南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (10): 1839-1849.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.10.01
• •
赵文( ), 阮何静(
), 阮何静( ), 汪思远, 程羽哲, 雷淼, 赵久法, 刘传苗(
), 汪思远, 程羽哲, 雷淼, 赵久法, 刘传苗( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-12
出版日期:2024-10-20
发布日期:2024-10-31
通讯作者:
刘传苗
E-mail:zhaowen6220@163.com;2930916898@qq.com;liuchuanmiao119@sina.com
作者简介:赵 文,博士,主治医师,E-mail: zhaowen6220@163.com基金资助:
Wen ZHAO( ), Hejing RUAN(
), Hejing RUAN( ), Siyuan WANG, Yuzhe CHENG, Miao LEI, Jiufa ZHAO, Chuanmiao LIU(
), Siyuan WANG, Yuzhe CHENG, Miao LEI, Jiufa ZHAO, Chuanmiao LIU( )
)
Received:2024-04-12
Online:2024-10-20
Published:2024-10-31
Contact:
Chuanmiao LIU
E-mail:zhaowen6220@163.com;2930916898@qq.com;liuchuanmiao119@sina.com
摘要:
目的 探索Yes相关蛋白(YAP)可否通过调控上皮间质转化影响肝纤维化的发生发展。 方法 将8周龄C57BL/6小鼠18只随机分为对照组、肝纤维化模型组和YAP抑制剂维替泊芬干预组,6只/组。肝纤维化模型采用四氯化碳(CCl4)溶液腹腔注射8周造模;维替泊芬干预组在CCl4基础上第7~9周采用维替泊芬腹腔注射干预。HE染色、Masson染色、肝脏生化学检测观察小鼠肝脏纤维化程度;转录组、蛋白组学测序及联合生信分析探明肝纤维化过程中上皮间质转化通路是否受YAP调控;免疫组化染色和Western blotting检测YAP及上皮间质转化关键基因E-cadherin、N-cadherin、Twist等表达变化。采集健康体检、慢性乙型肝炎、乙肝肝硬化患者血清各60例,酶联免疫吸附法检测其中YAP、N-cadherin、Vimentin、Twist血清表达水平。C57BL/6小鼠24只随机分为对照组、肝纤维化模型组、Twist抑制剂干预组和Twist抑制剂与YAP激动剂共同干预组,6只/组。HE染色、Masson染色、网状纤维染色观察小鼠肝脏纤维化程度,Western blotting检测各组α-SMA、YAP和Twist表达变化。 结果 小鼠肝组织病理学结果提示肝纤维化小鼠与对照组相比肝小叶结构破坏、假小叶形成,维替泊芬干预组纤维间隔变性,部分小叶结构恢复。随肝纤维化发生,血浆ALT、AST水平显著升高(P<0.01),维替泊芬干预组肝功能改善(P<0.01)。采用肝组织转录组、蛋白组测序及联合分析找到在肝纤维化形成和维替泊芬干预过程中同时在mRNA和蛋白水平差异表达的基因,发现了N-cadherin和Twist在3组间差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05),并进行PPI分析显示YAP与E-cadherin、N-cadherin存在关联。免疫组化和Western blotting结果提示N-cadherin、Twist、Vimentin随肝纤维化形成升高,E-cadherin在肝纤维化组织中表达下降(P<0.01)。抑制YAP可下调肝组织N-cadherin、Twist蛋白表达(P<0.01)。慢性乙型肝炎患者血清YAP、N-cadherin、Vimentin和Twist水平均随肝炎及肝硬化发生升高,在APRI>0.5或FIB-4>1.45患者中显著升高(P<0.01)。血清YAP在健康对照、肝炎、肝硬化患者中平均水平分别为4.09、5.69和5.36 ng/mL(P<0.01),其与N-cadherin、Vimentin、Twist水平均呈显著正相关,相关系数分别为0.626、0.435、0.526。采用Harmine抑制小鼠肝组织Twist表达,并在Harmine基础上予以YAP激动剂XMU-MP-1干预,肝组织病理学结果提示抑制Twist使肝纤维化小鼠肝组织炎症及纤维化程度减轻,同时激活YAP表达可再次加重胶原纤维沉积。Western blotting检测结果提示Harmine下调肝纤维化小鼠肝组织中α-SMA、YAP及Twist蛋白表达,同时激活YAP使肝组织α-SMA和YAP表达升高(P=0.079,P<0.05)。 结论 上皮间质转化是肝纤维化发生的重要机制之一,抑制YAP可通过减少上皮间质转化发生减轻肝纤维化。
赵文, 阮何静, 汪思远, 程羽哲, 雷淼, 赵久法, 刘传苗. 抑制Yes相关蛋白通过抑制上皮间质转化减轻CCl4诱导的小鼠肝纤维化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(10): 1839-1849.
Wen ZHAO, Hejing RUAN, Siyuan WANG, Yuzhe CHENG, Miao LEI, Jiufa ZHAO, Chuanmiao LIU. Inhibiting Yes-associated protein alleviates CCl4 liver fibrosis in mice by reducing epithelial mesenchymal transition[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(10): 1839-1849.
