南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (7): 1471-1478.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.07.13
张梦影( ), 赵晨玲, 田丽伟, 余郭芳, 杨文明, 董婷(
), 赵晨玲, 田丽伟, 余郭芳, 杨文明, 董婷( )
)
收稿日期:2025-01-24
出版日期:2025-07-20
发布日期:2025-07-17
通讯作者:
董婷
E-mail:1649392726@qq.com;876786557@qq.com
作者简介:张梦影,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 1649392726@qq.com
基金资助:
Mengying ZHANG( ), Chenling ZHAO, Liwei TIAN, Guofang YU, Wenming YANG, Ting DONG(
), Chenling ZHAO, Liwei TIAN, Guofang YU, Wenming YANG, Ting DONG( )
)
Received:2025-01-24
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-07-17
Contact:
Ting DONG
E-mail:1649392726@qq.com;876786557@qq.com
摘要:
目的 基于GPX4/ACSL4/ALOX15信号通路探讨肝豆扶木汤(GDFMD)对tx-J小鼠抑制铁死亡改善肝脏脂肪变性作用的机制。 方法 以6只同系野生型WT小鼠作为对照组,30只tx-J小鼠随机分为模型组、GDFMD低、中、高剂量组、Fer-1组。对照组及模型组予以等量生理盐水,GDFMD低中高剂量分别予以3.48 g/kg、6.96 g/kg、13.92 g/kg灌胃,Fer-1组1 mg/(kg·d),腹腔注射,1次/d,持续14 d;油红、HE染色观察肝脏组织脂质沉积与病理情况;采用谷丙转氨酶(ALT)、谷草转氨酶(AST)、白蛋白(ALB)、碱性磷酸酶(AKP)试剂盒观察肝功能指标;WB及PCR测量小鼠内GPX4、ACSL4、ALOX15、FTH1、FLT、TFR1、FAS、SCD1、ACOX1蛋白及mRNA的表达;测定肝脏组织内Fe2+、Cu2+的含量;丙二醛(MDA)、活性氧(ROS)、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、还原型谷胱甘肽(GSH)、4-羟基壬烯醛(4-HNE)试剂盒测定氧化应激指标。 结果 与对照组相比,模型组小鼠的肝脏组织出现明显的脂肪变性;血清ALT、AST、AKP水平显著升高(P<0.01),ALB水平下降(P<0.05);Fe2+、Cu2+、MDA、4-HNE、ROS的水平增高(P<0.05),SOD和GSH的水平降低(P<0.05);ACOX1、GPX4、FTH1、FLT、FAS、SCD1蛋白含量下降,TFR1、ACSL4、ALOX15蛋白含量上升;与模型组相比,GDFMD及Fer-1组肝脏组织病理出现不同程度的好转;血清ALT、AST水平降低;Fe2+、Cu2+、MDA、4-HNE、ROS的水平降低,SOD和GSH的水平升高;ACOX1、GPX4、FTH1、FLT、FAS、SCD1、蛋白含量上升,TFR1、ACSL4、ALOX15蛋白含量下降。 结论 GDFMD可能通过GPX4/ACSL4/ALOX15信号通路抑制铁死亡改善wilson病小鼠的肝脏脂肪变性。
张梦影, 赵晨玲, 田丽伟, 余郭芳, 杨文明, 董婷. 肝豆扶木汤通过GPX4/ACSL4/ALOX15通路抑制铁死亡改善Wilson病小鼠的肝脏脂肪变性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1471-1478.
Mengying ZHANG, Chenling ZHAO, Liwei TIAN, Guofang YU, Wenming YANG, Ting DONG. Gandou Fumu Decoction improves liver steatosis by inhibiting hepatocyte ferroptosis in mice with Wilson's disease through the GPX4/ACSL4/ALOX15 signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1471-1478.
