Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (11): 2405-2415.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.11.13
Xingxu PAN1( ), Bingqi ZHANG2, Zhihua ZHANG1,3(
), Bingqi ZHANG2, Zhihua ZHANG1,3( ), Qiushi CAO1,3(
), Qiushi CAO1,3( )
)
Received:2025-06-24
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-11-28
Contact:
Zhihua ZHANG, Qiushi CAO
E-mail:17860358705@163.com;1868@hbucm.edu.cn;2987@hbucm.edu.cn
Supported by:Xingxu PAN, Bingqi ZHANG, Zhihua ZHANG, Qiushi CAO. Reduced intestinal abundance of Gordonibacter increases risk of kidney stones: a Mendelian randomization study and evidence from rat models[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(11): 2405-2415.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.11.13
| Exposure and outcome | Sample size | Number of SNPs | Data source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gut microbiota | S=18 340 | 122 110 | https://mibiogen.gcc.rug.nl/menu/main/home/ |
| Kidney stones | N=462 933 | 9 851 867 | https://gwas.mrcieu.ac.uk/ |
Tab.1 Exposure factors and outcome variables in Mendelian randomization analysis
| Exposure and outcome | Sample size | Number of SNPs | Data source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gut microbiota | S=18 340 | 122 110 | https://mibiogen.gcc.rug.nl/menu/main/home/ |
| Kidney stones | N=462 933 | 9 851 867 | https://gwas.mrcieu.ac.uk/ |
| Gut microbiota and SNPs | EA | OA | Beta | P | R2 | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lachnospiraceae NK4A136 group | ||||||
| rs10952110 | G | T | 0.05 | 9.08×10-6 | 0.001179 | 19.794033 |
| rs11263806 | A | G | -0.05 | 5.07×10-6 | 0.001169 | 20.186367 |
| rs12611395 | A | G | -0.09 | 5.83×10-6 | 0.001238 | 20.432599 |
| rs160061 | A | G | 0.05 | 2.12×10-6 | 0.001309 | 22.593643 |
| rs28540839 | A | C | 0.05 | 9.34×10-6 | 0.001258 | 21.121397 |
| rs2880566 | T | C | 0.06 | 5.61×10-6 | 0.001149 | 19.813151 |
| rs68104925 | T | C | -0.06 | 2.37×10-6 | 0.001313 | 22.644336 |
| rs954878 | A | G | -0.05 | 1.78×10-6 | 0.001321 | 22.779485 |
| Gordonibacter | ||||||
| rs13412653 | A | C | 0.11 | 8.61×10-6 | 0.005404 | 20.218430 |
| rs322296 | G | A | 0.18 | 4.02×10-6 | 0.006203 | 22.426840 |
| rs35042269 | C | A | -0.18 | 8.11×10-6 | 0.005528 | 19.974041 |
| rs4596722 | A | G | 0.10 | 9.06×10-6 | 0.005276 | 19.737801 |
| rs71545975 | A | G | -0.15 | 7.04×10-6 | 0.005771 | 20.627711 |
| rs7294633 | C | T | 0.13 | 3.44×10-7 | 0.007068 | 26.486697 |
| rs768830 | G | A | 0.15 | 7.76×10-6 | 0.005398 | 20.201590 |
Tab.2 SNP characteristics of bacterial genera associated with kidney stones
| Gut microbiota and SNPs | EA | OA | Beta | P | R2 | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lachnospiraceae NK4A136 group | ||||||
| rs10952110 | G | T | 0.05 | 9.08×10-6 | 0.001179 | 19.794033 |
| rs11263806 | A | G | -0.05 | 5.07×10-6 | 0.001169 | 20.186367 |
| rs12611395 | A | G | -0.09 | 5.83×10-6 | 0.001238 | 20.432599 |
| rs160061 | A | G | 0.05 | 2.12×10-6 | 0.001309 | 22.593643 |
| rs28540839 | A | C | 0.05 | 9.34×10-6 | 0.001258 | 21.121397 |
| rs2880566 | T | C | 0.06 | 5.61×10-6 | 0.001149 | 19.813151 |
| rs68104925 | T | C | -0.06 | 2.37×10-6 | 0.001313 | 22.644336 |
| rs954878 | A | G | -0.05 | 1.78×10-6 | 0.001321 | 22.779485 |
| Gordonibacter | ||||||
