Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (11): 2416-2426.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.11.14
Xuening JIANG1( ), Qingqing HUANG2, Ying XU2, Shunyin² WANG2, Xiaofeng² ZHANG2, Lian¹ WANG1, Yueyue² WANG2, Lugen ZUO1,2(
), Qingqing HUANG2, Ying XU2, Shunyin² WANG2, Xiaofeng² ZHANG2, Lian¹ WANG1, Yueyue² WANG2, Lugen ZUO1,2( )
)
Received:2025-05-06
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-11-28
Contact:
Lugen ZUO
E-mail:jiangxn1202@163.com;zuolugen@126.com
Supported by:Xuening JIANG, Qingqing HUANG, Ying XU, Shunyin² WANG, Xiaofeng² ZHANG, Lian¹ WANG, Yueyue² WANG, Lugen ZUO. High YEATS2 expression promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer cells by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(11): 2416-2426.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.11.14

Fig.1 Expression and correlation analysis of YEATS2 and Ki67 in gastric cancer. A: Expression of YEATS2 in different human tumors. B: Expression of YEATS2 in gastric cancer. C: Immunohistochemical staining of YEATS2 and Ki67. D,E: Relative IOD values of YEATS2 and Ki67. F: Correlation between YEATS2 and Ki67 in gastric cancer tissues. *P<0.05,***P<0.001 vs adjacent tissue.
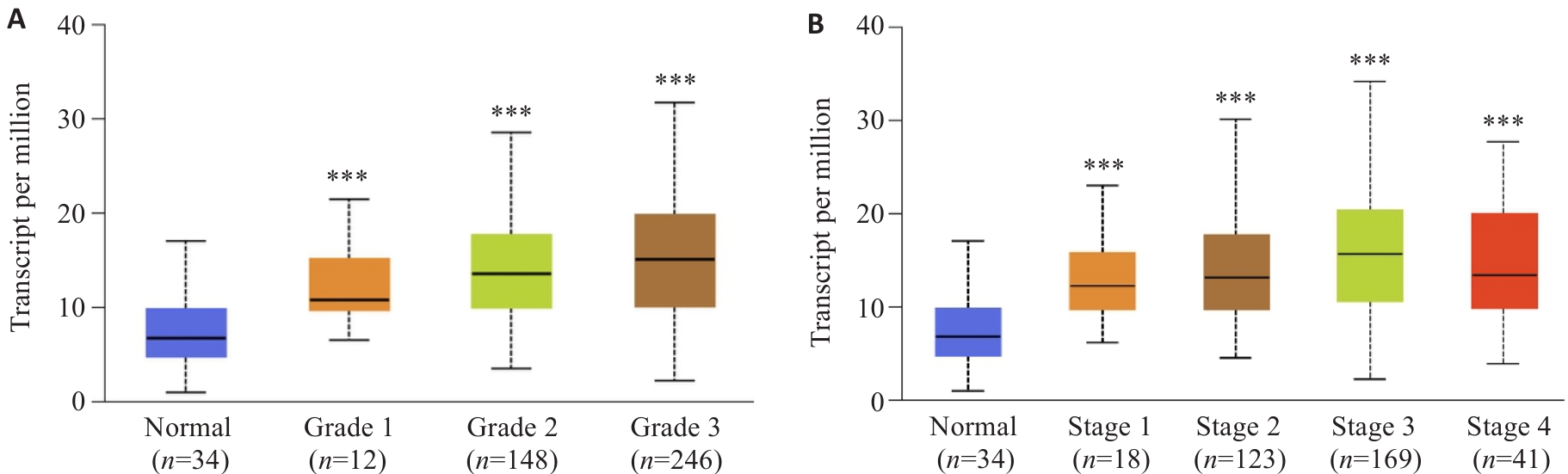
Fig.2 High YEATS2 expression is significantly associated with tumor grading and staging in gastric cancer patients. A: Correlation between YEATS2 TPM and tumor grading in gastric cancer. B: Correlation between YEATS2 TPM and tumor staging in gastric cancer. ***P<0.001 vs adjacent tissue.
