Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2026, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 191-199.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.21
Shufen ZHANG1( ), Tianrong HUANG2(
), Tianrong HUANG2( ), Canhong YANG2, Jiayi CHEN2, Tianming LÜ2, Jiafa ZHANG2(
), Canhong YANG2, Jiayi CHEN2, Tianming LÜ2, Jiafa ZHANG2( )
)
Received:2025-09-15
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2026-01-16
Contact:
Jiafa ZHANG
E-mail:120064577@qq.com;596471200@qq.com
Shufen ZHANG, Tianrong HUANG, Canhong YANG, Jiayi CHEN, Tianming LÜ, Jiafa ZHANG. Sulforaphane reduces reactive astrocyte-mediated neuron apoptosis in vitro by inhibiting the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway in Aβ42 oligomer-activated astrocytes[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2026, 46(1): 191-199.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.21
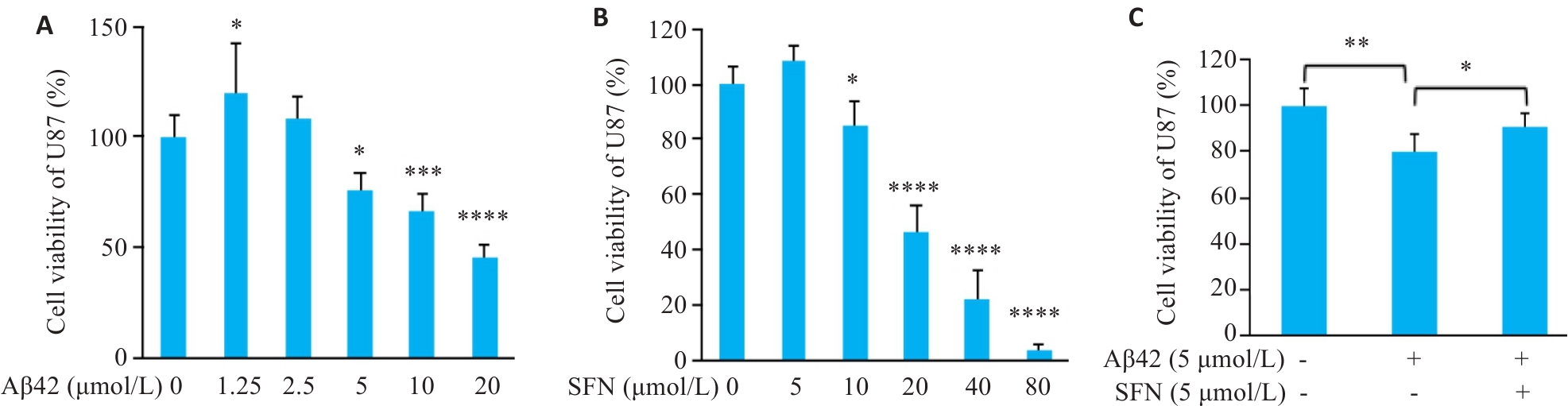
Fig.1 CCK-8 assay for assessing viability of U87 cells treated with different concentration of Aβ42, sulforaphane (SFN) and both. A: Viability of U87 cells treated with 0, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, and 20 μmol/L Aβ42 for 48 h (*P˂0.05, ***P˂0.001, ****P˂0.0001 vs 0 μmol/L group). B: Viability of U87 cells treated with 0, 5, 10, 20, 40, and 80 μmol/L SFN for 24 h (*P˂0.05, ****P˂0.0001 vs 0 μmol/L group). C: Viability of U87 cells treated with vehicle, Aβ42 (5 μmol/L), and Aβ42 (5 μmol/L)+SFN (5 μmol/L) (*P˂0.05, **P˂0.01).
