南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (9): 1850-1858.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.05
• • 上一篇
闫爱丽1( ), 罗梦瑶2(
), 罗梦瑶2( ), 常晋瑞1, 李新华1, 朱娟霞1(
), 常晋瑞1, 李新华1, 朱娟霞1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-02
出版日期:2025-09-20
发布日期:2025-09-28
通讯作者:
朱娟霞
E-mail:1342748096@qq.com;1657238862@qq.com;1120270539@qq.com
作者简介:闫爱丽,硕士,副教授,E-mail: 1342748096@qq.com基金资助:
Aili YAN1( ), Mengyao LUO2(
), Mengyao LUO2( ), Jinrui CHANG1, Xinhua LI1, Juanxia ZHU1(
), Jinrui CHANG1, Xinhua LI1, Juanxia ZHU1( )
)
Received:2025-02-02
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Juanxia ZHU
E-mail:1342748096@qq.com;1657238862@qq.com;1120270539@qq.com
摘要:
目的 探讨橙皮素(Hes)通过调控AMP依赖的蛋白激酶(AMPK)/NOD热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3(NLRP3)信号减轻炎症反应改善阿霉素(DOX)诱导的心肌损伤。 方法 采用DOX处理C57/bl6小鼠和H9c2细胞,并随机分为:对照组/假手术组、DOX处理组、Hes干预DOX组(DOX+Hes)以及Hes联合AMPK抑制剂Compound C干预DOX组(DOX+Hes+CC)。观察细胞形态变化,采用CCK-8法检测细胞活力,超声检测心脏功能,ELISA法检测培养基和心肌组织中LDH活性,TUNEL染色法检测细胞凋亡,RT-PCR检测TNF-α、IL-6和IL-1β的mRNA水平,Western blotting法检测cleaved caspase-3、Bcl2、Bax、IL-1β、IL-18、p-AMPK、AMPK、p-mTOR、mTOR、NLRP3、ASC和caspase-1的表达。 结果 与对照组相比,DOX组细胞肿胀,活力降低,培养基中LDH活性增加(P<0.01);cleaved caspase-3表达和TUNEL染色阳性细胞数增加,Bcl2/Bax比值降低(P<0.01)。与假手术组相比,DOX组心肌纤维肿胀并出现炎性浸润,心脏功能降低,LDH活性增加;同时TNF-α、IL-6和IL-1β的mRNA水平以及IL-1β和IL-18的蛋白表达增加(P<0.01),p-AMPK和p-mTOR蛋白表达降低,NLRP3、ASC和caspase-1的表达增加(P<0.01)。与DOX组相比,DOX+Hes组细胞肿胀减轻,活力增加,培养基中LDH活性降低(P<0.01);cleaved caspase-3表达和TUNEL染色阳性细胞数减少,Bcl2/Bax比值增加(P<0.01);TNF-α、IL-6和IL-1β的mRNA水平以及IL-1β和IL-18的蛋白表达降低(P<0.01);p-AMPK和p-mTOR蛋白表达增加,NLRP3、ASC和caspase-1的表达降低(P<0.01)。与DOX+Hes组相比,Compound C可以阻断Hes对DOX诱导的细胞损伤、心脏功能、炎症反应和AMPK/NLRP3通路的作用。 结论 Hes通过调控AMPK/NLRP3通路抑制炎症反应减轻DOX诱导的心脏毒性。
闫爱丽, 罗梦瑶, 常晋瑞, 李新华, 朱娟霞. 橙皮素通过调控AMPK/NLRP3通路减轻阿霉素诱导的小鼠心肌毒性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1850-1858.
Aili YAN, Mengyao LUO, Jinrui CHANG, Xinhua LI, Juanxia ZHU. Hesperetin alleviates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by regulating the AMPK/NLRP3 pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1850-1858.
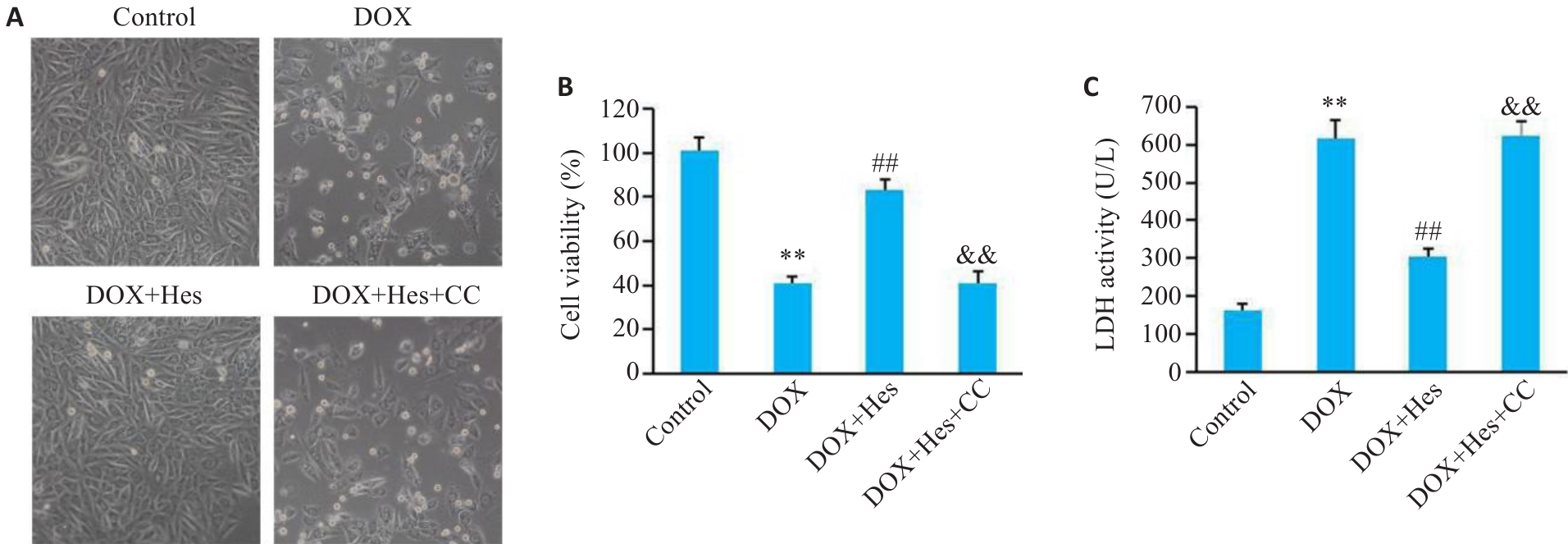
图1 Compound C阻断Hes对DOX引起的细胞损伤的改善作用
Fig.1 Compound C blocks the protective effects of Hes against DOX-induced cell injury in H9c2 cells. A: Cell morphology in each group (Original magnification: ×100). B: Comparison of cell viability among the 4 groups. C: LDH activity in the cells in the 4 groups. **P<0.01 vs Control group; ##P<0.01 vs DOX group; &&P<0.01 vs DOX+Hes group (n=6).
