南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (8): 1450-1458.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.08.03
• • 上一篇
张先恒1,2( ), 刘健1,3(
), 刘健1,3( ), 韩琦1,2, 陈一鸣1,2, 丁香1,2, 陈晓露2
), 韩琦1,2, 陈一鸣1,2, 丁香1,2, 陈晓露2
收稿日期:2024-04-28
出版日期:2024-08-20
发布日期:2024-09-06
通讯作者:
刘健
E-mail:1148465915@qq.com;liujianahzy@126.com
作者简介:张先恒,在读博士研究生,E-mail: 1148465915@qq.com
基金资助:
Xianheng ZHANG1,2( ), Jian LIU1,3(
), Jian LIU1,3( ), Qi HAN1,2, Yiming CHEN1,2, Xiang DING1,2, Xiaolu CHEN2
), Qi HAN1,2, Yiming CHEN1,2, Xiang DING1,2, Xiaolu CHEN2
Received:2024-04-28
Online:2024-08-20
Published:2024-09-06
Contact:
Jian LIU
E-mail:1148465915@qq.com;liujianahzy@126.com
摘要:
目的 探究黄芩清热除痹胶囊(HQC)对痛风性关节炎(GA)大鼠炎症反应及尿酸、脂质代谢的影响,并探讨其可能机制。 方法 随机将60只SD大鼠分为6组:正常组,模型组,HQC低、中、高剂量组,秋水仙碱组(n=10);以单钠尿酸盐注射右踝关节腔进行GA大鼠造模,HQC低、中、高剂量组及秋水仙碱组予相应剂量药物灌胃,模型组予等量生理盐水,连续7 d。造模后4、8、24、48、72 h检测各组大鼠足趾肿胀度;HE染色法进行滑膜组织学分析;ELISA检测血清中白细胞介素(IL)-10、IL-18、肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)-α、转化生长因子(TGF)-β1、脂联素(APN)、瘦素(LP)、抵抗素(RS)、内脂素(VF)的表达,检测滑膜中APN、LP、RS、VF的表达;生化法检测血清中高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)、甘油三酯(TG)、总胆固醇(TC)、血尿酸(BUA)的水平;RT-qPCR检测滑膜中磷酸酶与紧张素同源物(PTEN)、磷脂酰肌醇-3-激酶(PI3K)、蛋白激酶B(AKT) mRNA的表达;Western blotting检测PTEN、PI3K、p-PI3K、AKT、p-AKT 蛋白表达。 结果 与正常组比较,模型组足趾肿胀度升高(P<0.05),且在48 h达到高峰;HE染色显示大量炎性细胞浸润和滑膜组织增生;TNF-α、TGF-β1、IL-18、TC、TG、LP、RS、VF、BUA、p-PI3K、p-AKT的表达增加(P<0.05),IL-10、APN、HDL-C、PTEN的表达降低(P<0.05)。与模型组比较,HQC和秋水仙碱可降低TNF-α、TGF-β1、IL-18、TC、TG、LP、RS、VF、BUA、p-PI3K、p-AKT的表达(P<0.05),升高IL-10、APN、HDL-C、PTEN的表达(P<0.05),减轻滑膜组织病理损伤,改善足趾肿胀度。 结论 HQC可改善GA大鼠炎症反应及尿酸、脂质代谢失衡,可能与抑制PTEN/PI3K/AKT信号通路有关。
张先恒, 刘健, 韩琦, 陈一鸣, 丁香, 陈晓露. 黄芩清热除痹胶囊通过PTEN/PI3K/AKT信号通路改善痛风性关节炎大鼠的炎症反应及尿酸、脂质代谢失衡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1450-1458.
Xianheng ZHANG, Jian LIU, Qi HAN, Yiming CHEN, Xiang DING, Xiaolu CHEN. Huangqin Qingrechubi Capsule alleviates inflammation and uric acid and lipid metabolism imbalance in rats with gouty arthritis by inhibiting the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1450-1458.
