南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (11): 2172-2183.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.11.14
• • 上一篇
邱建国1,2( ), 邱一桐1, 李国荣1, 张林生1, 郑雪1,3, 姚泳江1, 王熙丹2, 黄海阳2, 张凤敏2, 苏冀彦4, 郑学宝1,3(
), 邱一桐1, 李国荣1, 张林生1, 郑雪1,3, 姚泳江1, 王熙丹2, 黄海阳2, 张凤敏2, 苏冀彦4, 郑学宝1,3( ), 黄晓其1,3(
), 黄晓其1,3( )
)
收稿日期:2024-07-07
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2024-11-29
通讯作者:
郑学宝,黄晓其
E-mail:1194883143@qq.com;xuebaozheng@ gzucm.edu.cn;huangxiaoqi@gzucm.edu.cn
作者简介:邱建国,硕士,E-mail: 1194883143@qq.com
基金资助:
Jianguo QIU1,2( ), Yitong QIU1, Guorong LI1, Linsheng ZHANG1, Xue ZHENG1,3, Yongjiang YAO1, Xidan WANG2, Haiyang HUANG2, Fengmin ZHANG2, Jiyan SU4, Xuebao ZHENG1,3(
), Yitong QIU1, Guorong LI1, Linsheng ZHANG1, Xue ZHENG1,3, Yongjiang YAO1, Xidan WANG2, Haiyang HUANG2, Fengmin ZHANG2, Jiyan SU4, Xuebao ZHENG1,3( ), Xiaoqi HUANG1,3(
), Xiaoqi HUANG1,3( )
)
Received:2024-07-07
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-11-29
Contact:
Xuebao ZHENG, Xiaoqi HUANG
E-mail:1194883143@qq.com;xuebaozheng@ gzucm.edu.cn;huangxiaoqi@gzucm.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 观察黄芩汤对小鼠溃疡性结肠炎(UC)细胞凋亡的影响并探讨其作用机制。 方法 将雄性Balb/c小鼠随机分为:正常组、模型组、美沙拉嗪组(5-ASA,200 mg/kg)、黄芩汤低、中、高剂量组(HQDL,2.275 g/kg;HQDM,4.55 g/kg;HQDH,9.1 g/kg),8只/组。各组自由饮食,除正常组自由饮用无菌水外,其余各组小鼠自由饮用3% DSS溶液,持续7d以建立UC模型。取结肠组织采用HE、AB-PAS和TUNEL染色分别观察结肠损伤和细胞凋亡情况,采用ELISA法检测炎症因子表达变化;采用Western blotting、免疫组化和qRT-PCR法分别检测肠道化学屏障、机械屏障、内质网应激等相关指标的蛋白或基因表达变化。 结果 与模型组相比,黄芩汤干预下的UC小鼠,DAI评分和宏观评分下降(P<0.01),TUNEL染色荧光强度下降(P<0.01)。促炎因子IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-8表达减少(P<0.01),MUC2和TFF3的基因表达升高(P<0.05),Claudin-1、Occludin和E-cadherin的蛋白表达升高(P<0.05),GRP78、CHOP和Caspase-12的基因和蛋白表达下降(P<0.01)、PERK、eIF2α和IRE1α的磷酸化表达降低(P<0.05),Bcl-2/Bax蛋白表达比例升高(P<0.01)和Caspase-3的蛋白表达降低(P<0.01)。 结论 黄芩汤能够抑制UC小鼠的细胞凋亡反应并改善肠道屏障功能,其机制可能与PERK和IRE1α信号通路介导的内质网应激有关。
邱建国, 邱一桐, 李国荣, 张林生, 郑雪, 姚泳江, 王熙丹, 黄海阳, 张凤敏, 苏冀彦, 郑学宝, 黄晓其. 黄芩汤通过调控内质网应激减轻小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2172-2183.
