南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (7): 1345-1354.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.07.14
• • 上一篇
陶怀祥1,2( ), 骆金光1,2, 闻志远1, 虞亘明1,2, 苏萧1, 王鑫玮1, 关翰1, 陈志军1(
), 骆金光1,2, 闻志远1, 虞亘明1,2, 苏萧1, 王鑫玮1, 关翰1, 陈志军1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-12-18
出版日期:2024-07-20
发布日期:2024-07-25
通讯作者:
陈志军
E-mail:2240489402@qq.com;byczj@bbmc.edu.cn
作者简介:陶怀祥,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 2240489402@qq.com
基金资助:
Huaixiang TAO1,2( ), Jinguang LUO1,2, Zhiyuan WEN1, Genming YU1,2, Xiao SU1, Xinwei WANG1, Han GUAN1, Zhijun CHEN1(
), Jinguang LUO1,2, Zhiyuan WEN1, Genming YU1,2, Xiao SU1, Xinwei WANG1, Han GUAN1, Zhijun CHEN1( )
)
Received:2023-12-18
Online:2024-07-20
Published:2024-07-25
Contact:
Zhijun CHEN
E-mail:2240489402@qq.com;byczj@bbmc.edu.cn
摘要:
目的 探讨STING在肾缺血再灌注损伤(IRI)中的表达水平以及相关作用机制。 方法 在体内水平,将24只C57BL/6小鼠分为假手术组(Sham)、IRI组、IRI+药物溶剂组(IRI+DMSO)、IRI+SN-011组,6只/组。通过肾动脉夹闭方法建立IRI模型,通过血清肌酐和尿素氮检测、PAS染色检测肾组织损伤变化,采用RT-qPCR、ELISA、Western blotting和IHC法检测肾组织中STING、KIM-1、Bcl-2、Bax、caspase-3、TLR4、P65、NLRP3、caspase-1、CD68、MPO、 IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α的水平。在体外水平,将HK-2细胞分为对照组、缺氧复氧(H/R)组、H/R+药物溶剂组(H/R+DMSO)、H/R+SN-011组,用厌氧包模拟缺氧环境,RT-qPCR和Western blotting法检测STING表达水平,流式细胞术检测各组细胞凋亡率。 结果 在体内水平,与Sham组相比,IRI组的PAS染色显示组织损伤增加(P<0.05),小鼠血清肌酐、尿素氮含量以及组织KIM-1、STING、TLR4、P65、NLRP3、caspase-1、caspase-3、Bax、CD68、MPO、IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α表达水平升高(P<0.05),Bcl-2水平降低(P<0.05),SN-011抑制STING表达后,逆转了上述结果(P<0.05)。在体外水平,与对照组相比,H/R组STING的mRNA与蛋白水平升高(P<0.05),流式细胞仪检测显示细胞凋亡率上升(P<0.05),SN-011抑制STING表达,细胞凋亡率下降(P<0.05)。 结论 STING在肾脏IRI中表达水平上升,且可通过作用于TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3通路以及影响炎症与凋亡水平促进肾损伤。
陶怀祥, 骆金光, 闻志远, 虞亘明, 苏萧, 王鑫玮, 关翰, 陈志军. STING高表达通过调控TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3通路和影响炎症与凋亡水平促进小鼠肾脏缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1345-1354.
Huaixiang TAO, Jinguang LUO, Zhiyuan WEN, Genming YU, Xiao SU, Xinwei WANG, Han GUAN, Zhijun CHEN. High STING expression exacerbates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by regulating the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway and promoting inflammation and apoptosis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1345-1354.
