南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 829-836.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.04.18
收稿日期:2024-12-06
出版日期:2025-04-20
发布日期:2025-04-28
通讯作者:
张晓微
E-mail:mazhennan8888@163.com;12348450@qq.com
作者简介:马振南,博士,主治医师,E-mail: mazhennan8888@163.com
基金资助:
Zhennan MA( ), Fuquan LIU, Xuefeng ZHAO, Xiaowei ZHANG(
), Fuquan LIU, Xuefeng ZHAO, Xiaowei ZHANG( )
)
Received:2024-12-06
Online:2025-04-20
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
Xiaowei ZHANG
E-mail:mazhennan8888@163.com;12348450@qq.com
摘要:
目的 探讨DTX2对奥沙利铂耐药的结直肠癌(CRC/OXA)细胞的影响及作用机制。 方法 利用CCK8检测奥沙利铂(OXA)对CRC细胞的抑制率,构建CRC/OXA细胞系,检测CRC/OXA细胞中DTX2的表达水平,利用基因工具干预CRC/OXA细胞,分为未转染组(con)、敲低组(DTX2-shRNA)及共转染组(DTX2-shRNA+ pcDNA-Notch2)。采用平板克隆、划痕和Transwell侵袭实验检测改变DTX2的表达对CRC/OXA细胞增值、迁移侵袭能力的影响,并通过Western blotting检测各组中Notch2、NICD、E-cadherin、N-cadherin及Vimentin蛋白的表达水平。利用SW620/OXA细胞同样分组行裸鼠移植瘤实验,体内验证对裸鼠成瘤及蛋白的影响。 结果 OXA对CRC细胞有明显抑制作用,SW620和LoVo细胞IC50分别为6.00和8.00 μmol/L,成功构建CRC/OXA细胞系,CRC/OXA细胞中DTX2表达量明显升高(P<0.01)。DTX2-shRNA组中CRC/OXA细胞明显抑制增值、迁移侵袭能力(P<0.05),DTX2-shRNA+pcDNA-Notch2组可逆转增强CRC/OXA细胞增值、迁移侵袭的能力(P<0.05)。Notch2、NICD及Vimentin蛋白平均表达水平,在DTX2-shRNA组中明显降低,而DTX2-shRNA+pcDNA-Notch2组明显升高(P<0.01);E-cadherin蛋白表达水平在以上两组中的趋势相反且有明显差异(P<0.01)。体内实验显示DTX2可明显促进SW620/OXA细胞移植瘤的生长及对应蛋白的变化(P<0.05)。 结论 DTX2通过Notch2信号通路促进 CRC/OXA细胞增值、迁移侵袭及上皮间质转化,DTX2可能作为提高OXA疗效的分子标志物。
马振南, 刘福全, 赵雪峰, 张晓微. DTX2促进奥沙利铂耐药的结直肠癌细胞增殖、侵袭和上皮间质转化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 829-836.
Zhennan MA, Fuquan LIU, Xuefeng ZHAO, Xiaowei ZHANG. High expression of DTX2 promotes proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of oxaliplatin-resistant colorectal cancer cells[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 829-836.
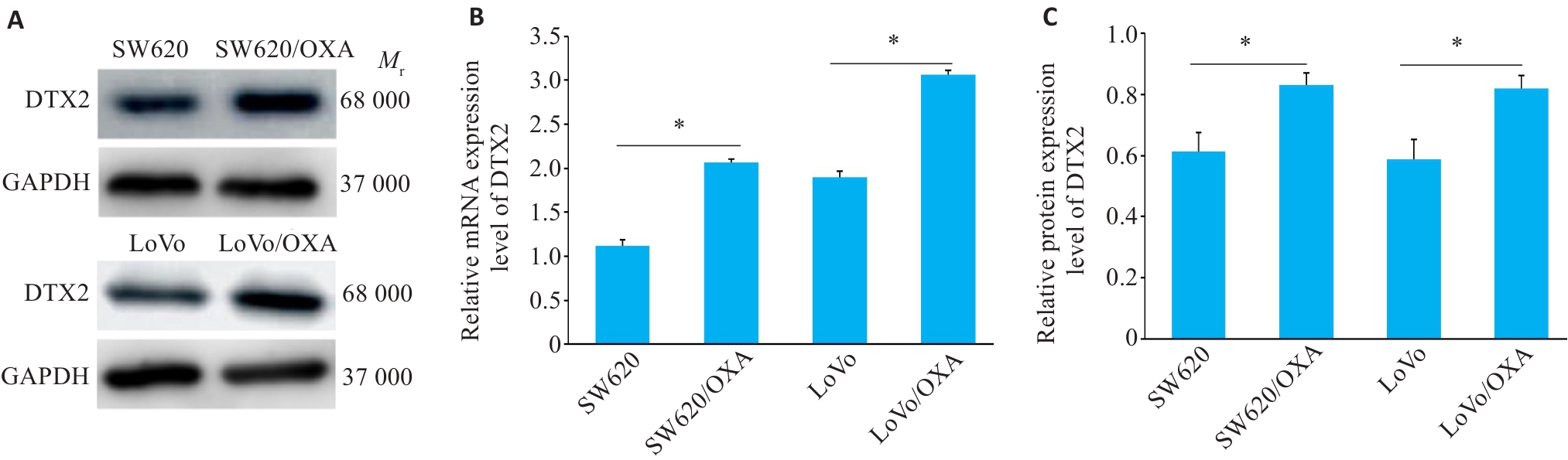
图2 CRC/OXA细胞中DTX2 mRNA和蛋白的表达水平
Fig 2 Western blotting for detecting protein expressions of DTX2 (A) and its relative protein (B) and mRNA (C) expression levels in CRC and CRC/OXA cells. SW620/OXA: Oxaliplatin-resistant SW620 cells; LoVo /OXA: Oxaliplatin-resistant LoVo cell. *P<0.01.