| Factor | n | YEATS2 expression | χ2 | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n=50) | High (n=50) | |||||
| Gender | Female | 19 | 6 (31.58%) | 13 (68.42%) | 3.184 | 0.074 |
| Male | 81 | 44 (54.32%) | 37 (45.68%) | |||
| Age (year) | ˂60 | 35 | 18 (51.43%) | 17 (48.57%) | 0.044 | 0.834 |
| ≥60 | 65 | 32 (49.23%) | 33 (50.77%) | |||
| Cancer cell type | Adenocarcinoma | 79 | 42 (53.16%) | 37 (46.84%) | 1.507 | 0.220 |
| Other | 21 | 8 (38.10%) | 13 (61.90%) | |||
| CEA (μg/L) | ˂5 | 35 | 24 (68.57%) | 11 (31.43%) | 7.429 | 0.006 |
| ≥5 | 65 | 26 (40.00%) | 39 (60.00%) | |||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | ˂37 | 44 | 27 (61.36%) | 17 (38.64%) | 4.058 | 0.044 |
| ≥37 | 56 | 23 (41.07%) | 33 (58.93%) | |||
| Tumor size (cm) | ˂5 | 49 | 27 (55.10%) | 22 (44.90%) | 1.000 | 0.317 |
| ≥5 | 51 | 23 (45.10%) | 28 (54.90%) | |||
| T stage | T1-T2 | 36 | 25 (69.44%) | 11 (30.56%) | 8.507 | 0.004 |
| T3-T4 | 64 | 25 (39.06%) | 39 (60.94%) | |||
| N stage | N0-N1 | 43 | 27 (62.79%) | 16 (37.21%) | 4.937 | 0.026 |
| N2-N3 | 57 | 23 (40.35%) | 34 (59.65%) | |||
Tab.1 Relationship between YEATS2 expression level and parameters of malignant progression in gastric cancer tissues (n=50)
| Factor | n | YEATS2 expression | χ2 | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n=50) | High (n=50) | |||||
| Gender | Female | 19 | 6 (31.58%) | 13 (68.42%) | 3.184 | 0.074 |
| Male | 81 | 44 (54.32%) | 37 (45.68%) | |||
| Age (year) | ˂60 | 35 | 18 (51.43%) | 17 (48.57%) | 0.044 | 0.834 |
| ≥60 | 65 | 32 (49.23%) | 33 (50.77%) | |||
| Cancer cell type | Adenocarcinoma | 79 | 42 (53.16%) | 37 (46.84%) | 1.507 | 0.220 |
| Other | 21 | 8 (38.10%) | 13 (61.90%) | |||
| CEA (μg/L) | ˂5 | 35 | 24 (68.57%) | 11 (31.43%) | 7.429 | 0.006 |
| ≥5 | 65 | 26 (40.00%) | 39 (60.00%) | |||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | ˂37 | 44 | 27 (61.36%) | 17 (38.64%) | 4.058 | 0.044 |
| ≥37 | 56 | 23 (41.07%) | 33 (58.93%) | |||
| Tumor size (cm) | ˂5 | 49 | 27 (55.10%) | 22 (44.90%) | 1.000 | 0.317 |
| ≥5 | 51 | 23 (45.10%) | 28 (54.90%) | |||
| T stage | T1-T2 | 36 | 25 (69.44%) | 11 (30.56%) | 8.507 | 0.004 |
| T3-T4 | 64 | 25 (39.06%) | 39 (60.94%) | |||
