Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2747-2755.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.22
Renjie ZHOU1,2( ), Jingjing YANG1,2, Bowen SONG1,2, Xiaohua CHEN1,2, Lian WANG1,2, Yueyue WANG2, Lugen ZUO1,2, Bing ZHU1(
), Jingjing YANG1,2, Bowen SONG1,2, Xiaohua CHEN1,2, Lian WANG1,2, Yueyue WANG2, Lugen ZUO1,2, Bing ZHU1( )
)
Received:2025-05-07
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Bing ZHU
E-mail:18879997869@163.com;bbmczhubing@163.com
Renjie ZHOU, Jingjing YANG, Bowen SONG, Xiaohua CHEN, Lian WANG, Yueyue WANG, Lugen ZUO, Bing ZHU. PSMD11 overexpression promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer and affects patient prognosis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2747-2755.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.22
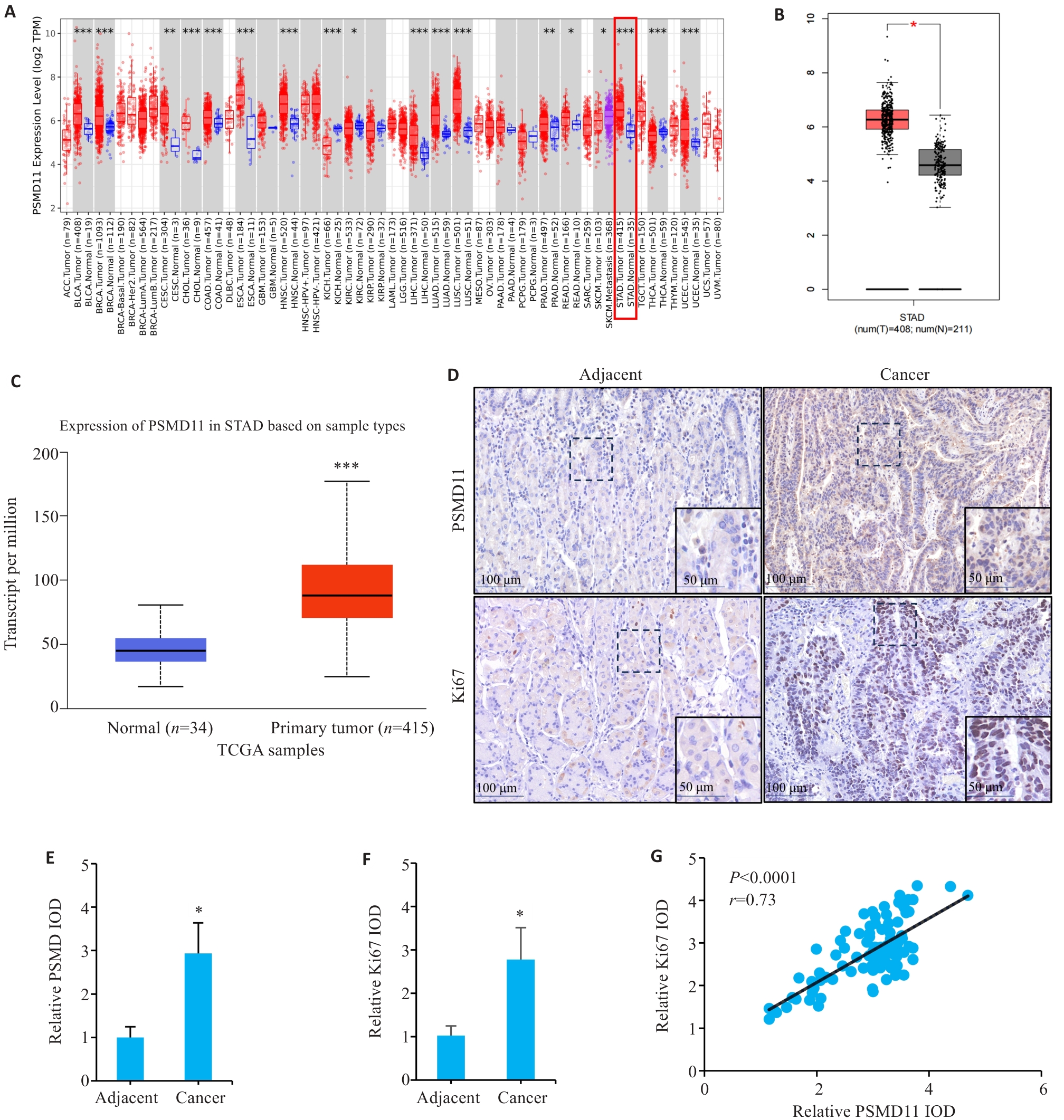
Fig.1 Expressions and correlation analysis of PSMD11 and Ki67 in gastric cancer tissues. A: Expression of PSMD11 in pan-cancer. B, C: Expression of PSMD11 in gastric cancer and adjacent tissues. D: Immunohistochemical staining of PSMD11 and Ki67. E, F: Relative IOD values of PSMD11 and Ki67. G: Correlation between PSMD11 and Ki67. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Normal/Adjacent group.