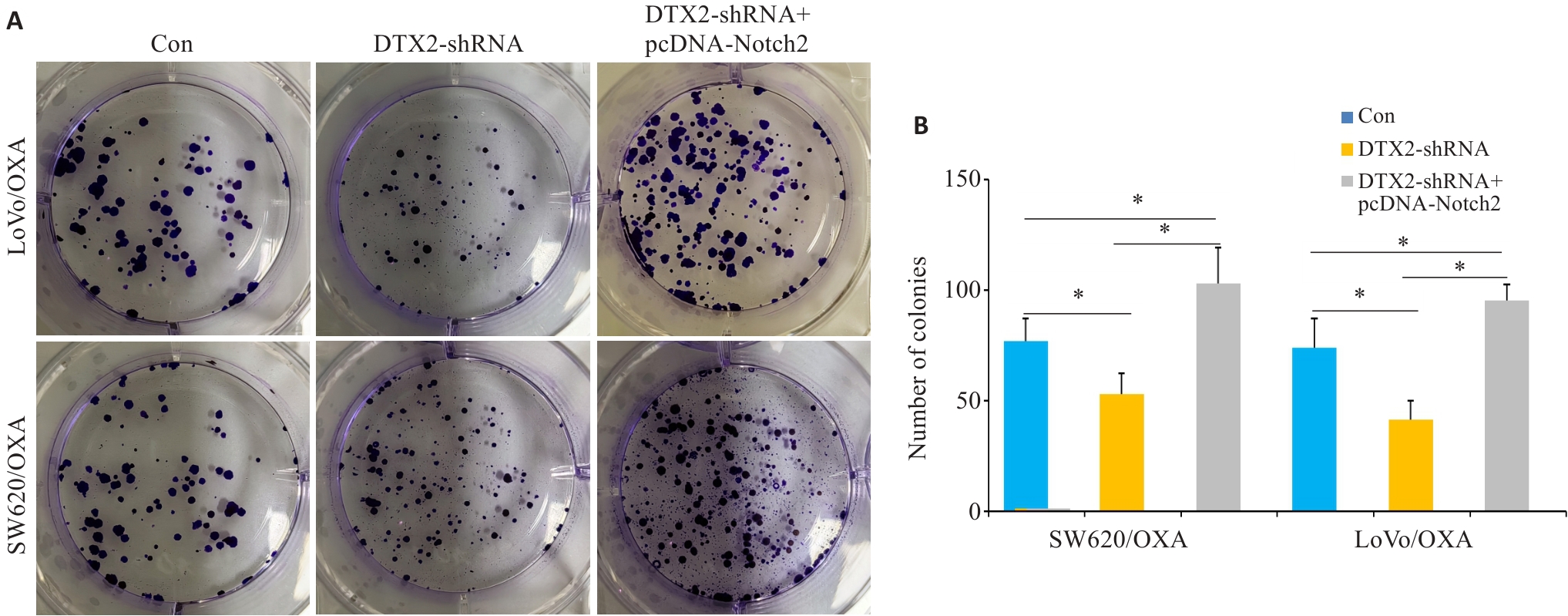
图3 CRC/OXA细胞共转染DTX2-shRNA和pcDNA-Notch2后对其增殖能力的影响
Fig.3 Plate cloning assays showing the proliferation capacity of CRC/OXA cells after transfection with DTX2-shRNA and DTX2-shRNA+pcDNA-Notch2 (A) and the mean number of colonies formed (B). *P<0.05.
