南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2527-2540.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.01
• •
夏士程1,3( ), 韦慧芳1,3, 洪维灿1,3, 张钰明2,3, 尹菲玚1,3, 张贻欣1,3, 张淋淋2,3, 高琴2,3(
), 韦慧芳1,3, 洪维灿1,3, 张钰明2,3, 尹菲玚1,3, 张贻欣1,3, 张淋淋2,3, 高琴2,3( ), 叶红伟2,3(
), 叶红伟2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-04
接受日期:2025-07-15
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-12-22
通讯作者:
高琴,叶红伟
E-mail:12210110342@stu.bbmc.edu.cn;bbmcgq@126.com;yehongwei223@163.com
作者简介:夏士程,本科,E-mail:12210110342@stu.bbmc.edu.cn
Shicheng XIA1,3( ), Huifang WEI1,3, Weican HONG1,3, Yuming ZHANG2,3, Feiyang YIN1,3, Yixin ZHANG1,3, Linlin ZHANG2,3, Qin GAO2,3(
), Huifang WEI1,3, Weican HONG1,3, Yuming ZHANG2,3, Feiyang YIN1,3, Yixin ZHANG1,3, Linlin ZHANG2,3, Qin GAO2,3( ), Hongwei YE2,3(
), Hongwei YE2,3( )
)
Received:2025-03-04
Accepted:2025-07-15
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Qin GAO, Hongwei YE
E-mail:12210110342@stu.bbmc.edu.cn;bbmcgq@126.com;yehongwei223@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨金银花(LJF)对阿霉素(DOX)诱导的心肌损伤的保护作用及其机制。 方法 通过网络药理学、生物信息学分析与分子对接技术预测核心靶点,并通过动物实验加以验证。动物实验中,检测DOX诱导的心肌损伤及不同剂量LJF提取物治疗后小鼠心功能、心肌酶学、心肌组织形态、炎症因子及相关蛋白表达的变化。 结果 网络药理学筛选出LJF的10个核心活性成分可与AKT、EGFR、GSK3β良好结合。动物实验结果显示,与假手术组相比,DOX组小鼠心输出量、每搏输出量、左室射血分数及左室短轴缩短率显著降低,血清CK-MB、LDH水平升高,心肌IL-18、IL-1β含量增加;HE染色示心肌结构损伤;心肌组织NLRP3、caspase-1、GSDMD及GSDMD-N蛋白表达上调,EGFR蛋白表达下调,p-AKT、p-GSK3β蛋白水平降低。与DOX组相比,LJF治疗后小鼠心功能明显改善,心肌组织中IL-18、IL-1β水平降低,NLRP3、caspase-1、GSDMD及GSDMD-N蛋白表达下调, EGFR蛋白水平上调,p-AKT、p-GSK3β蛋白磷酸化水平提高。 结论 金银花可能通过靶向作用于EGFR、AKT、GSK3β调控ErbB信号通路,抑制心肌组织炎症反应与细胞焦亡,从而减轻阿霉素诱导的心肌损伤。
夏士程, 韦慧芳, 洪维灿, 张钰明, 尹菲玚, 张贻欣, 张淋淋, 高琴, 叶红伟. 金银花提取物对阿霉素诱导的小鼠心肌损伤的保护作用及其机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2527-2540.
Shicheng XIA, Huifang WEI, Weican HONG, Yuming ZHANG, Feiyang YIN, Yixin ZHANG, Linlin ZHANG, Qin GAO, Hongwei YE. Protective effect of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos extract against doxorubicin-induced myocardial injury in mice and the possible mechanisms[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2527-2540.