| rs13412653 | A | C | 0.11 | 8.61×10-6 | 0.005404 | 20.218430 |
| rs322296 | G | A | 0.18 | 4.02×10-6 | 0.006203 | 22.426840 |
| rs35042269 | C | A | -0.18 | 8.11×10-6 | 0.005528 | 19.974041 |
| rs4596722 | A | G | 0.10 | 9.06×10-6 | 0.005276 | 19.737801 |
| rs71545975 | A | G | -0.15 | 7.04×10-6 | 0.005771 | 20.627711 |
| rs7294633 | C | T | 0.13 | 3.44×10-7 | 0.007068 | 26.486697 |
| rs768830 | G | A | 0.15 | 7.76×10-6 | 0.005398 | 20.201590 |
| Gut microbiota and methods | Number of SNPs | Beta | P | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lachnospiraceae NK4A136 group | ||||
| MR-Egger | 8 | -0.0124 | 0.1751 | 0.9877 (0.9723, 1.0034) |
| WME | 8 | -0.0017 | 0.3190 | 0.9983 (0.9950, 1.0016) |
| IVW | 8 | -0.0026 | 0.0393 | 0.9974 (0.9948, 0.9999) |
| SM | 8 | -0.0003 | 0.9142 | 0.9997 (0.9944, 1.0051) |
| WM | 8 | -0.0003 | 0.9148 | 0.9997 (0.9943, 1.0051) |
| Gordonibacter | ||||
| MR-Egger | 7 | -0.0012 | 0.7112 | 0.9988 (0.9926, 1.0050) |
| WME | 7 | -0.0013 | 0.1220 | 0.9987 (0.9970, 1.0004) |
| IVW | 7 | -0.0013 | 0.0403 | 0.9987 (0.9974, 0.9999) |
| SM | 7 | -0.0014 | 0.2828 | 0.9986 (0.9963, 1.0009) |
| WM | 7 | -0.0014 | 0.3155 | 0.9986 (0.9960, 1.0011) |
Tab.3 Main results of Mendelian randomization analysis after excluding palindromic and confounding factors
| Gut microbiota and methods | Number of SNPs | Beta | P | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lachnospiraceae NK4A136 group | ||||
| MR-Egger | 8 | -0.0124 | 0.1751 | 0.9877 (0.9723, 1.0034) |
| WME | 8 | -0.0017 | 0.3190 | 0.9983 (0.9950, 1.0016) |
| IVW | 8 | -0.0026 | 0.0393 | 0.9974 (0.9948, 0.9999) |
| SM | 8 | -0.0003 | 0.9142 | 0.9997 (0.9944, 1.0051) |
| WM | 8 | -0.0003 | 0.9148 | 0.9997 (0.9943, 1.0051) |
| Gordonibacter | ||||
| MR-Egger | 7 | -0.0012 | 0.7112 | 0.9988 (0.9926, 1.0050) |
| WME | 7 | -0.0013 | 0.1220 | 0.9987 (0.9970, 1.0004) |
| IVW | 7 | -0.0013 | 0.0403 | 0.9987 (0.9974, 0.9999) |
| SM | 7 | -0.0014 | 0.2828 | 0.9986 (0.9963, 1.0009) |
| WM | 7 | -0.0014 | 0.3155 | 0.9986 (0.9960, 1.0011) |
| Exposure factor | Cochran's Q heterogeneity test | Genetic pleiotropy | MR-PRESSO | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methods | Q | P | MR-Egger intercept | P | P | |
| Lachnospiraceae NK4A136 group | IVW | 6.031 | 0.536 | 5.40×10-4 | 0.267 | 0.543 |
| MR-Egger | 4.533 | 0.605 | ||||
| Gordonibacter | IVW | 4.719 | 0.580 | -1.32×10-5 | 0.976 | 0.594 |
| MR-Egger | 4.718 | 0.451 | ||||
Tab.4 Sensitivity analysis
| Exposure factor | Cochran's Q heterogeneity test | Genetic pleiotropy | MR-PRESSO | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methods | Q | P | MR-Egger intercept | P | P | |
| Lachnospiraceae NK4A136 group | IVW | 6.031 | 0.536 | 5.40×10-4 | 0.267 | 0.543 |
| MR-Egger | 4.533 | 0.605 | ||||
| Gordonibacter | IVW | 4.719 | 0.580 | -1.32×10-5 | 0.976 | 0.594 |
| MR-Egger | 4.718 | 0.451 | ||||
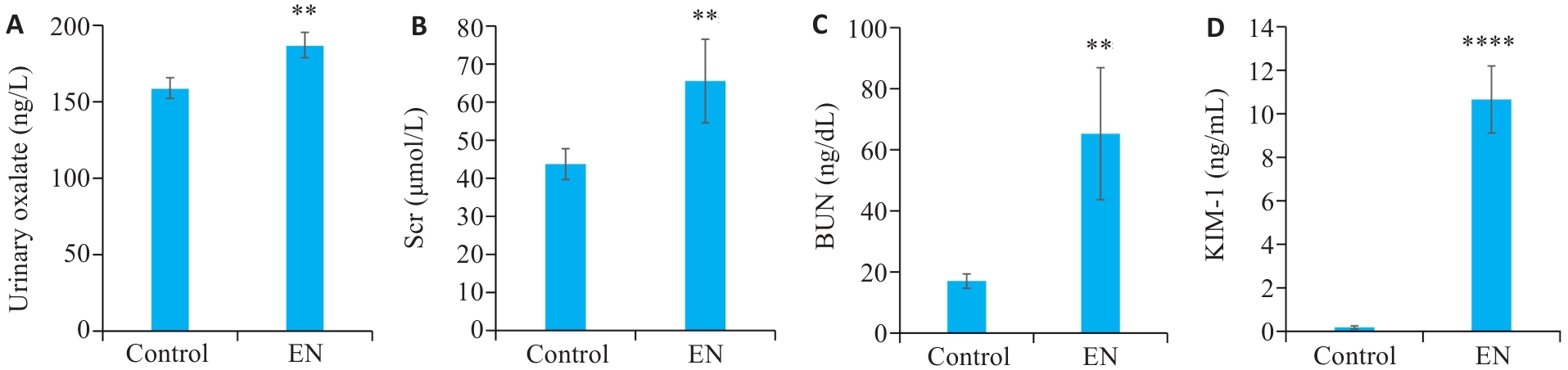
Fig.4 Changes in metabolism and renal-related indicators in the rat models of calcium oxalate kidney stone. A: Urinary oxalate. B: Serum creatinine. C: Blood urea nitrogen. D: Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1). (Mean±SD, n=6). **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001 vs control group. EN: Model group.