Jianguo QIU, Yitong QIU, Guorong LI, Linsheng ZHANG, Xue ZHENG, Yongjiang YAO, Xidan WANG, Haiyang HUANG, Fengmin ZHANG, Jiyan SU, Xuebao ZHENG, Xiaoqi HUANG. Huangqin Decoction alleviates ulcerative colitis in mice by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2172-2183.
| Weight loss (%) | Feces consistency | Hemafecia | Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Normal | N/A | 0 |
| 1-5 | Mild soft | Slight bleeding | 1 |
| 5-10 | Soft and wet | Moderate bleeding | 2 |
| 10-20 | Half loose stool | Gross bleeding | 3 |
| >20 | loose stool | Blood clot around anus | 4 |
表 1 DAI评分量化表
Tab.1 Quantitative table of DAI score
| Weight loss (%) | Feces consistency | Hemafecia | Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Normal | N/A | 0 |
| 1-5 | Mild soft | Slight bleeding | 1 |
| 5-10 | Soft and wet | Moderate bleeding | 2 |
| 10-20 | Half loose stool | Gross bleeding | 3 |
| >20 | loose stool | Blood clot around anus | 4 |
| Inflammation degree | Inflammation range | Colonic crypt damage | Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| N/A | N/A | Normal | 0 |
| Mild inflammation | Inflammation of the mucosa | One-third of crypt damage | 1 |
| Moderate inflammation | Inflammation of the mucosa and submucosa | Two thirds of crypt damage | 2 |
| Severe inflammation | Inflammation of the mucosa and intestinal wall | Crypts disappeared but epithelium remains | 3 |
| Acute severe inflammation | Transmural inflammation | Both crypts and epithelium disappeared | 4 |
表 2 结肠组织病理学评分
Tab.2 Histopathological score of the colon
| Inflammation degree | Inflammation range | Colonic crypt damage | Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| N/A | N/A | Normal | 0 |
| Mild inflammation | Inflammation of the mucosa | One-third of crypt damage | 1 |
| Moderate inflammation | Inflammation of the mucosa and submucosa | Two thirds of crypt damage | 2 |
| Severe inflammation | Inflammation of the mucosa and intestinal wall | Crypts disappeared but epithelium remains | 3 |
| Acute severe inflammation | Transmural inflammation | Both crypts and epithelium disappeared | 4 |