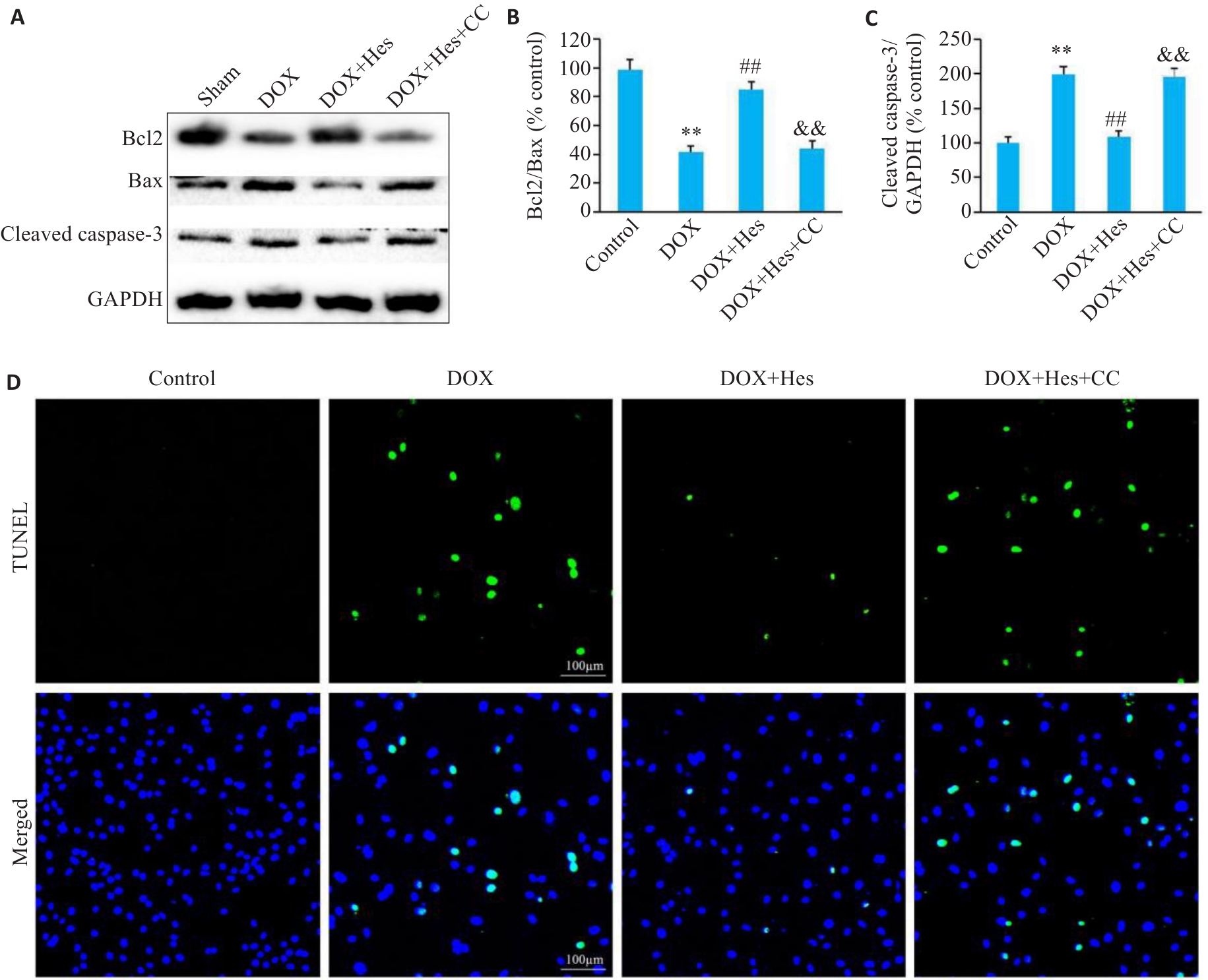
图2 Compound C阻断Hes对DOX引起的细胞凋亡的改善作用
Fig.2 Compound C reduces the protective effect of Hes against DOX-induced cell apoptosis.A: Representative Western blots of Bcl2, Bax, cleaved caspase-3 and GAPDH in each group. B: Bcl2/Bax ratios in each group. C: Cleaved caspase-3 expression levels in each group. D: TUNEL staining of the cells in each group (Scale bar=100 μm). **P<0.01 vs Control group; ##P<0.01 vs DOX group; &&P<0.01 vs DOX+Hes group (n=6).