| Gene | Amplicon size | Primer sequence (5'→3') |
|---|---|---|
| PTEN | 140 | F:TATCTTGTGCTCACCCTGAC R:CTGCTAGCCTCTGGATTTGA |
| PI3K | 123 | F:CGAAACAAAGCCGAGAACCT R:GACGCAATGTTTGACTTCGC |
| AKT | 143 | F:CAGGTTCACCCAGTGACAAC R:CTCCTTCACCAGGATCACCT |
| β-actin | 150 | F:CCCATCTATGAGGGTTACGC R:TTTAATGTCACGCACGATTTC |
表1 引物设计表
Tab.1 Primer design table
| Gene | Amplicon size | Primer sequence (5'→3') |
|---|---|---|
| PTEN | 140 | F:TATCTTGTGCTCACCCTGAC R:CTGCTAGCCTCTGGATTTGA |
| PI3K | 123 | F:CGAAACAAAGCCGAGAACCT R:GACGCAATGTTTGACTTCGC |
| AKT | 143 | F:CAGGTTCACCCAGTGACAAC R:CTCCTTCACCAGGATCACCT |
| β-actin | 150 | F:CCCATCTATGAGGGTTACGC R:TTTAATGTCACGCACGATTTC |
| Antibody | Dilution rate | Species |
|---|---|---|
| PI3K | 1:1000 | Rabbit |
| p-PI3K | 1:5000 | Mouse |
| AKT | 1:1000 | Rabbit |
| p-AKT | 1:1000 | Rabbit |
| PTEN | 1:1000 | Rabbit |
| GAPDH | 1:2000 | Mouse |
表2 抗体信息
Tab.2 Antibody information
| Antibody | Dilution rate | Species |
|---|---|---|
| PI3K | 1:1000 | Rabbit |
| p-PI3K | 1:5000 | Mouse |
| AKT | 1:1000 | Rabbit |
| p-AKT | 1:1000 | Rabbit |
| PTEN | 1:1000 | Rabbit |
| GAPDH | 1:2000 | Mouse |
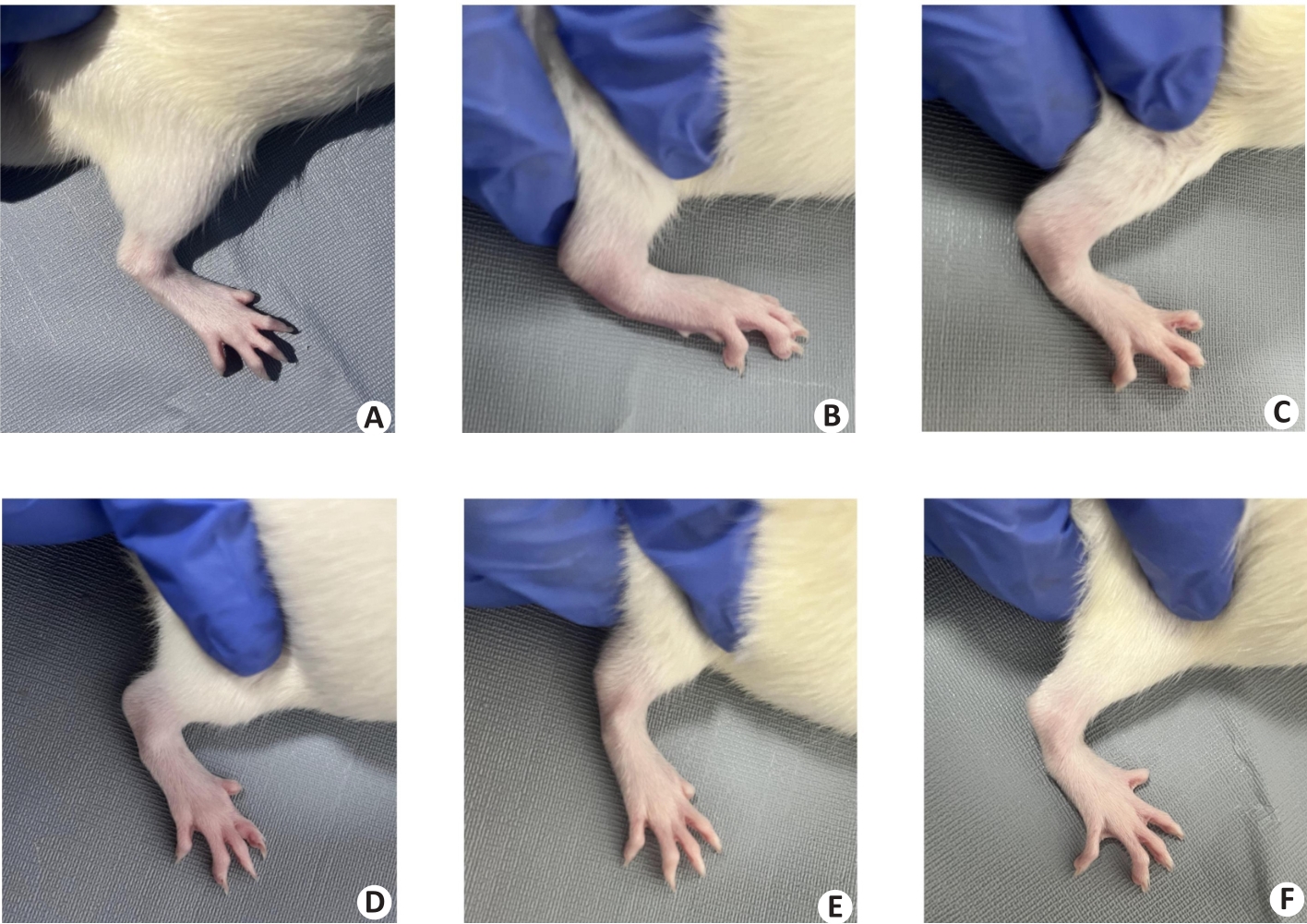
图1 注射MSU 48 h后各组大鼠右踝关节图像
Fig.1 Right ankle joints of the rats in each group after MSU injection 48 h. A: Normal control group; B: Model group; C: HQC-L group; D: HQC-M group; E: HQC-H group; F: Colchicine group.