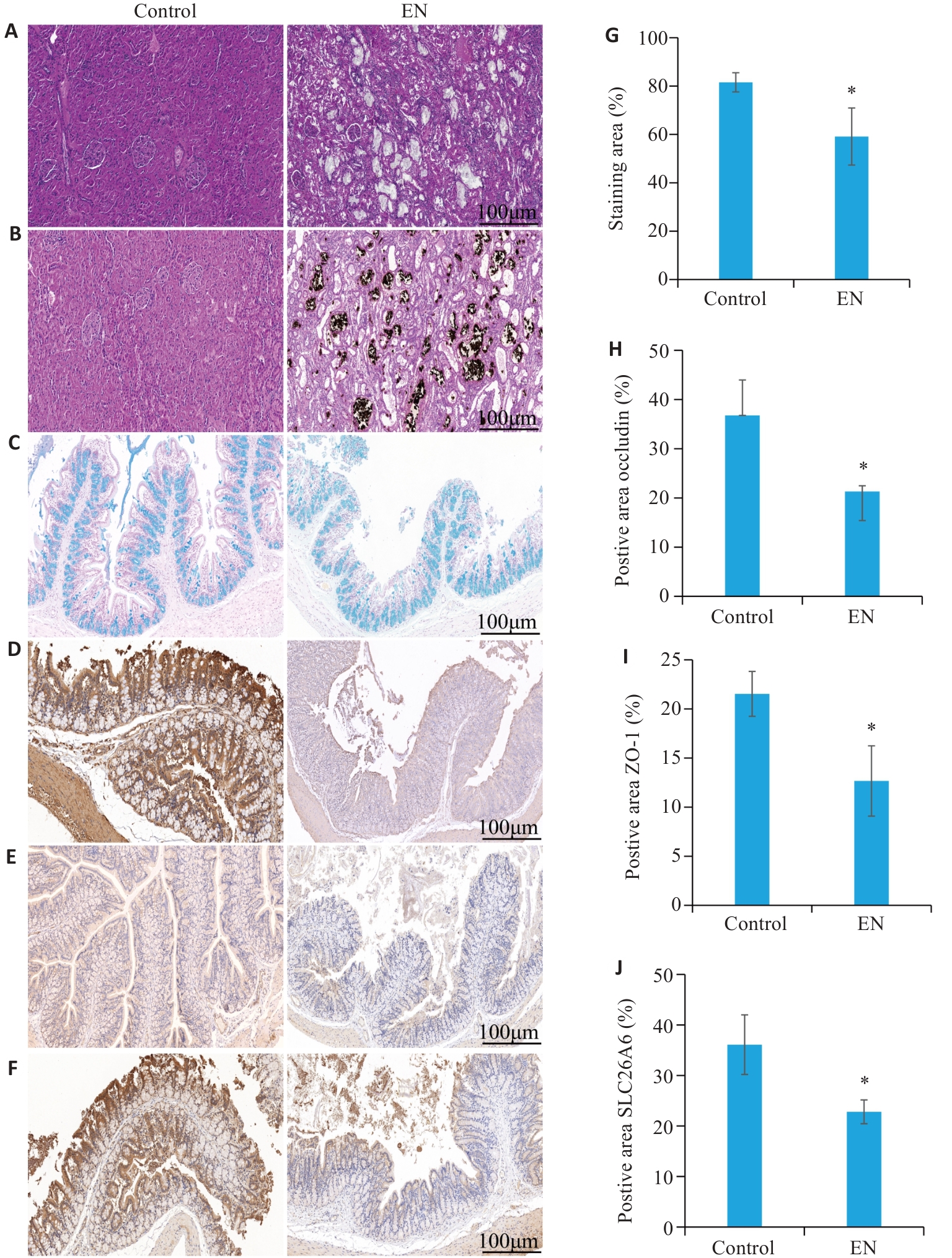
Fig.5 Changes in renal and intestinal tissue morphology in the rat modes of calcium oxalate kidney stone. A: HE staining. B: Von Kossa staining. C: Alcian blue staining of the intestine (scale bar=100 μm). D-F: Immunohistochemical staining showing changes in Occludin, ZO-1, and the oxalate transporter SLC26A6 in the intestine. G: Quantitative analysis of mucin by Alcian blue staining. H-J: Optical density (OD) values of Occludin, ZO-1, and SLC26A6 (Mean±SD, n=3). *P<0.05 vs control group.
