南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (10): 2191-2198.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.10.15
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2025-04-26
出版日期:2025-10-20
发布日期:2025-10-24
作者简介:肖 蓉,教授,博士,E-mail: xr@smu.edu.cn
基金资助:Received:2025-04-26
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-10-24
摘要:
目的 对Wong和Law情绪智力量表(WLEIS)中文版进行修订并评价其测量学性能。 方法 对Wong和Law情绪智力量表(WLEIS)中文版的11个条目内容表述进行了修改,形成了Wong和Law情绪智力量表中文修订版(WLEIS-CR),使用广泛性焦虑障碍量表(GAD-7)、9条目病人健康问卷(PHQ-9)和心盛量表(FS)为效标对1546名成年被试进行施测,对192名大学生被试进行重测,用所得数据对WLEIS-CR进行项目分析、验证性因素分析、信度、效度检验和等值性检验。 结果 WLEIS-CR的16个项目鉴别力指数均在0.4以上(r=0.570~0.764,P<0.001);验证性因素分析所得结构方程模型具有良好的拟合度(χ2/df=4.610,GFI=0.965,PGFI=0.674,RMR=0.028,NFI=0.975,CFI=0.980,RMSEA=0.048)。WLEIS-CR与FS 、GAD-7,PHQ-9的效标相关分别为0.674、-0.347、-0.368(P<0.001)。WLEIS-CR总量表α系数为0.913,各分量表的α系数在0.867~0.916之间,总量表的分半信度为0.956,各分量表的分半信度在0.865~0.924之间。总量表的重测信度为0.701,各因子的重测信度在0.610~0.684之间。制定并检验了WLEIS-CR结果解释标准,情绪智力为低水平者占7.6%、较低水平者占19.3%、中等水平占22.3%、较高水平占34.3%、很高水平占16.5%。WLEIS-CR具有跨性别、跨年龄和跨身份的等值性。 结论 WLEIS-CR具有良好的信、效度和测量等值性,适用于对中国成年人的情绪智力进行评估,测量他们的情绪健康状况。
肖蓉, 吕夏. 情绪健康的测量:Wong和Law情绪智力量表的修订及其信效度评价[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2191-2198.
Rong XIAO, Xia LÜ. The modified Chinese version of Wong and Law Emotional Intelligence Scale for measurement of emotional health: revision and psychometric evaluation[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(10): 2191-2198.
| Item | Item score (n=1546) | Low score group (n=458) | High score group (n=589) | t | Correlation with total score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 | 3.76±0.75 | 3.07±0.67 | 4.25±0.5 | 32.664*** | 0.731*** |
| Q2 | 3.82±0.77 | 3.07±0.73 | 4.34±0.51 | 33.052*** | 0.764*** |
| Q3 | 3.87±0.77 | 3.18±0.75 | 4.36±0.54 | 28.471*** | 0.727*** |
| Q4 | 3.95±0.76 | 3.32±0.77 | 4.38±0.52 | 25.303*** | 0.679*** |
| Q5 | 3.9±0.72 | 3.33±0.73 | 4.34±0.54 | 24.854*** | 0.685*** |
| Q6 | 3.86±0.82 | 3.27±0.79 | 4.37±0.59 | 25.049*** | 0.637*** |
| Q7 | 3.83±0.83 | 3.29±0.8 | 4.29±0.64 | 22.051*** | 0.570*** |
| Q8 | 3.76±0.81 | 3.16±0.73 | 4.27±0.63 | 26.454*** | 0.645*** |
