Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (9): 1989-1996.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.18
Lu RAO1,2( ), Jiahe DING1,2, Jiangping WEI1,2, Yong YANG1,2, Xiaomei ZHANG1,2(
), Jiahe DING1,2, Jiangping WEI1,2, Yong YANG1,2, Xiaomei ZHANG1,2( ), Jirui WANG1,2(
), Jirui WANG1,2( )
)
Received:2025-03-07
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Xiaomei ZHANG, Jirui WANG
E-mail:2473601792@qq.com;ZXM761@163.com;wangjiruizyy@163.com
Lu RAO, Jiahe DING, Jiangping WEI, Yong YANG, Xiaomei ZHANG, Jirui WANG. Flos Sophorae improves psoriasis in mice by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1989-1996.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.18
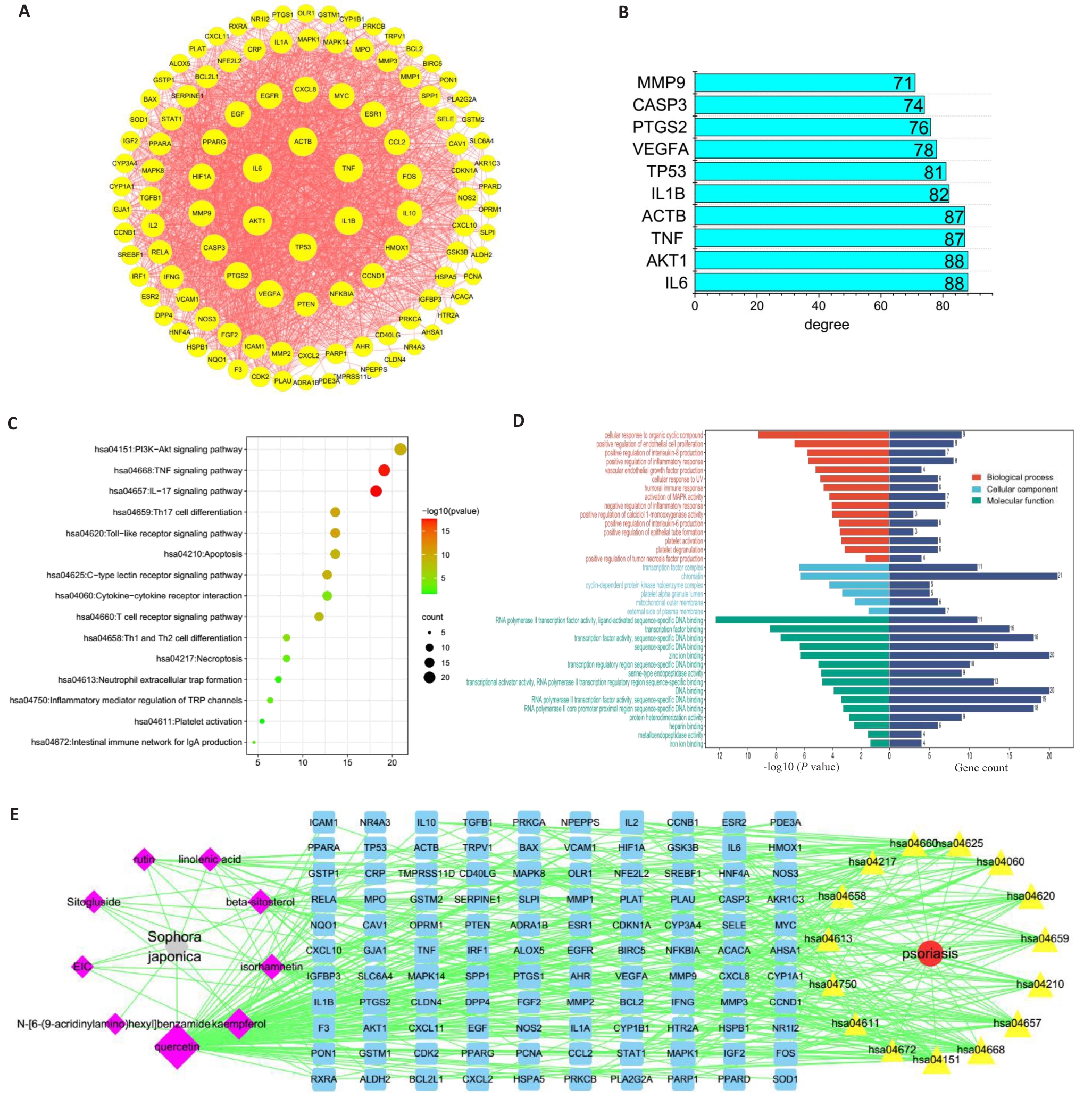
Fig.1 Network pharmacological analysis of the components of Flos Sophorae. A: PPI network diagram of the core targets of Flos Sophorae for treatment of psoriasis. B: Degree values of the targets in the PPI network. C: KEGG pathway enrichment analysis. D: GO enrichment analysis. E: Traditional Chinese Medicine-Active Ingredients-Key Targets-Signalling Pathways-Disease pathway network.