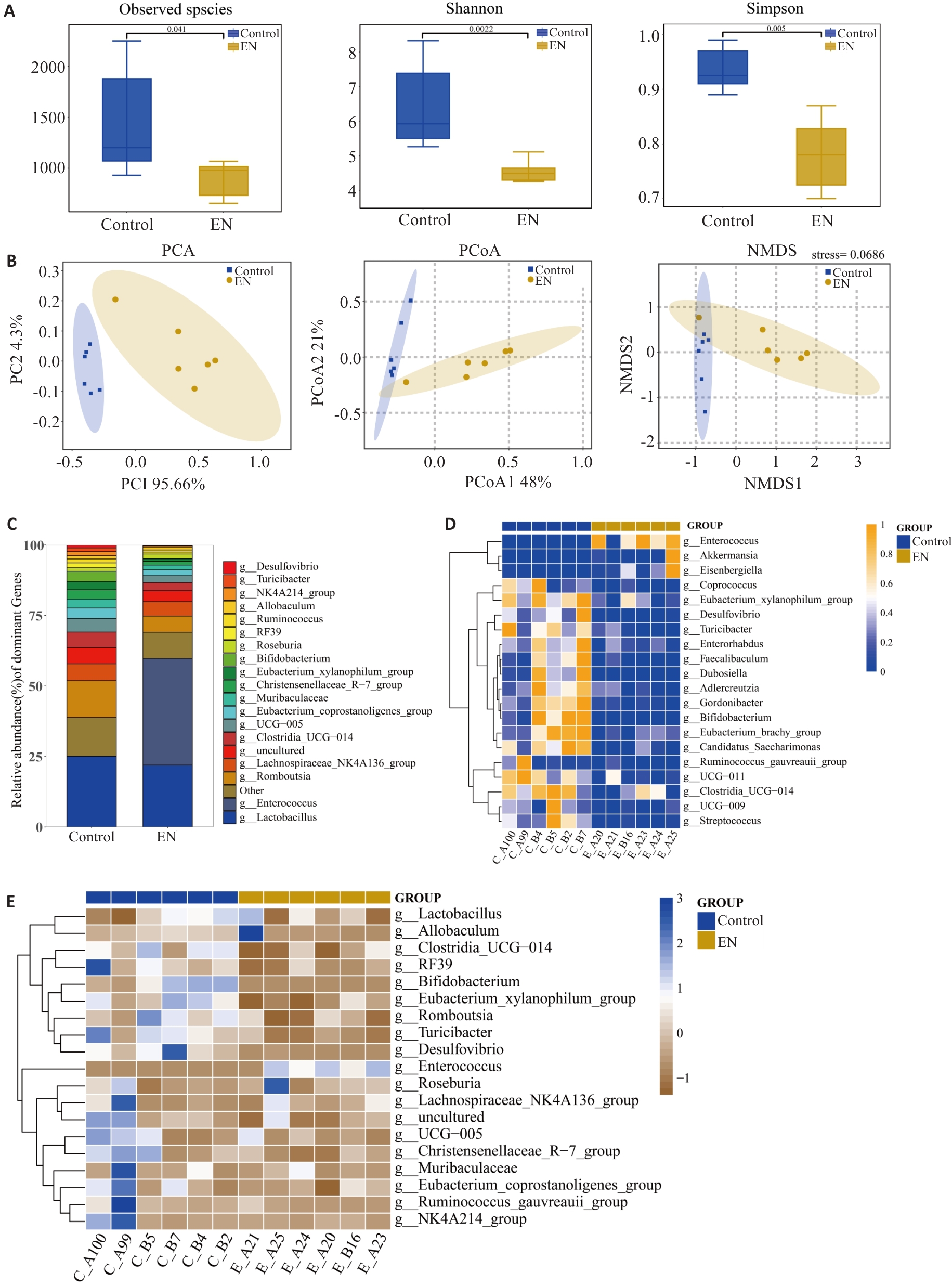
Fig.6 Changes in the composition of gut microbiota in the rat modes of calcium oxalate kidney stones. A: α-diversity assessed using Observed species, Shannon, and Simpson indices. B: β-diversity evaluated by PCA, PCoA, and NMDS analyses. C: Bar chart of bacterial community composition at the genus level. D: Heatmap of the differential genera identified by Wilcoxon rank-sum test. E: Heatmap analysis of the control and model groups at the genus level further illustrates that the relative abundance of bacterial taxa is positively correlated with color intensity.
