Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (10): 2146-2159.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.10.11
Xiaotao LIANG1( ), Xiaoshan LIANG2, Yifan XIONG1, Shiru XIE1, Xiaoyu ZHU1, Wei XIE1,2(
), Xiaoshan LIANG2, Yifan XIONG1, Shiru XIE1, Xiaoyu ZHU1, Wei XIE1,2( )
)
Received:2025-07-25
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-10-24
Contact:
Wei XIE
E-mail:1092296938@qq.com;xieweizn@126.com
Supported by:Xiaotao LIANG, Xiaoshan LIANG, Yifan XIONG, Shiru XIE, Xiaoyu ZHU, Wei XIE. Modified Chaihu Guizhi Decoction alleviates anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in mice with chronic unpredictable mild stress by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(10): 2146-2159.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.10.11
| Primer name | Sequence |
|---|---|
| IFN-γ Forward | AGCAACAACATAAGCGTCATTGA |
| IFN-γ Reverse | TGACCTCAAACTTGGCAATACTC |
| TNF-α Forward | GCCTCCCTCTCATCAGTTCTATG |
| TNF-α Reverse | ACCTGGGAGTAGACAAGGTACAA |
| IL-1β Forward | GCAACTGTTCCTGAACTCAACT |
| IL-1β Reverse | ATCTTTTGGGGTCCGTCAACT |
| IL-4 Forward | TCCTCACAGCAACGAAGAACA |
| IL-4 Reverse | AGGCATCGAAAAGCCCGAAA |
| IL-6 Forward | ACAACCACGGCCTTCCCTACTT |
| IL-6 Reverse | CACGATTTCCCAGAGAACATGTG |
| IL-10 Forward | GGTTGCCAAGCCTTATCGGA |
| IL-10 Reverse | AGACACCTTGGTCTTGGAGCTTA |
| Bmal1 Forward | CTCCAGGAGGCAAGAAGATTC |
| Bmal1 Reverse | ATAGTCCAGTGGAAGGAATG |
| Clock Forward | TTCCTTCCTTAGAGACGAGACT |
| Clock Reverse | CTAAATGCTACCCTGAGGATAGAG |
| Cry1 Forward | GATCCACCATTTAGCCAGACAC |
| Cry1 Reverse | ACAGCCACATCCAACTTCCA |
| Cry2 Forward | CAAGCACTTGGAACGGAAGG |
| Cry2 Reverse | GAAGAGGCGGCAGGAGAG |
| Per1 Forward | CAGGCTAACCAGGAATATTACCAGC |
| Per1 Reverse | CACAGCCACAGAGAAGGTGTCCTGG |
| Per2 Forward | CCACACTTGCCTCCGAAATA |
| Per2 Reverse | ACTGCCTCTGGACTGGAAGA |
| GAPDH Forward | CAACTACATGGTCTACATGTTC |
| GAPDH Reverse | CTCGCTCCTGGAAGATG |
Tab.1 Primer sequences used for RT-qPCR in this study
| Primer name | Sequence |
|---|---|
| IFN-γ Forward | AGCAACAACATAAGCGTCATTGA |
| IFN-γ Reverse | TGACCTCAAACTTGGCAATACTC |
| TNF-α Forward | GCCTCCCTCTCATCAGTTCTATG |
| TNF-α Reverse | ACCTGGGAGTAGACAAGGTACAA |
| IL-1β Forward | GCAACTGTTCCTGAACTCAACT |
| IL-1β Reverse | ATCTTTTGGGGTCCGTCAACT |
| IL-4 Forward | TCCTCACAGCAACGAAGAACA |
| IL-4 Reverse | AGGCATCGAAAAGCCCGAAA |
| IL-6 Forward | ACAACCACGGCCTTCCCTACTT |
| IL-6 Reverse | CACGATTTCCCAGAGAACATGTG |
| IL-10 Forward | GGTTGCCAAGCCTTATCGGA |
| IL-10 Reverse | AGACACCTTGGTCTTGGAGCTTA |
| Bmal1 Forward | CTCCAGGAGGCAAGAAGATTC |
| Bmal1 Reverse | ATAGTCCAGTGGAAGGAATG |
| Clock Forward | TTCCTTCCTTAGAGACGAGACT |
| Clock Reverse | CTAAATGCTACCCTGAGGATAGAG |
| Cry1 Forward | GATCCACCATTTAGCCAGACAC |
| Cry1 Reverse | ACAGCCACATCCAACTTCCA |
| Cry2 Forward | CAAGCACTTGGAACGGAAGG |
| Cry2 Reverse | GAAGAGGCGGCAGGAGAG |
| Per1 Forward | CAGGCTAACCAGGAATATTACCAGC |
| Per1 Reverse | CACAGCCACAGAGAAGGTGTCCTGG |
| Per2 Forward | CCACACTTGCCTCCGAAATA |
| Per2 Reverse | ACTGCCTCTGGACTGGAAGA |
| GAPDH Forward | CAACTACATGGTCTACATGTTC |
| GAPDH Reverse | CTCGCTCCTGGAAGATG |
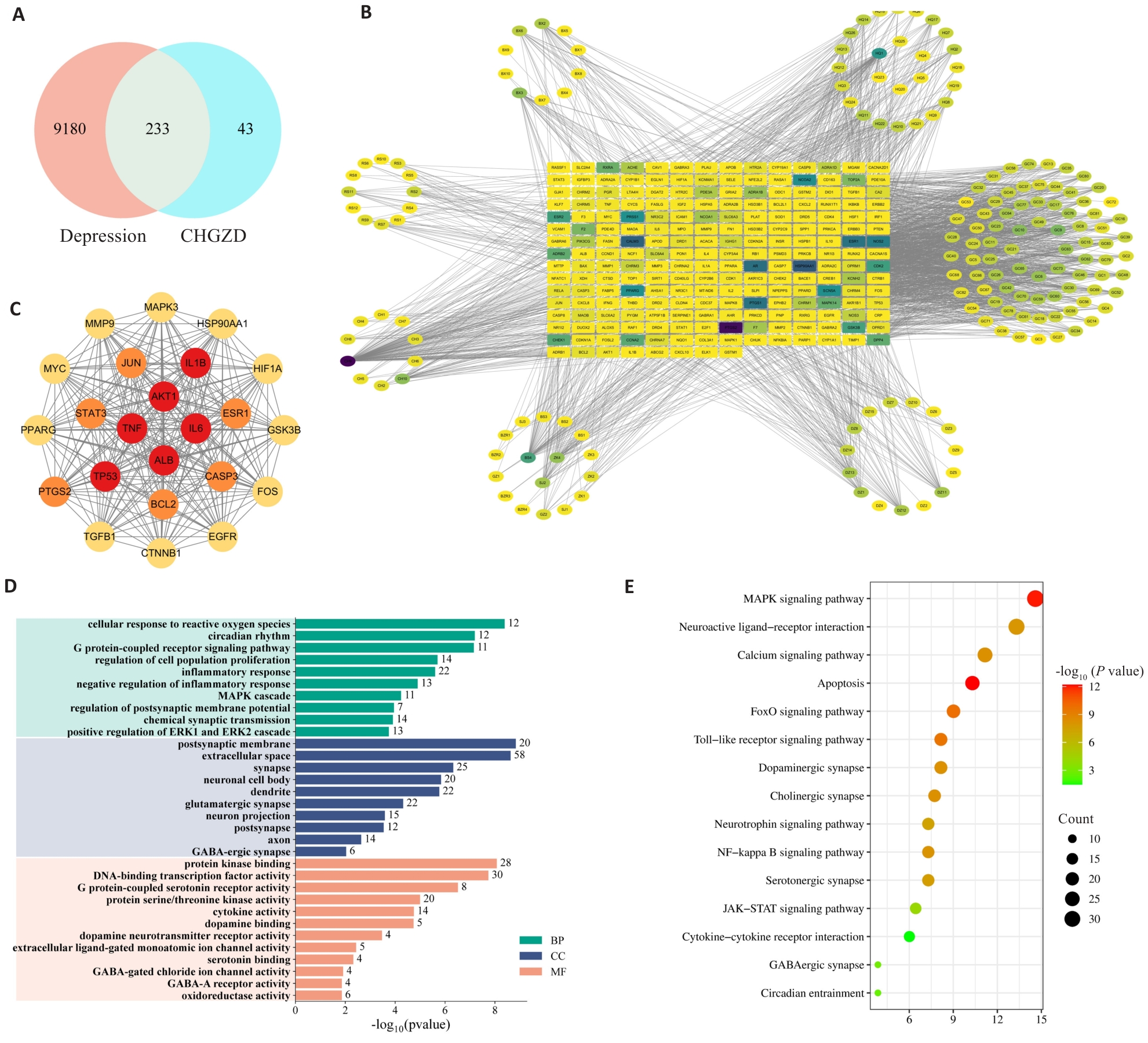
Fig.1 Network pharmacology analysis of the mechanisms by which Modified Chaihu Guizhi Decoction (MCGD) alleviates anxiety- and depression-like behavior in CUMS. A: Venn diagram of shared targets between MCGD and depression. B: Component-target-disease map. C: Core intersection targets. D: Gene Ontology (GO) analysis of the shared targets, categorized into Biological Processes (BP), Molecular Functions (MF), and Cellular Components (CC). E: Bubble chart of Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis for the shared targets.