| Groups | 4 h | 8 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 1.856±0.025 | 1.796±0.023 | 1.702±0.027 | 1.650±0.025 | 1.645±0.029 |
| Model | 2.015±0.073* | 2.156±0.045* | 2.335±0.058* | 2.547±0.059* | 2.456±0.068* |
| HQC-L | 1.945±0.059△# | 2.096±0.045△# | 2.170±0.059△# | 1.954±0.057△# | 1.741±0.065△# |
| HQC-M | 1.908±0.033△# | 1.995±0.036△# | 1.896±0.026△# | 1.805±0.040△# | 1.693±0.040△# |
| HQC-H | 1.896±0.038△# | 1.920±0.035△ | 1.855±0.030△ | 1.727±0.040△ | 1.642±0.034△ |
| Colchicine | 1.853±0.036△ | 1.914±0.040△ | 1.857±0.047△ | 1.714±0.063△ | 1.638±0.030△ |
表3 HQC对GA大鼠足趾肿胀度的影响
Tab.3 Effect of HQC on toe swelling in GA rats (Mean±SD, mL, n=10)
| Groups | 4 h | 8 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 1.856±0.025 | 1.796±0.023 | 1.702±0.027 | 1.650±0.025 | 1.645±0.029 |
| Model | 2.015±0.073* | 2.156±0.045* | 2.335±0.058* | 2.547±0.059* | 2.456±0.068* |
| HQC-L | 1.945±0.059△# | 2.096±0.045△# | 2.170±0.059△# | 1.954±0.057△# | 1.741±0.065△# |
| HQC-M | 1.908±0.033△# | 1.995±0.036△# | 1.896±0.026△# | 1.805±0.040△# | 1.693±0.040△# |
| HQC-H | 1.896±0.038△# | 1.920±0.035△ | 1.855±0.030△ | 1.727±0.040△ | 1.642±0.034△ |
| Colchicine | 1.853±0.036△ | 1.914±0.040△ | 1.857±0.047△ | 1.714±0.063△ | 1.638±0.030△ |
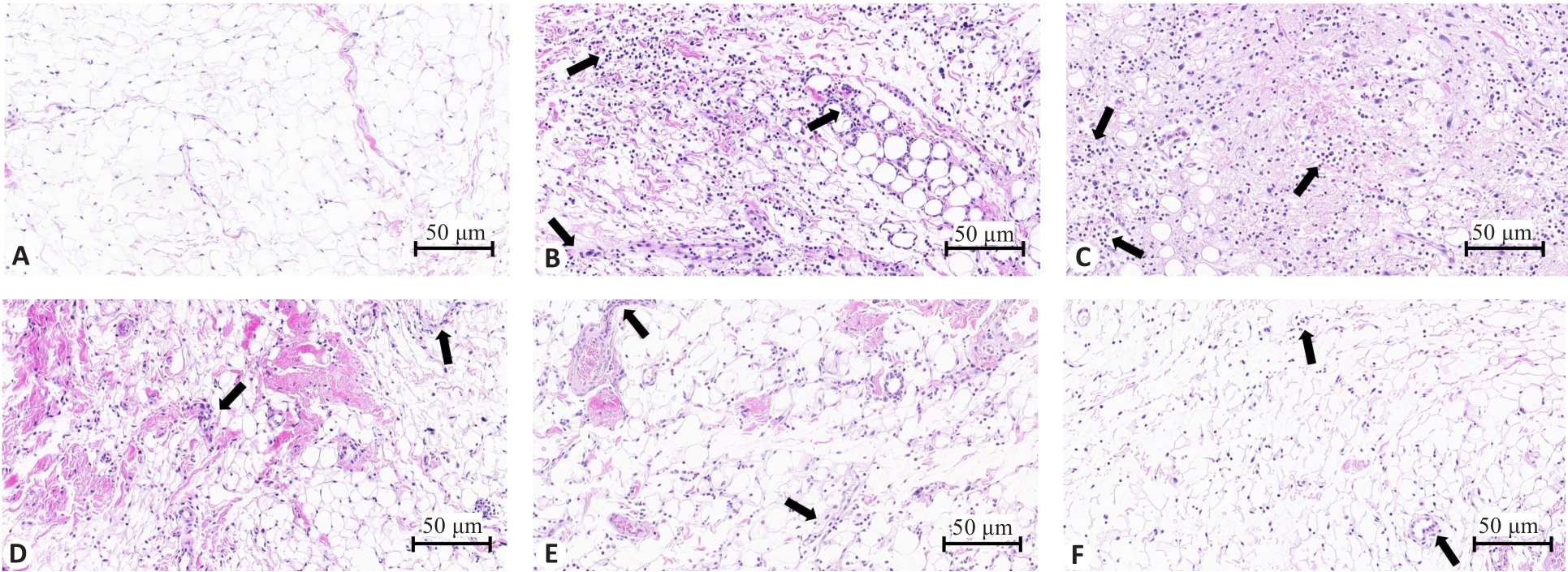
图2 各组大鼠滑膜组织HE染色图像
Fig.2 HE staining of synovial tissue of the rats in each group. Arrows indicate infiltration of inflammatory cells. A: Normal control group; B: Model group; C: HQC-L group; D: HQC-M group; E: HQC-H group; F: Colchicine group.