| Gene | Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| STING | F:GTCCCTTGCACATGGTGTTG |
| R:CAGGTCATGCTGTCGCCTAT | |
| KIM-1 | F:AGAAGACCCACAACTACAAGGC |
| R:TAGATGTTGGAGGAGTGGAGGT | |
| IL-1β | F:GCCTGTGTTTTCCTCCTTGC |
| R:TGCTGCCTAATGTCCCCTTG | |
| IL-6 | F:GTGGCTAAGGACCAAGACCAT |
| R:TCTGACCACAGTGAGGAATGTC | |
| TNF-α | F:AGCCGATGGGTTGTACCTTG |
| R:ATAGCAAATCGGCTGACGGT | |
| GAPDH | F:TGGAAAGCTGTGGCGTGAT |
| R:AGATCCACGACGGACACATT |
表 1 RT-qPCR引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequence for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| STING | F:GTCCCTTGCACATGGTGTTG |
| R:CAGGTCATGCTGTCGCCTAT | |
| KIM-1 | F:AGAAGACCCACAACTACAAGGC |
| R:TAGATGTTGGAGGAGTGGAGGT | |
| IL-1β | F:GCCTGTGTTTTCCTCCTTGC |
| R:TGCTGCCTAATGTCCCCTTG | |
| IL-6 | F:GTGGCTAAGGACCAAGACCAT |
| R:TCTGACCACAGTGAGGAATGTC | |
| TNF-α | F:AGCCGATGGGTTGTACCTTG |
| R:ATAGCAAATCGGCTGACGGT | |
| GAPDH | F:TGGAAAGCTGTGGCGTGAT |
| R:AGATCCACGACGGACACATT |
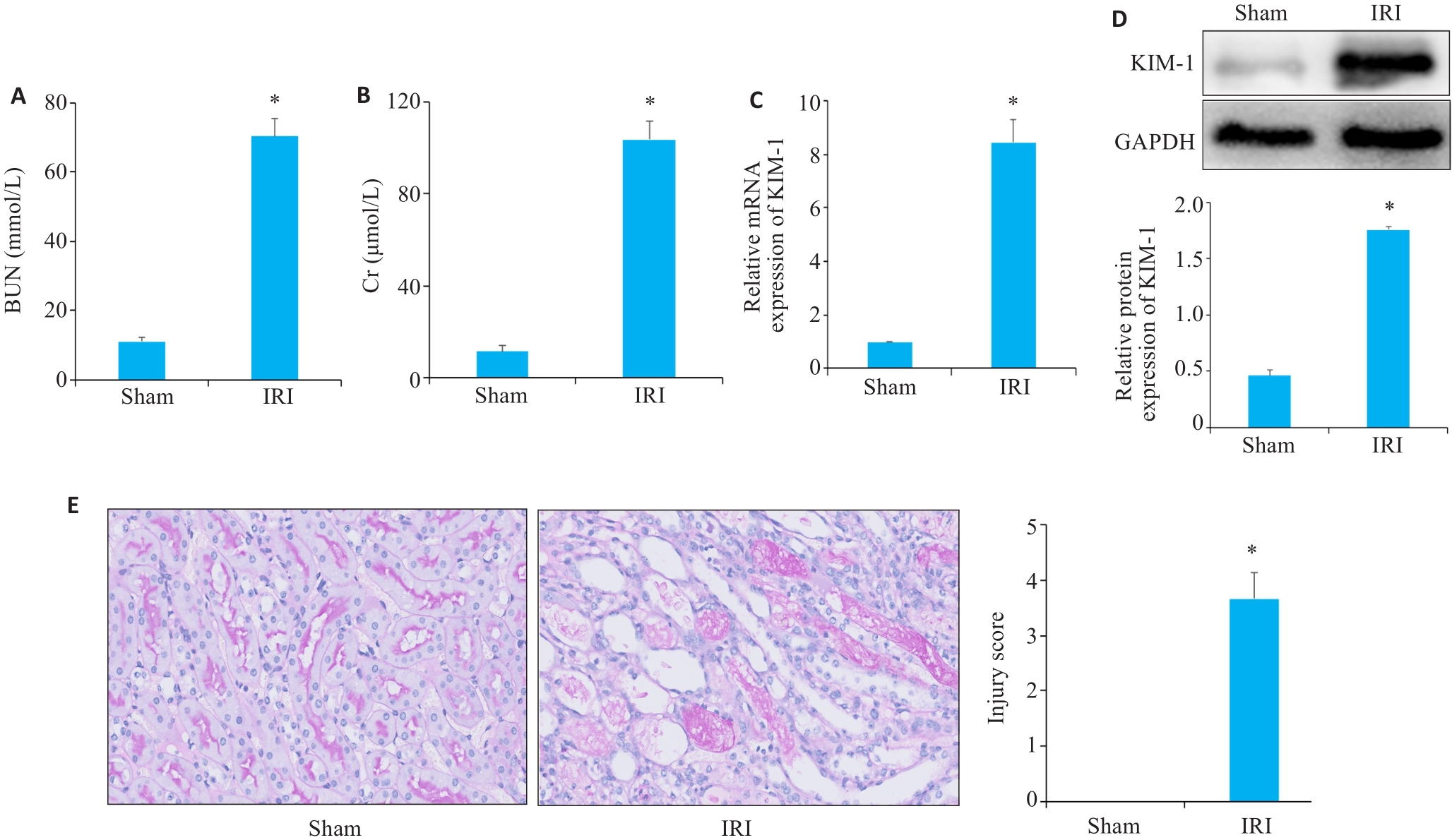
图2 血清生化、Western blotting、RT-qPCR、PAS染色验证小鼠缺血再灌注模型构建效果
Fig.2 Serum biochemistry, Western blotting, RT-qPCR and PAS staining for assessing the effect of ischemia-reperfusion modeling. A, B: Serum BUN (A) and Cr (B) levels of the mice in sham and IRI group. C: RT-qPCR analysis of KIM-1 in Sham and IRI groups mice. D: Western blotting of KIM-1 in sham and IRI group. E: PAS staining of renal tissue from mice in sham and IRI groups (Original magnification: ×400). *P<0.05 vs Sham group.