| Code | ID | Name | Relevance | Soucre |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH9 | MOL000098 | Quercetin | 128 | Chinese thorawax root |
| HQ1 | MOL001689 | Acacetin | 62 | Baikal skullcap root |
| BS4 | MOL000422 | Kaempferol | 55 | White peony root |
| GC9 | MOL003896 | 7-Methoxy-2-methyl Isoflavone | 40 | Liquorice root |
| GC10 | MOL000392 | Formononetin | 36 | Liquorice root |
| ZK4 | MOL005828 | Nobiletin | 33 | Submature bitter orange |
| CH10 | MOL000354 | Isorhamnetin | 32 | Chinese thorawax root |
| GC6 | MOL002565 | Medicarpin | 32 | Liquorice root |
| BX3 | MOL002714 | Baicalein | 31 | Ternate pinellia |
| GC63 | MOL000497 | Licochalcone a | 30 | Liquorice root |
Tab.2 Key active components in Modified Chaihu Guizhi Decoction (MCGD) for treatment of depression
| Code | ID | Name | Relevance | Soucre |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH9 | MOL000098 | Quercetin | 128 | Chinese thorawax root |
| HQ1 | MOL001689 | Acacetin | 62 | Baikal skullcap root |
| BS4 | MOL000422 | Kaempferol | 55 | White peony root |
| GC9 | MOL003896 | 7-Methoxy-2-methyl Isoflavone | 40 | Liquorice root |
| GC10 | MOL000392 | Formononetin | 36 | Liquorice root |
| ZK4 | MOL005828 | Nobiletin | 33 | Submature bitter orange |
| CH10 | MOL000354 | Isorhamnetin | 32 | Chinese thorawax root |
| GC6 | MOL002565 | Medicarpin | 32 | Liquorice root |
| BX3 | MOL002714 | Baicalein | 31 | Ternate pinellia |
| GC63 | MOL000497 | Licochalcone a | 30 | Liquorice root |
| Target | Sample | Estimated ΔG (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| JAK2 | CH9 | -6.45 |
| JAK2 | HQ1 | -6.48 |
| JAK2 | BS4 | -6.40 |
| JAK2 | GC9 | -5.53 |
| JAK2 | GC10 | -6.27 |
| JAK2 | ZK4 | -6.27 |
| JAK2 | CH10 | -6.7 |
| JAK2 | GC6 | -5.73 |
| JAK2 | BX3 | -5.43 |
| JAK2 | GC63 | -6.13 |
| STAT3 | CH9 | -5.48 |
| STAT3 | HQ1 | -5.16 |
| STAT3 | BS4 | -5.08 |
| STAT3 | GC9 | -5.9 |
| STAT3 | GC10 | -5.09 |
| STAT3 | ZK4 | -7.44 |
| STAT3 | CH10 | -5.64 |
| STAT3 | GC6 | -5.02 |
| STAT3 | BX3 | -4.78 |
| STAT3 | GC63 | -5.8 |
Tab.3 Binding energies of the core active components of MCGD for depression treatment for docking with the core target molecules JAK2 and STAT3
| Target | Sample | Estimated ΔG (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| JAK2 | CH9 | -6.45 |
| JAK2 | HQ1 | -6.48 |
| JAK2 | BS4 | -6.40 |
| JAK2 | GC9 | -5.53 |
| JAK2 | GC10 | -6.27 |
| JAK2 | ZK4 | -6.27 |
| JAK2 | CH10 | -6.7 |
| JAK2 | GC6 | -5.73 |
| JAK2 | BX3 | -5.43 |
| JAK2 | GC63 | -6.13 |
| STAT3 | CH9 | -5.48 |
| STAT3 | HQ1 | -5.16 |
| STAT3 | BS4 | -5.08 |
| STAT3 | GC9 | -5.9 |
| STAT3 | GC10 | -5.09 |
| STAT3 | ZK4 | -7.44 |
| STAT3 | CH10 | -5.64 |
| STAT3 | GC6 | -5.02 |
| STAT3 | BX3 | -4.78 |
| STAT3 | GC63 | -5.8 |
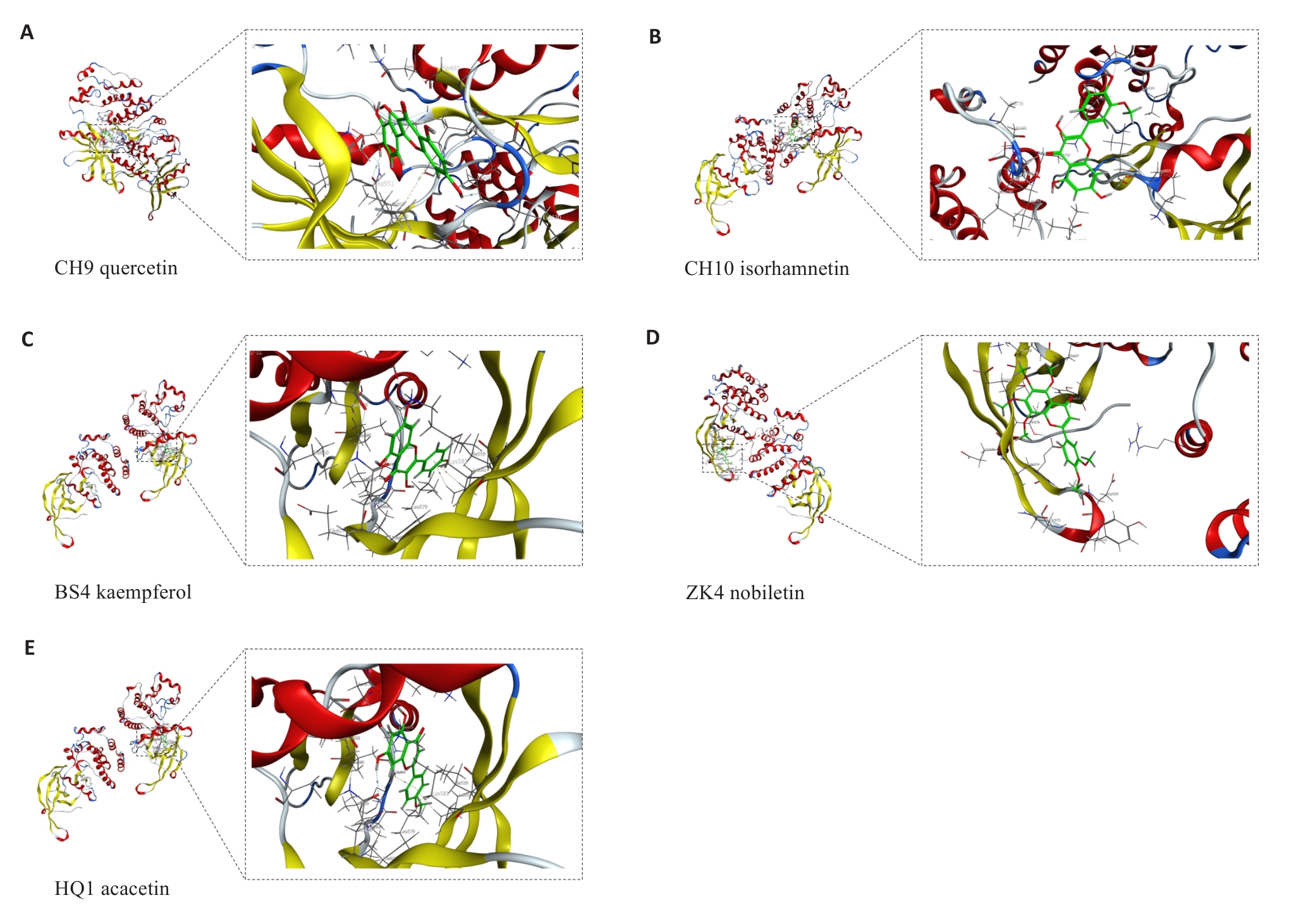
Fig.2 Visualization of the results of molecular docking analysis. A: Docked molecular conformation of JAK2 with CH9. B: Molecular conformation of JAK2 docked with CH10. C: Molecular conformation of JAK2 docked with BS4. D: Molecular conformation of JAK2 docked with ZK4. E: Molecular conformation of JAK2 docked with HQ1.
