Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (9): 1959-1966.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.15
Chen ZHANG1, Zhi XU2, Xiang LI3, Pengyixiang HE1, Kailin QU1, Qi NING2, Yile JIN1, Surui YANG1, Xu WU1( )
)
Received:2025-02-24
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Xu WU
E-mail:wuxu_southhospital@163.com
Chen ZHANG, Zhi XU, Xiang LI, Pengyixiang HE, Kailin QU, Qi NING, Yile JIN, Surui YANG, Xu WU. Polydopamine-modified phycocyanin nanoparticles with photothermal antimicrobial activity promote skin wound healing in mice[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1959-1966.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.15
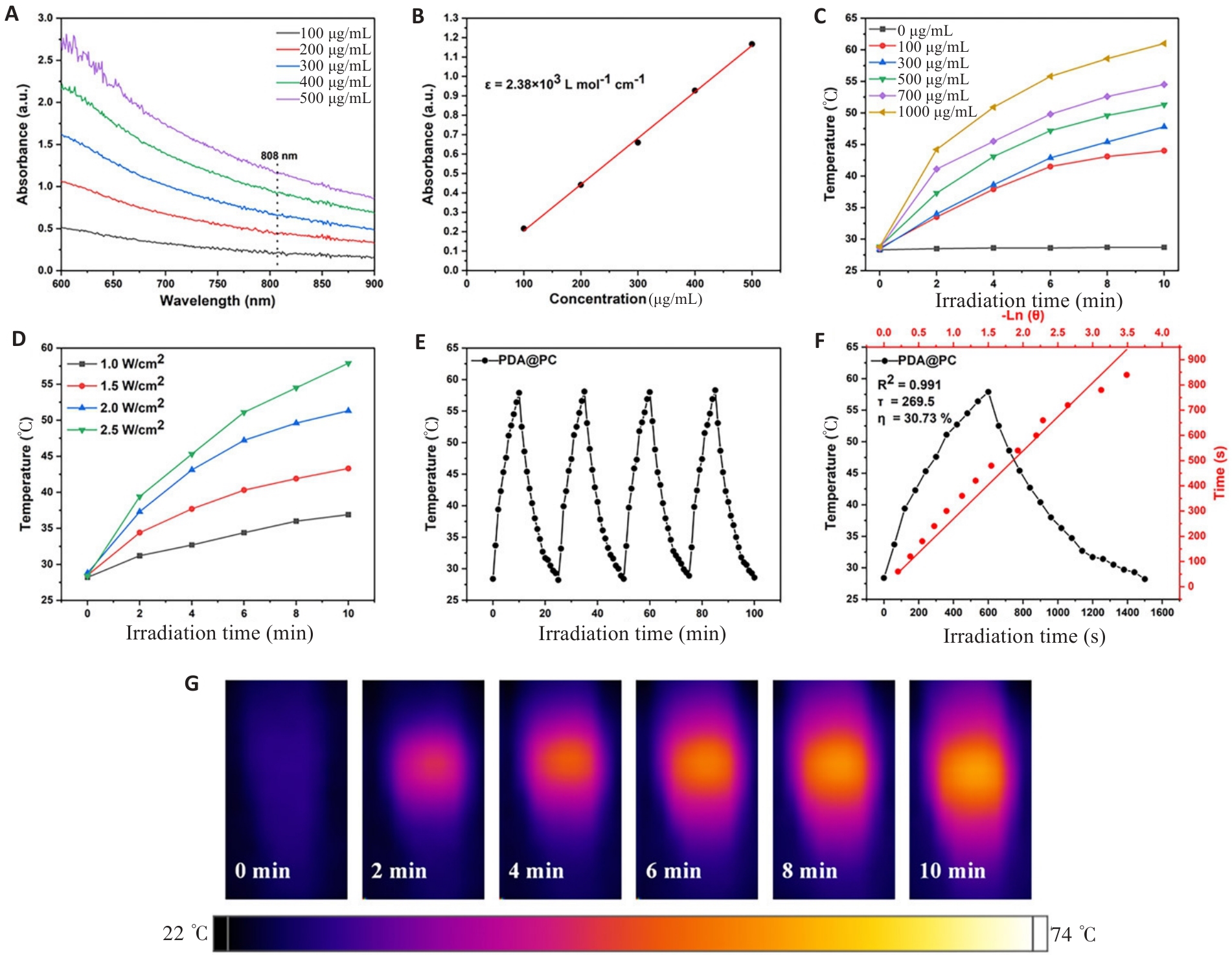
Fig.2 Ultraviolet absorption spectrum and photothermal characterization of the nanoparticles. A: UV-vis spectra of PDA@PC NPs with different concentrations. B: Mass absorption coefficient of PDA@PC NPs. C: Temperature curves of PDA@PC NPs with varying concentrations under 808 nm laser irradiation at 2.0 W/cm2. D: Temperature curves of PDA@PC NPs (500 μg/mL) under 808 nm laser irradiation at different power densities. E: Thermostability of PDA@PC NPs(500 μg/mL) in water exposed to 808 nm laser (2.5 W/cm2) for 4 on/off cycles. F: Photothermal conversion profiles of PDA@PC NPs. G: In vitro photothermal images of centrifuge tubes filled with various concentrations of PDA@PC NPs.