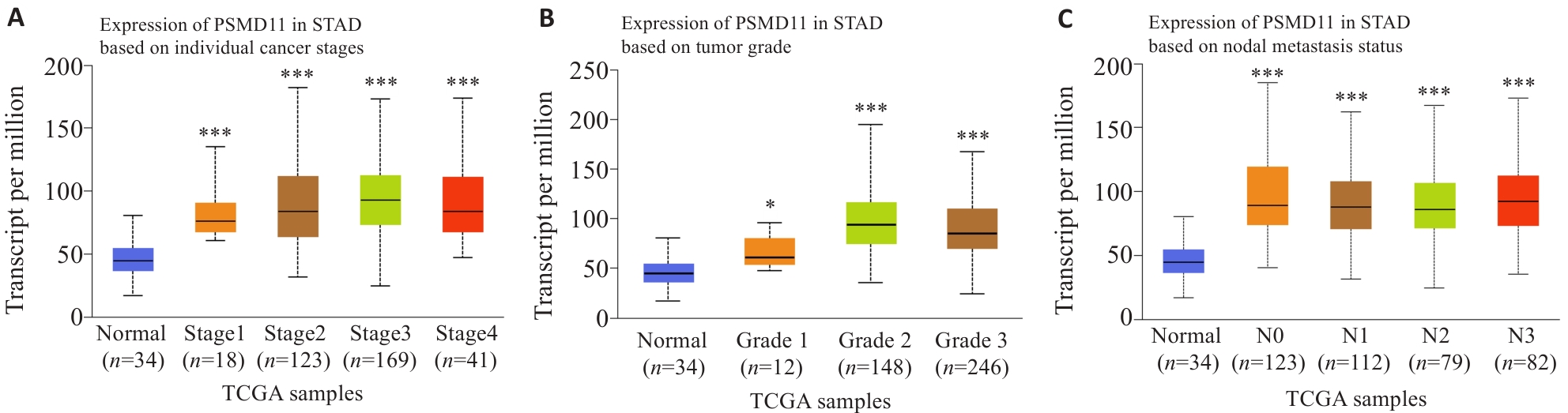
Fig.2 Relationship between PSMD11 expression in gastric cancer tissues and clinicopathological parameters of the patients. A, B: Correlation of PSMD11 expression levels with tumor grades and stages. C: Correlation of PSMD11 expression level with lymph node metastasis of gastric cancer. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 vs adjacent tissue.
| Characteristics | n | PSMD11 expression (n=47) | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | ||||
| Gender | 0.048 | 0.826 | |||
| Female | 31 | 15 (48.39%) | 16 (51.61%) | ||
| Male | 63 | 32 (50.79%) | 31 (49.21%) | ||
| Age (year) | 0.048 | 0.826 | |||
| <60 | 31 | 16 (51.61%) | 15 (48.39%) | ||
| ≥60 | 63 | 31 (49.21%) | 32 (50.79%) | ||
| Pathohistological type | 0.052 | 0.82 | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 67 | 34 (50.75%) | 33 (49.25%) | ||
| Other | 27 | 13 (48.15%) | 14 (51.85%) | ||
| CEA (μg/L) | 13.155 | <0.001 | |||
| <5 | 35 | 26 (74.29%) | 9 (25.71%) | ||
| ≥5 | 59 | 21 (35.59%) | 38 (64.41%) | ||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | 10.938 | 0.001 | |||
| <37 | 44 | 30 (68.18%) | 14 (31.82%) | ||
| ≥37 | 50 | 17 (34%) | 33 (66%) | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | 1.549 | 0.213 | |||
| <5 | 42 | 24 (57.14%) | 18 (42.86%) | ||
| ≥5 | 52 | 23 (44.23%) | 29 (55.77%) | ||
| Histological Grading | 4.257 | 0.039 | |||
| G1-G2 | 46 | 28 (60.87%) | 18 (39.13%) | ||
| G3-G4 | 48 | 19 (39.58%) | 29 (60.42%) | ||
| T Stage | 11.525 | 0.001 | |||
| T1-T2 | 36 | 26 (72.22%) | 10 (27.78%) | ||
| T3-T4 | 58 | 21 (36.21%) | 37 (63.79%) | ||
| N Stage | 11.141 | 0.001 | |||
| N0-N1 | 40 | 28 (70%) | 12 (30%) | ||
| N2-N3 | 54 | 19 (35.19%) | 35 (64.81%) | ||
