南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (7): 1479-1489.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.07.14
庞金龙1,2( ), 赵新丽1,2(
), 赵新丽1,2( ), 张振1,2, 王豪杰1,2, 周星琦1,2, 杨玉梅1,2, 李姗姗1,2, 常小强1,2, 李锋1,2(
), 张振1,2, 王豪杰1,2, 周星琦1,2, 杨玉梅1,2, 李姗姗1,2, 常小强1,2, 李锋1,2( ), 李娴1,2(
), 李娴1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-06
出版日期:2025-07-20
发布日期:2025-07-17
通讯作者:
李锋,李娴
E-mail:834752819@qq.com;1850466372@qq.com;1583635955@qq.com;Lixian0813@126.com
作者简介:庞金龙,硕士,E-mail: 834752819@qq.com基金资助:
Jinlong PANG1,2( ), Xinli ZHAO1,2(
), Xinli ZHAO1,2( ), Zhen ZHANG1,2, Haojie WANG1,2, Xingqi ZHOU1,2, Yumei YANG1,2, Shanshan LI1,2, Xiaoqiang CHANG1,2, Feng LI1,2(
), Zhen ZHANG1,2, Haojie WANG1,2, Xingqi ZHOU1,2, Yumei YANG1,2, Shanshan LI1,2, Xiaoqiang CHANG1,2, Feng LI1,2( ), Xian LI1,2(
), Xian LI1,2( )
)
Received:2025-03-06
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-07-17
Contact:
Feng LI, Xian LI
E-mail:834752819@qq.com;1850466372@qq.com;1583635955@qq.com;Lixian0813@126.com
摘要:
目的 采用生物信息学探讨多聚蛋白-2(MMRN2)抑制皮肤黑色素瘤(SKCM)生长和转移的影响。 方法 从GEO数据库获得SKCM患者的临床信息,比较正常组织和黑色素瘤中MMRN2的表达差异;通过STRING数据库获得和MMRN2互相作用蛋白,构建蛋白网络,利用GEPIA2.0数据库下载SKCM中MMRN2相关性基因,对交集基因进行GO/KEGG功能富集分析;利用“timeROC”包处理数据,使用“stats”包和“car”包,分析MMRN2和SKCM的临床相关性;使用survival包进行比例风险假设检验并进行Cox回归分析筛选独立预后因素并构建临床列线图;利用GSCA数据库和ssGSEA算法分析MMRN2与免疫细胞浸润的相关性;利用Spearman分析研究MMRN2和血管生成相关基因的相关性;集落克隆、transwell、划痕实验检测SKCM细胞的增殖和转移能力;采用HE染色观察病理学变化;Kaplan-Meier曲线观察生存时间;ELISA实验检测黑色素瘤细胞上清中GM-CSF、CXCL9、TGF-β1的表达水平。 结果 MMRN2在SKCM转移瘤中的水平升高(P<0.001);在STRING数据库中获得30个互作分子构建蛋白互作网络,和GEPIA2.0数据库中获得的基因取交集得到15个共同基因,进行GO/KEGG分析主要是是endothelium development、cell-cell junction等。在SKCM患者中MMRN2高表达的患者预后更差,MMRN2的水平在pathologic T satge、breslow depth、melanoma ulceration中差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05),免疫浸润结果显示,MMRN2和24中免疫细胞丰度呈正相关(P<0.001),并与肿瘤成纤维细胞和内皮细胞具有较强的正相关性(P<0.001),MMRN2的表达水平和大多数血管生产基因的表达水平呈正相关,和KCNJ8、SLCO2A1、NRP1、COL3A1的表达相关性较强(P<0.001);敲低MMRN2后,SKCM细胞B16F10的增殖(P<0.01)、侵袭和迁移能力减弱(P<0.01),重塑免疫微环境(P<0.001),进而抑制黑色素瘤的转移。 结论 多聚蛋白-2可能成为治疗SKCM的新靶点,为SKCM的诊断和治疗提供新的策略与思路。
庞金龙, 赵新丽, 张振, 王豪杰, 周星琦, 杨玉梅, 李姗姗, 常小强, 李锋, 李娴. 皮肤黑色素瘤中MMRN2高表达促进肿瘤细胞的侵袭和迁移并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1479-1489.
Jinlong PANG, Xinli ZHAO, Zhen ZHANG, Haojie WANG, Xingqi ZHOU, Yumei YANG, Shanshan LI, Xiaoqiang CHANG, Feng LI, Xian LI. Overexpression of multimerin-2 promotes cutaneous melanoma cell invasion and migration and is associated with poor prognosis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1479-1489.
