Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2026, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 200-207.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.22
Songsong SUN1,2( ), Quan TAO1,2, Kaixuan ZHAO3, Qiugen HU4, Yanqiu FENG1,2,4(
), Quan TAO1,2, Kaixuan ZHAO3, Qiugen HU4, Yanqiu FENG1,2,4( )
)
Received:2025-07-20
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2026-01-16
Contact:
Yanqiu FENG
E-mail:sunsongsong02@163.com;foree@163.com
Supported by:Songsong SUN, Quan TAO, Kaixuan ZHAO, Qiugen HU, Yanqiu FENG. A high temporal resolution dynamic T2*W imaging study based on step oxygen stimulation of rat kidneys[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2026, 46(1): 200-207.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.22
| MR scan sequence | RARE | mGRE | FID-EPI |
|---|---|---|---|
| TE (ms) | 45 | 2-33.05 (∆TE=2.07) | 8.458 |
| TR (ms) | 3500 | 40.553 | 1000 |
| FA (°) | - | 15 | 60 |
| FOV (mm2) | 55×55 | 55×55 | 55×55 |
| Matrix size | 110×110 | 110×110 | 110×110 |
| Slice thickness (mm) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Resolution (mm2) | 0.5×0.5 | 0.5×0.5 | 0.5×0.5 |
| Averages | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Rare factor | 16 | - | - |
| Bandwidth (kHz) | - | - | 666.7 |
| Scan time (s) | 42 | 9 | 1 |
Tab.1 MR scan parameters for each sequence
| MR scan sequence | RARE | mGRE | FID-EPI |
|---|---|---|---|
| TE (ms) | 45 | 2-33.05 (∆TE=2.07) | 8.458 |
| TR (ms) | 3500 | 40.553 | 1000 |
| FA (°) | - | 15 | 60 |
| FOV (mm2) | 55×55 | 55×55 | 55×55 |
| Matrix size | 110×110 | 110×110 | 110×110 |
| Slice thickness (mm) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Resolution (mm2) | 0.5×0.5 | 0.5×0.5 | 0.5×0.5 |
| Averages | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Rare factor | 16 | - | - |
| Bandwidth (kHz) | - | - | 666.7 |
| Scan time (s) | 42 | 9 | 1 |
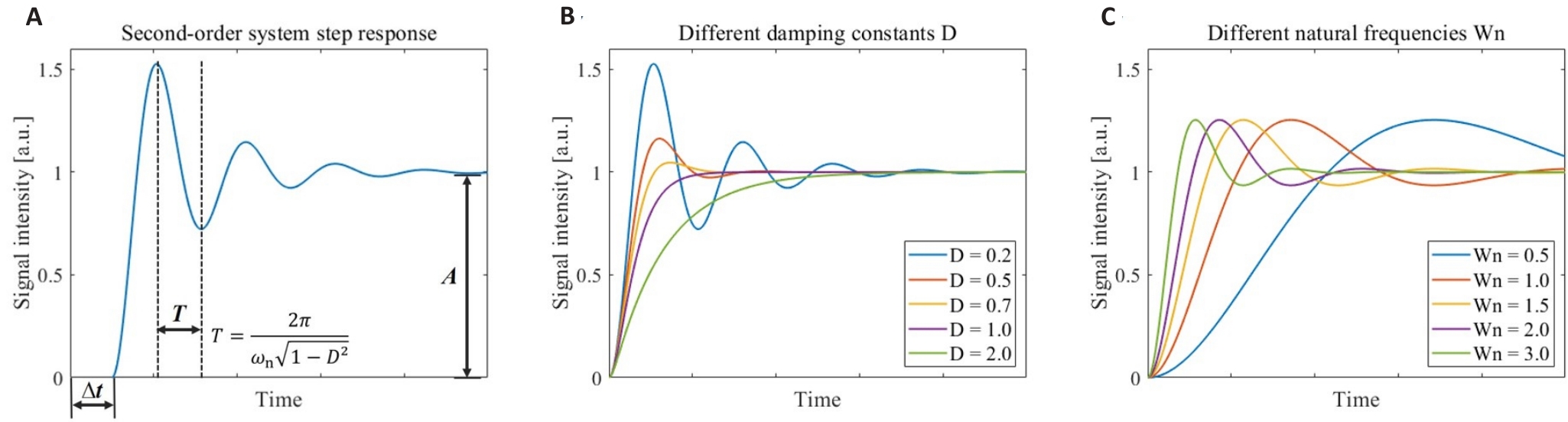
Fig.1 Step response models for the second-order continuous-time system. A: Step response of the second-order system and the significance of its model parameters. B: Step response of the second-order system corresponding to different damping constants D. C: Step response of the second-order system corresponding to different natural frequencies ωn.