Tab.1 Relationship between PSMD11 expression level in gastric cancer tissues and parameters of malignant progression in gastric cancer patients (n, %)
| Characteristics | n | PSMD11 expression (n=47) | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | ||||
| Gender | 0.048 | 0.826 | |||
| Female | 31 | 15 (48.39%) | 16 (51.61%) | ||
| Male | 63 | 32 (50.79%) | 31 (49.21%) | ||
| Age (year) | 0.048 | 0.826 | |||
| <60 | 31 | 16 (51.61%) | 15 (48.39%) | ||
| ≥60 | 63 | 31 (49.21%) | 32 (50.79%) | ||
| Pathohistological type | 0.052 | 0.82 | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 67 | 34 (50.75%) | 33 (49.25%) | ||
| Other | 27 | 13 (48.15%) | 14 (51.85%) | ||
| CEA (μg/L) | 13.155 | <0.001 | |||
| <5 | 35 | 26 (74.29%) | 9 (25.71%) | ||
| ≥5 | 59 | 21 (35.59%) | 38 (64.41%) | ||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | 10.938 | 0.001 | |||
| <37 | 44 | 30 (68.18%) | 14 (31.82%) | ||
| ≥37 | 50 | 17 (34%) | 33 (66%) | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | 1.549 | 0.213 | |||
| <5 | 42 | 24 (57.14%) | 18 (42.86%) | ||
| ≥5 | 52 | 23 (44.23%) | 29 (55.77%) | ||
| Histological Grading | 4.257 | 0.039 | |||
| G1-G2 | 46 | 28 (60.87%) | 18 (39.13%) | ||
| G3-G4 | 48 | 19 (39.58%) | 29 (60.42%) | ||
| T Stage | 11.525 | 0.001 | |||
| T1-T2 | 36 | 26 (72.22%) | 10 (27.78%) | ||
| T3-T4 | 58 | 21 (36.21%) | 37 (63.79%) | ||
| N Stage | 11.141 | 0.001 | |||
| N0-N1 | 40 | 28 (70%) | 12 (30%) | ||
| N2-N3 | 54 | 19 (35.19%) | 35 (64.81%) | ||
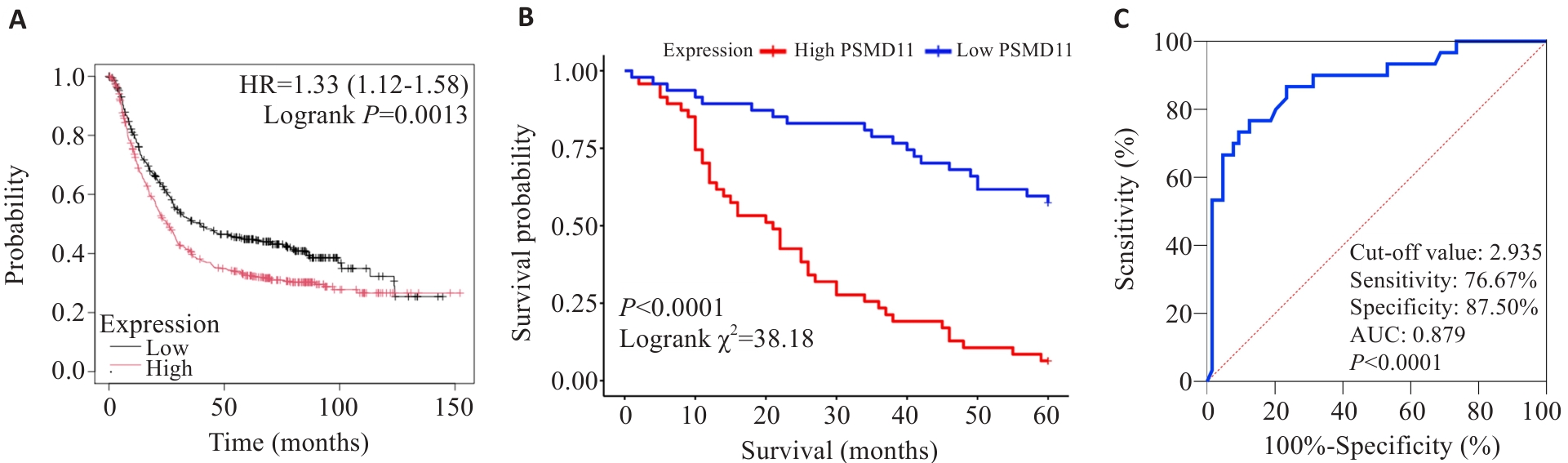
Fig.3 Effect of PSMD11 on prognosis of patients with gastric cancer. A: Kaplan-Meier analysis. B: Survival curves. C: Predictive value of PSMD11 for 5-year postoperative survival in gastric cancer patients.