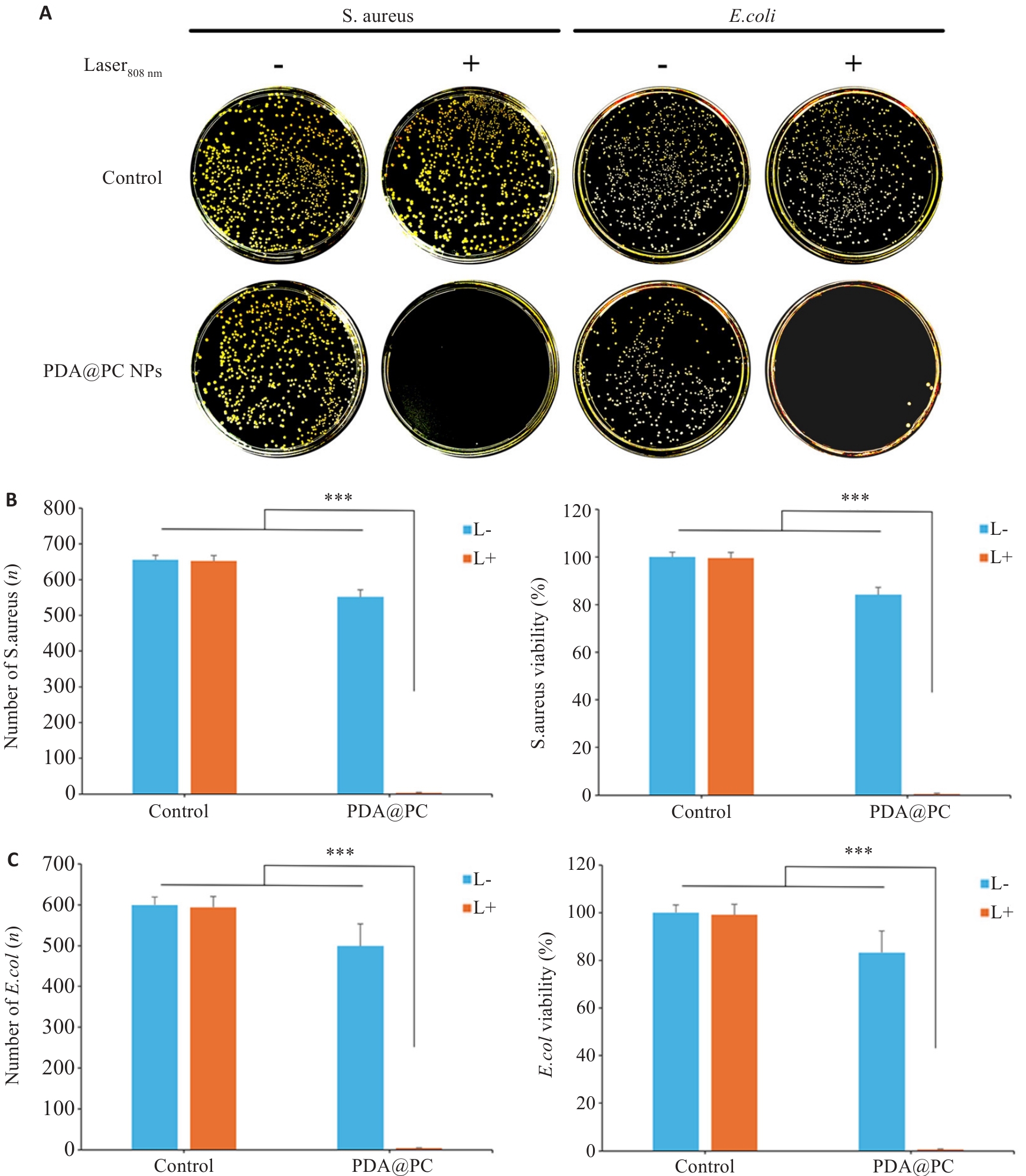
Fig.4 Evaluation of antimicrobial ability of the nanoparticles. A: Plate colony growth. B: Staphylococcus aureus colony formation and bacterial survival rate. C: E. coli colony formation and bacterial survival rate. ***P<0.001.
