南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (7): 1372-1379.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.07.03
范正媛1,2,3( ), 沈子涵3, 李亚1,2,3, 沈婷婷1,2,3, 李高峰3, 李素云2,3(
), 沈子涵3, 李亚1,2,3, 沈婷婷1,2,3, 李高峰3, 李素云2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-21
出版日期:2025-07-20
发布日期:2025-07-17
通讯作者:
李素云
E-mail:fanzhengyuan0225@163.com;lisuyun2000@126.com
作者简介:范正媛,博士,副研究员,E-mail: fanzhengyuan0225@163.com
基金资助:
Zhengyuan FAN1,2,3( ), Zihan SHEN3, Ya LI1,2,3, Tingting SHEN1,2,3, Gaofeng LI3, Suyun LI2,3(
), Zihan SHEN3, Ya LI1,2,3, Tingting SHEN1,2,3, Gaofeng LI3, Suyun LI2,3( )
)
Received:2025-03-21
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-07-17
Contact:
Suyun LI
E-mail:fanzhengyuan0225@163.com;lisuyun2000@126.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨补肺益肾方对香烟烟雾提取物(CSE)诱导的人支气管上皮BEAS-2B细胞损伤的保护作用及机制。 方法 以CSE诱导的BEAS-2B细胞构建模型,以羧甲司坦(S-CMC)为阳性对照,将细胞分为对照组、CSE组、补肺益肾方(BYF)含药血清低剂量(BYL)组、BYF高剂量(BYH)组、NF-κB抑制剂PDTC组、BYH+PDTC组及S-CMC组。CCK-8法筛选CSE最佳造模浓度、作用时间及BYF含药血清、S-CMC给药浓度;ELISA法检测细胞上清炎症因子水平及细胞MUC5AC、MUC5B表达;透射电镜观察细胞超微结构;流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡率;qRT-PCR及Western blotting法检测细胞TLR4/NF-κB通路相关mRNA和蛋白表达。 结果 与Control组相比,CSE组细胞IL-1β、IL-6及TNF-α的分泌升高(P<0.01),细胞MUC5AC、MUC5B mRNA和蛋白表达升高(P<0.01),细胞出现凋亡小体,早期凋亡率及总凋亡率升高(P<0.01),细胞TLR4,I-κB,NF-κB mRNA和蛋白表达升高(P<0.01),AQP5 mRNA和蛋白表达降低(P<0.01)。与CSE组相比,各给药组可降低细胞上清炎症因子水平,细胞MUC5AC、MUC5B mRNA和蛋白水平,细胞早期凋亡率及总凋亡率,细胞超微结构损伤及TLR4/NF-κB通路相关mRNA和蛋白表达被部分逆转,其中以BYH+PDTC组更明显。 结论 补肺益肾方可通过抑制TLR4/NF-κB信号通路抑制CSE诱导的BEAS-2B细胞凋亡、炎症和黏液高分泌。
范正媛, 沈子涵, 李亚, 沈婷婷, 李高峰, 李素云. 补肺益肾方对香烟烟雾提取物诱导的人支气管上皮细胞损伤的保护作用及其机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1372-1379.
Zhengyuan FAN, Zihan SHEN, Ya LI, Tingting SHEN, Gaofeng LI, Suyun LI. Protective effect of Bufei Yishen Formula against cigarette smoke extract-induced human bronchial epithelial cell damage and its mechanism[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1372-1379.
| Group | Intervention methods |
|---|---|
| Control | DMEM+10% blank serum |
| CSE | DMEM+10%CSE+10% blank serum |
| BYL | DMEM+10%CSE+5% medicated serum+5%blank serum |
| BYH | DMEM+10%CSE+10% medicated serum |
| PDTC | DMEM+10%CSE+10% blank serum+10 μmol/L PDTC |
| BYH+PDTC | DMEM+10%CSE+10% medicated serum+10 μmol/L PDTC |
| S-CMC | DMEM+10%CSE+10% blank serum+10 μmol/L S-CMC |
表1 细胞分组及干预方法