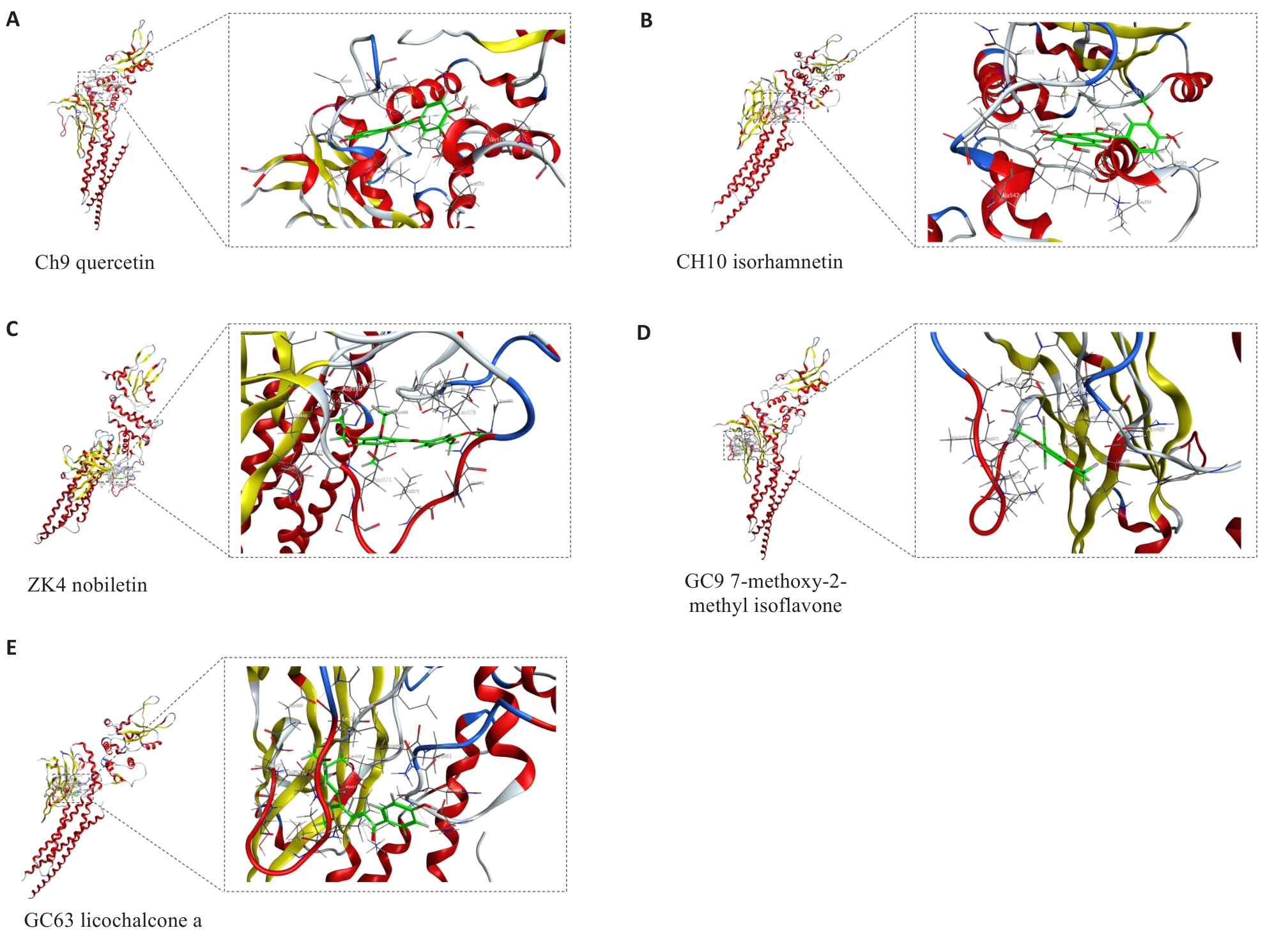
Fig.3 Visualization of the results of molecular docking analysis. A: Docked molecular conformation of STAT3 with CH9. B: Molecular conformation of STAT3 docked with CH10. C: Molecular conformation of STAT3 docked with ZK4. D: Molecular conformation of STAT3 docked with GC9. E: Molecular conformation of STAT3 docked with GC63.
