Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2646-2657.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.12
Xinyue SUN( ), Kuanyu WANG(
), Kuanyu WANG( ), Gang WANG, Qingquan DAI, Jing CHEN, Xiangding KONG, Jia LUAN
), Gang WANG, Qingquan DAI, Jing CHEN, Xiangding KONG, Jia LUAN
Received:2025-06-01
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Kuanyu WANG
E-mail:429050968@qq.com;wangkuanyu_1964@163.com
Xinyue SUN, Kuanyu WANG, Gang WANG, Qingquan DAI, Jing CHEN, Xiangding KONG, Jia LUAN. Fuzheng Xiaoyan Granules ameliorate cancer-related fatigue during breast cancer chemotherapy by regulating the AKT1/BAD/BCL-2 pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2646-2657.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.12
| Group | Behavioral dimension | Emotion dimension | Physical dimension | Cognition dimension | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | |
| Control | 5.84±0.69 | 4.88±0.65 | 5.93±0.84 | 4.32±1.06 | 5.17±1.12 | 4.64±0.54 | 6.39±1.09 | 4.29±1.32 |
| Treatment | 5.55±0.88 | 3.14±1.23a | 5.60±0.92 | 2.77±1.56a | 5.38±0.51 | 2.96±1.00a | 6.35±0.97 | 2.87±1.41a |
| t | 1.754 | 8.381 | 1.799 | 6.617 | -1.138 | 9.894 | 0.187 | 4.93 |
| P | 0.083 | <0.001 | 0.075 | <0.001 | 0.258 | <0.001 | 0.852 | <0.001 |
Tab.1 Comparison of PFS scores between the two groups before and after treatment (Mean±SD, n=45)
| Group | Behavioral dimension | Emotion dimension | Physical dimension | Cognition dimension | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | |
| Control | 5.84±0.69 | 4.88±0.65 | 5.93±0.84 | 4.32±1.06 | 5.17±1.12 | 4.64±0.54 | 6.39±1.09 | 4.29±1.32 |
| Treatment | 5.55±0.88 | 3.14±1.23a | 5.60±0.92 | 2.77±1.56a | 5.38±0.51 | 2.96±1.00a | 6.35±0.97 | 2.87±1.41a |
| t | 1.754 | 8.381 | 1.799 | 6.617 | -1.138 | 9.894 | 0.187 | 4.93 |
| P | 0.083 | <0.001 | 0.075 | <0.001 | 0.258 | <0.001 | 0.852 | <0.001 |
| Group | Before treatment | After treatment | Z | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 70 (60, 80) | 80 (70, 80) | -4.849 | <0.001 |