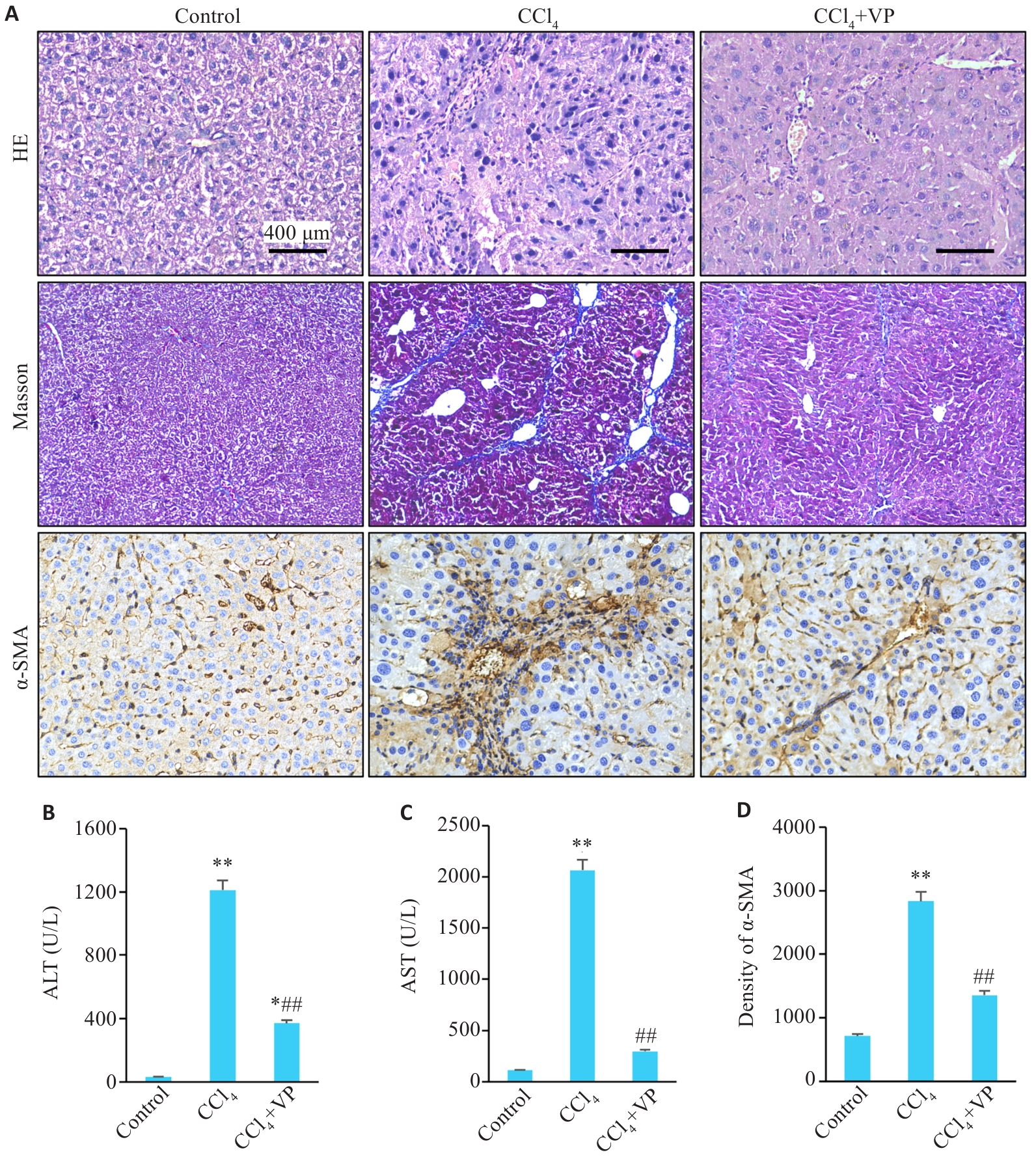
图1 小鼠肝组织病理表现及血清AST、ALT水平
Fig.1 Liver histopathology and serum levels of ALT and AST in mice. A: HE staining (Original magnification: ×200), Masson's trichrome staining (×100), and immunohistochemical staining of α-SMA (×200). B, C: Serum levels of ALT and AST. D: Quantitative data of immunohistochemistry for α-SMA in liver tissues. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs control group; ##P<0.01 vs CCl4 group.