| Mol ID | Molecule | OB | DL | Core ingredients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOL000006 | luteolin | 36.16 | 0.25 | Yes |
| MOL000098 | quercetin | 46.43 | 0.28 | Yes |
| MOL000358 | beta-sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.75 | No |
| MOL000422 | kaempferol | 41.88 | 0.24 | Yes |
| MOL000449 | Stigmasterol | 43.83 | 0.76 | No |
| MOL001494 | Mandenol | 42 | 0.19 | No |
| MOL001495 | Ethyl linolenate | 46.1 | 0.2 | No |
| MOL002707 | phytofluene | 43.18 | 0.5 | No |
| MOL002773 | beta-carotene | 37.18 | 0.58 | No |
| MOL002914 | eriodyctiol (flavanone) | 41.35 | 0.24 | Yes |
| MOL003006 | (-)-(3R,8S,9R,9aS,10aS)-9-ethenyl-8-(beta-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-2,3,9,9a,10, 10a-hexahydro-5-oxo-5H,8H-pyrano[4,3-d]oxazolo[3,2-a]pyridine-3-carboxylic acid_qt | 87.47 | 0.23 | Yes |
| MOL003014 | secologanic dibutylacetal_qt | 53.65 | 0.29 | Yes |
| MOL003036 | ZINC03978781 | 43.83 | 0.76 | No |
| MOL003044 | chryseriol | 35.85 | 0.27 | Yes |
| MOL003059 | kryptoxanthin | 47.25 | 0.57 | No |
| MOL003062 | 4,5'-Retro-.beta.,.beta.-Carotene-3,3'-dione, 4',5'-didehydro- | 31.22 | 0.55 | No |
| MOL003095 | 5-hydroxy-7-methoxy-2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)chromone | 51.96 | 0.41 | Yes |
| MOL003101 | 7-epi-Vogeloside | 46.13 | 0.58 | No |
| MOL003108 | caeruloside C | 55.64 | 0.73 | No |
| MOL003111 | centauroside_qt | 55.79 | 0.5 | Yes |
| MOL003117 | niceracetalides B_qt | 61.19 | 0.19 | Yes |
| MOL003124 | XYLOSTOSIDINE | 43.17 | 0.64 | No |
| MOL003128 | dinethylsecologanoside | 48.46 | 0.48 | No |
Tab.1 Main active components and the core ingredients in Lonicerae Japonicae Flos (LJF)
| Mol ID | Molecule | OB | DL | Core ingredients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOL000006 | luteolin | 36.16 | 0.25 | Yes |
| MOL000098 | quercetin | 46.43 | 0.28 | Yes |
| MOL000358 | beta-sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.75 | No |
| MOL000422 | kaempferol | 41.88 | 0.24 | Yes |
| MOL000449 | Stigmasterol | 43.83 | 0.76 | No |
| MOL001494 | Mandenol | 42 | 0.19 | No |
| MOL001495 | Ethyl linolenate | 46.1 | 0.2 | No |
| MOL002707 | phytofluene | 43.18 | 0.5 | No |