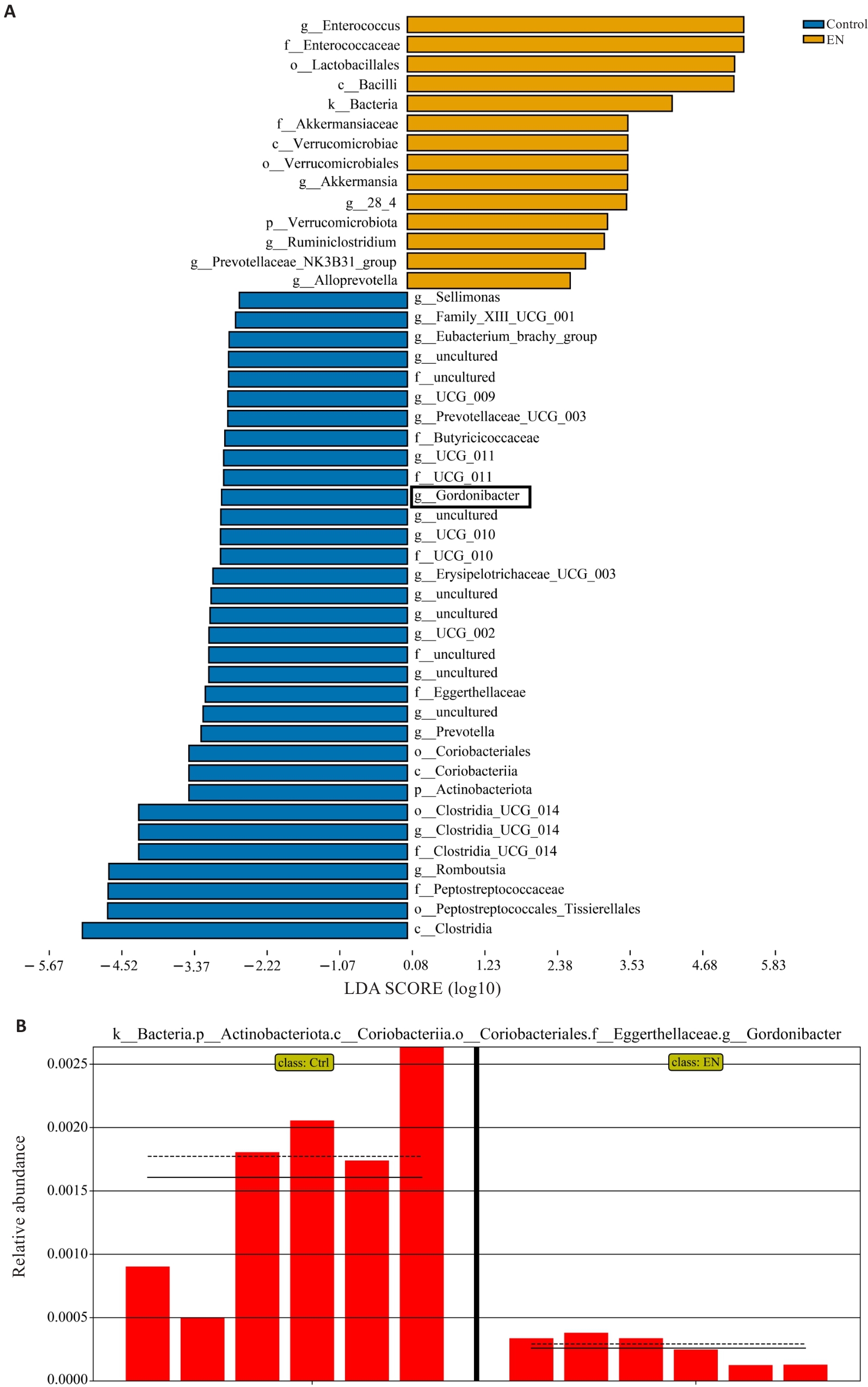
Fig.7 LEfSe analysis. A: Bar chart showing the major differential taxa between the control and model groups identified by LEfSe analysis. B: Bar chart of intergroup differences in Gordonibacter (the solid line represents the mean, and the dashed line represents the median).