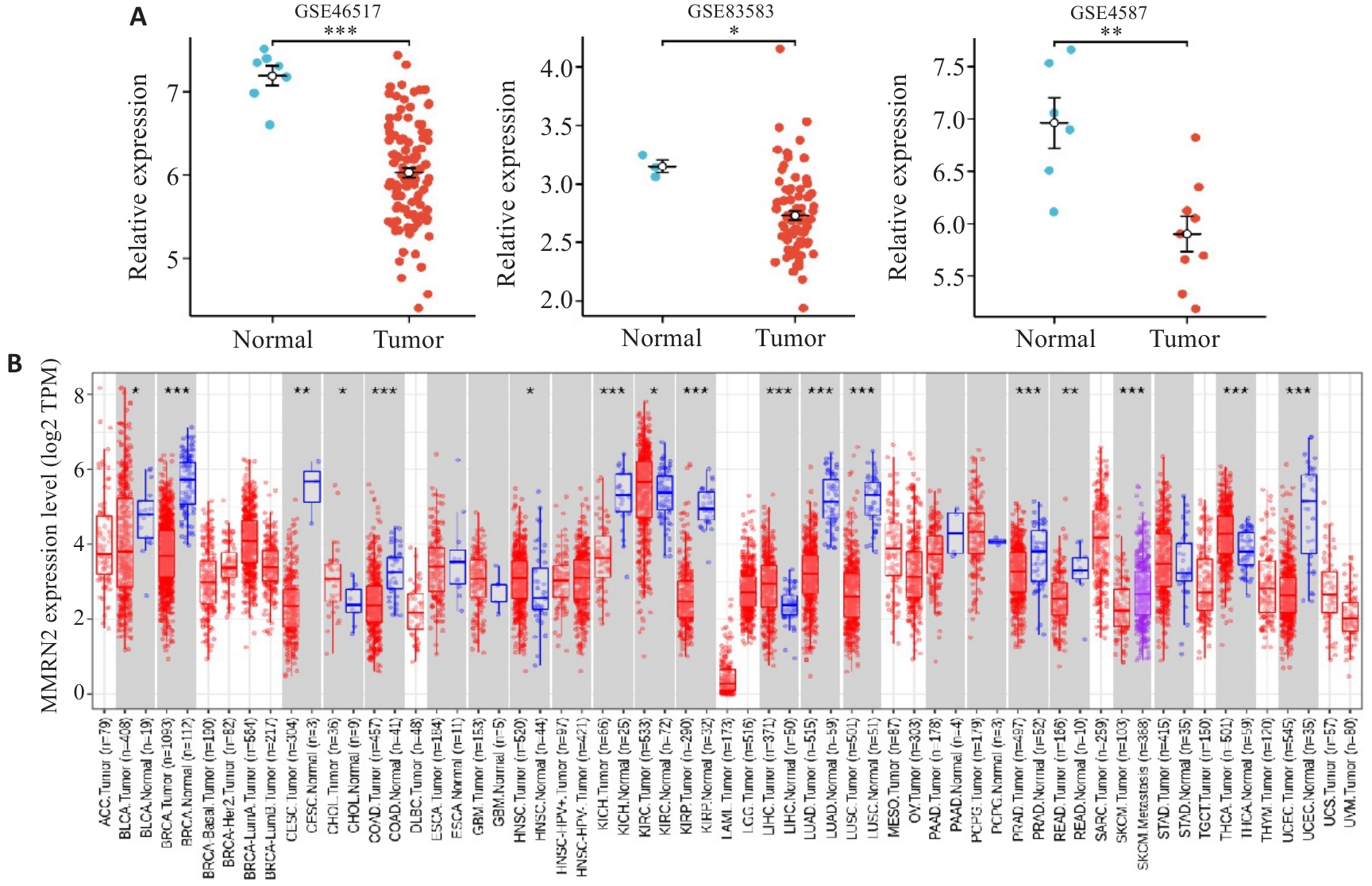
图1 正常组织和SKCM中MMRN2的表达情况
Fig.1 MMRN2 expression in normal and cutaneous melanoma tissues. A: Differential gene expression analysis between tumor and normal tissues using data from GSE46517, GSE83583, and GSE4587 datasets. B: MMRN2 expression levels are significantly higher in metastatic cutaneous melanoma than in normal tissues. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs normal tissue; ***P<0.001 vs cutaneous melanoma.
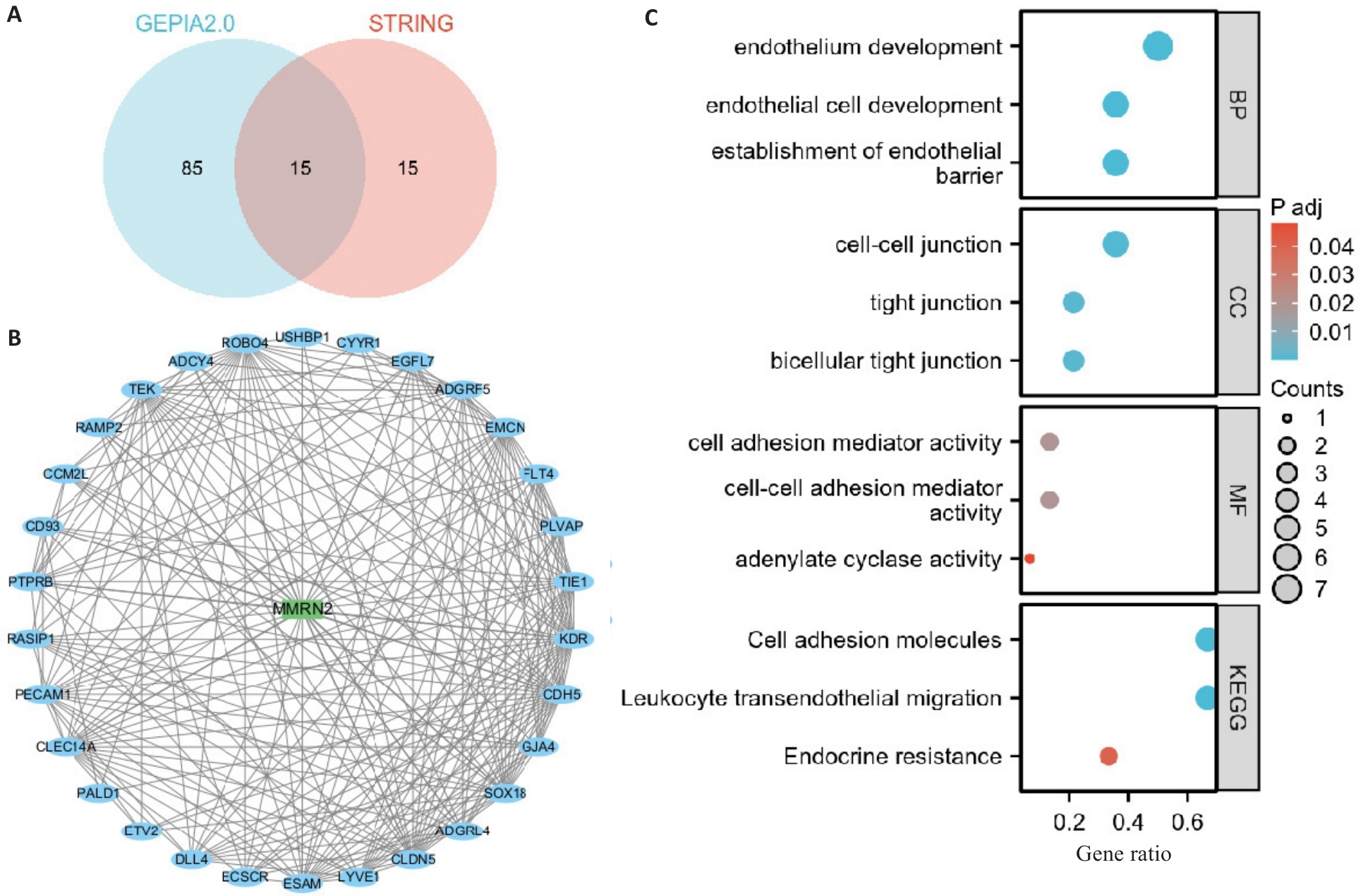
图2 SKCM相关性基因和蛋白互作网络
Fig.2 Cutaneous melanoma-related genes and the protein-protein interaction network. A: Intersection analysis of genes associated with cutaneous melanoma using the GEPIA2.0 database. B: Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network constructed by retrieving 30 interacting molecules from the STRING database, resulting in 15 hub genes shared across analyses. C: Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses of the hub genes.