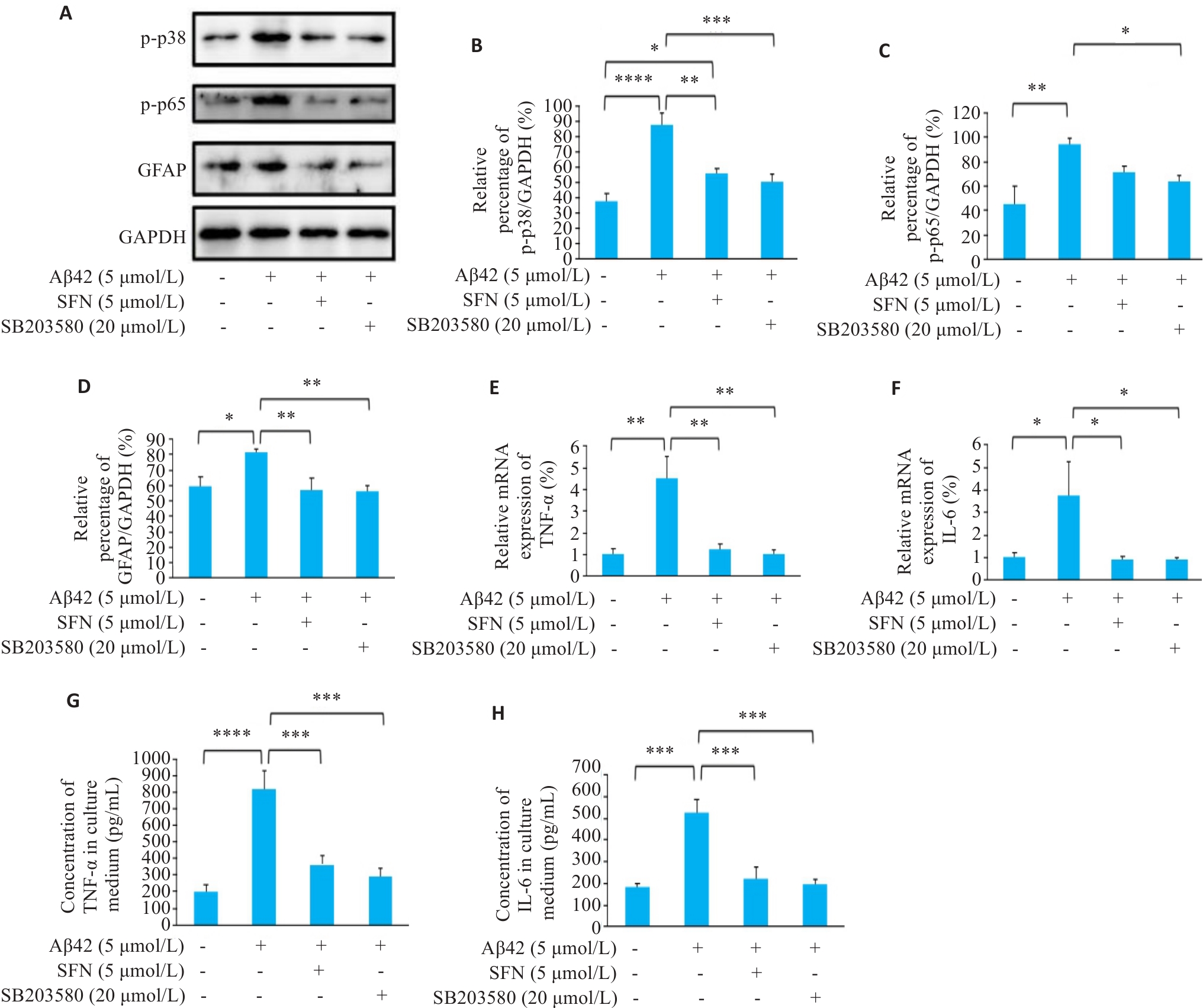
Fig.2 Effects of Aβ42 (5 μmol/L), SFN (5 μmol/L) and SB203580 (20 μmol/L) on protein expressions of p-p38, p-p65 and GFAP, mRNA expressions of TNF‑α and IL-6, and TNF‑α and IL-6 levels in culture supernatant of U87 cells. A-D: Protein expression levels of p-p38, p-p65 and GFAP in U87 cells treated with vehicle, Aβ42, Aβ42+SFN, and Aβ42+ SB203580 detected by Western blotting (*P˂0.05, **P˂0.01, ***P˂0.001, ****P˂0.0001). E, F: Expression levels of TNF-α and IL-6 mRNA in treated U87 cells detected by RT-qPCR (*P˂0.05, **P˂0.01). G-H: TNF-α and IL-6 levels in culture supernatant of the treated U87 cells (***P˂0.001, ****P˂0.0001).