| [1] | Singh P, Harris PC, Sas DJ, et al. The genetics of kidney stone disease and nephrocalcinosis[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2022, 18(4): 224-40. doi:10.1038/s41581-021-00513-4 |
| [2] | Geraghty R, Lovegrove C, Howles S, et al. Role of genetic testing in kidney stone disease: a narrative review[J]. Curr Urol Rep, 2024, 25(12): 311-23. doi:10.1007/s11934-024-01225-5 |
| [3] | Ming SX, Tian J, Ma K, et al. Oxalate-induced apoptosis through ERS-ROS-NF-κB signalling pathway in renal tubular epithelial cell[J]. Mol Med, 2022, 28(1): 88. doi:10.1186/s10020-022-00494-5 |
| [4] | Miller AW, Penniston KL, Fitzpatrick K, et al. Mechanisms of the intestinal and urinary microbiome in kidney stone disease[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2022, 19(12): 695-707. doi:10.1038/s41585-022-00647-5 |
| [5] | Jin X, Jian ZY, Chen XT, et al. Short chain fatty acids prevent glyoxylate-induced calcium oxalate stones by GPR43-dependent immunomodulatory mechanism[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 729382. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.729382 |
| [6] | Arvans D, Jung YC, Antonopoulos D, et al. Oxalobacter formigenes- derived bioactive factors stimulate oxalate transport by intestinal epithelial cells[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2017, 28(3): 876-87. doi:10.1681/asn.2016020132 |
| [7] | Ariceta G, Collard L, Abroug S, et al. ePHex: a phase 3, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized study to evaluate long-term efficacy and safety of Oxalobacter formigenes in patients with primary hyperoxaluria[J]. Pediatr Nephrol, 2023, 38(2): 403-15. doi:10.1007/s00467-022-05591-5 |
| [8] | Milliner D, Hoppe B, Groothoff J. A randomised Phase II/III study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of orally administered Oxalobacter formigenes to treat primary hyperoxaluria[J]. Urolithiasis, 2018, 46(4): 313-23. doi:10.1007/s00240-017-0998-6 |
| [9] | Xu MY, Qin YG, Xia YJ, et al. Screening of oxalate-degrading probiotics and preventive effect of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum AR1089 on kidney stones[J]. Food Funct, 2024, 15(19): 10163-78. doi:10.1039/d4fo03133d |
| [10] | Yuan TH, Xia YQ, Li BJ, et al. Gut microbiota in patients with kidney stones: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. BMC Microbiol, 2023, 23(1): 143. doi:10.1186/s12866-023-02891-0 |
| [11] | Ticinesi A, Milani C, Guerra A, et al. Understanding the gut-kidney axis in nephrolithiasis: an analysis of the gut microbiota composition and functionality of stone formers[J]. Gut, 2018, 67(12): 2097-106. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2017-315734 |
| [12] | Emdin CA, Khera AV, Kathiresan S. Mendelian randomization[J]. JAMA, 2017, 318(19): 1925. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.17219 |
| [13] | Davey Smith G, Hemani G. Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2014, 23(R1): R89-98. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddu328 |
| [14] | 李文婕, 洪耀南, 黄 蕊, 等. 自身免疫性疾病是再生障碍性贫血的危险因素: 一项孟德尔随机化分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 871-9. |
| [15] | 姚 辰, 李文佳, 庞瑞明, 等. 臀肌腱炎、原发性髋关节病可能导致髂胫束综合征: 一项孟德尔随机化研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1821-30. |
| [16] | Liu MH, Zhang YJ, Wu J, et al. Causal relationship between kidney stones and gut microbiota contributes to the gut-kidney axis: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study[J]. Front Microbiol, 2023, 14: 1204311. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1204311 |
| [17] | Gronau QF, Wagenmakers EJ. Limitations of Bayesian leave-one-out cross-validation for model selection[J]. Comput Brain Behav, 2019, 2(1): 1-11. doi:10.1007/s42113-018-0011-7 |
| [18] | Verbanck M, Chen CY, Neale B, et al. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases[J]. Nat Genet, 2018, 50(5): 693-8. doi:10.1038/s41588-018-0099-7 |
| [19] | Hussain B, Wu CC, Tsai HC, et al. Species-level characterization of gut microbiota and their metabolic role in kidney stone formation using full-length 16S rRNA sequencing[J]. Urolithiasis, 2024, 52(1): 115. doi:10.1007/s00240-024-01610-2 |
| [20] | Davies NM, Holmes MV, Davey Smith G. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: a guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians[J]. BMJ, 2018, 362: k601. doi:10.1136/bmj.k601 |
| [21] | Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Burgess S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through egger regression[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2015, 44(2): 512-25. doi:10.1093/ije/dyv080 |
| [22] | Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Haycock PC, et al. Consistent estimation in mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted Median estimator[J]. Genet Epidemiol, 2016, 40(4): 304-14. doi:10.1002/gepi.21965 |