| N stage | N0-N1 | 43 | 27 (62.79%) | 16 (37.21%) | 4.937 | 0.026 |
| N2-N3 | 57 | 23 (40.35%) | 34 (59.65%) | |||
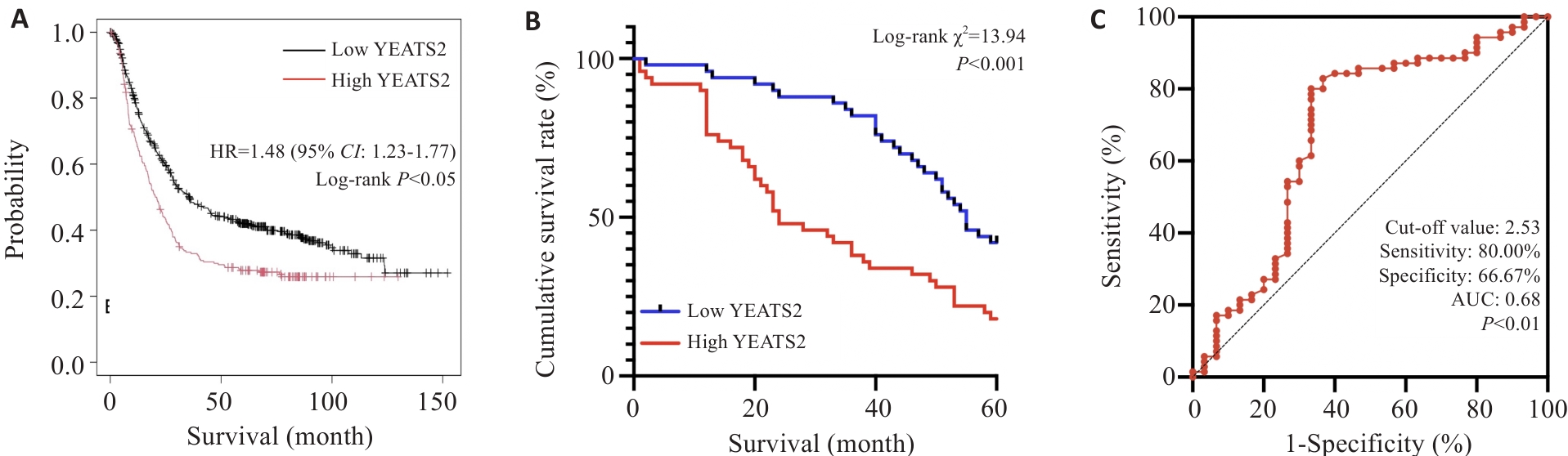
Fig.3 Effect of YEATS2 on prognosis of patients with gastric cancer. A: Kaplan-Meier analysis. B: Survival curves. C: Predictive value of YEATS2 for 5-year survival after radical gastrectomy.
| Factor | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log-rank χ2 | P | HR | 95% CI | P | ||
| Gender (male vs female) | <0.001 | 0.989 | ||||
| Age (˂60 years vs ≥60 years ) | 0.014 | 0.907 | ||||
| Cancer cell type (adenocarcinoma vs other) | 0.539 | 0.463 | ||||
| CEA (˂5 μg/L vs ≥5 μg/L) | 24.128 | <0.001 | 2.760 | 1.480-5.147 | 0.001 | |
| CA19-9 (˂37kU/L vs ≥37 kU/L) | 30.316 | <0.001 | 2.600 | 1.480-4.569 | <0.001 | |
| Tumor size (˂5 cm vs ≥5 cm) | 1.041 | 0.308 | ||||
| T stage (T1-T2 vs T3-T4) | 15.477 | <0.001 | 2.015 | 1.129-3.593 | 0.018 | |
| N stage (N0-N1 vs N2-N3) | 25.115 | <0.001 | 2.238 | 1.275-3.928 | 0.005 | |
| YEATS2 expression (high vs low) | 13.939 | <0.001 | 1.675 | 1.013-2.771 | 0.045 | |
Tab.2 Analysis of risk factors affecting 5-year survival rate of gastric cancer patients after radical gastrectomy
| Factor | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log-rank χ2 | P | HR | 95% CI | P | ||
| Gender (male vs female) | <0.001 | 0.989 | ||||
| Age (˂60 years vs ≥60 years ) | 0.014 | 0.907 | ||||
| Cancer cell type (adenocarcinoma vs other) | 0.539 | 0.463 | ||||
| CEA (˂5 μg/L vs ≥5 μg/L) | 24.128 | <0.001 | 2.760 | 1.480-5.147 | 0.001 | |
| CA19-9 (˂37kU/L vs ≥37 kU/L) | 30.316 | <0.001 | 2.600 | 1.480-4.569 | <0.001 | |
| Tumor size (˂5 cm vs ≥5 cm) | 1.041 | 0.308 | ||||
| T stage (T1-T2 vs T3-T4) | 15.477 | <0.001 | 2.015 | 1.129-3.593 | 0.018 | |
| N stage (N0-N1 vs N2-N3) | 25.115 | <0.001 | 2.238 | 1.275-3.928 | 0.005 | |
| YEATS2 expression (high vs low) | 13.939 | <0.001 | 1.675 | 1.013-2.771 | 0.045 | |

Fig.5 YEATS2 promotes migration of gastric cancer cells. A-D: Validation of YEATS2 knockdown and overexpression in gastric cancer cells. E, F: High expression of YEATS2 promotes HGC-27 cell migration. G, H: High expression of YEATS2 promotes AGS cell migration. n=3, *P<0.05 vs shNC or vs Vector.