| MOL002773 | beta-carotene | 37.18 | 0.58 | No |
| MOL002914 | eriodyctiol (flavanone) | 41.35 | 0.24 | Yes |
| MOL003006 | (-)-(3R,8S,9R,9aS,10aS)-9-ethenyl-8-(beta-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-2,3,9,9a,10, 10a-hexahydro-5-oxo-5H,8H-pyrano[4,3-d]oxazolo[3,2-a]pyridine-3-carboxylic acid_qt | 87.47 | 0.23 | Yes |
| MOL003014 | secologanic dibutylacetal_qt | 53.65 | 0.29 | Yes |
| MOL003036 | ZINC03978781 | 43.83 | 0.76 | No |
| MOL003044 | chryseriol | 35.85 | 0.27 | Yes |
| MOL003059 | kryptoxanthin | 47.25 | 0.57 | No |
| MOL003062 | 4,5'-Retro-.beta.,.beta.-Carotene-3,3'-dione, 4',5'-didehydro- | 31.22 | 0.55 | No |
| MOL003095 | 5-hydroxy-7-methoxy-2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)chromone | 51.96 | 0.41 | Yes |
| MOL003101 | 7-epi-Vogeloside | 46.13 | 0.58 | No |
| MOL003108 | caeruloside C | 55.64 | 0.73 | No |
| MOL003111 | centauroside_qt | 55.79 | 0.5 | Yes |
| MOL003117 | niceracetalides B_qt | 61.19 | 0.19 | Yes |
| MOL003124 | XYLOSTOSIDINE | 43.17 | 0.64 | No |
| MOL003128 | dinethylsecologanoside | 48.46 | 0.48 | No |
| Gene name | Betweenness unDir | Closeness unDir | Degree unDir |
|---|---|---|---|
| Akt1 | 3568.885 | 0.004608 | 83 |
| Stat3 | 1519.647 | 0.004149 | 66 |
| Pparg | 1574.181 | 0.004032 | 57 |
| Gsk3b | 2449.064 | 0.004082 | 55 |
| Egfr | 632.9566 | 0.003906 | 54 |
| Esr1 | 1016.3 | 0.003861 | 50 |
| Mmp9 | 1198.398 | 0.003861 | 49 |
| Hif1a | 515.0458 | 0.003876 | 49 |
| Ptgs2 | 971.437 | 0.003861 | 49 |
| Mapk14 | 546.9512 | 0.003831 | 48 |
Tab.2 Top 10 target genes based on degree values
| Gene name | Betweenness unDir | Closeness unDir | Degree unDir |
|---|---|---|---|
| Akt1 | 3568.885 | 0.004608 | 83 |
| Stat3 | 1519.647 | 0.004149 | 66 |
| Pparg | 1574.181 | 0.004032 | 57 |
| Gsk3b | 2449.064 | 0.004082 | 55 |
| Egfr | 632.9566 | 0.003906 | 54 |
| Esr1 | 1016.3 | 0.003861 | 50 |
| Mmp9 | 1198.398 | 0.003861 | 49 |
| Hif1a | 515.0458 | 0.003876 | 49 |
| Ptgs2 | 971.437 | 0.003861 | 49 |
| Mapk14 | 546.9512 | 0.003831 | 48 |
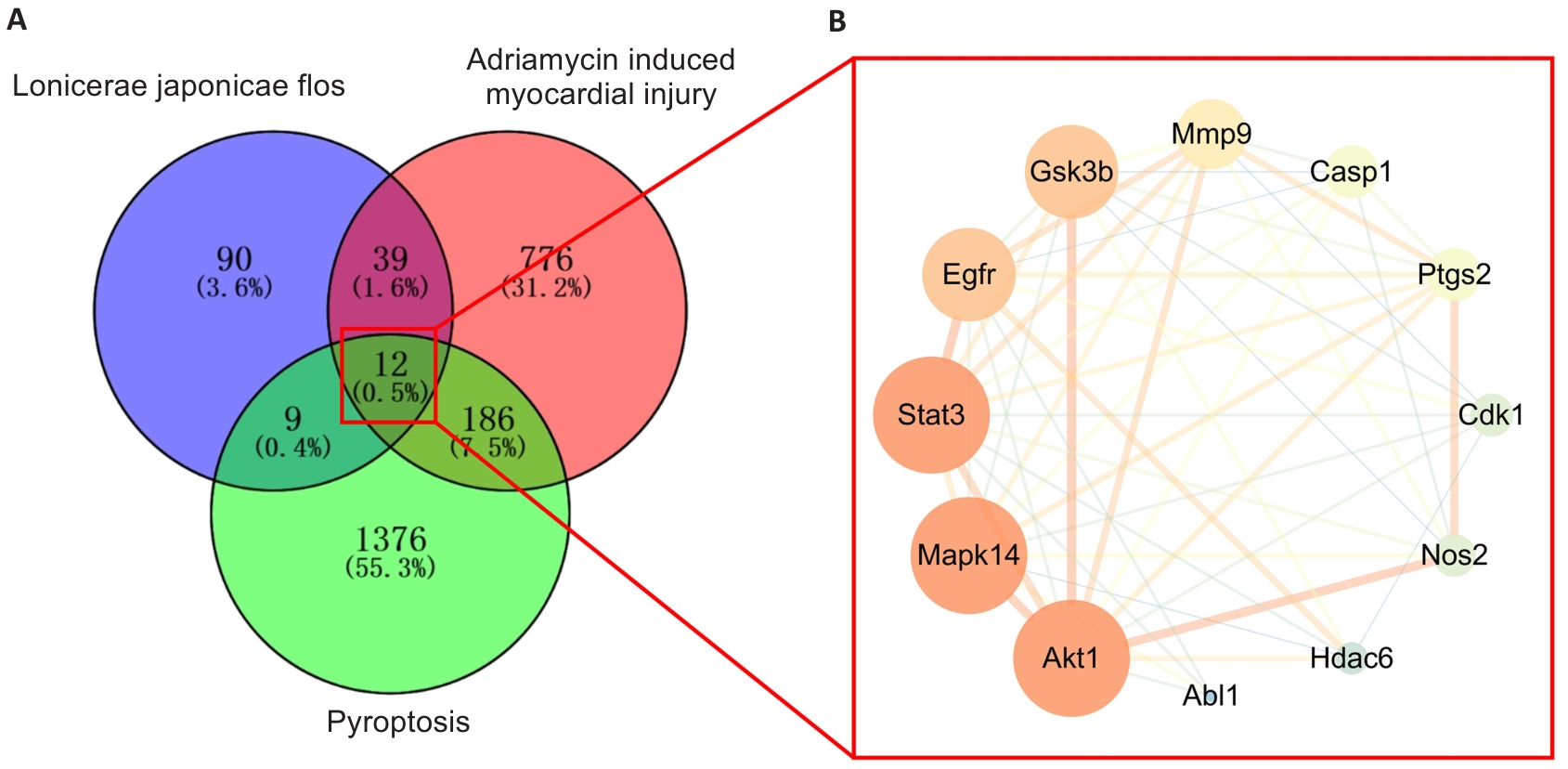
Fig.3 Venn diagram of the target genes of LJF, adriamycin-induced myocardial injury and pyroptosis-related targets (A) and the intersection genes network diagram (B).