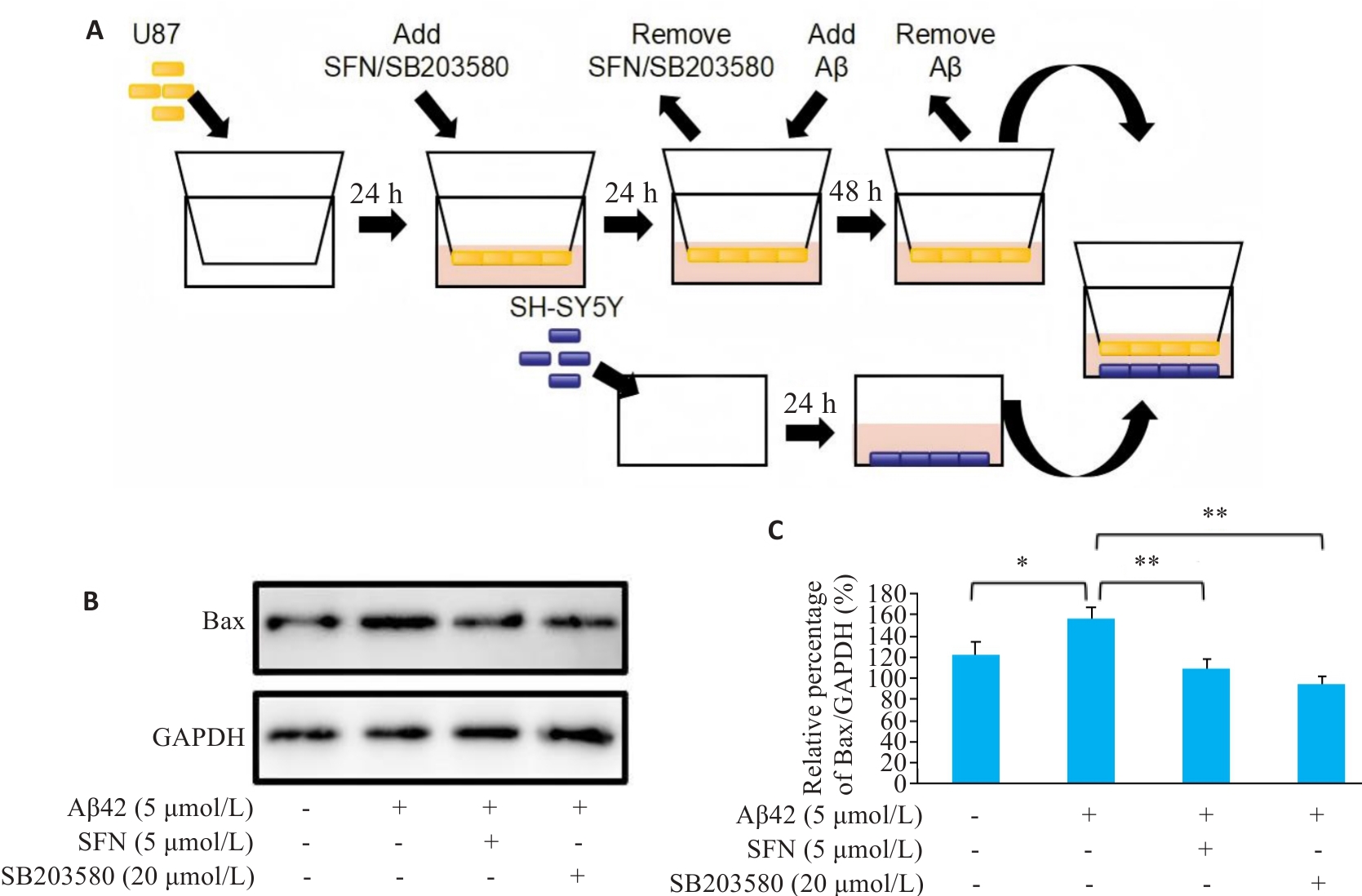
Fig.3 Indirect effects of Aβ42, SFN and SB203580 treatment of U87 cells on co-cultured SH-SY5Y neurons. A: Transwell co-culture scheme of U87 and SH-SY5Y Cells. B: Protein expression of Bax in SH-SY5Y cells co-cultured with U87 cells treated with vehicle, Aβ42, Aβ42+SFN, and Aβ42+SB203580. C: Quantification of Bax expression levels. *P˂0.05, **P˂0.01.