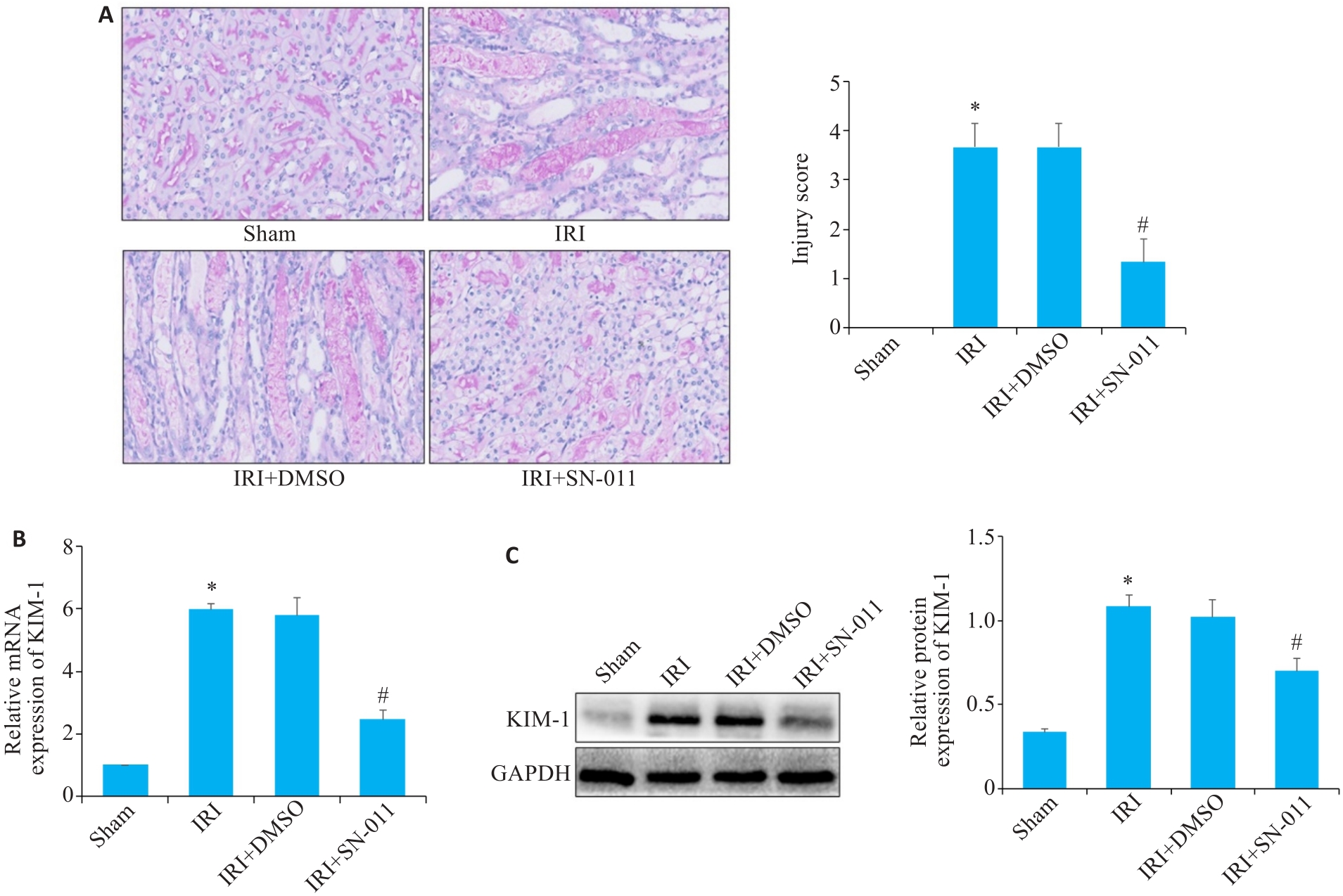
图5 RT-qPCR、Western blotting、PAS染色检测肾组织损伤程度
Fig.5 RT-qPCR, Western blotting and PAS staining for detecting renal tissue injury. A: PAS staining of kidney tissues from mice in the sham, IRI, IRI+DMSO and IRI+SN-011 groups (×400). B, C: RT-qPCR and Western blotting of the expressions of KIM-1 in sham, IRI, IRI+DMSO and IRI+SN-011 groups. *P<0.05 vs Sham; #P<0.05 vs IRI.