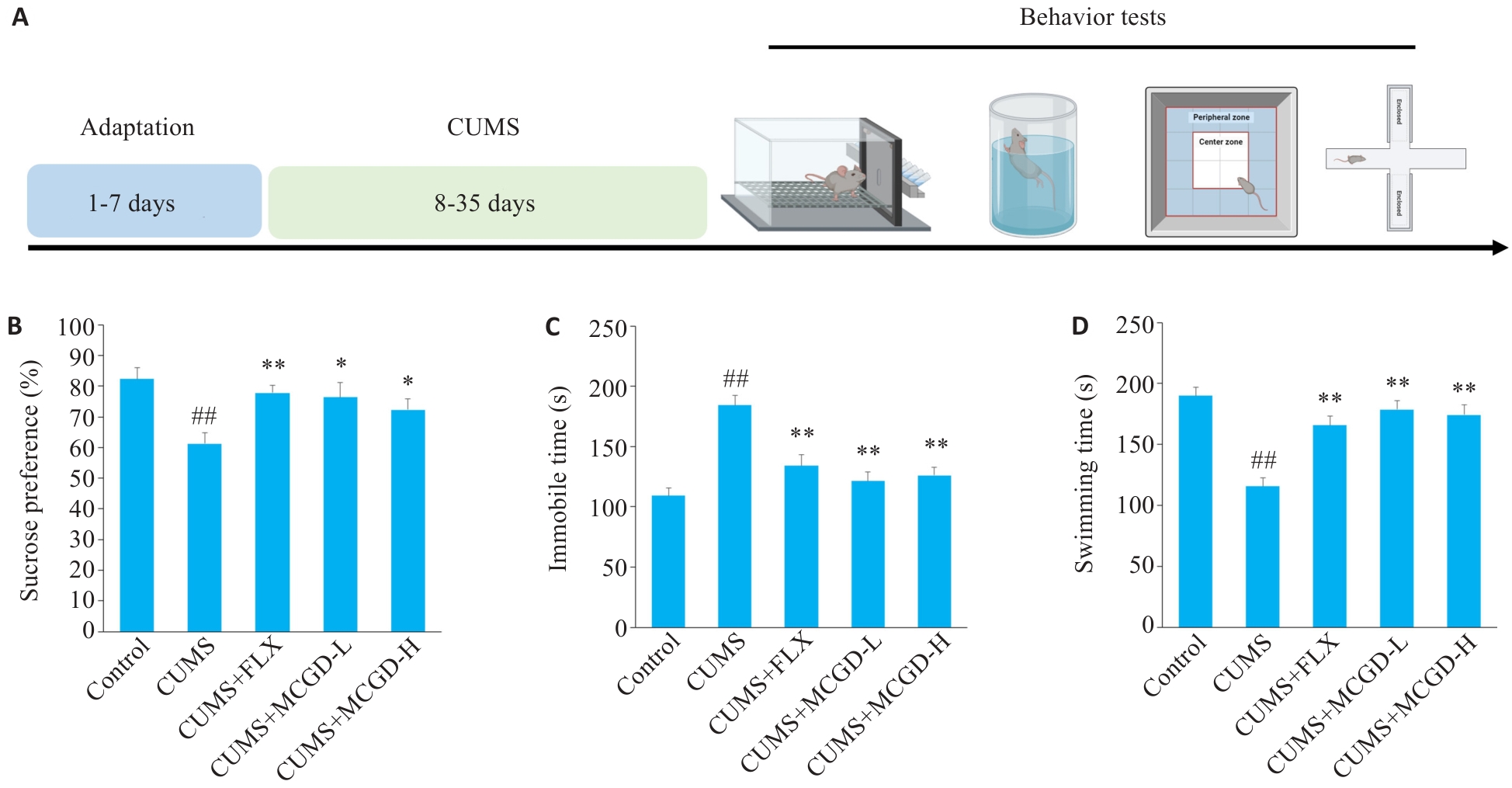
Fig.4 MCGD significantly improves depression-like behavior in CUMS mice. A: Experimental design. B: Sucrose preference percentage in the sucrose preference test (SPT). C: Immobility time in the forced swim test (FST). D: Swimming times in the FST. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=15). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. ##P<0.01 vs Control group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs CUMS group.
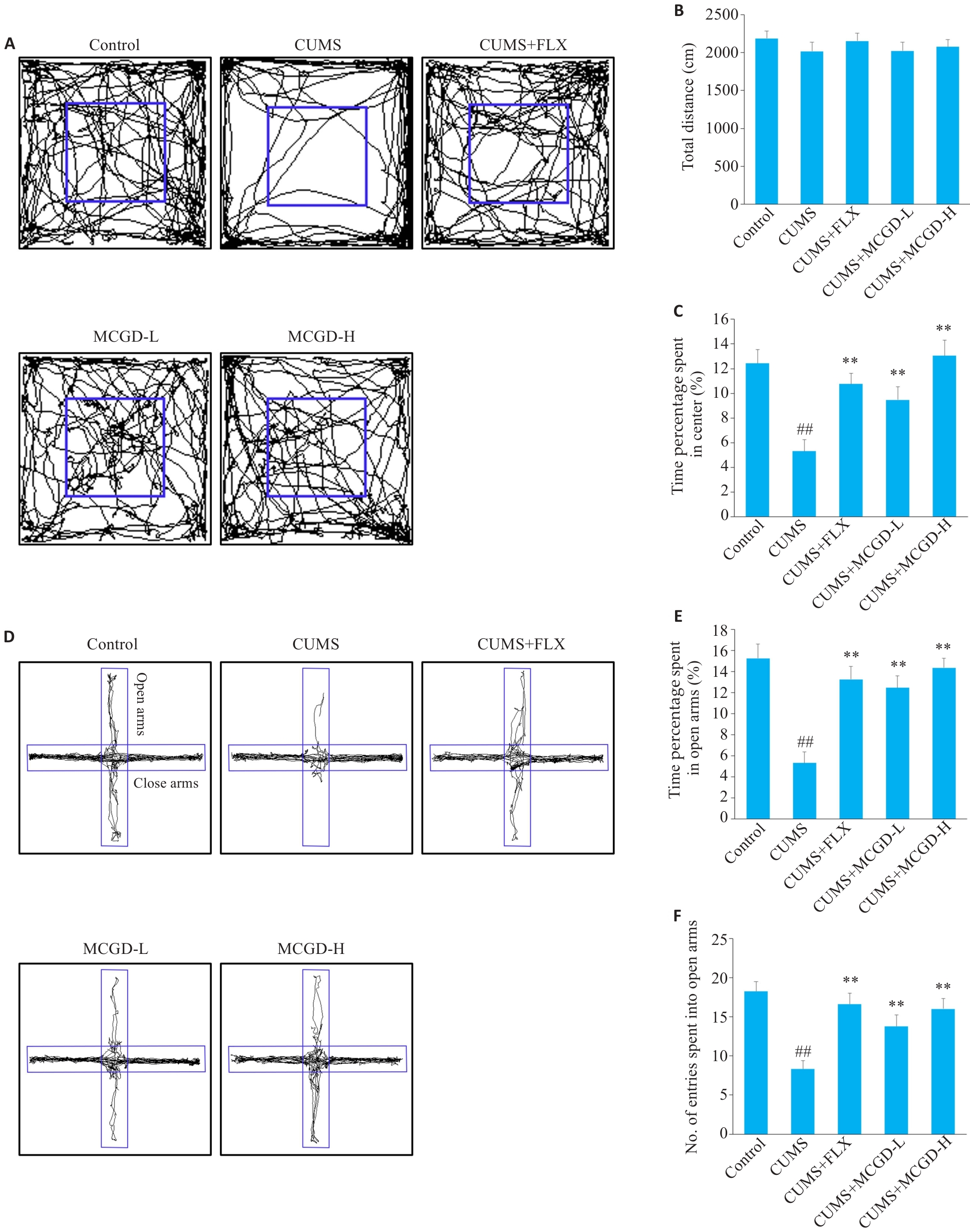
Fig.5 MCGD significantly improves anxiety-like behavior in CUMS mice. A: Trajectory map in the open field test (OFT). B: Total distance in OFT. C: Time percentage spent in center of OFT. D: Trajectory map in the elevated plus maze test (EPM). E: Time percentage spent in open arms of EPM. F: Number of entries spent into open arms of EPM. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=15). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. ##P<0.01 vs Control group; **P<0.01 vs CUMS group.