| Q9 | 3.41±0.91 | 2.71±0.71 | 4.01±0.71 | 29.145*** | 0.634*** |
| Q10 | 3.53±0.92 | 2.75±0.76 | 4.17±0.63 | 32.372*** | 0.702*** |
| Q11 | 3.61±0.9 | 2.83±0.74 | 4.21±0.66 | 31.909*** | 0.694*** |
| Q12 | 3.8±0.81 | 3.1±0.76 | 4.29±0.6 | 28.365*** | 0.698*** |
| Q13 | 3.68±0.82 | 2.92±0.66 | 4.25±0.57 | 35.059*** | 0.743*** |
| Q14 | 3.7±0.83 | 2.93±0.72 | 4.29±0.55 | 34.673*** | 0.755*** |
| Q15 | 3.6±0.86 | 2.91±0.72 | 4.18±0.63 | 30.344*** | 0.677*** |
| Q16 | 3.6±0.86 | 2.86±0.7 | 4.21±0.61 | 33.122*** | 0.717*** |
表1 WLEIS-CR量表的项目分析
Tab.1 Item analysis of the Wong and Law's Emotional Intelligence Scale-Chinese Revised (WLEIS-CR)
| Item | Item score (n=1546) | Low score group (n=458) | High score group (n=589) | t | Correlation with total score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 | 3.76±0.75 | 3.07±0.67 | 4.25±0.5 | 32.664*** | 0.731*** |
| Q2 | 3.82±0.77 | 3.07±0.73 | 4.34±0.51 | 33.052*** | 0.764*** |
| Q3 | 3.87±0.77 | 3.18±0.75 | 4.36±0.54 | 28.471*** | 0.727*** |
| Q4 | 3.95±0.76 | 3.32±0.77 | 4.38±0.52 | 25.303*** | 0.679*** |
| Q5 | 3.9±0.72 | 3.33±0.73 | 4.34±0.54 | 24.854*** | 0.685*** |
| Q6 | 3.86±0.82 | 3.27±0.79 | 4.37±0.59 | 25.049*** | 0.637*** |
| Q7 | 3.83±0.83 | 3.29±0.8 | 4.29±0.64 | 22.051*** | 0.570*** |
| Q8 | 3.76±0.81 | 3.16±0.73 | 4.27±0.63 | 26.454*** | 0.645*** |
| Q9 | 3.41±0.91 | 2.71±0.71 | 4.01±0.71 | 29.145*** | 0.634*** |
| Q10 | 3.53±0.92 | 2.75±0.76 | 4.17±0.63 | 32.372*** | 0.702*** |
| Q11 | 3.61±0.9 | 2.83±0.74 | 4.21±0.66 | 31.909*** | 0.694*** |
| Q12 | 3.8±0.81 | 3.1±0.76 | 4.29±0.6 | 28.365*** | 0.698*** |
| Q13 | 3.68±0.82 | 2.92±0.66 | 4.25±0.57 | 35.059*** | 0.743*** |
| Q14 | 3.7±0.83 | 2.93±0.72 | 4.29±0.55 | 34.673*** | 0.755*** |
| Q15 | 3.6±0.86 | 2.91±0.72 | 4.18±0.63 | 30.344*** | 0.677*** |
| Q16 | 3.6±0.86 | 2.86±0.7 | 4.21±0.61 | 33.122*** | 0.717*** |
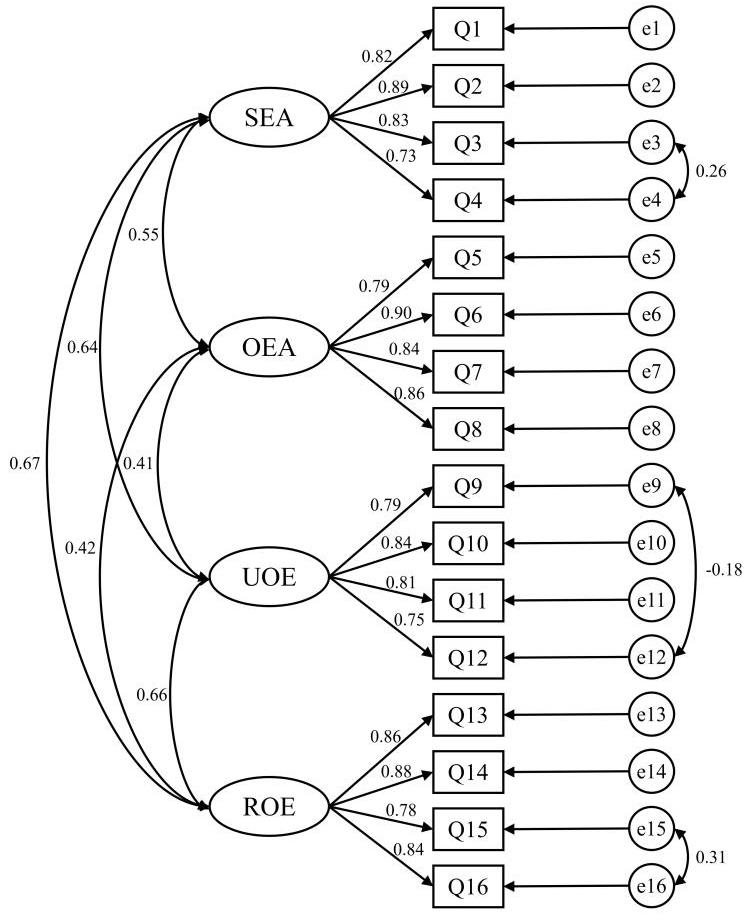
图1 WLEIS-CR的结构模型图
Fig.1 Structural model diagram of WLEIS-CR. SEA: Self emotional appraisal; OEA: Others'emotional appraisal; UOE: Use of emotion; ROE: Regulation of emotion.
