Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 962-968.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.05.08
Previous Articles Next Articles
Changfeng CHEN1( ), Qin FANG1, Yinhuan GAO1, Liecheng WANG1, Lei CHEN2(
), Qin FANG1, Yinhuan GAO1, Liecheng WANG1, Lei CHEN2( )
)
Received:2024-11-28
Online:2025-05-20
Published:2025-05-23
Contact:
Lei CHEN
E-mail:chenchangfeng89@126.com;azyfychenlei@ahtcm.edu.cn
Changfeng CHEN, Qin FANG, Yinhuan GAO, Liecheng WANG, Lei CHEN. Enriched environment reduces pyramidal neuron excitability in the anterior cingulate cortex to alleviate restraint stress-induced anxiety-like behaviors in mice[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 962-968.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.05.08
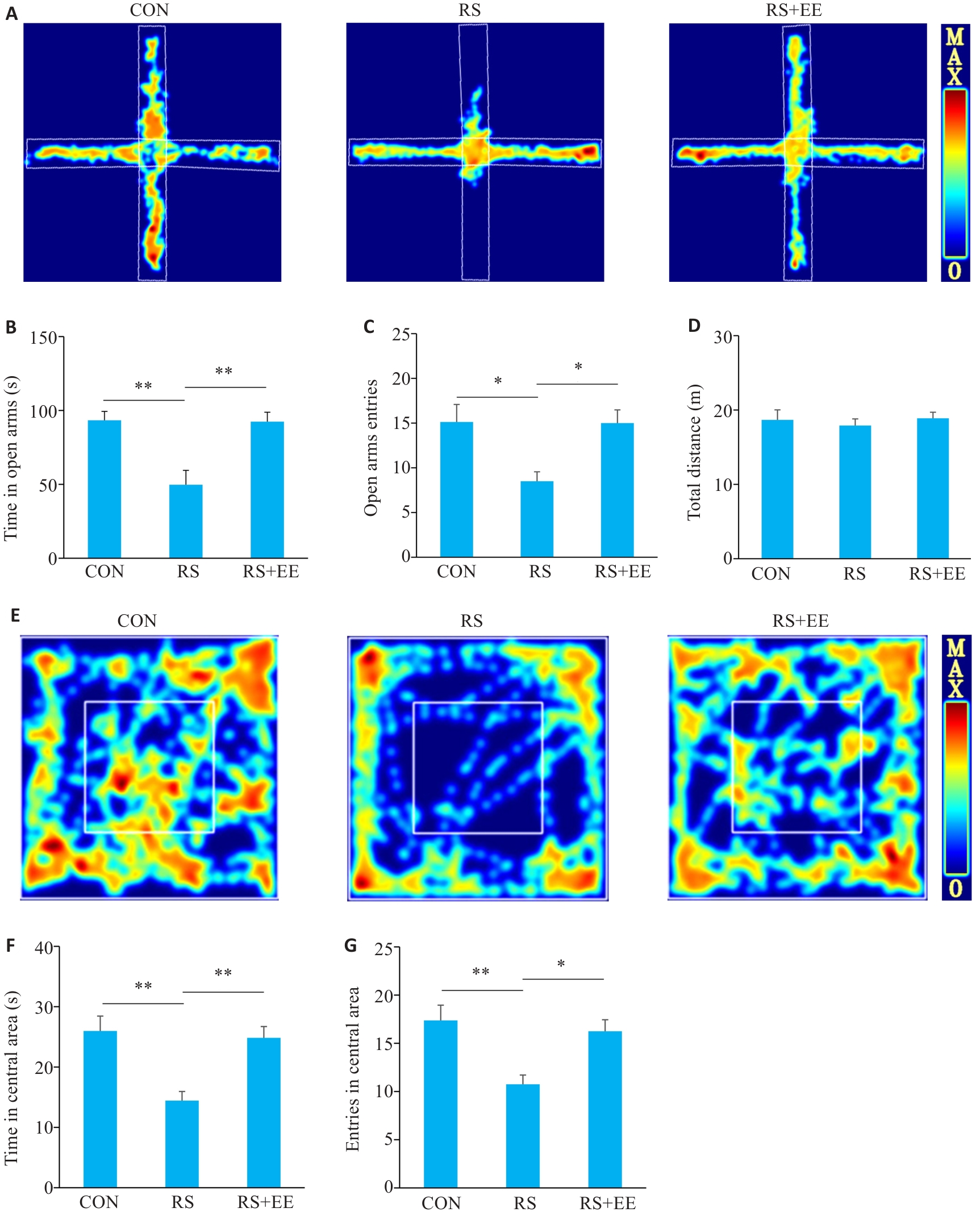
Fig.1 Enriched environment (EE) alleviates anxiety-like behaviors induced by restraint stress (RS) in mice. A: Heatmaps of 5-minute walking paths in the 3 groups in elevated plus-maze (EPM) tests. B: Time spent in open arms. C: Entries in open arms. D: Total distance in EPM tests. E: Heatmaps of 5-minute walking paths in the 3 groups in open field test (OFT). F: Entries in the central area. G: Time in the central area in OFT. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (n=8).
