南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (10): 2199-2209.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.10.16
• • 上一篇
张可妮1( ), 乔通1, 尹林1, 黄菊2,3, 耿志军2,3, 左芦根3, 胡建国1,3, 李静1,3(
), 乔通1, 尹林1, 黄菊2,3, 耿志军2,3, 左芦根3, 胡建国1,3, 李静1,3( )
)
收稿日期:2025-05-14
出版日期:2025-10-20
发布日期:2025-10-24
通讯作者:
李静
E-mail:kenizhang0906@163.com;lijingbyfy@bbmu.edu.cn
作者简介:张可妮,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: kenizhang0906@163.com
基金资助:
Keni¹ ZHANG1( ), Tong¹ QIAO1, Lin¹ YIN1, Ju HUANG2,3, Zhijun GENG2,3, Lugen³ ZUO3, Jianguo HU1,3, Jing LI1,3(
), Tong¹ QIAO1, Lin¹ YIN1, Ju HUANG2,3, Zhijun GENG2,3, Lugen³ ZUO3, Jianguo HU1,3, Jing LI1,3( )
)
Received:2025-05-14
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-10-24
Contact:
Jing LI
E-mail:kenizhang0906@163.com;lijingbyfy@bbmu.edu.cn
摘要:
目的 探讨天然黄酮类化合物球松素(PSB)调控巨噬细胞肠道浸润缓解葡聚糖硫酸钠(DSS)诱导的小鼠结肠炎的作用机制。 方法 将30只C57BL/6雄性小鼠随机分为对照组(WT)、DSS模型组(DSS)及PSB干预组(30、60、120 mg/kg),6只/组。通过体质量变化、疾病活动指数(DAI)、结肠长度及组织病理学评分评估结肠炎表型;免疫荧光检测紧密连接蛋白ZO-1/Claudin-1表达;流式细胞术定量分析结肠巨噬细胞(CD45+F4/80+CD11b+)浸润及极化表型(M1:iNOS+;M2:CD206+);ELISA及RT-qPCR检测炎症因子(TNF-α、IL-6)及趋化因子(CCL2、CXCL10、CX3CL1)表达;Western blotting分析PI3K/AKT磷酸化水平;体外浓度梯度实验明确PSB抑制CCL2的最佳剂量;Transwell实验验证CCL2介导的巨噬细胞迁移;结合网络药理学预测关键靶点通路。 结果 预实验确定PSB 60 mg/kg为最佳治疗剂量,缓解DSS诱导的结肠炎症状:与DSS组相比,PSB组体质量下降减少(P<0.05),DAI评分降低(P<0.05),结肠长度恢复(P<0.05)。PSB上调紧密连接蛋白ZO-1/Claudin-1表达(P<0.05),抑制结肠固有层巨噬细胞浸润(F4/80阳性细胞显著减少,P<0.05)并调控其极化(抑制M1促炎亚群,激活M2修复亚群,P<0.05)。分子机制分析结果显示,PSB抑制肠上皮细胞PI3K/AKT磷酸化水平(P<0.05),抑制趋化因子CCL2表达(P<0.05),并阻断CCL2介导的RAW264.7细胞迁移,该效应可被外源性CCL2逆转。网络药理学富集分析及体外补救实现证明PI3K/AKT及CCL2趋化因子信号通路为核心调控靶点。 结论 球松素通过靶向抑制肠上皮细胞PI3K/AKT通路活化,减少CCL2分泌,进而阻断巨噬细胞趋化迁移并调控其极化表型,缓解DSS诱导的小鼠结肠炎,为炎症性肠病的天然化合物干预提供新策略。
张可妮, 乔通, 尹林, 黄菊, 耿志军, 左芦根, 胡建国, 李静. 球松素靶向肠上皮细胞PI3K/AKT/CCL2轴抑制巨噬细胞肠道浸润缓解葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2199-2209.
Keni¹ ZHANG, Tong¹ QIAO, Lin¹ YIN, Ju HUANG, Zhijun GENG, Lugen³ ZUO, Jianguo HU, Jing LI. Pinostrobin targets the PI3K/AKT/CCL2 axis in intestinal epithelial cells to inhibit intestinal macrophage infiltration and alleviate dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(10): 2199-2209.