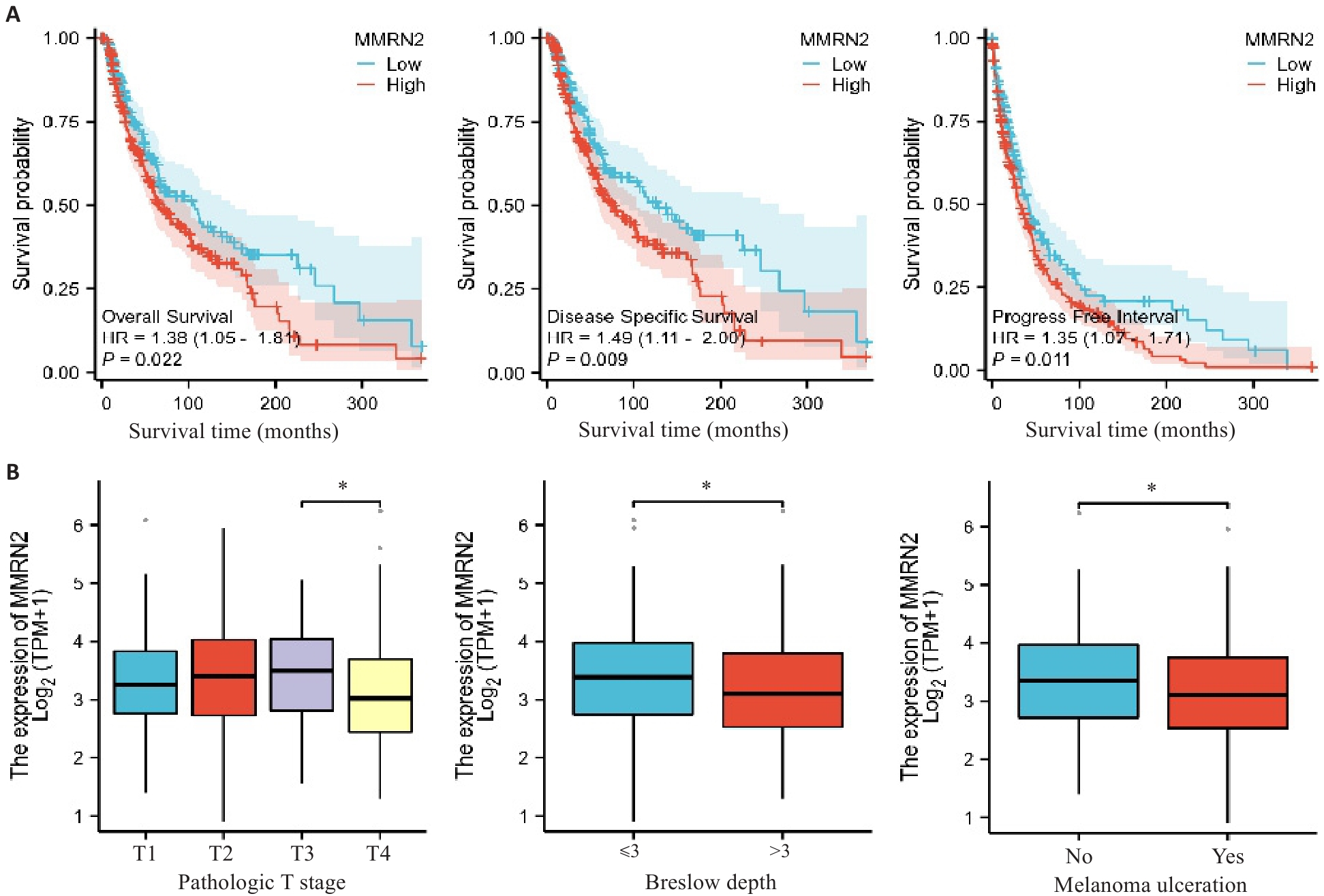
图3 MMRN2和SKCM的临床特征相关性
Fig.3 Association of MMRN2 expression levels with clinicopathological features of patients with cutaneous melanoma. A: Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of patients with cutaneous melanoma stratified by MMRN2 expression level. B: Correlations of MMRN2 expression level with pathological T stage, Breslow depth and melanoma ulceration in patients with cutaneous melanoma. *P<0.05.