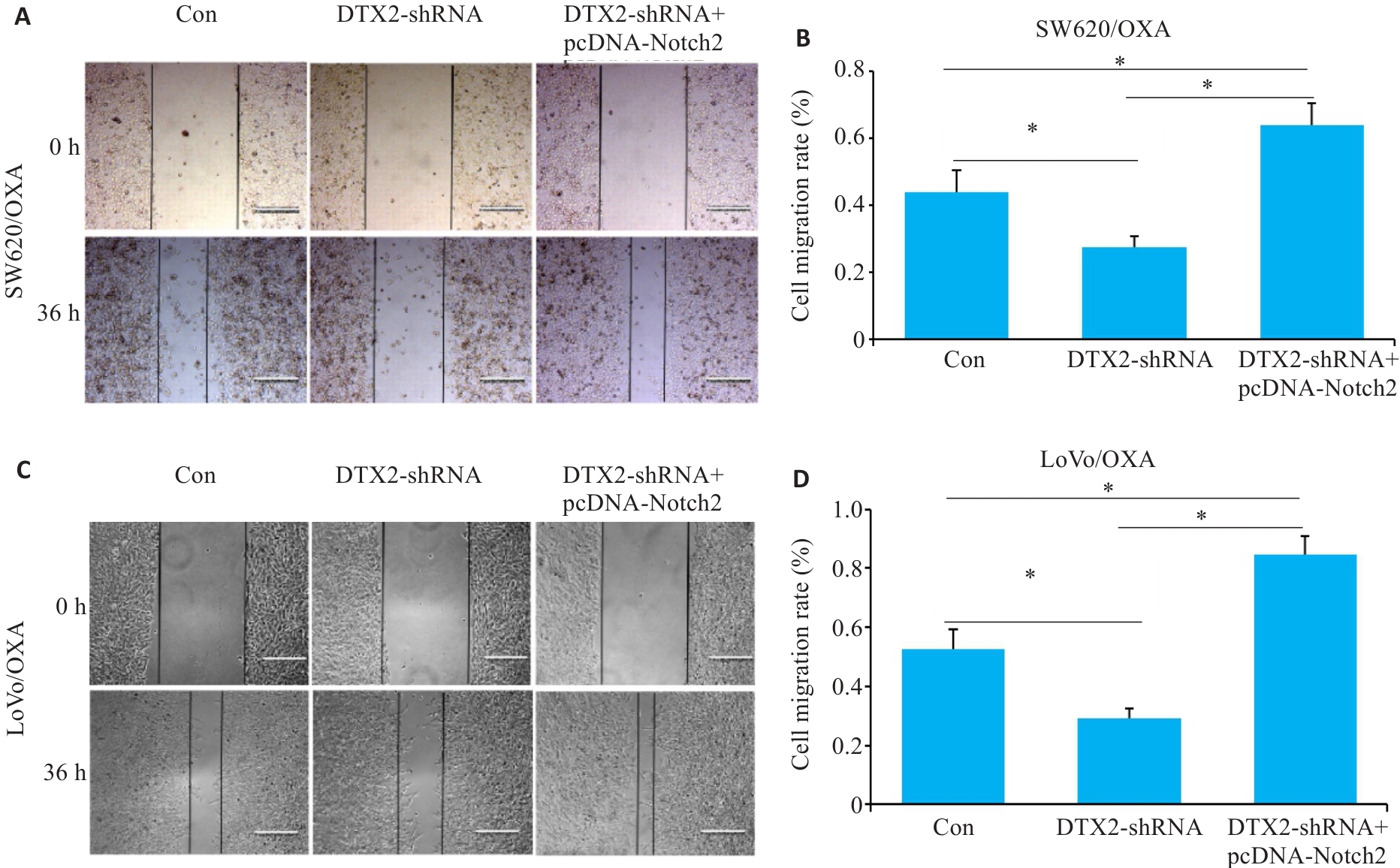
图4 CRC/OXA细胞共转染DTX2-shRNA和pcDNA-Notch2后对其迁移能力的影响
Fig.4 Scratch assay for assessing changes of migration ability of SW620/OXA (A, B) and LoVo/OXA (C, D) cells after transfection with DTX2-shRNA and DTX2-shRNA+pcDNA-Notch2. *P<0.05.