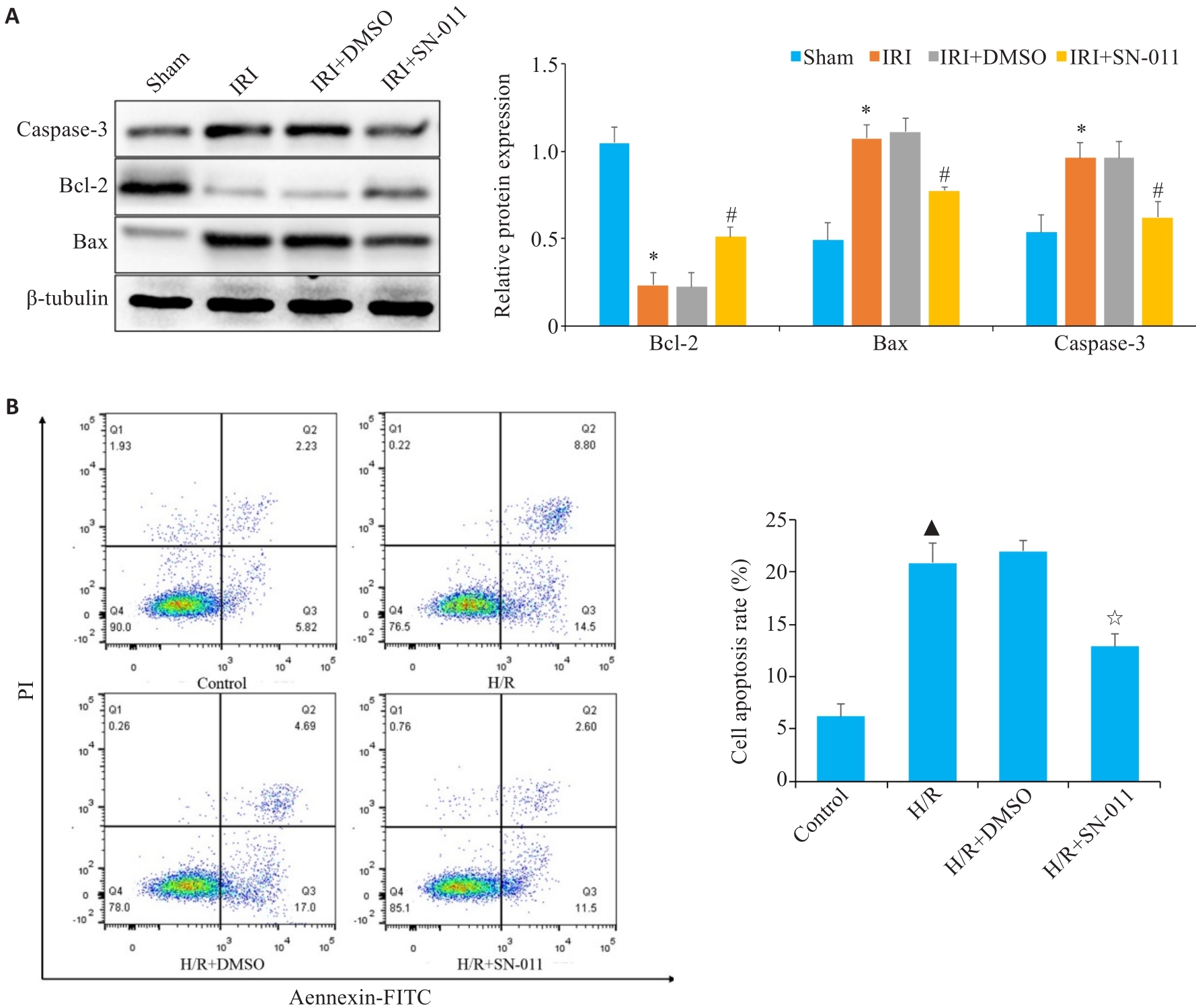
图7 Western blotting、流式细胞仪技术检测凋亡水平
Fig.7 Cell apoptosis analyzed using Western blotting and flow cytometry. A: Western blotting of relative expression levels of caspase-3, Bcl-2 and Bax in mouse kidney tissue from sham, IRI, IRI+DMSO and IRI+SN-011 groups. B: Flow cytometric analysis of HK-2 cell apoptosis in control, H/R, H/R+DMSO, and H/R+SN-011 groups. *P<0.05 vs Sham; #P<0.05 vs IRI; ▲P<0.05 vs control; ☆P<0.05 vs H/R.