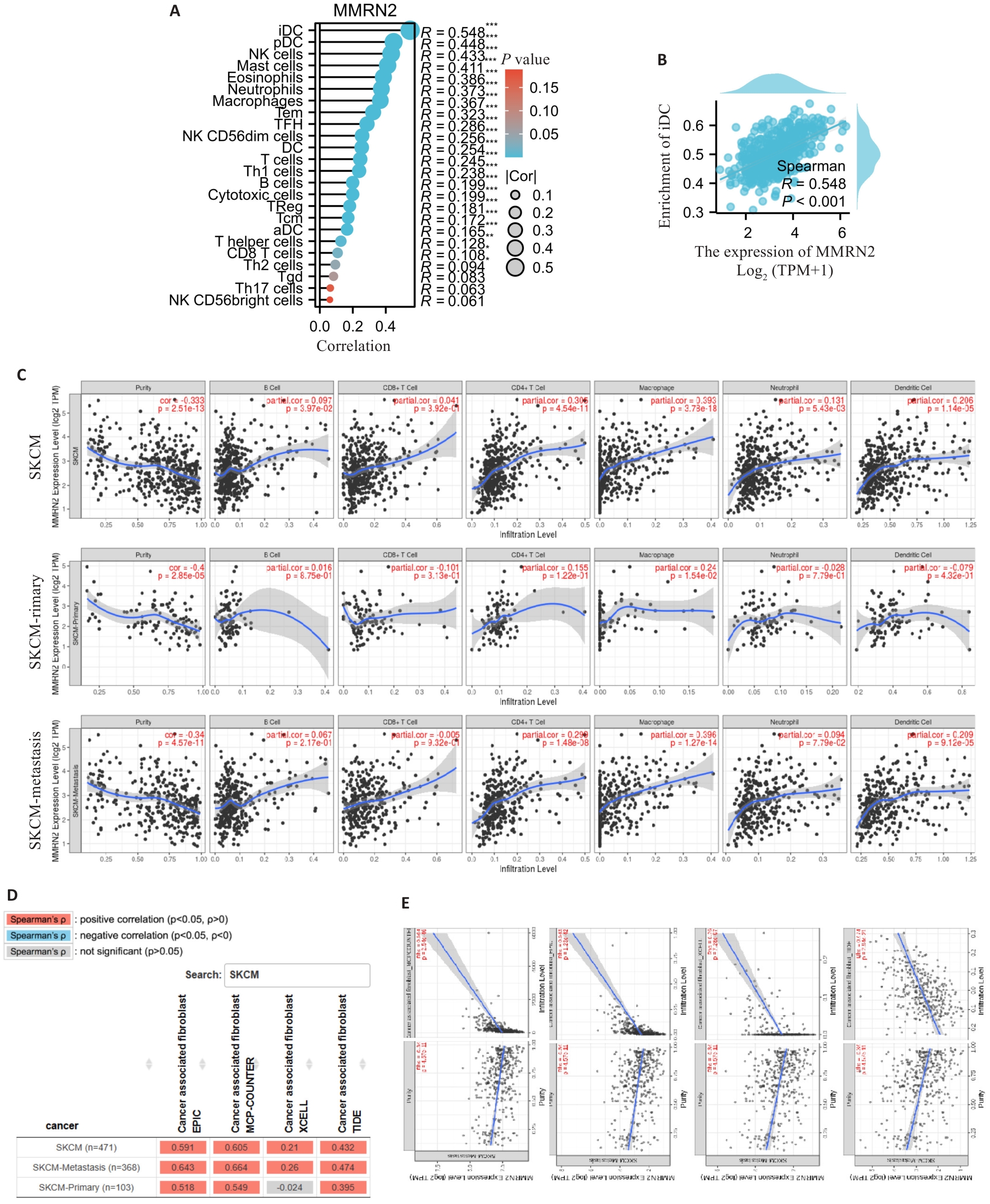
图5 MMRN2在皮肤黑色素瘤中的免疫细胞浸润分析结果
Fig.5 Immune infiltration analysis of MMRN2 in cutaneous melanoma. A: Correlation lollipop chart between MMRN2 and immune infiltration matrix data in TCGA database. The results are visualized using the ggplot2 package. The 24 types of immune cells included aDC (activated DC), B cells, CD8 T cells, cytotoxic cells, DC, eosinophils, iDC (immature DC), macrophages, mast cells, neutrophils, NK CD56bright cells, NK CD56dim cells, NK cells, pDC (plasmacytoid DC), T cells, T helper cells, Tcm (T central memory), Tem (T effector memory), TFH (T follicular helper), Tgd (T gamma delta), Th1 cells, Th17 cells, Th2 cells, and TReg. B: Scatter plot of the correlation between MMRN2 expression level and iDC abundance. C: Scatter plot of correlations between MMRN2 and immune cells in cutaneous melanoma. D, E: Scatter plots of correlations between MMRN2 and tumor fibroblasts in cutaneous melanoma. F: Scatter plot of correlations between MMRN2 and endothelial cells in cutaneous melanoma. Data source: TIMER database, http://timer.comp-genomics.org/timer/
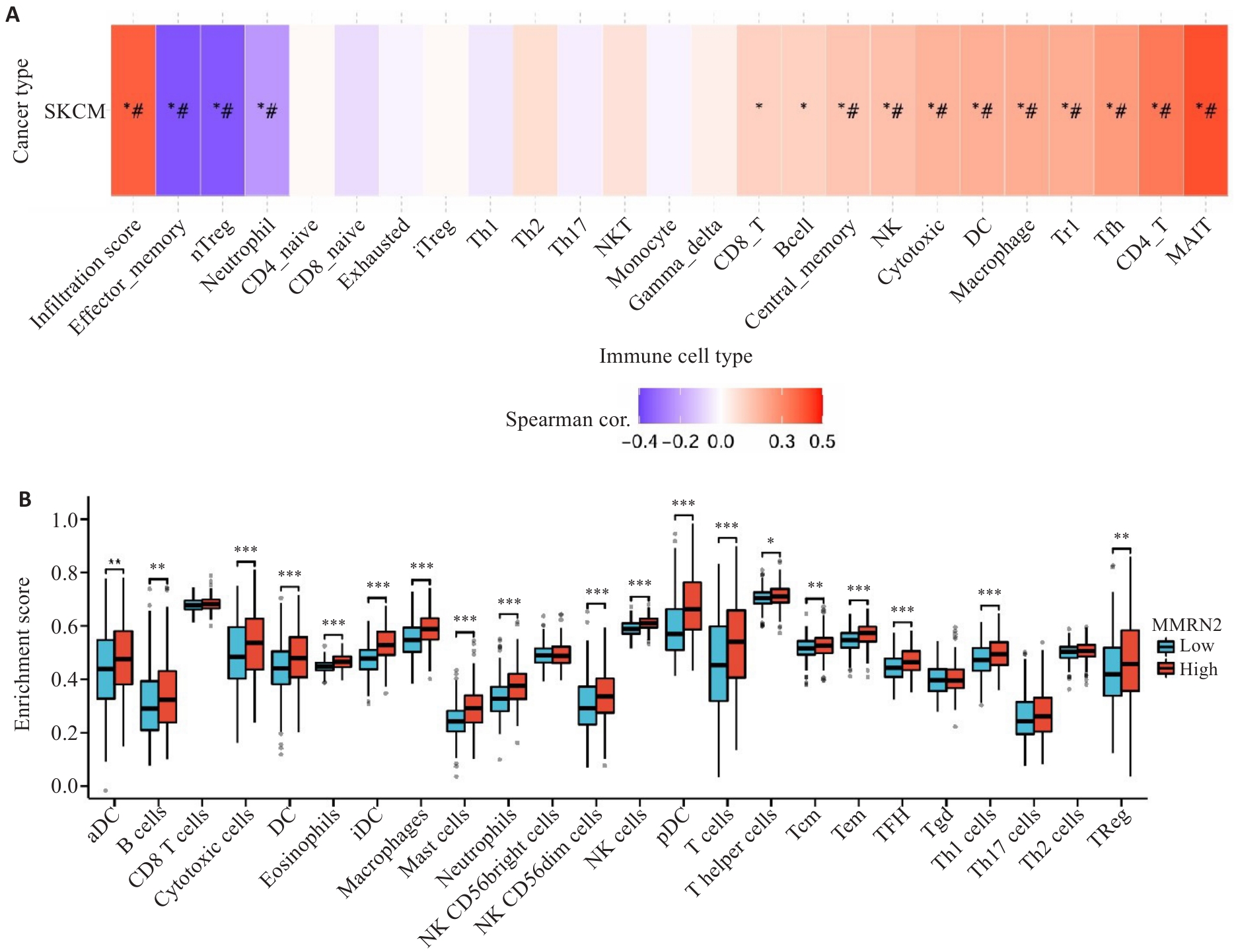
图6 MMRN2的免疫浸润分析
Fig.6 Immune infiltration analysis of MMRN2 in cutaneous melanoma. A: GSVA-based immune cell enrichment scores of MMRN2 in cutaneous melanoma. B: Immune infiltration profiles between high and low MMRN2 expression groups. #: FDR<0.05, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs low MMRN2 expression group.