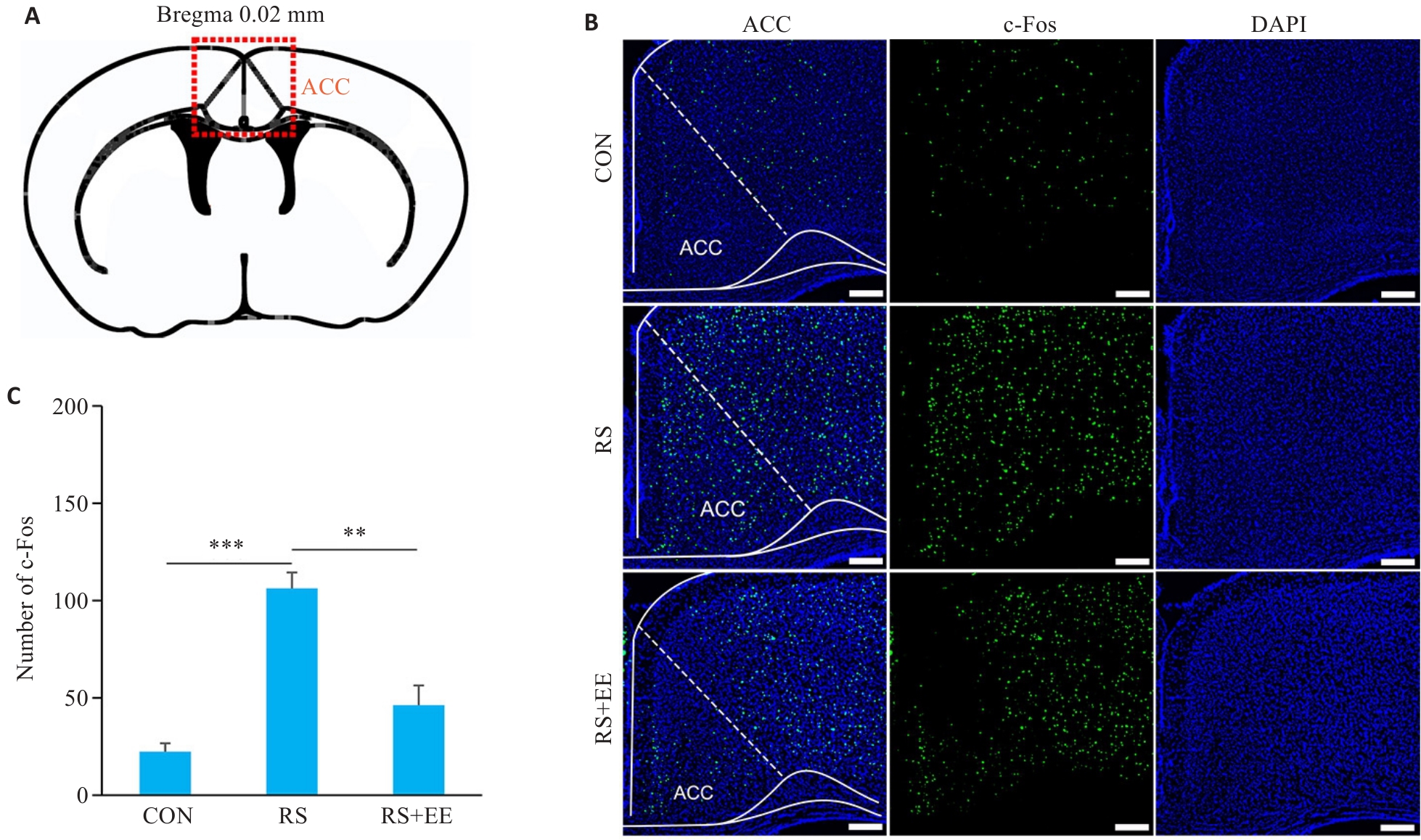
Fig.2 EE prevents the high c-Fos expression of the ACC induced by RS. A: The location of ACC in the brain atlas (Bregma 0.02 mm). B: The original diagram of c-Fos expression in ACC from each group. Scale bar=100 μm. C: Statistical graphs of c-Fos expression in each group. CON: n=3, RS: n=4, RS+EE: n=4. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
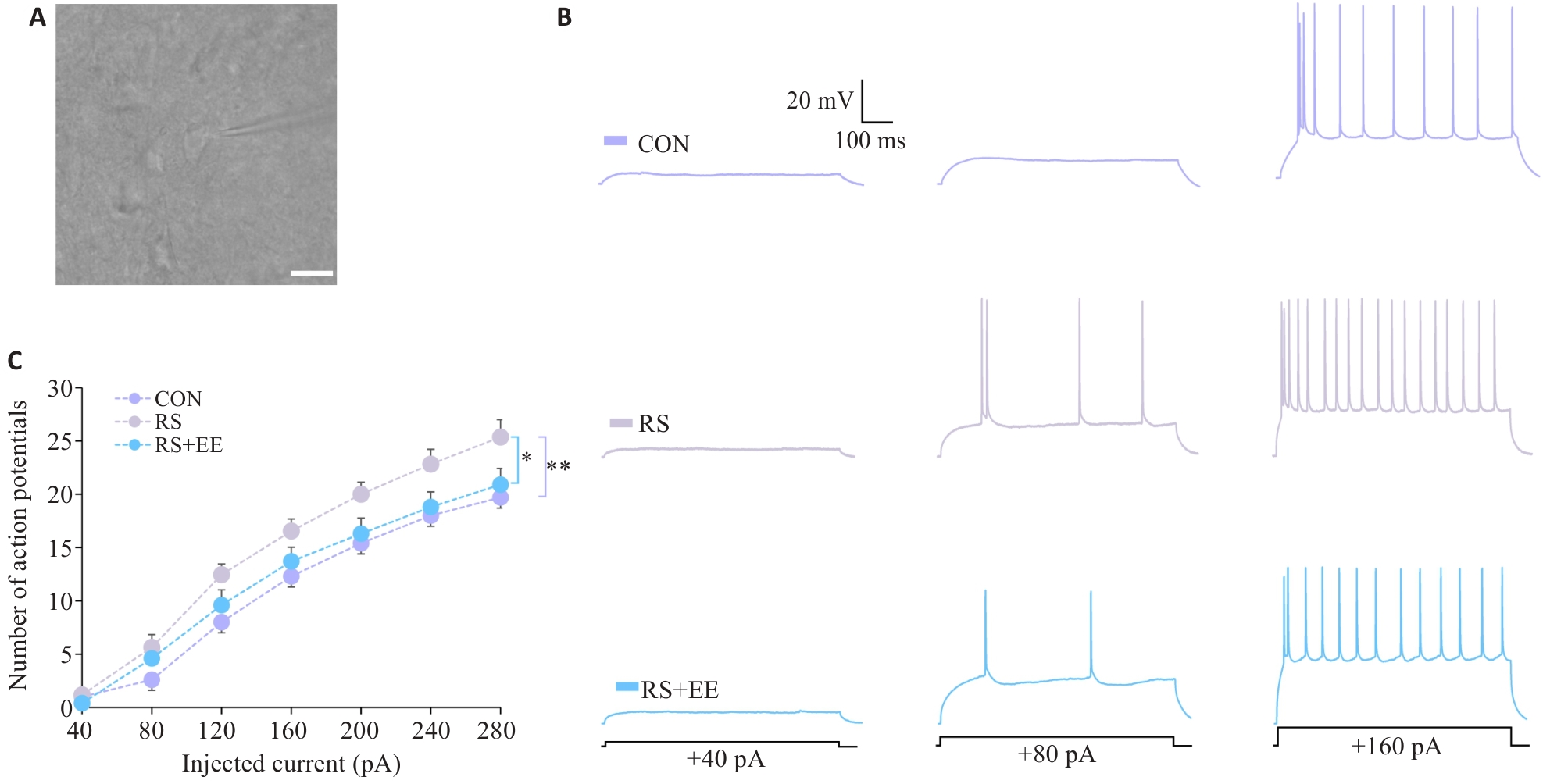
Fig.3 EE attenuates RS-induced increases in action potentials of PynACC. A: Representative