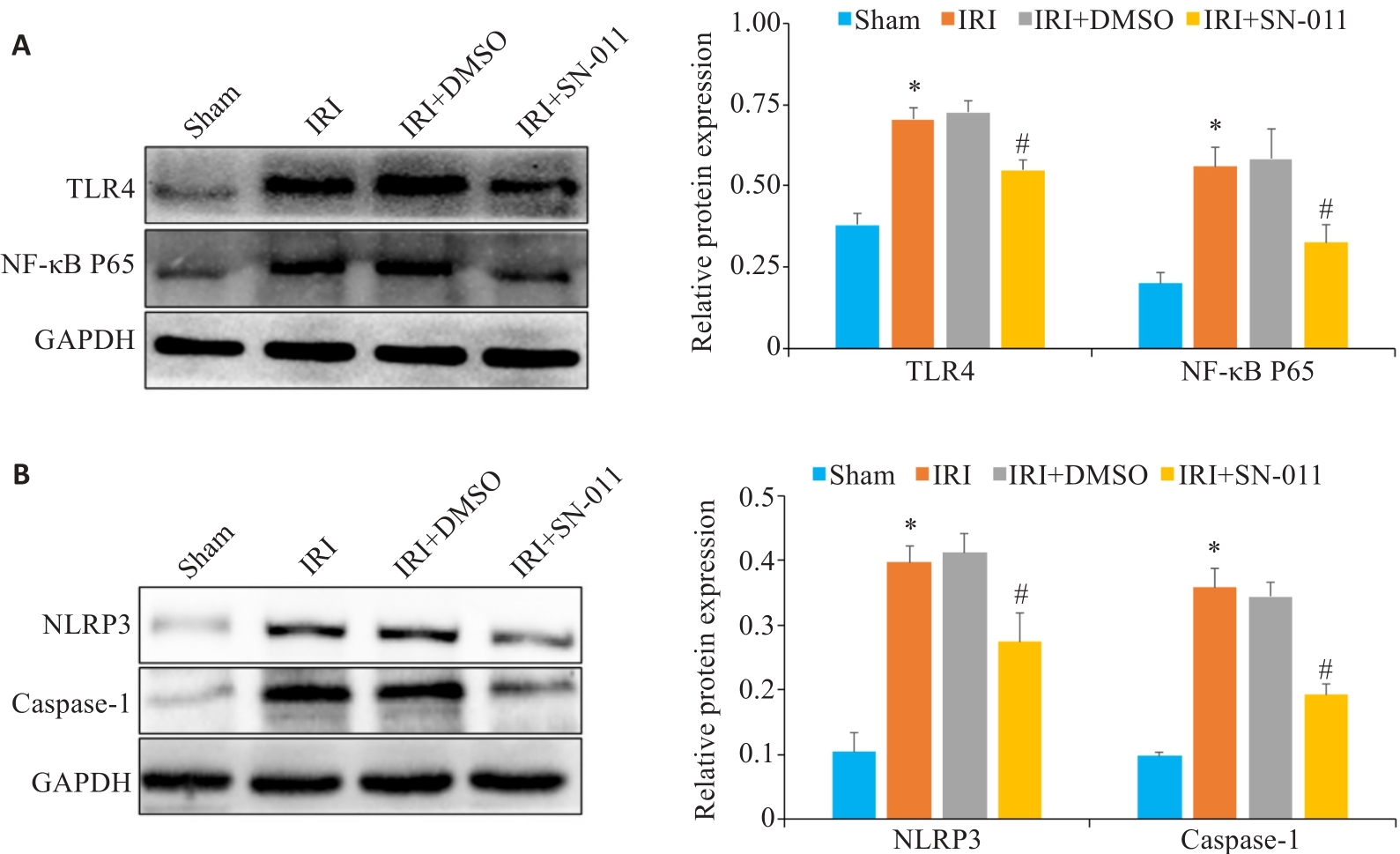
图8 Western blotting检测肾组织中TLR4、NF-κB P65、NLRP3、caspase-1蛋白表达水平
Fig.8 Western blotting for detecting TLR4, NF‑κB P65, NLRP3, and caspase-1 protein expressions in the renal tissue. A: Western blotting of TLR4 and NF-κB P65 in mouse kidney tissues from sham, IRI, IRI+DMSO and IRI+SN-011 groups. B: Western blotting of NLRP3 and caspase-1 in mice kidney tissue from the sham, IRI, IRI+DMSO and IRI+SN-011 groups. *P<0.05 vs Sham; #P<0.05 vs IRI.