Tab.1 Treatment protocols in each group
| Group | Intervention methods |
|---|---|
| Control | DMEM+10% blank serum |
| CSE | DMEM+10%CSE+10% blank serum |
| BYL | DMEM+10%CSE+5% medicated serum+5%blank serum |
| BYH | DMEM+10%CSE+10% medicated serum |
| PDTC | DMEM+10%CSE+10% blank serum+10 μmol/L PDTC |
| BYH+PDTC | DMEM+10%CSE+10% medicated serum+10 μmol/L PDTC |
| S-CMC | DMEM+10%CSE+10% blank serum+10 μmol/L S-CMC |
| Gene | Primer sequence (5'-3') | Length(bp) |
|---|---|---|
| TLR4 | Forward: CTCCCTGGTGTTGGATTTTACG Reverse: CTCGTTTCTCACCCAGTCCTCA | 226 |
| I-κB | Forward: CCCAAGTACCCGGATACAGCA Reverse: GTCATCGTAGGGCAACTCATCTT | 133 |
| NF-κB | Forward: GTATTGCTGTGCCTTCCCGA Reverse: CAAGGCCTGGTTTGAGATCTG | 146 |
| AQP5 | Forward: AGCCCCTCTCACTGGGTCTT Reverse: CTCTCGATGATCTTCCCAGTCC | 165 |
| MUC5AC | Forward: GGTCTTCTACTTCCCTGGTCTGTG Reverse: GTCAGCTCAACAACTAGGCCATC | 159 |
| MUC5B | Forward: CAGGCTAGTCCTCAACTTCCTGT Reverse: GTGTTGTGGGCGTAGAACTCATT | 141 |
表2 引物序列
Tab.2 Primer sequence for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Primer sequence (5'-3') | Length(bp) |
|---|---|---|
| TLR4 | Forward: CTCCCTGGTGTTGGATTTTACG Reverse: CTCGTTTCTCACCCAGTCCTCA | 226 |
| I-κB | Forward: CCCAAGTACCCGGATACAGCA Reverse: GTCATCGTAGGGCAACTCATCTT | 133 |
| NF-κB | Forward: GTATTGCTGTGCCTTCCCGA Reverse: CAAGGCCTGGTTTGAGATCTG | 146 |
| AQP5 | Forward: AGCCCCTCTCACTGGGTCTT Reverse: CTCTCGATGATCTTCCCAGTCC | 165 |
| MUC5AC | Forward: GGTCTTCTACTTCCCTGGTCTGTG Reverse: GTCAGCTCAACAACTAGGCCATC | 159 |
| MUC5B | Forward: CAGGCTAGTCCTCAACTTCCTGT Reverse: GTGTTGTGGGCGTAGAACTCATT | 141 |
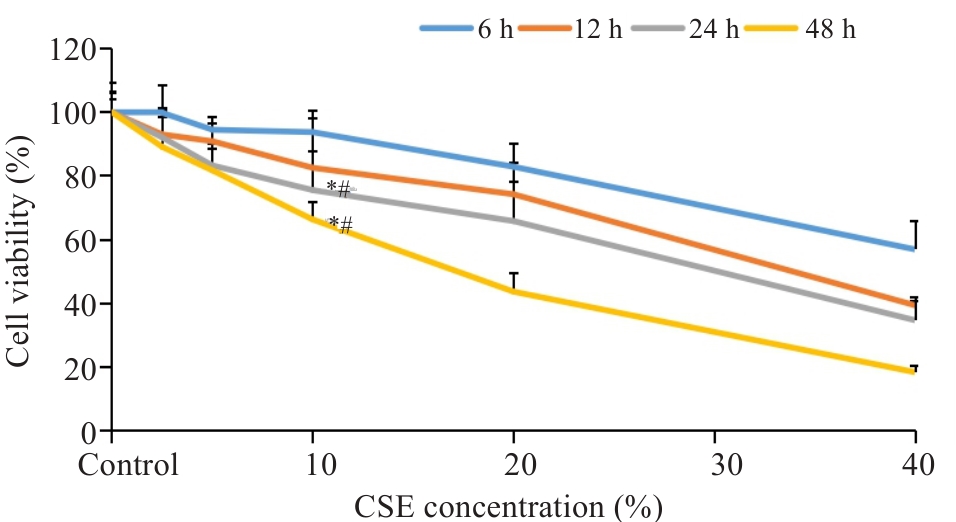
图1 CSE干预BEAS-2B细胞存活率
Fig.1 Survival rate of BEAS-2B cells treated with different concentrations of cigarette smoke extract (CSE). *P<0.05 vs Control; #P<0.05 vs 10% CSE for 6 h.
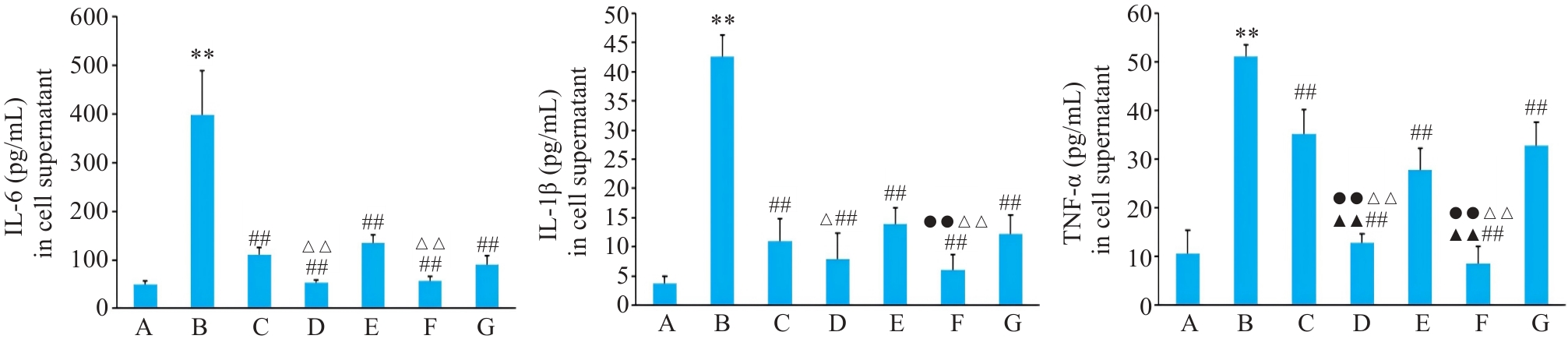
图3 各组BEAS-2B 细胞上清IL-6、IL-1β、TNF-α水平
Fig.3 Expressions of IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α in BEAS-2B cells with different treatments. A: Control group. B: CSE treatment group. C: Low-dose BYF-medicated serum group. D: High-dose BYF-medicated serum group. E: PDTC treatment group. F: High-dose BYF-medicated serum and PDTC treatment group. G: S-CMC treatment group. **P<0.01 vs A; ##P<0.01 vs B; ▲▲P<0.01 vs C; △P<0.05, △△P<0.01 vs E; ●●P<0.01 vs G.