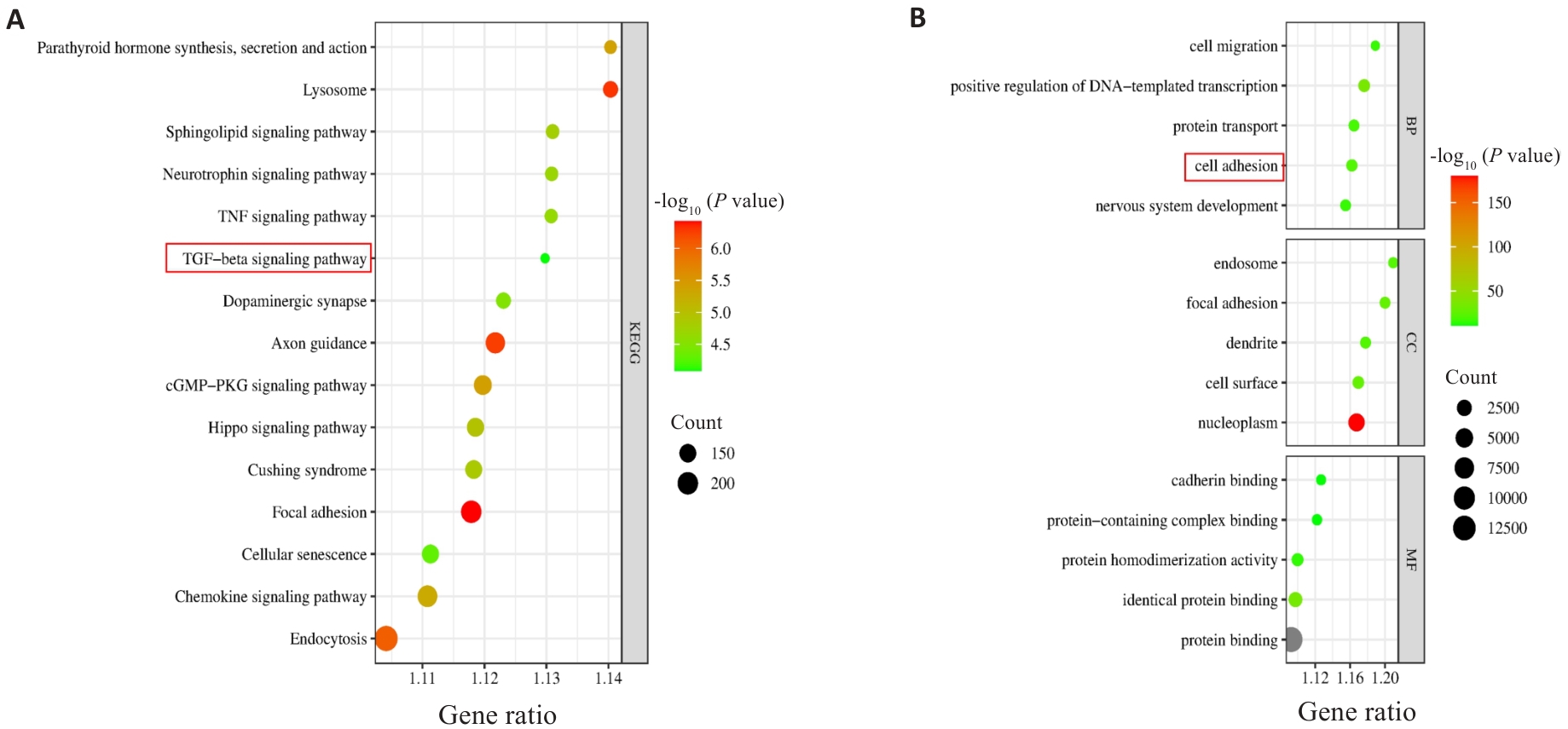
Fig.5 KEGG and GO enrichment analyses of PSMD11 and gastric cancer co-expressed genes. A: KEGG enrichment analysis results. B: GO enrichment analysis results.

Fig.6 PSMD11 overexpression promotes migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells (Transwell assay). A-C: Lentivirus-mediated knockdown and overexpression of PSMD11 in HGC-27 cells. D-I: Migration and invasion of the transfected HGC-27 cells (n=3), Si: siRNA; LV: Overexpression. *P<0.05 vs Si-NC or LV-Control.