| Gene name | Gene ID | Primer sequences (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | 16193 | F:TCTATACCACTTCACAAGTCGGA |
| R:GAATTGCCATTGCACAACTCTTT | ||
| TNF-α | 21926 | F:CAGGCGGTGCCTATGTCTC |
| R:CGATCACCCCGAAGTTCAGTAG | ||
| CCL2 | 20296 | F:TAAAAACCTGGATCGGAACCAAA |
| R:GCATTAGCTTCAGATTTACGGGT | ||
| CXCL10 | 15945 | F:CCAAGTGCTGCCGTCATTTTC |
| R:TCCCTATGGCCCTCATTCTCA | ||
| CX3CL1 | 20312 | F:CTGCCCTCACTAAAAATGGTGG |
| R:GAATTGCCATTGCACAACTCTTT | ||
| GAPDH | 14433 | F:TGGCCTTCCGTGTTCCTAC |
| R:GAGTTGCTGTTGAAGTCGCA |
表1 RT-qPCR的引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR
| Gene name | Gene ID | Primer sequences (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | 16193 | F:TCTATACCACTTCACAAGTCGGA |
| R:GAATTGCCATTGCACAACTCTTT | ||
| TNF-α | 21926 | F:CAGGCGGTGCCTATGTCTC |
| R:CGATCACCCCGAAGTTCAGTAG | ||
| CCL2 | 20296 | F:TAAAAACCTGGATCGGAACCAAA |
| R:GCATTAGCTTCAGATTTACGGGT | ||
| CXCL10 | 15945 | F:CCAAGTGCTGCCGTCATTTTC |
| R:TCCCTATGGCCCTCATTCTCA | ||
| CX3CL1 | 20312 | F:CTGCCCTCACTAAAAATGGTGG |
| R:GAATTGCCATTGCACAACTCTTT | ||
| GAPDH | 14433 | F:TGGCCTTCCGTGTTCCTAC |
| R:GAGTTGCTGTTGAAGTCGCA |
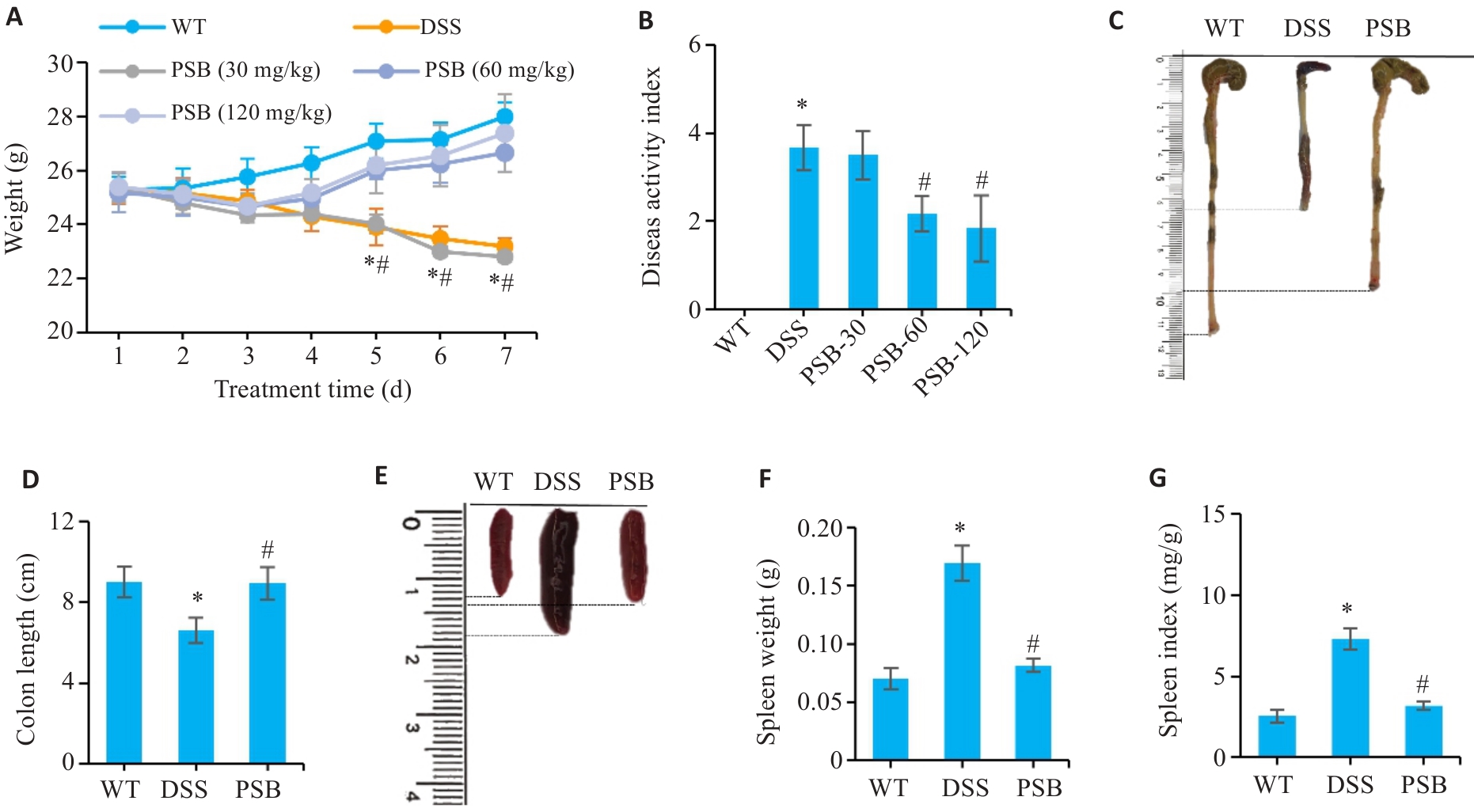
图1 PSB对小鼠DSS诱导的结肠炎症状的影响
Fig.1 Effect of pinostrobin (PSB) on symptoms of dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. A: Daily body weight changes in wild-type (WT), DSS, PSB-30 mg/kg, PSB-60 mg/kg and PSB-120 mg/kg groups. B: Disease activity index (DAI) scores in the 5 groups. C: Representative images of the mouse colon. D: Colon lengths of the mice. E: Representative images of mouse spleens. F: Spleen weight. G: Spleen index. *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs DSS.