| Gene | Sequence (5'to3') | |
|---|---|---|
| GPX4 | CGCCAAAGTCCTAGGAAACG | |
| ATGCACACGAAACCCCTGTA | ||
| ACSL4 | GACAGGCCAGTGTGAACGTA | |
| TCAGCCCATATCCCTGACCA | ||
| ALOX15 | CGGCGACCAGTATCTCTGAC | |
| TTCCAGGAGTTTCGAACCCG | ||
| FTH1 | GGAGCATGCCGAGAAACTGA | |
| GTCATCACGGTCTGGTTTCTTT | ||
| FTL | GATCGGGATGACGTGGCTC | |
| TTGAGATGGCTTCTGCACAT | ||
| TFR1 | GTGGAGTCTCCCGAGGGTTA | |
| TGGGCATTTGCAACCTTTTCT | ||
| ACOX1 | TTTGTGGAACCTGTTGGCCT | |
| TCGAAGATGAGTTCCGTGGC | ||
| SCD1 | ACAGCCTGTTCGTTAGCACC | |
| TATCCATAGAGATGCGCGGC | ||
| FAS | GTCCTGCCTCTGGTGCTTG | |
| AGCAAAATGGGCCTCCTTGA | ||
| GAPDH | GTGTTCCTACCCCCAATGTG | |
| GTCATTGAGAGCAATGCCAG |
表1 待测基因及内参引物表
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Sequence (5'to3') | |
|---|---|---|
| GPX4 | CGCCAAAGTCCTAGGAAACG | |
| ATGCACACGAAACCCCTGTA | ||
| ACSL4 | GACAGGCCAGTGTGAACGTA | |
| TCAGCCCATATCCCTGACCA | ||
| ALOX15 | CGGCGACCAGTATCTCTGAC | |
| TTCCAGGAGTTTCGAACCCG | ||
| FTH1 | GGAGCATGCCGAGAAACTGA | |
| GTCATCACGGTCTGGTTTCTTT | ||
| FTL | GATCGGGATGACGTGGCTC | |
| TTGAGATGGCTTCTGCACAT | ||
| TFR1 | GTGGAGTCTCCCGAGGGTTA | |
| TGGGCATTTGCAACCTTTTCT | ||
| ACOX1 | TTTGTGGAACCTGTTGGCCT | |
| TCGAAGATGAGTTCCGTGGC | ||
| SCD1 | ACAGCCTGTTCGTTAGCACC | |
| TATCCATAGAGATGCGCGGC | ||
| FAS | GTCCTGCCTCTGGTGCTTG | |
| AGCAAAATGGGCCTCCTTGA | ||
| GAPDH | GTGTTCCTACCCCCAATGTG | |
| GTCATTGAGAGCAATGCCAG |
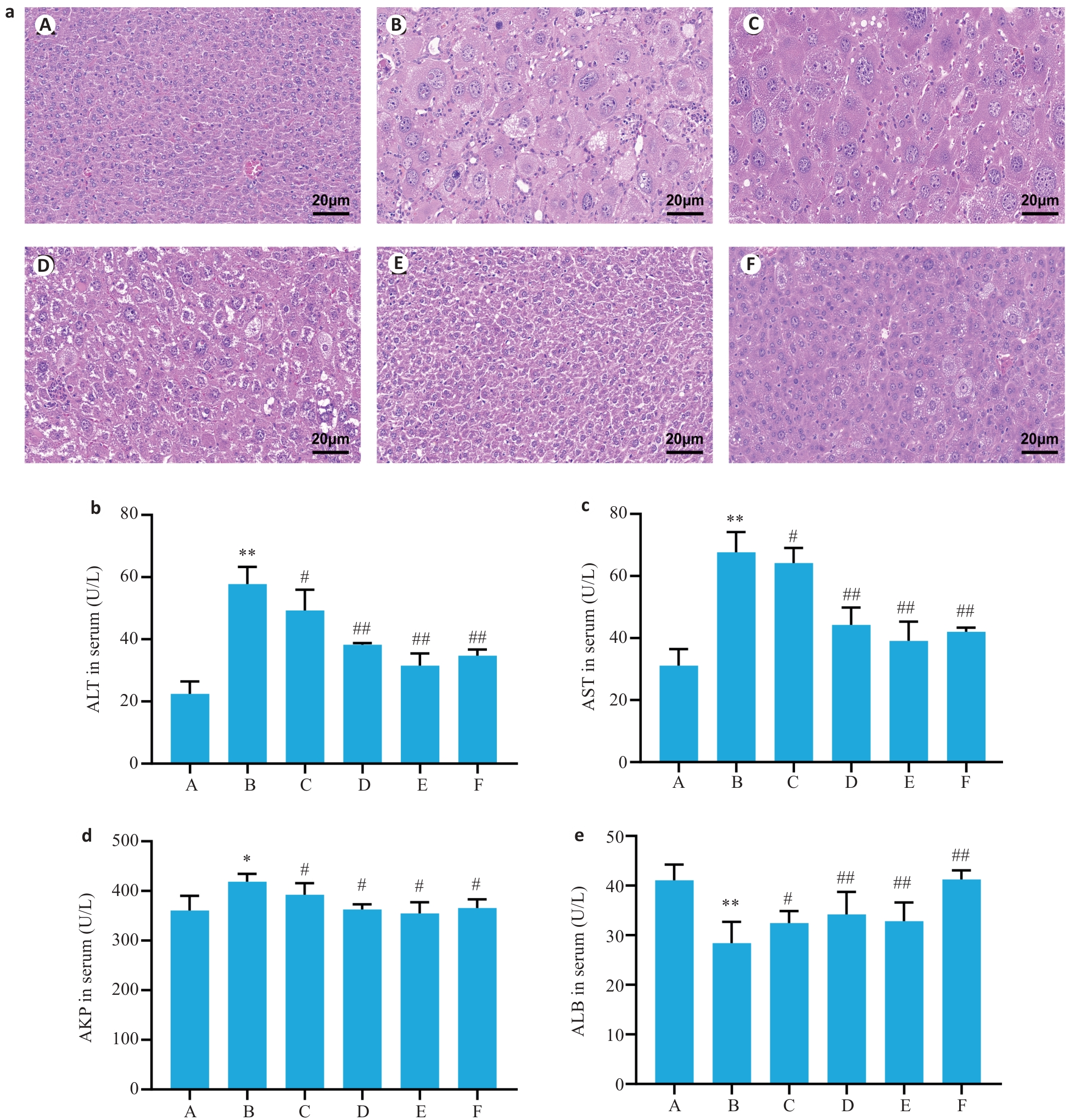
图1 GDFMD对tx-J小鼠肝脏组织形态学及血清肝功能的影响
Fig.1 Effects of Gandou Fumu Decoction (GDFMD) on liver histopathology and serum biochemical indicators of liver function in tx-J mouse models of Wilson's disease (WD). a: HE staining showing histopathological changes in the liver of the mice. b-e: Comparison of serum levels of ALT, AST, AKP, and albumin (ALB) among the groups (Mean±SD, n=6). A: Blank group; B: Model group; C: Low-dose GDFMD group; D: Medium-dose GDFMD group; E: High-dose GDFMD group; F: Fer-1 group (the same group names are used consistently in all the following figures). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs group A; #P<0.05,##P<0.01 vs group B.