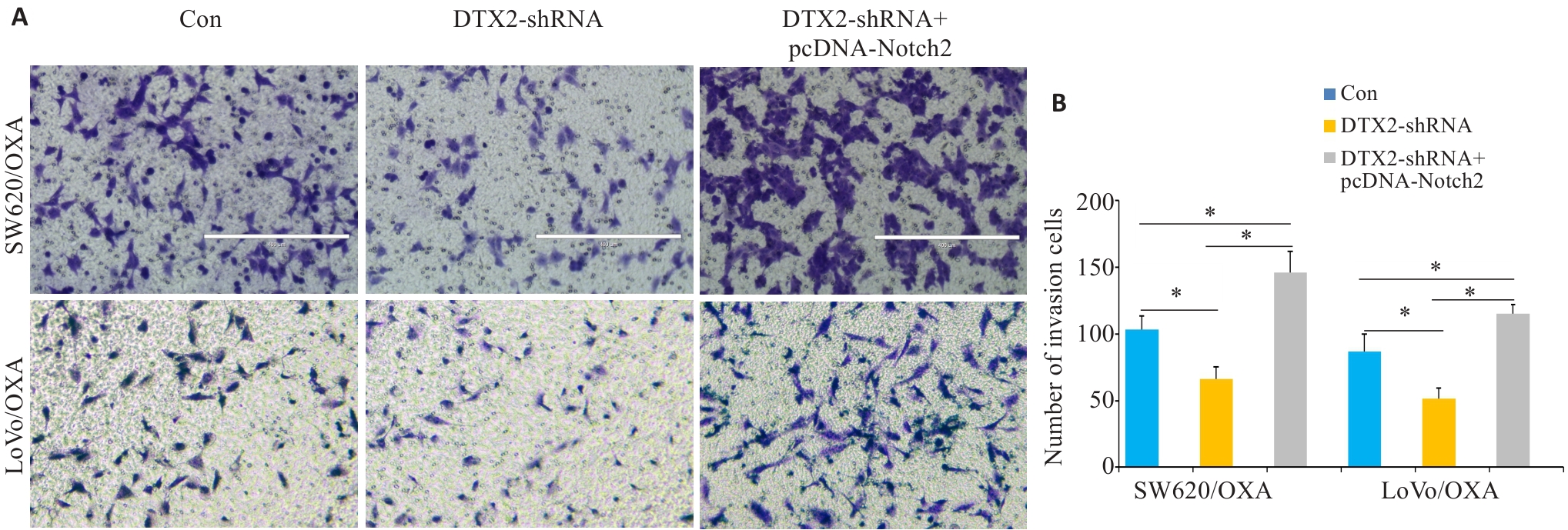
图5 CRC/OXA细胞共转染DTX2-shRNA和pcDNA-Notch2后对其侵袭能力的影响
Fig.5 Transwell invasion assay for assessing changes of migration ability of SW620/OXA and LoVo/OXA cells after transfection with DTX2-shRNA and DTX2-shRNA+pcDNA-Notch2. A: Microscopic observation of the cells (Original magnification: ×100). B: Average number of invasive cells in different groups. *P<0.01.
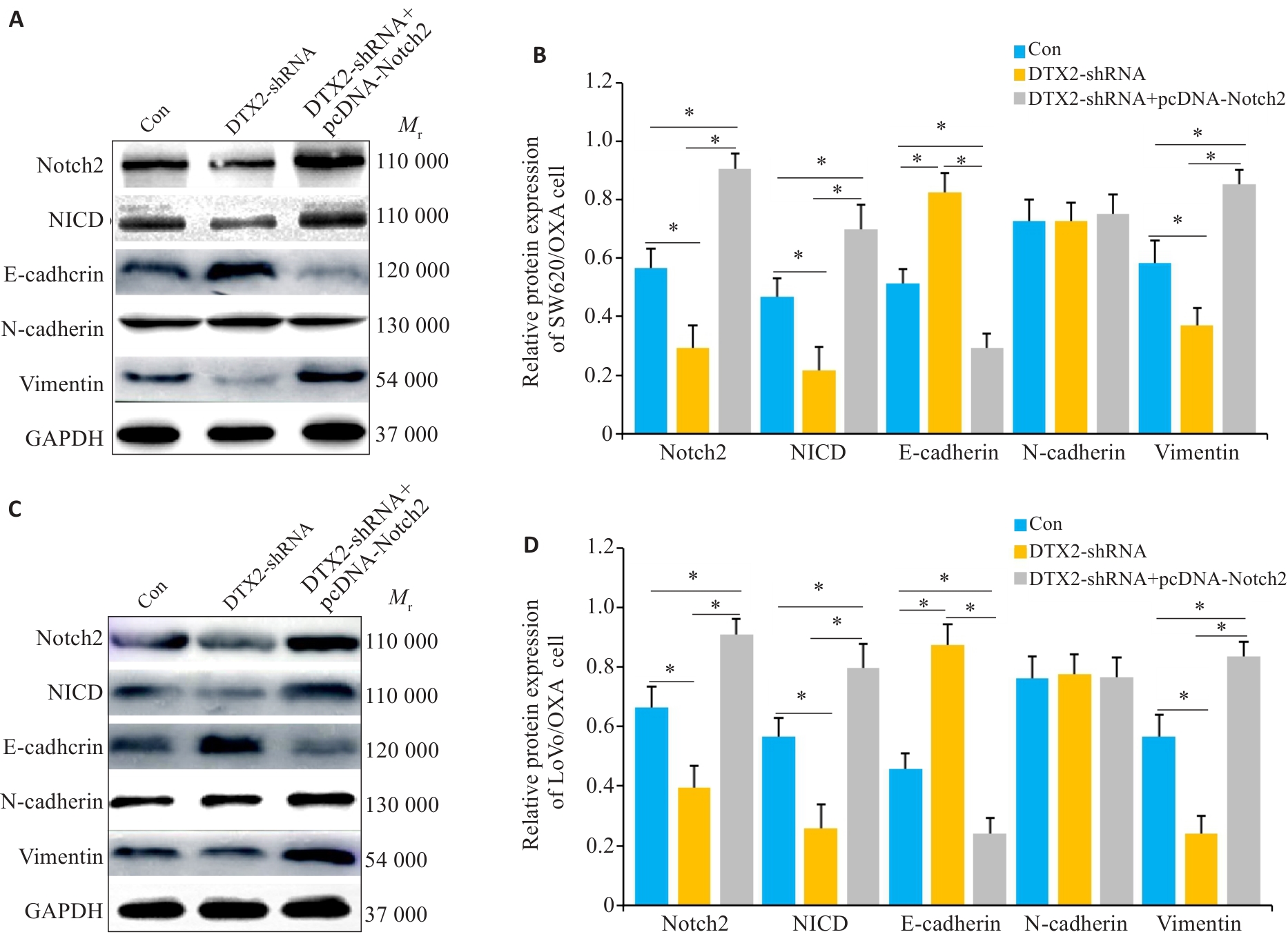
图6 CRC/OXA细胞共转染DTX2-shRNA和pcDNA-Notch2后Notch2信号通路及EMT中相关蛋白的变化
Fig.6 Changes of protein expressions in the Notch2 Signal pathway and EMT in SW620 and LoVo cells co-transfected with DTX2-shRNA and DTX2-shRNA+pcDNA-Notch2. A, C: Western blots of the proteins in SW620/OXA and LoVo/OXA cells. B, D: Quantitative analysis of the protein expressions. GAPDH was used as the internal control. *P<0.01.