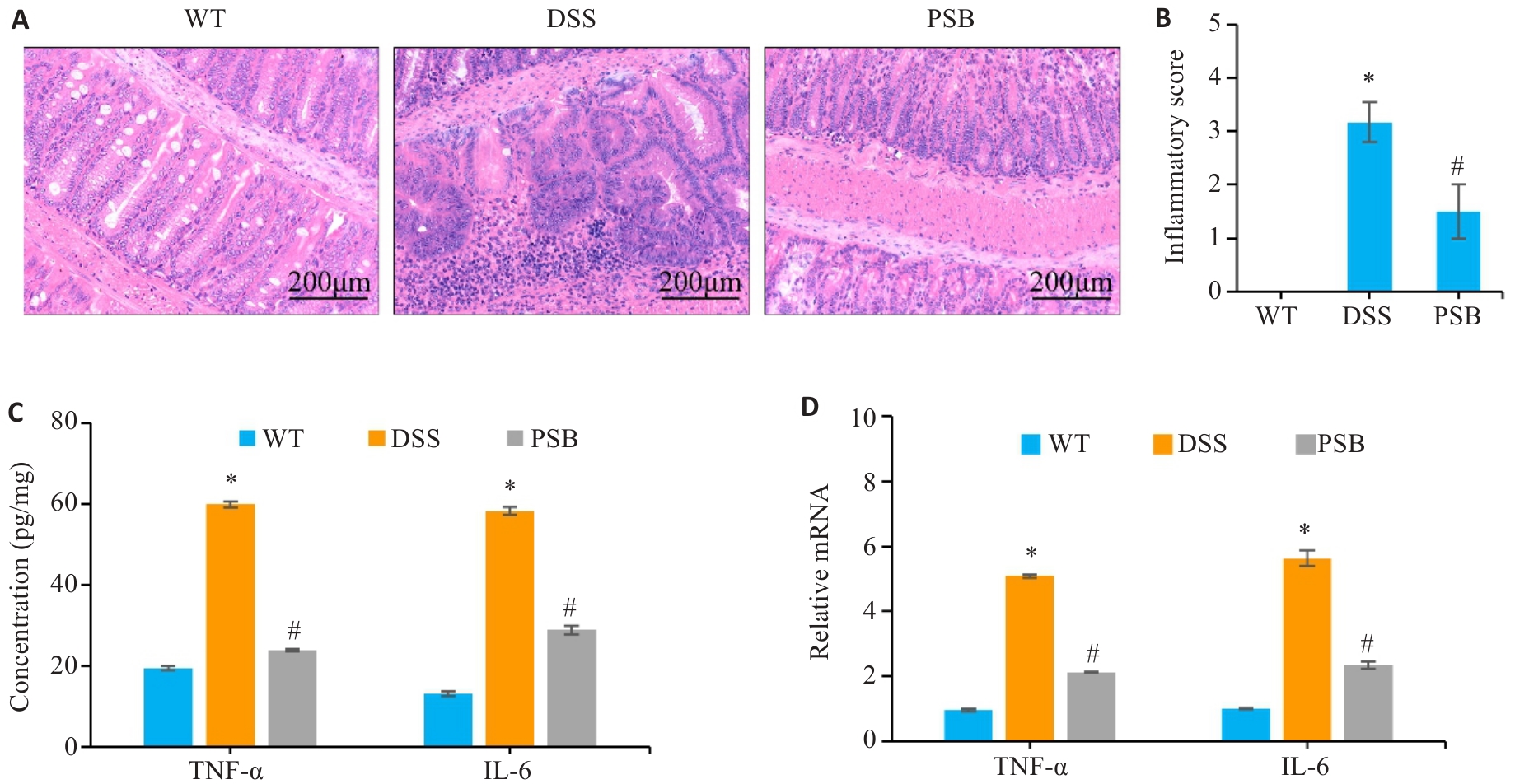
图2 PSB对小鼠实验性结肠炎肠组织损伤及炎症的影响
Fig.2 Effect of PSB on intestinal tissue injury and inflammation in the mouse models of colitis. A: HE staining of mouse colon tissues. B: Inflammation scores of mouse colon tissue. C: Levels of inflammatory factors (TNF-α and IL-6) in the colonic mucosa detected by ELISA. D: Relative mRNA expressions of TNF-α and IL-6 in the colonic mucosa detected by RT-qPCR. *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs DSS.
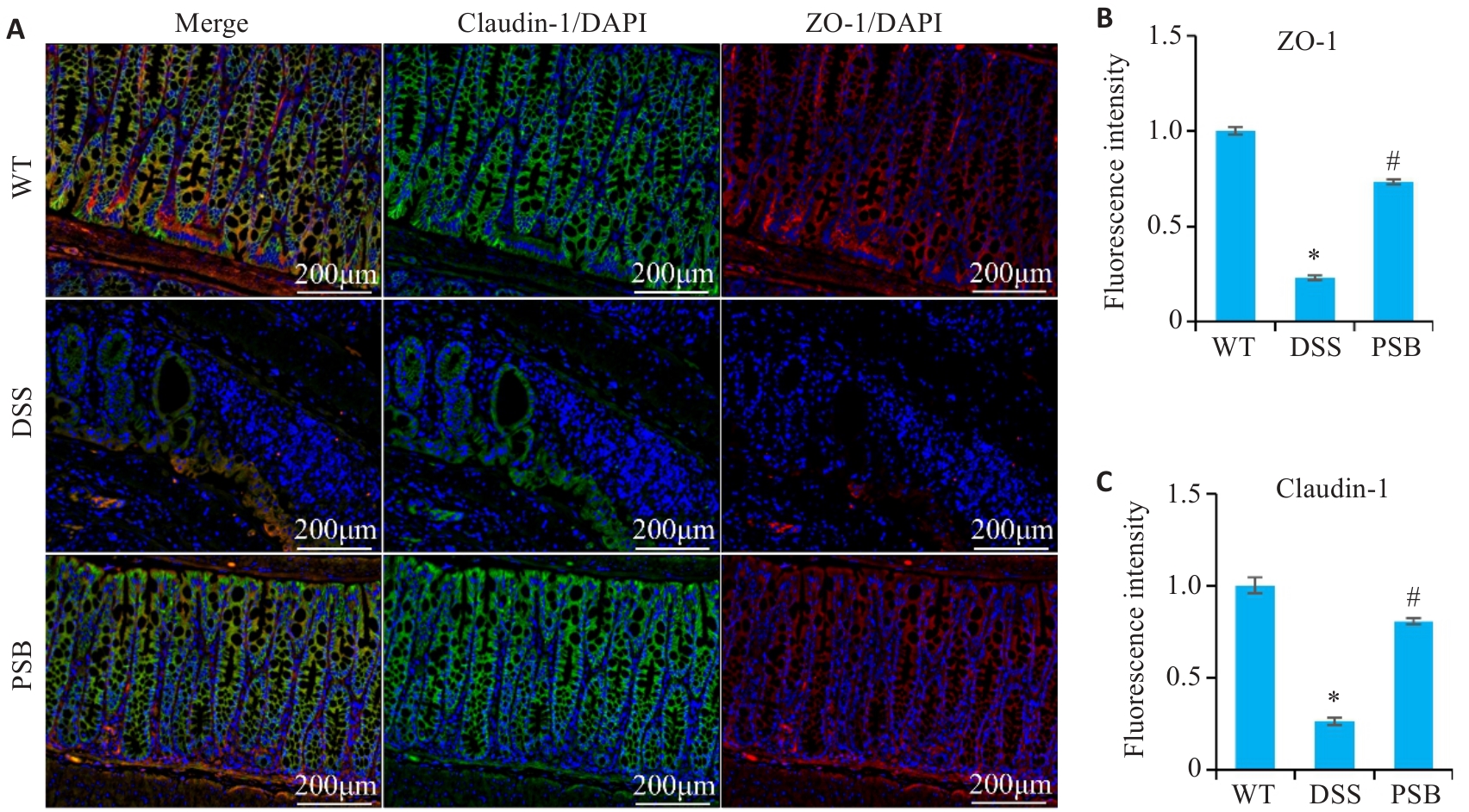
图3 PSB对小鼠实验性结肠炎肠屏障损伤的影响
Fig.3 Effect of PSB on intestinal barrier damage in mice with DSS-induced colitis. A: Immunofluorescence staining of ZO-1 and Claudin-1 in the colon of the mice. B: Fluorescence intensity of ZO-1. C: Fluorescence intensity of claudin-1. *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs DSS.