| Treatment | 70 (70, 80) | 80 (80, 90) | -6.474 | <0.001 |
| Z | -0.720 | -3.499 | ||
| P | 0.471 | <0.001 |
Tab.2 Comparison of KPS scores between the two groups before and after treatment [M (P25, P75), n=45]
| Group | Before treatment | After treatment | Z | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 70 (60, 80) | 80 (70, 80) | -4.849 | <0.001 |
| Treatment | 70 (70, 80) | 80 (80, 90) | -6.474 | <0.001 |
| Z | -0.720 | -3.499 | ||
| P | 0.471 | <0.001 |
| Group | Tiredness and weakness | Nausea and vomiting | Dizziness and dim vision | Palpitations and insomnia | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | |
| Control | 2.87±0.50 | 1.96±0.21 | 2.80±0.55 | 1.91±0.36 | 2.49±0.63 | 1.84±0.47 | 1.78±1.08 | 1.27±0.84 |
| Treatment | 2.87±0.46 | 0.91±0.29a | 2.87±0.46 | 1.36±0.74a | 2.33±0.64 | 0.69±0.56a | 1.76±1.00 | 0.91±0.73a |
| Z | -0.339 | -8.866 | -0.666 | -3.846 | -1.226 | -7.36 | -2.40 | -2.18 |
| P | 0.735 | <0.001 | 0.505 | <0.001 | 0.22 | <0.001 | 0.810 | 0.029 |
Tab.3 Comparison of TCM Syndrome Scores between the two groups of patients before and after treatment (Mean±SD, n=45)
| Group | Tiredness and weakness | Nausea and vomiting | Dizziness and dim vision | Palpitations and insomnia | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | |
| Control | 2.87±0.50 | 1.96±0.21 | 2.80±0.55 | 1.91±0.36 | 2.49±0.63 | 1.84±0.47 | 1.78±1.08 | 1.27±0.84 |
| Treatment | 2.87±0.46 | 0.91±0.29a | 2.87±0.46 | 1.36±0.74a | 2.33±0.64 | 0.69±0.56a | 1.76±1.00 | 0.91±0.73a |
| Z | -0.339 | -8.866 | -0.666 | -3.846 | -1.226 | -7.36 | -2.40 | -2.18 |
| P | 0.735 | <0.001 | 0.505 | <0.001 | 0.22 | <0.001 | 0.810 | 0.029 |
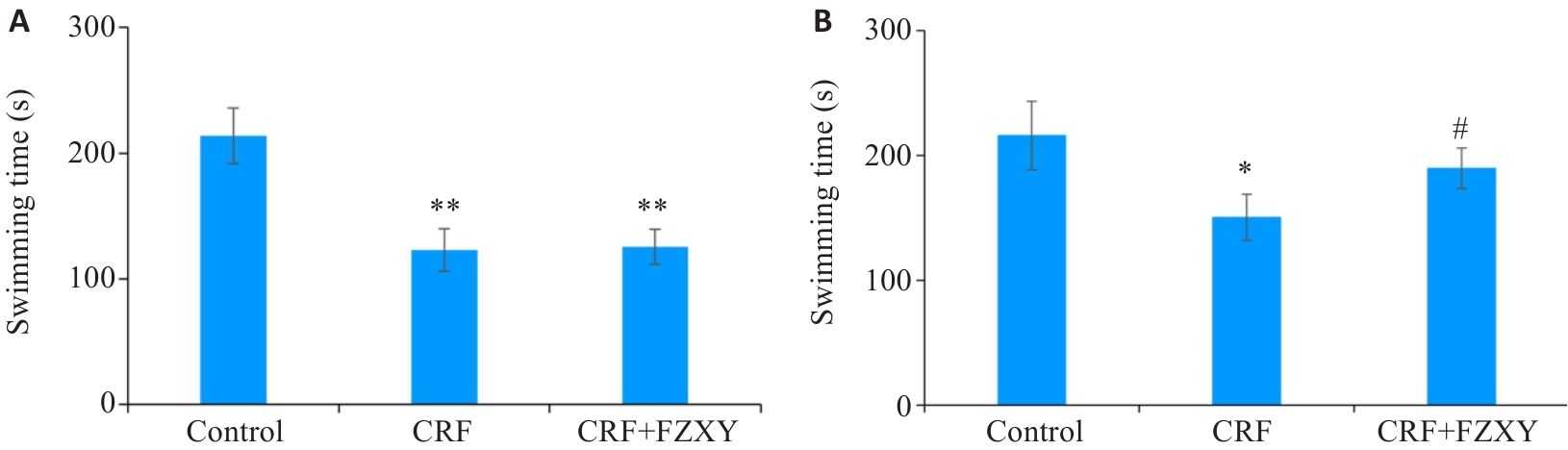
Fig.9 Performance of the mice in forced swimming test in different groups. A: After successful model establishment; B: After FZXY intervention. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs control group; #P<0.05 vs CRF group.