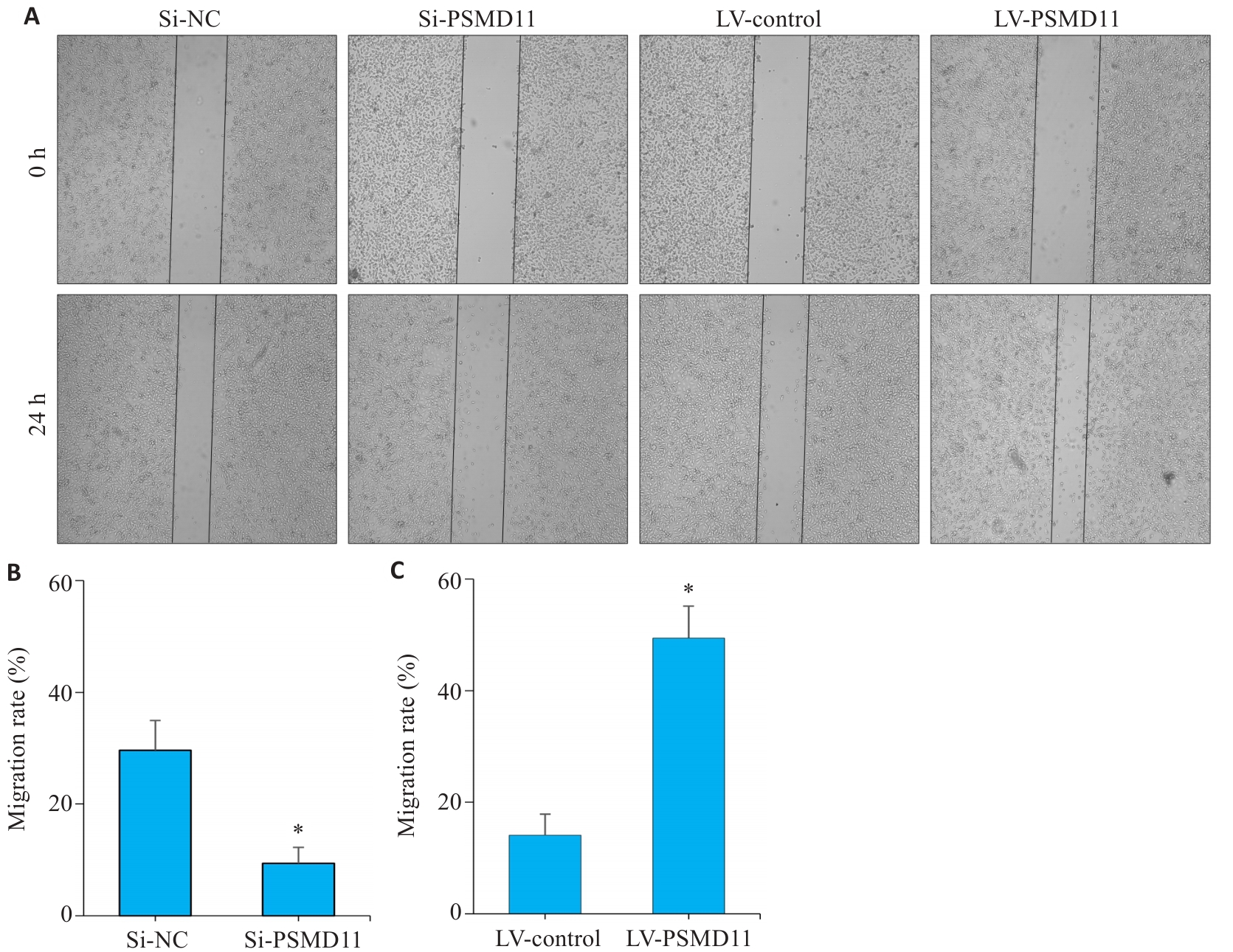
Fig.7 Wound healing assay showing that PSMD11 overexpression promotes migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells. A-C: PSMD11 overexpression promotes HGC-27 cell migration in Wound-Healing assay. n=3, Si: siRNA; LV: overexpression. *P<0.05 vs Si-NC or LV-Control.
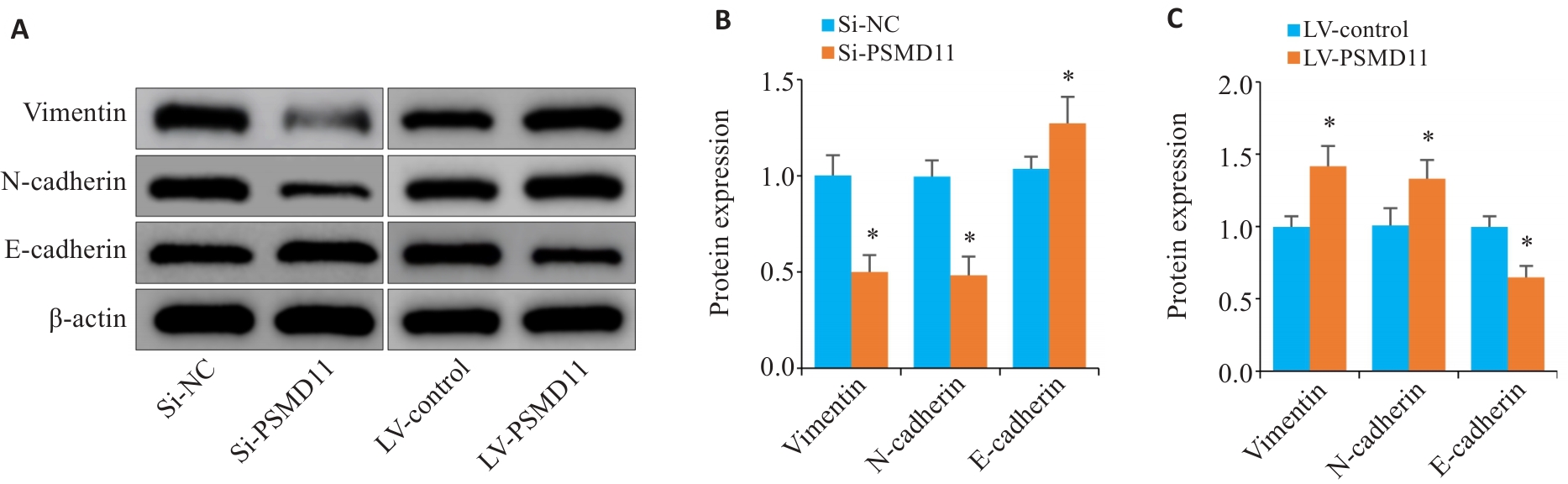
Fig.8 PSMD11 promotes EMT process in gastric cancer cells. A-C: Expressions of key proteins of EMT in gastric cancer cells (n=3). Si: siRNA. *P<0.05 vs Si-NC or LV-Control.