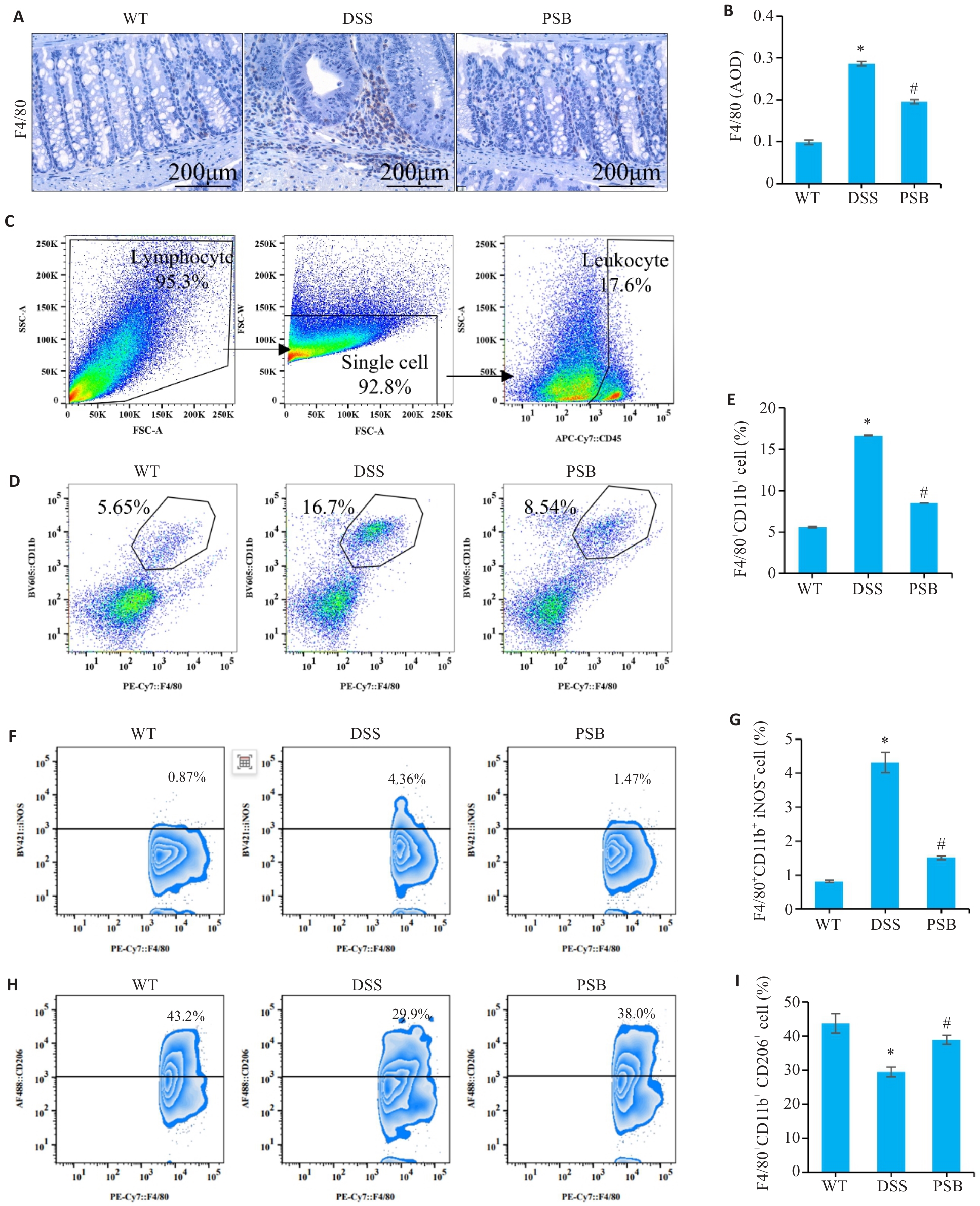
图4 PSB抑制对小鼠实验性结肠炎巨噬细胞浸润和极化的影响
Fig.4 Effect of PSB on macrophage infiltration and polarization in the mouse models of colitis. A: Expression of F4/80 analyzed by immunohistochemical staining. B: Average optical density (AOD) of F4/80. C: Flow cytometry gating strategy. D, E: Assessment of macrophage percentage (CD45+F4/80+CD11b+ population) in mouse intestinal tissue by flow cytometry. F,G: Assessment of M1 macrophage percentage (F4/80+ CD11b+iNOS+ population) in mouse intestinal tissue by flow cytometry. H,I: Assessment of M2 Macrophage percentage (F4/80+ CD11b+CD206+ population) in mouse intestinal tissue by flow cytometry. *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs DSS.