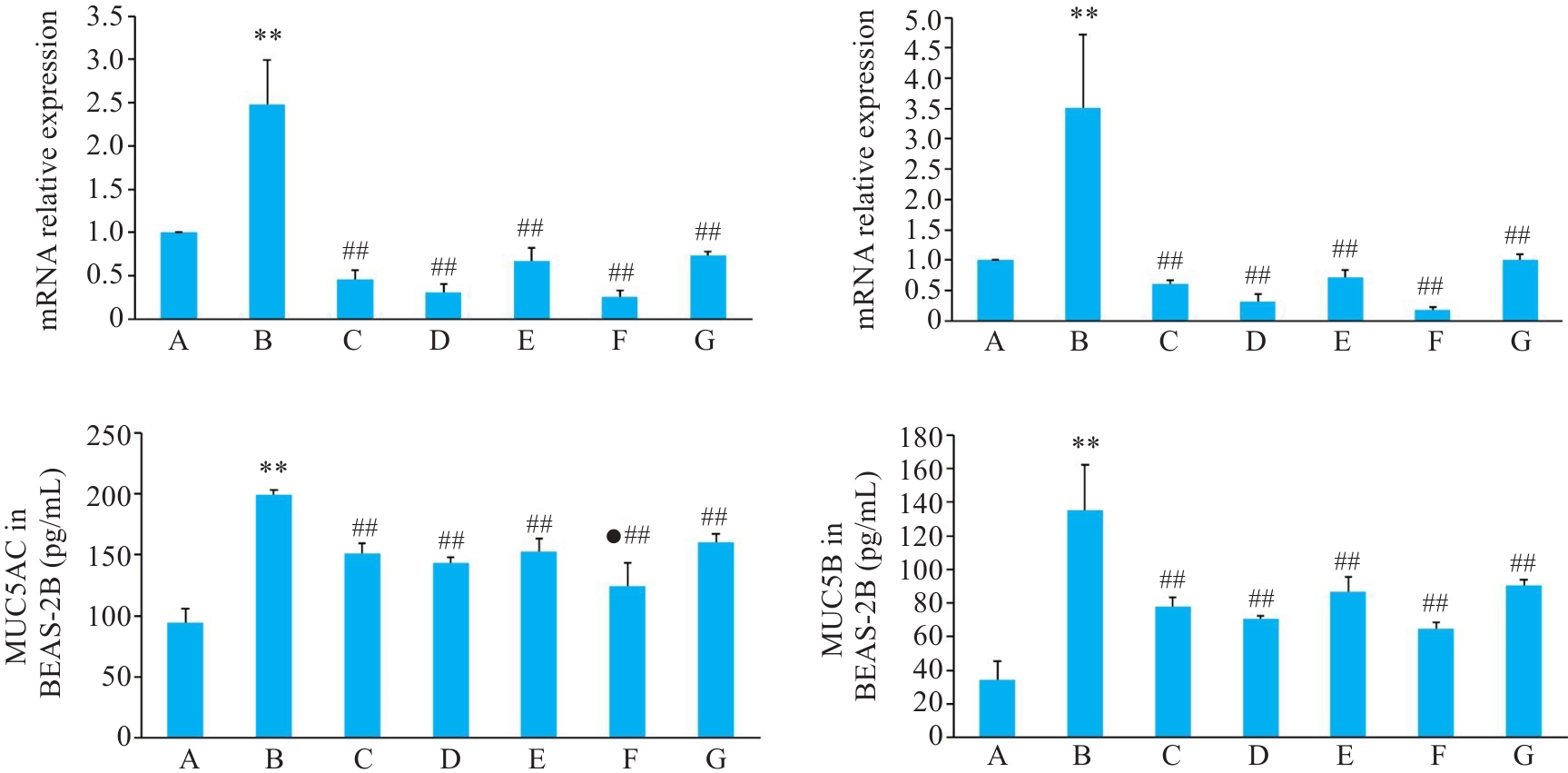
图4 各组BEAS-2B 细胞MUC5AC、MUC5B mRNA和蛋白表达影响
Fig.4 Relative mRNA and protein expressions of MUC5AC and MUC5B in BEAS-2B cells with different treatments. A: Control group. B: CSE treatment group. C: Low-dose BYF-medicated serum group. D: High-dose BYF-medicated serum group. E: PDTC treatment group. F: High-dose BYF-medicated serum and PDTC treatment group. G: S-CMC treatment group. **P<0.01 vs A; ##P<0.01 vs B; ●P<0.05 vs G.