image of a PynACC under whole-cell recording (Scale bar=100 μm). B: Groups of typical sequential spikes. C: Quantification of the numbers of spikes with different stimuli. CON: 10 cells from 4 mice; RS: 11 cells from 4 mice; RS+EE: 10 cells from 3 mice. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
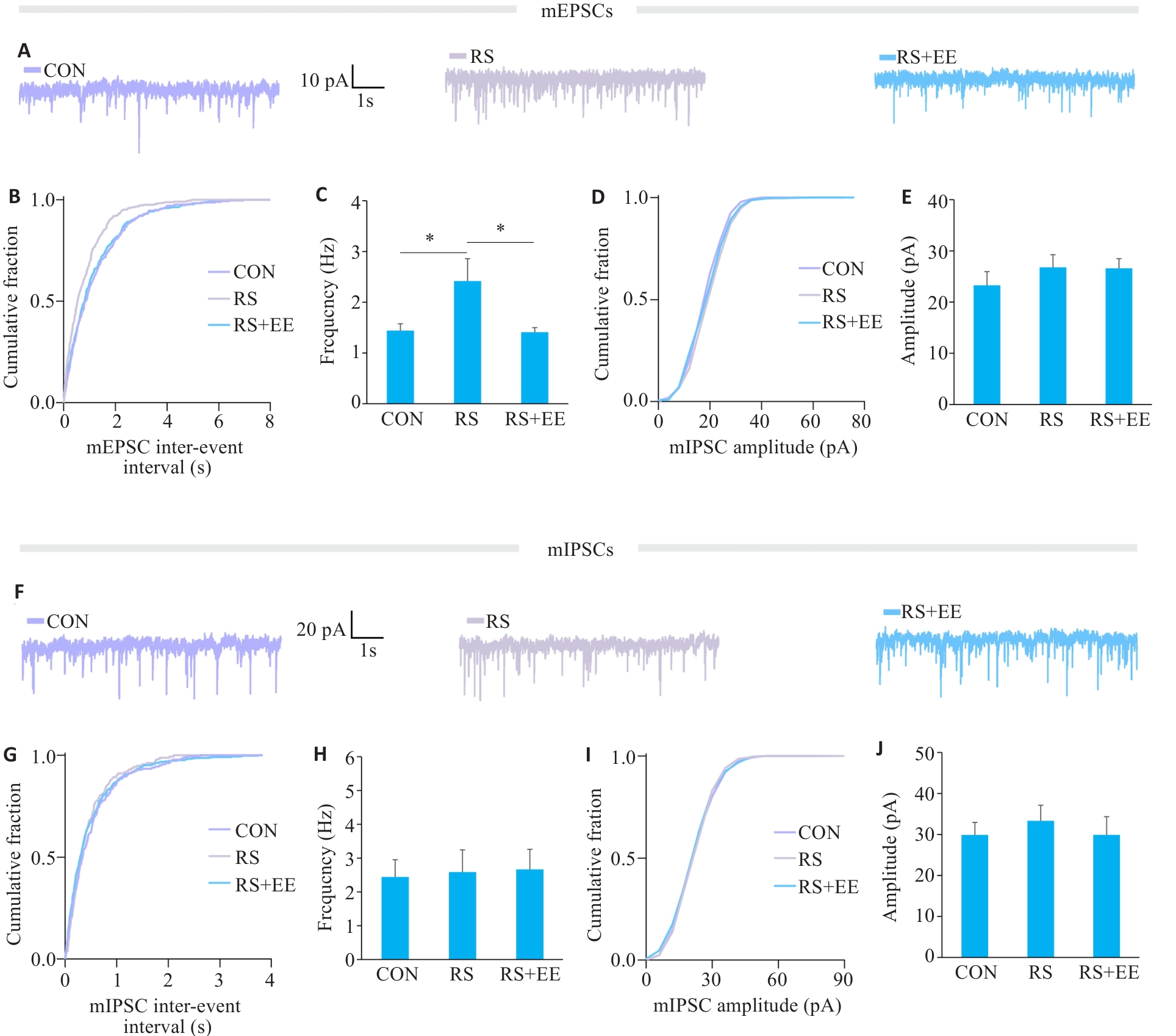
Fig.4 EE attenuates RS-induced increase of mEPSC frequency of PynACC. A: Representative traces of mEPSCs of PynACC. B: Cumulative plots of inter-event interval of mEPSC. C: Statistical results of mEPSC frequency. D: Cumulative plots of amplitude of mEPSC. E: Statistical results of mEPSC amplitude. CON: 12 cells from 4 mice; RS: 13 cells from 3 mice; RS+EE: 14 cells from 3 mice. F: Representative traces of mIPSCs of PynACC. G: Cumulative plots of inter-event interval of mIPSC. H: Statistical results of mIPSC frequency. I: Cumulative plots of amplitude of mIPSC. J: Statistical results of mIPSC amplitude. CON: 12 cells from 4 mice; RS: 11 cells from 4 mice; RS+EE: 11 cells from 3 mice. *P<0.05.