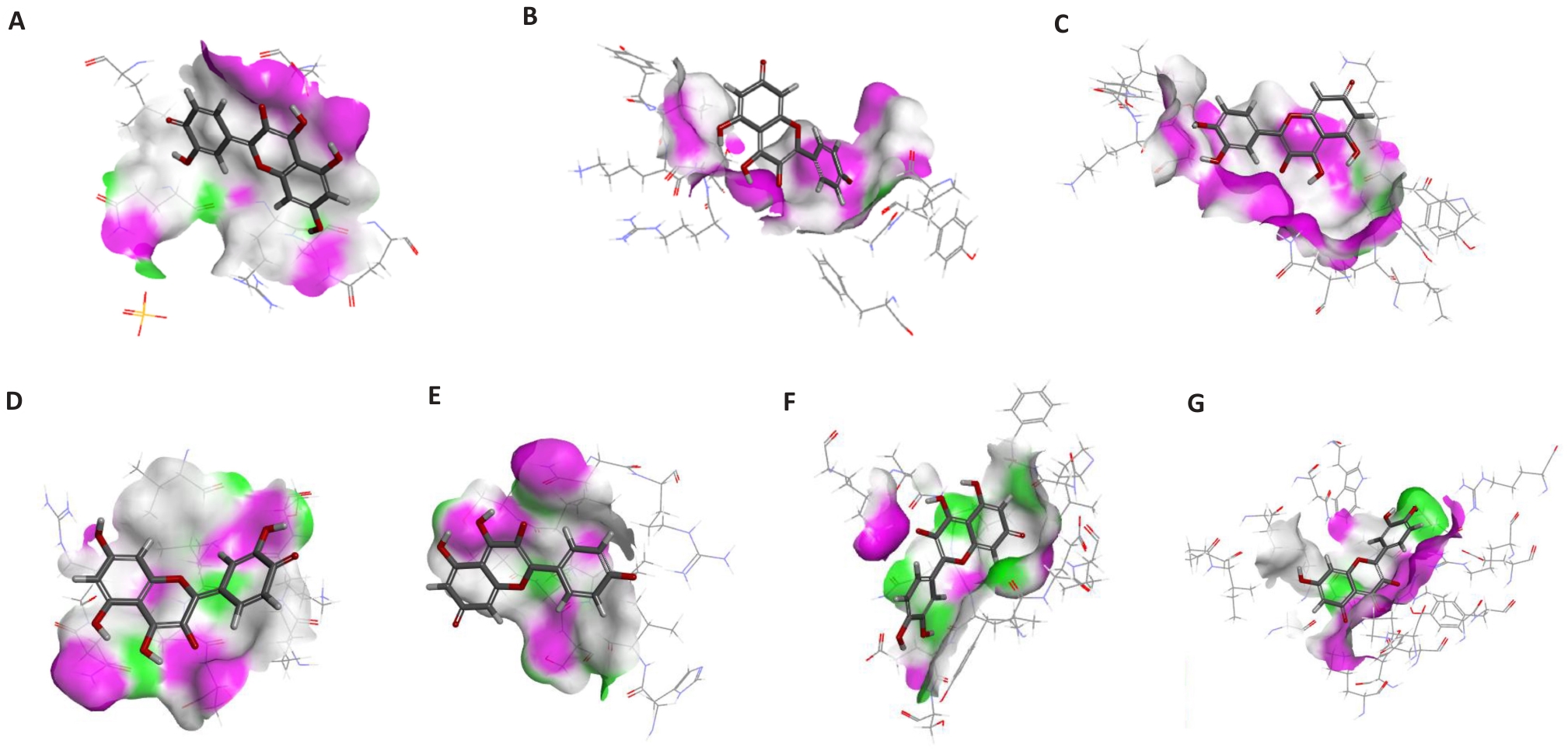
Fig.2 3D modelling of docking of Flos Sophorae active ingredients with the protein molecules. A: Docking results of IL-6 with quercetin. B: Docking results of AKT1 with quercetin. C: Docking results of AKT1 with kaempferol. D: Docking results of TNF with quercetin. E: Docking results of TNF with kaempferol. F: Docking results of IL-1Β with quercetin. G: Docking results of TP53 with quercetin.