| Fator | Total Score | SEA | OEA | UOE | ROE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEA | 0.833*** | 1 | |||
| OEA | 0.714*** | 0.515*** | 1 | ||
| UOE | 0.805*** | 0.563*** | 0.382*** | 1 | |
| ROE | 0.811*** | 0.586*** | 0.379*** | 0.578*** | 1 |
表2 总分与各分量表得分之间的相关性
Tab.2 Correlation between the total score and the subscale scores (n=1546)
| Fator | Total Score | SEA | OEA | UOE | ROE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEA | 0.833*** | 1 | |||
| OEA | 0.714*** | 0.515*** | 1 | ||
| UOE | 0.805*** | 0.563*** | 0.382*** | 1 | |
| ROE | 0.811*** | 0.586*** | 0.379*** | 0.578*** | 1 |
| Item | Total score | SEA | OEA | UOE | ROE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Well-being | 0.674*** | 0.553*** | 0.348*** | 0.669*** | 0.552*** |
| Anxiety | -0.347*** | -0.345*** | -0.084*** | -0.289*** | -0.376*** |
| Depression | -0.368*** | -0.350*** | -0.079*** | -0.360*** | -0.370*** |
表3 WLEIS-CR的效标相关分析
Tab.3 Correlation analysis of the criteria for WLEIS-CR
| Item | Total score | SEA | OEA | UOE | ROE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Well-being | 0.674*** | 0.553*** | 0.348*** | 0.669*** | 0.552*** |
| Anxiety | -0.347*** | -0.345*** | -0.084*** | -0.289*** | -0.376*** |
| Depression | -0.368*** | -0.350*** | -0.079*** | -0.360*** | -0.370*** |
| Item | SEA | OEA | UOE | ROE | Total score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internal consistency | 0.894*** | 0.908*** | 0.867*** | 0.916*** | 0.913*** |
| Split-half | 0.906*** | 0.916*** | 0.865*** | 0.924*** | 0.956*** |
| Test-retest | 0.610*** | 0.669*** | 0.679*** | 0.684*** | 0.701*** |
表4 WLEIS-CR的信度分析
Tab.4 Reliability analysis of WLEIS-CR
| Item | SEA | OEA | UOE | ROE | Total score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internal consistency | 0.894*** | 0.908*** | 0.867*** | 0.916*** | 0.913*** |
| Split-half | 0.906*** | 0.916*** | 0.865*** | 0.924*** | 0.956*** |
| Test-retest | 0.610*** | 0.669*** | 0.679*** | 0.684*** | 0.701*** |
| Model | χ 2 | df | RMSEA (95% CI) | CFI | TLI | SRMR | ΔRMSEA | ΔCFI | ΔTLI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 785.124 | 196 | 0.062 (0.058, 0.067) | 0.966 | 0.959 | 0.048 | |||
| M2 | 805.585 | 208 | 0.061 (0.057, 0.065) | 0.966 | 0.961 | 0.052 | -0.001 | 0 | 0.002 |
| M3 | 828.548 | 220 | 0.06 (0.056, 0.064) | 0.965 | 0.962 | 0.053 | -0.001 | -0.001 | 0.001 |
| M4 | 864.162 | 236 | 0.059 (0.055, 0.063) | 0.964 | 0.963 | 0.053 | -0.001 | -0.001 | 0.001 |
表5 WLEIS-CR不同性别等值性分析
Tab.5 Measurement invariance test of WLEIS-CR by gender
| Model | χ 2 | df | RMSEA (95% CI) | CFI | TLI | SRMR | ΔRMSEA | ΔCFI | ΔTLI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 785.124 | 196 | 0.062 (0.058, 0.067) | 0.966 | 0.959 | 0.048 | |||
| M2 | 805.585 | 208 | 0.061 (0.057, 0.065) | 0.966 | 0.961 | 0.052 | -0.001 | 0 | 0.002 |
| M3 | 828.548 | 220 | 0.06 (0.056, 0.064) | 0.965 | 0.962 | 0.053 | -0.001 | -0.001 | 0.001 |
| M4 | 864.162 | 236 | 0.059 (0.055, 0.063) | 0.964 | 0.963 | 0.053 | -0.001 | -0.001 | 0.001 |