| Primer | Sequuence (5' to 3') |
|---|---|
| GAPDH-F | CTA GGC CAC AGA ATT GAA AGA TCT |
| GAPDH-R | GTA GGT GGA AAT TCT AGC ATC ATC C |
| TNF-α-F | CTG TGA AGG GAA TGG GTG TT |
| TNF-α-R | CAG GGA AGA ATC TGG AAA GGT C |
| IL-6-F | GAG AGC ATT GGA AGT TGG GG |
| IL-6-R | CTT CCA GCC AGT TGC CTT CT |
Tab.1 Primers sequences for qRT-PCR
| Primer | Sequuence (5' to 3') |
|---|---|
| GAPDH-F | CTA GGC CAC AGA ATT GAA AGA TCT |
| GAPDH-R | GTA GGT GGA AAT TCT AGC ATC ATC C |
| TNF-α-F | CTG TGA AGG GAA TGG GTG TT |
| TNF-α-R | CAG GGA AGA ATC TGG AAA GGT C |
| IL-6-F | GAG AGC ATT GGA AGT TGG GG |
| IL-6-R | CTT CCA GCC AGT TGC CTT CT |
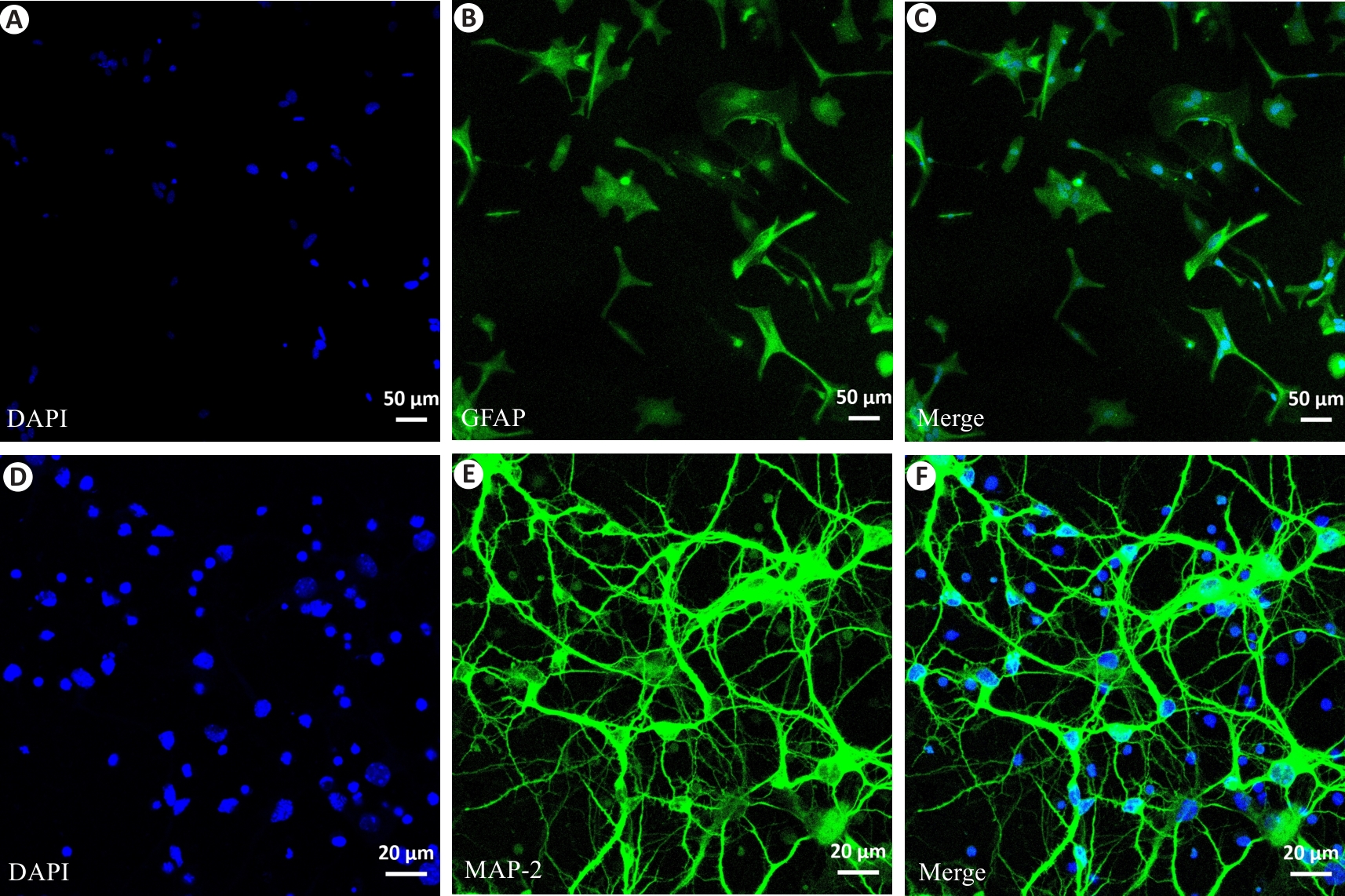
Fig.4 Purity identification of astrocytes and primary neurons isolated from mouse brain tissues. A-C: Immunofluorescence staining for assessing purity of the astrocytes labeled with GFAP (green). DAPI (blue) was used to label the cell nuclei (Scale bar=50 μm). D-F: Immunofluorescence staining for assessing purity of the primary neurons labeled with MAP-2 (green). DAPI (blue) was used to label the cell nuclei (Scale bar=20 μm).