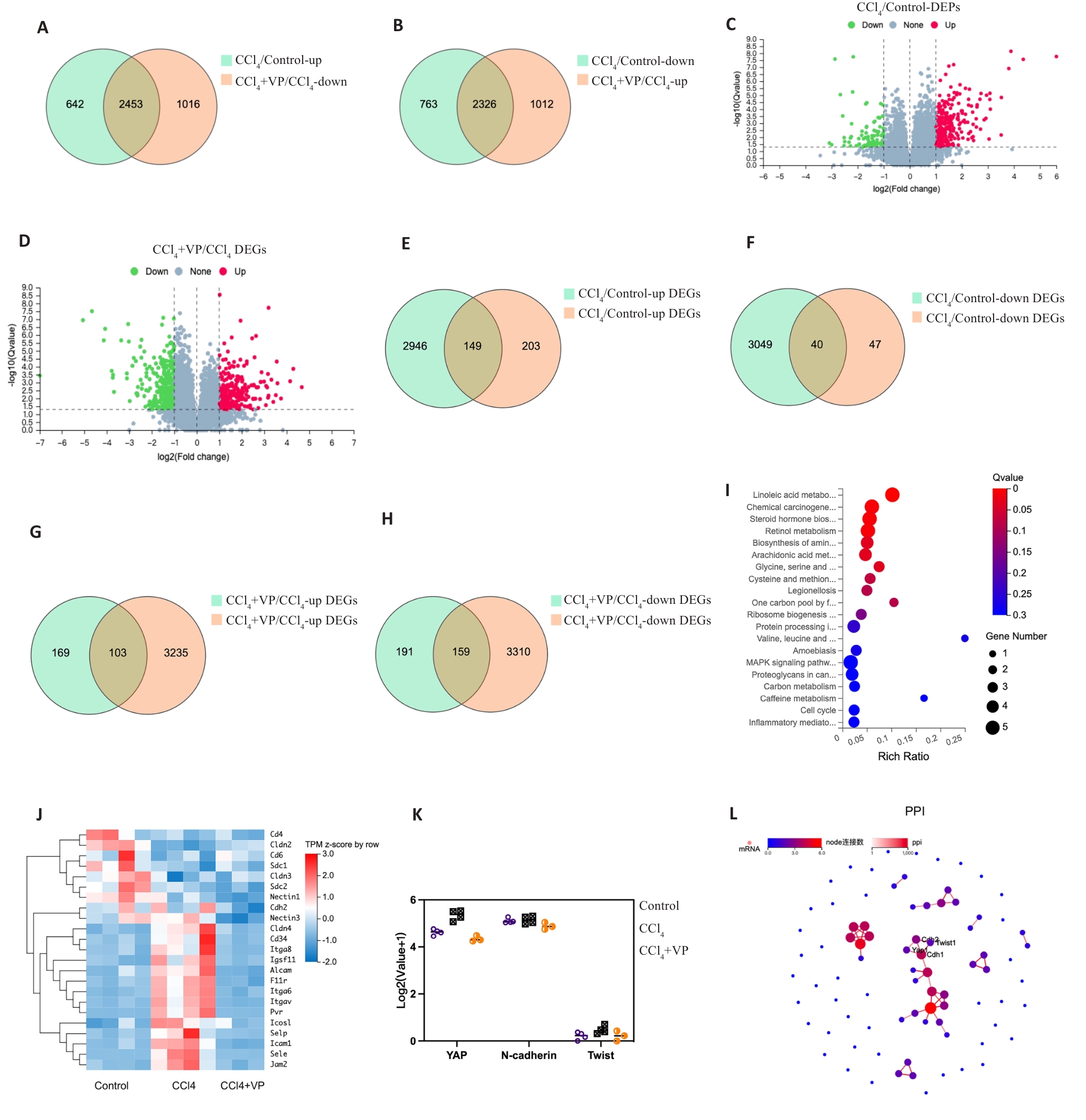
图2 小鼠肝组织转录组及蛋白组测序的差异基因及蛋白分析
Fig.2 Transcriptomic analysis of and proteomic analysis of differentially expression mRNAs and proteins in the liver tissue of mice. A, B: Venn diagram showing differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the groups. C, D: Volcano plot showing differentially expressed proteins (DEPs). The red and green dots indicate significantly upregulated and downregulated genes, respectively. E, F: Venn diagram showing differentially expressed mRNAs and proteins between control and CCl4 groups. G, H: Venn diagram showing differentially expressed mRNAs and proteins between the CCl4 and verteporfin (VP) treatment groups. I: Bubble chart of Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis of the DEGs. J: Heat map of the DEGs of cell adhesion molecules pathway. K: Expressions of YAP, N-cadherin and Twist mRNAs in the 3 groups. L: Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network of the DEGs.