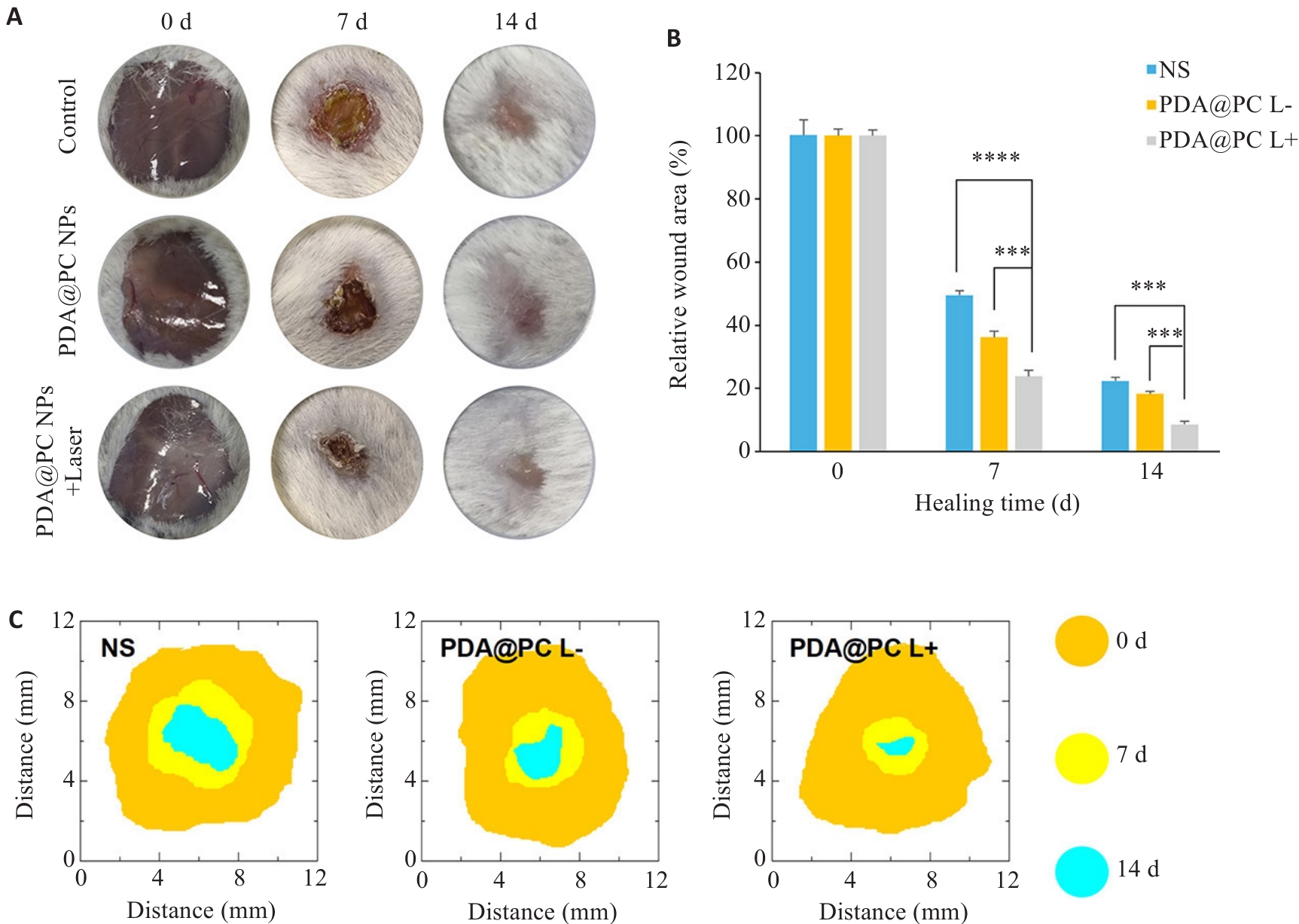
Fig.5 Representative images of wound healing in mice (A), the healing rates (B), and simulated images of the healing processes (C). ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
| [1] | Zhang CL, Merana GR, Harris-Tryon T, et al. Skin immunity: dissecting the complex biology of our body's outer barrier[J]. Mucosal Immunol, 2022, 15(4): 551-61. doi:10.1038/s41385-022-00505-y |
| [2] | Bernatchez SF, Bichel J. The science of skin: measuring damage and assessing risk[J]. Adv Wound Care: New Rochelle, 2023, 12(4): 187-204. doi:10.1089/wound.2022.0021 |
| [3] | Zhu Y, Yu X, Cheng G. Human skin bacterial microbiota homeostasis: a delicate balance between health and disease[J]. mLife, 2023, 2(2): 107-20. doi:10.1002/mlf2.12064 |
| [4] | Peña OA, Martin P. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of skin wound healing[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2024, 25(8): 599-616. doi:10.1038/s41580-024-00715-1 |
| [5] | He DF, Liao CY, Li PF, et al. Multifunctional photothermally responsive hydrogel as an effective whole-process management platform to accelerate chronic diabetic wound healing[J]. Acta Biomater, 2024, 174: 153-62. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2023.11.043 |
| [6] | Sen CK. Human wounds and its burden: an updated compendium of estimates[J]. Adv Wound Care: New Rochelle, 2019, 8(2): 39-48. doi:10.1089/wound.2019.0946 |
| [7] | Zhao X, Wu H, Guo BL, et al. Antibacterial anti-oxidant electroactive injectable hydrogel as self-healing wound dressing with hemostasis and adhesiveness for cutaneous wound healing[J]. Biomaterials, 2017, 122: 34-47. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.01.011 |
| [8] | Wang Y, Yang Y, Shi Y, et al. Antibiotic-free antibacterial strategies enabled by nanomaterials: progress and perspectives[J]. Adv Mater, 2020, 32(18): e1904106. doi:10.1002/adma.202070138 |
| [9] | 贝 颖, 李文靖, 李美运, 等. 普鲁士蓝纳米颗粒促进糖尿病皮肤创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(10): 1526-32. doi:10.12307/2024.249 |
| [10] | Joudeh N, Linke D. Nanoparticle classification, physicochemical properties, characterization, and applications: a comprehensive review for biologists[J]. J Nanobiotechnology, 2022, 20(1): 262. doi:10.1186/s12951-022-01477-8 |
| [11] | Zhou J, Chen N, Liao J, et al. Ag-activated metal-organic framework with peroxidase-like activity synergistic Ag+ release for safe bacterial eradication and wound healing[J]. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12(22): 4058. doi:10.3390/nano12224058 |
| [12] | Mamidi N, Delgadillo RMV, Sustaita AO, et al. Current nanocomposite advances for biomedical and environmental application diversity [J]. Med Res Rev. 2025, 45(2): 576-628. doi:10.1002/med.22082 |