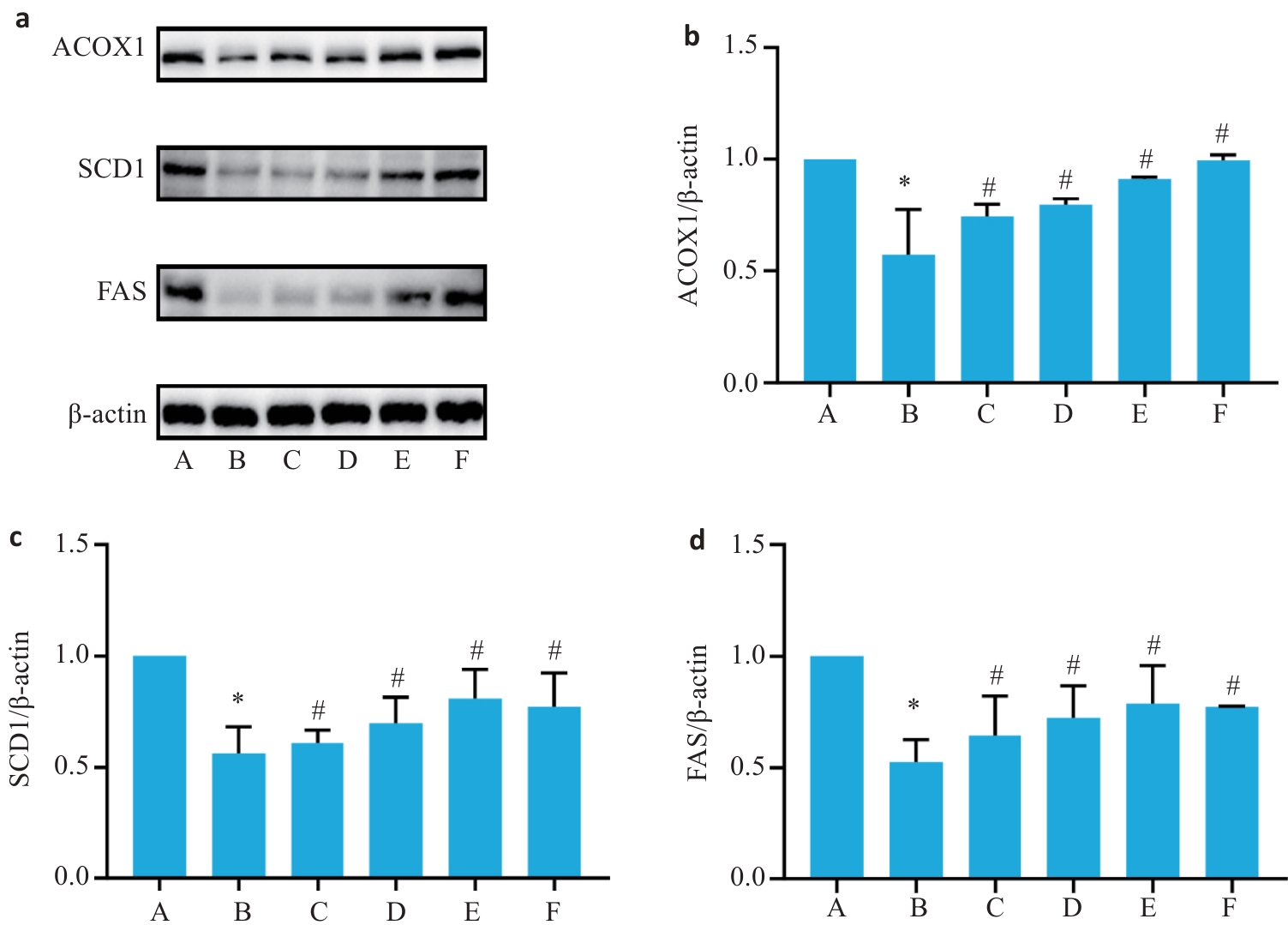
图3 各组小鼠肝脏组织脂质代谢ACOX1、SCD1、FAS相关蛋白表达水平
Fig.3 Expression levels of ACOX1, SCD1 and FAS protein in the liver tissue of the mice in each group (Mean±SD, n=6). a: Results of Western blotting of the proteins. b-d: Relative expressions of ACOX1, SCD1 and FAS proteins. *P<0.05 vs group A; #P<0.05 vs group B.