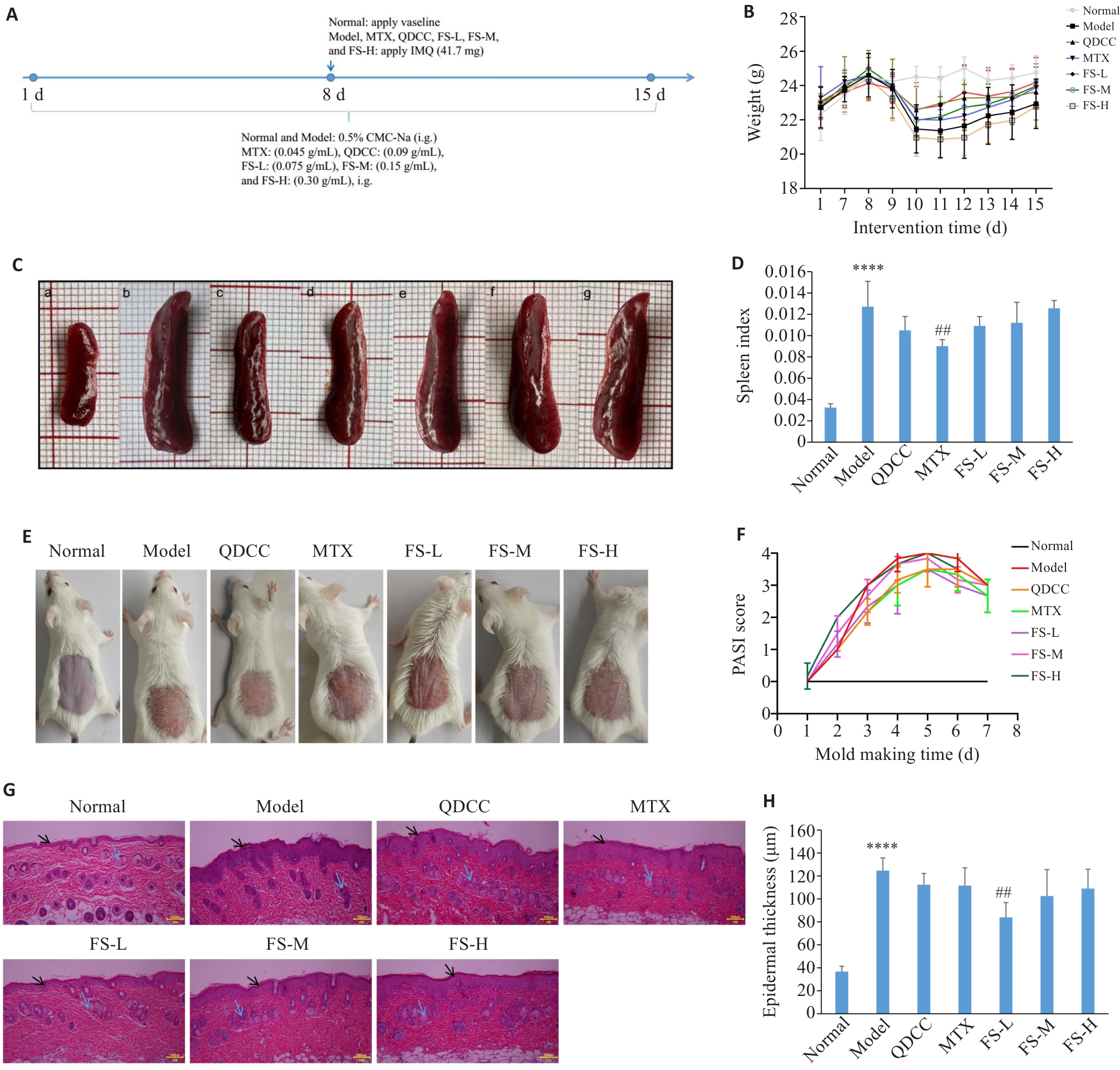
Fig.3 Flos Sophorae ameliorates IMQ-induced psoriasis in mice. A: Schematic diagram of IMQ modeling in mice. B: Changes in body weight of the mice of each group. C: Morphological changes in the spleen. D: Spleen index. E: Morphological characteristics of dorsal skin lesions in each group on the 15th day of modelling. F: Skin PASI scores of the mice in each group. G: HE staining of the dorsal skin of the mice in each group (scale bar=100 μm). H: Skin thickness. ****P<0.05 vs Normal; ##P<0.01 vs Model group. The black arrow indicate the stratum corneum, and the blue arrow indicate the infiltrating inflammatory cells. FS-L/M/H: Flos Sophorae low/medium/high; QDCC: Qingdai compound capsule; MTX: Methotrexate.
| Score | Severity | Erythema | Epidermal flaking | Plaque thickness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Asymptomatic | None | None | Flush with normal skin |
| 1 | Mild symptom | Patch of pale red colour | Epidermal flaking | Slightly higher than normal skin |
| 2 | Moderate symptomatology | Red patch | Covered with flaky epidermal flakes | Moderate bulge |
| 3 | Severe symptoms | Dark red patches | Thick, stratified epidermal flakes | Bulge |
| 4 | Extremely severe symptoms | Very dark red patches | There is thick, stratified epidermal flaking | Marked thickening of the bulge |
Tab.1 PASI scale for psoriasis-like mice
| Score | Severity | Erythema | Epidermal flaking | Plaque thickness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Asymptomatic | None | None | Flush with normal skin |
| 1 | Mild symptom | Patch of pale red colour | Epidermal flaking | Slightly higher than normal skin |
| 2 | Moderate symptomatology | Red patch | Covered with flaky epidermal flakes | Moderate bulge |
| 3 | Severe symptoms | Dark red patches | Thick, stratified epidermal flakes | Bulge |
| 4 | Extremely severe symptoms | Very dark red patches | There is thick, stratified epidermal flaking | Marked thickening of the bulge |
| Mol ID | Compound | OB (%) | DL |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOL000131 | Linoleic acid (EIC) | 41.90 | 0.14 |
| MOL000354 | isorhamnetin | 49.60 | 0.31 |
| MOL000357 | Sitogluside | 20.63 | 0.62 |
| MOL000358 | beta-sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| MOL000422 | kaempferol | 41.88 | 0.24 |
| MOL000432 | linolenic acid | 45.01 | 0.15 |