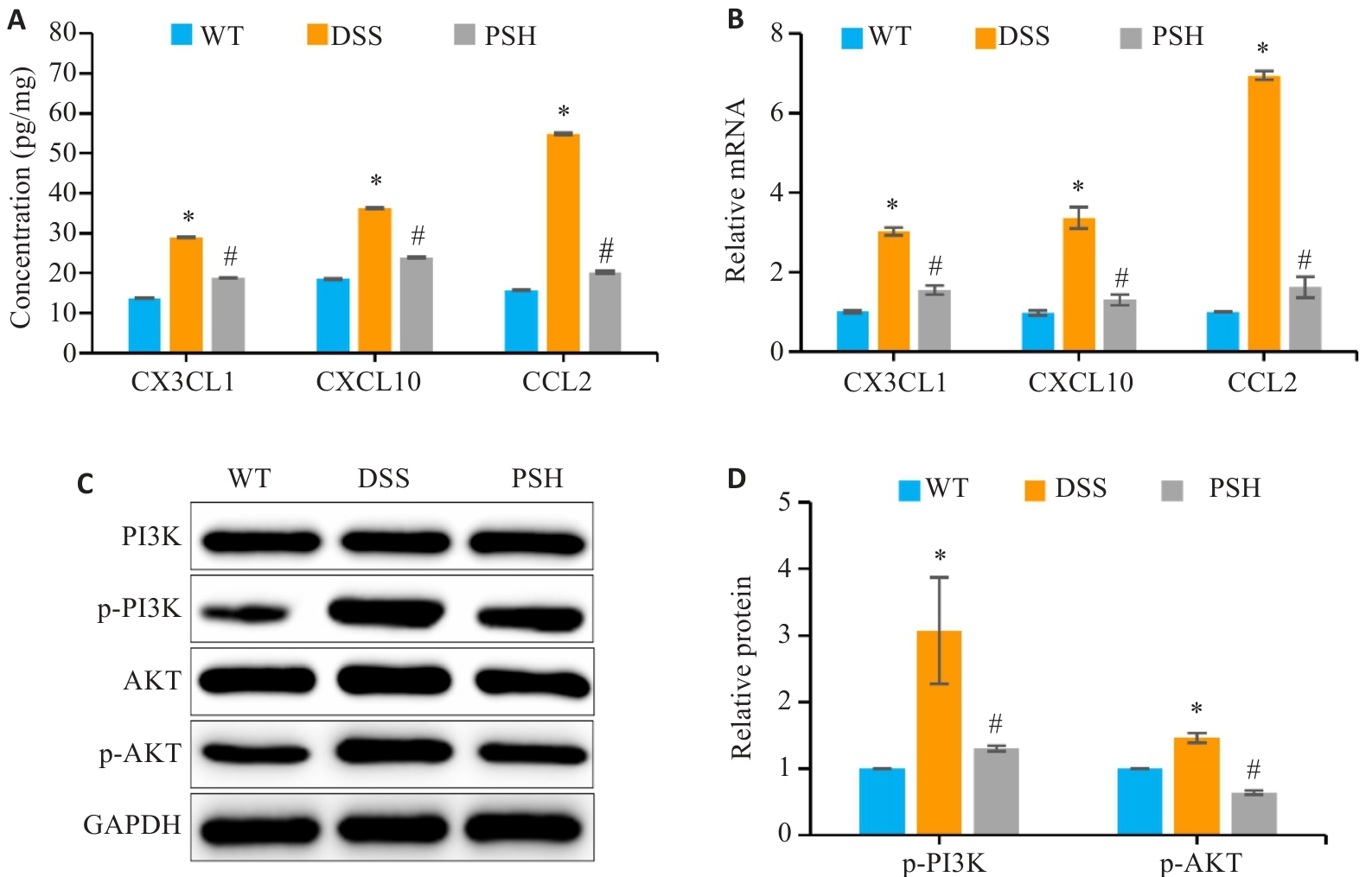
图6 PSB对巨噬细胞趋化因子和PI3K/AKT信号通路的影响
Fig.6 Effects of PSB on macrophage chemokines and the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. A: Levels of chemokines (CCL2, CXCL10 and CX3CL1) in the colonic mucosa detected by ELISA. B: Relative mRNA expressions of chemokines (CCL2, CXCL10 and CX3CL1) in the colonic mucosa detected by RT-qPCR. C, D: Western blot analysis of p-PI3K and p-AKT, the key proteins of the PI3K/AKT pathway, in mouse intestinal mucosal tissues. *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs DSS.