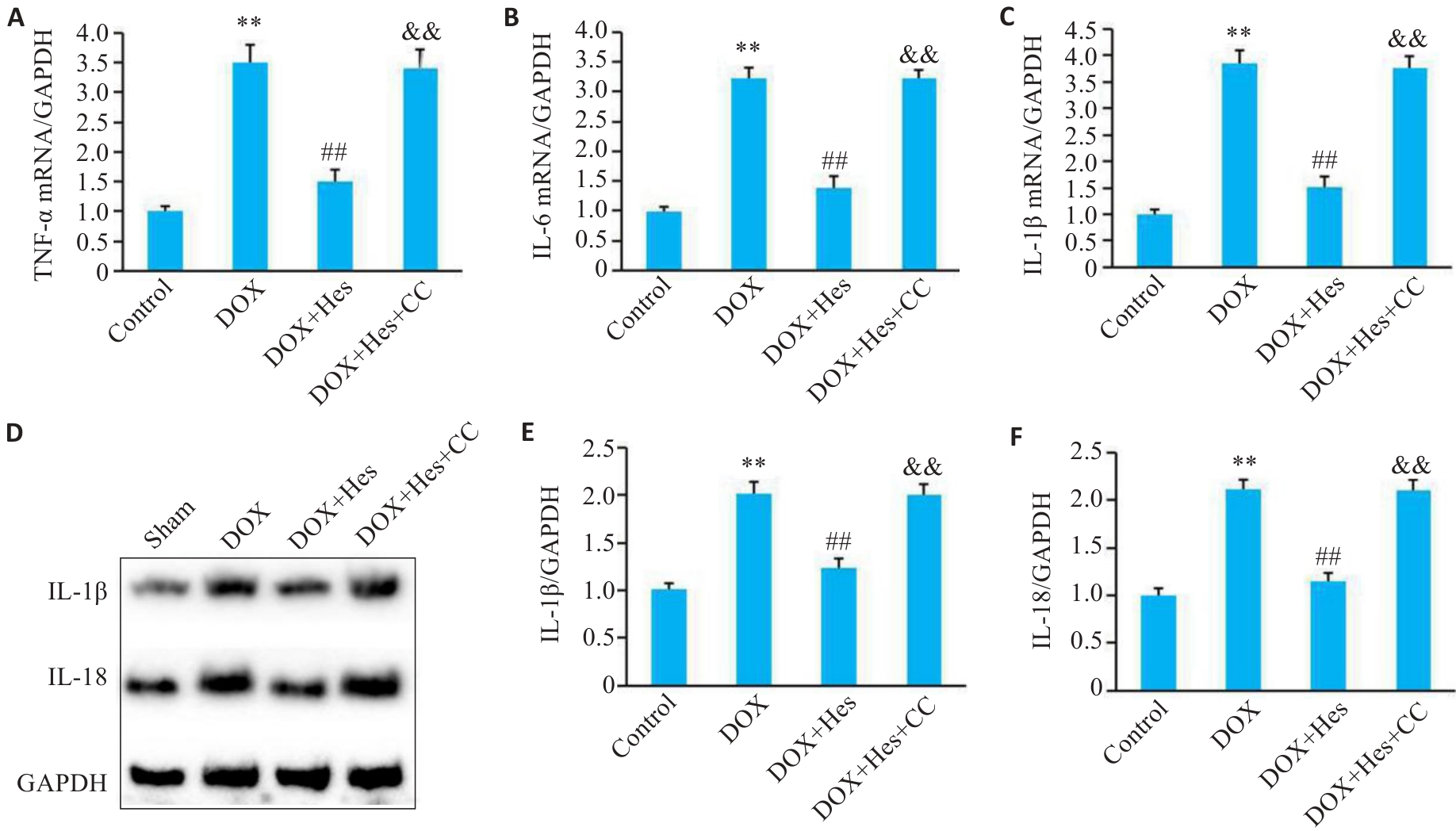
图3 Compound C阻断Hes对DOX引起的细胞炎症的改善作用
Fig.3 Compound C attenuates the protective effect of Hes against DOX-induced inflammation. A-C: Relative mRNA expressions of TNF‑α, IL-6 and IL-1β in each group. D: Representative Western blots of TNF‑α, IL-6, IL-1β and GAPDH in each group. E, F: Relative expression levels of IL-1β and IL-18 in the cells in each group. **P<0.01 vs Control group; ##P<0.01 vs DOX group; &&P<0.01 vs DOX+Hes group (n=6).