| Mol ID | Binding energy (kJ·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR | AKT1 | GSK3β | |
| MOL000006 | -5.51 | -6.98 | -5.83 |
| MOL000098 | -6.07 | -6.96 | -5.8 |
| MOL000422 | -5.87 | -7.41 | -6.45 |
| MOL002914 | -5.46 | -5.36 | -5.23 |
| MOL003006 | -5.81 | -5.92 | -5.06 |
| MOL003014 | -2.13 | -3.02 | -2.25 |
| MOL003044 | -4.83 | -7.2 | -5.66 |
| MOL003095 | -5 | -6.82 | -5.49 |
| MOL003111 | -6.29 | -3.99 | -3.37 |
| MOL003117 | -5.91 | -5.31 | -4.8 |
Tab.3 Binding energy of the core ingredients of LJF with their core target genes
| Mol ID | Binding energy (kJ·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR | AKT1 | GSK3β | |
| MOL000006 | -5.51 | -6.98 | -5.83 |
| MOL000098 | -6.07 | -6.96 | -5.8 |
| MOL000422 | -5.87 | -7.41 | -6.45 |
| MOL002914 | -5.46 | -5.36 | -5.23 |
| MOL003006 | -5.81 | -5.92 | -5.06 |
| MOL003014 | -2.13 | -3.02 | -2.25 |
| MOL003044 | -4.83 | -7.2 | -5.66 |
| MOL003095 | -5 | -6.82 | -5.49 |
| MOL003111 | -6.29 | -3.99 | -3.37 |
| MOL003117 | -5.91 | -5.31 | -4.8 |

Fig.5 Molecular docking study of the core ingredients of LJF with their core target genes and their interactions. A: Part of the results of molecular docking results. B: The "drug-component-site of action-type of action-protein" network of EGFR. C: The "drug-component-site of action-type of action-protein" network of GSK3β. D: The "drug-component-site of action-type of action-protein" network of AKT.
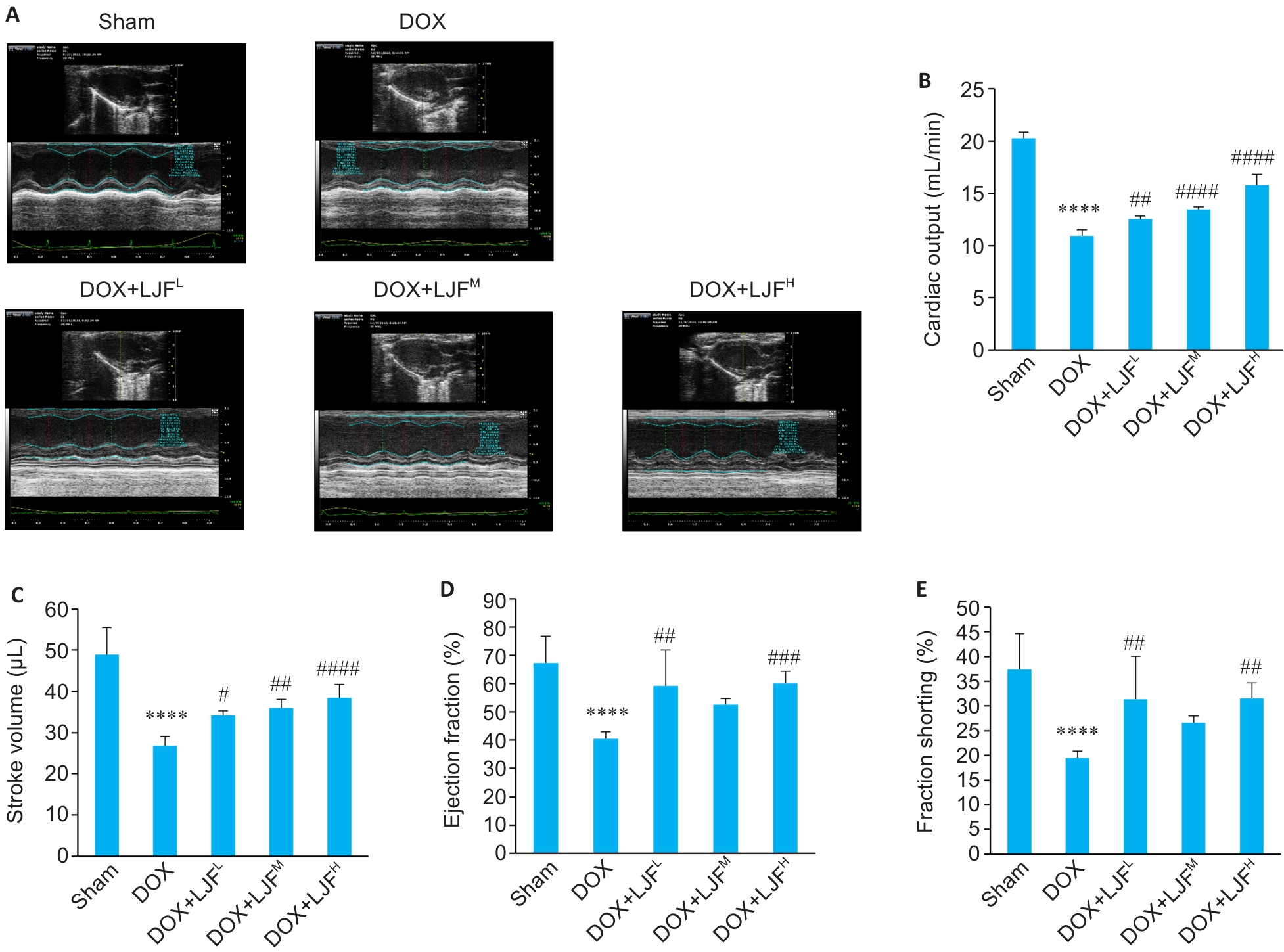
Fig. 6 Cardiac echocardiographic findings of the mice and the cardiac function parameters of the mice in each group. A: Cardiac echocardiography of the mice in each group. B: Comparison of cardiac output of the mice among the 5 groups. C: Comparison of the stroke volume of the mice among the 5 groups. D: Comparison of ejection fraction of the mice among the 5 groups. E: Comparison of fraction shorting of the mice among the 5 groups. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=6). ****P<0.0001 vs Sham group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001, ####P<0.0001 vs DOX group.

Fig.8 Serum levels of CK-MB (A) and LDH (B) and the levels of IL-18 (C) and IL-1β (D) in the myocardial tissue of the mice in each group (Mean±SD, n=6). ****P<0.0001 vs Sham group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001, ####P<0.0001 vs the DOX group.
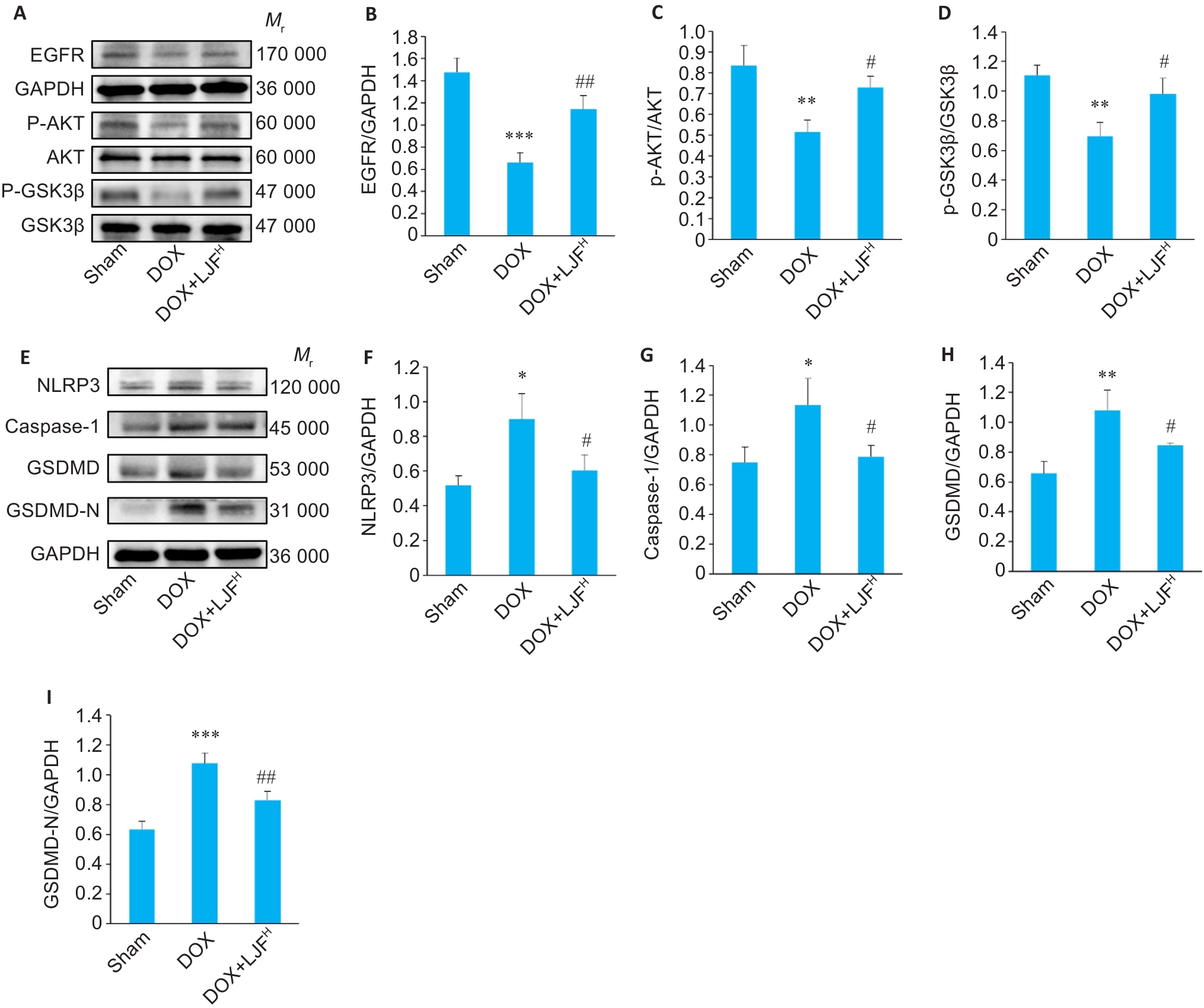
Fig.9 Expression levels of NLRP3, caspase-1, GSDMD, GSDMD-N, EGFR, AKT, GSK3β, p-AKT and p-GSK3β in the myocardial tissues detected by Western blotting. A-D: Western blotting for detecting the expression levels of EGFR, AKT, p-AKT, GSK3β and p-GSK3β proteins in each group. E-I: Western blotting for detecting the expression levels of NLRP3, caspase-1, GSDMD and GSDMD-N proteins in each group. ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, *P<0.05 vs Sham group; ##P<0.01, #P<0.05 vs DOX group (Mean±SD, n=3).