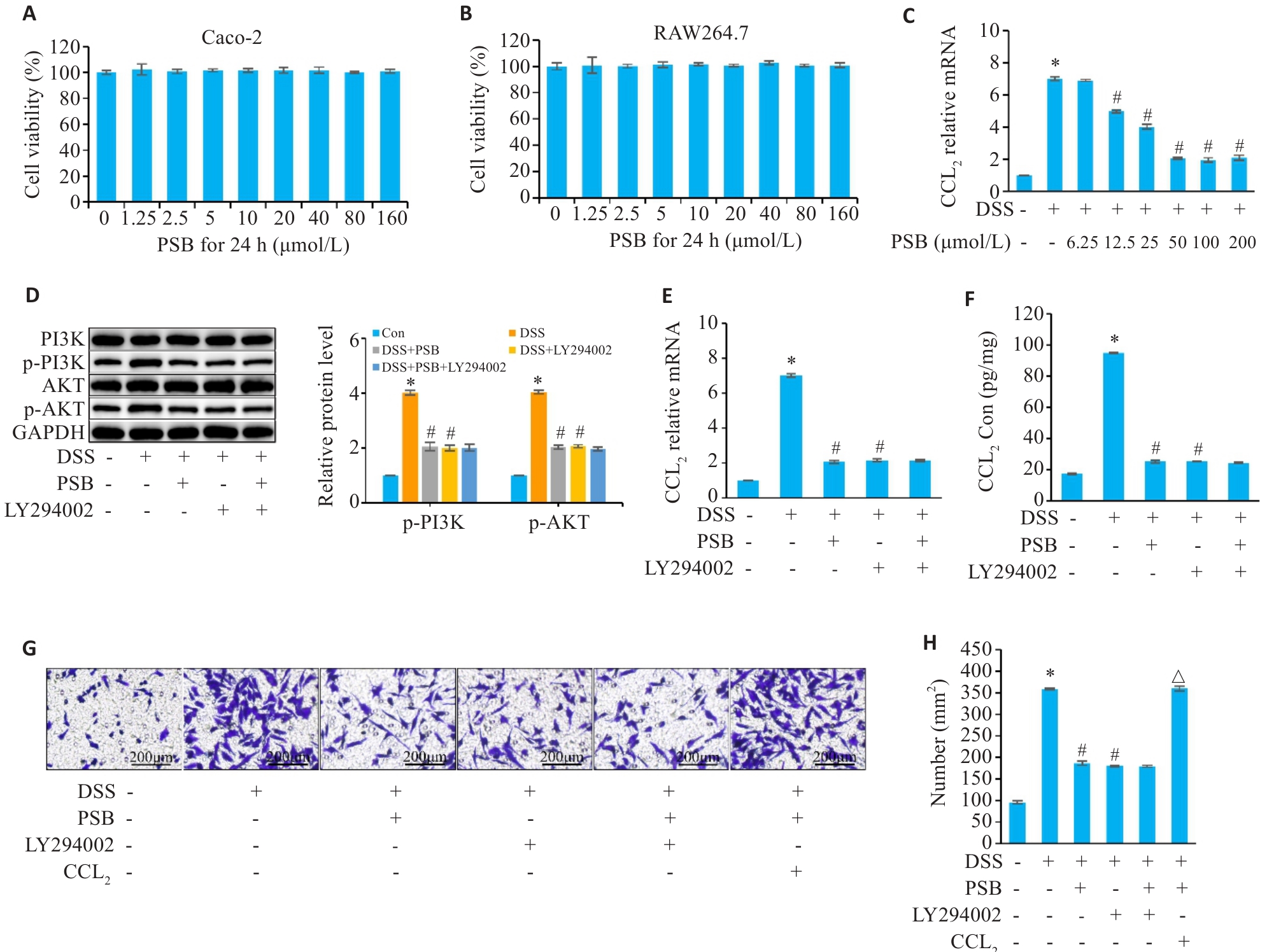
图7 PSB调控肠上皮细胞PI3K/AKT/CCL2信号轴对巨噬细胞趋化的影响
Fig.7 Effect of PSB on the chemotaxis of macrophages by regulating the PI3K/AKT/CCL2 signaling axis in intestinal epithelial cells. A, B: Determination of the cytotoxicity of PSB in Caco-2 and RAW264.7 cells by CCK-8 assay. C: Concentration-dependent inhibition of DSS-induced CCL2 mRNA expression by PSB (RT-qPCR). D: Western blot bands and quantitative analysis (p-PI3K and p-AKT). E, F: Expression levels of CCL2 mRNA (RT-qPCR) and protein (ELISA). G,H: Transwell migration images (crystal violet staining) and statistics of the number of migrated cells. *P<0.05 vs Con; #P<0.05 vs DSS; △P<0.05 vs DSS+PSB.