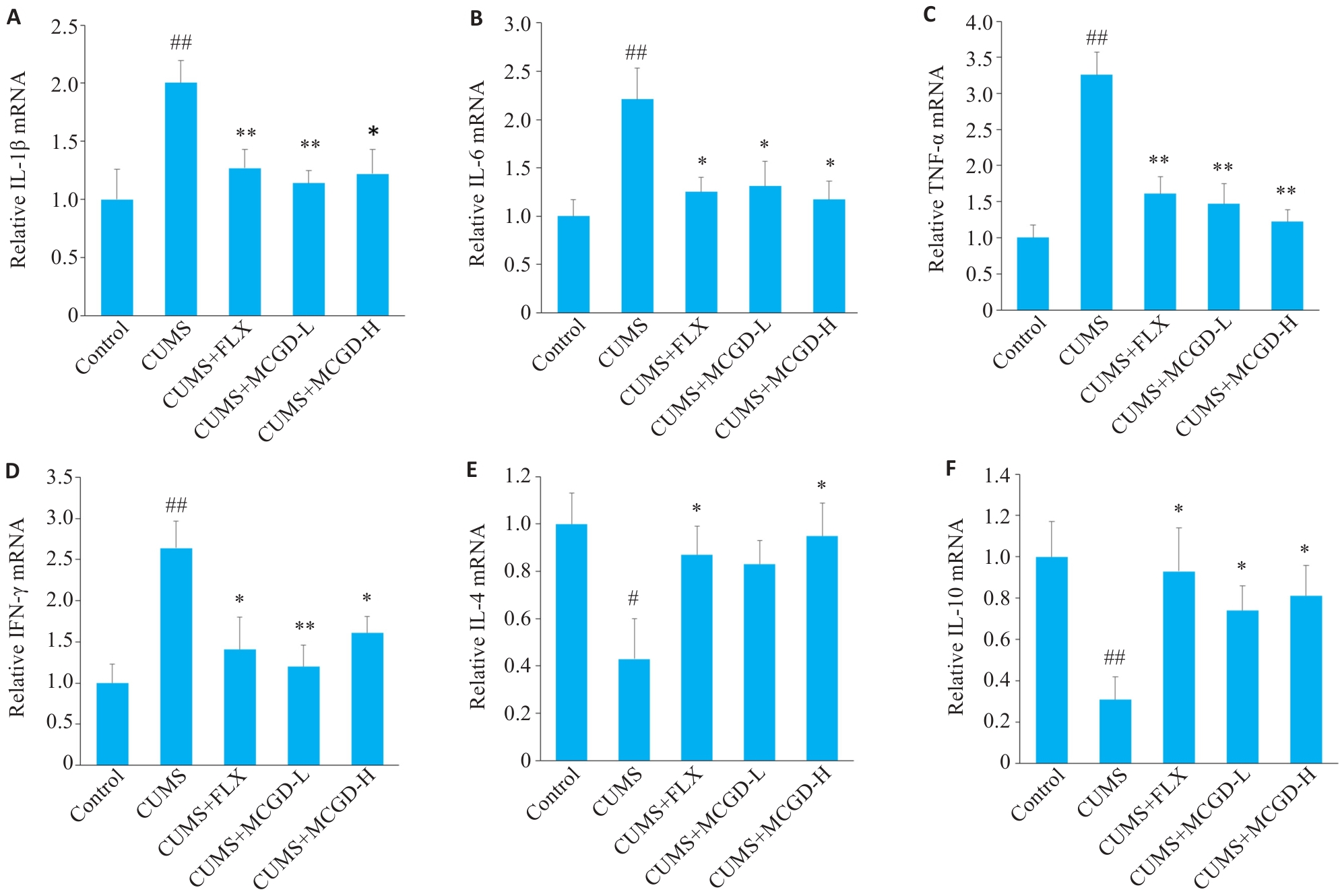
Fig.6 Effects of MCGD on mRNA expression of inflammatory factors in the hippocampus of CUMS mice. A: Relative mRNA level of IL-1β. B: Relative mRNA level of IL-6. C: Relative mRNA level of TNF-α. D: Relative mRNA level of IFN-γ. E: Relative mRNA level of IL-4. F: Relative mRNA level of IL-10. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=6). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs Control group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs CUMS group.
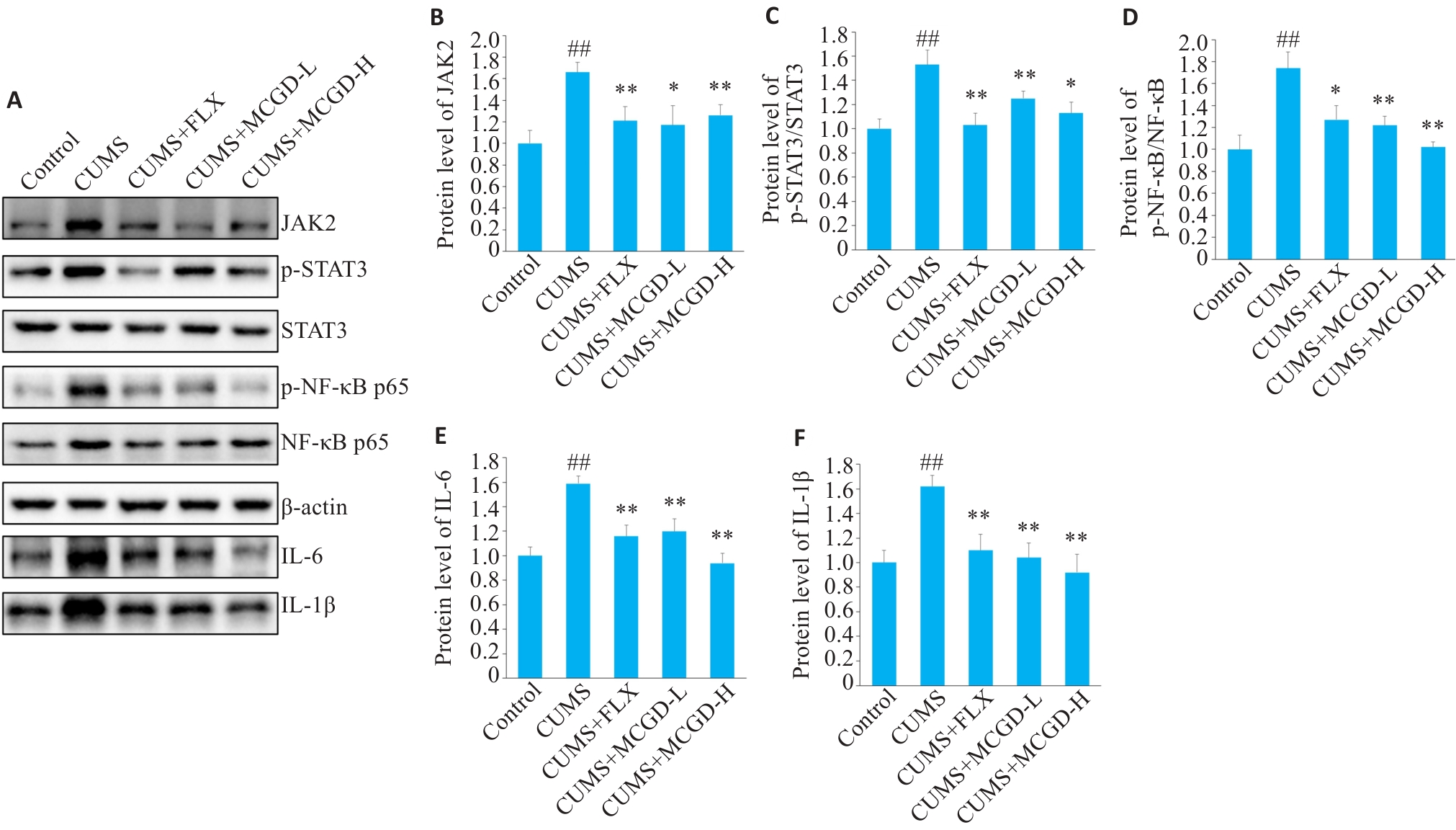
Fig.7 Effects of MCGD on the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in the hippocampus of CUMS mice. A: Protein bands of JAK2, p-STAT3, STAT3, p-NF-κB, NF-κB, IL-1β, and IL-6 detected by Western blotting. B-F: Quantitative analysis of JAK2, p-STAT3, STAT3, p-NF-κB, NF-κB, IL-6, and IL-1β protein expression levels. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=3). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. ##P<0.01 vs Control group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs CUMS group.