| MOL005935 | N-[6-(9-acridinylamino) hexyl]benzamide | 41.70 | 0.78 |
| MOL005940 | quercetin-3'-methyl ether | 46.44 | 0.3 |
| MOL000098 | quercetin | 46.43 | 0.28 |
| MOL000415 | rutin | 3.20153 | - |
Tab.2 General information of active ingredients of Flos Sophorae
| Mol ID | Compound | OB (%) | DL |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOL000131 | Linoleic acid (EIC) | 41.90 | 0.14 |
| MOL000354 | isorhamnetin | 49.60 | 0.31 |
| MOL000357 | Sitogluside | 20.63 | 0.62 |
| MOL000358 | beta-sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| MOL000422 | kaempferol | 41.88 | 0.24 |
| MOL000432 | linolenic acid | 45.01 | 0.15 |
| MOL005935 | N-[6-(9-acridinylamino) hexyl]benzamide | 41.70 | 0.78 |
| MOL005940 | quercetin-3'-methyl ether | 46.44 | 0.3 |
| MOL000098 | quercetin | 46.43 | 0.28 |
| MOL000415 | rutin | 3.20153 | - |
| Gene | Uniprot ID | PDB | Refinement resolution | Docking molecule | CDOCKER-ENERGY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | P05231 | 1ALU | 1.9A | quercetin | 35.587 4 |
| AKT1 | P31749 | 1UNQ | 0.98A | quercetin | 51.894 3 |
| kaempferol | 68.900 4 | ||||
| TNF | P01375 | 5UUI | 1.4A | quercetin | 26.816 3 |
| kaempferol | 34.701 2 | ||||
| IL-1β | P01584 | 5R8Q | 1.23A | quercetin | 47.096 9 |
| TP53 | P04637 | 5MHC | 1.2A | quercetin | 59.838 6 |
Tab.3 Target screening and docking results
| Gene | Uniprot ID | PDB | Refinement resolution | Docking molecule | CDOCKER-ENERGY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | P05231 | 1ALU | 1.9A | quercetin | 35.587 4 |
| AKT1 | P31749 | 1UNQ | 0.98A | quercetin | 51.894 3 |
| kaempferol | 68.900 4 | ||||
| TNF | P01375 | 5UUI | 1.4A | quercetin | 26.816 3 |
| kaempferol | 34.701 2 | ||||
| IL-1β | P01584 | 5R8Q | 1.23A | quercetin | 47.096 9 |
| TP53 | P04637 | 5MHC | 1.2A | quercetin | 59.838 6 |
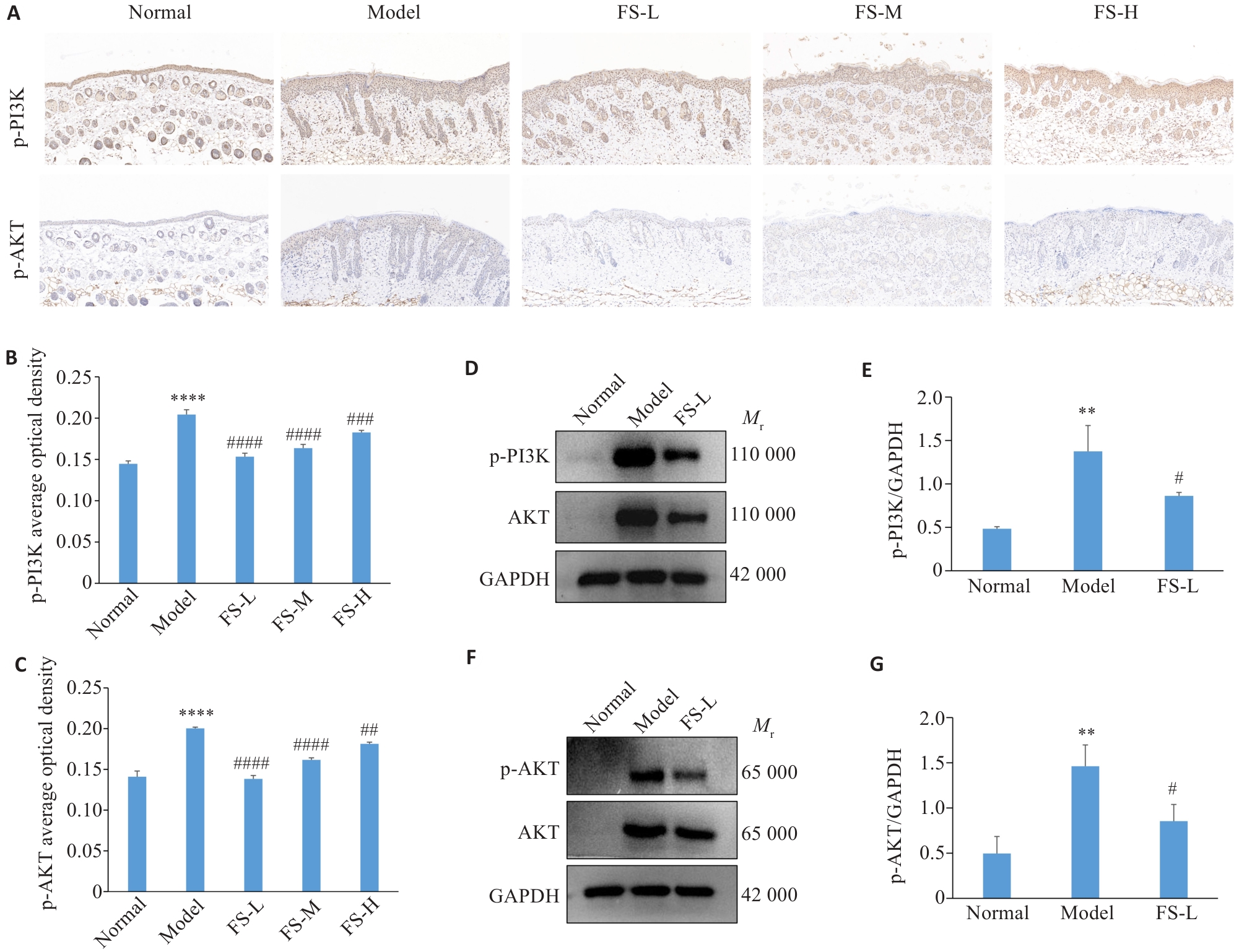
Fig.4 Expression of PI3K and AKT in the skin tissue of psoriasis mice. A: results of immunohistochemistry (×20). B, C: AOD diagram. D, F: Results of Western blotting for p-PI3K, PI3K, p-AKT, and AKT. E, G: Quantitative analysis of the protein expressions. **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001 vs Normal; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001, ####P<0.0001 vs Model.
| [1] | Armstrong AW, Read C. Pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment of psoriasis: a review[J]. JAMA, 2020, 323(19): 1945-60. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.4006 |