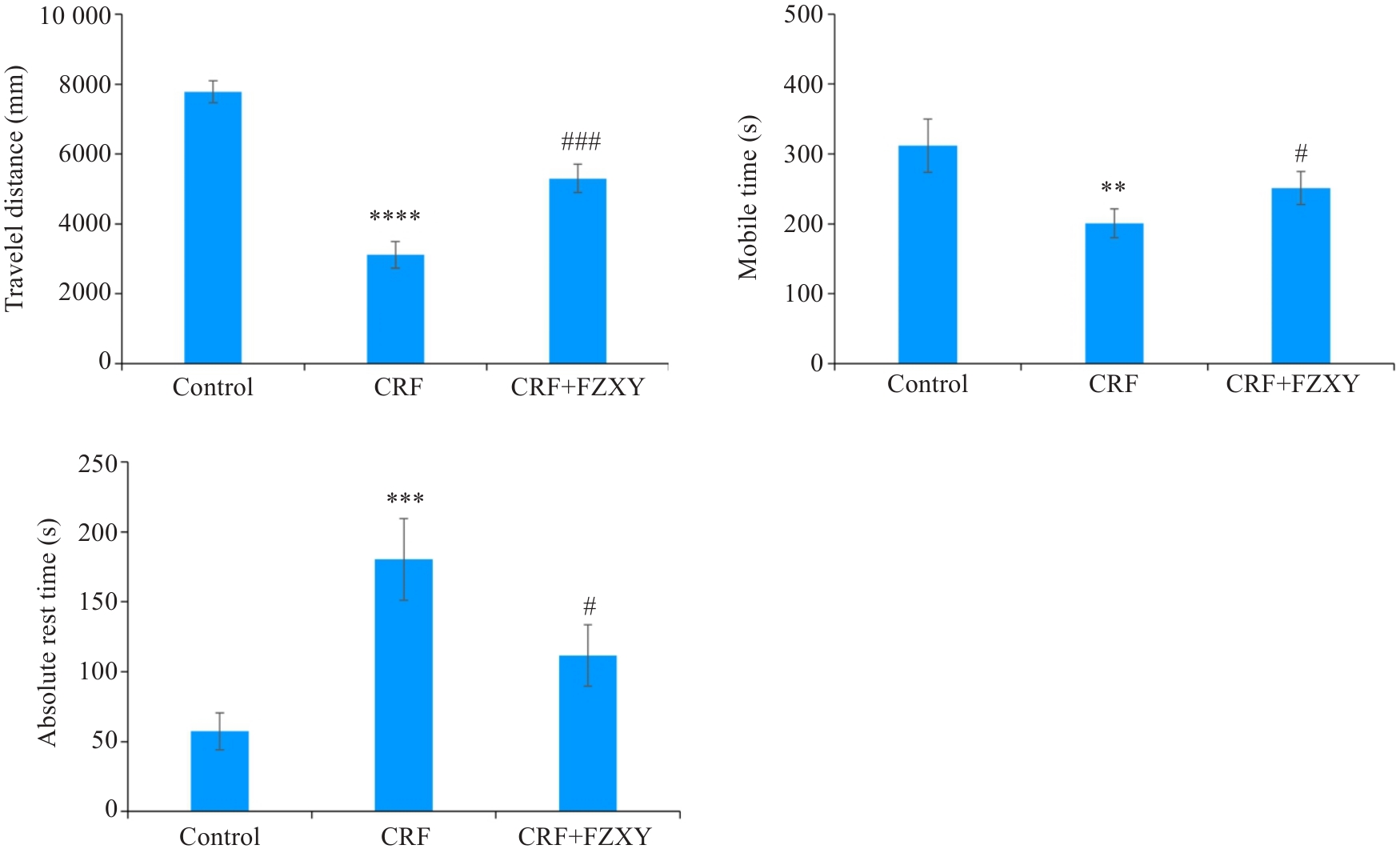
Fig.10 Comparison of open field test and tail suspension test of mice in different groups. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs Control group; #P<0.05,###P<0.001 vs CRF group.

Fig.11 Comparison of body weight and gastrocnemius muscle weight of the mice among the 3 groups. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs control group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs CRF group. Day 1 is defined as the day of doxorubicin injection.