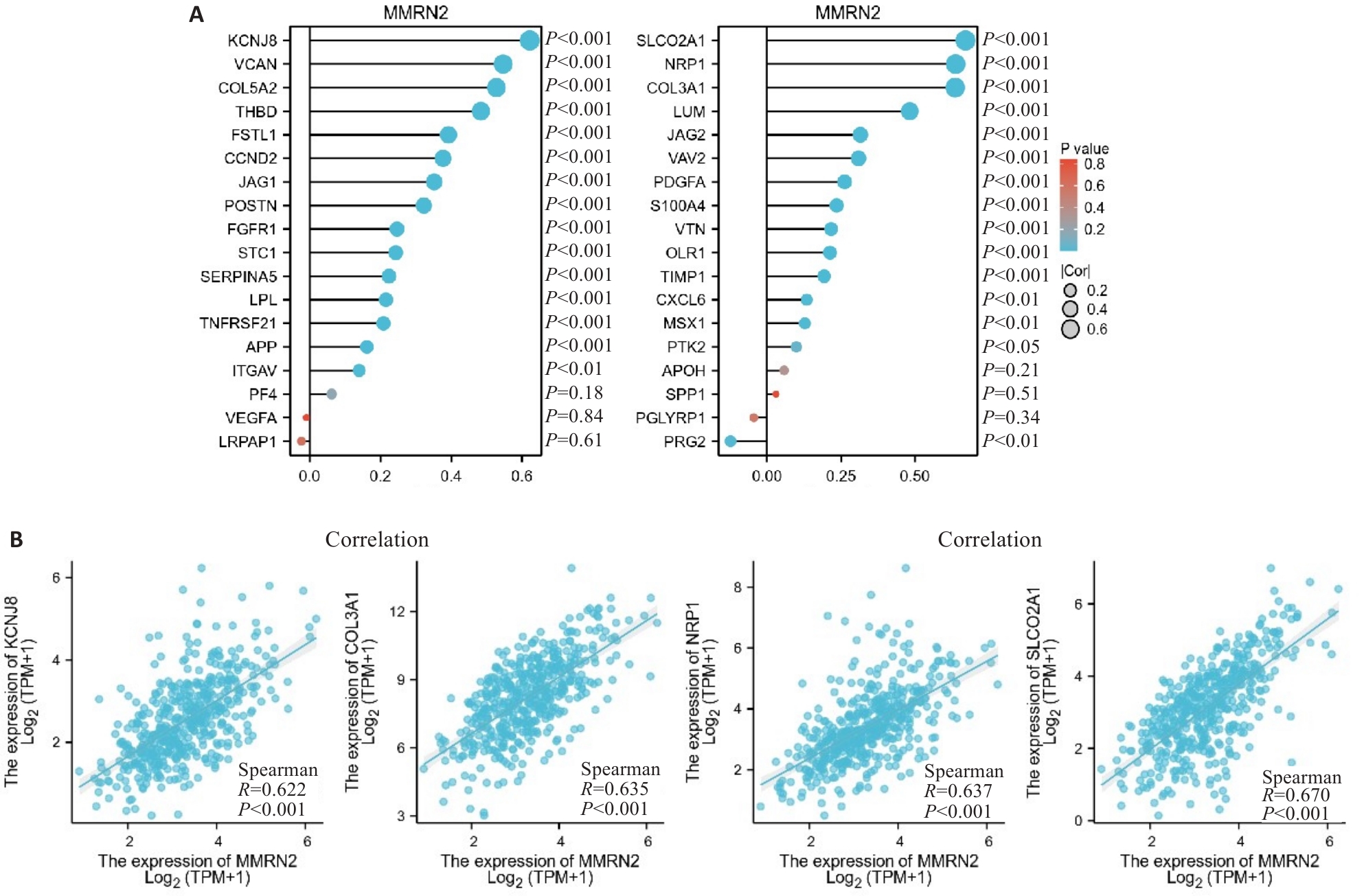
图7 MMRN2和血管生成基因相关性分析
Fig.7 Correlation analysis of MMRN2 and angiogenesis-related genes. A: MMRN2 expression is positively correlated with the majority of angiogenesis-associated genes. B: MMRN2 expression level is strongly correlated with KCNJ8, SLCO2A1, NRP1 and COL3A1.