| Model | χ 2 | df | RMSEA (95% CI) | CFI | TLI | SRMR | ΔRMSEA | ΔCFI | ΔTLI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 955.419 | 294 | 0.066 (0.061, 0.071) | 0.963 | 0.954 | 0.048 | |||
| M2 | 1013.823 | 318 | 0.065 (0.061, 0.070) | 0.961 | 0.956 | 0.058 | 0.001 | -0.002 | 0.002 |
| M3 | 1066.578 | 342 | 0.064 (0.060, 0.068) | 0.959 | 0.957 | 0.060 | -0.001 | -0.002 | 0.001 |
| M4 | 1242.370 | 374 | 0.067 (0.063, 0.071) | 0.951 | 0.953 | 0.064 | 0.003 | -0.008 | -0.004 |
表6 WLEIS-CR不同年龄等值性分析
Tab.6 Measurement invariance test of WLEIS-CR by age
| Model | χ 2 | df | RMSEA (95% CI) | CFI | TLI | SRMR | ΔRMSEA | ΔCFI | ΔTLI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 955.419 | 294 | 0.066 (0.061, 0.071) | 0.963 | 0.954 | 0.048 | |||
| M2 | 1013.823 | 318 | 0.065 (0.061, 0.070) | 0.961 | 0.956 | 0.058 | 0.001 | -0.002 | 0.002 |
| M3 | 1066.578 | 342 | 0.064 (0.060, 0.068) | 0.959 | 0.957 | 0.060 | -0.001 | -0.002 | 0.001 |
| M4 | 1242.370 | 374 | 0.067 (0.063, 0.071) | 0.951 | 0.953 | 0.064 | 0.003 | -0.008 | -0.004 |
| Model | χ2 | df | RMSEA(95%CI) | CFI | TLI | SRMR | ΔRMSEA | ΔCFI | ΔTLI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 803.992 | 196 | 0.063(0.059,0.068) | 0.965 | 0.958 | 0.046 | |||
| M2 | 861.589 | 208 | 0.064(0.059,0.068) | 0.963 | 0.957 | 0.056 | 0.001 | -0.002 | -0.001 |
| M3 | 894.238 | 220 | 0.063(0.059,0.067) | 0.962 | 0.958 | 0.058 | -0.001 | -0.001 | 0.001 |
| M4 | 1020.401 | 236 | 0.066(0.061,0.070) | 0.955 | 0.955 | 0.062 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 |
表7 WLEIS-CR不同身份等值性分析
Tab.7 Measurement invariance test of WLEIS-CR by identity
| Model | χ2 | df | RMSEA(95%CI) | CFI | TLI | SRMR | ΔRMSEA | ΔCFI | ΔTLI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 803.992 | 196 | 0.063(0.059,0.068) | 0.965 | 0.958 | 0.046 | |||
| M2 | 861.589 | 208 | 0.064(0.059,0.068) | 0.963 | 0.957 | 0.056 | 0.001 | -0.002 | -0.001 |
| M3 | 894.238 | 220 | 0.063(0.059,0.067) | 0.962 | 0.958 | 0.058 | -0.001 | -0.001 | 0.001 |
| M4 | 1020.401 | 236 | 0.066(0.061,0.070) | 0.955 | 0.955 | 0.062 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 |
| Item | Very low (n=118) | Low (n=298) | Moderate (n=344) | Higher (n=531) | Very high (n=255) | F | Post hoc comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anxiety | 10.05±5.13 | 7.49±4.53 | 6.45±4.84 | 4.57±4.12 | 4.18±4.8 | 54.015*** | 1>2>3>4>5 |
| Depression | 12.84±5.83 | 10.28±4.75 | 9±4.79 | 7.11±4.3 | 6.09±5.29 | 61.499*** | 1>2>3>4>5 |
| Well-being | 29.08±6.98 | 33.56±5.99 | 37.76±6.15 | 42.52±6.31 | 47.92±7.33 | 284.293*** | 1<2<3<4<5 |
表8 不同情绪智力水平者的抑郁、焦虑、幸福感得分比较
Tab.8 Comparison of depression, anxiety, and well-being scores among individuals with different levels of emotional intelligence (Mean±SD)
| Item | Very low (n=118) | Low (n=298) | Moderate (n=344) | Higher (n=531) | Very high (n=255) | F | Post hoc comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anxiety | 10.05±5.13 | 7.49±4.53 | 6.45±4.84 | 4.57±4.12 | 4.18±4.8 | 54.015*** | 1>2>3>4>5 |