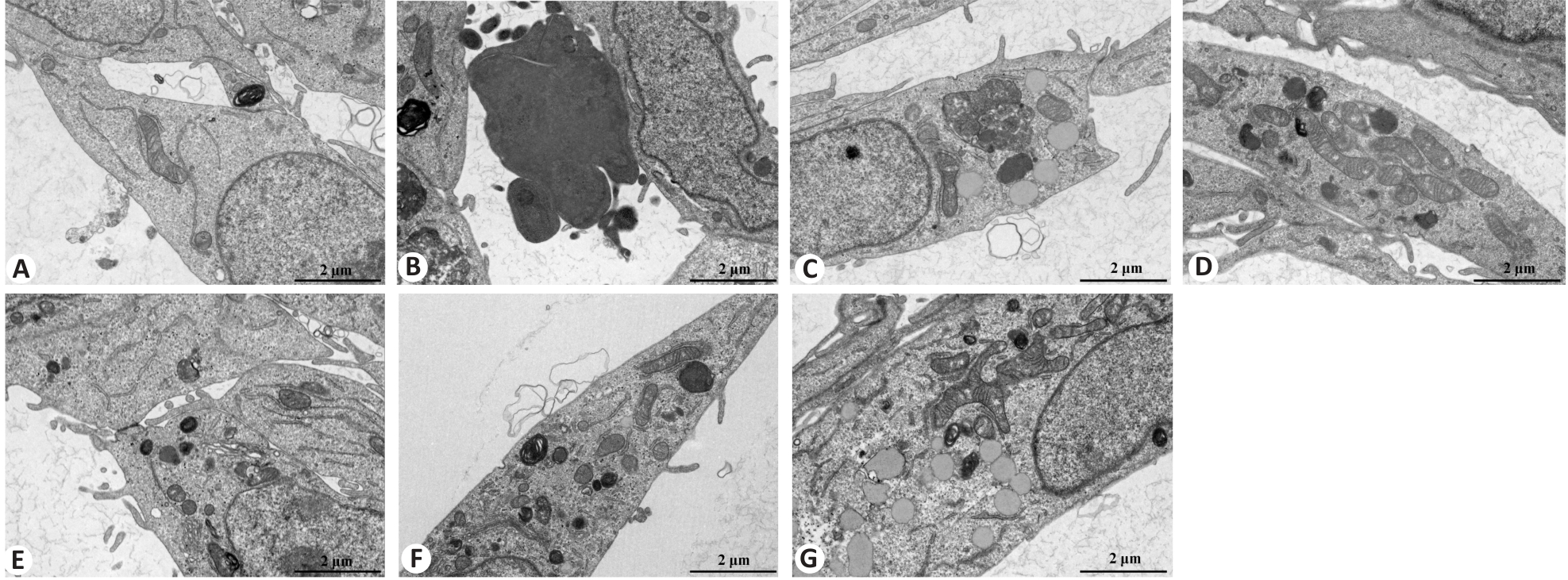
图5 透射电镜观察各组 BEAS-2B 细胞的超微结构
Fig.5 Transmission electron microscopy for examining ultrastructural changes in BEAS-2B cells following different treatments (Scale bar=2 μm). A: Control group. B: CSE treatment group. C: Low-dose BYF-medicated serum group. D: High-dose BYF-medicated serum group. E: PDTC treatment group. F: High-dose BYF-medicated serum and PDTC treatment group. G: S-CMC treatment group.
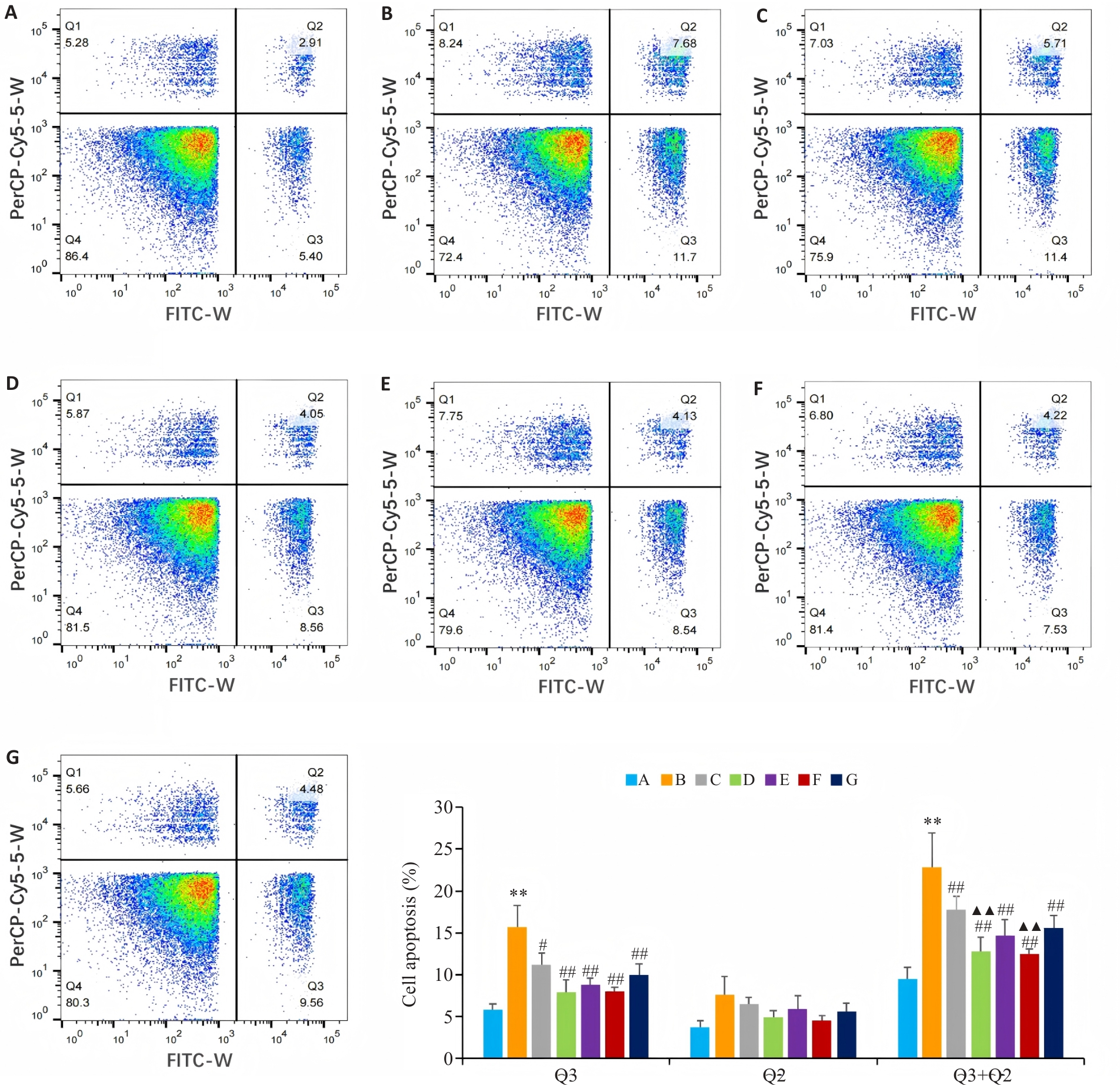
图6 流式细胞仪检测各组 BEAS-2B 细胞的凋亡率
Fig. 6 Flow cytometry of apoptosis rates of BEAS-2B cells in different groups. A: Control group. B: CSE treatment group. C: Low-dose BYF-medicated serum group. D: High-dose BYF-medicated serum group. E: PDTC group. F: High-dose BYF-medicated serum+PDTC group. G: S-CMC group. **P<0.01 vs A; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs B; ▲▲P<0.01 vs C.
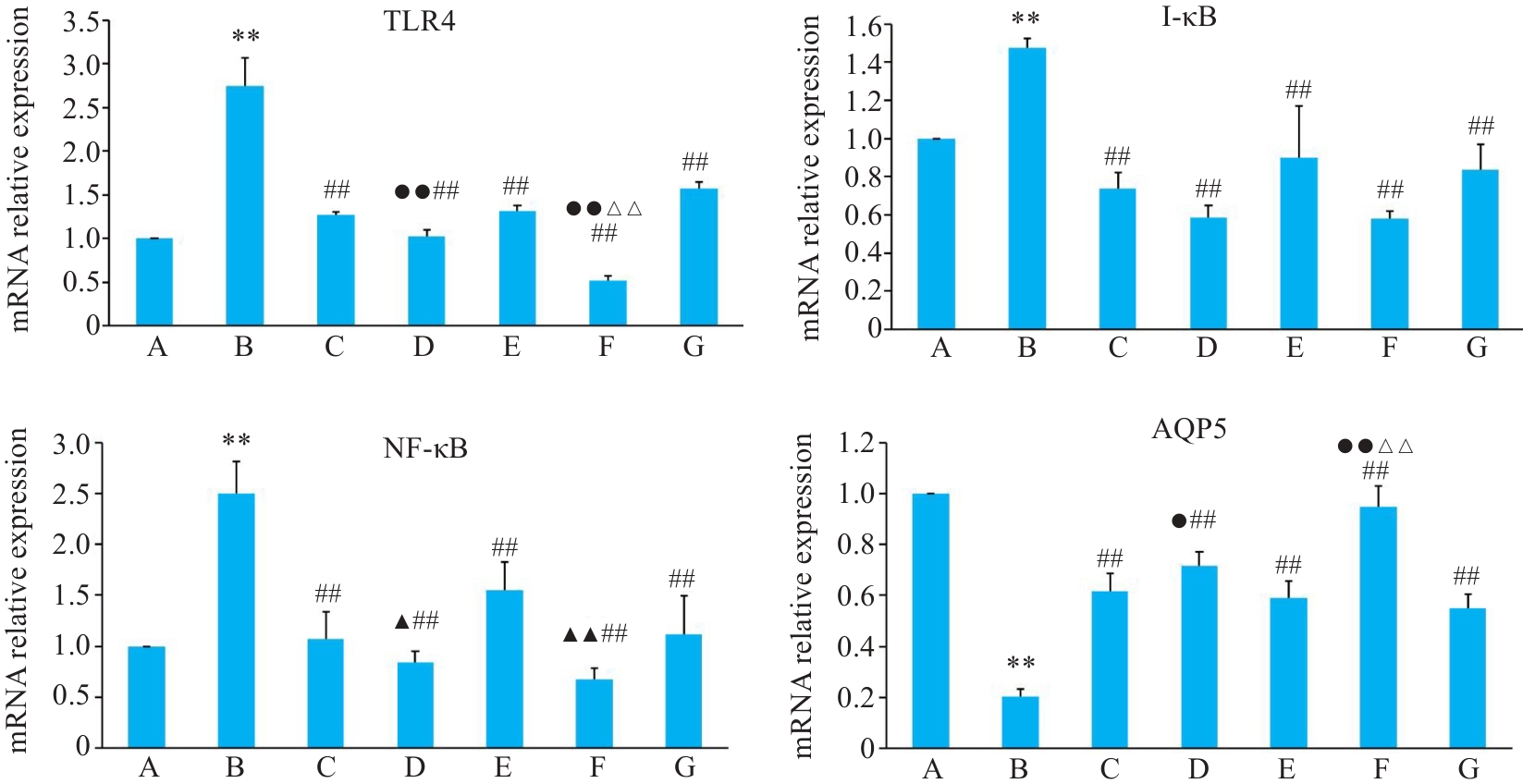
图7 各组BEAS-2B 细胞TLR4、I-κB、NF-κB、AQP5基因表达影响
Fig.7 Relative mRNA expressions of TLR4, I-κB, NF-κB and AQP5 in BEAS-2B cells in different groups. A: Control group. B: CSE treatment group. C: Low-dose BYF-medicated serum group. D: High-dose BYF-medicated serum group. E: PDTC group. F: High-dose BYF-medicated serum+PDTC group. G: S-CMC group. **P<0.01 vs A; ##P<0.01 vs B; ▲P<0.05, ▲▲P<0.01 vs C; △△P<0.01 vs E; ●P<0.05, ●●P<0.01 vs G.