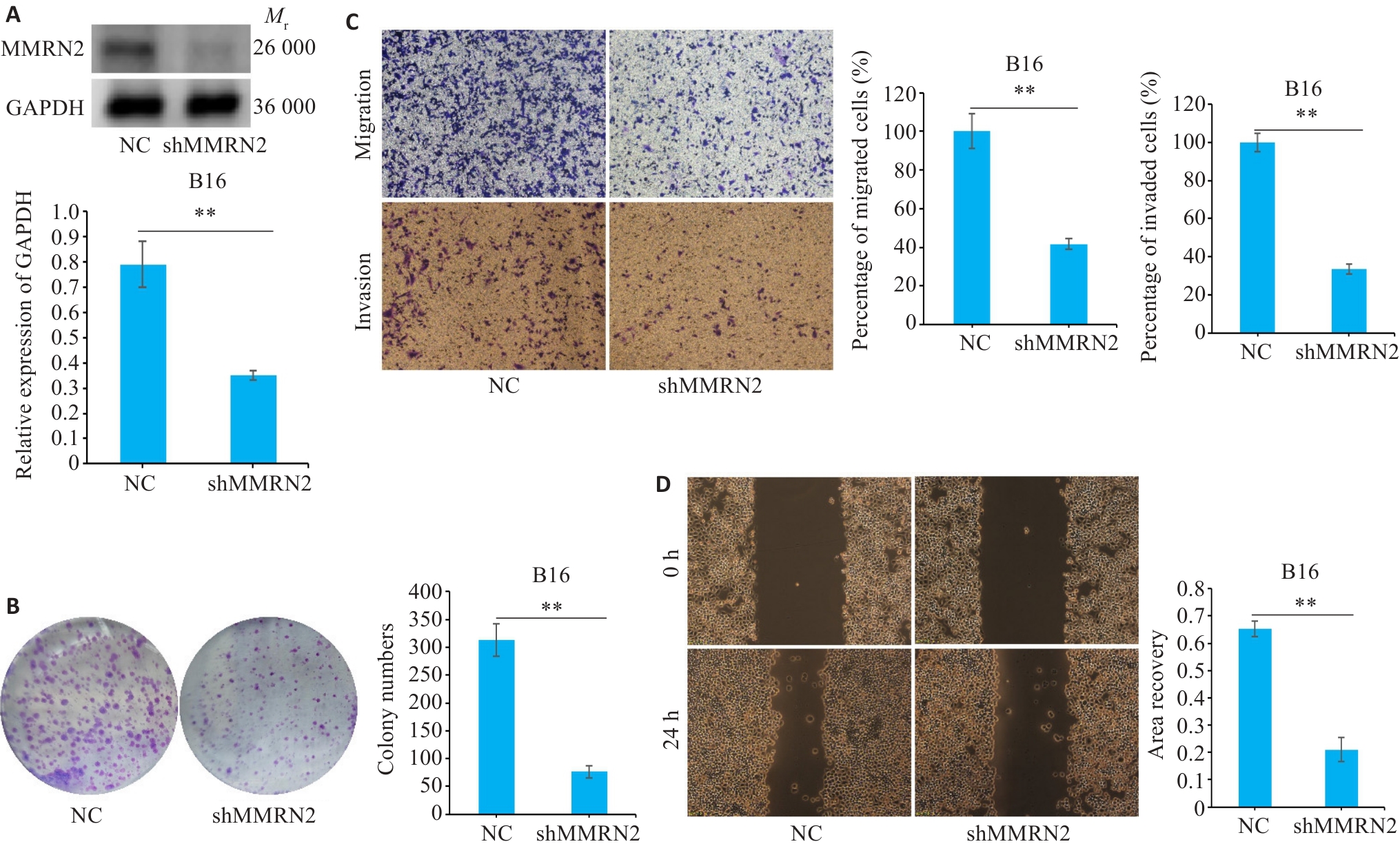
图8 敲低MMRN2抑制SKCM细胞的增殖、侵袭和迁移
Fig.8 Knockdown of MMRN2 suppresses proliferation, invasion, and migration of cutaneous melanoma cells. A: Western blotting of MMRN2 proteins. B: Colony formation assay for assessing cell proliferation. C: Transwell assay for assessing cell migration and invasion (Original magnification: ×10). D: Knockdown of MMRN2 impairs wound healing in B16 melanoma cells (×200). **P<0.01.
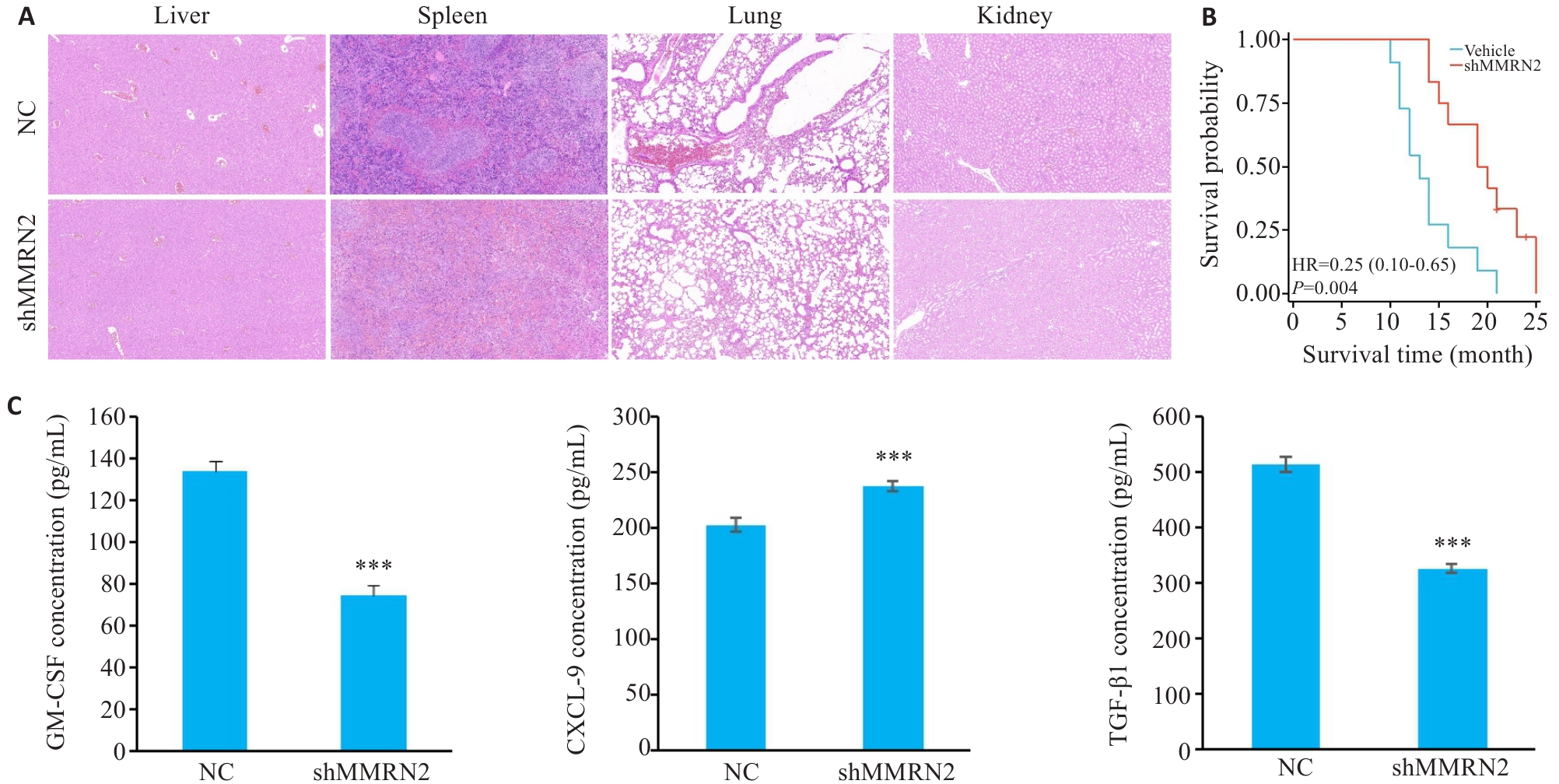
图9 敲低MMRN2能够改善小鼠病理特征并延长小鼠生存时间
Fig.9 Knockdown of MMRN2 attenuates pathological manifestations and extends survival of mice bearing cutaneous melanoma xenograft. A: HE staining of the liver, spleen, lung, and kidney of mice in MMRN2 knockdown group (×10). B: Kaplan-Meier curve. C: GM-CSF, CXCL9, and TGF-β1 expression levels measured by ELISA. ***P<0.001 vs NC group.
| [1] | Gosman LM, \u 021 aăpoi DA, Costache M. Cutaneous melanoma: a review of multifactorial pathogenesis, immunohistochemistry, and emerging biomarkers for early detection and management[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(21): 15881. doi:10.3390/ijms242115881 |
| [2] | Leonardi GC, Falzone L, Salemi R, et al. Cutaneous melanoma: from pathogenesis to therapy (review)[J]. Int J Oncol, 2018, 52(4): 1071-80. |
| [3] | Davis LE, Shalin SC, Tackett AJ. Current state of melanoma diagnosis and treatment[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2019, 20(11): 1366-79. doi:10.1080/15384047.2019.1640032 |
| [4] | Andreuzzi E, Colladel R, Pellicani R, et al. The angiostatic molecule Multimerin 2 is processed by MMP-9 to allow sprouting angiogenesis[J]. Matrix Biol, 2017, 64: 40-53. doi:10.1016/j.matbio.2017.04.002 |
| [5] | Khan KA, Naylor AJ, Khan A, et al. Multimerin-2 is a ligand for group 14 family C-type lectins CLEC14A, CD93 and CD248 spanning the endothelial pericyte interface[J]. Oncogene, 2017, 36(44): 6097-108. doi:10.1038/onc.2017.214 |
| [6] | Lorenzon E, Colladel R, Andreuzzi E, et al. MULTIMERIN2 impairs tumor angiogenesis and growth by interfering with VEGF-A/VEGFR2 pathway[J]. Oncogene, 2012, 31(26): 3136-47. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.487 |
| [7] | Galvagni F, Nardi F, Spiga O, et al. Dissecting the CD93-Multimerin 2 interaction involved in cell adhesion and migration of the activated endothelium[J]. Matrix Biol, 2017, 64: 112-27. doi:10.1016/j.matbio.2017.08.003 |
| [8] | Chen CJ, Kajita H, Aramaki-Hattori N, et al. Screening of autophagy-related prognostic genes in metastatic skin melanoma[J]. Dis Markers, 2022, 2022: 8556593. doi:10.1155/2022/8556593 |
| [9] | Liu JF, Lichtenberg T, Hoadley KA, et al. An integrated TCGA pan-cancer clinical data resource to drive high-quality survival outcome analytics[J]. Cell, 2018, 173(2): 400-16.e11. |
| [10] | Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Tosolini M, et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of intratumoral immune cells reveal the immune landscape in human cancer[J]. Immunity, 2013, 39(4): 782-95. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2013.10.003 |
| [11] | Qing X, Xu WJ, Liu SL, et al. Molecular characteristics, clinical significance, and cancer immune interactions of angiogenesis-associated genes in gastric cancer[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 843077. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.843077 |