| Gene | Orientation | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| MUC2 | Forward | AGGGCTCGGAACTCCAGAAA |
| Reverse | CCAGGGAATCGGTAGACATCG | |
| TFF3 | Forward | TTGCTGGGTCCTCTGGGATAG |
| Reverse | TACACTGCTCCGATGTGACAG | |
| AGR2 | Forward | ACAACTGACAAGCACCTTTCTC |
| Reverse | GTTTGAGTATCGTCCAGTGATGT | |
| GRP78 | Forward | ACTTGGGGACCACCTATTCCT |
| Reverse | GTTGCCCTGATCGTTGGCTA | |
| CHOP | Forward | AAGCCTGGTATGAGGATCTGC |
| Reverse | TTCCTGGGGATGAGATATAGGTG | |
| Caspase-12 | Forward | TTGGAAGGTAGGCAAGACTGGTTC |
| Reverse | TCAGTTCACCTGGGACCTCAAATG | |
| ATF4 | Forward | AACCTATAAAGGCTTGCGGC |
| Reverse | GATTTCGTGAAGAGCGCCAT | |
| XBP1s | Forward | AAGAACACGCTTGGGAATGG |
| Reverse | CTGCACCTGCTGCGGAC |
表 3 引物序列
Tab.3 Primer sequence
| Gene | Orientation | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| MUC2 | Forward | AGGGCTCGGAACTCCAGAAA |
| Reverse | CCAGGGAATCGGTAGACATCG | |
| TFF3 | Forward | TTGCTGGGTCCTCTGGGATAG |
| Reverse | TACACTGCTCCGATGTGACAG | |
| AGR2 | Forward | ACAACTGACAAGCACCTTTCTC |
| Reverse | GTTTGAGTATCGTCCAGTGATGT | |
| GRP78 | Forward | ACTTGGGGACCACCTATTCCT |
| Reverse | GTTGCCCTGATCGTTGGCTA | |
| CHOP | Forward | AAGCCTGGTATGAGGATCTGC |
| Reverse | TTCCTGGGGATGAGATATAGGTG | |
| Caspase-12 | Forward | TTGGAAGGTAGGCAAGACTGGTTC |
| Reverse | TCAGTTCACCTGGGACCTCAAATG | |
| ATF4 | Forward | AACCTATAAAGGCTTGCGGC |
| Reverse | GATTTCGTGAAGAGCGCCAT | |
| XBP1s | Forward | AAGAACACGCTTGGGAATGG |
| Reverse | CTGCACCTGCTGCGGAC |
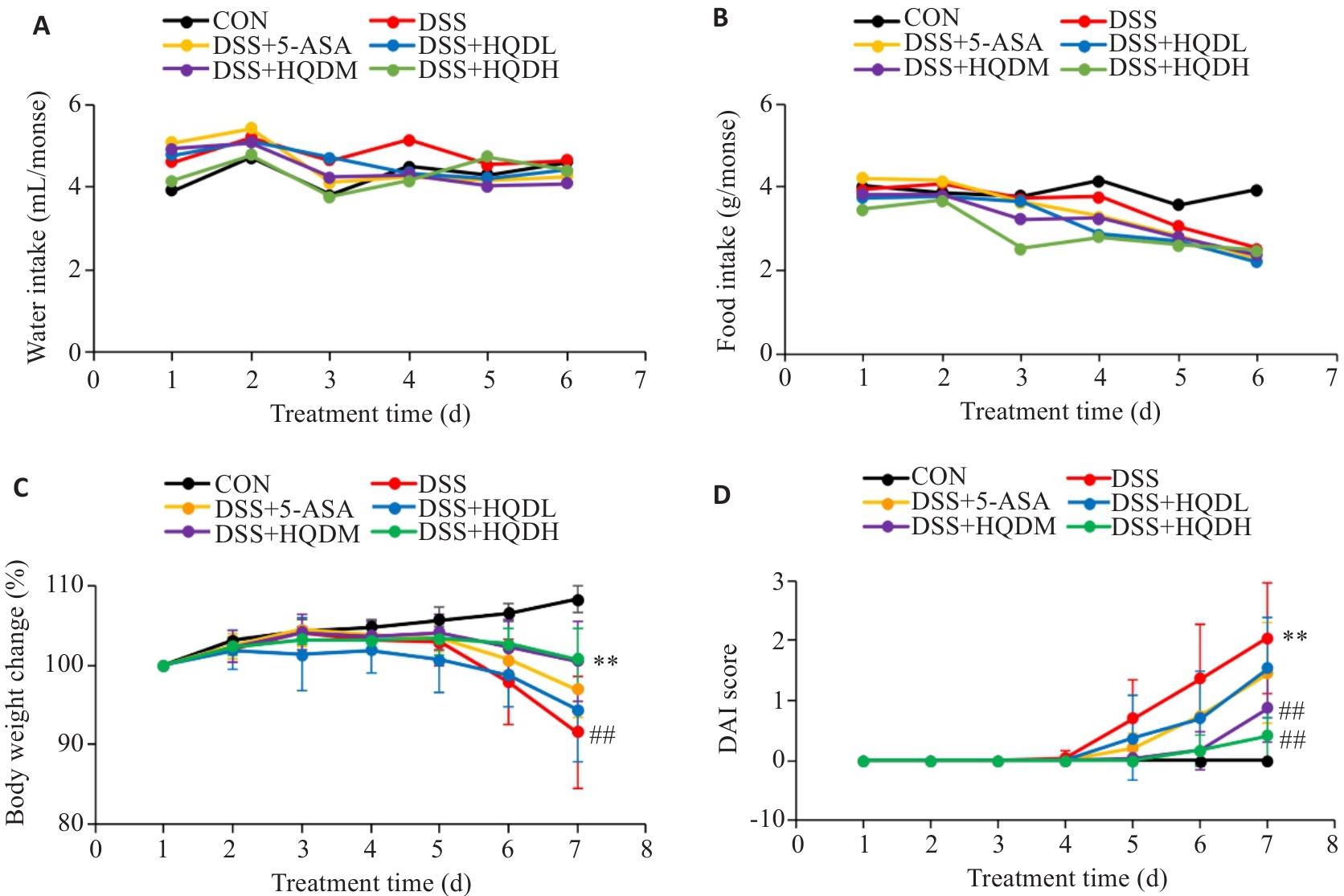
图 1 各组小鼠造模期间摄水、摄食及体质量、DAI评分动态变化
Fig.1 Changes of water intake (A), food intake (B), body weight (C) and DAI score (D) of the mice during modeling (Mean±SD, n=8). ##P<0.01 vs CON group; **P<0.01 vs DSS group.

图 2 黄芩汤对UC小鼠结肠长度及病理形态的影响
Fig. 2 Effect of Huangqin Decoction on colon length and pathology in UC mice. A: Colon length of the mice in each group. B: Statistics of colon length in each group. C: Histopathological score of the colon in each group (Mean±SD, n=8). D: HE staining of the colon tissues in each group (Original magnification: ×100 or 200). ##P<0.01 vs CON group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs DSS group.