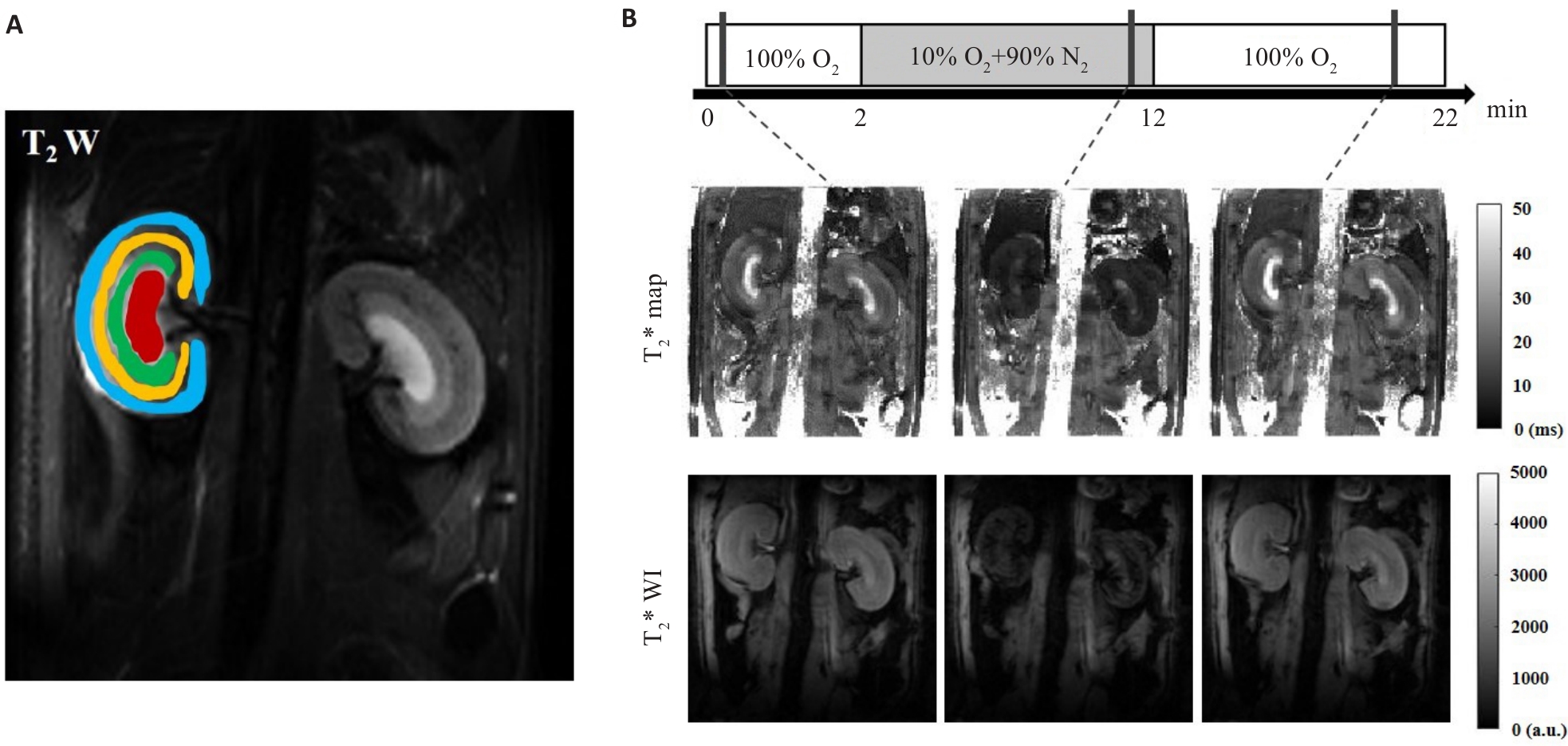
Fig.3 Placement of ROIs on T2WI obtained from MRI (A) and gas challenge protocol, T2*map and T2*WI acquired at each stage of gas challenge (B). ROI placement 4 anatomical layers of kidney-CO (blue), OSOM (yellow), ISOM (green), and IM (red) were used.