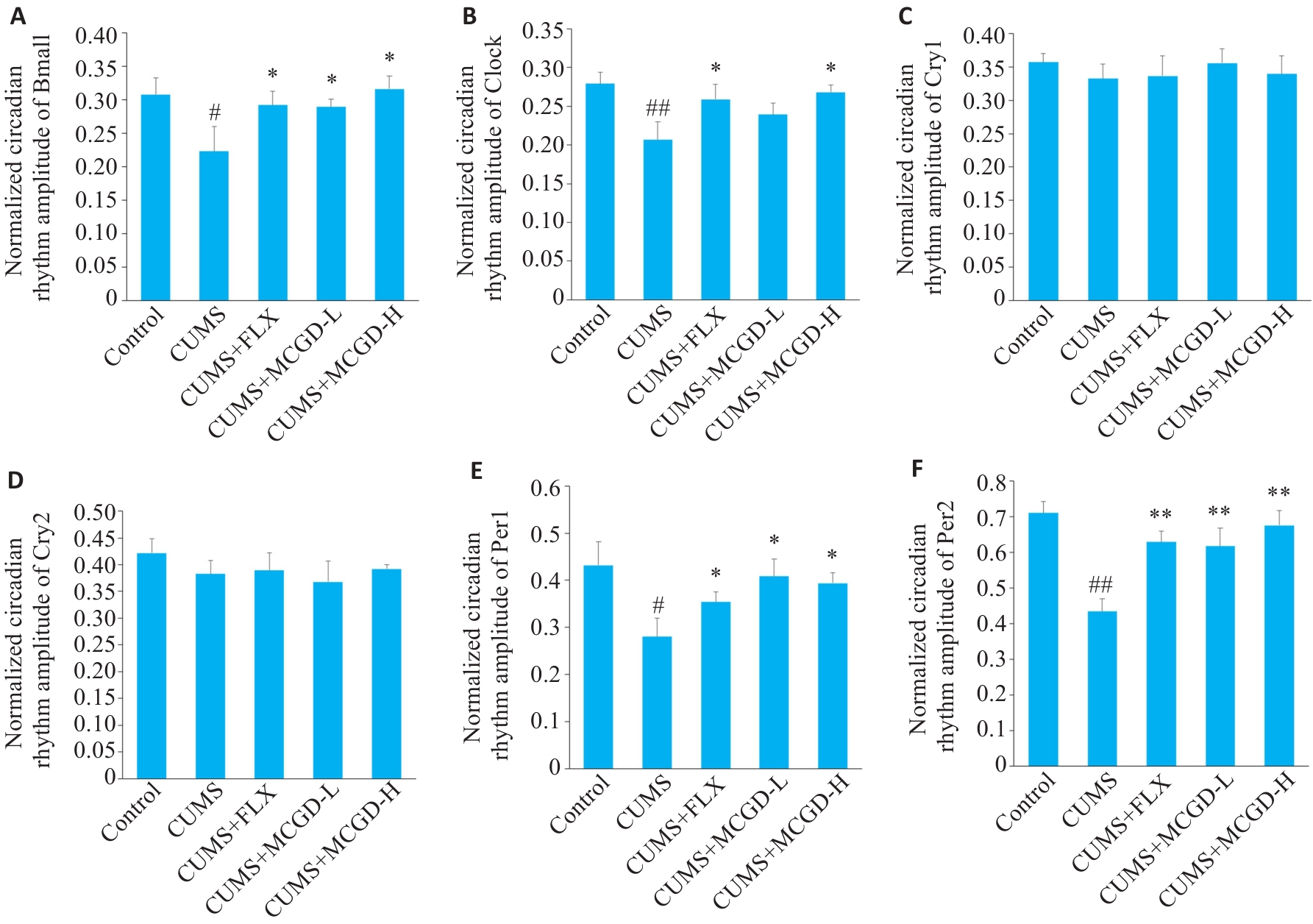
Fig.8 Regulatory effect of MCGD on expression levels of clock protein genes in the hippocampus of CUMS mice. A: Normalized circadian rhythm amplitude of Bmal1. B: Normalized circadian rhythm amplitude of Clock1. C: Normalized circadian rhythm amplitude of Cry1. D: Normalized circadian rhythm amplitude of Cry2. E: Normalized circadian rhythm amplitude of Per1. F: Normalized circadian rhythm amplitude of Per2. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=3). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs Control group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs CUMS group.
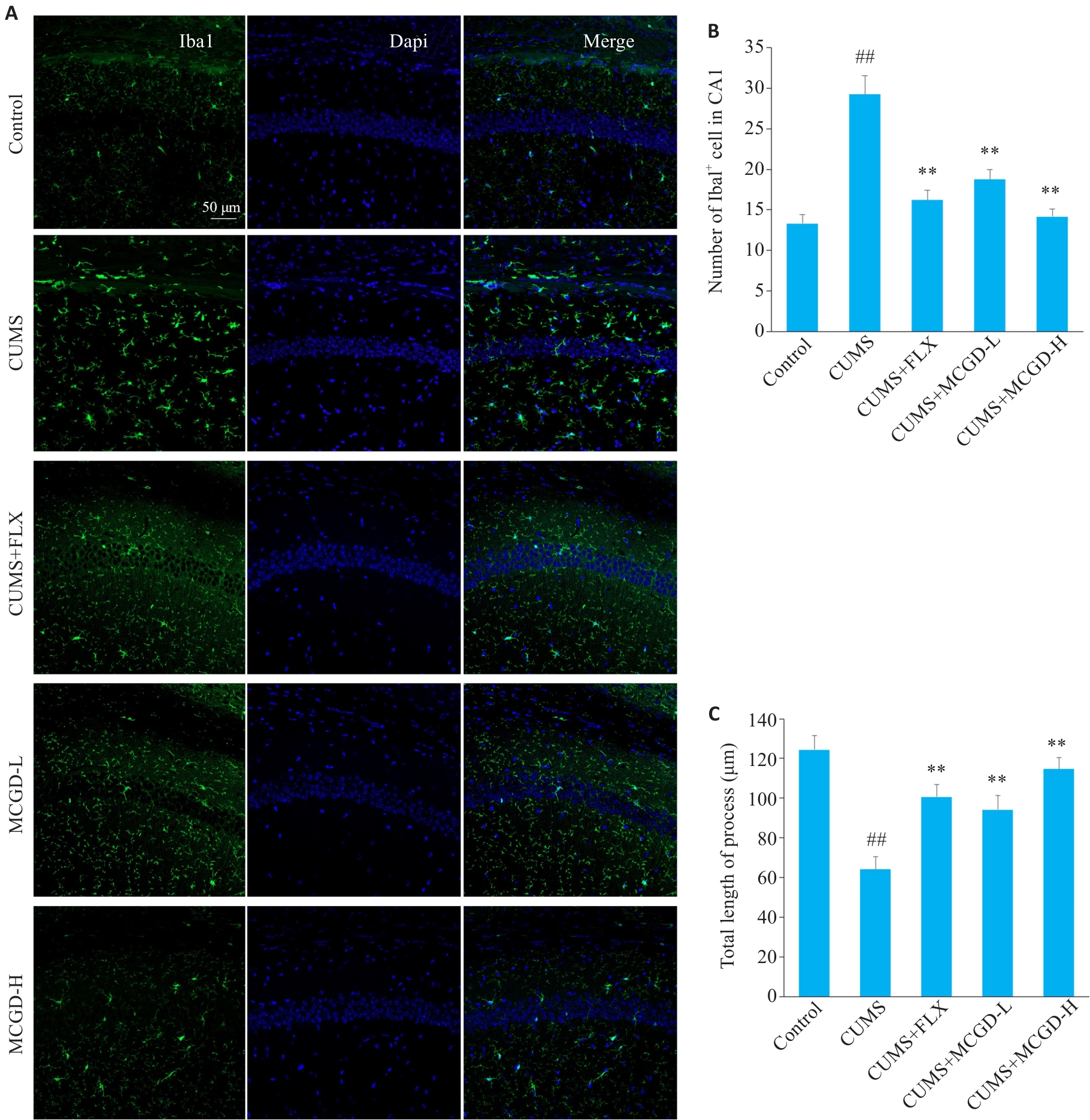
Fig.9 Effects of MCGD on microglia activation level in the hippocampal CA1 region of CUMS mice. A: Immunofluorescence images of Iba1 expression (Original magnification: ×200). B: Statistics of Iba1+ cells in the hippocampal CA1 region. C: Statistics of microglia total length of process in the hippocampal CA1 region. Each group included 3 mice, and 4 slices were analyzed per mouse. Data are presented as Mean±SD. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. ##P<0.01 vs Control group; **P<0.01 vs CUMS group.