图 3 黄芩汤对UC小鼠结肠上皮细胞凋亡的影响
Fig.3 Effect of Huangqin decoction on apoptosis of colonic epithelial cells in UC mice. A: TUNEL staining of the colon tissue in each group (×400 or 200). B: Mean fluorescence intensity in each group (Mean±SD, n=3) . ##P<0.01 vs CON group;**P<0.01 vs DSS group.

图 5 黄芩汤对UC小鼠黏蛋白和杯状细胞分泌的影响
Fig.5 Effect of Huangqin Decoction on mucin and goblet cell secretion in UC mice (Mean±SD, n=3). A: AB-PAS staining of mice in each group (×100, ×200). B:Expression of MUC2 MRNA. C: Expression of TFF3 MRNA. D: Expression of AGR2 mRNA. #P<0.005, ##P<0.01 vs CON group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs DSS group.

图 6 黄芩汤对UC小鼠结肠上皮机械屏障蛋白表达的影响
Fig 6 Effect of Huangqin Decoction on mechanical barrier function of the colonic epithelium in UC mice (Mean±SD, n=3). ##P<0.01 vs CON group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs DSS group. A: E-cadherin. B: Occludin. C: Claudin-1.

图 7 黄芩汤对UC小鼠GRP78基因和蛋白表达的影响
Fig.7 Effect of Huangqin Decoction on expression of GRP78 mRNA and protein in UC mice (Mean±SD, n=6). A: Immunohistochemistry staining of GRP78 protein of mice in each group (×200, ×400). B: Area fraction of GRP78 protein of mice in each group. C: Expression of GRP78 mRNA; ##P<0.01 vs CON group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs DSS group.

图 8 黄芩汤对UC小鼠内质网应激通路相关蛋白和基因的影响
Fig.8 Effect of Huangqin decoction on protein and mRNA expressions related to endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway in UC mice (Mean±SD, n=3). ##P<0.01 vs CON group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs DSS group. A: p-PERK/PERK. B: p-IRElα/IRElα. C: p-eIF2α/eIF2α. D: ATF4 mRNA level (fold change). E: XBPls mRNA level (fold change).

图 9 黄芩汤对UC小鼠ERS中CHOP和Caspase-12的影响
Fig.9 Effect of Huangqin Decoction on CHOP and Caspase-12 expressions in UC mice (Mean±SD, n=3). A: Immunohistochemistry staining of CHOP and Caspase-12 protein of mice in each group (×200, ×400). B-C: Area fraction of immunohistochemistry staining of CHOP and Caspase-12 protein of mice in each group. D-E: Expression of CHOP and Caspase-12 mRNA; ##P<0.01 vs CON group; **P<0.01 vs DSS group.

图 10 黄芩汤对UC小鼠Bcl-2、Bax、Cleaved-Caspase-3的影响
Fig 10 Effect of Huangqin Decoction on Bcl-2, Bax and Caspase-3 expressions in UC mice (Mean±SD, n=3). ##P<0.01 vs CON group; **P<0.01 vs DSS group. A: Bcl-2/Bax. B: Cleaved-Caspase-3/β-tubulin.