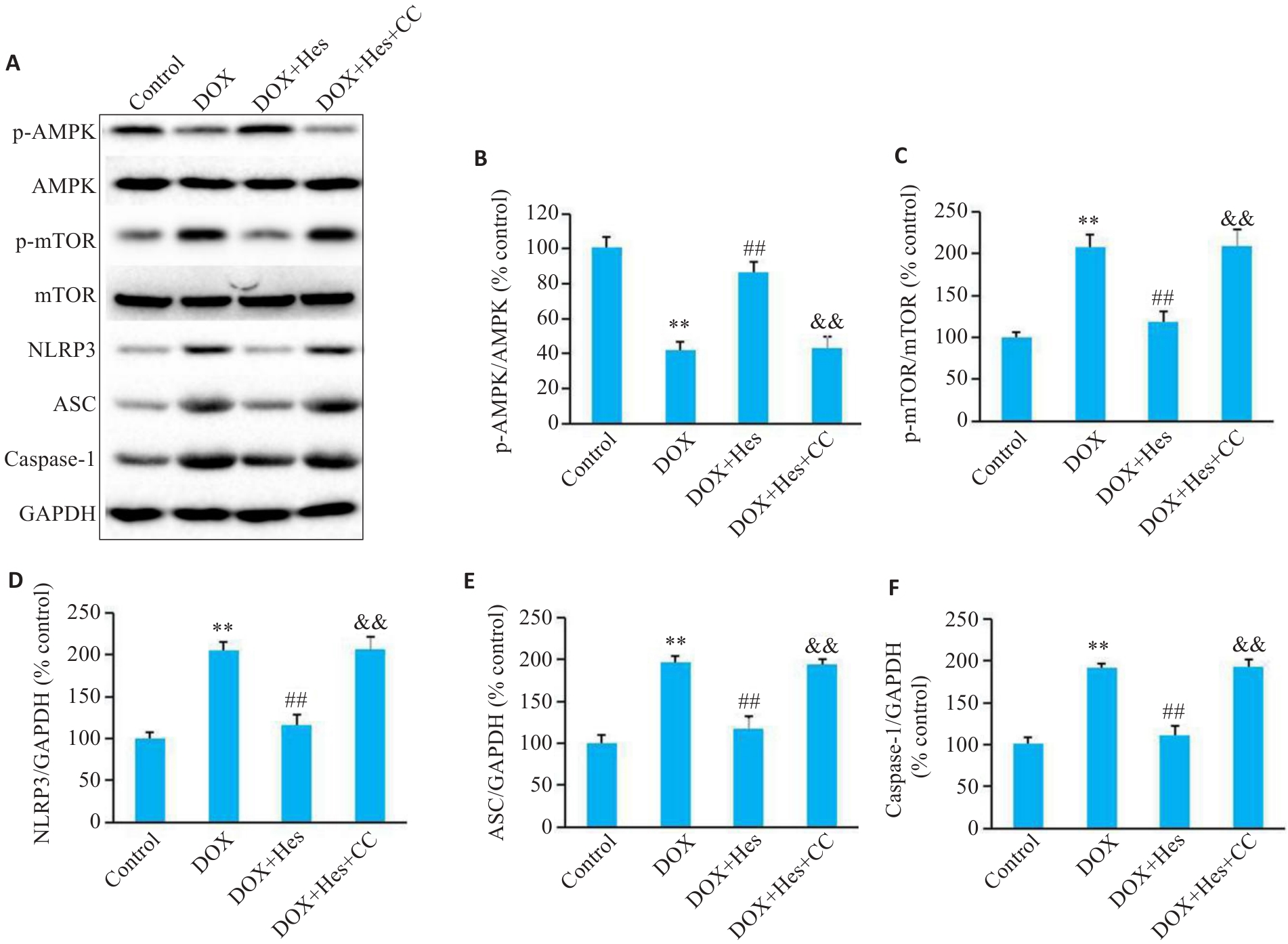
图4 Compound C阻断Hes对DOX引起的AMPK/NLRP3表达的变化
Fig.4 Compound C blocks the effect of Hes against DOX-induced changes in protein expressions of AMPK/NLRP3 signaling. A: Representative Western blots of p-AMPK, AMPK, p-mTOR, mTOR, NLRP3, ASC, caspase-1 and GAPDH in each group. B-F: Relative expression levels of p-AMPK, p-mTOR, NLRP3, ASC, and caspase-1 in each group. **P<0.01 vs Control group; ##P<0.01 vs DOX group; &&P<0.01 vs DOX+Hes group (n=6).
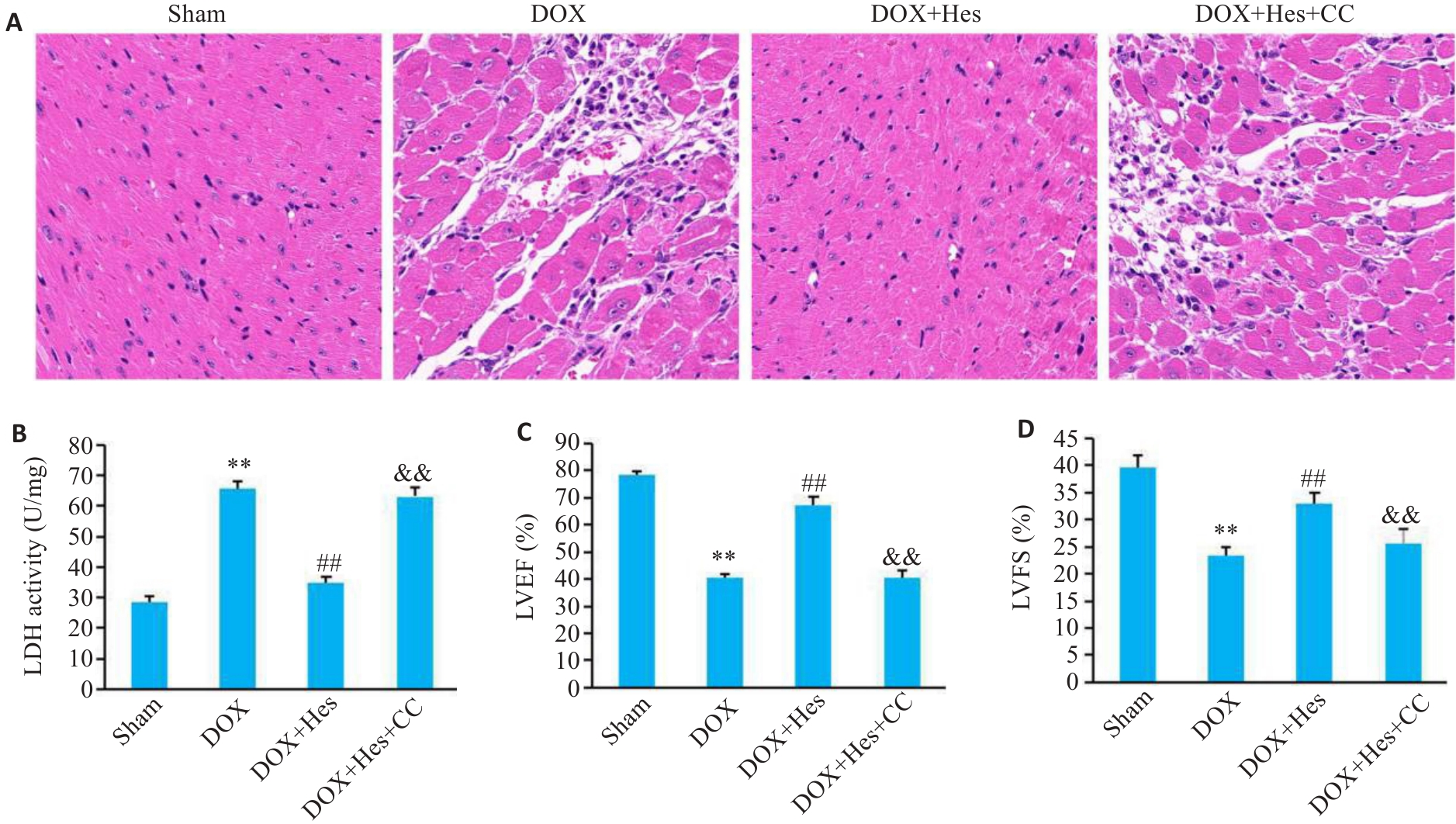
图5 Compound C阻断Hes对DOX引起的心肌损伤的改善作用
Fig.5 Compound C blocks the protective effect of Hes against DOX-induced myocardial injury in mice. A: HE staining of the myocardial tissues