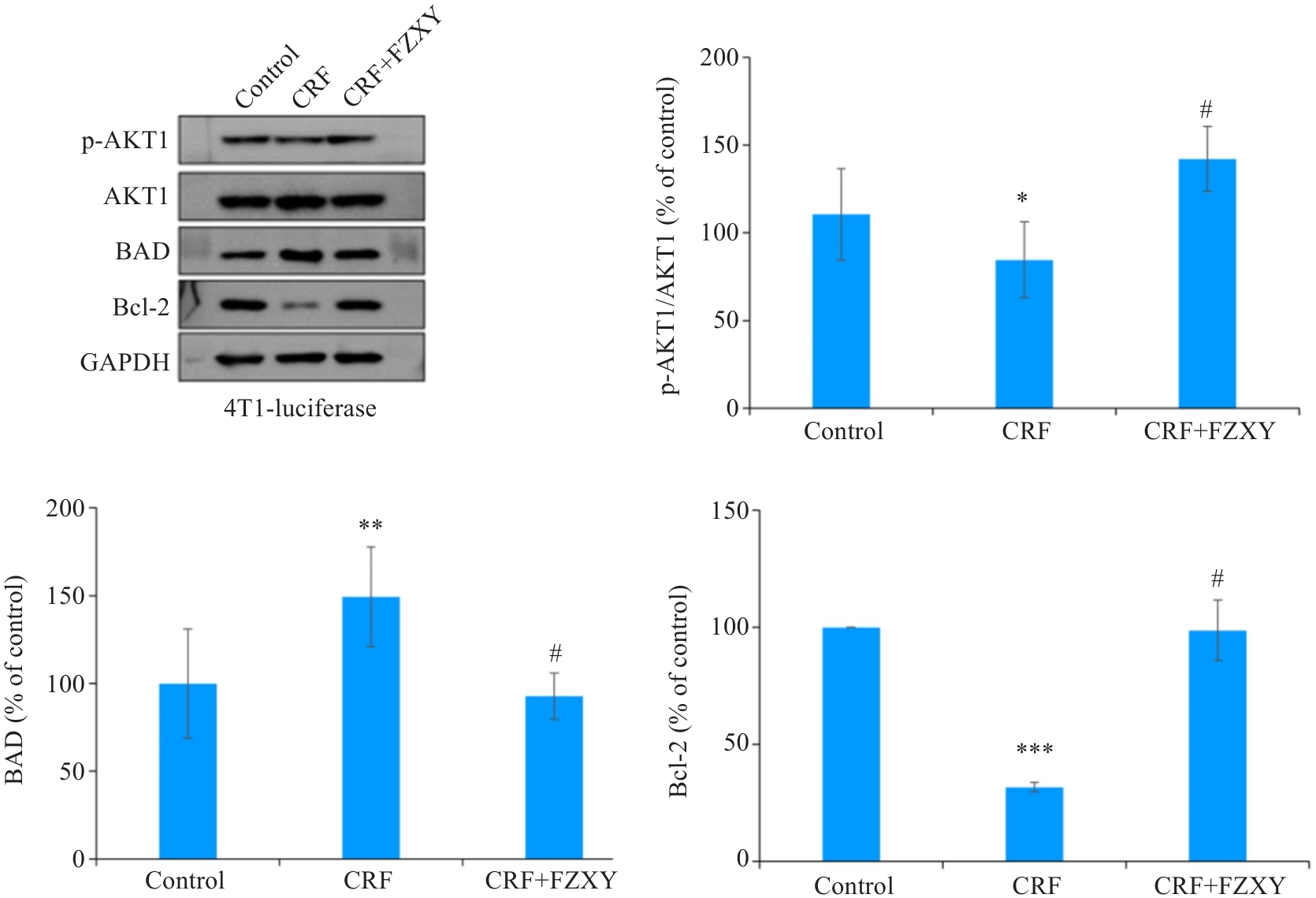
Fig.13 Comparison of protein expression levels in the gastrocnemius muscles of the mice among the 3 groups. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Control group; #P<0.05 vs CRF group.