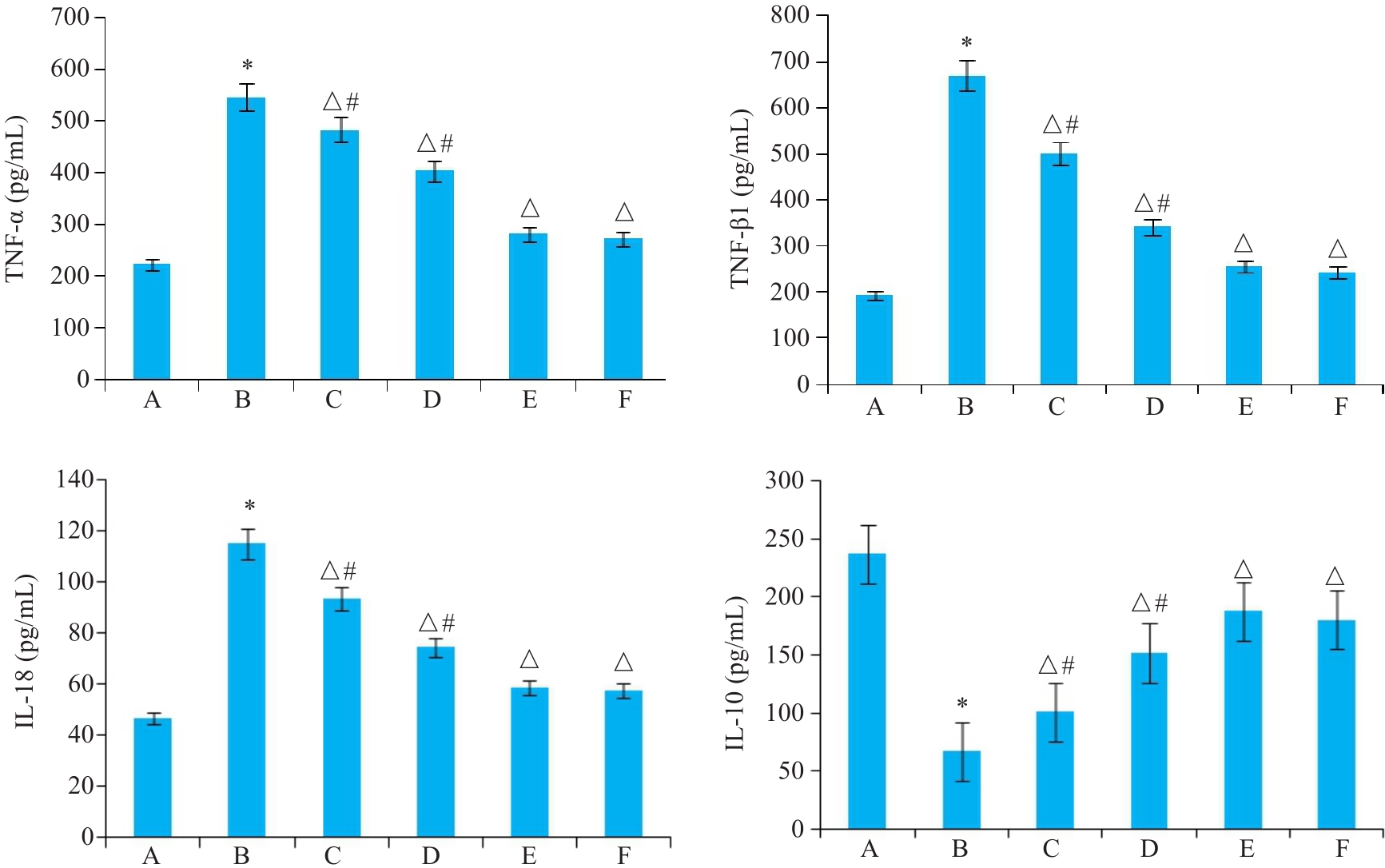
图3 各组大鼠TNF-α、TGF-β1、IL-18、IL-10表达比较
Fig.3 Comparison of TNF-α, TGF-β1, IL-18 and IL-10 expressions among the groups. *P<0.05 vs A; △P<0.05 vs B; #P<0.05 vs F. A: Normal control group; B: Model group; C: HQC-L group; D: HQC-M group; E: HQC-H group; F: Colchicine group.