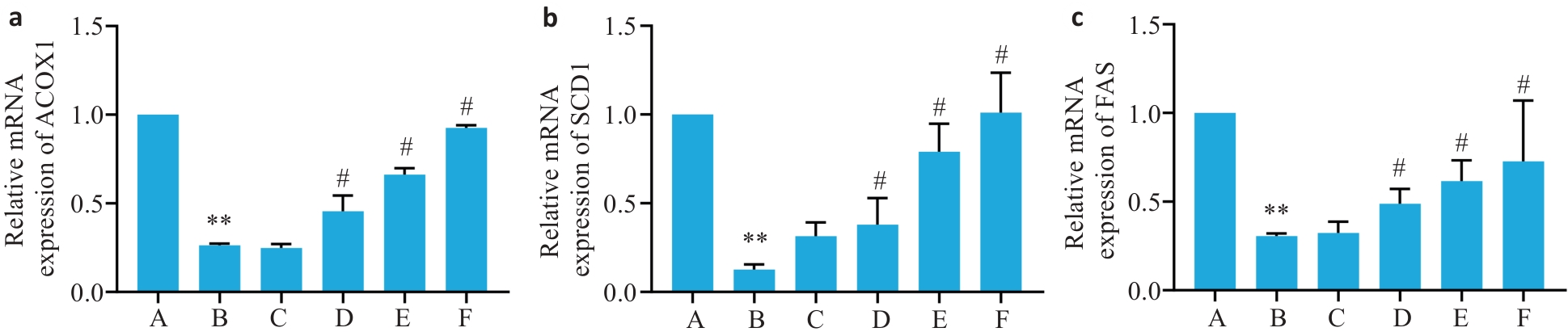
图4 各组小鼠肝脏组织脂质代谢ACOX1、SCD1、FAS mRNA表达水平
Fig.4 Expression levels of ACOX1 (a), SCD1 (b) and FAS (c) mRNA in the liver tissues of the mice (Mean±SD, n=6). **P<0.01 vs group A; #P<0.05 vs group B.
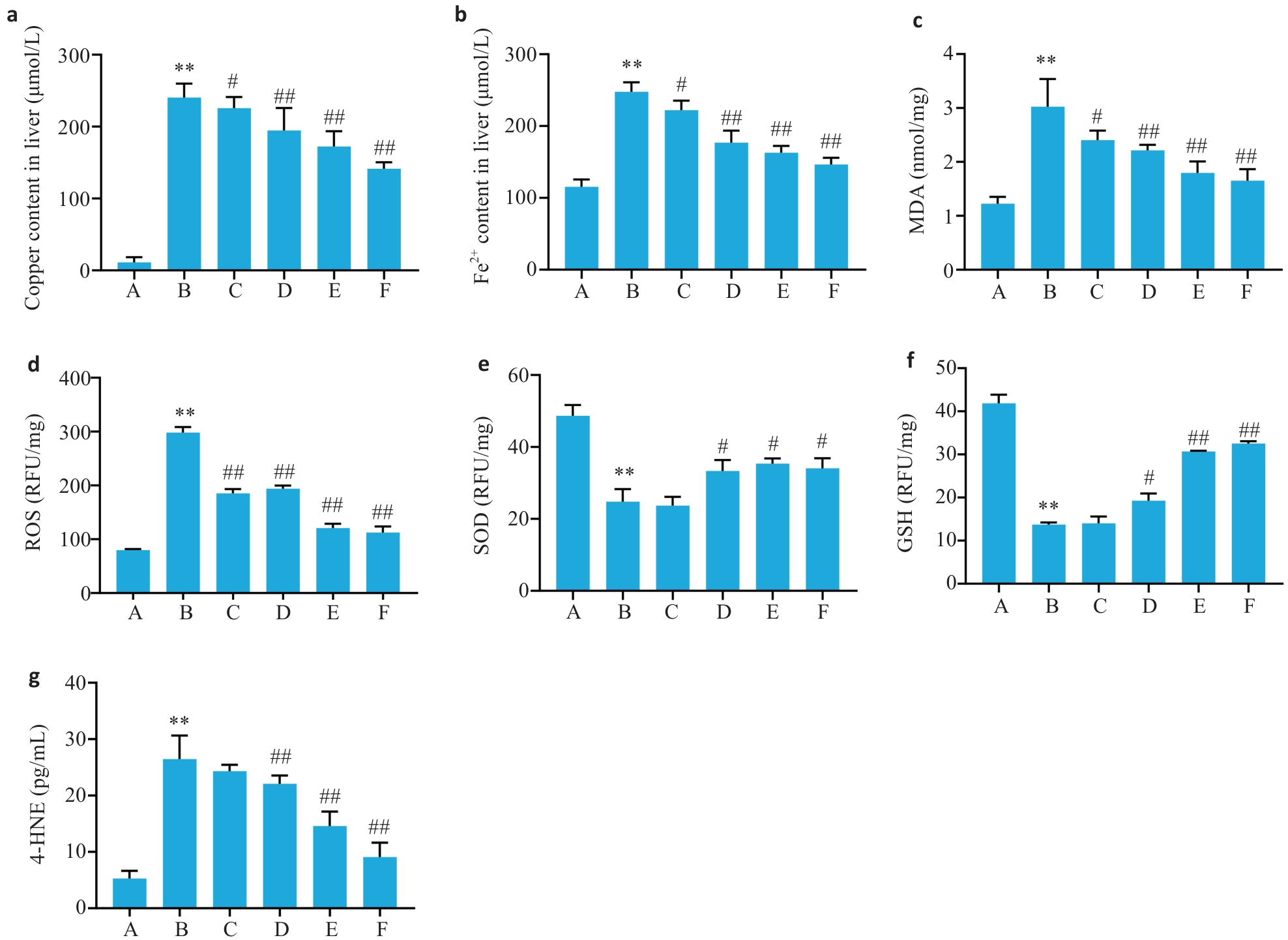
图5 tx-J小鼠肝脏组织中Fe2+、Cu2+及氧化应激MDA、ROS、SOD、GSH的含量
Fig.5 Levels of Fe2+ (a), Cu2+ (b), MDA (c), ROS (d), SOD (e), GSH (f) and 4-HNE (g) in the liver tissues of the tx-J mice (Mean±SD, n=6). **P<0.01 vs group A; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs group B.