| [2] | 胡安徽. 槐花入药的本草考证[J]. 中成药, 2018, 40(11): 2587-9. |
| [3] | Chen YT, Long PT, Xu HX, et al. The inhibitory activity of Flos Sophorae Immaturus extract and its major flavonoid components on pancreatic lipase[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2024, 277(Pt 1): 134092. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134092 |
| [4] | Zhang ZL, Zhang YR, Zhang AN, et al. Flos Sophorae Immaturus extracts: Effects of different extraction solvents on antioxidant, antimicrobial activities and active ingredients[J]. S Afr N J Bot, 2024, 170: 358-66. doi:10.1016/j.sajb.2024.05.045 |
| [5] | Peters RA, Shorthouse M. Identification of a volatile constituent formed by homogenates of Acacia georginae exposed to fluoride[J]. Nature, 1971, 231(5298): 123-4. doi:10.1038/231123a0 |
| [6] | Mou QQ, He JX, Yin RL, et al. Response surface optimized infrared-assisted extraction and UHPLC determination of flavonoid types from Flos sophorae[J]. Molecules, 2017, 22(6): 1000. doi:10.3390/molecules22061000 |
| [7] | 张 珩, 石晓琳. 槐米总黄酮的抗炎和镇痛作用[J]. 临床医学研究与实践, 2018, 3(31): 4-6. |
| [8] | Kim JM, Lee JH, Lee GS, et al. Sophorae Flos extract inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation by suppressing the NF-κB/NFATc1 pathway in mouse bone marrow cells[J]. BMC Complement Altern Med, 2017, 17(1): 164. doi:10.1186/s12906-017-1745-9 |
| [9] | 任晓莉, 杨 璐, 乔 鹏, 等. 复合酶法提取槐花多糖的工艺优化及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业科技, 2024, 45(7): 8-14. doi:10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2023070216 |
| [10] | 蒋 楠, 王富静, 封 亮, 等. 基于非酶糖基化反应的槐花抑制AGEs形成的活性组分筛选[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2019, 44(14): 3100-6. doi:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190424.201 |
| [11] | 强 燕, 王瑞平, 孙晓颖, 等. 银屑病血热证中药治疗用药规律及疗效分析[J]. 中国皮肤性病学杂志, 2020, 34(9): 1073-7. |
| [12] | 翟永丽. 凉血活血汤治疗银屑病98例[J]. 实用中医药杂志, 2015, 31(3): 208. |
| [13] | 张 玲. 段行武治疗寻常型银屑病经验[J]. 中国民间疗法, 2017, 25(4): 4-5. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-5798.2017.04.005 |
| [14] | 明瑞蕊, 张彦琼, 徐 颖, 等. 基于网络药理学和实验验证探讨盘龙七片从PI3K/AKT信号通路干预大鼠椎动脉型颈椎病的机制[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2022, 47(16): 4454-61. |
| [15] | Tang ZL, Zhang K, Lv SC, et al. LncRNA MEG3 suppresses PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway to enhance autophagy and inhibit inflammation in TNF-α-treated keratinocytes and psoriatic mice[J]. Cytokine, 2021, 148: 155657. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155657 |