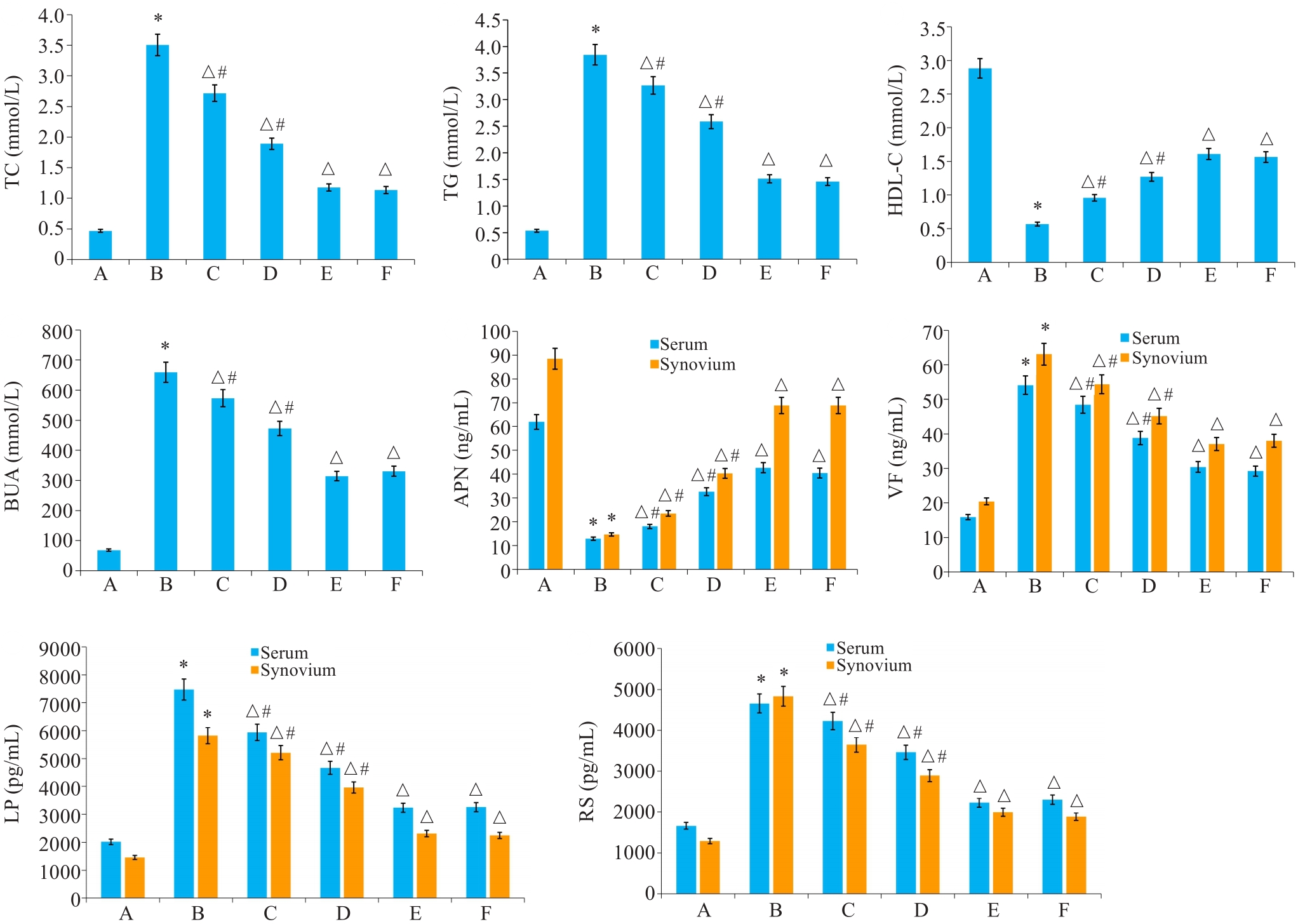
图4 各组大鼠TC、TG、HDL-C、APN、LP、RS、VF、BUA水平比较
Fig.4 Comparison of TC, TG, HDL-C, APN, LP, RS, VF and BUA levels among the groups. *P<0.05 vs A; △P<0.05 vs B; #P<0.05 vs F. A: Normal control group; B: Model group; C: HQC-L group; D: HQC-M group; E: HQC-H group; F: Colchicine group.