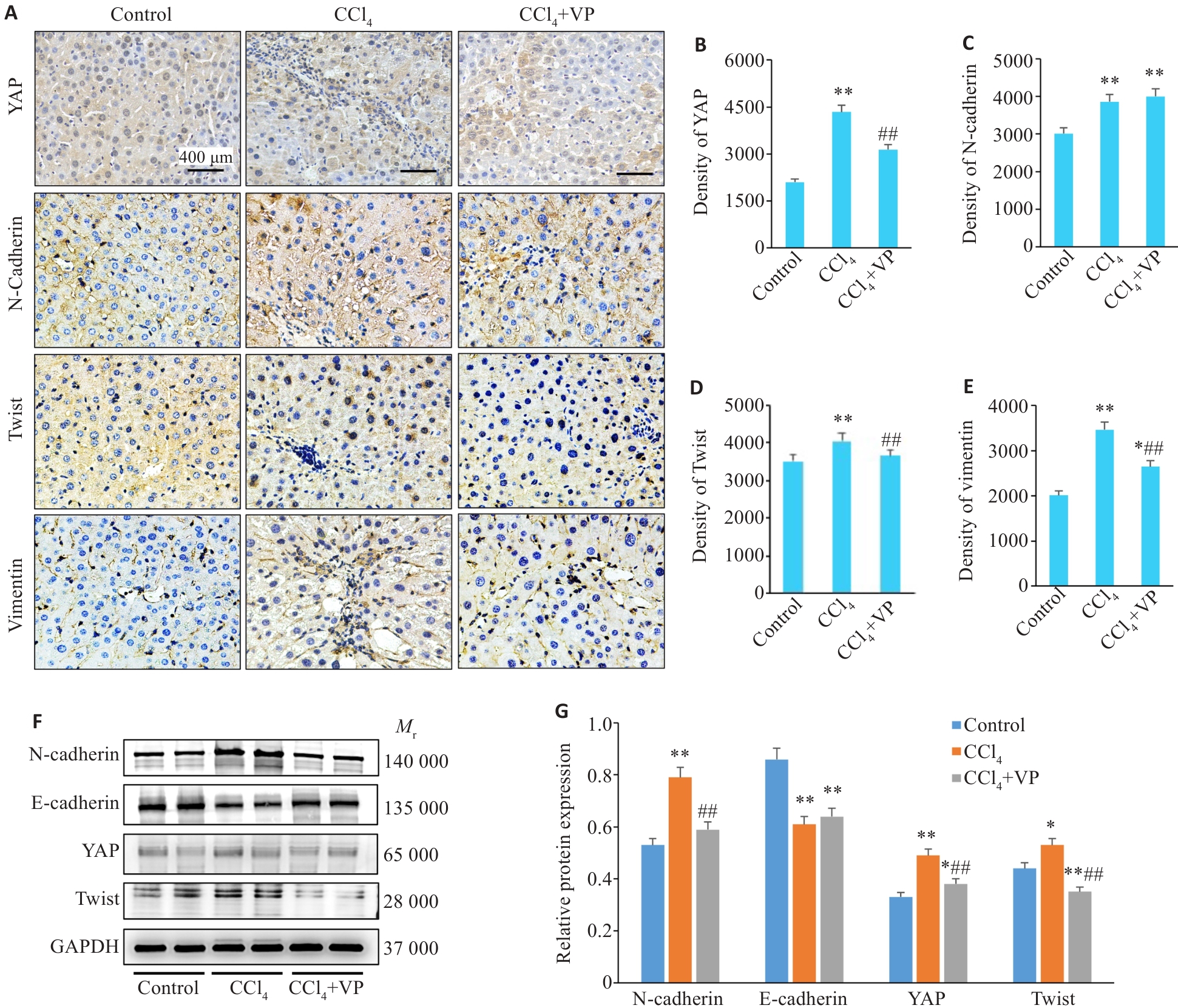
图3 小鼠肝组织YAP及EMT关键蛋白表达
Fig.3 Expression of YAP and EMT-related proteins in the liver tissue of the mice. A: Immunohistochemical staining of YAP, N-cadherin, Twist and vimentin (×400). B-E: Quantitative data of immunohistochemical staining for YAP, N-cadherin, Twist and vimentin. F: Western blotting of hepatic YAP, N-cadherin, E-cadherin and Twist protein expressions. G: Quantification of the protein expression levels. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs control group; ##P<0.01 vs CCl4 group.
| Parameters | Healthy controls (n=60) | CHB (n=60) | Liver cirrhosis (n=60) | F/Z/χ2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male [n (%)] | 40 (66.7) | 30 (50.0) | 41 (68.3) | 5.217 | 0.074 |
| Age (year) | 50.1±0.5 | 46.6±1.1 | 51.0±1.3 | 5.377 | 0.095 |
| WBC (109/L) | 6.17 (5.38, 7.15) | 5.48 (4.54, 6.56) | 4.21 (2.72, 5.43) | 32.55 | <0.001 |
| PLT (109/L) | 232 (200, 275) | 187 (155, 227) | 89 (48, 134) | 54.95 | <0.001 |
| ALB (g/L) | 45.8 (42.8, 47.4) | 46.5 (44.6, 48.2) | 32.4 (28.0, 36.2) | 104.93 | <0.001 |
| ALT (U/L) | 22 (17, 32) | 18 (15, 25) | 32 (18, 56) | 19.42 | <0.001 |
| AST (U/L) | 21 (18, 25) | 22 (19, 26) | 47 (34., 76) | 72.43 | <0.001 |