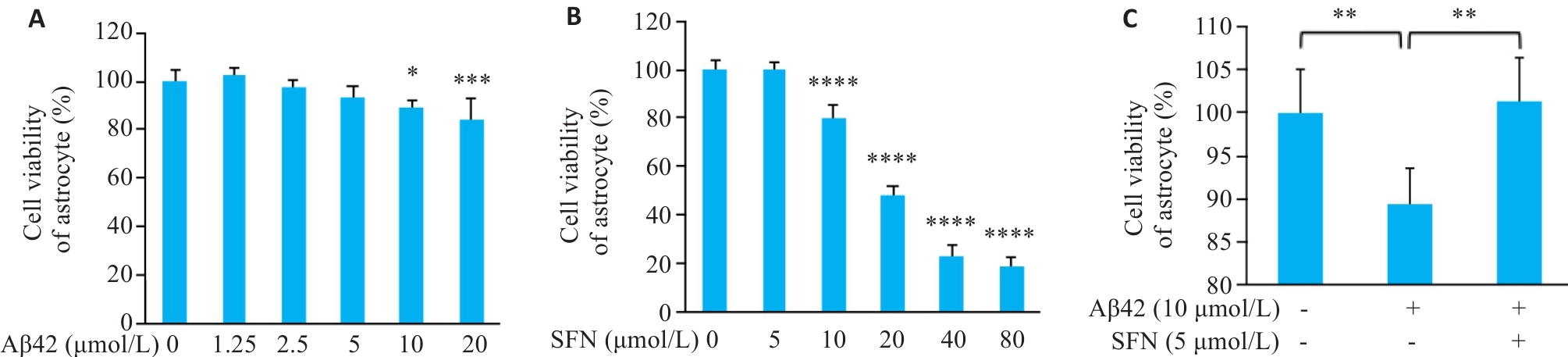
Fig.5 CCK-8 assay for assessing the effect of different concentrations of Aβ42, SFN and their combination on viability of isolated mouse astrocytes. A: Viability of mouse astrocytes treated with 0, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, and 20 μmol/L Aβ42 for 48 h (*P˂0.05, ***P˂0.001 vs control group). B: Viability of mouse astrocytes treated with 0, 5, 10, 20, 40, and 80 μmol/L SFN for 24 h (****P˂0.0001 vs control group). C: Viability of mouse astrocytes treated with vehicle, Aβ42 (10 μmol/L), and Aβ42 (10 μmol/L) + SFN (5 μmol/L) (*P˂0.05, **P˂0.01).
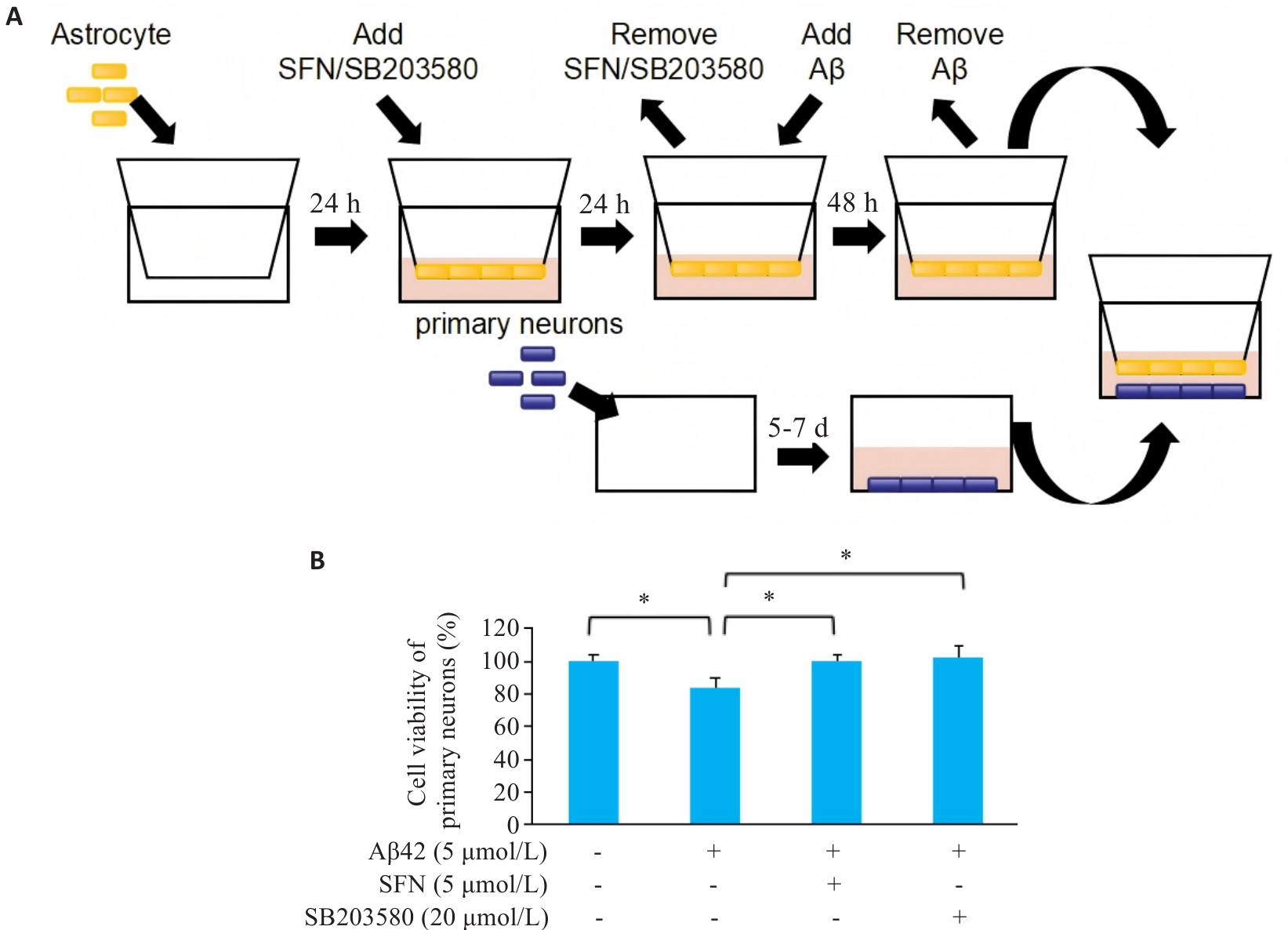
Fig.6 Indirect effects of Aβ42, SFN and SB203580 treatment of isolated mouse astrocytes on the primary neurons. A: Transwell co-culture scheme for mouse astrocytes and primary neurons. B: Viability of primary neurons co-cultured with mouse astrocytes treated with vehicle, Aβ42 (10 μmol/L), Aβ42 (10 μmol/L)+SFN (5 μmol/L), and Aβ42 (10 μmol/L)+SB203580 (20 μmol/L). *P˂0.05.
| [1] | Ji QQ, Chen JQ, Li YF, et al. Incidence and prevalence of Alzheimer's disease in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2024, 39(7): 701-14. doi:10.1007/s10654-024-01144-2 |
| [2] | Jorfi M, Maaser-Hecker A, Tanzi RE. The neuroimmune axis of Alzheimer's disease[J]. Genome Med, 2023, 15(1): 6. doi:10.1186/s13073-023-01155-w |
| [3] | Kim J, Lee HJ, Park SK, et al. Donepezil regulates LPS and aβ-stimulated neuroinflammation through MAPK/NLRP3 inflammas ome/STAT3 signaling[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(19): 10637. doi:10.3390/ijms221910637 |
| [4] | Qiu S, Palavicini JP, Wang J, et al. Adult-onset CNS myelin sulfatide deficiency is sufficient to cause Alzheimer's disease-like neuroinflam -mation and cognitive impairment[J]. Mol Neurodegener, 2021, 16(1): 64. doi:10.1186/s13024-021-00488-7 |
| [5] | Du Z, Li M, Ren J, et al. Current strategies for modulating aβ aggregation with multifunctional agents[J]. Acc Chem Res, 2021, 54(9): 2172-84. doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00055 |
| [6] | Ding B, Lin C, Liu Q, et al. Tanshinone IIA attenuates neuroinflammation via inhibiting RAGE/NF-κB signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro [J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2020, 17(1): 302. doi:10.1186/s12974-020-01981-4 |
| [7] | Bernabeu-Zornoza A, Coronel R, Palmer C, et al. Oligomeric and fibrillar species of Aβ42 diversely affect human neural stem cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(17): 9537. doi:10.3390/ijms22179537 |
| [8] | Calabrese EJ, Kozumbo WJ. The phytoprotective agent sulforaphane prevents inflammatory degenerative diseases and age-related pathologies via Nrf2-mediated hormesis[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2021, 163: 105283. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105283 |
| [9] | Kim J. Pre-clinical neuroprotective evidences and plausible mechanisms of sulforaphane in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(6): 2929. doi:10.3390/ijms22062929 |
| [10] | Allen NJ, Lyons DA. Glia as architects of central nervous system formation and function[J]. Science, 2018, 362(6411): 181-5. doi:10.1126/science.aat0473 |
| [11] | Endo F, Kasai A, Soto JS, et al. Molecular basis of astrocyte diversity and morphology across the CNS in health and disease[J]. Science, 2022, 378(6619): eadc9020. doi:10.1126/science.adc9020 |