in each group (×200). B: Myocardial LDH activity in each group. C: LVEF in each group. D: LVFS in each group. **P<0.01 vs Sham group; ##P<0.01 vs DOX group; &&P<0.01 vs DOX+Hes group (n=6).
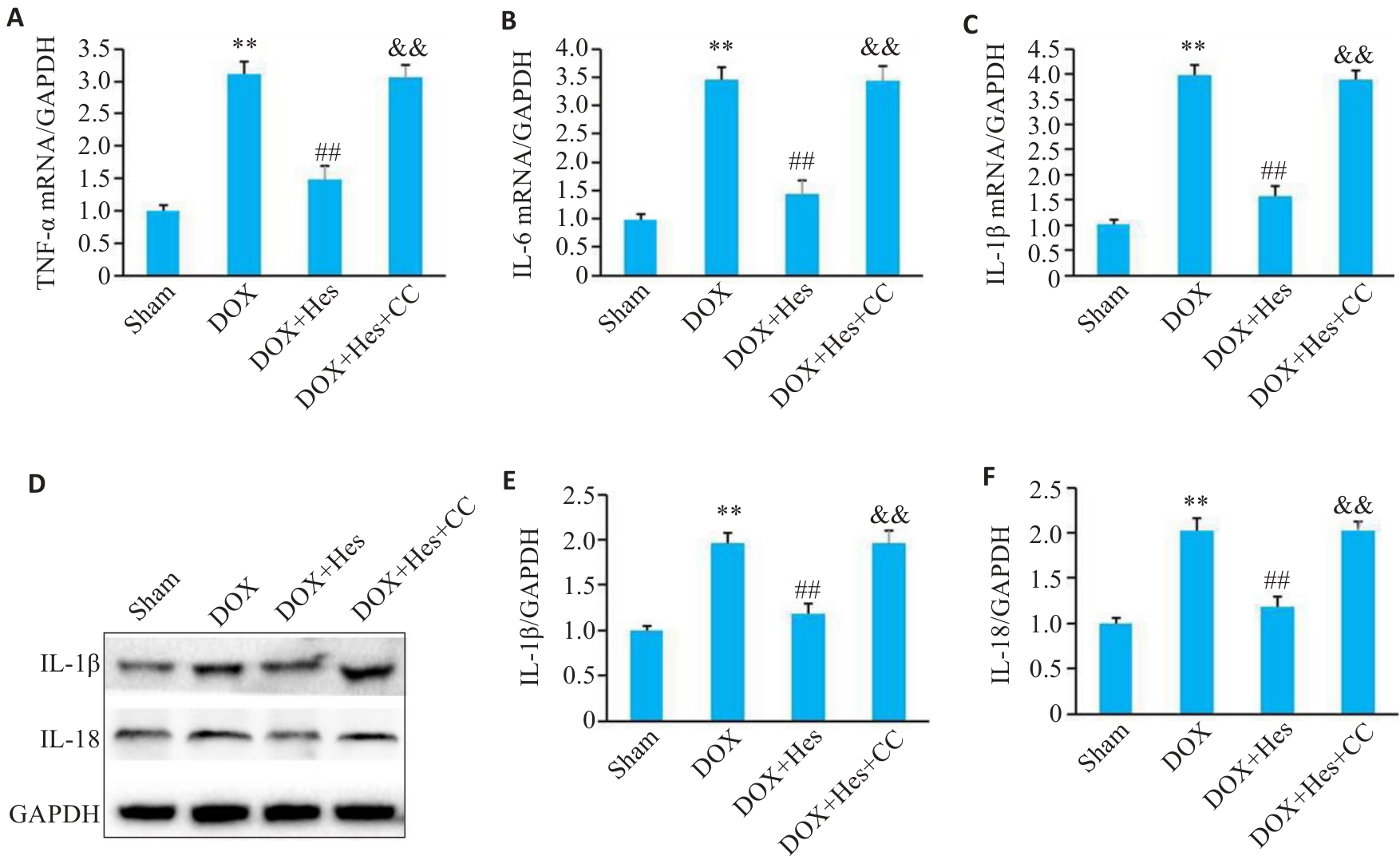
图6 Compound C阻断Hes对DOX引起炎症的改善作用
Fig.6 Compound C attenuates the protective effect of Hes against DOX-induced inflammation in the myocardial tissues of the mice. A-C: Relative mRNA expressions of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β in each group. D: Representative Western blots of IL-1β, IL-18 and GAPDH. E, F: Relative expression levels of IL-1β and IL-18 in each group. **P<0.01 vs Sham group; ##P<0.01 vs DOX group; &&P<0.01 vs DOX+Hes group (n=6).