| [1] | Mock V, Atkinson A, Barsevick A, et al. NCCN practice guidelines for cancer-related fatigue[J]. Oncology: Williston Park, 2000, 14(11a): 151-61. |
| [2] | 曹玉瑶, 宋 祎, 陈凤敏, 等. 有氧运动对乳腺癌化疗患者癌因性疲乏的影响及相关机制[J]. 天津医药, 2016, 44(4): 401-4. |
| [3] | 谢晓冬, 张潇宇. 癌因性疲乏最新进展 —NCCN(2018 版) 癌因性疲乏指南解读[J]. 中国肿瘤临床,2018, 45(16): 817-20. |
| [4] | Groenvold M, Petersen MA, Idler E, et al. Psychological distress and fatigue predicted recurrence and survival in primary breast cancer patients[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2007, 105(2): 209-19. doi:10.1007/s10549-006-9447-x |
| [5] | Fabi A, Bhargava R, Fatigoni S, et al. Cancer-related fatigue: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment[J]. Ann Oncol, 2020, 31(6): 713-23. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2020.02.016 |
| [6] | 李泽龙,鲁 凯. 八珍汤联合靶向治疗HER-2阳性乳腺癌气血亏虚证的效果观察 [J]. 实用中西医结合临床, 2025, 25 (12): 28-30, 34. |
| [7] | 杨书贤,洪 禹,曹丽娟. 癌因性疲乏发病机制及中医药干预研究进展 [J]. 南京中医药大学学报, 2025, 41 (06): 838-46. |
| [8] | 莫文菊,黄孝闻,叶魏武,等. 去壁灵芝孢子粉改善乳腺癌患者辅助化疗期间癌因性疲乏研究 [J]. 中国现代应用药学, 2024, 41 (14): 1921-8. |
| [9] | 王子承,王海波,王 颖,等.《中成药治疗优势病种临床应用指南》标准化项目组. 中成药治疗癌因性疲乏临床应用指南(2020年) [J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2021, 41(5): 534-41. |
| [10] | “虚劳干血”理论指导下复元活血汤合大黄蛰虫丸对乳腺癌癌因性疲乏的干预效果研究 [J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2025, 43 (02): 84-7. |
| [11] | 陈 静,樊锐锋,李 威,等.扶正消岩汤抑制三阴性乳腺癌细胞增殖的机制研究[J].时珍国医国药,2023,34(02):302-5. |
| [12] | 王 钢,陈 静,孔祥定,等.扶正消岩汤对气阴两虚型乳腺癌术后化疗患者生存质量的改善作用观察[J].中国中医药科技,2022,29(06):1011-3. |
| [13] | 冯月男,孙思邈,孔祥定,等.扶正消岩汤对乳腺癌肿瘤微环境调控机制的研究[J].中医药学报,2021,49(12):52-6. |
| [14] | 中国临床肿瘤学会指南工作委员会 .中国临床肿瘤学会(CSCO)乳腺癌诊疗指南-2022[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2022. |
| [15] | Portenoy RK, Itri LM. Cancer-related fatigue: guidelines for evaluation and management[J]. Oncologist, 1999, 4(1): 1-10. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.4-1-1 |
| [16] | 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典-一部: 2020年版[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020. |
| [17] | 中国抗癌协会癌症康复与姑息治疗专业委员会,中国临床肿瘤学会肿瘤支持与康复治疗专家委员会 .癌症相关性疲乏诊断与治疗中国专家共识[J].中华医学杂志,2022,102(3):10. |
| [18] | Sprangers MA, Cull A, Groenvold M, et al. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer approach to developing questionnaire modules: an update and overview. EORTC Quality of Life Study Group[J]. Qual Life Res, 1998, 7(4): 291-300. doi:10.1023/a:1024977728719 |
| [19] | 金 铭,谢露露,毛 妮,等. 癌因性疲劳动物模型的研究进展 [J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2021, 48 (07): 738-42. |
| [20] | Zombeck JA, Fey EG, Lyng GD, et al. A clinically translatable mouse model for chemotherapy-related fatigue[J]. Comp Med, 2013, 63(6): 491-7. |
| [21] | 徐叔云. 药理实验方法学[M]. 3版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2002: 1560-8. |
| [22] | Wang Y, Liu Y, Zhang Y, et al. Effects of the polysaccharides extracted from Chinese yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) on cancer-related fatigue in mice[J]. Food Funct, 2021, 12(21): 10602-14. doi:10.1039/d1fo00375e |
| [23] | 吴人杰, 谢长生. 癌因性疲乏发病机制及治疗的研究进展[J].肿瘤学杂志,2020,26(3):240-4. |
| [24] | 沈志祥,陆为民,石 川,等. 徐氏参芪苡术汤联合化疗治疗胃癌术后癌因性疲乏脾虚瘀毒型的临床观察及机制 [J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2025, 31 (08): 143-51. |
| [25] | Mohandas H, Jaganathan SK, Mani MP, et al. Cancer-related fatigue treatment: an overview[J]. J Cancer Res Ther, 2017, 13(6): 916-29. |