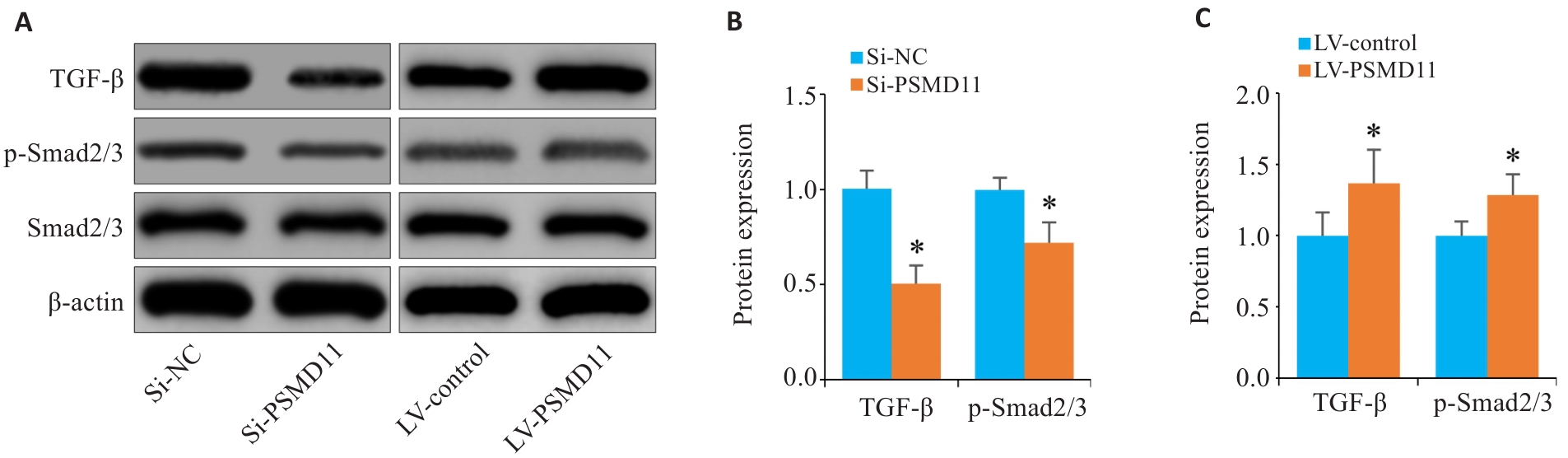
Fig.9 Overexpression of PSMD11 in gastric cancer activates the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. A-C: Expressions of TGF-β1, p-Smad2/3, and Smad2/3 in HGC-27 cells. *P<0.05 vs Si-NC or LV-Control.