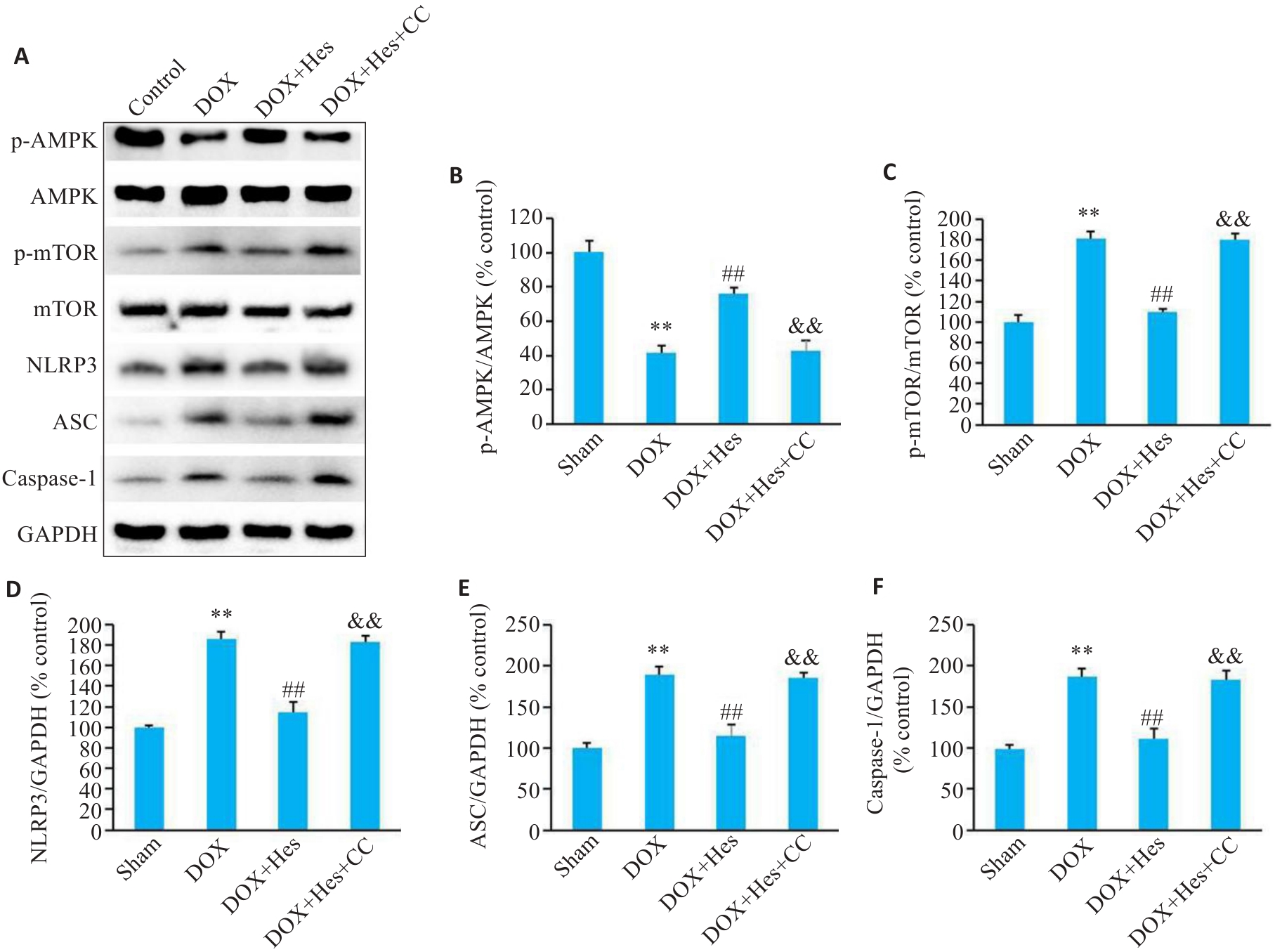
图7 Compound C阻断Hes对DOX引起的小鼠心肌AMPK/NLRP3表达的变化
Fig.7 Compound C blocks the effect of Hes against DOX-induced changes in expression of AMPK/NLRP3 signaling in the mice. A: Representative Western blots of p-AMPK, AMPK, p-mTOR, mTOR, NLRP3, ASC, caspase-1 and GAPDH. B-F: Relative expression levels of p-AMPK, p-mTOR, NLRP3, ASC, and caspase-1 in the myocardial tissues of the mice in each group. **P<0.01 vs Sham group; ##P<0.01 vs DOX group; &&P<0.01 vs DOX+Hes group (n=6).