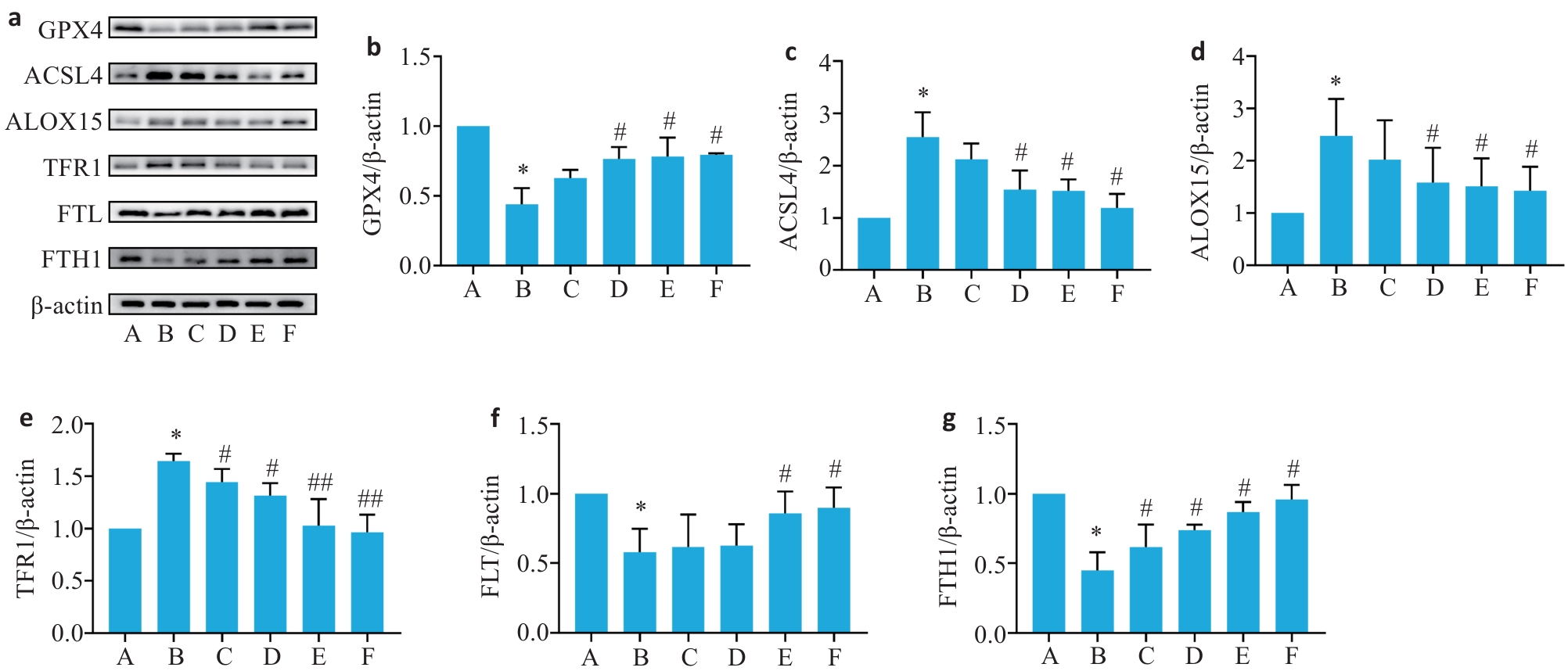
图6 各组小鼠肝脏组织通路GPX4、ACSL4、ALOX15及铁死亡FTH1、FLT、TFR1相关蛋白表达水平
Fig.6 Relative expression levels of FTH1, FLT, TFR1, GPX4, ACSL4, and ALOX15 proteins in the liver tissues of the mice in each group. a: Protein bands detected by Western blotting. b-g: Relative expressions of GPX4, ACSL4, ALOX15, TFR1, FLT, and FTH1 proteins (Mean±SD, n=6) . *P<0.05 vs group A; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs group B.