| [16] | Langley RG, Ellis CN. Evaluating psoriasis with psoriasis area and severity index, psoriasis global assessment, and lattice system physician's global assessment[J]. J Am Acad Dermatol, 2004, 51(4): 563-9. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.04.012 |
| [17] | 王胜利, 于 虹, 李超群, 等. 制备色谱法从槐米中同时精制芦丁和槲皮素[J]. 食品科技, 2022, 47(2): 245-50. |
| [18] | Ma J, Wang FF, Wang L, et al. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/GLUT1 signaling pathway by quercetin in the treatment of psoriasis[J]. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed), 2025, 30(2): 26884. doi:10.31083/fbl26884 |
| [19] | 贺凌宇. 从“血” 论治银屑病[J]. 中国临床医生杂志, 2025, 53(1): 116-9. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-8552.2025.01.030 |
| [20] | 叶晟桢, 凌桂华, 肖 敏, 等. 基于四川地域特色探讨寻常性银屑病的中医治疗[J]. 皮肤科学通报, 2024, 41(3): 348-51. doi:10.13735/j.cjdv.1001-7089.202208209 |
| [21] | Georgescu SR, Tampa M, Caruntu C, et al. Advances in understanding the immunological pathways in psoriasis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(3): 739. doi:10.3390/ijms20030739 |
| [22] | Boehncke WH, Brembilla NC. Unmet needs in the field of psoriasis: pathogenesis and treatment[J]. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol, 2018, 55(3): 295-311. doi:10.1007/s12016-017-8634-3 |
| [23] | Mercurio L, Albanesi C, Madonna S. Recent updates on the involvement of PI3K/AKT/mTOR molecular cascade in the pathogenesis of hyperproliferative skin disorders[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2021, 8: 665647. doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.665647 |
| [24] | Buerger C. Epidermal mTORC1 signaling contributes to the pathogenesis of psoriasis and could serve as a therapeutic target[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 2786. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.02786 |
| [25] | Liu JL, Li LY, He GH. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction conditions for five major bioactive compounds from Flos sophorae immaturus (cultivars of Sophora Japonica L.) using response surface methodology[J]. Molecules, 2016, 21(3): 296. doi:10.3390/molecules21030296 |
| [26] | Teng Y, Fan YB, Ma JW, et al. The PI3K/Akt pathway: emerging roles in skin homeostasis and a group of non-malignant skin disorders[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(5): 1219. doi:10.3390/cells10051219 |