| [1] | Karlstaedt A, Taegtmeyer H. Cardio-Onco-Metabolism–Metabolic vulnerabilities in cancer and the heart[J]. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2022, 171: 71-80. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2022.06.008 |
| [2] | Sangweni NF, Gabuza K, Huisamen B, et al. Molecular insights into the pathophysiology of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: a graphical representation[J]. Arch Toxicol, 2022, 96(6): 1541-50. doi:10.1007/s00204-022-03262-w |
| [3] | Hulst MB, Grocholski T, Neefjes JJC, et al. Anthracyclines: biosynthesis, engineering and clinical applications[J]. Nat Prod Rep, 2022, 39(4): 814-41. doi:10.1039/d1np00059d |
| [4] | Schmidt AF, Bourfiss M, Alasiri A, et al. Druggable proteins influencing cardiac structure and function: Implications for heart failure therapies and cancer cardiotoxicity[J]. Sci Adv, 2023, 9(17): eadd4984. doi:10.1126/sciadv.add4984 |
| [5] | Kong CY, Guo Z, Song P, et al. Underlying the mechanisms of doxorubicin-induced acute cardiotoxicity: oxidative stress and cell death[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2022, 18(2): 760-70. doi:10.7150/ijbs.65258 |
| [6] | Wu L, Wang LT, Du YX, et al. Mitochondrial quality control mechanisms as therapeutic targets in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2023, 44(1): 34-49. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2022.10.003 |
| [7] | Vitale R, Marzocco S, Popolo A. Role of oxidative stress and inflammation in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: a brief account[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(13): 7477. doi:10.3390/ijms25137477 |
| [8] | Ji Z, Deng W, Chen D, et al. Recent understanding of the mechanisms of the biological activities of hesperidin and hesperetin and their therapeutic effects on diseases[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(5): e26862. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26862 |
| [9] | Zhang YX, Chen XJ, Wang XX, et al. Hesperetin ameliorates spinal cord injury in rats through suppressing apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammatory response[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2024, 971: 176541. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176541 |
| [10] | Liu PP, Li JH, Liu MM, et al. Hesperetin modulates the Sirt1/Nrf2 signaling pathway in counteracting myocardial ischemia through suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, 139: 111552. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111552 |
| [11] | Li X, Yan A, Chang J, et al. Hesperetin alleviates doxorubicin-induced cytotoxicity in H9c2 cells by activating SIRT1/NRF2 signaling[J]. Sichuan da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban, 2023, 54(5): 947-53. |
| [12] | Chen MC. Empagliflozin attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardioto-xicity by activating AMPK/SIRT-1/PGC-1α-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis[J]. Toxicol Res, 2023, 12(2): 216-23. doi:10.1093/toxres/tfad007 |
| [13] | Zhao XY, Ren JM, Liu HR, et al. DJ-1 activates the AMPK/mTOR pathway by binding RACK1 to induce autophagy and protect the myocardium from ischemia/hypoxia injury[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2022, 637: 276-85. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.10.100 |
| [14] | Zhu M, Hu J, Pan Y, et al. Magnoflorine attenuates Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling via promoting AMPK-regulated autophagy[J]. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther, 2024, 14(4): 576-88. doi:10.21037/cdt-24-130 |
| [15] | 魏 佳, 杨 强, 林 琳, 等. 二甲双胍减轻阿霉素诱导的心脏毒性:基于AMPK通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(10): 1682-8. |
| [16] | Liu D, Ma ZQ, Di SY, et al. AMPK/PGC1α activation by melatonin attenuates acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity via alleviating mitochondrial oxidative damage and apoptosis[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2018, 129: 59-72. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.08.032 |
| [17] | Wang WL, Jiang JL, Huang Y, et al. Aconitine induces autophagy via activating oxidative DNA damage-mediated AMPK/ULK1 signaling pathway in H9c2 cells[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2022, 282: 114631. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2021.114631 |
| [18] | Ta N, Qu C, Wu H, et al. Mitochondrial outer membrane protein FUNDC2 promotes ferroptosis and contributes to doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2022, 119(36): e2117396119. doi:10.1073/pnas.2117396119 |
| [19] | Kitakata H, Endo J, Matsushima H, et al. MITOL/MARCH5 determines the susceptibility of cardiomyocytes to doxorubicin-induced ferroptosis by regulating GSH homeostasis[J]. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2021, 161: 116-29. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2021.08.006 |