| Depression | 12.84±5.83 | 10.28±4.75 | 9±4.79 | 7.11±4.3 | 6.09±5.29 | 61.499*** | 1>2>3>4>5 |
| Well-being | 29.08±6.98 | 33.56±5.99 | 37.76±6.15 | 42.52±6.31 | 47.92±7.33 | 284.293*** | 1<2<3<4<5 |
| [1] | Tian W, Yan GC, Xiong SZ, et al. Burden of depressive and anxiety disorders in China and its provinces, 1990-2021: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021[J]. Br J Psychiatry, 2025: 1-11. doi:10.1192/bjp.2024.267 |
| [2] | Wang XQ, Zhang DJ, Wang JL. Dual-factor model of mental health: surpass the traditional mental health model[J]. Psychology, 2011, 2(8): 767-72. |
| [3] | Xiao R, Zhang C, Lai QZ, et al. Applicability of the dual-factor model of mental health in the mental health screening of Chinese college students[J]. Front Psychol, 2021, 11: 549036. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2020.549036 |
| [4] | Mayer JD, Caruso DR, Salovey P. The ability model of emotional intelligence: principles and updates[J]. Emot Rev, 2016, 8(4): 290-300. doi:10.1177/1754073916639667 |
| [5] | Martins A, Ramalho N, Morin E. A comprehensive meta-analysis of the relationship between Emotional Intelligence and health[J]. Pers Individ Differ, 2010, 49(6): 554-64. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2010.05.029 |
| [6] | 桑青松, 李楠楠, 童张梦子. 羞怯在中学生情绪智力与社会适应间的中介作用: 基于阶层回归分析和Bootstrap法的检验[J]. 安徽师范大学学报: 人文社会科学版, 2016, 44(5): 646-54. |
| [7] | 肖 凤, 李 爽, 任 英, 等. 临床护士情绪智力、自我效能感、工作环境与关怀行为的相关性[J]. 护理研究, 2021, 35(3): 396-401. |
| [8] | Guerra-Bustamante J, León-Del-Barco B, Yuste-Tosina R, et al. Emotional intelligence and psychological well-being in adolescents[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2019, 16(10): 1720. doi:10.3390/ijerph16101720 |
| [9] | Martínez-Monteagudo MC, Inglés CJ, Granados L, et al. Trait emotional intelligence profiles, burnout, anxiety, depression, and stress in secondary education teachers[J]. Pers Individ Differ, 2019, 142: 53-61. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2019.01.036 |
| [10] | Suslow T, Hoepfel D, Günther V, et al. Positive attentional bias mediates the relationship between trait emotional intelligence and trait affect[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 20733. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-25317-9 |
| [11] | Wong CS, Law KS. The effects of leader and follower emotional intelligence on performance and attitude An exploratory study[J]. Leadersh Q, 2002, 13(3): 243-74. doi:10.1016/s1048-9843(02)00099-1 |
| [12] | Shi JQ, Wang L. Validation of emotional intelligence scale in Chinese university students[J]. Pers Individ Differ, 2007, 43(2): 377-87. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2006.12.012 |
| [13] | Libbrecht N, Lievens F, Schollaert E. Measurement equivalence of the wong and law emotional intelligence scale across self and other ratings[J]. Educ Psychol Meas, 2010, 70(6): 1007-20. doi:10.1177/0013164410378090 |