| GGT (U/L) | 26 (18, 41.5) | 15 (12, 20) | 47 (28, 109) | 71.92 | <0.001 |
| APRI | 0.24 (0.17, 0.30) | 0.29 (0.23, 0.47) | 1.80 (0.90, 2.89) | 93.61 | <0.001 |
| FIB-4 | 0.96 (0.80, 1.19) | 1.29 (0.96, 1.69) | 5.06 (3.35, 10.02) | 97.86 | <0.001 |
表1 健康体检者、慢性乙型肝炎和乙肝肝硬化患者临床特征
Tab.1 General characteristics of healthy controls and patients with CHB and HBV-related liver cirrhosis
| Parameters | Healthy controls (n=60) | CHB (n=60) | Liver cirrhosis (n=60) | F/Z/χ2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male [n (%)] | 40 (66.7) | 30 (50.0) | 41 (68.3) | 5.217 | 0.074 |
| Age (year) | 50.1±0.5 | 46.6±1.1 | 51.0±1.3 | 5.377 | 0.095 |
| WBC (109/L) | 6.17 (5.38, 7.15) | 5.48 (4.54, 6.56) | 4.21 (2.72, 5.43) | 32.55 | <0.001 |
| PLT (109/L) | 232 (200, 275) | 187 (155, 227) | 89 (48, 134) | 54.95 | <0.001 |
| ALB (g/L) | 45.8 (42.8, 47.4) | 46.5 (44.6, 48.2) | 32.4 (28.0, 36.2) | 104.93 | <0.001 |
| ALT (U/L) | 22 (17, 32) | 18 (15, 25) | 32 (18, 56) | 19.42 | <0.001 |
| AST (U/L) | 21 (18, 25) | 22 (19, 26) | 47 (34., 76) | 72.43 | <0.001 |
| GGT (U/L) | 26 (18, 41.5) | 15 (12, 20) | 47 (28, 109) | 71.92 | <0.001 |
| APRI | 0.24 (0.17, 0.30) | 0.29 (0.23, 0.47) | 1.80 (0.90, 2.89) | 93.61 | <0.001 |
| FIB-4 | 0.96 (0.80, 1.19) | 1.29 (0.96, 1.69) | 5.06 (3.35, 10.02) | 97.86 | <0.001 |