| [1] | Wang M, Xie D, Zhang M, et al. Multiple ingredients of a Chinese medicine formula Sheng-Mai-San coordinately attenuate doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity [J]. Pharmacol Res Mod Chin Med, 2023, 8: 100281. doi:10.1016/j.prmcm.2023.100281 |
| [2] | Powers SK, Duarte JA, Le Nguyen B, et al. Endurance exercise protects skeletal muscle against both doxorubicin-induced and inactivity-induced muscle wasting [J]. Pflugers Arch, 2019, 471(3): 441-53. doi:10.1007/s00424-018-2227-8 |
| [3] | Li D, Zhang W, Fu H, et al. DL-3-n-butylphthalide attenuates doxorubicin-induced acute cardiotoxicity via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway [J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(5): e27644. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27644 |
| [4] | Chen M, Yi Y, Chen B, et al. Metformin inhibits OCTN1- and OCTN2-mediated hepatic accumulation of doxorubicin and alleviates its hepatotoxicity in mice [J]. Toxicology, 2024, 503: 153757. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2024.153757 |
| [5] | Badi RM, Khaleel EF, Satti HH, et al. Eriodictyol attenuates doxorubicin-induced nephropathy by activating the AMPK/Nrf2 signalling pathway [J]. J Tradit Complement Med, 2024, 14(2): 203-14. doi:10.1016/j.jtcme.2023.11.003 |
| [6] | Qu Y. Gasdermin D mediates endoplasmic reticulum stress via FAM134B to regulate cardiomyocyte autophagy and apoptosis in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity [J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(1): 1-12. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-05400-9 |
| [7] | Meng L, Lin H, Zhang J, et al. Doxorubicin induces cardiomyocyte pyroptosis via the TINCR-mediated posttranscriptional stabilization of NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 [J]. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2019, 136: 15-26. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.08.009 |
| [8] | Lai KH, Chen YL, Lin MF, et al. Lonicerae japonicae flos attenuates neutrophilic inflammation by inhibiting oxidative stress [J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2022, 11(9): 1781. doi:10.3390/antiox11091781 |
| [9] | Zheng S, Liu S, Hou A, et al. Systematic review of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos: a significant food and traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 1013992. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.1013992 |
| [10] | Wang L, Jiang Q, Hu J, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents of Lonicerae japonicae flos [J]. Biomed Res Int, 2016, 2016: 1-18. doi:10.1155/2016/8968940 |
| [11] | Han MH, Lee WS, Nagappan A, et al. Flavonoids isolated from flowers of Lonicera japonica Thunb. inhibit inflammatory responses in BV2 microglial cells by suppressing TNF-α and IL-β through PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathways [J]. Phytother Res, 2016, 30(11): 1824-32. doi:10.1002/ptr.5688 |