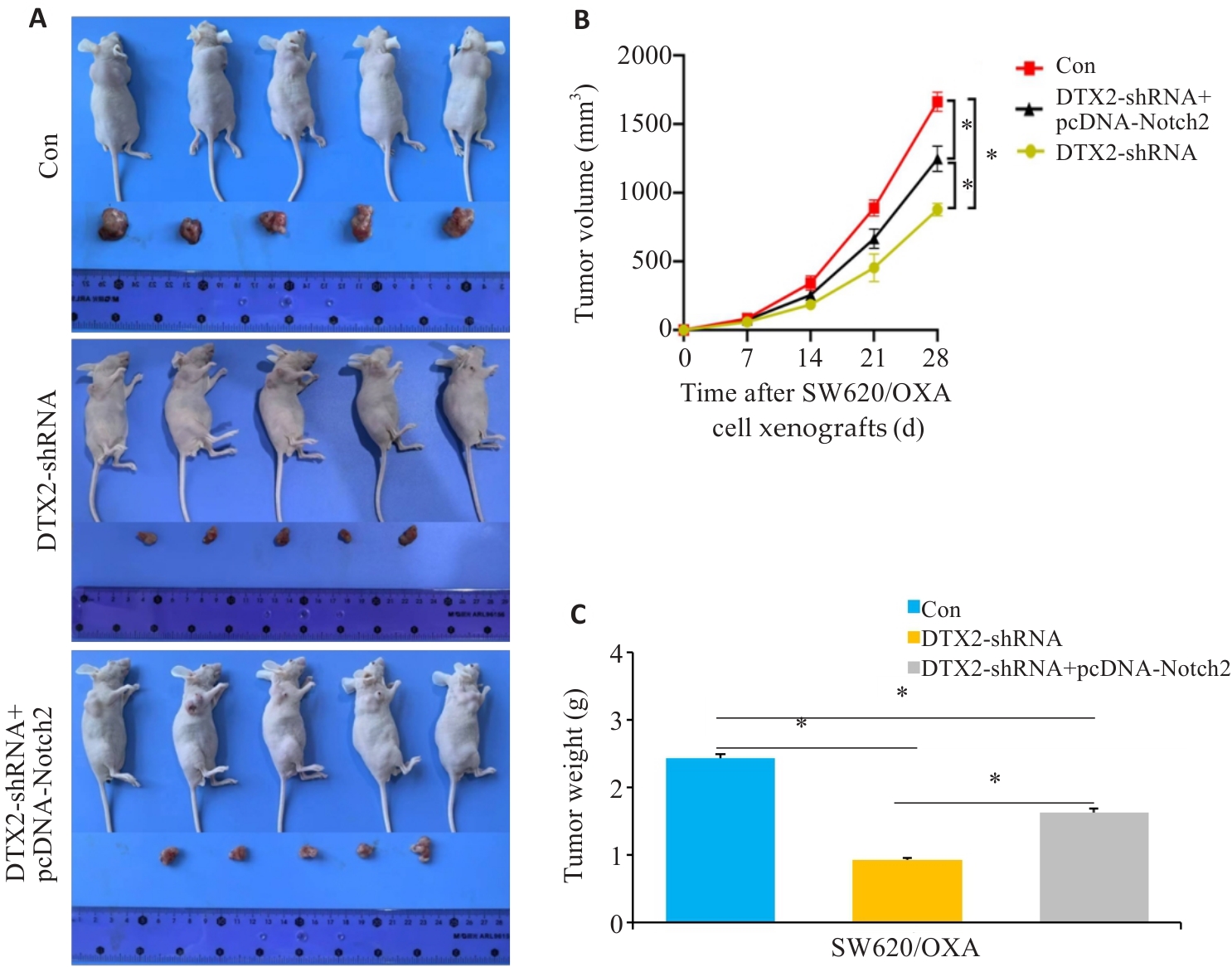
图7 SW620/OXA细胞干预后对裸鼠移植瘤的影响
Fig.7 Growth of SW620/OXA cell xenografts transfected with DTX2-shRNA or DTX2-shRNA+pcDNA-Notch2 in nude mice. A: Observation of the tumor-bearing mice and the dissected tumors. B: Changes in the volume of the xenografts over time. C: Xenograft weight measurement. *P<0.05.