| [13] | Lin ZX, Jiang BP, Liang JZ, et al. Phycocyanin functionalized single-walled carbon nanohorns hybrid for near-infrared light-mediated cancer phototheranostics[J]. Carbon, 2019, 143: 814-27. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2018.12.011 |
| [14] | Bannu SM, Lomada D, Gulla S, et al. Potential therapeutic applications of C-phycocyanin[J]. Curr Drug Metab, 2019, 20(12): 967-76. doi:10.2174/1389200220666191127110857 |
| [15] | Blas-Valdivia V, Moran-Dorantes DN, Rojas-Franco P, et al. C-Phycocyanin prevents acute myocardial infarction-induced oxidative stress, inflammation and cardiac damage[J]. Pharm Biol, 2022, 60(1): 755-63. doi:10.1080/13880209.2022.2055089 |
| [16] | 王晓真, 付 聪, 董鸿春, 等. 藻蓝蛋白稳定性及稳态化的研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2022, 13(1): 103-9. |
| [17] | Li FP, Huang K, Chang HS, et al. A polydopamine coated nanoscale FeS theranostic platform for the elimination of drug-resistant bacteria via photothermal-enhanced Fenton reaction[J]. Acta Biomater, 2022, 150: 380-90. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2022.07.046 |
| [18] | Liu Y, Ai K, Lu L. Polydopamine and its derivative materials: synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields[J]. Chem Rev, 2014, 114(9): 5057-115. doi:10.1021/cr400407a |
| [19] | Xu N, Huang QQ, Shi L, et al. A bioinspired polydopamine-FeS nanocomposite with high antimicrobial efficiency via NIR-mediated Fenton reaction[J]. Dalton Trans, 2023, 52(6): 1687-701. doi:10.1039/d2dt03765c |
| [20] | Liang Z, Liu W, Wang Z, et al. Near-infrared laser-controlled nitric oxide-releasing gold nanostar/hollow polydopamine Janus nano-particles for synergistic elimination of methicillin-resistant Staphylo-coccus aureus and wound healing[J]? Acta Biomater, 2022, 143: 428-44. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2022.02.029 |
| [21] | Yuwen LH, Xiao HY, Lu P, et al. Amylase degradation enhanced NIR photothermal therapy and fluorescence imaging of bacterial biofilm infections[J]. Biomater Sci, 2023, 11(2): 630-40. doi:10.1039/d2bm01570f |
| [22] | Chen Y, Gao Y, Chen Y, et al. Nanomaterials-based photothermal therapy and its potentials in antibacterial treatment[J]. J Control Release, 2020, 328: 251-62. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.08.055 |
| [23] | 宋居星私, 张黎明, 王倩倩. 纳米材料应用于伤口敷料的研究进展[J]. 海军医学杂志, 2025, 46(3): 319-23. |
| [24] | Frykberg RG, Banks J. Challenges in the treatment of chronic wounds[J]. Adv Wound Care: New Rochelle, 2015, 4(9): 560-82. doi:10.1089/wound.2015.0635 |
| [25] | Nussbaum SR, Carter MJ, Fife CE, et al. An economic evaluation of the impact, cost, and medicare policy implications of chronic nonhealing wounds[J]. Value Health, 2018, 21(1): 27-32. doi:10.1016/j.jval.2017.07.007 |