Fig.6 YEATS2 promotes migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells. A-D: High expression of YEATS2 promotes HGC-27 cell migration and invasion. E-H: High expression of YEATS2 promotes AGS cell migration and invasion. n=3, *P<0.05 vs shNC or vs Vector.
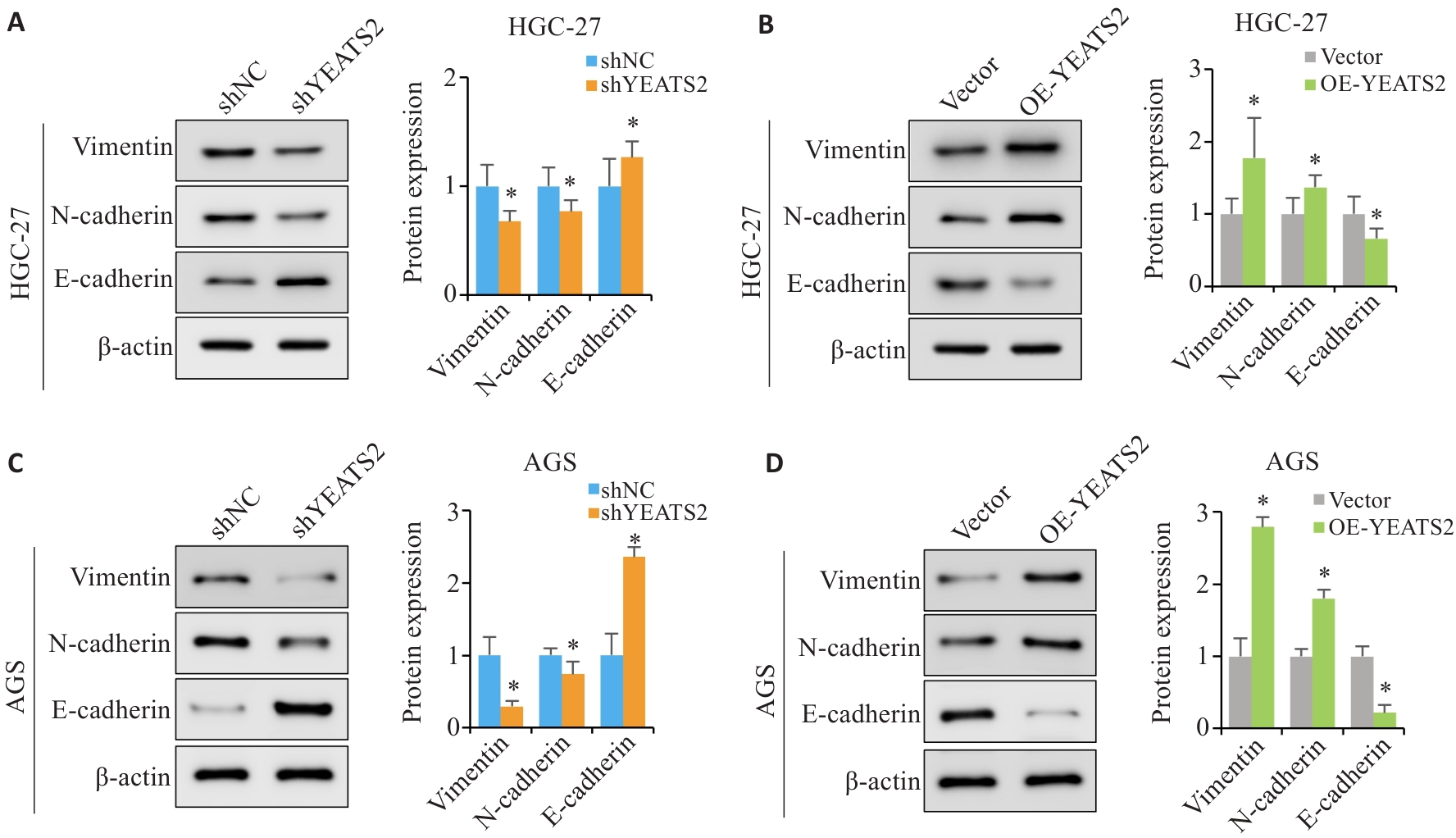
Fig.7 YEATS2 promotes EMT process in gastric cancer cells. A, B : Expressions of key EMT-related proteins in HGC27 cells. C, D: Expressions of key EMT-related proteins in AGS cells. n=3, *P<0.05 vs shNC or vs Vector.

Fig.8 Elevated expression of YEATS2 in gastric cancer cells activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. A, B: Expressions of Wnt, active β-catenin and c-myc in HGC-27 cells. C, D: Expressions of Wnt, active β-catenin and c-myc in AGS cells. E: Expressions of key EMT-related proteins in HGC27 cells. F: Expressions of key EMT-related proteins in AGS cells. n=3, *P<0.05 vs shNC or vs Vector or vs OE-YEATS2.
| [1] | Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, et al. Gastric cancer[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10251): 635-48. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31288-5 |
| [2] | Thrift AP, Wenker TN, El-Serag HB. Global burden of gastric cancer: epidemiological trends, risk factors, screening and prevention[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2023, 20(5): 338-49. doi:10.1038/s41571-023-00747-0 |
| [3] | Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74(3): 229-63. doi:10.3322/caac.21834 |
| [4] | Cho H, Yamada M, Sekine S, et al. Gastric cancer is highly prevalent in Lynch syndrome patients with atrophic gastritis[J]. Gastric Cancer, 2021, 24(2): 283-91. doi:10.1007/s10120-020-01113-0 |
| [5] | Wei J, Lu XF, Liu Q, et al. Neoadjuvant sintilimab in combination with concurrent chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma: a single-arm phase 2 trial[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1): 4904. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-40480-x |
| [6] | Zhang CM, Tang RY, Zhu HL, et al. Comparison of treatment strategies and survival of early-onset gastric cancer: a population-based study[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 6288. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-10156-5 |
| [7] | Markouli M, Strepkos D, Basdra EK, et al. Prominent role of histone modifications in the regulation of tumor metastasis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(5): 2778. doi:10.3390/ijms22052778 |
| [8] | Nopour R. Prediction of five-year survival among esophageal cancer patients using machine learning[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(12): e22654. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22654 |