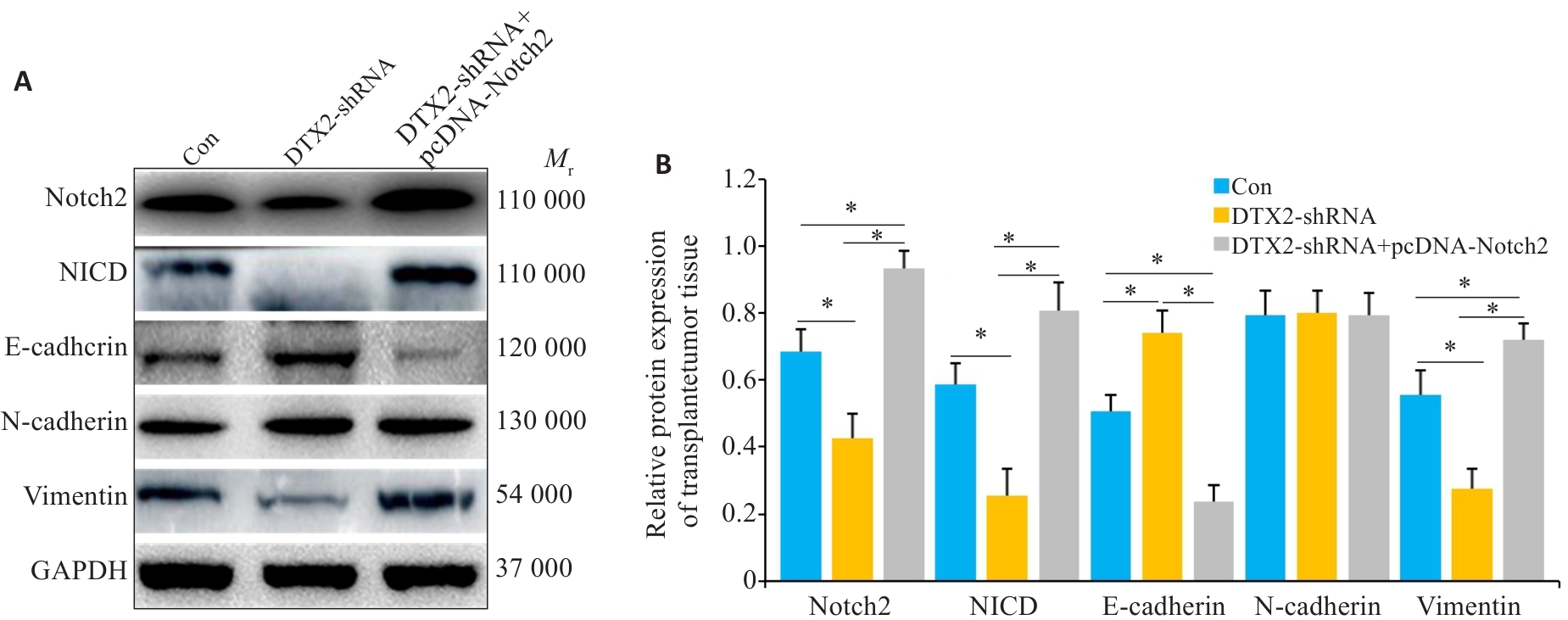
图8 SW620/OXA细胞裸鼠成瘤组织中蛋白的影响
Fig.8 Protein expressions in SW620/OXA cell xenografts transfected with DTX2-shRNA or DTX2-shRNA+pcDNA-Notch2. A: Western blotting of the proteins in SW620/OXA cell xenografts. B: Quantitative analysis of the protein expressions. GAPDH was used as the internal control. *P<0.01.