| 1 | Eisenstein M. Ulcerative colitis: towards remission[J]. Nature, 2018, 563(7730): S33. |
| 2 | Ungaro R, Mehandru S, Allen PB, et al. Ulcerative colitis[J]. Lancet, 2017, 389(10080): 1756-70. |
| 3 | Rieder F, Karrasch T, Ben-Horin S, et al. Results of the 2nd scientific workshop of the ECCO (III): basic mechanisms of intestinal healing[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2012, 6(3): 373-85. |
| 4 | Ho GT, Cartwright JA, Thompson EJ, et al. Resolution of inflammation and gut repair in IBD: translational steps towards complete mucosal healing[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2020, 26(8): 1131-43. |
| 5 | Adolph TE, Meyer M, Schwärzler J, et al. The metabolic nature of inflammatory bowel diseases[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 19(12): 753-67. |
| 6 | Solà-Tapias N, Vergnolle N, Denadai-Souza A, et al. The interplay between genetic risk factors and proteolytic dysregulation in the pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2020, 14(8): 1149-61. |
| 7 | Larabi A, Barnich N, Nguyen HTT. New insights into the interplay between autophagy, gut microbiota and inflammatory responses in IBD[J]. Autophagy, 2020, 16(1): 38-51. |
| 8 | Eugene SP, Reddy VS, Trinath J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and intestinal inflammation: a perilous union[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 543022. |
| 9 | van der Post S, Jabbar KS, Birchenough G, et al. Structural weakening of the colonic mucus barrier is an early event in ulcerative colitis pathogenesis[J]. Gut, 2019, 68(12): 2142-51. |
| 10 | Ren MT, Gu ML, Zhou XX, et al. Sirtuin 1 alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells in ulcerative colitis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25(38): 5800-13. |
| 11 | Naama M, Telpaz S, Awad A, et al. Autophagy controls mucus secretion from intestinal goblet cells by alleviating ER stress[J]. Cell Host Microbe, 2023, 31(3): 433-46. e4. |
| 12 | Coleman OI, Haller D. ER stress and the UPR in shaping intestinal tissue homeostasis and immunity[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 2825. |
| 13 | 黄 煌. 黄芩汤的拓展应用与适用人群特征[J]. 南京中医药大学学报, 2022, 38(9): 761-4. |
| 14 | 铉 力, 王晓红, 胡 兵, 等. 复方黄芩汤治疗湿热型溃疡性结肠炎临床观察[J]. 光明中医, 2024, 39(2): 281-4. |
| 15 | 高 勤, 陈一川, 杨 宸, 等. 黄芩汤治疗溃疡性结肠炎疗效与安全性的Meta分析[J]. 海南医学, 2021, 32(10): 1343-9. |
| 16 | Li MY, Li MX, Xu N, et al. Effects of Huangqin Decoction on ulcerative colitis by targeting estrogen receptor alpha and ameliorating endothelial dysfunction based on system pharmacology[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2021, 271: 113886. |
| 17 | Li MY, Luo HJ, Wu X, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Huangqin Decoction on dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice through regulation of the gut microbiota and suppression of the ras-PI3K-akt-HIF-1α and NF‑κB pathways[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 10: 1552. |
| 18 | Li MY, Wu YZ, Qiu JG, et al. Huangqin Decoction ameliorates ulcerative colitis by regulating fatty acid metabolism to mediate macrophage polarization via activating FFAR4-AMPK-PPARα pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 311: 116430. |
| 19 | Li MX, Li MY, Lei JX, et al. Huangqin decoction ameliorates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis: role of gut microbiota and amino acid metabolism, mTOR pathway and intestinal epithelial barrier[J]. Phytomedicine, 2022, 100: 154052. |
| 20 | Rodrigues BL, Dotti I, Pascoal LB, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in colonic mucosa of ulcerative colitis patients is mediated by PERK and IRE1 pathway activation[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2022: 6049500. |
| 21 | Lebeaupin C, Proics E, de Bieville CHD, et al. ER stress induces NLRP3 inflammasome activation and hepatocyte death[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2015, 6(9): e1879. |
| 22 | Akbal A, Dernst A, Lovotti M, et al. How location and cellular signaling combine to activate the NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2022, 19(11): 1201-14. |