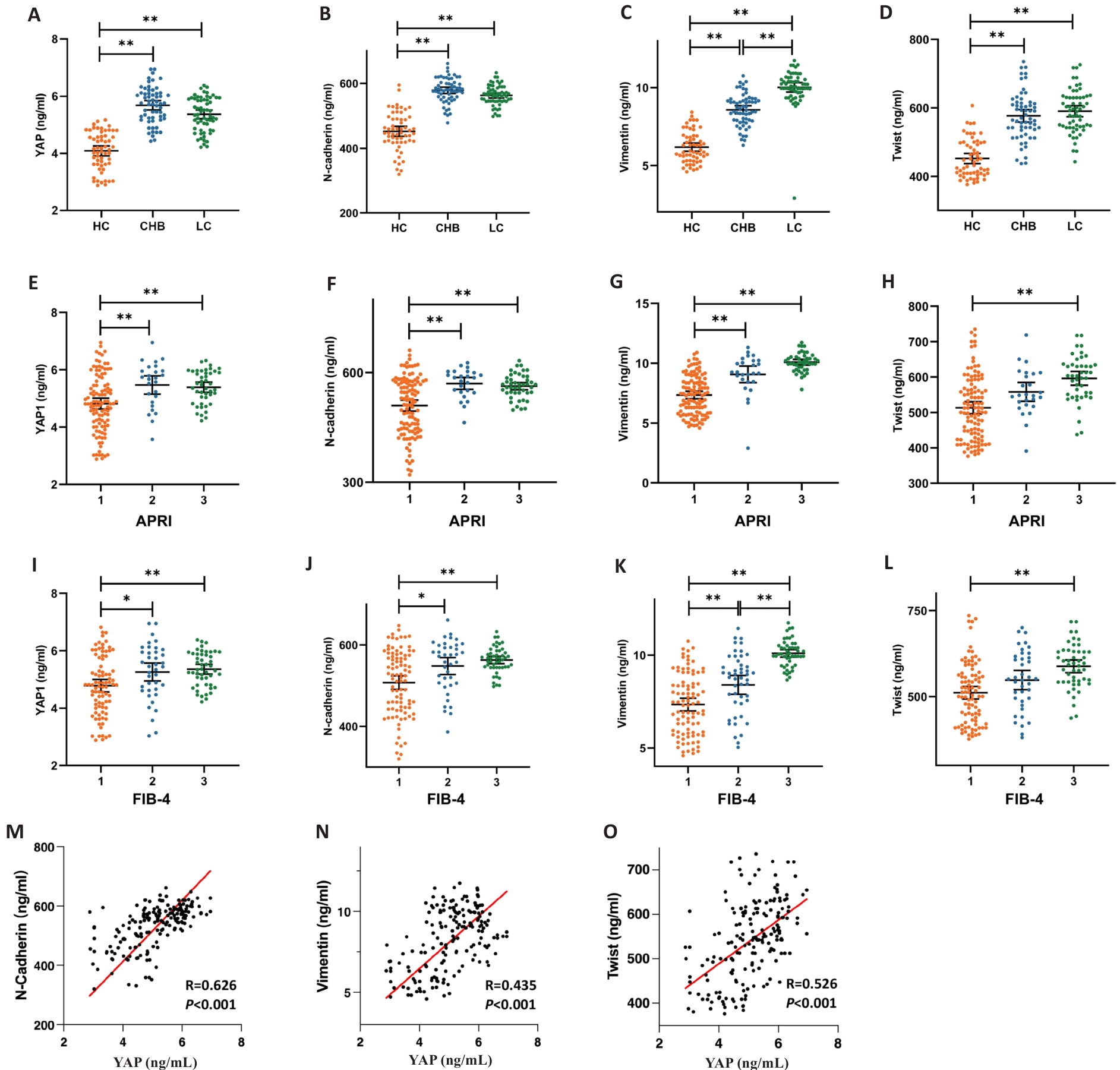
图4 患者血清YAP、N-cadherin、vimentin及Twist表达水平及相关性分析
Fig.4 Plasma YAP, N-cadherin, vimentin and Twist levels in healthy controls and patients with CHB and HBV-related liver cirrhosis. A-D: Distribution of plasma YAP, N-cadherin, vimentin and Twist levels in the 3 groups. E-H: Distribution of plasma YAP, N-cadherin, vimentin and Twist levels in patients with APRI <0.5, =0.5-1.5, and >1.5. I-L: Distribution of plasma YAP, N-cadherin, vimentin and Twist levels in patients with FIB-4<1.45, 1.45-3.25, and >3.25. M-O: Correlation analysis of serum YAP level with serum N-cadherin, vimentin and Twist levels. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
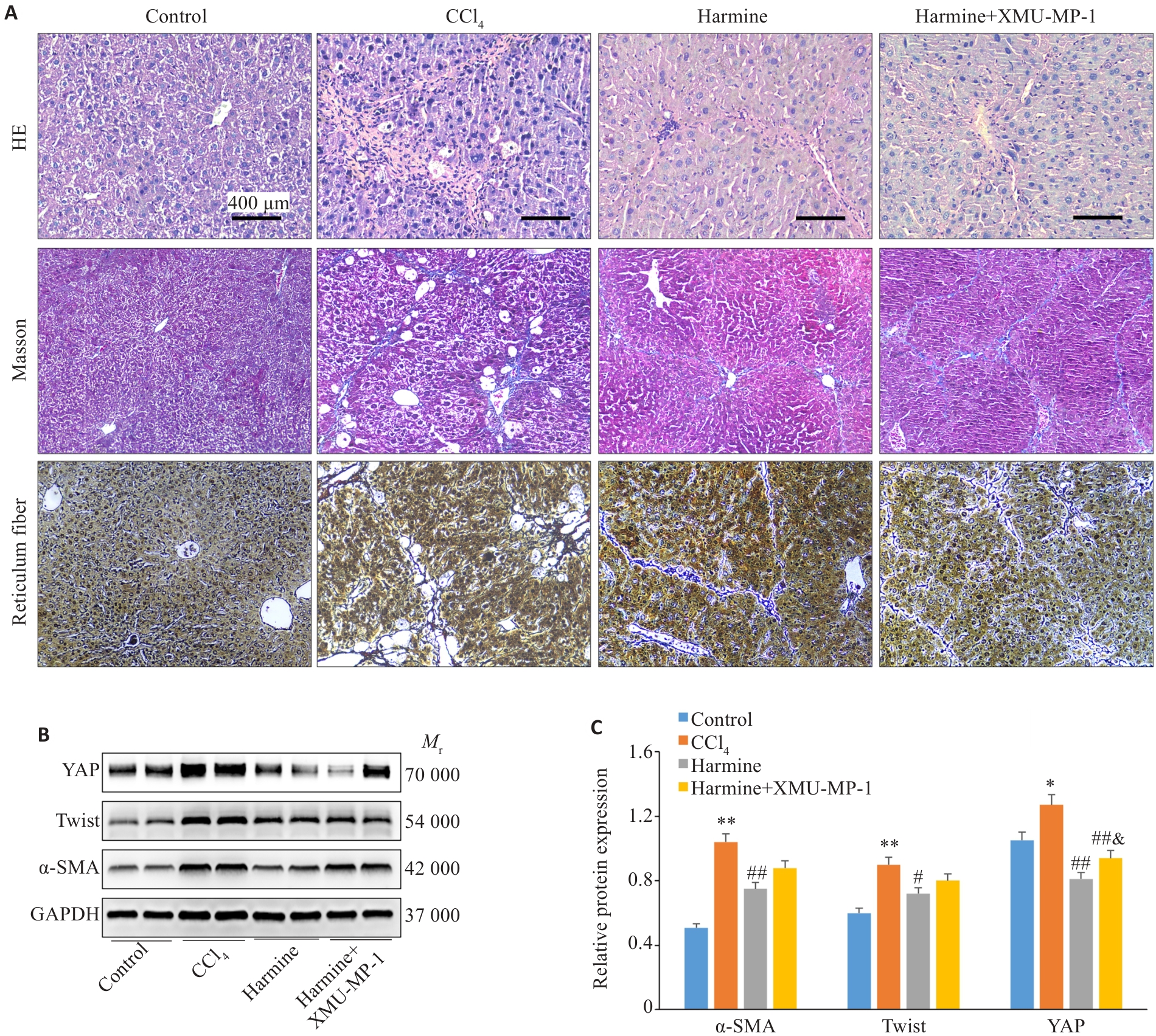
图5 激活YAP逆转抑制Twist引起的肝纤维化改善
Fig.5 Activation of YAP reverses Twist inhibition-induced improvement of liver fibrosis in mice. A: HE staining (×200), Masson's trichrome staining (×100), and Reticulum fiber staining (×100). B: Western blotting of protein levels of hepatic YAP, Twist, and α-SMA in mice. C: Quantification of protein expression levels. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs control group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs CCl4 group; &P<0.05 vs Harmine group.