| [12] | Yu X, Nagai J, Khakh BS. Improved tools to study astrocytes[J]. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2020, 21(3): 121-38. doi:10.1038/s41583-020-0264-8 |
| [13] | Nagai J, Yu X, Papouin T, et al. Behaviorally consequential astrocytic regulation of neural circuits[J]. Neuron, 2021, 109(4): 576-96. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2020.12.008 |
| [14] | Lee HG, Wheeler MA, Quintana FJ. Function and therapeutic value of astrocytes in neurological diseases[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2022, 21(5): 339-58. doi:10.1038/s41573-022-00390-x |
| [15] | Jung E, Koh SH, Yoo M, et al. Regenerative potential of carbon monoxide in adult neural circuits of the central nervous system[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(7): E2273. doi:10.3390/ijms21072273 |
| [16] | Qin SS, Yang CH, Huang WH, et al. Sulforaphane attenuates microglia-mediated neuronal necroptosis through down-regulation of MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways in LPS-activated BV-2 microglia[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2018, 133: 218-35. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2018.01.014 |
| [17] | Wang H, Ma J, Tan Y, et al. Amyloid-beta1-42 induces reactive oxygen species-mediated autophagic cell death in U87 and SH-SY5Y cells[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2010, 21(2): 597-610. doi:10.3233/jad-2010-091207 |
| [18] | Lopez-Suarez L, Al Awabdh S, Coumoul X, et al. The SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell line, a relevant in vitro cell model for investigating neurotoxicology in human: Focus on organic pollutants[J]. NeuroToxicology, 2022, 92: 131-55. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2022.07.008 |
| [19] | Ozbolat G, Alizade A. Investigation of the protective effect of thymoquinone of U87 cells induced by beta-amyloid[J]. Bratisl Lek Listy, 2021, 122(10): 748-52. doi:10.4149/bll_2021_120 |
| [20] | Pandey M, Karmakar V, Majie A, et al. The SH-SY5Y cell line: a valuable tool for Parkinson's disease drug discovery[J]. Expert Opin Drug Discov, 2024, 19(3): 303-16. doi:10.1080/17460441.2023.2293158 |
| [21] | Saeed Y, Xie B, Xu J, et al. Glial U87 cells protect neuronal SH-SY5Y cells from indirect effect of radiation by reducing oxidative stress and apoptosis[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin: Shanghai, 2015, 47(4): 250-7. doi:10.1093/abbs/gmv004 |
| [22] | Fu Y, Zhang J, Yang C, et al. Effects of solvent dimethyl sulfoxide invites a rethink of its application in amyloid beta cytotoxicity[J]. Int J Toxicol, 2025, 44(4): 297-313. doi:10.1177/10915818251338235 |
| [23] | Liu T, Guo WH, Gong M, et al. Pericyte loss: a key factor inducing brain Aβ40 accumulation and neuronal degeneration in cerebral amyloid angiopathy[J]. Exp Brain Res, 2025, 243(8): 191. doi:10.1007/s00221-025-07134-4 |
| [24] | White JA, Manelli AM, Holmberg KH, et al. Differential effects of oligomeric and fibrillar amyloid-β1-42 on astrocyte-mediated inflammation[J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2005, 18(3): 459-65. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2004.12.013 |
| [25] | Kim S, Chun H, Kim Y, et al. Astrocytic autophagy plasticity modulates Aβ clearance and cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Mol Neurodegener, 2024, 19(1): 55. doi:10.1186/s13024-024-00740-w |