| [1] | McIntyre RS, Berk M, Brietzke E, et al. Bipolar disorders[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10265): 1841-56. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31544-0 |
| [2] | Malhi GS, Mann JJ. Depression[J]. Lancet, 2018, 392(10161): 2299-312. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(18)31948-2 |
| [3] | Otte C, Gold SM, Penninx BW, et al. Major depressive disorder[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2016, 2: 16065. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2016.65 |
| [4] | Hickie IB, Rogers NL. Novel melatonin-based therapies: potential advances in the treatment of major depression[J]. Lancet, 2011, 378(9791): 621-31. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(11)60095-0 |
| [5] | Marwaha S, Palmer E, Suppes T, et al. Novel and emerging treatm-ents for major depression[J]. Lancet, 2023, 401(10371): 141-53. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(22)02080-3 |
| [6] | Jha MK, Mathew SJ. Pharmacotherapies for treatment-resistant depression: how antipsychotics fit in the rapidly evolving therapeutic landscape[J]. Am J Psychiatry, 2023, 180(3): 190-9. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.20230025 |
| [7] | Crowell AL, Riva-Posse P, Holtzheimer PE, et al. Long-term outcomes of subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression[J]. Am J Psychiatry, 2019, 176(11): 949-56. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2019.18121427 |
| [8] | Lundberg J, Cars T, Lööv SÅ, et al. Association of treatment-resistant depression with patient outcomes and health care resource utilization in a population-wide study[J]. JAMA Psychiatry, 2023, 80(2): 167-75. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2022.3860 |
| [9] | 梁小珊, 熊一凡, 梁晓涛, 等. 谢炜教授基于“少阳为枢” 理论运用柴胡桂枝汤临床辨治经验[J]. 河北中医, 2020, 42(7): 977-80. |
| [10] | 梁晓涛, 梁小珊, 杨 路, 等. 谢炜教授“调肝安神,调和阴阳” 辨治失眠[J]. 环球中医药, 2021, 14(10): 1815-8. |
| [11] | 熊一凡, 梁小珊, 梁晓涛, 等. 柴胡皂甙a减轻戊四氮诱发的皮质酮抑郁模型小鼠的急性癫痫发作:基于小胶质细胞介导的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 515-22. |
| [12] | Zhu XY, Huang YY, Qiu J, et al. Chaihu Guizhi Decoction prevents cognitive, memory impairments and sensorimotor gating deficit induced by N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antibody in mice[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2025, 337(Pt 1): 118806. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118806 |
| [13] | Kanan MF, Sheehan PW, Haines JN, et al. Neuronal deletion of the circadian clock gene Bmal1 induces cell-autonomous dopaminergic neurodegeneration[J]. JCI Insight, 2024, 9(2): e162771. doi:10.1172/jci.insight.162771 |
| [14] | Guzmán-Ruiz MA, Guerrero-Vargas NN, Lagunes-Cruz A, et al. Circadian modulation of microglial physiological processes and immune responses[J]. Glia, 2023, 71(2): 155-67. doi:10.1002/glia.24261 |
| [15] | Brooks JF 2nd, Behrendt CL, Ruhn KA, et al. The microbiota coordinates diurnal rhythms in innate immunity with the circadian clock[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(16): 4154-67.e12. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.07.001 |
| [16] | Yang BQ, Han Y, Hu SQ, et al. Polystyrene microplastics induce depression-like behavior in zebrafish via neuroinflammation and circadian rhythm disruption[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2025, 959: 178085. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.178085 |
| [17] | Kou L, Chi XS, Sun YD, et al. The circadian clock protein Rev-erbα provides neuroprotection and attenuates neuroinflammation against Parkinson’s disease via the microglial NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2022, 19(1): 133. doi:10.1186/s12974-022-02494-y |
| [18] | Lananna BV, Nadarajah CJ, Izumo M, et al. Cell-autonomous regulation of astrocyte activation by the circadian clock protein BMAL1[J]. Cell Rep, 2018, 25(1): 1-9. e5. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2018.09.015 |
| [19] | Yao D, Li R, Hao JH, et al. Melatonin alleviates depression-like behaviors and cognitive dysfunction in mice by regulating the circadian rhythm of AQP4 polarization[J]. Transl Psychiatry, 2023, 13(1): 310. doi:10.1038/s41398-023-02614-z |
| [20] | Liang XT, Ding YW, Zhu XY, et al. Suprachiasmatic nucleus dysfunction induces anxiety- and depression-like behaviors via activating the BDNF-TrkB pathway of the striatum[J]. Transl Psychiatry, 2025, 15(1): 92. doi:10.1038/s41398-025-03313-7 |
| [21] | Chen X, Gan YT, Zhang KQ, et al. microRNA-204-5p deficiency within the vmPFC region contributes to neuroinflammation and behavioral disorders via the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in rats[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2025, 12(10): e2403080. doi:10.1002/advs.202403080 |
| [22] | Cavadini G, Petrzilka S, Kohler P, et al. TNF-alpha suppresses the expression of clock genes by interfering with E-box-mediated transcription[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2007, 104(31): 12843-8. doi:10.1073/pnas.0701466104 |
| [23] | Song N, Liu ZH, Gao Y, et al. NAc-DBS corrects depression-like behaviors in CUMS mouse model via disinhibition of DA neurons in the VTA[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2024, 29(5): 1550-66. doi:10.1038/s41380-024-02476-x |
| [24] | Liang XS, Liang XT, Zhao YY, et al. Dysregulation of the suprachiasmatic nucleus disturbs the circadian rhythm and aggravates epileptic seizures by inducing hippocampal GABAergic dysfunction in C57BL/6 mice[J]. J Pineal Res, 2024, 76(5): e12993. doi:10.1111/jpi.12993 |
| [25] | Pizzagalli DA, Roberts AC. Prefrontal cortex and depression[J]. Neuropsychopharmacology, 2022, 47(1): 225-46. doi:10.1038/s41386-021-01101-7 |
| [26] | Luo HR, Wang XQ, Zhang YL, et al. Can circadian rhythm predict changes in neurocognitive functioning in bipolar disorder: protocol of a 12-month longitudinal cohort study based on research domain criteria[J]. Ann Med, 2023, 55(2): 2240422. doi:10.1080/07853890.2023.2240422 |
| [27] | Mirchandaney R, Asarnow LD, Kaplan KA. Recent advances in sleep and depression[J]. Curr Opin Psychiatry, 2023, 36(1): 34-40. doi:10.1097/yco.0000000000000837 |
| [28] | Crouse JJ, Carpenter JS, Song YJC, et al. Circadian rhythm sleep-wake disturbances and depression in young people: implications for prevention and early intervention[J]. Lancet Psychiatry, 2021, 8(9): 813-23. doi:10.1016/s2215-0366(21)00034-1 |
| [29] | Hao WZ, Ma QY, Wang L, et al. Gut dysbiosis induces the development of depression-like behavior through abnormal synapse pruning in microglia-mediated by complement C3[J]. Microbiome, 2024, 12(1): 34. doi:10.1186/s40168-024-01756-6 |
| [30] | Xian X, Cai LL, Li Y, et al. Neuron secrete exosomes containing miR-9-5p to promote polarization of M1 microglia in depression[J]. J Nanobiotechnology, 2022, 20(1): 122. doi:10.1186/s12951-022-01332-w |
| [31] | Shen SY, Liang LF, Shi TL, et al. Microglia-derived interleukin-6 triggers astrocyte apoptosis in the hippocampus and mediates depression-like behavior[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2025, 12(11): e2412556. doi:10.1002/advs.202412556 |