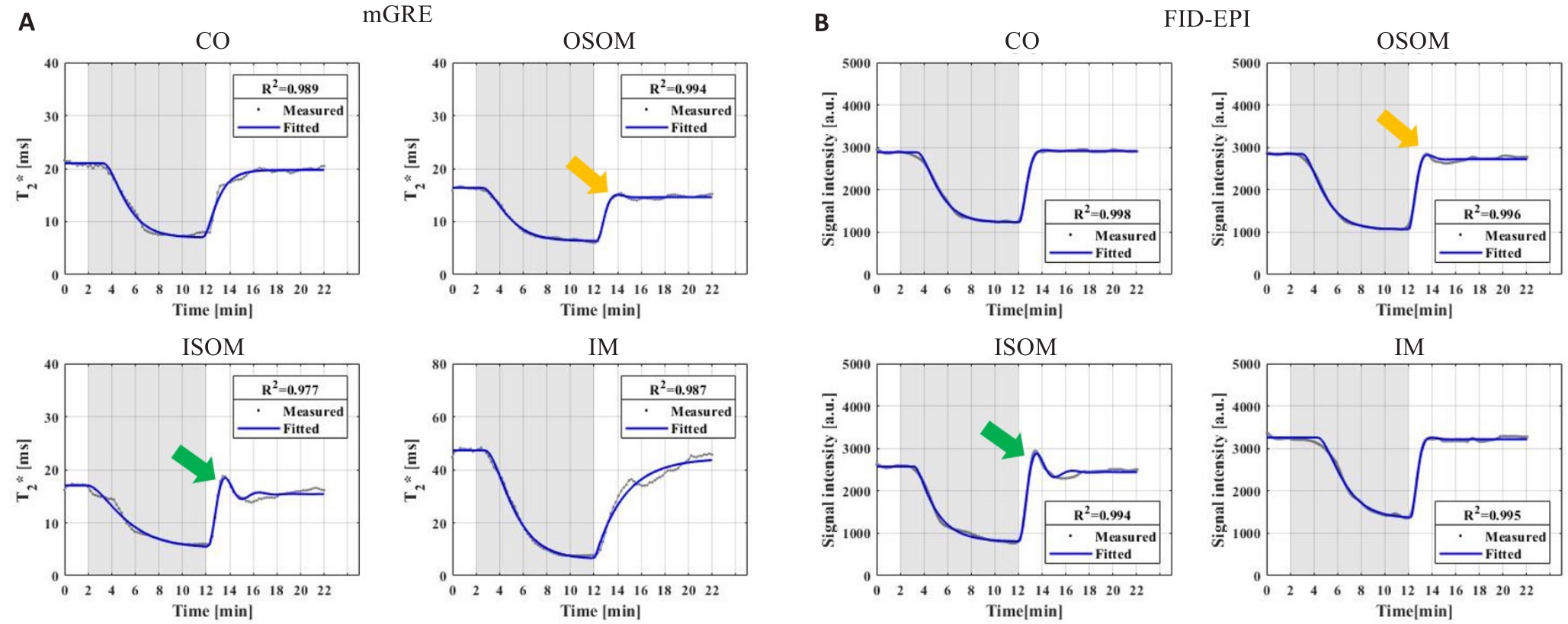
Fig.4 Dynamic T2* sequence curves (A) and dynamic T2*W signal sequence curves (B) in renal CO, OSOM, ISOM and IM of the same rat. The yellow and green arrows represent the overshoot phenomena of OSOM and ISOM, respectively.