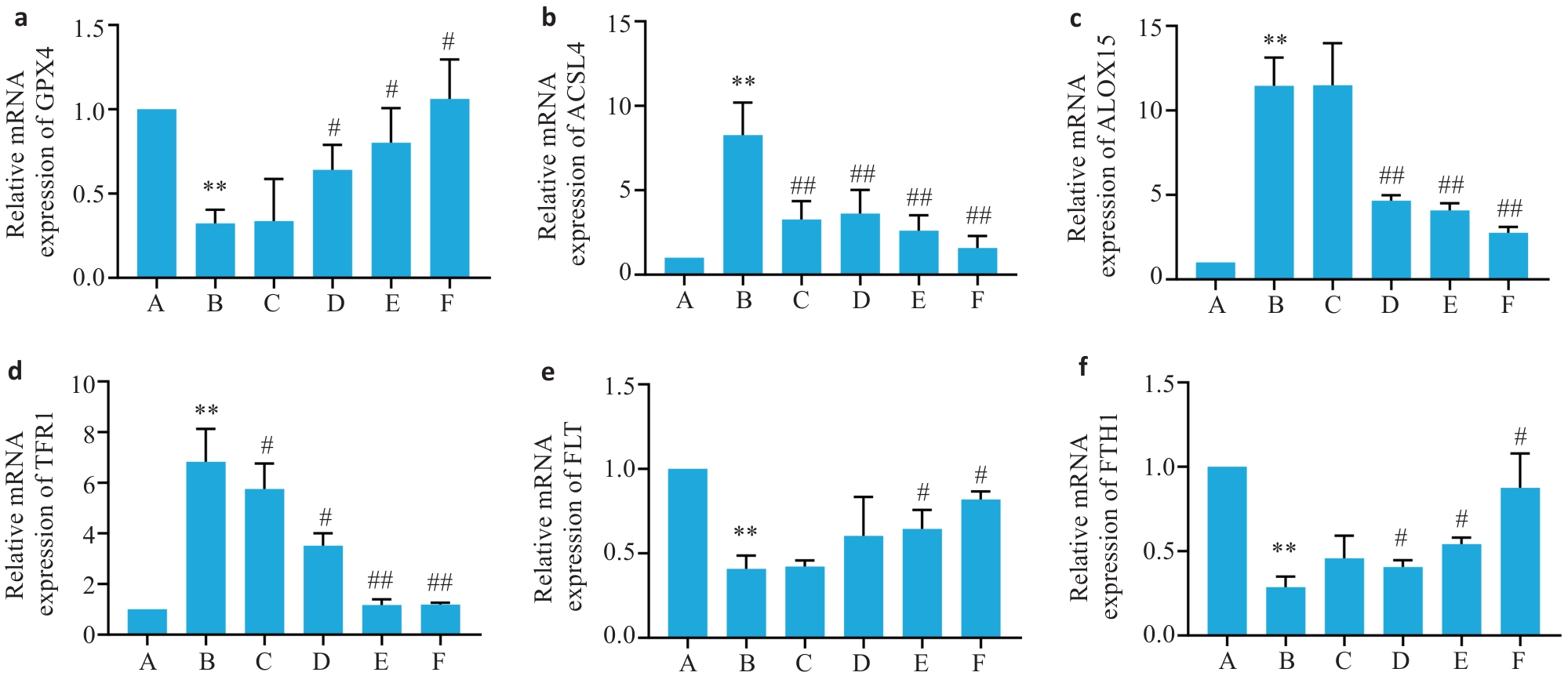
图7 各组小鼠肝脏组织通路GPX4、ACSL4、ALOX15及铁死亡FTH1、FLT、TFR1相关基因mRNA相对表达量
Fig.7 Relative mRNA expression levels of FTH1, FLT, TFR1, GPX4, ACSL4 and ALOX15 in the liver tissues of the mice in each group. a-f: Relative mRNA expression levels of GPX4, ACSL4, ALOX15, TFR1, FLT and FTH1 (Mean±SD, n=6). **P<0.01 vs group A; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs group B.