| [1] | Huang JJ, Lucero-Prisno DE III, Zhang L, et al. Updated epidemiology of gastrointestinal cancers in east Asia[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 20(5): 271-87. doi:10.1038/s41575-022-00726-3 |
| [2] | Zhao LL, Zhao DB, Chen YT. Neoadjuvant treatment for locally advanced gastric cancer[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2020, 42(11): 907-11. |
| [3] | Shah MA, Kennedy EB, Alarcon-Rozas AE, et al. Immunotherapy and targeted therapy for advanced gastroesophageal cancer: ASCO guideline[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2023, 41(7): 1470-91. |
| [4] | Fiorica F, Cartei F, Enea M, et al. The impact of radiotherapy on survival in resectable gastric carcinoma: a meta-analysis of literature data[J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2007, 33(8): 729-40. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2007.08.005 |
| [5] | Carter SK, Comis RL. Gastric cancer: current status of treatment[J]. JNCI J Natl Cancer Inst, 1977, 58(3): 567-78. doi:10.1093/jnci/58.3.567 |
| [6] | 王 阳, 张保贵. 胃癌上皮间质转化相关LncRNA研究进展[J]. 济宁医学院学 报, 2024, 47(2): 165-8. |
| [7] | Vaquero J, Guedj N, Clapéron A, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cholangiocarcinoma: from clinical evidence to regulatory networks[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 66(2): 424-41. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2016.09.010 |
| [8] | Vilchez D, Boyer L, Morantte I, et al. Increased proteasome activity in human embryonic stem cells is regulated by PSMD11[J]. Nature, 2012, 489(7415): 304-8. doi:10.1038/nature11468 |
| [9] | 孙 亮. PSMD11通过调控CDK4的泛素化降解促进肝细胞癌的增殖[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2024. |
| [10] | Zhang C, Xu T, Ji K, et al. An integrative analysis reveals the prognostic value and potential functions of PSMD11 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2023, 62(9): 1355-68. doi:10.1002/mc.23568 |
| [11] | Sahni S, Krisp C, Molloy MP, et al. PSMD11, PTPRM and PTPRB as novel biomarkers of pancreatic cancer progression[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA Gen Subj, 2020, 1864(11): 129682. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2020.129682 |
| [12] | Zhou XJ, Liu XF, Wang X, et al. SITP: a single cell bioinformatics analysis flow captures proteasome markers in the development of breast cancer[J]. Methods, 2025, 233: 1-10. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2024.11.011 |
| [13] | Huang Q, Tian R, Yu J, et al. Identification of PSMD11 as a novel cuproptosis- and immune-related prognostic biomarker promoting lung adenocarcinoma progression[J]. Cancer Med, 2024, 13(11): e7379. doi:10.1002/cam4.7379 |
| [14] | Xu Z, Liao H, Huang L, et al. IBPGNET: lung adenocarcinoma recurrence prediction based on neural network interpretability[J]. Brief Bioinform, 2024, 25(3): bbae080. doi:10.1093/bib/bbae080 |
| [15] | 褚以忞. MiR-1254下调PSMD10抑制结直肠癌细胞迁移的机制研究[D]: 第 二军医大学, 2018. |
| [16] | 刘志勇. PSMD14促进骨肉瘤进展及安罗替尼耐药的功能和机制研究[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2023. |
| [17] | Wang R, Huang W, Cai K, et al. FLOT1 promotes gastric cancer progression and metastasis through BCAR1/ERK signaling[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2023, 19(16): 5104-19. doi:10.7150/ijbs.82606 |
| [18] | Zhang L, Li Q, Yang J, et al. Cytosolic TGM2 promotes malignant progression in gastric cancer by suppressing the TRIM21-mediated ubiquitination/degradation of STAT1 in a GTP binding-dependent modality[J]. Cancer Commun: Lond, 2023, 43(1): 123-49. doi:10.1002/cac2.12386 |
| [19] | Moreno D, Viana R, Sanz P. Two-hybrid analysis identifies PSMD11, a non-ATPase subunit of the proteasome, as a novel interaction partner of AMP-activated protein kinase[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2009, 41(12): 2431-9. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2009.07.002 |
| [20] | Yang YH, Xing ZH, Wang H, et al. PSMD11 and PSMD14 may serve as novel biomarkers for the prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2025, 15: 1555649. doi:10.3389/fonc.2025.1555649 |
| [21] | Sun L, Liu ZT, Wu ZY, et al. PSMD11 promotes the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the ubiquitination degradation of CDK4[J]. Cell Signal, 2024, 121: 111279. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111279 |
| [22] | Wang L, Zhao L, Wei G, et al. Homoharringtonine could induce quick protein synthesis of PSMD11 through activating MEK1/ERK1/2 signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer cells[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2018, 119(8): 6644-56. doi:10.1002/jcb.26847 |
| [23] | Salah Fararjeh A, Al-Khader A, Al-Saleem M, et al. The prognostic significance of proteasome 26S subunit, non-ATPase (PSMD) genes for bladder urothelial carcinoma patients[J]. Cancer Inform, 2021, 20: 11769351211067692. doi:10.1177/11769351211067692 |
| [24] | Li S, Cong X, Gao H, et al. Tumor-associated neutrophils induce EMT by IL-17a to promote migration and invasion in gastric cancer cells[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 6. doi:10.1186/s13046-018-1003-0 |
| [25] | Wang R, Sun Y, Yu W, et al. Downregulation of miRNA-214 in cancer-associated fibroblasts contributes to migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells through targeting FGF9 and inducing EMT[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 20. doi:10.1186/s13046-018-0995-9 |