| [26] | Huo SM, Li B, Du JY, et al. Dibutyl phthalate induces liver fibrosis via p38MAPK/NF-κB/NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2023, 897: 165500. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.165500 |
| [27] | Kim KM, Yoo GD, Heo W, et al. TAZ stimulates exercise-induced muscle satellite cell activation via Pard3-p38 MAPK-TAZ signalling axis[J]. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2023, 14(6): 2733-46. doi:10.1002/jcsm.13348 |
| [28] | Dey P, Biswas S, Das R, et al. p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 enhances anticancer activity of PARP inhibitor olaparib in a synergistic way on non-small cell lung carcinoma A549 cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2023, 670: 55-62. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.05.116 |
| [29] | Bahattab S, Assiri A, Alhaidan Y, et al. Pharmacological p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 enhances AML stem cell line KG1a chemosensitivity to daunorubicin by promoting late apoptosis, cell growth arrest in S-phase, and miR-328-3p upregulation[J]. Saudi Pharm J, 2024, 32(6): 102055. doi:10.1016/j.jsps.2024.102055 |
| [30] | Santoro A, Martucci M, Conte M, et al. Inflammaging, hormesis and the rationale for anti-aging strategies[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2020, 64: 101142. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2020.101142 |
| [31] | Balusu S, De Strooper B. The necroptosis cell death pathway drives neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Acta Neuropathol, 2024, 147(1): 96. doi:10.1007/s00401-024-02747-5 |
| [32] | Lou S, Gong D, Yang M, et al. Curcumin improves neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease mice via the upregulation of Wnt/β-catenin and BDNF[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(10): 5123. doi:10.3390/ijms25105123 |
| [33] | Huang JH, Xu ZW, Yu CS, et al. The volatile oil of Acorus tatarinowii Schott ameliorates Alzheimer's disease through improving insulin resistance via activating the PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 135: 156168. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156168 |
| [34] | Li Q, Yuan Y, Huang S, et al. Excess ub-K48 induces neuronal apoptosis in Alzheimer's disease[J]. J Integr Neurosci, 2024, 23(12): 223. doi:10.31083/j.jin2312223 |
| [1] | Tong QIAO, Lin YIN, Keni ZHANG, Minzhu NIU, Ju HUANG, Zhijun Geng, Jing LI, Jianguo HU. Poricoic acid A alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by regulating AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy and inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2026, 46(1): 131-140. |
| [2] | Xiaoyu CHANG, Hanwen ZHANG, Hongting CAO, Ling HOU, Xin MENG, Hong TAO, Yan LUO, Guanghua LI. Heat stress affects expression levels of circadian clock gene Bmal1 and cyclins in rat thoracic aortic endothelial cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1353-1362. |
| [3] | Dongning TANG, Yunyun KANG, Wenjie HE, Qing XIA. Electroacupuncture combined with rehabilitation training improves neurological function of mice with cerebral ischemia by promoting astrocyte transdifferentiation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1434-1441. |