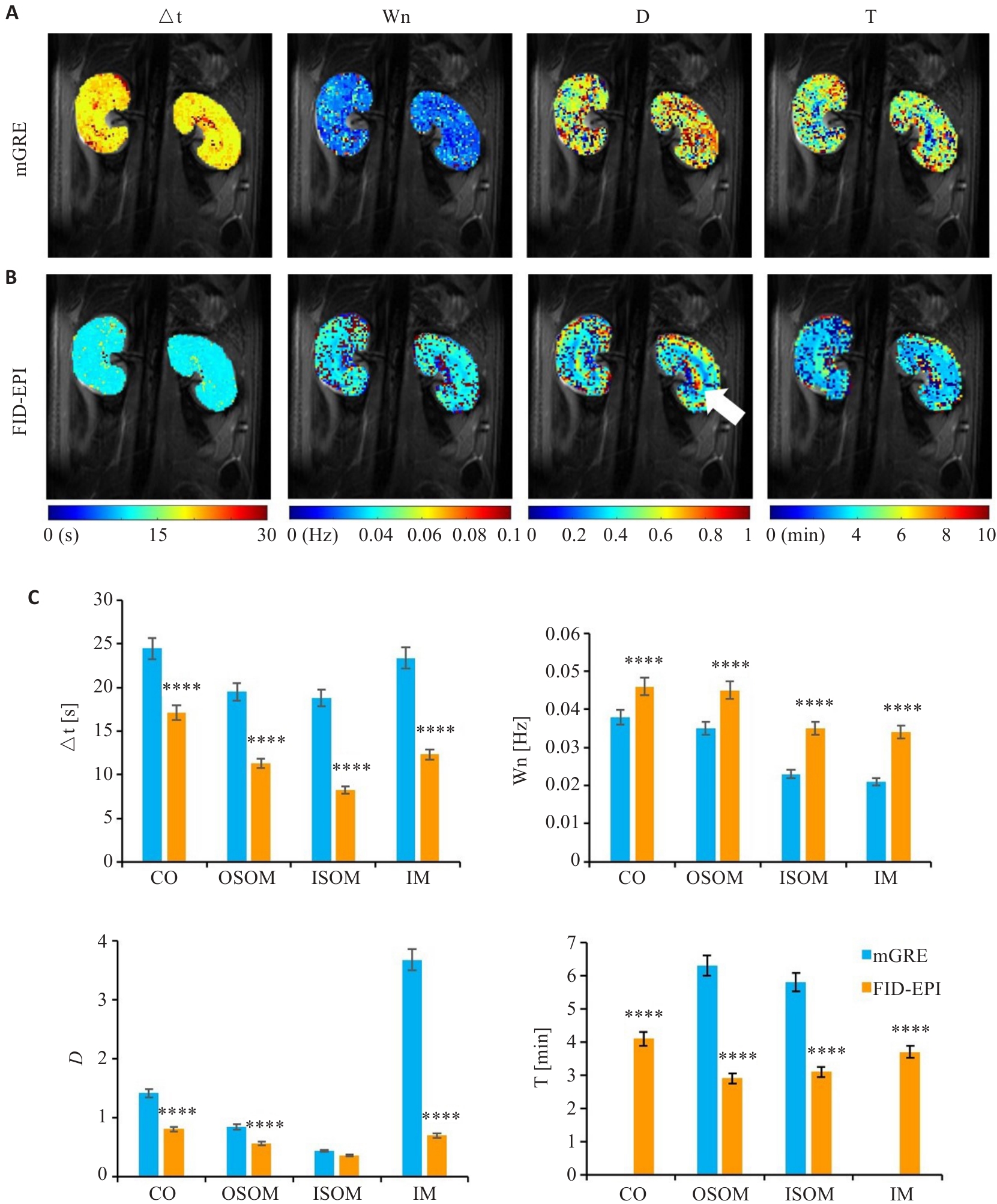
Fig.5 Model parameter analysis of dynamic data of mGRE and FID-EPI sequences. A: Model parameter maps of mGRE. B: Model parameter maps of FID-EPI. C: Comparison of model parameters. ****P<0.0001 vs mGRE.
| [1] | Preuss HG. Basics of renal anatomy and physiology[J]. Clin Lab Med, 1993, 13(1): 1-11. doi:10.1016/s0272-2712(18)30456-6 |
| [2] | Bane O, Seeliger E, Cox E, et al. Renal MRI: from nephron to NMR signal[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2023, 58(6): 1660-79. doi:10.1002/jmri.28828 |
| [3] | Levassort H, Essig M. The kidney, its anatomy and main functions[J]. Soins Gerontol, 2024, 29(165): 10-20. doi:10.1016/j.sger.2023.12.003 |
| [4] | Brezis M, Rosen S, Silva P, et al. Renal ischemia: a new perspective[J]. Kidney Int, 1984, 26(4): 375-83. doi:10.1038/ki.1984.185 |
| [5] | Brezis M, Rosen S. Hypoxia of the renal medulla: its implications for disease[J]. N Engl J Med, 1995, 332(10): 647-55. doi:10.1056/nejm199503093321006 |
| [6] | Hirakawa Y, Tanaka T, Nangaku M. Renal hypoxia in CKD; pathophysiology and detecting methods[J]. Front Physiol, 2017, 8: 99. doi:10.3389/fphys.2017.00099 |
| [7] | Gueutin V, Deray G, Isnard-Bagnis C. Renal physiology [J]. Bull Cancer, 2012, 99(3): 237-49. doi:10.1684/bdc.2011.1482 |
| [8] | Franzin R, Stasi A, Fiorentino M, et al. Renal delivery of pharmacologic agents during machine perfusion to prevent ischaemia-reperfusion injury: from murine model to clinical trials[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 673562. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.673562 |
| [9] | Shu S, Wang Y, Zheng M, et al. Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in kidney injury and repair[J]. Cells, 2019, 8(3): E207. doi:10.3390/cells8030207 |
| [10] | Cantow K, Evans RG, Grosenick D, et al. Quantitative assessment of renal perfusion and oxygenation by invasive probes: basic concepts[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2021, 2216: 89-107. doi:10.1007/978-1-0716-0978-1_6 |
| [11] | Cantow K, Ladwig-Wiegard M, Flemming B, et al. Monitoring renal hemodynamics and oxygenation by invasive probes: experimental protocol[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2021, 2216: 327-47. doi:10.1007/978-1-0716-0978-1_19 |
| [12] | Yeh TH, Tu KC, Wang HY, et al. From acute to chronic: unraveling the pathophysiological mechanisms of the progression from acute kidney injury to acute kidney disease to chronic kidney disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(3): 1755. doi:10.3390/ijms25031755 |
| [13] | Niendorf T, Gladytz T, Cantow K, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of renal oxygenation[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2025, 21(7): 483-502. doi:10.1038/s41581-025-00956-z |
| [14] | Ogawa S, Lee TM, Nayak AS, et al. Oxygenation-sensitive contrast in magnetic resonance image of rodent brain at high magnetic fields[J]. Magn Reson Med, 1990, 14(1): 68-78. doi:10.1002/mrm.1910140108 |
| [15] | Prasad PV, Edelman RR, Epstein FH. Noninvasive evaluation of intrarenal oxygenation with BOLD MRI[J]. Circulation, 1996, 94(12): 3271-5. doi:10.1161/01.cir.94.12.3271 |
| [16] | 杨桂香, 梅颖洁, 吕 健, 等. 血氧水平依赖磁共振成像评估急性马兜铃酸肾病大鼠肾脏氧合水平变化 [J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(5): 528. |