| [1] | Zhang YZ, Li YY. Inflammatory bowel disease: pathogenesis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(1): 91-9. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.91 |
| [2] | Kaplan GG. The global burden of IBD: from 2015 to 2025[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 12(12): 720-7. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2015.150 |
| [3] | Chen YY, Cui WW, Li X, et al. Interaction between commensal bacteria, immune response and the intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 761981. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.761981 |
| [4] | 郭 琳, 耿 燕, 岳远佳, 等. 猴头菌粉与5-氨基水杨酸联用抑制小鼠急性溃疡性结肠炎并提高肠道共生菌Parabacteroides distasonis丰度[J]. 菌物学报, 2021, 40(5): 1148-59. |
| [5] | van Deventer SJ. Review article: chemokine production by intestinal epithelial cells: a therapeutic target in inflammatory bowel disease?[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 1997, 11(): 116-20;discussion120-1. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.1997.tb00816.x |
| [6] | Kotla NG, Rochev Y. IBD disease-modifying therapies: insights from emerging therapeutics[J]. Trends Mol Med, 2023, 29(3): 241-53. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2023.01.001 |
| [7] | Zhu YF, Yang SH, Zhao N, et al. CXCL8 chemokine in ulcerative colitis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, 138: 111427. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111427 |
| [8] | Alghamdi KS, Kassar RH, Farrash WF, et al. Key disease-related genes and immune cell infiltration landscape in inflammatory bowel disease: a bioinformatics investigation[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(17): 9751. doi:10.3390/ijms25179751 |
| [9] | Geng ZJ, Zuo LG, Li J, et al. Ginkgetin improved experimental colitis by inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis through EGFR/PI3K/AKT signaling[J]. FASEB J, 2024, 38(14): e23817. doi:10.1096/fj.202400211rr |
| [10] | Pozzi S, Satchi-Fainaro R. The role of CCL2/CCR2 axis in cancer and inflammation: The next frontier in nanomedicine[J]. Adv Drug Deliv Rev, 2024, 209: 115318. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2024.115318 |
| [11] | Trivedi PJ, Adams DH. Chemokines and chemokine receptors as therapeutic targets in inflammatory bowel disease; pitfalls and promise[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2018, 12(): S641-52. doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjx145 |
| [12] | Patel NK, Jaiswal G, Bhutani KK. A review on biological sources, chemistry and pharmacological activities of pinostrobin[J]. Nat Prod Res, 2016, 30(18): 2017-27. doi:10.1080/14786419.2015.1107556 |
| [13] | 朱学鑫, 庞敏霞, 黄燕芬, 等. 山核桃叶球松素制备工艺研究[J]. 中国现代应用药学, 2017, 34(11): 1512-6. |
| [14] | González AS, Soto Tellini VH, Benjumea Gutiérrez DM. Study of the dermal anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and analgesic activity of pinostrobin[J]. Heliyon, 2022, 8(9): e10413. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10413 |
| [15] | Abdelwahab SI, Mohan S, Abdulla MA, et al. The methanolic extract of Boesenbergia rotunda (L.) Mansf. and its major compound pinostrobin induces anti-ulcerogenic property in vivo: possible involvement of indirect antioxidant action[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2011, 137(2): 963-70. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2011.07.010 |
| [16] | Shareef SH, Al-Medhtiy MH, Al Rashdi AS, et al. Hepatoprotective effect of pinostrobin against thioacetamide-induced liver cirrhosis in rats[J]. Saudi J Biol Sci, 2023, 30(1): 103506. doi:10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.103506 |
| [17] | Murthy SN, Cooper HS, Shim H, et al. Treatment of dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine colitis by intracolonic cyclosporin[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 1993, 38(9): 1722-34. doi:10.1007/bf01303184 |
| [18] | 张 敏, 刘生宝, 张 诺, 等. 改进型“瑞士卷”法在小鼠肠道组织切片中的应用[J]. 中华病理学杂志, 2024,53(04):393-7. |
| [19] | Le Naour J, Montégut L, Joseph A, et al. Improved Swiss-rolling method for histological analyses of colon tissue[J]. MethodsX, 2022, 9: 101630. doi:10.1016/j.mex.2022.101630 |
| [20] | Schultz M, Tonkonogy SL, Sellon RK, et al. IL-2-deficient mice raised under germfree conditions develop delayed mild focal intestinal inflammation[J]. Am J Physiol, 1999, 276(6): G1461-72. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.1999.276.6.g1461 |
| [21] | Rath HC, Herfarth HH, Ikeda JS, et al. Normal luminal bacteria, especially Bacteroides species, mediate chronic colitis, gastritis, and arthritis in HLA-B27/human beta2 microglobulin transgenic rats[J]. J Clin Invest, 1996, 98(4): 945-53. doi:10.1172/jci118878 |
| [22] | Mallawaaratchy DM, Mactier S, Kaufman KL, et al. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor LY294002, decreases aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, chaperones and glycolytic enzymes in human HT-29 colorectal cancer cells[J]. J Proteomics, 2012, 75(5): 1590-9. doi:10.1016/j.jprot.2011.11.032 |
| [23] | Athapaththu AMGK, Sanjaya SS, Lee KT, et al. Pinostrobin suppresses the α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone-induced melanogenic signaling pathway[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(1): 821. doi:10.3390/ijms24010821 |
| [24] | Gomes RN, Teixeira-Cunha MGA, Figueiredo RT, et al. Bacterial clearance in septic mice is modulated by MCP-1/CCL2 and nitric oxide[J]. Shock, 2013, 39(1): 63-9. doi:10.1097/shk.0b013e31827802b5 |