| [27] | Guo J, Zhang HY, Lin WR, et al. Signaling pathways and targeted therapies for psoriasis[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 437. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01655-6 |
| [28] | 王 昊, 冉立伟, 惠 珂, 等. Survivin和PI3K、AKT在寻常型银屑病皮损角质形成细胞中的表达及其相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2017, 37(11): 1512-6. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2017.11.14 |
| [29] | 张梦欣, 高铭淑, 周宇航, 等. 基于MAPK/NF-κB通路研究丹参白疕消方联合甲氨蝶呤治疗银屑病的作用机制[J]. 中草药, 2025, 56(12): 4316-26. |
| [30] | Wang MX, Ma XX, Gao CJ, et al. Rutin attenuates inflammation by downregulating AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in psoriasis: Network pharmacology analysis and experimental evidence[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 125(Pt A): 111033. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111033 |
| [31] | 杨素清, 林 立, 王姗姗. 花类药治疗银屑病经验[J]. 吉林中医药, 2021, 41(11): 1450-3. |
| [1] | Qin HU, Hua JIN. Qingshen Granules improves renal function of patients with chronic kidney disease damp-heat syndrome by activating the miR-23b and Nrf2 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1867-1879. |
| [2] | Ziwei YANG, Chang LÜ, Zhu DONG, Shulei JI, Shenghui BI, Xuehua ZHANG, Xiaowu WANG. Rosa laevigata Michx. inhibits pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation in hypertension by modulating the Src-AKT1 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1889-1902. |
| [3] | Qi YUN, Ruoli DU, Yuying HE, Yixin ZHANG, Jiahui WANG, Hongwei YE, Zhenghong LI, Qin GAO. Cinnamic acid ameliorates doxorubicin-induced myocardial injury in mice by attenuating cardiomyocyte ferroptosis via inhibiting TLR4 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1946-1958. |
| [4] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [5] | Liming WANG, Hongrui CHEN, Yan DU, Peng ZHAO, Yujie WANG, Yange TIAN, Xinguang LIU, Jiansheng LI. Yiqi Zishen Formula ameliorates inflammation in mice with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [6] | Yinfu ZHU, Yiran LI, Yi WANG, Yinger HUANG, Kunxiang GONG, Wenbo HAO, Lingling SUN. Therapeutic mechanism of hederagenin, an active component in Guizhi Fuling Pellets, against cervical cancer in nude mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [7] | Lijun HE, Xiaofei CHEN, Chenxin YAN, Lin SHI. Inhibitory effect of Fuzheng Huaji Decoction against non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and the possible molecular mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152. |