| [9] | Huang CM, Liu H, Hu YF, et al. Laparoscopic vs open distal gastrectomy for locally advanced gastric cancer: five-year outcomes from the CLASS-01 randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA Surg, 2022, 157(1): 9-17. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2021.7583 |
| [10] | Zhou Q, Wu XY, Wang XF, et al. The reciprocal interaction between tumor cells and activated fibroblasts mediated by TNF-α/IL-33/ST2L signaling promotes gastric cancer metastasis[J]. Oncogene, 2020, 39(7): 1414-28. doi:10.1038/s41388-019-1078-x |
| [11] | 左芦根, 王 炼, 杨 子, 等. 高表达CAMSAP2通过上调TGF-β信号促进胃癌细胞的侵袭和转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1460-8. doi:10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.09.02 |
| [12] | Xia X, Zhang ZZ, Zhu CC, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps promote metastasis in gastric cancer patients with postoperative abdominal infectious complications[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13: 1017. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-28492-5 |
| [13] | Wang ZH, Liu ZW, Lv MX, et al. Novel histone modifications and liver cancer: emerging frontiers in epigenetic regulation[J]. Clin Epigenetics, 2025, 17(1): 30. doi:10.1186/s13148-025-01838-8 |
| [14] | Li CX, Hou SN, Ma XY, et al. Epigenetic regulation of virulence and the transcription of ribosomal protein genes involves a YEATS family protein in Cryptococcus deneoformans [J]. FEMS Yeast Res, 2021, 21(1): foab001. doi:10.1093/femsyr/foab001 |
| [15] | Zhai YF, Zhang FY, Shi XY, et al. YEATS2 promotes malignant phenotypes of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via H3K27ac activated-IL6ST[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2025, 13: 1497290. doi:10.3389/fcell.2025.1497290 |
| [16] | Wu Q, Zheng Q, Yuan L, et al. Repression of YEATS2 induces cellular senescence in hepatocellular carcinoma and inhibits tumor growth[J]. Cell Cycle, 2024, 23(4): 478-94. doi:10.1080/15384101.2024.2342714 |
| [17] | Sheng H, Zheng F, Lan T, et al. YEATS2 regulates the activation of TAK1/NF-κB pathway and is critical for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell survival[J]. Cell Biol Toxicol, 2023, 39(3): 1-16. doi:10.1007/s10565-021-09671-4 |
| [18] | Alipour M, Moghanibashi M, Naeimi S, et al. LINC00894 YEATS2-AS1 and SUGP2 genes as novel biomarkers for N0 status of lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Sci Rep, 2025, 15(1): 10628. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-84640-5 |
| [19] | 李世超, 许文娟, 王玉兰. YEATS2在肝细胞癌中的表达及临床意义[J]. 中国癌症防治杂志, 2020, 12(3): 297-302. |
| [20] | Ren XL, Zhou Y, Xue ZY, et al. Histone benzoylation serves as an epigenetic mark for DPF and YEATS family proteins[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2021, 49(1): 114-26. doi:10.1093/nar/gkaa1130 |
| [21] | Yeewa R, Chaiya P, Jantrapirom S, et al. Multifaceted roles of YEATS domain-containing proteins and novel links to neurological diseases[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2022, 79(3): 183. doi:10.1007/s00018-022-04218-0 |