| 1 | Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-49. |
| 2 | Guo JF, Yu Z, Das M, et al. Nano codelivery of oxaliplatin and folinic acid achieves synergistic chemo-immunotherapy with 5-fluorouracil for colorectal cancer and liver metastasis[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(4): 5075-89. |
| 3 | Rasmussen MH, Lyskjær I, Jersie-Christensen RR, et al. miR-625-3p regulates oxaliplatin resistance by targeting MAP2K6-p38 signalling in human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells[J]. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 12436. |
| 4 | Zacharakis G, Almasoud A, Arahmaner O, et al. A 5-year evaluation of early-and late-onset sporadic colorectal cancer screening in central Saudi Arabia[J]. Saudi J Gastroenterol, 2023, 29(2): 95-101. |
| 5 | Shi YX, Niu Y, Yuan YC, et al. PRMT3-mediated arginine methylation of IGF2BP1 promotes oxaliplatin resistance in liver cancer[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1): 1932. |
| 6 | Wu SZ, Shen SH, Lu F, et al. Bromodomain containing 4 transcriptionally activated Deltex E3 ubiquitin ligase 2 contributes to glioma progression and predicts an unfavorable prognosis[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2022, 10(6): 313. |
| 7 | Li R, Chen Y, Yang B, et al. DTX2 promotes glioma development via regulation of HLTF[J]. Biol Direct, 2024, 19(1): 2. |
| 8 | 黄小强. 基于生信分析DTX2相关基因在肝癌中的表达及临床价值[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2024. |
| 9 | Liu Z, Liu C, Fan CH, et al. E3 ubiquitin ligase DTX2 fosters ferroptosis resistance via suppressing NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Drug Resist Updat, 2024, 77: 101154. |
| 10 | Song M, Kuerban M, Zhao L, et al. Inhibition of RFX6 suppresses the invasive ability of tumor cells through the Notch pathway and affects tumor immunity in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 801222. |
| 11 | 马振南, 许广大, 刘福全, 等. 结直肠癌组织中DTX2分子的表达及临床意义[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2021, 28(7): 861-6. |
| 12 | 马振南, 赵雪峰, 张晓微, 等. DTX2通过Notch2/Akt轴促进结直肠癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 340-8. |
| 13 | De Mattia E, Dreussi E, Montico M, et al. A clinical-genetic score to identify surgically resected colorectal cancer patients benefiting from an adjuvant fluoropyrimidine-based therapy[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2018, 9: 1101. |
| 14 | 邓金海, 潘 腾, 周广林, 等. 高表达分泌颗粒蛋白Ⅱ增加结直肠癌细胞对奥沙利铂的耐药性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(10): 1657-64. |
| 15 | Mayer RJ. Flashback foreword: oxaliplatin plus LV5FU2 in colorectal cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2023, 41(33): 5077-8. |
| 16 | Cai M, Hu WL, Huang CJ, et al. lncRNA MCF2L-AS1/miR-105/IL-1β axis regulates colorectal cancer cell oxaliplatin resistance[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2021, 13: 8685-94. |
| 17 | Mora Y, Reyes ME, Zanella L, et al. Resistance to platinum-based cancer drugs: a special focus on epigenetic mechanisms[J]. Pharmacogenomics, 2021, 22(12): 777-90. |
| 18 | Kosugi C, Koda K, Ishibashi K, et al. Safety of mFOLFOX6/XELOX as adjuvant chemotherapy after curative resection of stage III colon cancer: phase II clinical study (The FACOS study)[J]. Int J Colorectal Dis, 2018, 33(6): 809-17. |
| 19 | Li HR, Yang BB. Friend or foe: the role of microRNA in chemo-therapy resistance[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2013, 34(7): 870-9. |
| 20 | Yu ZL, Deng P, Chen YF, et al. Inhibition of the PLK1-coupled cell cycle machinery overcomes resistance to oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer[J]. Adv Sci, 2021, 8(23): e2100759. |
| 21 | Zhang CY, Xu C, Gao XY, et al. Platinum-based drugs for cancer therapy and anti-tumor strategies[J]. Theranostics, 2022, 12(5): 2115-32. |
| 22 | Hölzel M, Bovier A, Tüting T. Plasticity of tumour and immune cells: a source of heterogeneity and a cause for therapy resistance [J]? Nat Rev Cancer, 2013, 13(5): 365-76. |