| [26] | Baum B, Georgiou M. Dynamics of adherens junctions in epithelial establishment, maintenance, and remodeling[J]. J Cell Biol, 2011, 192(6): 907-17. doi:10.1083/jcb.201009141 |
| [27] | Macara IG, Guyer R, Richardson G, et al. Epithelial homeostasis[J]. Curr Biol, 2014, 24(17): R815-25. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2014.06.068 |
| [28] | Park YJ, Bang IJ, Jeong MH, et al. Effects of β-sitosterol from corn silk on TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung alveolar epithelial cells[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2019, 67(35): 9789-95. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.9b02730 |
| [29] | Deng L, Bao W, Zhang B, et al. AZGP1 activation by lenvatinib suppresses intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the TGF‑β1/Smad3 pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(9): 590. doi:10.1038/s41419-023-06092-5 |
| [30] | Chen J, Zhu H, Liu Q, et al. DEPTOR induces a partial epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis via autocrine TGFβ1 signaling and is associated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 273. doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1220-1 |
| [31] | Fan C, González-Prieto R, Kuipers TB, et al. The lncRNA LETS1 promotes TGF‑β‑induced EMT and cancer cell migration by transcriptionally activating a TβR1-stabilizing mechanism[J]. Sci Signal, 2023, 16(790): eadf1947. doi:10.1126/scisignal.adf1947 |
| [1] | Ying WANG, Jing LI, Yidi WANG, Mingyu HUA, Weibin HU, Xiaozhi ZHANG. Construction and verification of a prognostic model combining anoikis and immune prognostic signatures for primary liver cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1967-1979. |
| [2] | Yu ZHANG, Haitao LI, Yuqing PAN, Jiexian CAO, Li ZHAI, Xi ZHANG. Pan-cancer analysis of MZB1 expression and its association with immune infiltration and clinical prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 2006-2018. |
| [3] | Siyuan MA, Bochao ZHANG, Chun PU. Circ_0000437 promotes proliferation, invasion, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells by targeting the let-7b-5p/CTPS1 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1682-1696. |
| [4] | Ziliang WANG, Xiaohua CHEN, Jingjing YANG, Chen YAN, Zhizhi ZHANG, Bingyi HUANG, Meng ZHAO, Song LIU, Sitang GE, Lugen ZUO, Deli CHEN. High expression of SURF4 promotes migration, invasion and proliferation of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting tight junction proteins [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1732-1742. |
| [5] | Jinlong PANG, Xinli ZHAO, Zhen ZHANG, Haojie WANG, Xingqi ZHOU, Yumei YANG, Shanshan LI, Xiaoqiang CHANG, Feng LI, Xian LI. Overexpression of multimerin-2 promotes cutaneous melanoma cell invasion and migration and is associated with poor prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1479-1489. |
| [6] | Xuan WU, Jiamin FANG, Weiwei HAN, Lin CHEN, Jing SUN, Qili JIN. High PRELID1 expression promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1535-1542. |
| [7] | Kang WANG, Haibin LI, Jing YU, Yuan MENG, Hongli ZHANG. High expression of ELFN1 is a prognostic biomarker and promotes proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1543-1553. |
| [8] | Zhennan MA, Fuquan LIU, Xuefeng ZHAO, Xiaowei ZHANG. High expression of DTX2 promotes proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of oxaliplatin-resistant colorectal cancer cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 829-836. |
| [9] | Yi ZHANG, Yu SHEN, Zhiqiang WAN, Song TAO, Yakui LIU, Shuanhu WANG. High expression of CDKN3 promotes migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating the p53/NF-κB signaling pathway and inhibiting cell apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [10] | Lu TAO, Zhuoli WEI, Yueyue WANG, Ping XIANG. CEACAM6 inhibits proliferation and migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 566-576. |
| [11] | Qingqing HUANG, Wenjing ZHANG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Lian WANG, Xue SONG, Zhijun GENG, Lugen ZUO, Yueyue WANG, Jing LI, Jianguo HU. High MYO1B expression promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor patient prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 622-631. |
| [12] | Huali LI, Ting SONG, Jiawen LIU, Yongbao LI, Zhaojing JIANG, Wen DOU, Linghong ZHOU. Prognosis-guided optimization of intensity-modulated radiation therapy plans for lung cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 643-649. |
| [13] | Xue SONG, Yue CHEN, Min ZHANG, Nuo ZHANG, Lugen ZUO, Jing LI, Zhijun GENG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Yueyue WANG, Lian WANG, Jianguo HU. GPSM2 is highly expressed in gastric cancer to affect patient prognosis by promoting tumor cell proliferation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 229-238. |
| [14] | Tianwei TANG, Luan LI, Yuanhan CHEN, Li ZHANG, Lixia XU, Zhilian LI, Zhonglin FENG, Huilin ZHANG, Ruifang HUA, Zhiming YE, Xinling LIANG, Ruizhao LI. High serum cystatin C is an independent risk factor for poor renal prognosis in IgA nephropathy [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 379-386. |
| [15] | Bowen SONG, Renjie ZHOU, Ying XU, Jinran SHI, Zhizhi ZHANG, Jing LI, Zhijun GENG, Xue SONG, Lian WANG, Yueyue WANG, Lugen ZUO. Elevated TMCO1 expression in gastric cancer is associated poor prognosis and promotes malignant phenotypes of tumor cells by inhibiting apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(11): 2385-2393. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||