| 1 | Hoste EAJ, Kellum JA, Selby NM, et al. Global epidemiology and outcomes of acute kidney injury[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2018, 14(10): 607-25. |
| 2 | Zuk A, Bonventre JV. Acute kidney injury[J]. Annu Rev Med, 2016, 67: 293-307. |
| 3 | Arai S, Kitada K, Yamazaki T, et al. Apoptosis inhibitor of macrophage protein enhances intraluminal debris clearance and ameliorates acute kidney injury in mice[J]. Nat Med, 2016, 22(2): 183-93. |
| 4 | Inagi R, Ishimoto Y, Nangaku M. Proteostasis in endoplasmic reticulum: new mechanisms in kidney disease[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2014, 10(7): 369-78. |
| 5 | Yan MJ, Tang CY, Ma ZW, et al. DNA damage response in nephrotoxic and ischemic kidney injury[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2016, 313: 104-8. |
| 6 | Malek M, Nematbakhsh M. Renal ischemia/reperfusion injury; from pathophysiology to treatment[J]. J Renal Inj Prev, 2015, 4(2): 20-7. |
| 7 | Fang R, Wang CG, Jiang QF, et al. NEMO-IKKβ are essential for IRF3 and NF-κB activation in the cGAS-STING pathway[J]. J Immunol, 2017, 199(9): 3222-33. |
| 8 | Fang R, Jiang QF, Guan YK, et al. Golgi apparatus-synthesized sulfated glycosaminoglycans mediate polymerization and activation of the cGAMP sensor STING[J]. Immunity, 2021, 54(5): 962-75.e8. |
| 9 | Ren P, Cao JL, Lin PL, et al. Molecular mechanism of luteolin regulating lipoxygenase pathway against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion injury in H9c2 cardiomyocytes based on molecular docking[J]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi, 2021, 46(21): 5665-73. |
| 10 | Bi R, Yang YL, Liao HW, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis induces an inflammatory response via the cGAS-STING signaling pathway in a periodontitis mouse model[J]. Front Microbiol, 2023, 14: 1183415. |
| 11 | Pressly JD, Park F. DNA repair in ischemic acute kidney injury[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2017, 312(4): F551-5. |
| 12 | Hu HL, Zou C. Mesenchymal stem cells in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury: biological and therapeutic perspectives[J]. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther, 2017, 12(3): 183-7. |
| 13 | Inagi R. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the kidney as a novel mediator of kidney injury[J]. Nephron Exp Nephrol, 2009, 112(1): e1-9. |
| 14 | Cao Q, Wang YP, Niu ZG, et al. Potentiating tissue-resident type 2 innate lymphoid cells by IL-33 to prevent renal ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2018, 29(3): 961-76. |
| 15 | Havasi A, Borkan SC. Apoptosis and acute kidney injury[J]. Kidney Int, 2011, 80(1): 29-40. |
| 16 | Yang DH, Tang M, Zhang MM, et al. Downregulation of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 4 protects against kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Kidney Int, 2023, 103(4): 719-34. |
| 17 | Li XR, Liao J, Su XJ, et al. Human urine-derived stem cells protect against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in a rat model via exosomal miR-146a-5p which targets IRAK1 [J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(21): 9561-78. |
| 18 | Wang J, Xiong MR, Fan Y, et al. Mecp2 protects kidney from ischemia-reperfusion injury through transcriptional repressing IL-6/STAT3 signaling[J]. Theranostics, 2022, 12(8): 3896-910. |
| 19 | van Timmeren MM, van den Heuvel MC, Bailly V, et al. Tubular kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) in human renal disease[J]. J Pathol, 2007, 212(2): 209-17. |
| 20 | Gkirtzimanaki K, Kabrani E, Nikoleri D, et al. IFNα impairs autophagic degradation of mtDNA promoting autoreactivity of SLE monocytes in a STING-dependent fashion[J]. Cell Rep, 2018, 25(4): 921-33.e5. |