| [12] | Bang BW, Park D, Kwon KS, et al. BST-104, a water extract of Lonicera japonica, has a gastroprotective effect via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities [J]. J Med Food, 2019, 22(2): 140-51. doi:10.1089/jmf.2018.4231 |
| [13] | Wang T, Yang B, Guan Q, et al. Transcriptional regulation of Lonicera japonica Thunb. during flower development as revealed by comprehensive analysis of transcription factors [J]. BMC Plant Biol, 2019, 19(1): 198. doi:10.1186/s12870-019-1803-1 |
| [14] | Miao H, Zhang Y, Huang Z, et al. Lonicera japonica attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice: molecular mechanisms of action [J]. Am J Chin Med, 2019, 47(2): 355-72. doi:10.1142/s0192415x19500174 |
| [15] | Li W, Zhang L, He P, et al. Traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Lonicerae japonicae flos and Lonicerae flos: a systematic comparative review [J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 322: 117278. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117278 |
| [16] | Yu P, Zhang X, Liu N, et al. Pyroptosis: mechanisms and diseases [J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2021, 6(1): 128. doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00507-5 |
| [17] | Tao RH, Kobayashi M, Yang Y, et al. Exercise inhibits doxorubicin-induced damage to cardiac vessels and activation of hippo/YAP-mediated apoptosis [J]. Cancers, 2021, 13(11): 2740. doi:10.3390/cancers13112740 |
| [18] | Zhang G, Yang X, Su X, et al. Understanding the protective role of exosomes in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity [J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022, 2022: 1-14. doi:10.1155/2022/2852251 |
| [19] | Ju YN, Zou ZW, Jia BW, et al. Ac2-26 activated the AKT1/GSK3β pathway to reduce cerebral neurons pyroptosis and improve cerebral function in rats after cardiopulmonary bypass [J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disord, 2024, 24: 266. doi:10.1186/s12872-024-03909-9 |
| [20] | Wei Y, Lan B, Zheng T, et al. GSDME-mediated pyroptosis promotes the progression and associated inflammation of atherosclerosis [J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14: 929. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-36614-w |
| [21] | Gong Y, Qiu J, Jiang T, et al. Maltol ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration through inhibiting PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway and regulating NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis [J]. Inflammopharmacology, 2023, 31(1): 369-84. doi:10.1007/s10787-022-01098-5 |
| [22] | Zhou P, Song NC, Zheng ZK, et al. MMP2 and MMP9 contribute to lung ischemia-reperfusion injury via promoting pyroptosis in mice [J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2022, 22: 230. doi:10.1186/s12890-022-02018-7 |