| [17] | Pohlmann A, Hentschel J, Fechner M, et al. High temporal resolution parametric MRI monitoring of the initial ischemia/reperfusion phase in experimental acute kidney injury[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(2): e57411. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0057411 |
| [18] | Zhao K, Pohlmann A, Feng Q, et al. Physiological system analysis of the kidney by high-temporal-resolution T2 monitoring of an oxygen-ation step response[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2021, 85(1): 334-45. doi:10.1002/mrm.28399 |
| [19] | Priatna A, Epstein FH, Spokes K, et al. Evaluation of changes in intrarenal oxygenation in rats using multiple gradient-recalled echo (mGRE) sequence[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 1999, 9(6): 842-6. doi:10.1002/(sici)1522-2586(199906)9:6<842::aid-jmri12>3.3.co;2-m |
| [20] | Markl M, Leupold J. Gradient echo imaging[J]. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2012, 35(6): 1274-89. doi:10.1002/jmri.23638 |
| [21] | Stehling MK, Turner R, Mansfield P. Echo-planar imaging: magnetic resonance imaging in a fraction of a second[J]. Science, 1991, 254(5028): 43-50. doi:10.1126/science.1925560 |
| [22] | Mansfield SP. EPI - in the beginning[J]. J Magn Reson, 2011, 213(2): 532. doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2011.08.017 |
| [23] | Jin N, da Silveira JS, Jolly MP, et al. Free-breathing myocardial T2* mapping using GRE-EPI and automatic non-rigid motion correction[J]. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson, 2015, 17: 113. doi:10.1186/1532-429x-17-s1-w8 |
| [24] | Kundu P, Inati SJ, Evans JW, et al. Differentiating BOLD and non-BOLD signals in fMRI time series using multi-echo EPI[J]. NeuroImage, 2012, 60(3): 1759-70. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.12.028 |
| [25] | Wronski T, Seeliger E, Persson PB, et al. The step response: a method to characterize mechanisms of renal blood flow auto-regulation[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2003, 285(4): F758-64. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00420.2002 |
| [26] | Boss A, Martirosian P, Jehs MC, et al. Influence of oxygen and carbogen breathing on renal oxygenation measured by T2*-weighted imaging at 3.0 T[J]. NMR Biomed, 2009, 22(6): 638-45. doi:10.1002/nbm.1378 |
| [27] | Seeliger E, Wronski T, Ladwig M, et al. The renin-angiotensin system and the third mechanism of renal blood flow autoregulation[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2009, 296(6): F1334-45. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.90476.2008 |
| [28] | Edwards A, Kurtcuoglu V. Renal blood flow and oxygenation[J]. Pflügers Arch Eur J Physiol, 2022, 474(8): 759-70. doi:10.1007/s00424-022-02690-y |
| [29] | Gloviczki ML, Glockner J, Gomez SI, et al. Comparison of 1.5 and 3 T BOLD MR to study oxygenation of kidney cortex and medulla in human renovascular disease[J]. Invest Radiol, 2009, 44(9): 566-71. doi:10.1097/rli.0b013e3181b4c1e8 |
| [30] | Pohlmann A, Arakelyan K, Hentschel J, et al. Detailing the relation between renal T2* and renal tissue PO2 using an integrated approach of parametric magnetic resonance imaging and invasive physiological measurements[J]. Invest Radiol, 2014, 49(8): 547-60. doi:10.1097/rli.0000000000000054 |