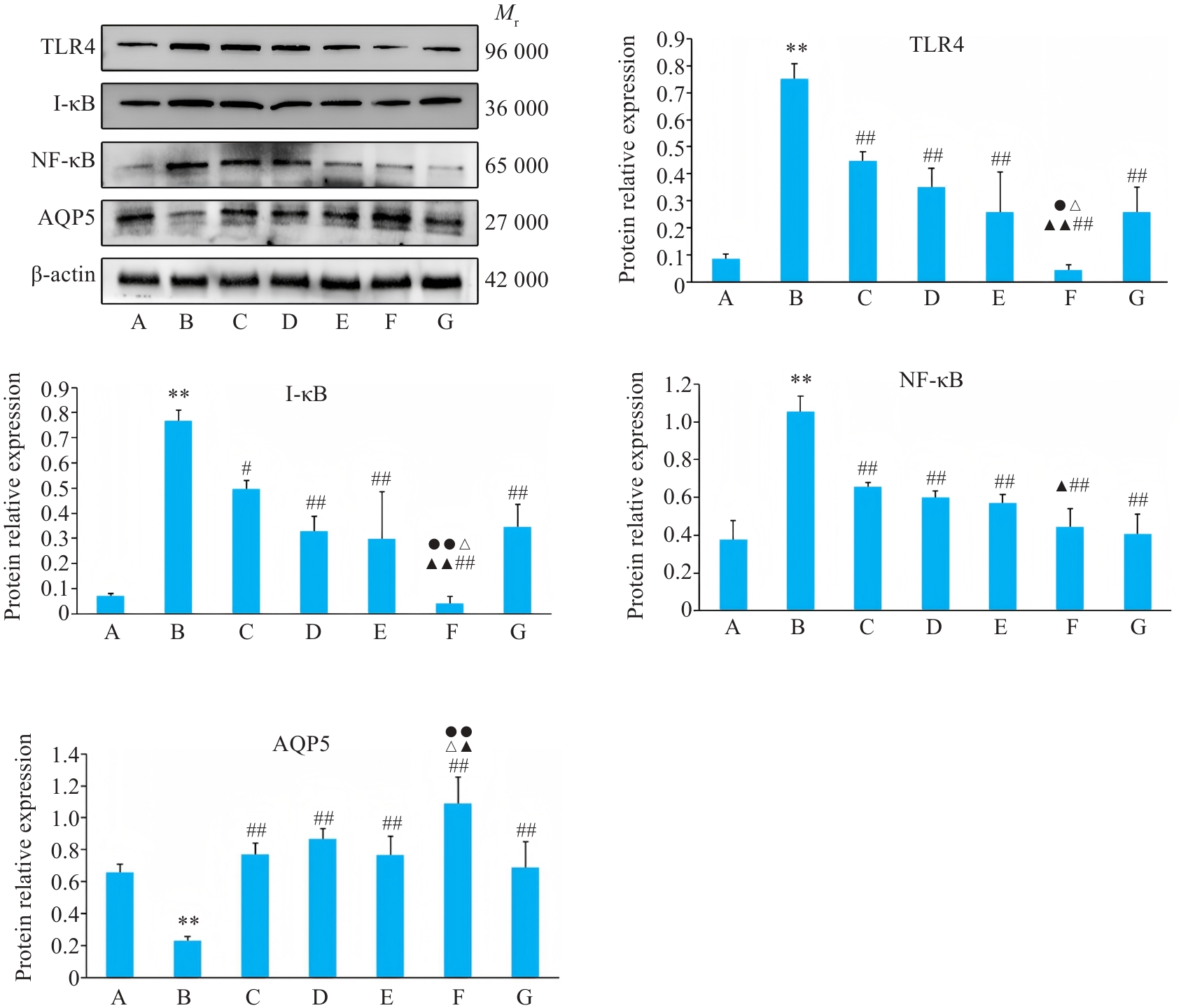
图8 各组BEAS-2B 细胞TLR4、I-κB、NF-κB、AQP5蛋白表达影响
Fig.8 Relative protein expressions of TLR4, I-κB, NF-κB and AQP5 of BEAS-2B cells in different groups. A: Control group. B: CSE treatment group. C: Low-dose BYF-medicated serum group. D: High-dose BYF-medicated serum group. E: PDTC group. F: High-dose BYF-medicated serum+PDTC group. G: S-CMC group. **P<0.01 vs A; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs B; ▲P<0.05, ▲▲P<0.01 vs C; △P<0.05, △△P<0.01 vs E; ●P<0.05, ●●P<0.01 vs G.