| [25] | Yu KY, Li QQ, Sun X, et al. Bacterial indole-3-lactic acid affects epithelium-macrophage crosstalk to regulate intestinal homeostasis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2023, 120(45): e2309032120. doi:10.1073/pnas.2309032120 |
| [26] | Zhang HL, Zheng YJ, Pan YD, et al. A mutation that blocks integrin α4β7 activation prevents adaptive immune-mediated colitis without increasing susceptibility to innate colitis[J]. BMC Biol, 2020, 18(1): 64. doi:10.1186/s12915-020-00784-6 |
| [27] | Hou QK, Zhu SL, Zhang CR, et al. Berberine improves intestinal epithelial tight junctions by upregulating A20 expression in IBS-D mice[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 118: 109206. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109290 |
| [28] | Borges GA, Elias ST, Amorim B, et al. Curcumin downregulates the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway and inhibits growth and progression in head and neck cancer cells[J]. Phytother Res, 2020, 34(12): 3311-24. doi:10.1002/ptr.6780 |
| [29] | Mei CX, Meng FX, Wang X, et al. CD30L is involved in the regulation of the inflammatory response through inducing homing and differentiation of monocytes via CCL2/CCR2 axis and NF-κB pathway in mice with colitis[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2022, 110: 108934. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108934 |
| [30] | Gholamalizadeh H, Ensan B, Sukhorukov VN, et al. Targeting the CCL2-CCR2 signaling pathway: potential implications of statins beyond cardiovascular diseases[J]. J Pharm Pharmacol, 2024, 76(2): 138-53. doi:10.1093/jpp/rgad112 |
| [31] | Mostafa DK, Eissa MM, Ghareeb DA, et al. Resveratrol protects against Schistosoma mansoni-induced liver fibrosis by targeting the Sirt-1/NF-κB axis[J]. Inflammopharmacology, 2024, 32(1): 763-75. doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01382-y |
| [32] | Zhang H, Shan Y, Wu Y, et al. Berberine suppresses LPS-induced inflammation through modulating Sirt1/NF-κB signaling pathway in RAW264.7 cells[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2017, 52: 93-100. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2017.08.032 |
| [33] | Zhao JJ, Guo MM, Yan YP, et al. The miR-7/EGFR axis controls the epithelial cell immunomodulation and regeneration and orchestrates the pathology in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. J Adv Res, 2024, 57: 119-34. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2023.04.011 |
| [34] | Atarashi K, Tanoue T, Ando M, et al. Th17 cell induction by adhesion of microbes to intestinal epithelial cells[J]. Cell, 2015, 163(2): 367-80. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.058 |
| [35] | He J, Song YJ, Li GP, et al. Fbxw7 increases CCL2/7 in CX3CR1hi macrophages to promote intestinal inflammation[J]. J Clin Invest, 2019, 129(9): 3877-93. doi:10.1172/jci123374 |
| [36] | Carson WF, Salter-Green SE, Scola MM, et al. Enhancement of macrophage inflammatory responses by CCL2 is correlated with increased miR-9 expression and downregulation of the ERK1/2 phosphatase Dusp6[J]. Cell Immunol, 2017, 314: 63-72. doi:10.1016/j.cellimm.2017.02.005 |
| [1] | 何榕茂, 方泽扬, 张芸芸, 吴友谅, 梁世秀, 计涛, 陈科全, 王斯琪. 铁死亡相关基因对溃疡性结肠炎具有诊断预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1927-1937. |
| [2] | 饶璐, 丁家和, 魏江平, 阳勇, 张小梅, 王计瑞. 槐花通过抑制PI3K/AKT通路减轻炎症反应治疗银屑病[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1989-1996. |
| [3] | 刘辰菲, 张玮, 曾尧, 梁艳, 王梦婷, 张明芳, 李新元, 王凤超, 杨燕青. 2,6-二甲氧基-1,4-苯醌通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化改善葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1654-1662. |
| [4] | 申琳, 宋翠豪, 王聪敏, 高西, 安俊红, 李承新, 梁斌, 李霞. 溃疡性结肠炎并发坏疽性脓皮病患者发生营养风险的因素及预测模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 514-521. |
| [5] | 徐皓男, 张放, 黄钰莹, 姚其盛, 管悦琴, 陈浩. 百蕊草通过调节肠道菌群和调控EGFR/PI3K/Akt信号通路改善小鼠抗生素相关性腹泻[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [6] | 裴月娇, 刘慧敏, 昕宇, 刘波. miR-124通过调控PI3K/AKT信号通路改善睡眠剥夺大鼠认知功能[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 340-346. |
| [7] | 张玉如, 万磊, 方昊翔, 李方泽, 王丽文, 李柯霏, 闫佩文, 姜辉. miR-155-5p介导PIK3R1负调控PI3K/AKT信号通路促进原发性干燥综合征人唾液腺上皮细胞增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 65-71. |
| [8] | 张先恒, 刘健, 韩琦, 陈一鸣, 丁香, 陈晓露. 黄芩清热除痹胶囊通过PTEN/PI3K/AKT信号通路改善痛风性关节炎大鼠的炎症反应及尿酸、脂质代谢失衡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1450-1458. |
| [9] | 赵娜, 沈梦迪, 赵睿, 奥迪, 骆泽谭, 张银亮, 徐志东, 范方田, 郑海伦. 血根碱通过调控Nrf2/NF-κB通路缓解小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1467-1475. |
| [10] | 于官正, 程炜强, 涂星, 张满, 李鸿, 聂娟. 隔山消治疗溃疡性结肠炎的机制:基于UPLC-QE-MS、网络药理学及代谢组学技术[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1485-1496. |
| [11] | 向珊, 张宗星, 江露, 刘道忠, 李玮怡, 包卓玛, 田瑞, 陈丹, 袁林. 三百棒通过调控PI3K/Akt信号通路改善胶原诱导性类风湿性关节炎大鼠的血管翳[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1582-1588. |
| [12] | 王媛媛, 陈腾, 从小凡, 李依然, 陈蕊, 张配, 孙小锦, 赵素容. 扁蒴藤素通过活性氧调控PI3K/AKT通路增强顺铂诱导鼻咽癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 904-912. |
| [13] | 邱建国, 邱一桐, 李国荣, 张林生, 郑雪, 姚泳江, 王熙丹, 黄海阳, 张凤敏, 苏冀彦, 郑学宝, 黄晓其. 黄芩汤通过调控内质网应激减轻小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2172-2183. |
| [14] | 宋泽军, 董海滨, 马 娜, 任渝棠, 姜 泊. 改进的MAYO内镜评分对活动期溃疡性结肠炎疗效有较高的评估价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1204-1213. |
| [15] | 张雪芳, 陈延华, 李宗恒, 尚 靖, 袁泽婷, 邓皖利, 骆 莺, 韩 娜, 殷佩浩, 殷 军. 六神丸治疗小鼠结肠炎相关性结直肠癌的作用机制:基于网络药理学和体内验证方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1051-1062. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||