| [26] | Chuang CH, Tai YA, Wu TJ, et al. Quercetin attenuates cisplatin-induced fatigue through mechanisms associated with the regulation of the HPA axis and MCP-1 signaling[J]. Front Nutr, 2025, 12: 1530132. doi:10.3389/fnut.2025.1530132 |
| [27] | Wang YF, Liu MF, Huang N, et al. Quercetin-targeted AKT1 regulates the Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway to protect against doxorubicin-induced nephropathy in mice[J]. Tissue Cell, 2023, 85: 102229. doi:10.1016/j.tice.2023.102229 |
| [28] | 陈 言,代 婷,郭长胜,等. 基于PI3K/Akt信号通路探讨中医药治疗肌肉减少症的研究进展 [J/OL]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 1-19[2025-06-12]. |
| [29] | Regué L, Ji F, Flicker D, et al. IMP2 increases mouse skeletal muscle mass and voluntary activity by enhancing autocrine insulin-like growth factor 2 production and optimizing muscle metabolism[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2019, 39(7): e00528-18. doi:10.1128/mcb.00528-18 |
| [30] | Hu M, Han M, Zhang H, et al. Curcumin (CUMINUP60®) mitigates exercise fatigue through regulating PI3K/Akt/AMPK/mTOR pathway in mice[J]. Aging: Albany NY, 2023, 15(6): 2308-20. doi:10.18632/aging.204614 |
| [31] | Chao DT, Korsmeyer SJ. BCL-2 family: regulators of cell death[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 1998, 16: 395-419. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.16.1.395 |
| [32] | Liu S, Meng F, Zhang D, et al. Lonicera caerulea berry polyphenols extract alleviates exercise fatigue in mice by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, skeletal muscle cell apoptosis, and by increasing cell proliferation[J]. Front Nutr, 2022, 9: 853225. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.853225 |
| [33] | Hiensch AE, Bolam KA, Mijwel S, et al. Doxorubicin-induced skeletal muscle atrophy: Elucidating the underlying molecular pathways[J]. Acta Physiol: Oxf, 2020, 229(2): e13400. doi:10.1111/apha.13400 |
| [34] | Cruz FM, Munhoz BA, Alves BC, et al. Biomarkers of fatigue related to adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: evaluation of plasma and lymphocyte expression[J]. Clin Transl Med, 2015, 4: 4. doi:10.1186/s40169-015-0051-8 |
| [35] | Wang XS, Williams LA, Krishnan S, et al. Serum sTNF-R1, IL-6, and the development of fatigue in patients with gastrointestinal cancer undergoing chemoradiation therapy[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2012, 26(5): 699-705. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2011.12.007 |
| [36] | Bower JE, Ganz PA, Irwin MR, et al. Inflammation and behavioral symptoms after breast cancer treatment: do fatigue, depression, and sleep disturbance share a common underlying mechanism?[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2011, 29(26): 3517-22. doi:10.1200/jco.2011.36.1154 |
| [37] | Guo W, Liu S, Xia H, et al. Shenqi Fuzheng injection facilitates skeletal muscle mitophagy mediated by the ubiquitination of HIF-1α to ameliorate cancer-associated fatigue[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2024, 28(12): e18455. doi:10.1111/jcmm.18455 |
| [38] | 何 晶,王林元,陈亚文,等. 基于JAK2/STAT3通路研究灵芝孢子多糖通过免疫调节改善脾虚证小鼠癌因性疲乏的机制 [J/OL]. 中国中药杂志, 2025: 1-9[2025-06-21]. |
| [39] | 崔艺馨,米继伟,冯 宇,等. 黄芪四君子汤治疗乳腺癌癌因性疲乏的疗效及机制:基于94例临床随机对照实验和网络药理学 [J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42 (05): 649-57. |
| [1] | Liying ZHANG, Tongzhen ZHANG, Xin ZHAO. Diagnostic value of morphological features of breast lesions on DWI and T2WI assessed using Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System lexicon descriptors [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1809-1817. |