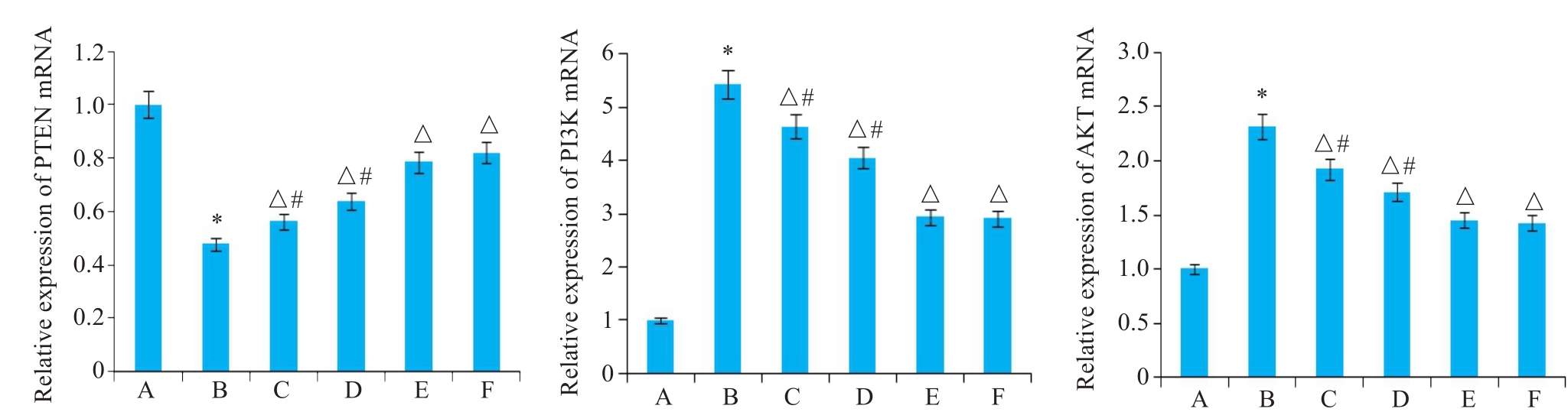
图5 各组大鼠PTEN、PI3K、AKT mRNA表达比较
Fig.5 Comparison of mRNA expressions of PTEN, PI3K and AKT among the groups. *P<0.05 vs A; △P<0.05 vs B; #P<0.05 vs F. A: Normal control group; B: Model group; C: HQC-L group; D: HQC-M group; E: HQC-H group; F: Colchicine group.
| 1 | Neogi T, Jansen TL, Dalbeth N, et al. 2015 Gout classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2015, 74(10): 1789-98. |
| 2 | Yu XH, Wang T, Huang SP, et al. Evaluation of the causal effects of blood lipid levels on gout with summary level GWAS data: two-sample Mendelian randomization and mediation analysis[J]. J Hum Genet, 2021, 66(5): 465-73. |
| 3 | 张先恒, 刘 健, 周 琴, 等. 痛风性关节炎患者脂代谢变化及其与免疫、炎症指标和血尿酸的相关性分析[J]. 风湿病与关节炎, 2021, 10(8): 1-5. |
| 4 | 朱子文, 李 琳, 李晓玲, 等. 胆固醇/三酰甘油水平升高对痛风发病频率的影响[J]. 蚌埠医学院学报, 2022, 47(12): 1639-42, 1646. |
| 5 | Suh YS, Noh HS, Kim HJ, et al. Differences in clinical and dietary characteristics, serum adipokine levels, and metabolomic profiles between early- and late-onset gout[J]. Metabolites, 2021, 11(6): 399. |
| 6 | Liang WD, Chen LT, Cheng XC, et al. Analysis of the relationship of refractory gout between potential biomarkers and diet structure and lifestyle based on 1H-NMR[J]. J Orthop Surg Res, 2024, 19(1): 78. |
| 7 | 王 颖, 高惠英. 脂联素介导免疫炎症机制在常见风湿性疾病中的研究进展[J]. 临床医药实践, 2023, 32(7): 517-21, 526. |
| 8 | 郑 戈, 毕 兵, 朱 晶, 等.血清缺氧诱导因子-1α、Dickkopf-1、抵抗素与痛风性关节炎疼痛、骨破坏的相关性及临床意义[J].安徽医药,2022, 26(11): 2280-4. |
| 9 | 李中南, 周媛媛, 邢宇婷, 等. 萆苓祛痛方对糖尿病痛风大鼠心肌组织内脂素蛋白表达干预及对心脏病理影响[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2020, 22(4): 17-20. |
| 10 | 汪 元, 刘 健, 黄传兵, 等. 中药内服外敷治疗湿热瘀阻型痛风性关节炎急性发作30例临床观察[J]. 中医杂志, 2014, 55(15): 1299-302. |
| 11 | 张先恒, 刘 健, 周 琴, 等. 基于数据挖掘分析黄芩清热除痹胶囊对痛风合并高脂血症患者生化检测指标的影响[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报, 2021, 41(9): 1389-94. |
| 12 | 孙广瀚, 刘 健, 万 磊, 等. 黄芩清热除痹胶囊含药血清对痛风性关节炎CD4+T细胞与心肌细胞共培养后miR-23a-3p/PTEN表达的影响[J]. 北京中医药大学学报, 2021, 44(8): 735-43. |
| 13 | Zhang XH, Liu J, Sun YQ, et al. Chinese herbal compound Huangqin Qingrechubi capsule reduces lipid metabolism disorder and inflammatory response in gouty arthritis via the LncRNA H19/APN/PI3K/AKT cascade[J]. Pharm Biol, 2023, 61(1): 541-55. |
| 14 | Sun K, Luo J, Guo J, et al. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in osteoarthritis: a narrative review[J]. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2020, 28(4): 400-9. |
| 15 | Zhou P, Meng XW, Nie ZM, et al. PTEN: an emerging target in rheumatoid arthritis?[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2024, 22(1): 246. |
| 16 | Liu YC, Han YQ, Liu YQ, et al. Xanthoceras sorbifolium leaves alleviate hyperuricemic nephropathy by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to regulate uric acid transport[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 327: 117946. |
| 17 | Zhang MQ, Sun KX, Guo X, et al. The antihyperuricemia activity of Astragali Radix through regulating the expression of uric acid transporters via PI3K/Akt signalling pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 317: 116770. |
| 18 | Kwon M, Kim Y, Lee J, et al. Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone and neohesperidin dihydrochalcone-O-glycoside attenuate subcutaneous fat and lipid accumulation by regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in vivo and in vitro [J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14(5): 1087. |
| 19 | Xu YJ, Wei RS, Li XH, et al. MiR-421 promotes lipid metabolism by targeting PTEN via activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Epigenomics, 2022,79: 1305-17. |