| [23] | Hartwig FP, Davey Smith G, Bowden J. Robust inference in summary data Mendelian randomization via the zero modal pleiotropy assumption[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2017, 46(6): 1985-98. doi:10.1093/ije/dyx102 |
| [24] | 曹秋实, 巴元明, 罗俊华, 等. 排石冲剂对大鼠草酸钙结石生成的干预效果及其机制研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2015, 18(18): 2205-9. |
| [25] | Li NN, Niu LL, Liu Y, et al. Taking SCFAs produced by Lactobacillus reuteri orally reshapes gut microbiota and elicits antitumor responses[J]. J Nanobiotechnology, 2024, 22(1): 241. doi:10.1186/s12951-024-02506-4 |
| [26] | Zhou SK, Xu JD, Gao XQ, et al. Fructus Jujubae cooperated with water-expelling members in Shizao decoction alleviated intestinal injury and malignant ascites by modulating gut microbiota and metabolic homeostasis[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 133: 155895. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155895 |
| [27] | Ye JM, Meng Q, Jin KZ, et al. Phage cocktail alleviated type 2 diabetes by reshaping gut microbiota and decreasing proinfla-mmatory cytokines[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2024, 108(1): 9. doi:10.1007/s00253-023-12912-7 |
| [28] | Maslowski KM, Vieira AT, Ng A, et al. Regulation of inflammatory responses by gut microbiota and chemoattractant receptor GPR43[J]. Nature, 2009, 461(7268): 1282-6. doi:10.1038/nature08530 |
| [29] | Noonin C, Thongboonkerd V. Beneficial roles of gastrointestinal and urinary microbiomes in kidney stone prevention via their oxalate-degrading ability and beyond[J]. Microbiol Res, 2024, 282: 127663. doi:10.1016/j.micres.2024.127663 |
| [30] | Zhang MW, Cui SM, Mao BY, et al. Ellagic acid and intestinal microflora metabolite urolithin A: a review on its sources, metabolic distribution, health benefits, and biotransformation[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2023, 63(24): 6900-22. doi:10.1080/10408398.2022.2036693 |
| [31] | Yasuda T, Takagi T, Asaeda K, et al. Urolithin A-mediated augmentation of intestinal barrier function through elevated secretory mucin synthesis[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 15706. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-65791-x |
| [32] | Han DD, Wu YJ, Lu DD, et al. Polyphenol-rich diet mediates interplay between macrophage-neutrophil and gut microbiota to alleviate intestinal inflammation[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(10): 656. doi:10.1038/s41419-023-06190-4 |
| [33] | Hering NA, Luettig J, Jebautzke B, et al. The punicalagin metabolites ellagic acid and urolithin a exert different strengthening and anti-inflammatory effects on tight junction-mediated intestinal barrier function in vitro [J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 610164. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.610164 |
| [34] | Ma LY, Ni YH, Wang Z, et al. Spermidine improves gut barrier integrity and gut microbiota function in diet-induced obese mice[J]. Gut Microbes, 2020, 12(1): 1-19. doi:10.1080/19490976.2020.1832857 |
| [35] | Hu SW, Wang JH, Xu YL, et al. Anti-inflammation effects of fucosylated chondroitin sulphate from Acaudina molpadioides by altering gut microbiota in obese mice[J]. Food Funct, 2019, 10(3): 1736-46. doi:10.1039/c8fo02364f |
| [36] | Portincasa P, Bonfrate L, Vacca M, et al. Gut microbiota and short chain fatty acids: implications in glucose homeostasis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(3): 1105. doi:10.3390/ijms23031105 |
| [37] | Huang G, Zhou YZ, Cheng H, et al. Genome and transcriptome analysis of Enterococcus faecium from intestinal colonization and Enterococcus faecium from urinary tract infection[J]. Front Microbiol, 2023, 14: 1273949. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1273949 |
| [38] | Notting F, Pirovano W, Sybesma W, et al. The butyrate-producing and spore-forming bacterial genus Coprococcus as a potential biomarker for neurological disorders[J]. Gut Microbiome (Camb), 2023, 4: e16. doi:10.1017/gmb.2023.14 |
| [39] | Zhou ZJ, Feng DX, Shi DH, et al. Untargeted and targeted metabolomics reveal bile acid profile changes in rats with ethylene glycol-induced calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2023, 381: 110570. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110570 |
| [40] | Shi JY, Wang YJ, Bao QW, et al. Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua polysaccharide alleviates ulcerative colitis via gut microbiota-independent modulation of inflammatory immune response[J]. Carbohydr Polym, 2025, 356: 123387. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2025.123387 |
| [41] | Kuo WT, Odenwald MA, Turner JR, et al. Tight junction proteins occludin and ZO-1 as regulators of epithelial proliferation and survival[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2022, 1514(1): 21-33. doi:10.1111/nyas.14798 |