| 1 | Bandelow B, Michaelis S. Epidemiology of anxiety disorders in the 21st century[J]. Dialogues Clin Neurosci, 2015, 17(3): 327-35. |
| 2 | GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016[J]. Lancet, 2017, 390(10100): 1211-59. |
| 3 | Baldwin DS, Waldman S, Allgulander C. Evidence-based pharmacological treatment of generalized anxiety disorder[J]. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol, 2011, 14(5): 697-710. |
| 4 | Fagan HA, Baldwin DS. Pharmacological treatment of generalised anxiety disorder: current practice and future directions[J]. Expert Rev Neurother, 2023, 23(6): 535-48. |
| 5 | Thamizhoviya G, Vanisree AJ. Enriched environment modulates behavior, myelination and augments molecules governing the plasticity in the forebrain region of rats exposed to chronic immobilization stress[J]. Metab Brain Dis, 2019, 34(3): 875-87. |
| 6 | Vanisree AJ, Thamizhoviya G. Enriched environment minimizes anxiety/depressive-like behavior in rats exposed to immobilization stress and augments hippocampal neurogenesis (In vitro)[J]. J Mol Neurosci, 2021, 71(10): 2071-84. |
| 7 | Keller J, Gomez R, Williams G, et al. HPA axis in major depression: cortisol, clinical symptomatology and genetic variation predict cognition[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2017, 22(4): 527-36. |
| 8 | Li X, Du ZJ, Xu JN, et al. mGluR5 in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons mediates stress-induced anxiety-like behavior[J]. Neuropsychopharmacology, 2023, 48(8): 1164-74. |
| 9 | Calhoon GG, Tye KM. Resolving the neural circuits of anxiety[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2015, 18(10): 1394-404. |
| 10 | Murrough JW, Russo SJ. The neurobiology of resilience: complexity and hope[J]. Biol Psychiatry, 2019, 86(6): 406-9. |
| 11 | Guo H, Hu WC, Xian H, et al. CCL2 potentiates inflammation pain and related anxiety-like behavior through NMDA signaling in anterior cingulate cortex[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2024, 61(8): 4976-91. |
| 12 | Sheena MK, Jimmy J, Burkhouse KL, et al. Anterior cingulate cortex activity during attentional control corresponds with rumination in depression and social anxiety[J]. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging, 2021, 317: 111385. |
| 13 | Bliss TVP, Collingridge GL, Kaang BK, et al. Synaptic plasticity in the anterior cingulate cortex in acute and chronic pain[J]. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2016, 17(8): 485-96. |
| 14 | Zhu MY, Dong WY, Guo JR, et al. A neural circuit for bergamot essential oil-induced anxiolytic effects[J]. Adv Sci, 2025, 12(1): e2406766. |
| 15 | Veena J, Srikumar BN, Mahati K, et al. Enriched environment restores hippocampal cell proliferation and ameliorates cognitive deficits in chronically stressed rats[J]. J Neurosci Res, 2009, 87(4): 831-43. |
| 16 | Xu LL, Qu CH, Qu CJ, et al. Improvement of autophagy dysfunction as a potential mechanism for environmental enrichment to protect blood-brain barrier in rats with vascular cognitive impairment[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2020, 739: 135437. |
| 17 | Ji NN, Xia M. Enriched environment alleviates adolescent visceral pain, anxiety- and depression-like behaviors induced by neonatal maternal separation[J]. Transl Pediatr, 2022, 11(8): 1398-407. |
| 18 | Valero J, España J, Parra-Damas A, et al. Short-term environmental enrichment rescues adult neurogenesis and memory deficits in APP(Sw, Ind) transgenic mice[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(2): e16832. |
| 19 | Díez-León M, Mason G. Effects of environmental enrichment and stereotypic behavior on maternal behavior and infant viability in a model carnivore, the American mink (Neovison vison)[J]. Zoo Biol, 2016, 35(1): 19-28. |