| 20 | Coderre TJ, Wall PD. Ankle joint urate arthritis in rats provides a useful tool for the evaluation of analgesic and anti-arthritic agents[J]. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 1988, 29(3): 461-6. |
| 21 | 蔡唐彦, 王 旭, 何 浈, 等. 急性痛风性关节炎大鼠模型的建立及模型维持时间观察[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2017, 25(5): 494-9. |
| 22 | Zhou WW, Wang YT, Huang YR, et al. Huangqin Qingre Qubi Capsule inhibits RA pathology by binding FZD8 and further inhibiting the activity of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 302(Pt A): 115886. |
| 23 | Sandoval-Plata G, Nakafero G, Chakravorty M, et al. Association between serum urate, gout and comorbidities: a case-control study using data from the UK Biobank[J]. Rheumatology, 2021, 60(7): 3243-51. |
| 24 | Ran ZJ, Xue XM, Han L, et al. Decrease in serum urate level is associated with loss of visceral fat in male gout patients[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2021, 12: 724822. |
| 25 | Fang YJ, Wu TY, Lin CL, et al. Effects of urate-lowering therapy on risk of hyperlipidemia in gout by a population-based cohort study and on in vitro hepatic lipogenesis-related gene expression[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2020, 2020: 8890300. |
| 26 | Wu J, Zhang YP, Qu Y, et al. Efficacy of uric acid-lowering therapy on hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia in gouty patients[J]. Int J Rheum Dis, 2019, 22(8): 1445-51. |
| 27 | Zhang J, Ji XP, Dong ZH, et al. Impact of fenofibrate therapy on serum uric acid concentrations: a review and meta-analysis[J]. Endocr J, 2021, 68(7): 829-37. |
| 28 | 龚发萍, 郑 鸣. 黄芩的化学成分及药理作用[J]. 临床合理用药杂志, 2021, 14(34): 176-8. |
| 29 | 张嘉豪, 呼 田, 周雪薇, 等.栀子药理作用及临床应用研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报, 2024, 26(5): 93-8. |
| 30 | 李 伟, 徐 伟. 黄芩苷药理作用研究进展[J]. 中西医结合研究, 2022, 14(3): 193-6. |
| 31 | 曹 玲, 崔琳琳, 孙 艳, 等. 威灵仙的药理作用及其机制研究进展[J]. 药物评价研究, 2022, 45(11): 2364-70. |
| 32 | 吴静雨, 陈晓凡, 徐万爱, 等. 薏苡仁活性成分研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2024, 49(6): 1474-84. |
| 33 | 王文娟, 王海明, 王胜军, 等. 苦杏仁苷对骨质疏松大鼠骨折愈合的影响[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2024, 40(8): 1198-202. |
| 34 | Hao GF, Xu XF, Song JY, et al. Lipidomics analysis facilitate insight into the molecular mechanisms of urate nephropathy in a gout model induced by combination of MSU crystals injection and high-fat diet feeding[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2023, 10: 1190683. |
| 35 | Spartalis M, Spartalis E, Tzatzaki E, et al. The beneficial therapy with colchicine for atherosclerosis via anti-inflammation and decrease in hypertriglyceridemia[J]. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem, 2018, 16(2): 74-80. |
| 36 | Mylonas KS, Kapelouzou A, Spartalis M, et al. KLF4 upregulation in atherosclerotic thoracic aortas: exploring the protective effect of colchicine-based regimens in a hyperlipidemic rabbit model[J]. Ann Vasc Surg, 2022, 78: 328-35. |
| 37 | Lee SJ, Nam WD, Na HJ, et al. CT20126, a novel immunosuppressant, prevents collagen-induced arthritis through the down-regulation of inflammatory gene expression by inhibiting NF-kappaB activation[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2008, 76(1): 79-90. |
| 38 | Zhang D, Li L, Li J, et al. Colchicine improves severe acute pancreatitis-induced acute lung injury by suppressing inflammation, apoptosis and oxidative stress in rats[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2022, 153: 113461. |
| 39 | Liu PY, Xu Y, Ye JX, et al. Qingre Huazhuo Jiangsuan Decoction promotes autophagy by inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway to relieve acute gouty arthritis[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 302(Pt A): 115875. |