| [42] | Anbazhagan AN, Ge Y, Priyamvada S, et al. A direct link implicating loss of SLC26A6 to gut microbial dysbiosis, compromised barrier integrity, and inflammation[J]. Gastroenterology, 2024, 167(4): 704-17.e3. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2024.05.002 |
| [43] | Whittamore JM, Hatch M. Oxalate flux across the intestine: contributions from membrane transporters[J]. Compr Physiol, 2021, 12(1): 2835-75. doi:10.1002/j.2040-4603.2022.tb00199.x |
| [44] | 陈健鑫, 李生华. 基于孟德尔随机化方法分析肠道菌群与肾结石病的关联性研究[J]. 医药前沿, 2024(12): 6-11. |
| [45] | Yatsunenko T, Rey FE, Manary MJ, et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography[J]. Nature, 2012, 486(7402): 222-7. doi:10.1038/nature11053 |
| [46] | Ticinesi A, Nouvenne A, Chiussi G, et al. Calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis and gut microbiota: not just a gut-kidney axis. a nutritional perspective[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(2): 548. doi:10.3390/nu12020548 |
| [1] | Chuyu DENG, Xueying WANG, Lixiang GAN, Dayu WANG, Xiaoyan ZHENG, Chunzhi TANG. Electroacupuncture at Zusanli improves blood lipid disorders in hyperlipidemic mice by improving gut microbiota structure [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1633-1642. |
| [2] | Yuexuan ZHU, Zhangrui ZHU, Peng WU. Pentosan polysulfate alleviates cyclophosphamide-induced interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome in mice by modulating gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1270-1279. |
| [3] | Anbang ZHANG, Xiuqi SUN, Bo PANG, Yuanhua WU, Jingyu SHI, Ning ZHANG, Tao YE. Electroacupuncture pretreatment alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting ferroptosis through the gut-brain axis and the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 911-920. |
| [4] | Wenjie LI, Yaonan HONG, Rui HUANG, Yuchen LI, Ying ZHANG, Yun ZHANG, Dijiong WU. Causal relationship between autoimmune diseases and aplastic anemia: A Mendelian randomization study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 871-879. |
| [5] | Jiachun LUO, Sodnomjamts Batzaya, Xuefeng GAO, Jingyu CHEN, Zhengying YU, Shasha XIONG, Hong CAO. Akkermansia muciniphila gavage improves gut-brain interaction disorders in gp120 transgenic mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 554-565. |
| [6] | Junjie GAO, Kai YE, Jing WU. Quercetin inhibits proliferation and migration of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells by regulating TP53 gene [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 313-321. |
| [7] | Huihua MA, Kuipo YAN, Gang LIU, Yazhou XU, Lei ZHANG, Yizhuo LI. Epidemiology of atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter and its risk factors from 1990 to 2021: a systematic analysis and Mendelian randomization study based on the China and Global Burden of Disease Study 2021 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(10): 2182-2190. |
| [8] | Chen YAO, Wenjia LI, Ruiming PANG, Jihong ZHOU. Gluteal tendinitis and primary coxarthrosis may lead to iliotibial band syndrome: a Mendelian randomization study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1821-1830. |
| [9] | Weitao ZHONG, Weisong LI, Zelin LI, Qiang WANG, Wangming ZHANG. Causal relationship between sleep phenotype and idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1612-1619. |
| [10] | Heping LI, Gaohua LI, Xuehua ZHANG, Yanan WANG. Genetic drivers for inflammatory protein markers in colorectal cancer: a Mendelian randomization approach to clinical prognosis study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1361-1370. |
| [11] | Jiajin LIU, Changhong MIAO, Jiankang XU, Weijie YU, Jixin CHEN, Haozhi TANG, Aifeng LIU. Causal relationship between gut microbiota and pigmented villonodular synovitis: a Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1397-1406. |
| [12] | ZHU Jiwei, LU Manlu, JIAO Qianqian, SUN Yunliang, LIU Lu, DING Honghong, YU Yan, PAN Lei. Analysis of gut target microbiota and species difference in patients with obstructive sleep apnea based on 16S rRNA sequencing [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 146-155. |
| [13] | ZHAN Wenjie, ZHAO Ling. Type 1 diabetes mellitus is likely to increase the risk of thyrotoxicdsis: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(8): 1396-1401. |
| [14] | ZHAO Huanling, LING Yuxiao, MI Shuai, ZHU Jiahao, FAN Jiayao, YANG Ye, WANG Jing, LI Yingjun. Associations of circulating leptin levels with colorectal adenoma and colorectal cancer: a case-control and Mendelian randomization study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(12): 1989-1997. |
| [15] | SU Chao, TIAN Yuxiao, ZHANG Qing, WAN Tianhao, XIA Di. Increased muscle mass increases risks of intervertebral disc degeneration: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(12): 2029-2034. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||