| [22] | Liu X, Hu Y, Li CR, et al. Overexpression of YEATS2 remodels the extracellular matrix to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression via the PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2023, 15(6): 1850. doi:10.3390/cancers15061850 |
| [23] | Roy J, Kumar A, Chakravarty S, et al. Dynamic interaction of MYC enhancer RNA with YEATS2 protein regulates MYC gene transcription in pancreatic cancer[J]. EMBO Rep, 2025, 26(10): 2519-44. doi:10.1038/s44319-025-00446-0 |
| [24] | Zeng ZR, Lei S, He ZW, et al. YEATS2 is a target of HIF1α and promotes pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and migration[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2021, 236(3): 2087-98. doi:10.1002/jcp.29995 |
| [25] | Du N, Yi LL, Wang JM, et al. High expression of YEATS2 as a predictive factor of poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 17246. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-68348-0 |
| [26] | Lan T, Chen HF, Zheng F, et al. Cinobufacini retards progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through targeting YEATS2/TAK1/NF-κB axis[J]. Phytomedicine, 2023, 109: 154564. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154564 |
| [27] | Manfioletti G, Fedele M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(14): 11386. doi:10.3390/ijms241411386 |
| [28] | Akrida I, Mulita F, Plachouri KM, et al. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in metaplastic breast cancer and Phyllodes breast tumors[J]. Med Oncol, 2023, 41(1): 20. doi:10.1007/s12032-023-02259-4 |
| [29] | 张文静, 张 诺, 杨 子, 等. BZW1高表达促进胃癌细胞的侵袭和转移: 基于调控Wnt//β-catenin通路和促进上皮间质转化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 354-62. |
| [30] | Zhang J, Hu ZM, Horta CA, et al. Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition by tumor microenvironmental signals and its implication in cancer therapeutics[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2023, 88: 46-66. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.12.002 |
| [1] | Ying WANG, Jing LI, Yidi WANG, Mingyu HUA, Weibin HU, Xiaozhi ZHANG. Construction and verification of a prognostic model combining anoikis and immune prognostic signatures for primary liver cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1967-1979. |
| [2] | Yu ZHANG, Haitao LI, Yuqing PAN, Jiexian CAO, Li ZHAI, Xi ZHANG. Pan-cancer analysis of MZB1 expression and its association with immune infiltration and clinical prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 2006-2018. |
| [3] | Siyuan MA, Bochao ZHANG, Chun PU. Circ_0000437 promotes proliferation, invasion, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells by targeting the let-7b-5p/CTPS1 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1682-1696. |