| [1] | Lucena-Valera A, Ruz-Zafra P, Ampuero J. Wilson's disease: overview[J]. Med Clin (Barc), 2023, 160(6): 261-7. doi:10.1016/j.medcle.2022.12.004 |
| [2] | Członkowska A, Litwin T, Dusek P, et al. Wilson disease[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2018, 4: 21. doi:10.1038/s41572-018-0018-3 |
| [3] | 文佩华, 汪世靖, 董健健, 等. 肝豆汤通过PPARγ-CD36通路调控Wilson病模型小鼠肝脏脂质代谢[J]. 安徽中医药大学学报, 2024, 43(6): 80-5. |
| [4] | Wu J, Wang Y, Jiang RT, et al. Ferroptosis in liver disease: new insights into disease mechanisms[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2021, 7(1): 276. doi:10.1038/s41420-021-00660-4 |
| [5] | 张榆雪, 蓝洁莹, 马昕怡, 等. 化橘红配方颗粒通过维持铁稳态并抑制脂质过氧化和铁死亡缓解斑马鱼脂肪性肝病[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2265-75. doi:10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.12.01 |
| [6] | Li Y, Du YH, Zhou YJ, et al. Iron and copper: critical executioners of ferroptosis, cuproptosis and other forms of cell death[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2023, 21(1): 327. doi:10.1186/s12964-023-01267-1 |
| [7] | 曾靖喻, 唐露露, 陈 洁, 等. 肝豆扶木汤对Wilson病小鼠肝纤维化和上皮-间质转化的干预作用[J]. 河北中医, 2024, 46(10): 1654-60. |
| [8] | 唐露露, 杨文明. 杨文明创肝豆扶木汤治疗肝豆状核变性肝纤维化经验[J]. 中医药临床杂志, 2021, 33(10): 1878-80. |
| [9] | Zhao CL, Chen J, Tian LW, et al. Gandouling ameliorates liver injury in Wilson’s disease through the inhibition of ferroptosis by regulating the HSF1/HSPB1 pathway[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2024, 28(17): e70018. doi:10.1111/jcmm.70018 |
| [10] | 郝文杰, 杨文明, 魏涛华, 等. 基于生物信息学和细胞实验探讨肝豆扶木汤调控铁死亡治疗肝豆状核变性的作用[J]. 中成药, 2023, 45(10): 3461-8. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2023.10.053 |
| [11] | Pang YL, Liu XJ, Wang X, et al. Edaravone modulates neuronal GPX4/ACSL4/5-LOX to promote recovery after spinal cord injury[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 10: 849854. doi:10.3389/fcell.2022.849854 |
| [12] | 杨 悦, 杨文明, 魏涛华, 等. 肝豆扶木汤通过JNK信号通路对Wilson病肝纤维化小鼠的干预作用[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2022, 28(12): 119-26. |
| [13] | 杨玉龙, 杨文明, 魏涛华, 等. 基于UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap-MS技术分析肝豆扶木汤中化学成分[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2024, 39(4): 2001-9. |
| [14] | 康 帅, 汪美霞, 陶 庄, 等. 基于网络药理学和临床研究探讨肝豆扶木颗粒调节肝豆状核变性肝纤维化的机制[J]. 中成药, 2024, 46(9): 3099-103. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2024.09.042 |
| [15] | 张孟莲, 张耀文, 唐林峰, 等. 天麻素通过调节SREBP1c信号通路抑制非酒精性脂肪肝[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2024, 30(11): 70-7. |
| [16] | Jackson SH, Devadas S, Kwon J, et al. T cells express a phagocyte-type NADPH oxidase that is activated after T cell receptor stimulation[J]. Nat Immunol, 2004, 5(8): 818-27. doi:10.1038/ni1096 |
| [17] | Liang DG, Minikes AM, Jiang XJ. Ferroptosis at the intersection of lipid metabolism and cellular signaling[J]. Mol Cell, 2022, 82(12): 2215-27. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2022.03.022 |
| [18] | Chen JR, Ding CF, Chen YH, et al. ACSL4 reprograms fatty acid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma via c-Myc/SREBP1 pathway[J]. Cancer Lett, 2021, 502: 154-65. doi:10.1038/s41389-020-0226-z |
| [19] | Zhang M, Zhou WH, Cao Y, et al. O-GlcNAcylation regulates long-chain fatty acid metabolism by inhibiting ACOX1 ubiquitination-dependent degradation[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2024, 266(Pt 2): 131151. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131151 |
| [20] | Ru Q, Li YS, Chen L, et al. Iron homeostasis and ferroptosis in human diseases: mechanisms and therapeutic prospects[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2024, 9(1): 271. doi:10.1038/s41392-024-01969-z |
