncogene, 2019, 38(12): 2108-22. doi:10.1038/s41388-018-0566-8 |
| [22] | Wang HH, Guo QN, Nampoukime KB, et al. Long non-coding RNA LINC00467 drives hepatocellular carcinoma progression via inhibiting NR4A3[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2020, 24(7): 3822-36. doi:10.1111/jcmm.14942 |
| [23] | Shi DM, Dong SS, Zhou HX, et al. Genomic and transcriptomic profiling reveals key molecules in metastatic potentials and organ-tropisms of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Signal, 2023, 104: 110565. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2022.110565 |
| [24] | Wang DY, Zheng XH, Fu BQ, et al. Hepatectomy promotes recurrence of liver cancer by enhancing IL-11-STAT3 signaling[J]. EBioMedicine, 2019, 46: 119-32. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.07.058 |
| [25] | Yu LD, Wang S, Lin XJ, et al. microRNA-124a inhibits cell proliferation and migration in liver cancer by regulating interleukin-11[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018, 17(3): 3972-8. |
| [26] | Sun RF, Zhao CY, Chen S, et al. Androgen receptor stimulates hexokinase 2 and induces glycolysis by PKA/CREB signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2021, 66(3): 802-13. doi:10.1007/s10620-020-06229-y |
| [27] | Xu RZ, Lin LB, Zhang B, et al. Identification of prognostic markers for hepatocellular carcinoma based on the epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related gene BIRC5 [J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21(1): 687. doi:10.1186/s12885-021-08390-7 |
| [28] | Zhang LY, Yuan LY, Li DH, et al. Identification of potential prognostic biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Gastrointest Oncol, 2022, 13(2): 812-21. doi:10.21037/jgo-22-303 |
| [29] | Wang X, Liang C, Yao X, et al. PKM2-induced the phosphorylation of histone H3 contributes to EGF-mediated PD-L1 transcription in HCC[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 577108. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.577108 |
| [30] | Zhao HL, Chen Q, Alam A, et al. The role of osteopontin in the progression of solid organ tumour[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9: 356. doi:10.1038/s41419-018-0391-6 |
| [31] | Wang JQ, Hao FJ, Fei XC, et al. SPP1 functions as an enhancer of cell growth in hepatocellular carcinoma targeted by miR-181c[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2019, 11(11): 6924-37. |
| [32] | Eun JW, Yoon JH, Ahn HR, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived secreted phosphoprotein 1 contributes to resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib and lenvatinib[J]. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2023, 43(4): 455-79. doi:10.1002/cac2.12414 |
| [33] | Fu JX, Li KR, Zhang WB, et al. Large-scale public data reuse to model immunotherapy response and resistance[J]. Genome Med, 2020, 12(1): 21. doi:10.1186/s13073-020-0721-z |
| [34] | Hou ZQ, Liu J, Jin ZX, et al. Use of chemotherapy to treat hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Biosci Trends, 2022, 16(1): 31-45. doi:10.5582/bst.2022.01044 |
| [1] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | Ying YU, Li TU, Yang LIU, Xueyi SONG, Qianqian SHAO, Xiaolong TANG. The TGF‑β/miR-23a-3p/IRF1 axis mediates immune escape of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting major histocompatibility complex class I [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1397-1408. |
| [3] | Kang WANG, Haibin LI, Jing YU, Yuan MENG, Hongli ZHANG. High expression of ELFN1 is a prognostic biomarker and promotes proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1543-1553. |
| [4] | Zhi GAO, Ao WU, Zhongxiang HU, Peiyang SUN. Bioinformatics analysis of oxidative stress and immune infiltration in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 862-870. |
| [5] | Huaiwen XU, Li WENG, Hong XUE. CXCL12 is a potential therapeutic target for type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 100-109. |
| [6] | Mengnan YE, Hongmei WU, Yan MEI, Qingling ZHANG. High expression of CREM is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1776-1782. |
| [7] | Kai JI, Guanyu YU, Leqi ZHOU, Tianshuai ZHANG, Qianlong LING, Wenjiang MAN, Bing ZHU, Wei ZHANG. HNRNPA1 gene is highly expressed in colorectal cancer: its prognostic implications and potential as a therapeutic target [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1685-1695. |
| [8] | Hongli YANG, Yayun XIANG, Tingting TAN, Yang LEI. ORY-1001 inhibits glioblastoma cell growth by downregulating the Notch/HES1 pathway via suppressing lysine-specific demethylase 1 expression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1620-1630. |
| [9] | Wei ZHOU, Jun NIE, Jia HU, Yizhi JIANG, Dafa ZHANG. Differential expressions of endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated genes in aortic dissection and their correlation with immune cell infiltration [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 859-866. |
| [10] | Bei PEI, Yi ZHANG, Siyuan WEI, Yu MEI, Biao SONG, Gang DONG, Ziang WEN, Xuejun LI. Identification of potential pathogenic genes of intestinal metaplasia based on transcriptomic sequencing and bioinformatics analysis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 941-949. |
| [11] | Qinzhi WANG, Bing SONG, Shirui HAO, Zhiyuan XIAO, Lianhui JIN, Tong ZHENG, Fang CHAI. Bioinformatic analysis of CCND2 expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma and its impact on immune infiltration [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 981-988. |
| [12] | LIANG Yihao, LAI Yingjun, YUAN Yanwen, YUAN Wei, ZHANG Xibo, ZHANG Bashan, LU Zhifeng. Screening of differentially expressed genes in gastric cancer based on GEO database and function and pathway enrichment analysis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 605-616. |
| [13] | Peipei ZHAO, Zhigang ZHOU, Yuanyuan YANG, Shusheng HUANG, Yixuan TU, Jian TU. Ferroptosis inducer Erastin inhibits proliferation of liver cancer cells in vitro by down-regulating ACSL4 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2131-2136. |
| [14] | Zijing REN, Peiyang ZHOU, Jing TIAN. Plasma long noncoding RNA expression profiles in patients with Parkinson's disease and the role of lnc-CTSD-5:1 in a PD cell model: a ceRNA microarray-based study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2146-2155. |
| [15] | CHENG Jiacong, LI Zhihui, LIU Yao, LI Cheng, HUANG Xin, TIAN Yinxin, SHEN Fubing. Bioinformatics analysis and validation of the interaction between PML protein and TAB1 protein [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 179-186. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||