| [14] | Jeong H, Choi H, Park M. The reliability and validity of Korean version of wong and law emotional intelligence scale (K-WLEIS)[J]. J Korean Acad Nurs, 2020, 50(4): 611-20. doi:10.4040/jkan.20109 |
| [15] | Rathore D, Chadha NK. Psychometric evaluation of Wong and Law Emotional Intelligence Scale (WLEIS) in Indian college students[J]. Int J Indian Psychol, 2021(1). |
| [16] | Carvalho VS, Guerrero E, Chambel MJ, et al. Psychometric properties of WLEIS as a measure of emotional intelligence in the Portuguese and Spanish medical students[J]. Eval Program Plann, 2016, 58: 152-9. doi:10.1016/j.evalprogplan.2016.06.006 |
| [17] | 刘 薇. 变革型领导对工作场所员工学习的影响: 员工情绪的中介作用和情绪智力的调节作用[J]. 管理评论, 2018, 30(10): 128-40. |
| [18] | 李永占. 情绪智力在身体自尊与进食障碍倾向间的调节作用[J]. 心理与行为研究, 2022, 20(4): 570-6. |
| [19] | 杨 婷, 周戈耀, 程远芬, 等. 硕士研究生情绪智力与生活满意度的关系: 压力知觉与孤独感的链式中介作用[J]. 现代预防医学, 2024, 51(12): 2228-34. |
| [20] | 高 莹, 李 义, 乔俊英, 等. 突发公共卫生事件中正念对一线护士心理健康的影响: 情绪智力的中介作用[J]. 中国护理管理, 2024, 24(2): 266-71. |
| [21] | 王叶飞. 情绪智力量表中文版的信效度研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2010. |
| [22] | 黄明明, 王立君. 基于WLEIS情绪智力测验的IRT分析[J]. 心理技术与应用, 2015, 3(3): 21-6. |
| [23] | 毕重增. 心理测量学[M]. 重庆: 西南师范大学出版社, 2016: 132-139. |
| [24] | Diener E, Wirtz D, Tov W, et al. New well-being measures: short scales to assess flourishing and positive and negative feelings[J]. Soc Indic Res, 2010, 97(2): 143-56. doi:10.1007/s11205-009-9493-y |
| [25] | Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB. The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure[J]. J Gen Intern Med, 2001, 16(9): 606-13. doi:10.1046/j.1525-1497.2001.016009606.x |
| [26] | Levis B, Benedetti A, Levis AW, et al. Selective cutoff reporting in studies of diagnostic test accuracy: a comparison of conventional and individual-patient-data meta-analyses of the patient health questionnaire-9 depression screening tool[J]. Am J Epidemiol, 2017, 185(10): 954-64. doi:10.1093/aje/kww191 |
| [27] | Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JBW, et al. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7[J]. Arch Intern Med, 2006, 166(10): 1092-7. doi:10.1001/archinte.166.10.1092 |
| [28] | Rutter LA, Brown TA. Psychometric properties of the generalized anxiety disorder scale-7 (GAD-7) in outpatients with anxiety and mood disorders[J]. J Psychopathol Behav Assess, 2017, 39(1): 140-6. doi:10.1007/s10862-016-9571-9 |
| [29] | 吴明隆. 问卷统计分析实务: SPSS操作与应用[M]. 重庆: 重庆大学出版社, 2010. |
| [30] | Chamizo-Nieto MT, Arrivillaga C, Rey L, et al. The role of emotional intelligence, the teacher-student relationship, and flourishing on academic performance in adolescents: a moderated mediation study[J]. Front Psychol, 2021, 12: 695067. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2021.695067 |
| [31] | Sánchez-Álvarez N, Extremera N, Fernández-Berrocal P. The relation between emotional intelligence and subjective well-being: a meta-analytic investigation[J]. J Posit Psychol, 2016, 11(3): 276-85. doi:10.1080/17439760.2015.1058968 |
| [32] | 李 杰. 临床医学专业本科生情绪智力、自尊与主观幸福感的关系[J]. 首都医科大学学报, 2020, 41(3): 428-32. |