| [1] | Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(2024 report)[EB/OL].[2023-11-15]. . doi:10.1111/j.1440-1843.2005.00692.x |
| [2] | Wang C, Xu JY, Yang L, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in China (the China Pulmonary Health [CPH] study): a national cross-sectional study[J]. Lancet, 2018, 391(10131): 1706-17. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(18)30841-9 |
| [3] | Chen SM, Kuhn M, Prettner K, et al. The global economic burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease for 204 countries and territories in 2020-50: a health-augmented macroeconomic mo-delling study[J]. Lancet Glob Health, 2023, 11(8): e1183-93. doi:10.1016/s2214-109x(23)00217-6 |
| [4] | Shin DU, Eom JE, Song HJ, et al. Camellia sinensis L. alleviates pulmonary inflammation induced by porcine pancreas elastase and cigarette smoke extract[J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2022, 11(9): 1683. doi:10.3390/antiox11091683 |
| [5] | 中华医学会, 中华医学会杂志社, 中华医学会全科医学分会, 等. 中国慢性阻塞性肺疾病基层诊疗与管理指南(2024年)[J]. 中华全科医师杂志, 2024, 23(6): 578-602. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn114798-20240326-00177 |
| [6] | Li SY, Li JS, Wang MH, et al. Effects of comprehensive therapy based on traditional Chinese medicine patterns in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a four-center, open-label, randomized, controlled study[J]. BMC Complement Altern Med, 2012, 12: 197. doi:10.1186/1472-6882-12-197 |
| [7] | Wang MH, Li JS, Li SY, et al. Effects of comprehensive therapy based on traditional Chinese medicine patterns on older patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a subgroup analysis from a four-center, randomized, controlled study[J]. Front Med, 2014, 8(3): 368-75. doi:10.1007/s11684-014-0360-0 |
| [8] | Asada M, Yoshida M, Hatachi Y, et al. L-carbocisteine inhibits respiratory syncytial virus infection in human tracheal epithelial cells[J]. Respir Physiol Neurobiol, 2012, 180(1): 112-8. doi:10.1016/j.resp.2011.10.017 |
| [9] | 梅晓峰, 任周新, 余海滨. 补肺益肾方通过调控Notch信号通路改善香烟烟雾提取物诱导气道上皮细胞黏液高分泌[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2022, 34(7): 704-9. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20220397 |
| [10] | Jia LD, Liu XF, Liu XG, et al. Bufei Yishen formula protects the airway epithelial barrier and ameliorates COPD by enhancing autophagy through the Sirt1/AMPK/Foxo3 signaling pathway[J]. Chin Med, 2024, 19(1): 32. doi:10.1186/s13020-024-00905-1 |
| [11] | 李建生. 正虚积损为慢性阻塞性肺疾病的主要病机[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2011, 26(8): 710-3. |
| [12] | Li JS, Xie Y, Zhao P, et al. A Chinese herbal formula ameliorates COPD by inhibiting the inflammatory response via downregulation of p65, JNK, and p38[J]. Phytomedicine, 2021, 83: 153475. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153475 |
| [13] | Li JS, Ma JD, Tian YG, et al. Effective-component compatibility of Bufei Yishen formula II inhibits mucus hypersecretion of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease rats by regulating EGFR/PI3K/mTOR signaling[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2020, 257: 112796. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.112796 |
| [14] | 李高峰, 刘淑娟, 李 亚, 等. 调补肺肾三法通过抑制ERK1/2信号通路改善COPD大鼠气道黏液高分泌[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2024, 32(4): 411-22. |
| [15] | Fang X, Wang ZH, Qi CZ, et al. The changes of MRP2 expression in three kinds of pulmonary inflammation models: the downregulation occurred in cigarette smoke extract (CSE) stimulation group and CSE plus LPS stimulation group, unchanged in LPS stimulation group[J]. Toxicol Mech Methods, 2021, 31(6): 413-24. doi:10.1080/15376516.2021.1903638 |
| [16] | Yamaguchi NH. Smoking, immunity, and DNA damage[J]. Transl Lung Cancer Res, 2019, 8(): S3-6. doi:10.21037/tlcr.2019.03.02 |
| [17] | Heinzelmann K, Fysikopoulos A, Jaquin TJ, et al. Pulmonary-delivered Anticalin Jagged-1 antagonists reduce experimental airway mucus hyperproduction and obstruction[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2025, 328(1): L75-92. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00059.2024 |