| [2] | Qin HU, Hua JIN. Qingshen Granules improves renal function of patients with chronic kidney disease damp-heat syndrome by activating the miR-23b and Nrf2 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1867-1879. |
| [3] | Ziwei YANG, Chang LÜ, Zhu DONG, Shulei JI, Shenghui BI, Xuehua ZHANG, Xiaowu WANG. Rosa laevigata Michx. inhibits pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation in hypertension by modulating the Src-AKT1 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1889-1902. |
| [4] | Qi YUN, Ruoli DU, Yuying HE, Yixin ZHANG, Jiahui WANG, Hongwei YE, Zhenghong LI, Qin GAO. Cinnamic acid ameliorates doxorubicin-induced myocardial injury in mice by attenuating cardiomyocyte ferroptosis via inhibiting TLR4 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1946-1958. |
| [5] | Lu RAO, Jiahe DING, Jiangping WEI, Yong YANG, Xiaomei ZHANG, Jirui WANG. Flos Sophorae improves psoriasis in mice by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1989-1996. |
| [6] | Siyuan MA, Bochao ZHANG, Chun PU. Circ_0000437 promotes proliferation, invasion, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells by targeting the let-7b-5p/CTPS1 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1682-1696. |
| [7] | Zhaojun ZHANG, Qiong WU, Miaomiao XIE, Ruyin YE, Chenchen GENG, Jiwen SHI, Qingling YANG, Wenrui WANG, Yurong SHI. Layered double hydroxide-loaded si-NEAT1 regulates paclitaxel resistance and tumor-associated macrophage polarization in breast cancer by targeting miR-133b/PD-L1 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1718-1731. |
| [8] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [9] | Liming WANG, Hongrui CHEN, Yan DU, Peng ZHAO, Yujie WANG, Yange TIAN, Xinguang LIU, Jiansheng LI. Yiqi Zishen Formula ameliorates inflammation in mice with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [10] | Yinfu ZHU, Yiran LI, Yi WANG, Yinger HUANG, Kunxiang GONG, Wenbo HAO, Lingling SUN. Therapeutic mechanism of hederagenin, an active component in Guizhi Fuling Pellets, against cervical cancer in nude mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [11] | Lijun HE, Xiaofei CHEN, Chenxin YAN, Lin SHI. Inhibitory effect of Fuzheng Huaji Decoction against non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and the possible molecular mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152. |
| [12] | Jiahao LI, Ruiting XIAN, Rong LI. Down-regulation of ACADM-mediated lipotoxicity inhibits invasion and metastasis of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1163-1173. |
| [13] | Guoyong LI, Renling LI, Yiting LIU, Hongxia KE, Jing LI, Xinhua WANG. Therapeutic mechanism of Arctium lappa extract for post-viral pneumonia pulmonary fibrosis: a metabolomics, network pharmacology analysis and experimental verification [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [14] | Liping GUAN, Yan YAN, Xinyi LU, Zhifeng LI, Hui GAO, Dong CAO, Chenxi HOU, Jingyu ZENG, Xinyi LI, Yang ZHAO, Junjie WANG, Huilong FANG. Compound Centella asiatica formula alleviates Schistosoma japonicum-induced liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting the inflammation-fibrosis cascade via regulating the TLR4/MyD88 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [15] | Peipei TANG, Yong TAN, Yanyun YIN, Xiaowei NIE, Jingyu HUANG, Wenting ZUO, Yuling LI. Tiaozhou Ziyin recipe for treatment of premature ovarian insufficiency: efficacy, safety and mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||