| [12] | Yin QL, Shi XM, Lan SJ, et al. Effect of melanoma stem cells on melanoma metastasis[J]. Oncol Lett, 2021, 22(1): 566. doi:10.3892/ol.2021.12827 |
| [13] | Holderfield M, Deuker MM, McCormick F, et al. Targeting RAF kinases for cancer therapy: BRAF-mutated melanoma and beyond[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2014, 14(7): 455-67. doi:10.1038/nrc3760 |
| [14] | Cicaloni V, Karmakar M, Frusciante L, et al. Bioinformatics approaches to predict mutation effects in the binding site of the proangiogenic molecule CD93[J]. Front Bioinform, 2022, 2: 891553. doi:10.3389/fbinf.2022.891553 |
| [15] | Pellicani R, Poletto E, Andreuzzi E, et al. Multimerin-2 maintains vascular stability and permeability[J]. Matrix Biol, 2020, 87: 11-25. doi:10.1016/j.matbio.2019.08.002 |
| [16] | Wang DY, Xing CY, Liang Y, et al. Ultrasound imaging of tumor vascular CD93 with MMRN2 modified microbubbles for immune microenvironment prediction[J]. Adv Mater, 2024, 36(18): e2310421. doi:10.1002/adma.202470134 |
| [17] | Liu H, Zhang JH, Zhao YJ, et al. CD93 regulates breast cancer growth and vasculogenic mimicry through the PI3K/AKT/SP2 signaling pathway activated by integrin β1[J]. J Biochem Mol Toxicol, 2024, 38(4): e23688. doi:10.1002/jbt.23688 |
| [18] | Li Y, Fu L, Wu BK, et al. Angiogenesis modulated by CD93 and its natural ligands IGFBP7 and MMRN2: a new target to facilitate solid tumor therapy by vasculature normalization[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2023, 23(1): 189. doi:10.1186/s12935-023-03044-z |
| [19] | Cao Z, Zhang ZJ, Tang XY, et al. Comprehensive analysis of tissue proteomics in patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma uncovers the underlying mechanism of lymph node metastasis and its significant sex disparities[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 887977. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.887977 |
| [20] | Zheng WZ, Zhang SQ, Guo H, et al. Multi-omics analysis of tumor angiogenesis characteristics and potential epigenetic regulation mechanisms in renal clear cell carcinoma[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2021, 19(1): 39. doi:10.1186/s12964-021-00728-9 |
| [21] | Zhao YH, Zhang X, Yao JC, et al. Expression patterns and the prognostic value of the EMILIN/Multimerin family members in low-grade glioma[J]. PeerJ, 2020, 8: e8696. doi:10.7717/peerj.8696 |
| [22] | Zheng Y, Fang MJ, Sanan S, et al. Investigating angiogenesis-related biomarkers in osteoarthritis patients through transcriptomic profiling[J]. J Inflamm Res, 2024, 17: 10681-97. doi:10.2147/jir.s493889 |
| [23] | Simiczyjew A, Dratkiewicz E, Mazurkiewicz J, et al. The influence of tumor microenvironment on immune escape of melanoma[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(21): 8359. doi:10.3390/ijms21218359 |
| [24] | Tordesillas L, Berin MC. Mechanisms of oral tolerance[J]. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol, 2018, 55(2): 107-17. doi:10.1007/s12016-018-8680-5 |
| [25] | Marzagalli M, Ebelt ND, Manuel ER. Unraveling the crosstalk between melanoma and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2019, 59: 236-50. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.08.002 |