| [33] | 潘明军, 钱 兵. 大学生情绪智力与心理健康的关系[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2012, 33(1): 43-5. |
| [34] | 周立业, 原雅彬, 刘瑞华. 肿瘤科护士情绪智力与焦虑、抑郁情绪的相关性研究[J]. 中国卫生产业, 2015, 12(3): 147-9. |
| [35] | 田 奥, 陈宝利, 张 萌. 情绪智力对新入狱罪犯抑郁和焦虑水平的影响[J]. 中国监狱学刊, 2022(4): 109-15. |
| [36] | Sun JW, Zhang X, Wang Y, et al. The associations of interpersonal sensitivity with mental distress and trait aggression in early adulthood: a prospective cohort study[J]. J Affect Disord, 2020, 272: 50-7. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2020.03.161 |
| [37] | 戴忠恒. 心理与教育测量[M]. 上海: 华东师范大学出版社, 1987. |
| [38] | Law KS, Wong CS, Song LJ. The construct and criterion validity of emotional intelligence and its potential utility for management studies[J]. J Appl Psychol, 2004, 89(3): 483-96. doi:10.1037/0021-9010.89.3.483 |
| [39] | Sulaiman WSW, Noor MZM. Examining the psychometric properties of the Wong and Law Emotional Intelligences Scale (WLEIS)[J]. JSSH, 2015,2(2):81-90. |
| [40] | Kong F. The validity of the wong and law emotional intelligence scale in a Chinese sample: tests of measurement invariance and latent mean differences across gender and age[J]. Pers Individ Differ, 2017, 116: 29-31. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2017.04.025 |
| [41] | Putnick DL, Bornstein MH. Measurement invariance conventions and reporting: the state of the art and future directions for psychological research[J]. Dev Rev, 2016, 41: 71-90. doi:10.1016/j.dr.2016.06.004 |
| [42] | 陈 冬, 程东阳, 孙洋洋, 等. 黑龙江省高职护生中文版情绪智力量表的常模构建[J]. 护理学杂志, 2022, 37(11): 18-20, 42. |
| [43] | Downey LA, Johnston PJ, Hansen KR, et al. The relationship between emotional intelligence and depression in a clinical sample[J]. Eur J Psychiat, 2008, 22(2): S0213-61632008000200005. doi:10.4321/s0213-61632008000200005 |
| [44] | Enns A, Eldridge GD, Montgomery C, et al. Perceived stress, coping strategies, and emotional intelligence: a cross-sectional study of university students in helping disciplines[J]. Nurse Educ Today, 2018, 68: 226-31. doi:10.1016/j.nedt.2018.06.012 |
| [1] | 肖 蓉, 杜静雯. 6条目孤独感量表(ULS-6)是测量中国成年人群孤独感的有效工具[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 900-905. |
| [2] | 刘 倩, 黄 晨, 蒋丽洁, 邱 恒, 许 军. 健康适能评定量表评价广州市大学生健康适能状况的信效度[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(1): 47-54. |
| [3] | 许 欢, 孟庆林, 樊文萍, 王 雪, 刘梦琦, 陈志晔. 正常人脑皮层下灰质核团定量磁敏感成像的可重复性分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(12): 1810-1815. |
| [4] | 林连虹,许晓珩,方乐琴,谢丽凯,林晓敏,陈燚林,郑馥盈,贝燕柔,张 璐,张 斌. 中文版手机依赖性问卷在大学生群体的信度和效度分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(05): 746-751. |
| [5] | 肖蓉,赖巧珍,杨家平. 中文修订版生命意义量表在大学生中应用的信效度[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2017, 37(04): 499-. |
| [6] | 何藻鹏,杨德鸿,李丽. 中国人骨质疏松症生存质量简明量表的编制与信效度[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2014, 34(11): 1637-. |
| [7] | 付忠泉,关宏刚,曹正霖,霍智铭,肖隆艺. 脊柱结核GATA、SMU分型的可信度及可重复性对比分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2014, 34(08): 1188-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