| [4] | Bing XIA, Jin PENG, Jiuyang DING, Jie WANG, Guowei TANG, Guojie LIU, Yun WANG, Changwu WAN, Cuiyun LE. ATF3 regulates inflammatory response in atherosclerotic plaques in mice through the NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1131-1142. |
| [5] | Guoyong LI, Renling LI, Yiting LIU, Hongxia KE, Jing LI, Xinhua WANG. Therapeutic mechanism of Arctium lappa extract for post-viral pneumonia pulmonary fibrosis: a metabolomics, network pharmacology analysis and experimental verification [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [6] | Yujia YANG, Lifang YANG, Yaling WU, Zhaoda DUAN, Chunze YU, Chunyun WU, Jianyun YU, Li YANG. Cannabidiol inhibits neuronal endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in rats with multiple concussions by regulating the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1240-1250. |
| [7] | Yang YANG, Kai WANG, Jianxiu LIU, Zhimo ZHOU, Wen JIA, Simou WU, Jinxing LI, Fang HE, Ruyue CHENG. Early life Bifidobacterium bifidum BD-1 intervention alleviates hyperactivity of juvenile female rats with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 702-710. |
| [8] | Shuting GUO, Fuyang CAO, Yongxin GUO, Yanxiang LI, Xinyu HAO, Zhuoning ZHANG, Zhikang ZHOU, Li TONG, Jiangbei CAO. Activation of astrocytes in the dorsomedial hypothalamus accelerates sevoflurane anesthesia emergence in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 751-759. |
| [9] | Yue CHEN, Linyu XIAO, Lü REN, Xue SONG, Jing LI, Jianguo HU. Monotropein improves motor function of mice with spinal cord injury by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to suppress neuronal apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 774-784. |
| [10] | Fei CHU, Xiaohua CHEN, Bowen SONG, Jingjing YANG, Lugen ZUO. Moslosooflavone ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by suppressing intestinal epithelium apoptosis via inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 819-828. |
| [11] | Yi ZHANG, Yu SHEN, Zhiqiang WAN, Song TAO, Yakui LIU, Shuanhu WANG. High expression of CDKN3 promotes migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating the p53/NF-κB signaling pathway and inhibiting cell apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [12] | Lixia YIN, Minzhu NIU, Keni ZHANG, Zhijun GENG, Jianguo HU, Jiangyan LI, Jing LI. Cimifugin ameliorates Crohn's disease-like colitis in mice by modulating Th-cell immune balance via inhibiting the MAPK pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 595-602. |
| [13] | Di CHEN, Ying LÜ, Yixin GUO, Yirong ZHANG, Ruixuan WANG, Xiaoruo ZHOU, Yuxin CHEN, Xiaohui WU. Dihydroartemisinin enhances doxorubicin-induced apoptosis of triple negative breast cancer cells by negatively regulating the STAT3/HIF-1α pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 254-260. |
| [14] | Pengwei HUANG, Jie CHEN, Jinhu ZOU, Xuefeng GAO, Hong CAO. Quercetin mitigates HIV-1 gp120-induced rat astrocyte neurotoxicity via promoting G3BP1 disassembly in stress granules [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 304-312. |
| [15] | Yu BIN, Ziwen LI, Suwei ZUO, Sinuo SUN, Min LI, Jiayin SONG, Xu LIN, Gang XUE, Jingfang WU. High expression of apolipoprotein C1 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells by activating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 359-370. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||