| 1 | Devarbhavi H, Asrani SK, Arab JP, et al. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update[J]. J Hepatol, 2023, 79(2): 516-37. |
| 2 | Ginès P, Krag A, Abraldes JG, et al. Liver cirrhosis[J]. Lancet, 2021, 398(10308): 1359-76. |
| 3 | Younossi ZM, Wong G, Anstee QM, et al. The global burden of liver disease[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 21(8): 1978-91. |
| 4 | GBD Alcohol Collaborators. Alcohol use and burden for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016[J]. Lancet, 2018, 392(10152): 1015-35. |
| 5 | Zhai MM, Long JH, Liu SS, et al. The burden of liver cirrhosis and underlying etiologies: results from the global burden of disease study 2017[J]. Aging, 2021, 13(1): 279-300. |
| 6 | Allen AM, Kim WR, Moriarty JP, et al. Time trends in the health care burden and mortality of acute on chronic liver failure in the United States[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 64(6): 2165-72. |
| 7 | Fabrellas N, Moreira R, Carol M, et al. Psychological burden of hepatic encephalopathy on patients and caregivers[J]. Clin Transl Gastroenterol, 2020, 11(4): e00159. |
| 8 | Arroyo V, Moreau R, Jalan R. Acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 382(22): 2137-45. |
| 9 | Zhang DY, Zhang YG, Sun B. The molecular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its potential therapy in application[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(20): 12572. |
| 10 | Mannaerts I, Leite SB, Verhulst S, et al. The Hippo pathway effector YAP controls mouse hepatic stellate cell activation[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 63(3): 679-88. |
| 11 | Martin K, Pritchett J, Llewellyn J, et al. PAK proteins and YAP-1 signalling downstream of integrin beta-1 in myofibroblasts promote liver fibrosis[J]. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 12502. |
| 12 | Grijalva JL, Huizenga M, Mueller K, et al. Dynamic alterations in Hippo signaling pathway and YAP activation during liver regeneration[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2014, 307(2): G196-G204. |
| 13 | Machado MV, Michelotti GA, Pereira TA, et al. Accumulation of duct cells with activated YAP parallels fibrosis progression in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 63(4): 962-70. |
| 14 | Piersma B, Bank RA, Boersema M. Signaling in fibrosis: TGF-β, WNT, and YAP/TAZ converge[J]. Front Med, 2015, 2: 59. |
| 15 | Swiderska-Syn M, Xie GH, Michelotti GA, et al. Hedgehog regulates yes-associated protein 1 in regenerating mouse liver[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 64(1): 232-44. |
| 16 | Grannas K, Arngården L, Lönn P, et al. Crosstalk between hippo and TGFβ: subcellular localization of YAP/TAZ/smad complexes[J]. J Mol Biol, 2015, 427(21): 3407-15. |
| 17 | Serrano-Gomez SJ, Maziveyi M, Alahari SK. Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through epigenetic and post-translational modifications[J]. Mol Cancer, 2016, 15: 18. |
| 18 | Xie GH, Diehl AM. Evidence for and against epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in the liver[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2013, 305(12): G881-90. |
| 19 | Zhao W, Zhang XX, Hou MM, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine Yiqi Huoxue recipe attenuates hepatic fibrosis via YAP/TAZ signaling[J]. Histol Histopathol, 2021, 36(9): 967-79. |
| 20 | Zhao W, Lei M, Li JF, et al. Yes-associated protein inhibition ameliorates liver fibrosis and acute and chronic liver failure by decreasing ferroptosis and necroptosis[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(4): e15075. |
| 21 | Zhang Y, Weinberg RA. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer: complexity and opportunities[J]. Front Med, 2018, 12(4): 361-73. |
| 22 | Mizutani A, Koinuma D, Tsutsumi S, et al. Cell type-specific target selection by combinatorial binding of Smad2/3 proteins and hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha in HepG2 cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2011, 286(34): 29848-60. |
| 23 | Syn WK, Choi SS, Liaskou E, et al. Osteopontin is induced by hedgehog pathway activation and promotes fibrosis progression in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Hepatology, 2011, 53(1): 106-15. |
| 24 | Xie GH, Karaca G, Swiderska-Syn M, et al. Cross-talk between Notch and Hedgehog regulates hepatic stellate cell fate in mice[J]. Hepatology, 2013, 58(5): 1801-13. |