| [31] | Ganesh T, Estrada M, Duffin J, et al. T2* and T1 assessment of abdominal tissue response to graded hypoxia and hypercapnia using a controlled gas mixing circuit for small animals[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2016, 44(2): 305-16. doi:10.1002/jmri.25169 |
| [32] | Gardiner BS, Smith DW, O' Connor PM, et al. A mathematical model of diffusional shunting of oxygen from arteries to veins in the kidney[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2011, 300(6): F1339-52. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00544.2010 |
| [33] | Donati OF, Nanz D, Serra AL, et al. Quantitative BOLD response of the renal medulla to hyperoxic challenge at 1.5 T and 3.0 T[J]. NMR Biomed, 2012, 25(10): 1133-8. doi:10.1002/nbm.2781 |
| [34] | Evans RG, Smith DW, Lee CJ, et al. What makes the kidney susceptible to hypoxia[J]? Anat Rec: Hoboken, 2020, 303(10): 2544-52. doi:10.1002/ar.24260 |
| [35] | Wang R, Lin Z, Yang X, et al. Noninvasive evaluation of renal hypoxia by multiparametric functional MRI in early diabetic kidney disease[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2022, 55(2): 518-27. doi:10.1002/jmri.27814 |
| [36] | Li ZL, Liu BC. Hypoxia and renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2019, 1165: 467-85. doi:10.1007/978-981-13-8871-2_23 |
| [37] | Crislip GR, Patel B, Mohamed R, et al. Ultrasound measurement of change in kidney volume is a sensitive indicator of severity of renal parenchymal injury[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2020, 319(3): F447-57. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00221.2020 |
| [38] | Jufar AH, Lankadeva YR, May CN, et al. Renal and cerebral hypoxia and inflammation during cardiopulmonary bypass[J]. Compr Physiol, 2021, 12(1): 2799-834. doi:10.1002/j.2040-4603.2022.tb00202.x |
| [39] | Arnoux G, Serre J, Verissimo T, et al. The preferential injury of outer renal medulla after ischemia-reperfusion relies on high oxidative metabolism [J]. bioRxiv, 2024: 2024.09. 12.612245. |
| [40] | Sgouralis I, Evans RG, Layton AT. Renal medullary and urinary oxygen tension during cardiopulmonary bypass in the rat[J]. Math Med Biol, 2017, 34(3): 313-33. |
| [41] | 游 勇, 陈 丽. 呼吸衰竭的相关研究 [J]. 临床医学进展, 2025, 15(4): 2024-30. |
| [42] | Kim N, Voicu L, Hare GM, et al. Response of the renal inner medulla to hypoxia: possible defense mechanisms[J]. Nephron Physiol, 2012, 121(1/2): 1-7. doi:10.1159/000345516 |
| [43] | Lee CJ, Gardiner BS, Evans RG, et al. Analysis of the critical determinants of renal medullary oxygenation[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2019, 317(6): F1483-502. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00315.2019 |
| [44] | Selby NM, Francis ST. Assessment of acute kidney injury using MRI[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2025, 61(1): 25-41. doi:10.1002/jmri.29281 |
| [45] | 叶常红, 杨燕玲. 七氟烷与异氟烷吸入麻醉对肝肾功能影响的比较 [J]. 中国基层医药, 2012, 19(10): 1560-1. |
| [46] | Evans RG, Goddard D, Eppel GA, et al. Factors that render the kidney susceptible to tissue hypoxia in hypoxemia[J]. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, 2011, 300(4): R931-40. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00552.2010 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||