| 40 | Tavares LD, Galvão I, Costa VV, et al. Phosphoinositide-3 kinase gamma regulates caspase-1 activation and leukocyte recruitment in acute murine gout[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2019, 106(3): 619-29. |
| 41 | Liu L, Zhu XX, Zhao TY, et al. Sirt1 ameliorates monosodium urate crystal-induced inflammation by altering macrophage polarization via the PI3K/Akt/STAT6 pathway[J]. Rheumatology, 2019, 58(9): 1674-83. |
| 42 | Yang BD, Xin ML, Liang SF, et al. Naringenin ameliorates hyperuricemia by regulating renal uric acid excretion via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and renal inflammation through the NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2023, 71(3): 1434-46. |
| 43 | 甘 斌, 李华南, 李 松, 等. 基于脂代谢和炎症反应探讨两种湿热证痛风性关节炎大鼠模型的构建[J]. 中国比较医学杂志, 2023, 33(1): 26-33. |
| 44 | Lyu S, Ding RW, Liu P, et al. LC-MS analysis of serum for the metabolomic investigation of the effects of pulchinenoside b4 administration in monosodium urate crystal-induced gouty arthritis rat model[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(17): 3161. |
| 45 | Yang Y, Xian W, Wu DD, et al. The role of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic factors in gout: a Mendelian randomization study[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2022, 13: 917056. |
| [1] | 陶怀祥, 骆金光, 闻志远, 虞亘明, 苏萧, 王鑫玮, 关翰, 陈志军. STING高表达通过调控TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3通路和影响炎症与凋亡水平促进小鼠肾脏缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1345-1354. |
| [2] | 李和平, 李高桦, 张学华, 王亚楠. 直肠癌炎症蛋白因子的遗传驱动:孟德尔随机化方法在临床预后研究中的应用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1361-1370. |
| [3] | 张玮, 邓蒙蒙, 曾尧, 刘辰菲, 尚菲菲, 许文豪, 蒋昊轶, 王凤超, 杨燕青. 2,6-二甲氧基-1,4-苯醌通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化缓解小鼠的感染性休克[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1024-1032. |
| [4] | 鲁玲君, 杨小迪, 张华平, 梁媛, 石秀兰, 周鑫. 重组日本血吸虫半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂对急性肝损伤小鼠的保护作用及机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1126-1134. |
| [5] | 曹家樊, 孙 跃, 丁 鑫, 李盛文, 陈 博, 兰 天. 熊果苷通过抑制巨噬细胞募集并调控Akt/NF-κB和Smad信号通路改善小鼠肝纤维化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 652-659. |
| [6] | 何 程, 陈 炜, 张念志, 栾 军, 王三凤, 张 尤. 参七虫草方通过ASS1/src/STAT3信号通路改善肺纤维化大鼠的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 644-651. |
| [7] | 席 进, 张 敏, 张永玉, 张 晨, 张雨路, 王 锐, 申 林, 李 静, 宋 雪. 上调KLF11可改善结肠炎模型小鼠的肠道炎症:基于抑制JAK2/STAT3信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 765-772. |
| [8] | 包汉生, 王苏童, 吕穆杰, 王永成, 姜 萍, 李 晓. 激活α7nAchR促进肥胖小鼠的脂肪稳态和米色脂肪生成及产热作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 499-506. |
| [9] | 凌旭光, 徐雯雯, 庞观来, 洪旭星, 刘凤芹, 李 洋. 茶多酚通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体改善脓毒症小鼠的急性肺损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 381-386. |
| [10] | 武若杰, 刘 睿, 张一粟, 李晓红. 帕瑞昔布钠改善腹腔镜下直肠癌根治术患者的炎症微环境并促进患者恢复:基于下调CXCL8-CXCR1/2表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 363-369. |
| [11] | 徐小惠, 冯金梅, 罗 颖, 何昕觎, 臧金宝, 黄道超. NDUFA13过表达可减轻CCl4诱导的小鼠肝纤维化:基于抑制NLRP3活化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 201-209. |
| [12] | 黄丹梅, 刘雅清, 李丹彤, 张静兰, 杨翌晨, 孙良忠. C/EBPβ介导NPHP1敲低的肾小管上皮细胞TNF-α通路下游炎症因子的表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 156-165. |
| [13] | 孙晓鹏, 史 航, 张 磊, 刘 中, 李克威, 钱玲玲, 朱星宇, 杨康佳, 付 强, 丁 华. 外胚层间充质干细胞来源的外泌体通过控制炎症和氧化损伤减少M1型小胶质细胞并促进H2O2处理后PC12细胞的存活[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 119-128. |
| [14] | 徐桂铃, 龚钊乾, 王珺娆, 马妍妍, 许懋升, 陈美佳, 胡大鹏, 梁健鹏, 赵文驱, 赵海金. 2型炎症对慢阻肺大、小气道支气管舒张反应性的不同影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 93-99. |
| [15] | 于佳池, 李芮冰, 夏 天, 王佳楠, 金家丞, 袁漫秋, 李绵洋. 沉默PDCD4表达可减轻脓毒症血管内皮细胞损伤:基于改善线粒体动力学[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 25-35. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||