| [8] | Guoyong LI, Renling LI, Yiting LIU, Hongxia KE, Jing LI, Xinhua WANG. Therapeutic mechanism of Arctium lappa extract for post-viral pneumonia pulmonary fibrosis: a metabolomics, network pharmacology analysis and experimental verification [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [9] | Liping GUAN, Yan YAN, Xinyi LU, Zhifeng LI, Hui GAO, Dong CAO, Chenxi HOU, Jingyu ZENG, Xinyi LI, Yang ZHAO, Junjie WANG, Huilong FANG. Compound Centella asiatica formula alleviates Schistosoma japonicum-induced liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting the inflammation-fibrosis cascade via regulating the TLR4/MyD88 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [10] | Peipei TANG, Yong TAN, Yanyun YIN, Xiaowei NIE, Jingyu HUANG, Wenting ZUO, Yuling LI. Tiaozhou Ziyin recipe for treatment of premature ovarian insufficiency: efficacy, safety and mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| [11] | Xiaotao LIANG, Yifan XIONG, Xueqi LIU, Xiaoshan LIANG, Xiaoyu ZHU, Wei XIE. Huoxue Shufeng Granule alleviates central sensitization in chronic migraine mice via TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 986-994. |
| [12] | Niandong RAN, Jie LIU, Jian XU, Yongping ZHANG, Jiangtao GUO. n-butanol fraction of ethanol extract of Periploca forrestii Schltr.: its active components, targets and pathways for treating Alcheimer's disease in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 785-798. |
| [13] | Haonan¹ XU, Fang³ ZHANG, Yuying² HUANG, Qisheng⁴ YAO, Yueqin⁴ GUAN, Hao CHEN. Thesium chinense Turcz. alleviates antibiotic-associated diarrhea in mice by modulating gut microbiota structure and regulating the EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [14] | Junjie GAO, Kai YE, Jing WU. Quercetin inhibits proliferation and migration of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells by regulating TP53 gene [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 313-321. |
| [15] | Yuejiao PEI, Huimin LIU, Yu XIN, Bo LIU. High expression of miR-124 improves cognitive function of sleep-deprived rats by modulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 340-346. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||