| 23 | McMillin DW, Negri JM, Mitsiades CS. The role of tumour-stromal interactions in modifying drug response: challenges and opportunities[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2013, 12(3): 217-28. |
| 24 | Wang Q, Chen X, Jiang YH, et al. Elevating H3K27me3 level sensitizes colorectal cancer to oxaliplatin[J]. J Mol Cell Biol, 2020, 12(2): 125-37. |
| 25 | Dhanyamraju PK. Drug resistance mechanisms in cancers: execution of pro-survival strategies[J]. J Biomed Res, 2024, 38(2): 95-121. |
| 26 | Chen G, Gong T, Wang Z, et al. Colorectal cancer organoid models uncover oxaliplatin- resistant mechanisms at single cell resolution [J]. Cell Oncol (Dordr), 2022, 45(6):1155-67. |
| 27 | Aliabadi F, Sohrabi B, Mostafavi E, et al. Ubiquitin-proteasome system and the role of its inhibitors in cancer therapy[J]. Open Biol, 2021, 11(4): 200390. |
| 28 | Han DW, Wang LJ, Jiang S, et al. The ubiquitin-proteasome system in breast cancer[J]. Trends Mol Med, 2023, 29(8): 599-621. |
| 29 | Park J, Cho J, Song EJ. Ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) as a target for anticancer treatment[J]. Arch Pharm Res, 2020, 43(11): 1144-61. |
| 30 | 李向阳. 甲状腺乳头状癌中DTX2的表达与临床意义[D]. 沈阳: 中国医科大学, 2018. |
| 31 | Cui YH, Wei JB, Fan H, et al. Targeting DTX2/UFD1-mediated FTO degradation to regulate antitumor immunity[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2024, 121(51): e2407910121. |
| 32 | Maki K, Sasaki K, Sugita F, et al. Acute myeloid leukemia with t(7;21)(q11.2;q22) expresses a novel, reversed-sequence RUNX1-DTX2 Chimera[J]. Int J Hematol, 2012, 96(2): 268-73. |
| 33 | Yonezawa T, Takahashi H, Hao YY, et al. The E3 ligase DTX2 inhibits RUNX1 function by binding its C terminus and prevents the growth of RUNX1-dependent leukemia cells[J]. FEBS J, 2023, 290(21): 5141-57. |
| 34 | Zhou BH, Lin WL, Long YL, et al. Notch signaling pathway: architecture, disease, and therapeutics[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2022, 7(1): 95. |
| [1] | 吴璇, 方家敏, 韩玮玮, 陈琳, 孙菁, 金齐力. 高表达PRELID1促进胃癌细胞上皮间质转化并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1535-1542. |
| [2] | 翁诺舟, 谭彬, 曾文涛, 古家宇, 翁炼基, 郑克鸿. 过表达RGL1通过激活CDC42/RAC1复合体上调运动型黏着斑组装促进结直肠癌转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 1031-1038. |
| [3] | 庆顺杰, 沈智勇. 过表达己糖激酶2通过激活JAK/STAT途径促进结直肠癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭并调节肿瘤免疫微环境[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 542-553. |
| [4] | 陶露, 韦卓利, 王月月, 项平. CEACAM6通过调控上皮间质转化抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 566-576. |
| [5] | 纪凯, 于冠宇, 周乐其, 张天帅, 凌潜龙, 满文江, 朱冰, 张卫. HNRNPA1基因在结直肠癌组织中高表达及其潜在的诊断和治疗价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1685-1695. |
| [6] | 朱梦云, 王剑锋. 康柏西普可逆转TGF-β2诱导的晶状体上皮细胞发生上皮间质转化:基于调节TGF-β/Smad信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1459-1466. |
| [7] | 张银亮, 骆泽谭, 赵睿, 赵娜, 徐志东, 奥迪, 丛古一, 刘新宇, 郑海伦. 血根碱通过调控STUB1/GPX4诱导直肠癌细胞发生铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1537-1544. |
| [8] | 张富星, 刘国庆, 董锐, 高磊, 陆伟晨, 高连霞, 赵忠扩, 陆飞, 刘牧林. 高表达CRTAC1通过调控PI3K信号通路促进胃癌细胞增殖、迁移及免疫浸润[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2421-2433. |
| [9] | 赵文, 阮何静, 汪思远, 程羽哲, 雷淼, 赵久法, 刘传苗. 抑制Yes相关蛋白通过抑制上皮间质转化减轻CCl4诱导的小鼠肝纤维化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(10): 1839-1849. |
| [10] | 郗雪艳, 邓婷, 杜伯雨. 结直肠成纤维细胞通过激活ERK信号通路促进结直肠癌细胞的恶性生物学行为[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(10): 1866-1873. |
| [11] | 刘雪柔, 杨玉梅, 蔡 慧, 张耀帅, 范方田, 李 娴, 李姗姗. 阿美替尼具有较好的抗神经母细胞瘤作用:基于下调MMP2和MMP9的表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1493-1499. |
| [12] | 郭晓娟, 陈丽平, 吕 芹, 杜瑞娟, 罗 琴, 张 阳, 卞 华, 韩 立. 桂枝茯苓胶囊通过调控NF-κB通路抑制卵巢癌细胞的迁移和诱导卵巢癌细胞的凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1315-1321. |
| [13] | 谢紫平, 刘立威, 房锦存, 钟星怡, 林俊豪, 陈逢生. ARHGAP21通过失活WNT信号通路抑制非小细胞肺癌中的上皮间质转化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1322-1332. |
| [14] | 颜 畅, 刘 爽, 宋庆志, 胡艺冰. 二甲双胍通过抑制线粒体氧化磷酸化降低结直肠癌干细胞的自我更新能力[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1279-1286. |
| [15] | 魏 可, 石纪雯, 肖雨寒, 王文锐, 杨清玲, 陈昌杰. miR-30e-5p过表达促进结直肠癌细胞的增殖和迁移:基于下调PTEN激活CXCL12轴[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1081-1092. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||