| [26] | Sakata J, Sasaki S, Handa K, et al. A retrospective, longitudinal study to evaluate healing lower extremity wounds in patients with diabetes mellitus and ischemia using standard protocols of care and platelet-rich plasma gel in a Japanese wound care program[J]. Ostomy Wound Manage, 2012, 58(4): 36-49. |
| [27] | 邵丽林, 解佑银, 张雷芳. 藻蓝蛋白对小鼠皮肤损伤的治疗效果[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2024, 63(6): 141-50. |
| [28] | Dong J, Lang YT, He J, et al. Phycocyanin-based multifunctional microspheres for treatment of infected radiation-induced skin injury[J]. Biomaterials, 2025, 317: 123061. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.123061 |
| [29] | Liang HZ, Sun YL, Li CM, et al. Facile synthesis of phycocyanin/polydopamine hierarchical nanocomposites for synergizing PTT/PDT against cancer[J]. RSC Adv, 2022, 12(54): 34815-21. doi:10.1039/d2ra05863d |
| [30] | 刘宇炜, 郭 卓. 聚多巴胺-阿霉素纳米颗粒对癌细胞的化疗-光热治疗协同作用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(7): 1389-94. doi:10.7503/cjcu20141108 |
| [31] | Peng N, Du Y, Liu J, et al. Injectable polydopamine nanoparticle-incorporated hydrogels for antiangiogenesis and stimulating tumoricidal immunity to inhibit metastasis and recurrence postresection[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2024, 16(47): 64447-62. doi:10.1021/acsami.4c10363 |
| [32] | Lin JY, Tan SI, Yi YC, et al. High-level production and extraction of C-phycocyanin from cyanobacteria Synechococcus sp. PCC7002 for antioxidation, antibacterial and lead adsorption[J]. Environ Res, 2022, 206: 112283. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2021.112283 |
| [33] | Gong W, Huang HB, Wang XC, et al. Coassembly of fiber hydrogel with antibacterial activity for wound healing[J]. ACS Biomater Sci Eng, 2023, 9(1): 375-87. doi:10.1021/acsbiomaterials.2c00716 |
| [34] | Solmaz H, Ulgen Y, Gulsoy M. Photobiomodulation of wound healing via visible and infrared laser irradiation[J]. Lasers Med Sci, 2017, 32(4): 903-10. doi:10.1007/s10103-017-2191-0 |
| [35] | Duan QQ, Wang JL, Zhang BY, et al. Polydopamine coated Au-Pt nanorods: enhanced photothermal properties and efficient reactive oxygen scavengers[J]. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces, 2022, 210: 112247. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2021.112247 |
| [36] | Li ZY, Qian CY, Zheng XD, et al. Collagen/chitosan/genipin hydrogel loaded with phycocyanin nanoparticles and ND-336 for diabetic wound healing[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2024, 266: 131220. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131220 |
| [1] | Linyue WANG, Wenyue QI, Jihua GAO, Maosheng TIAN, Jiancheng XU. Tongyangxiao Lotion promotes postoperative wound healing in a rat model of anal fistula by downregulating inflammatory factors and suppressing inflammation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1256-1265. |