| [20] | 熊凤梅, 刘瑞萍, 李 洋, 等. 和厚朴酚可体外减轻阿霉素诱导的心肌毒性: 基于激活AMPK/Nrf2信号通路抑制细胞焦亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(8): 1205-11. doi:10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.08.13 |
| [21] | Nakamura M, Sadoshima J. Mechanisms of physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2018, 15(7): 387-407. doi:10.1038/s41569-018-0007-y |
| [22] | Zaafar D, Khalil HMA, Rasheed RA, et al. Hesperetin mitigates sorafenib-induced cardiotoxicity in mice through inhibition of the TLR4/NLRP3 signaling pathway[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(8): e0271631. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0271631 |
| [23] | Zhang Z, Shen C, Wu N, et al. Gab1 overexpression alleviates doxorubicin-induced cardiac oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 2022, 80(6): 804-12. doi:10.1097/fjc.0000000000001333 |
| [24] | Quagliariello V, De Laurentiis M, Rea D, et al. The SGLT-2 inhibitor empagliflozin improves myocardial strain, reduces cardiac fibrosis and pro-inflammatory cytokines in non-diabetic mice treated with doxorubicin[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2021, 20(1): 150. doi:10.1186/s12933-021-01346-y |
| [25] | Yildirim C, Cangi S, Orkmez M, et al. Sinapic acid attenuated cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting oxidative stress and İnflammation with GPX4-mediated NF-kB modulation[J]. Cardiovasc Toxicol, 2023, 23(1): 10-22. doi:10.1007/s12012-022-09773-3 |
| [26] | Morsy MA, Abdel-Gaber SA, Mokhemer SA, et al. Pregnenolone inhibits doxorubicin-induced cardiac oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis-role of matrix metalloproteinase 2 and NADPH oxidase 1[J]. Pharmaceuticals: Basel, 2023, 16(5): 665. doi:10.3390/ph16050665 |
| [27] | Toldo S, Abbate A. The role of the NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis in cardiovascular diseases[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2024, 21(4): 219-37. doi:10.1038/s41569-023-00946-3 |
| [28] | Townsend LK, Steinberg GR. AMPK and the endocrine control of metabolism[J]. Endocr Rev, 2023, 44(5): 910-33. doi:10.1210/endrev/bnad012 |
| [29] | Steinberg GR, Hardie DG. New insights into activation and function of the AMPK[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2023, 24(4): 255-72. doi:10.1038/s41580-022-00547-x |
| [30] | Liu C, Guo X, Zhou Y, et al. AMPK signalling pathway: a potential strategy for the treatment of heart failure with Chinese medicine[J]. J Inflamm Res, 2023, 16: 5451-64. doi:10.2147/jir.s441597 |
| [1] | 范正媛, 沈子涵, 李亚, 沈婷婷, 李高峰, 李素云. 补肺益肾方对香烟烟雾提取物诱导的人支气管上皮细胞损伤的保护作用及其机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1372-1379. |
| [2] | 夏冰, 彭进, 丁九阳, 王杰, 唐国伟, 刘国杰, 王沄, 万昌武, 乐翠云. ATF3通过NF-κB信号通路调控动脉粥样硬化斑块内的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1131-1142. |
| [3] | 陈镝, 吕莹, 郭怡欣, 张怡荣, 王蕊璇, 周小若, 陈雨欣, 武晓慧. 双氢青蒿素可显著增强阿霉素诱导的三阴性乳腺癌细胞凋亡:基于负向调控STAT3/HIF-1α通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 254-260. |
| [4] | 左涵珺, 段兆达, 王朝, 郭涛, 石金沙, 石浩龙, 李娟娟. 天麻素经PI3K/AKT通路改善新生大鼠缺氧缺血性脑损伤后小胶质细胞介导的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1712-1719. |
| [5] | 张钰明, 夏士程, 张淋淋, 陈梦茜, 刘晓婧, 高琴, 叶红伟. 金银花提取物对小鼠阿霉素肝脏损伤的保护作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1571-1581. |
| [6] | 何 程, 陈 炜, 张念志, 栾 军, 王三凤, 张 尤. 参七虫草方通过ASS1/src/STAT3信号通路改善肺纤维化大鼠的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 644-651. |
| [7] | 包汉生, 王苏童, 吕穆杰, 王永成, 姜 萍, 李 晓. 激活α7nAchR促进肥胖小鼠的脂肪稳态和米色脂肪生成及产热作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 499-506. |
| [8] | 曾佑琴, 陈思雨, 刘燕, 刘奕彤, 张玲, 夏姣, 吴心语, 魏常友, 冷平. AKBA联合阿霉素抑制三阴性乳腺癌细胞MDA-MB-231的增殖、迁移和裸鼠移植瘤生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2449-2460. |
| [9] | 孙秀颀, 蔡静, 张安邦, 庞博, 陈春艳, 查琪琪, 全菲, 叶涛. 电针预处理通过抑制NF-kB/NLRP3信号通路介导炎症和凋亡改善大鼠脑卒中后痉挛[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2102-2109. |
| [10] | 姚宏, 刘珂娣, 刘澄曌, 李伟红, 代旗, 赵石, 丁子恒, 王鹤霏, 葛晓静, 卫培峰, 段佳林, 奚苗苗. 五谷虫通过抑制免疫应激-补体活化缓解咪喹莫特诱导的小鼠银屑病样皮肤损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2121-2130. |
| [11] | 程蒙蒙, 刘新光, 魏焱鑫, 邢小香, 刘览, 辛楠, 赵鹏. 通塞颗粒阻抑巨噬细胞炎症反应改善大鼠慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(10): 1995-2003. |
| [12] | 李 晒, 李 丽, 闵思敏, 刘赛赛, 秦志文, 熊志尚, 徐建国, 王博文, 丁渡山, 赵士弟. 大豆异黄酮可减轻大鼠脑缺血/再灌注损伤:基于抑制铁死亡及炎症级联反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 323-330. |
| [13] | 曹天然, 刘青芳, 潘美民, 张雪红. LncRNA SNHG8通过抑制miR-494-3p表达减轻脑缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(12): 2015-2022. |
| [14] | 魏 佳, 杨 强, 林 琳, 朱参战, 魏 瑾. 二甲双胍减轻阿霉素诱导的心脏毒性:基于AMPK通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(10): 1682-1688. |
| [15] | 熊凤梅, 刘瑞萍, 李 洋, 孙 娜. 和厚朴酚可体外减轻阿霉素诱导的心肌毒性:基于激活AMPK/Nrf2信号通路抑制细胞焦亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(8): 1205-1211. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||