| [26] | Ellis LM, Hicklin DJ. VEGF-targeted therapy: mechanisms of anti-tumour activity[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2008, 8(8): 579-91. doi:10.1038/nrc2403 |
| [27] | Thomas DA, Massagué J. TGF-beta directly targets cytotoxic T cell functions during tumor evasion of immune surveillance[J]. Cancer Cell, 2005, 8(5): 369-80. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2005.10.012 |
| [28] | Seeger P, Musso T, Sozzani S. The TGF-β superfamily in dendritic cell biology[J]. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2015, 26(6): 647-57. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2015.06.002 |
| [29] | Wang X, Cui ZD, Chen X, et al. The CXCR4/miR-1910-5p/MMRN2 axis is involved in corneal neovascularization by affecting vascular permeability[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2023, 64(4): 10. doi:10.1167/iovs.64.4.10 |
| [30] | Janka EA, Ványai B, Dajnoki Z, et al. Regional variability of melanoma incidence and prevalence in Hungary. Epidemiological impact of ambient UV radiation and socioeconomic factors[J]. Eur J Cancer Prev, 2022, 31(4): 377-84. doi:10.1097/cej.0000000000000716 |
| [1] | 陈鑫源, 吴成挺, 李瑞迪, 潘雪芹, 张耀丹, 陶俊宇, 林才志. 双术汤通过P53/SLC7A11/GPX4通路诱导胃癌细胞铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | 吴璇, 方家敏, 韩玮玮, 陈琳, 孙菁, 金齐力. 高表达PRELID1促进胃癌细胞上皮间质转化并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1535-1542. |
| [3] | 王康, 李海宾, 余靖, 孟源, 张虹丽. ELFN1高表达是结肠癌的预后生物标志物并促进结肠癌细胞的增殖转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1543-1553. |
| [4] | 计寰宇, 王蕊, 高盛祥, 车文刚. SG-UNet:基于全局注意力和自校准卷积增强的黑色素瘤分割模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1317-1326. |
| [5] | 郭晓娟, 杜瑞娟, 陈丽平, 郭克磊, 周彪, 卞华, 韩立. WW结构域E3泛素连接酶1调控卵巢癌肿瘤微环境中的免疫浸润[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 1063-1073. |
| [6] | 张毅, 沈昱, 万志强, 陶嵩, 柳亚魁, 王栓虎. CDKN3高表达促进胃癌细胞的迁移和侵袭:基于调控p53/NF-κB信号通路和抑制胃癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [7] | 高志, 吴傲, 胡仲翔, 孙培养. 类风湿性关节炎中氧化应激与免疫浸润的生物信息学分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 862-870. |
| [8] | 黄晴晴, 张文静, 张小凤, 王炼, 宋雪, 耿志军, 左芦根, 王月月, 李静, 胡建国. 高表达MYO1B促进胃癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭并与患者的不良预后有关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 622-631. |
| [9] | 李华莉, 宋婷, 刘嘉雯, 李永宝, 姜兆静, 窦文, 周凌宏. 预后导向的肺癌调强放疗计划优化新方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 643-649. |
| [10] | 宋雪, 陈悦, 张敏, 张诺, 左芦根, 李静, 耿志军, 张小凤, 王月月, 王炼, 胡建国. GPSM2在胃癌组织中高表达并通过促进肿瘤细胞的增殖影响患者预后[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 229-238. |
| [11] | 唐天威, 李路安, 陈源汉, 张丽, 徐丽霞, 李志莲, 冯仲林, 张辉林, 华瑞芳, 叶智明, 梁馨苓, 李锐钊. 高血清胱抑素C水平是IgA肾病不良预后的独立危险因素[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 379-386. |
| [12] | 许怀文, 翁丽, 薛鸿. CXCL12可作为2型糖尿病合并慢性阻塞性肺疾病的潜在治疗靶点[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 100-109. |
| [13] | 陈晓睿, 魏青政, 张宗亮, 原江水, 宋卫青. 过表达带电多泡体蛋白2B基因抑制肾透明细胞癌细胞的增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 126-136. |
| [14] | 王耀彬, 陈柳燕, 罗伊凌, 申继清, 周素芳. NUF2对泛癌的预后和免疫治疗效果的预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 137-149. |
| [15] | 周超, 张晶晶, 唐巧, 付双楠, 张宁, 何召云, 张瑾, 张田义, 刘鹏程, 宫嫚. 血清色氨酸用于乙肝相关慢加急性肝衰竭90 d死亡风险分层管理的潜在价值:一项多中心回顾性研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 59-64. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||