| [23] | Yue L, Liu X, Wu C, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 promotes the inflammatory response in septic acute kidney injury by promoting p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation [J]. J Bioenerg Biomembr, 2023, 55(5): 353-63. doi:10.1007/s10863-023-09972-9 |
| [24] | Wang Y, Wei J, Zhang P, et al. Neuregulin-1, a potential therapeutic target for cardiac repair [J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 945206. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.945206 |
| [25] | Wang X, Sun Q, Jiang Q, et al. Cryptotanshinone ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by targeting Akt-GSK-3β-mPTP pathway in vitro [J]. Molecules, 2021, 26(5): 1460. doi:10.3390/molecules26051460 |
| [26] | Yang K, Liu J, Zhang X, et al. H3 relaxin alleviates migration, apoptosis and pyroptosis through P2X7R-mediated nucleotide binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome activation in retinopathy induced by hyperglycemia [J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 603689. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.603689 |
| [27] | Huang L. The role of IL-17 family cytokines in cardiac fibrosis [J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2024, 11: 1470362. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2024.1470362 |
| [28] | Liu W, Wang X, Wu W. Role and functional mechanisms of IL-17/IL-17R signaling in pancreatic cancer (Review) [J]. Oncol Rep, 2024, 52(5): 144. doi:10.3892/or.2024.8803 |
| [29] | Hedhli N, Kalinowski A, Russell KS. Cardiovascular effects of neuregulin-1/ErbB signaling: role in vascular signaling and angiogenesis [J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2014, 20(30): 4899-905. doi:10.2174/1381612819666131125151058 |
| [30] | Yenerall P, Das AK, Wang S, et al. RUVBL1/RUVBL2 ATPase activity drives PAQosome maturation, DNA replication and radioresistance in lung cancer [J]. Cell Chem Biol, 2020, 27(1): 105-21.e14. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2019.12.005 |
| [31] | Andrei C, Zanfirescu A, Nițulescu GM, et al. Natural active ingredients and TRPV1 modulation: focus on key chemical moieties involved in ligand-target interaction [J]. Plants, 2023, 12(2): 339. doi:10.3390/plants12020339 |
| [32] | Zhang E, Yang Y, Chen S, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis potentially by attenuating Wnt/β-catenin signaling in rats [J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2018, 9: 311. doi:10.1186/s13287-018-1045-4 |
| [33] | Xiao L, Qi L, Zhang G, et al. Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharides attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced septic liver injury by suppression of pyroptosis via NLRP3/GSDMD signals [J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(18): 5943. doi:10.3390/molecules27185999 |
| [34] | Rogers C, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Mayes L, et al. Cleavage of DFNA5 by caspase-3 during apoptosis mediates progression to secondary necrotic/pyroptotic cell death [J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8: 14128. doi:10.1038/ncomms14128 |