| [2] | ZHAO Hong, WANG Yilin, WANG Yanfang, GONG Haihuan, YINJUN Feiyang, CUI Xiaojun, ZHANG Jiankai, HUANG Wenhua. Embedded 3D printing of porous silicon orbital implants and its surface modification [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(5): 783-792. |
| [3] | ZHANG Ming, YU Hao, SHAO Yang, SONG Guodong, CHEN Mingrui, LIU Shunli. Effect of nanofat combined with platelet-rich plasma for treatment of pressure injury wounds in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(12): 2061-2070. |
| [4] | WEN Haifei, HUANG Xianying. Cuprous oxide nanoparticles-based photothermal and chemodynamic synergistic therapy inhibits proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells in vitro [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(11): 1732-1738. |
| [5] | . Mn2+ doped Prussian blue nanoparticles for T1-T2 dual-mode magnetic resonance imaging and photothermal therapy in vitro [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(6): 909-915. |
| [6] | CHEN Dong, CHEN Zhifeng, WANG Zou, YANG Yajie, JIANG Yanping, HU Chen. Photothermal effect of nano-copper sulfide against tongue squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(12): 1843-1849. |
| [7] | . Efficacy of dermal scaffold for promoting repair of acute full-thickness skin defects in pigs [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2018, 38(03): 363-. |
| [8] |
.
Dynamic changes of tear fluid matrix metralloproteinase-9 within 1 year after laser in situ keratomileusis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2014, 34(08): 1079-. |
| [9] | . Effect of intramuscular bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the leg for treatment of diabetic foot ulcers in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2012, 32(12): 1730-. |
| [10] | LI Xue-feng, WANG Hui-jun, LUO Hong Department of Pathology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China; Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510215, China. Temporal relation of transforming growth factor-β1 mRNA expression with injury in the healing process of mouse skin wounds [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2006, 26(01): 59-61. |
| [11] | ZHU Xin-yong1, FANG Chi-hua1, ZHANG Li-yun2, ZUO Da-ming2, CHEN Zheng-liang2. Expressions and role of endogenetic matrix metalloproteinases-9 and transforming growth factor-beta during wound healing of blast injury [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2005, 25(07): 844-846. |
| [12] | QIU Xue-wen1, WANG Jia-han1, FANG Xiao-wen2, GONG Zhen-yu1, LI Zhi-qing1, YI Zhao-hui1. Anti-inframnatory activity and healing-promoting effects of topical application of emu oil on wound in scalded rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2005, 25(04): 407-410. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||