| 20 | Liu C, Gu JY, Han JH, et al. Enriched environment combined with fluoxetine ameliorates depression-like behaviors and hippocampal SYP expression in a rat CUS model[J]. Brain Res Bull, 2017, 135: 33-9. |
| 21 | 陈昌锋, 陈 磊, 江 勤, 等. 丰富环境干预对小鼠梨状皮层锥体神经元兴奋性的影响[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2018, 53(6): 898-902. DOI: 10.19405/j.cnki.issn1000-1492.2018.06.015 |
| 22 | Liu L, Luo ZH, Mai YY, et al. Dexmedetomidine relieves inflammatory pain by enhancing GABAergic synaptic activity in pyramidal neurons of the anterior cingulate cortex[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2023, 240: 109710. |
| 23 | Xu YX, Liu GY, Ji ZZ, et al. Restraint stress induced anxiety and sleep in mice[J]. Front Psychiatry, 2023, 14: 1090420. |
| 24 | 魏天祺, 罗家麒, 李紫娟, 等. 基于丰富环境的增强现实训练对脑卒中步行功能的影响[J]. 中国康复理论与实践, 2023, 29(12): 1439-45. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2023.12.008 |
| 25 | 徐欢岚, 梁冠军, 张何威, 等. 丰富环境康复训练对缺氧缺血性脑病新生儿的体格及神经行为发育的影响[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2023, 38(12): 1701-6. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2023.12.011 |
| 26 | Rosenzweig MR, Krech D, Bennett EL, et al. Effects of environmental complexity and training on brain chemistry and anatomy: a replication and extension[J]. J Comp Physiol Psychol, 1962, 55: 429-37. |
| 27 | Zhang TY, Keown CL, Wen XL, et al. Environmental enrichment increases transcriptional and epigenetic differentiation between mouse dorsal and ventral dentate gyrus[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 298. |
| 28 | Rattazzi L, Piras G, Brod S, et al. Impact of enriched environment on murine T cell differentiation and gene expression profile[J]. Front Immunol, 2016, 7: 381. |
| 29 | Cui MH, Yang Y, Yang JL, et al. Enriched environment experience overcomes the memory deficits and depressive-like behavior induced by early life stress[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2006, 404(1/2): 208-12. |
| 30 | Zhang WH, Liu WZ, He Y, et al. Chronic stress causes projection-specific adaptation of amygdala neurons via small-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel downregulation[J]. Biol Psychiatry, 2019, 85(10): 812-28. |
| 31 | Li XH, Matsuura T, Xue M, et al. Oxytocin in the anterior cingulate cortex attenuates neuropathic pain and emotional anxiety by inhibiting presynaptic long-term potentiation[J]. Cell Rep, 2021, 36(3): 109411. |
| 32 | Silveira LM, Tavares LRR, Baptista-de-Souza D, et al. Anterior cingulate cortex, but not amygdala, modulates the anxiogenesis induced by living with conspecifics subjected to chronic restraint stress in male mice[J]. Front Behav Neurosci, 2023, 16: 1077368. |
| 33 | Misquitta KA, Miles A, Prevot TD, et al. Reduced anterior cingulate cortex volume induced by chronic stress correlates with increased behavioral emotionality and decreased synaptic puncta density[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2021, 190: 108562. |
| 34 | Qi MR, Li CL, Li J, et al. Fluoxetine reverses hyperactivity of anterior cingulate cortex and attenuates chronic stress-induced hyperalgesia[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2022, 220: 109259. |
| 35 | Gualtieri F, Brégère C, Laws GC, et al. Effects of environmental enrichment on doublecortin and BDNF expression along the dorso-ventral axis of the dentate gyrus[J]. Front Neurosci, 2017, 11: 488. |
| 36 | Vogt BA, Paxinos G. Cytoarchitecture of mouse and rat cingulate cortex with human homologies[J]. Brain Struct Funct, 2014, 219(1): 185-92. |
| 37 | Song Q, Wei AQ, Xu HD, et al. An ACC-VTA-ACC positive-feedback loop mediates the persistence of neuropathic pain and emotional consequences[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2024, 27(2): 272-85. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||