| 21 | Gao YP, Zhang NN, Zeng ZH, et al. LncRNA PCAT1 activates SOX2 and suppresses radioimmune responses via regulating cGAS/STING signalling in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Clin Transl Med, 2022, 12(4): e792. |
| 22 | Li X, Liu YJ, Wang Y, et al. Epoxy triglyceride enhances intestinal permeability via caspase-1/NLRP3/GSDMD and cGAS-STING pathways in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis mice[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2023, 71(10): 4371-81. |
| 23 | Wu JJ, Zhao L, Hu HG, et al. Agonists and inhibitors of the STING pathway: potential agents for immunotherapy[J]. Med Res Rev, 2020, 40(3): 1117-41. |
| 24 | Barber GN. STING: infection, inflammation and cancer[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2015, 15(12): 760-70. |
| 25 | Lu L, Zhou HM, Ni M, et al. Innate immune regulations and liver ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Transplantation, 2016, 100(12): 2601-10. |
| 26 | DeWolf SE, Kasimsetty SG, Hawkes AA, et al. DAMPs released from injured renal tubular epithelial cells activate innate immune signals in healthy renal tubular epithelial cells[J]. Transplantation, 2022, 106(8): 1589-99. |
| 27 | Raup-Konsavage WM, Wang YM, Wang WW, et al. Neutrophil peptidyl arginine deiminase-4 has a pivotal role in ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury[J]. Kidney Int, 2018, 93(2): 365-74. |
| 28 | Salvadori M, Rosso G, Bertoni E. Update on ischemia-reperfusion injury in kidney transplantation: Pathogenesis and treatment[J]. World J Transplant, 2015, 5(2): 52-67. |
| 29 | Liu CH, Wang QD, Niu L. Sufentanil inhibits Pin1 to attenuate renal tubular epithelial cell ischemia-reperfusion injury by activating the PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 pathway[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2023, 55(8): 1903-16. |
| 30 | Wu B, Xu MM, Fan C, et al. STING inhibitor ameliorates LPS-induced ALI by preventing vascular endothelial cells-mediated immune cells chemotaxis and adhesion[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2022, 43(8): 2055-66. |
| 31 | Liu R, Li JY, Shao JC, et al. Innate immune response orchestrates phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetases to support DNA repair[J]. Cell Metab, 2021, 33(10): 2076-89.e9. |
| 32 | Yang B, Li X, Fu Y, et al. MEK inhibition remodels the immune landscape of mutant KRAS tumors to overcome resistance to PARP and immune checkpoint inhibitors[J]. Cancer Res, 2021, 81(10): 2714-29. |
| 33 | Zhang YN, Dong YL, Hao WP, et al. Increased cGAS/STING signaling components in patients with Mooren's ulcer[J]. Int J Ophthalmol, 2021, 14(11): 1660-5. |
| 34 | Hong Z, Mei JH, Li CH, et al. STING inhibitors target the cyclic dinucleotide binding pocket[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2021, 118(24): e2105465118. |
| 35 | Diao FF, Bai J, Jiang CL, et al. The papain-like protease of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus impedes STING translocation from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus by deubiquitinating STIM1[J]. J Virol, 2023, 97(4): e0018823. |
| 36 | Yang BX, Xie XR, Wu ZY, et al. DNA damage-mediated cellular senescence promotes hand-foot syndrome that can be relieved by thymidine prodrug[J]. Genes Dis, 2022, 10(6): 2557-71. |
| 37 | Ablasser A, Chen ZJ. cGAS in action: expanding roles in immunity and inflammation[J]. Science, 2019, 363(6431): eaat8657. |
| 38 | Gulen MF, Koch U, Haag SM, et al. Signalling strength determines proapoptotic functions of STING[J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8(1): 427. |
| 39 | Lehnardt S, Massillon L, Follett P, et al. Activation of innate immunity in the CNS triggers neurodegeneration through a Toll-like receptor 4-dependent pathway[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2003, 100(14): 8514-9. |