| [32] | Brécier A, Li VW, Smith CS, et al. Circadian rhythms and glial cells of the central nervous system[J]. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc, 2023, 98(2): 520-39. doi:10.1111/brv.12917 |
| [33] | 刘日群, 李字棋, 肖淑华, 等. 理气药抗抑郁作用及机制研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2024, 55(10): 3558-68. |
| [34] | 倪雨婷, 张欢欢, 赵丹丹, 等. 酸枣仁-柏子仁组分调控睡眠障碍中神经递质的研究[J]. 黑龙江医药, 2023, 36(05): 1000-4. |
| [35] | Agrawal K, Chakraborty P, Dewanjee S, et al. Neuropharm-acological interventions of quercetin and its derivatives in neurological and psychological disorders[J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2023, 144: 104955. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104955 |
| [36] | Wang MY, Wei X, Jia YG, et al. Quercetin alleviates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression-like behavior by inhibiting NMDAR1 with α2δ-1 in rats[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2024, 30(4): e14724. doi:10.1111/cns.14724 |
| [37] | Su P, Liu LM, Gong YH, et al. Kaempferol improves depression-like behaviors through shifting microglia polarization and suppressing NLRP3 via tilting the balance of PPARγ and STAT1 signaling[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 143(Pt 3): 113538. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113538 |
| [38] | Liu HT, Lin YN, Tsai MC, et al. Baicalein exerts therapeutic effects against endotoxin-induced depression-like behavior in mice by decreasing inflammatory cytokines and increasing brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels[J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2022, 11(5): 947. doi:10.3390/antiox11050947 |
| [39] | Zhang ML, Li XP, Gao LF, et al. Nobiletin, an activator of the pyruvate kinase isozyme M1/M2 protein, upregulated the glycolytic signalling pathway and alleviated depressive-like behaviour caused by artificial light exposure at night in zebrafish[J]. Food Chem, 2025, 463(Pt 2): 141328. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.141328 |
| [40] | Jin Y, Kang YL, Wang MH, et al. Targeting polarized phenotype of microglia via IL6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling to reduce NSCLC brain metastasis[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2022, 7(1): 52. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-00872-9 |
| [41] | Hao ZZ, Ji R, Su YJ, et al. Indole-3-propionic acid attenuates neuroinflammation and cognitive deficits by inhibiting the RAGE-JAK2-STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2025, 73(9): 5208-22. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.4c08548 |
| [42] | Liu PP, Liu XH, Ren MJ, et al. Neuronal cathepsin S increases neuroinflammation and causes cognitive decline via CX3CL1-CX3CR1 axis and JAK2-STAT3 pathway in aging and Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Aging Cell, 2025, 24(2): e14393. doi:10.1111/acel.14393 |
| [43] | 王 英, 巩子汉, 梁文青, 等. 基于JAK2/STAT3信号通路探讨温阳解郁方调节小鼠海马小胶质细胞激活的机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2025, 31(8): 88-96. |
| [44] | 杨晓珊, 王瑞瑞, 李 英, 等. IL-6介导JAK/STAT信号通路在胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠抑郁发生中的作用机制研究[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2021, 37(17): 2053-8. |
| [45] | Xu DD, Hou ZQ, Xu YY, et al. Potential role of Bmal1 in lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like behavior and its associated “inflammatory storm”[J]. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol, 2024, 19(1): 4. doi:10.1007/s11481-024-10103-3 |
| [1] | Qin HU, Hua JIN. Qingshen Granules improves renal function of patients with chronic kidney disease damp-heat syndrome by activating the miR-23b and Nrf2 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1867-1879. |
| [2] | Ziwei YANG, Chang LÜ, Zhu DONG, Shulei JI, Shenghui BI, Xuehua ZHANG, Xiaowu WANG. Rosa laevigata Michx. inhibits pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation in hypertension by modulating the Src-AKT1 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1889-1902. |
| [3] | Qi YUN, Ruoli DU, Yuying HE, Yixin ZHANG, Jiahui WANG, Hongwei YE, Zhenghong LI, Qin GAO. Cinnamic acid ameliorates doxorubicin-induced myocardial injury in mice by attenuating cardiomyocyte ferroptosis via inhibiting TLR4 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1946-1958. |
| [4] | Lu RAO, Jiahe DING, Jiangping WEI, Yong YANG, Xiaomei ZHANG, Jirui WANG. Flos Sophorae improves psoriasis in mice by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1989-1996. |
| [5] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [6] | Liming WANG, Hongrui CHEN, Yan DU, Peng ZHAO, Yujie WANG, Yange TIAN, Xinguang LIU, Jiansheng LI. Yiqi Zishen Formula ameliorates inflammation in mice with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [7] | Yinfu ZHU, Yiran LI, Yi WANG, Yinger HUANG, Kunxiang GONG, Wenbo HAO, Lingling SUN. Therapeutic mechanism of hederagenin, an active component in Guizhi Fuling Pellets, against cervical cancer in nude mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [8] | Lijun HE, Xiaofei CHEN, Chenxin YAN, Lin SHI. Inhibitory effect of Fuzheng Huaji Decoction against non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and the possible molecular mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152. |
| [9] | Guoyong LI, Renling LI, Yiting LIU, Hongxia KE, Jing LI, Xinhua WANG. Therapeutic mechanism of Arctium lappa extract for post-viral pneumonia pulmonary fibrosis: a metabolomics, network pharmacology analysis and experimental verification [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [10] | Xia LV, Rong XIAO. Materialistic values and their association with depression in medical postgraduates: materialism leads to higher risk of depression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1220-1225. |
| [11] | Minzhu NIU, Lixia YIN, Tong QIAO, Lin YIN, Keni ZHANG, Jianguo HU, Chuanwang SONG, Zhijun GENG, Jing LI. Ecliptasaponin A ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice by suppressing M1 macrophage polarization via inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1297-1306. |
| [12] | Liping GUAN, Yan YAN, Xinyi LU, Zhifeng LI, Hui GAO, Dong CAO, Chenxi HOU, Jingyu ZENG, Xinyi LI, Yang ZHAO, Junjie WANG, Huilong FANG. Compound Centella asiatica formula alleviates Schistosoma japonicum-induced liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting the inflammation-fibrosis cascade via regulating the TLR4/MyD88 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [13] | Peipei TANG, Yong TAN, Yanyun YIN, Xiaowei NIE, Jingyu HUANG, Wenting ZUO, Yuling LI. Tiaozhou Ziyin recipe for treatment of premature ovarian insufficiency: efficacy, safety and mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| [14] | Changfeng CHEN, Qin FANG, Yinhuan GAO, Liecheng WANG, Lei CHEN. Enriched environment reduces pyramidal neuron excitability in the anterior cingulate cortex to alleviate restraint stress-induced anxiety-like behaviors in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 962-968. |
| [15] | Xiaotao LIANG, Yifan XIONG, Xueqi LIU, Xiaoshan LIANG, Xiaoyu ZHU, Wei XIE. Huoxue Shufeng Granule alleviates central sensitization in chronic migraine mice via TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 986-994. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||