| [18] | Carpenter J, Wang Y, Gupta R, et al. Assembly and organization of the N-terminal region of mucin MUC5AC: indications for structural and functional distinction from MUC5B[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2021, 118(39): e2104490118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2104490118 |
| [19] | Yadav E, Yadav N, Hus A, et al. Aquaporins in lung health and disease: Emerging roles, regulation, and clinical implications[J]. Respir Med, 2020, 174: 106193. doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2020.106193 |
| [20] | Hill DB, Button B, Rubinstein M, et al. Physiology and pathophysiology of human airway mucus[J]. Physiol Rev, 2022, 102(4): 1757-836. doi:10.1152/physrev.00004.2021 |
| [21] | Fokkens WJ, Backer V, Lund VJ, et al. Pocket guide: biologics in upper and lower airways in adults[J]. Rhinology, 2025, 63(2): 242-4. |
| [22] | Bae CH, Na HG, Choi YS, et al. Clusterin induces MUC5AC expression via activation of NF-κB in human airway epithelial cells[J]. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol, 2018, 11(2): 124-32. doi:10.21053/ceo.2017.00493 |
| [23] | Fu HT, Zhang Y, Zhang P, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α promotes airway mucus hypersecretion by repressing miR-146a-5p and miR-134-5p levels in human airway epithelial cells[J]. Transl Cancer Res, 2021, 10(9): 4047-56. doi:10.21037/tcr-20-3375 |
| [24] | Liu HL, Zhou L, Wang XF, et al. Dexamethasone upregulates macro-phage PIEZO1 via SGK1, suppressing inflammation and increasing ROS and apoptosis[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2024, 222: 116050. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116050 |
| [25] | Zhang MY, Lu Y, Liu LL, et al. Role and mechanism of miR-181a-5p in mice with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by regulating HMGB1 and the NF‑κB pathway[J]. Cells Tissues Organs, 2023, 212(3): 245-57. doi:10.1159/000522155 |
| [1] | 夏冰, 彭进, 丁九阳, 王杰, 唐国伟, 刘国杰, 王沄, 万昌武, 乐翠云. ATF3通过NF-κB信号通路调控动脉粥样硬化斑块内的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1131-1142. |
| [2] | 左涵珺, 段兆达, 王朝, 郭涛, 石金沙, 石浩龙, 李娟娟. 天麻素经PI3K/AKT通路改善新生大鼠缺氧缺血性脑损伤后小胶质细胞介导的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1712-1719. |
| [3] | 何 程, 陈 炜, 张念志, 栾 军, 王三凤, 张 尤. 参七虫草方通过ASS1/src/STAT3信号通路改善肺纤维化大鼠的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 644-651. |
| [4] | 包汉生, 王苏童, 吕穆杰, 王永成, 姜 萍, 李 晓. 激活α7nAchR促进肥胖小鼠的脂肪稳态和米色脂肪生成及产热作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 499-506. |
| [5] | 孙秀颀, 蔡静, 张安邦, 庞博, 陈春艳, 查琪琪, 全菲, 叶涛. 电针预处理通过抑制NF-kB/NLRP3信号通路介导炎症和凋亡改善大鼠脑卒中后痉挛[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2102-2109. |
| [6] | 姚宏, 刘珂娣, 刘澄曌, 李伟红, 代旗, 赵石, 丁子恒, 王鹤霏, 葛晓静, 卫培峰, 段佳林, 奚苗苗. 五谷虫通过抑制免疫应激-补体活化缓解咪喹莫特诱导的小鼠银屑病样皮肤损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2121-2130. |
| [7] | 程蒙蒙, 刘新光, 魏焱鑫, 邢小香, 刘览, 辛楠, 赵鹏. 通塞颗粒阻抑巨噬细胞炎症反应改善大鼠慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(10): 1995-2003. |
| [8] | 徐 晨, 李春颖, 王 胜. 益肺健脾方降低香烟烟雾诱导的人支气管上皮细胞的炎性损伤和黏液高分泌:基于抑制TLR4/NF-κB信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(4): 507-515. |
| [9] | 李 晒, 李 丽, 闵思敏, 刘赛赛, 秦志文, 熊志尚, 徐建国, 王博文, 丁渡山, 赵士弟. 大豆异黄酮可减轻大鼠脑缺血/再灌注损伤:基于抑制铁死亡及炎症级联反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 323-330. |
| [10] | 曹天然, 刘青芳, 潘美民, 张雪红. LncRNA SNHG8通过抑制miR-494-3p表达减轻脑缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(12): 2015-2022. |
| [11] | 秦 娜, 黄 林, 董 瑞, 李 芬, 唐叙恒, 曾振华, 王兴民, 杨 翃. 虎杖苷减轻大鼠创伤性颅脑损伤后的肠损伤:基于激活Sirt1介导的SOD2和HMGB1去乙酰化抑制氧化应激和炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(1): 93-100. |
| [12] | 孔令恒, 徐臣年, 孙 娜, 梁 飞, 魏 明, 苏兴利. 褪黑素通过激活Nrf2信号和抑制炎症反应减轻小鼠心脏缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(8): 1165-1170. |
| [13] | 王德奖, 李 挺, 徐颖怡, 杨雪雯, 何铭垣, 张智勇, 吴 炜, 燕 翼. 富血小板血浆可减轻大鼠急性心肌缺血-再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(5): 775-782. |
| [14] | 霍 妍, 赵安鹏, 宋晶燕, 李加忠, 王 荣. 槟榔多酚对急进高原大鼠具有抗缺氧作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(5): 671-678. |
| [15] | 华 慧, 董 昕, 张雨钊, 方 凡, 张蓓蓓, 李向阳, 于 倩, 郑葵阳, 颜 超. 华支睾吸虫来源的分子伴侣rCsHscB对小鼠慢性溃疡性结肠炎有治疗作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(5): 664-670. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||