| 25 | Xu XC, Zhang Y, Wang X, et al. Substrate stiffness drives epithelial to mesenchymal transition and proliferation through the NEAT1-wnt/β-catenin pathway in liver cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(21): 12066. |
| 26 | Zhang K, Zhang MX, Yao QB, et al. The hepatocyte-specifically expressed lnc-HSER alleviates hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting hepatocyte apoptosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. Theranostics, 2019, 9(25): 7566-82. |
| 27 | Ma SH, Meng ZP, Chen R, et al. The hippo pathway: biology and pathophysiology[J]. Annu Rev Biochem, 2019, 88: 577-604. |
| 28 | Zhan YT, Tao QQ, Meng QS, et al. LncRNA-MIAT activates hepatic stellate cells via regulating Hippo pathway and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition[J]. Commun Biol, 2023, 6(1): 285. |
| 29 | Oh SH, Swiderska-Syn M, Jewell ML, et al. Liver regeneration requires Yap1-TGFβ-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocytes[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 69(2): 359-67. |
| 30 | Ge WS, Wang YJ, Wu JX, et al. β-catenin is overexpressed in hepatic fibrosis and blockage of Wnt/β‑catenin signaling inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2014, 9(6): 2145-51. |
| 31 | Dong WH, Kong M, Zhu YW, et al. Activation of TWIST transcription by chromatin remodeling protein BRG1 contributes to liver fibrosis in mice[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8: 340. |
| 32 | Yang XX, Ma LP, Wei R, et al. Twist1-induced miR-199a-3p promotes liver fibrosis by suppressing caveolin-2 and activating TGF-β pathway[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2020, 5(1): 75. |
| 33 | Luo XF, Zhang R, Schefczyk S, et al. Nuclear translocation of YAP drives BMI-associated hepatocarcinogenesis in hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Liver Int, 2023, 43(9): 2002-16. |
| 34 | Abdallah RA, Shaban MI, Taie DM, et al. Relation between immunohistochemical expression of hippo pathway effectors and chronic hepatitis induced fibrosis in Egyptian patients[J]. Turk Patoloji Derg, 2020, 36(1): 48-63. |
| 35 | Zhou ZX, Zhang RR, Li XM, et al. Circular RNA cVIM promotes hepatic stellate cell activation in liver fibrosis via miR-122-5p/miR-9-5p-mediated TGF-β signaling cascade[J]. Commun Biol, 2024, 7(1): 113. |
| [1] | 朱梦云, 王剑锋. 康柏西普可逆转TGF-β2诱导的晶状体上皮细胞发生上皮间质转化:基于调节TGF-β/Smad信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1459-1466. |
| [2] | 陈星梅, 刘琴文, 李镱, 钟晓宇, 樊奇灵, 马柯, 罗柳婷, 官道刚, 朱志博. 茵陈蒿汤治疗肝纤维化的核心功能成分群以及潜在通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1508-1517. |
| [3] | 曹家樊, 孙 跃, 丁 鑫, 李盛文, 陈 博, 兰 天. 熊果苷通过抑制巨噬细胞募集并调控Akt/NF-κB和Smad信号通路改善小鼠肝纤维化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 652-659. |
| [4] | 徐小惠, 冯金梅, 罗 颖, 何昕觎, 臧金宝, 黄道超. NDUFA13过表达可减轻CCl4诱导的小鼠肝纤维化:基于抑制NLRP3活化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 201-209. |
| [5] | 刘雪柔, 杨玉梅, 蔡 慧, 张耀帅, 范方田, 李 娴, 李姗姗. 阿美替尼具有较好的抗神经母细胞瘤作用:基于下调MMP2和MMP9的表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1493-1499. |
| [6] | 郭晓娟, 陈丽平, 吕 芹, 杜瑞娟, 罗 琴, 张 阳, 卞 华, 韩 立. 桂枝茯苓胶囊通过调控NF-κB通路抑制卵巢癌细胞的迁移和诱导卵巢癌细胞的凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1315-1321. |
| [7] | 谢紫平, 刘立威, 房锦存, 钟星怡, 林俊豪, 陈逢生. ARHGAP21通过失活WNT信号通路抑制非小细胞肺癌中的上皮间质转化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1322-1332. |
| [8] | 林嘉宜, 娄安妮, 李 旭. 脂多糖刺激巨噬细胞分泌含miR-155-5p的外泌体促进肝星状细胞的活化及迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 994-1001. |
| [9] | 张攀扬, 何明敏, 曾园媛, 蔡雄伟. 高级别浆液性卵巢癌复发相关的潜在功能性关键 miRNA-mRNA:基于生物信息学方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(1): 8-16. |
| [10] | 杨雪佳, 李玉杰, 吴登强, 马义丽, 周素芳. 肝细胞癌进展过程中的关键基因ATP1B3和ENAH的筛选与鉴定:基于数据挖掘和临床验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(6): 815-823. |
| [11] | 向茂翠, 王 瑜, 梅仁彪, 付计锋, 陈 静, 都昌乐. IL-17A与自发性高血压大鼠肾上皮间质转化密切相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(5): 772-779. |
| [12] | 邓 亚, 王春艳, 付懿铭, 李忠斌, 纪 冬. 慢性药物性肝损伤的复发风险与肝纤维化程度高度相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(11): 1655-1661. |
| [13] | 赵晨玲, 董 婷, 孙伦燕, 胡慧冰, 王 琼, 田丽伟, 江张胜. Wilson病脂代谢异常患者发生肝纤维化的列线图预测模型的建立与验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(11): 1720-1725. |
| [14] | 董洪亮, 曾莉莉, 武 艳, 苗 双, 倪 娜, 刘乃国, 陈微微, 杜 静. SOX2-OT/SOX2轴通过Gli1介导的上皮间质转化调控肺鳞癌H520细胞的迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(10): 1431-1439. |
| [15] | 赵治彬, 董 辉, 李兵航, 沈 波, 郭悦承, 顾天翊, 曲 颖, 蔡晓波, 陆伦根. 羟尼酮可阻止大鼠肝星状细胞活化: 基于抑制TGF-β1通路蛋白的磷酸化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(10): 1511-1516. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||