| [35] | Chen X, Tian PC, Wang K, et al. Pyroptosis: role and mechanisms in cardiovascular disease [J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9: 897815. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2022.897815 |
| [36] | Ye B, Shi X, Xu J, et al. Gasdermin D mediates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte pyroptosis and cardiotoxicity via directly binding to doxorubicin and changes in mitochondrial damage [J]. Transl Res, 2022, 248: 36-50. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2022.05.001 |
| [37] | Chai R, Li Y, Shui L, et al. The role of pyroptosis in inflammatory diseases [J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2023, 11: 1123456. doi:10.3389/fcell.2023.1173235 |
| [1] | 闫爱丽, 罗梦瑶, 常晋瑞, 李新华, 朱娟霞. 橙皮素通过调控AMPK/NLRP3通路减轻阿霉素诱导的小鼠心肌毒性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1850-1858. |
| [2] | 呼琴, 金华. 清肾颗粒通过调控miR-23b及Nrf2通路改善慢性肾脏病湿热证患者的肾功能:基于网络药理学和临床试验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1867-1879. |
| [3] | 杨子为, 吕畅, 董柱, 计书磊, 毕生辉, 张雪花, 王晓武. 金樱子通过调控Src-AKT1轴抑制肺动脉高压平滑肌增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1889-1902. |
| [4] | 云琦, 杜若丽, 贺玉莹, 张贻欣, 王佳慧, 叶红伟, 李正红, 高琴. 肉桂酸通过抑制TLR4减轻阿霉素诱导的小鼠心肌损伤铁死亡的发生[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1946-1958. |
| [5] | 饶璐, 丁家和, 魏江平, 阳勇, 张小梅, 王计瑞. 槐花通过抑制PI3K/AKT通路减轻炎症反应治疗银屑病[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1989-1996. |
| [6] | 罗善玉, 朱强, 闫玉翡, 纪宗红, 邹华杰, 张瑞霞, 巴应贵. 低氧环境下NLRP3信号通路促进非酒精性脂肪性肝炎小鼠的肝细胞焦亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 2026-2033. |
| [7] | 陈鑫源, 吴成挺, 李瑞迪, 潘雪芹, 张耀丹, 陶俊宇, 林才志. 双术汤通过P53/SLC7A11/GPX4通路诱导胃癌细胞铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [8] | 周海忆, 何斯怡, 韩瑞芳, 关永格, 董丽娟, 宋阳. 艾灸通过调控miR-223-3p/NLRP3焦亡通路修复薄型子宫内膜[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1380-1388. |
| [9] | 王立明, 陈宏睿, 杜燕, 赵鹏, 王玉洁, 田燕歌, 刘新光, 李建生. 益气滋肾方通过抑制PI3K/Akt/NF-κB通路改善小鼠慢性阻塞性肺疾病的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [10] | 朱胤福, 李怡燃, 王奕, 黄颖而, 龚昆翔, 郝文波, 孙玲玲. 桂枝茯苓丸活性成分常春藤皂苷元通过抑制JAK2/STAT3通路抑制宫颈癌细胞的生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [11] | 何丽君, 陈晓菲, 闫陈昕, 师林. 扶正化积汤治疗非小细胞肺癌的分子机制:基于网络药理学及体外实验验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152. |
| [12] | 李国永, 黎仁玲, 刘艺婷, 柯宏霞, 李菁, 王新华. 牛蒡子治疗小鼠病毒性肺炎后肺纤维化的机制:基于代谢组学、网络药理学和实验验证方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [13] | 管丽萍, 颜燕, 卢心怡, 李智峰, 高晖, 曹东, 侯晨曦, 曾靖宇, 李欣怡, 赵洋, 王俊杰, 方会龙. 复方积雪草减轻小鼠日本血吸虫引起的肝纤维化:通过调控TLR4/MyD88通路抑制炎症-纤维化级联反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [14] | 唐培培, 谈勇, 殷燕云, 聂晓伟, 黄菁宇, 左文婷, 李玉玲. 调周滋阴方治疗早发性卵巢功能不全的疗效、安全性及作用机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| [15] | 卞芬兰, 倪诗垚, 赵鹏, 戚毛男星, 唐碧, 王洪巨, 康品方, 刘进军. 积雪草苷通过抑制NLRP3炎症体介导的细胞焦亡减轻大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 977-985. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||