| 23 | Iwasaki Y, Suganami T, Hachiya R, et al. Activating transcription factor 4 links metabolic stress to interleukin-6 expression in macrophages[J]. Diabetes, 2014, 63(1): 152-61. |
| 24 | Oslowski CM, Hara T, O' Sullivan-Murphy B, et al. Thioredoxin-interacting protein mediates ER stress-induced β cell death through initiation of the inflammasome[J]. Cell Metab, 2012, 16(2): 265-73. |
| 25 | Choi EH, Park SJ. TXNIP: a key protein in the cellular stress response pathway and a potential therapeutic target[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2023, 55(7): 1348-56. |
| 26 | Heazlewood CK, Cook MC, Eri R, et al. Aberrant mucin assembly in mice causes endoplasmic reticulum stress and spontaneous inflammation resembling ulcerative colitis[J]. PLoS Med, 2008, 5(3): e54. |
| 27 | Zhao F, Edwards R, Dizon D, et al. Disruption of Paneth and goblet cell homeostasis and increased endoplasmic reticulum stress in Agr2-/ - mice[J]. Dev Biol, 2010, 338(2): 270-9. |
| 28 | Hu XM, Deng JL, Yu TM, et al. ATF4 deficiency promotes intestinal inflammation in mice by reducing uptake of glutamine and expression of antimicrobial peptides[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 156(4): 1098-111. |
| 29 | Kaser A, Lee AH, Franke A, et al. XBP1 links ER stress to intestinal inflammation and confers genetic risk for human inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Cell, 2008, 134(5): 743-56. |
| 30 | Zhang Q, Liu JN, Chen SL, et al. Caspase-12 is involved in stretch-induced apoptosis mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Apoptosis, 2016, 21(4): 432-42. |
| 31 | Yang L, Wang J, Yang J, et al. Antioxidant metallothionein alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced myocardial apoptosis and contractile dysfunction[J]. Free Radic Res, 2015, 49(10): 1187-98. |
| 32 | Sano R, Reed J C. ER stress-induced cell death mechanisms[J]. Biochimica et biophysica acta, 2013, 1833(12): 3460-70. |
| [1] | 赵娜, 沈梦迪, 赵睿, 奥迪, 骆泽谭, 张银亮, 徐志东, 范方田, 郑海伦. 血根碱通过调控Nrf2/NF-κB通路缓解小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1467-1475. |
| [2] | 于官正, 程炜强, 涂星, 张满, 李鸿, 聂娟. 隔山消治疗溃疡性结肠炎的机制:基于UPLC-QE-MS、网络药理学及代谢组学技术[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1485-1496. |
| [3] | 刘硕, 李静, 吴兴旺. Swertiamarin通过抑制肠上皮细胞细胞凋亡改善TNBS诱导的实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1545-1552. |
| [4] | 从小凡, 陈腾, 李硕, 王媛媛, 周龙云, 李小龙, 张配, 孙小锦, 赵素容. 双氢青蒿素通过促进活性氧的产生增强鼻咽癌细胞对顺铂诱导凋亡的敏感性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1553-1560. |
| [5] | 王元国, 张鹏. 铁死亡抑制基因在食管癌中的高表达分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1389-1396. |
| [6] | 任志军, 刁建新, 王奕婷. 芎归汤通过抑制氧化应激诱导的心肌凋亡减轻小鼠心梗后心衰引起的心肌损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1416-1424. |
| [7] | 陈桂玲, 廖晓凤, 孙鹏涛, 岑欢, 舒盛春, 李碧晶, 黎金华. 澳洲茄碱通过调控Bcl-2/Bax/caspase-3信号通路促进非小细胞肺癌发生凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1109-1116. |
| [8] | 鲁玲君, 杨小迪, 张华平, 梁媛, 石秀兰, 周鑫. 重组日本血吸虫半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂对急性肝损伤小鼠的保护作用及机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1126-1134. |
| [9] | 周伟, 聂军, 胡佳, 蒋艺枝, 张大发. 内质网应激相关基因在主动脉夹层疾病中的差异性表达及与免疫浸润的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 859-866. |
| [10] | 张笑颜, 王 谢, 王 杰, 邵 楠, 蔡 标, 谢道俊. 黄蒲通窍胶囊改善Wilson病铜负荷大鼠的认知损害:基于抑制内质网应激介导的凋亡途径[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 447-454. |
| [11] | 孙秀颀, 蔡静, 张安邦, 庞博, 陈春艳, 查琪琪, 全菲, 叶涛. 电针预处理通过抑制NF-kB/NLRP3信号通路介导炎症和凋亡改善大鼠脑卒中后痉挛[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2102-2109. |
| [12] | 兰 玉, 王凯风, 蓝智贤, 周何琪, 孙 剑. 脱醇红酒抑制肝细胞癌的发生和发展:基于诱导细胞周期的阻滞和凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1297-1305. |
| [13] | 宋泽军, 董海滨, 马 娜, 任渝棠, 姜 泊. 改进的MAYO内镜评分对活动期溃疡性结肠炎疗效有较高的评估价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1204-1213. |
| [14] | 郑庆委, 邵一丹, 郑婉婷, 邹映雪. 蛹虫草代谢产物虫草素抑制舌鳞癌裸鼠移植瘤的生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 873-878. |
| [15] | 石文惠, 刘小莲, 张贵明, 叶林萱, 周润华, 李亦蕾, 余 乐. RITA体外选择性抑制BAP1缺失的皮肤黑色素瘤细胞的生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(5): 710-717. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||