| [4] | Ziliang WANG, Xiaohua CHEN, Jingjing YANG, Chen YAN, Zhizhi ZHANG, Bingyi HUANG, Meng ZHAO, Song LIU, Sitang GE, Lugen ZUO, Deli CHEN. High expression of SURF4 promotes migration, invasion and proliferation of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting tight junction proteins [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1732-1742. |
| [5] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [6] | Jinlong PANG, Xinli ZHAO, Zhen ZHANG, Haojie WANG, Xingqi ZHOU, Yumei YANG, Shanshan LI, Xiaoqiang CHANG, Feng LI, Xian LI. Overexpression of multimerin-2 promotes cutaneous melanoma cell invasion and migration and is associated with poor prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1479-1489. |
| [7] | Xuan WU, Jiamin FANG, Weiwei HAN, Lin CHEN, Jing SUN, Qili JIN. High PRELID1 expression promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1535-1542. |
| [8] | Kang WANG, Haibin LI, Jing YU, Yuan MENG, Hongli ZHANG. High expression of ELFN1 is a prognostic biomarker and promotes proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1543-1553. |
| [9] | Yanxiu MO, Yang SHU, Yulan MO, Juntong LIU, Ouou XU, Huafei DENG, Qiben WANG. CRISPR-Cas9-mediated CDC20 gene knockout inhibits cervical cancer cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1200-1211. |
| [10] | Xinrui HOU, Zhendong ZHANG, Mingyuan CAO, Yuxin DU, Xiaoping WANG. Salidroside inhibits proliferation of gastric cancer cells by regulating the miR-1343-3p-OGDHL/PDHB glucose metabolic axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1226-1239. |
| [11] | Zhennan MA, Fuquan LIU, Xuefeng ZHAO, Xiaowei ZHANG. High expression of DTX2 promotes proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of oxaliplatin-resistant colorectal cancer cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 829-836. |
| [12] | Yi ZHANG, Yu SHEN, Zhiqiang WAN, Song TAO, Yakui LIU, Shuanhu WANG. High expression of CDKN3 promotes migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating the p53/NF-κB signaling pathway and inhibiting cell apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [13] | Lu TAO, Zhuoli WEI, Yueyue WANG, Ping XIANG. CEACAM6 inhibits proliferation and migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 566-576. |
| [14] | Qingqing HUANG, Wenjing ZHANG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Lian WANG, Xue SONG, Zhijun GENG, Lugen ZUO, Yueyue WANG, Jing LI, Jianguo HU. High MYO1B expression promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor patient prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 622-631. |
| [15] | Huali LI, Ting SONG, Jiawen LIU, Yongbao LI, Zhaojing JIANG, Wen DOU, Linghong ZHOU. Prognosis-guided optimization of intensity-modulated radiation therapy plans for lung cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 643-649. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||