| 40 | Wang L, Yang JW, Lin LT, et al. Acupuncture attenuates inflammation in microglia of vascular dementia rats by inhibiting miR-93-mediated TLR4/MyD88/NF‑κB signaling pathway[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2020, 2020: 8253904. |
| 41 | Zhang NX, Guan C, Liu ZY, et al. Calycosin attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing NF‑κB mediated inflammation via PPARγ/EGR1 pathway[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 970616. |
| 42 | Alaaeldin R, Bakkar SM, Mohyeldin RH, et al. Azilsartan modulates HMGB1/NF-κB/p38/ERK1/2/JNK and apoptosis pathways during renal ischemia reperfusion injury[J]. Cells, 2023, 12(1): 185. |
| 43 | Ding HS, Huang Y, Qu JF, et al. Panaxynol ameliorates cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing NLRP3-induced pyroptosis and apoptosis via HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB axis[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 121: 110222. |
| 44 | Liu YY, Lei ZL, Chai H, et al. Salidroside alleviates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury during liver transplant in rat through regulating TLR-4/NF‑κB/NLRP3 inflammatory pathway[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 13973. |
| 45 | Li N, Zhou H, Wu HM, et al. STING-IRF3 contributes to lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction, inflammation, apoptosis and pyroptosis by activating NLRP3[J]. Redox Biol, 2019, 24: 101215. |
| [1] | 张玮, 邓蒙蒙, 曾尧, 刘辰菲, 尚菲菲, 许文豪, 蒋昊轶, 王凤超, 杨燕青. 2,6-二甲氧基-1,4-苯醌通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化缓解小鼠的感染性休克[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1024-1032. |
| [2] | 陈桂玲, 廖晓凤, 孙鹏涛, 岑欢, 舒盛春, 李碧晶, 黎金华. 澳洲茄碱通过调控Bcl-2/Bax/caspase-3信号通路促进非小细胞肺癌发生凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1109-1116. |
| [3] | 鲁玲君, 杨小迪, 张华平, 梁媛, 石秀兰, 周鑫. 重组日本血吸虫半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂对急性肝损伤小鼠的保护作用及机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1126-1134. |
| [4] | 杨泽, 张秀森, 张旭东, 柳颖, 张嘉诚, 原翔. 基于YTHDF2介导凋亡相关因子降解途径研究牙龈卟啉单胞菌协助食管癌免疫逃逸[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1159-1165. |
| [5] | 梁国新, 唐红悦, 郭畅, 张明明. miR-224-5p调控PI3K/Akt/FoxO1轴抑制氧化应激减轻缺氧/复氧诱导的心肌细胞损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1173-1181. |
| [6] | 曹家樊, 孙 跃, 丁 鑫, 李盛文, 陈 博, 兰 天. 熊果苷通过抑制巨噬细胞募集并调控Akt/NF-κB和Smad信号通路改善小鼠肝纤维化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 652-659. |
| [7] | 何 程, 陈 炜, 张念志, 栾 军, 王三凤, 张 尤. 参七虫草方通过ASS1/src/STAT3信号通路改善肺纤维化大鼠的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 644-651. |
| [8] | 席 进, 张 敏, 张永玉, 张 晨, 张雨路, 王 锐, 申 林, 李 静, 宋 雪. 上调KLF11可改善结肠炎模型小鼠的肠道炎症:基于抑制JAK2/STAT3信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 765-772. |
| [9] | 包汉生, 王苏童, 吕穆杰, 王永成, 姜 萍, 李 晓. 激活α7nAchR促进肥胖小鼠的脂肪稳态和米色脂肪生成及产热作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 499-506. |
| [10] | 张笑颜, 王 谢, 王 杰, 邵 楠, 蔡 标, 谢道俊. 黄蒲通窍胶囊改善Wilson病铜负荷大鼠的认知损害:基于抑制内质网应激介导的凋亡途径[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 447-454. |
| [11] | 陈国栋, 罗素新. 秋水仙碱通过激活AMPK减轻小鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 226-235. |
| [12] | 房尚萍, 孙任珂, 苏 慧, 翟科程, 项 毓, 高杨梦娜, 郭文俊. 绿原酸减轻脓毒症诱导的小鼠急性肾损伤:基于抑制caspase-1经典细胞焦亡信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 317-323. |
| [13] | 桂建军, 孙晓东, 温 舒, 刘 欣, 覃冰清, 桑 明. 白藜芦醇对帕金森病模型小鼠多巴胺能神经元的保护作用:基于抑制TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 270-279. |
| [14] | 凌旭光, 徐雯雯, 庞观来, 洪旭星, 刘凤芹, 李 洋. 茶多酚通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体改善脓毒症小鼠的急性肺损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 381-386. |
| [15] | 吴广阳, 宋添力, 唐 浪, 王一民, 刘 绪, 黄 胜. 竹节参总皂苷缓解CCl4诱导的大鼠急性肝损伤:基于调控PI3K/Akt/NF-κB信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 244-251. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||