| [21] | Xiao MQ, Zhong HQ, Xia L, et al. Pathophysiology of mitochondrial lipid oxidation: role of 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) and other bioactive lipids in mitochondria[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2017, 111: 316-27. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.04.363 |
| [22] | Kwiecien S, Jasnos K, Magierowski M, et al. Lipid peroxidation, reactive oxygen species and antioxidative factors in the pathogenesis of gastric mucosal lesions and mechanism of protection against oxidative stress-induced gastric injury[J]. J Physiol Pharmacol, 2014, 65(5): 613-22. |
| [23] | Fang YY, Chen XC, Tan QY, et al. Inhibiting ferroptosis through disrupting the NCOA4-FTH1 interaction: a new mechanism of action[J]. ACS Cent Sci, 2021, 7(6): 980-9. doi:10.1021/acscentsci.0c01592 |
| [24] | Feng HZ, Schorpp K, Jin J, et al. Transferrin receptor is a specific ferroptosis marker[J]. Cell Rep, 2020, 30(10): 3411-23. e7. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2020.02.049 |
| [25] | Dijkstra M, Vonk RJ, Kuipers F. How does copper get into bile? New insights into the mechanism(s) of hepatobiliary copper transport[J]. J Hepatol, 1996, 24(): 109-20. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(96)00447-x |
| [26] | Wang B, Wang XP. Does ceruloplasmin defend against neuro-degenerative diseases[J]? Curr Neuropharmacol, 2019, 17(6): 539-49. doi:10.2174/1570159x16666180508113025 |
| [27] | Cai HX, Cheng X, Wang XP. ATP7B gene therapy of autologous reprogrammed hepatocytes alleviates copper accumulation in a mouse model of Wilson's disease[J]. Hepatology, 2022, 76(4): 1046-57. doi:10.1002/hep.32484 |
| [28] | Xue Q, Yan D, Chen X, et al. Copper-dependent autophagic degradation of GPX4 drives ferroptosis[J]. Autophagy, 2023, 19(7): 1982-96. doi:10.1080/15548627.2023.2165323 |
| [29] | Wang SD, Liu ZJ, Geng JF, et al. An overview of ferroptosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2022, 153: 113374. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113374 |
| [30] | Gaschler MM, Stockwell BR. Lipid peroxidation in cell death[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2017, 482(3): 419-25. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.10.086 |
| [31] | Song SJ, Su ZY, Kon N, et al. ALOX5-mediated ferroptosis acts as a distinct cell death pathway upon oxidative stress in Huntington's disease[J]. Genes Dev, 2023, 37(5/6): 204-17. doi:10.1101/gad.350211.122 |
| [1] | 陈鑫源, 吴成挺, 李瑞迪, 潘雪芹, 张耀丹, 陶俊宇, 林才志. 双术汤通过P53/SLC7A11/GPX4通路诱导胃癌细胞铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | 张安邦, 孙秀颀, 庞博, 吴远华, 时靖宇, 张宁, 叶涛. 电针预处理通过调节肠道-大脑轴及Nrf2/HO-1信号通路抑制铁死亡减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 911-920. |
| [3] | 张林落, 李长青, 皇玲玲, 周学平, 娄媛媛. 梓醇扶正制毒配伍从SLC7A11/GPX4通路抑制铁死亡减轻雷公藤甲素肝毒性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 810-818. |
| [4] | 季春斐, 左宗超, 王钧, 李妙男. N-乙酰神经氨酸中通过抑制Nrf2轴促进缺氧/复氧损伤的H9C2心肌细胞发生铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 72-79. |
| [5] | 陈凯, 孟兆菲, 闵静婷, 王佳慧, 李正红, 高琴, 胡俊锋. 姜黄素通过抑制TXNIP/TRX-1/GPX4通路介导的铁死亡减轻脓毒症小鼠肺损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1805-1813. |
| [6] | 欧阳明子, 崔佳琦, 王慧, 梁正, 皮大锦, 陈利国, 陈前军, 吴迎朝. 开心散通过减轻前额叶皮质铁死亡缓解小鼠的阿霉素化疗性抑郁[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1441-1449. |
| [7] | 张银亮, 骆泽谭, 赵睿, 赵娜, 徐志东, 奥迪, 丛古一, 刘新宇, 郑海伦. 血根碱通过调控STUB1/GPX4诱导直肠癌细胞发生铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1537-1544. |
| [8] | 王元国, 张鹏. 铁死亡抑制基因在食管癌中的高表达分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1389-1396. |
| [9] | 何华星, 刘璐琳, 刘颖茵, 陈纳川, 孙素霞. 丁酸钠与索拉非尼可能通过YAP诱导铁死亡协同抑制肝癌细胞增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1425-1430. |
| [10] | 任智先, 周倍贤, 王林鑫, 李菁, 张荣平, 潘锡平. 5-羟基-6,7-二甲氧基黄酮抑制流感病毒诱导A549细胞炎症反应和铁死亡的作用及机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1070-1078. |
| [11] | 张方圆, 刘刚. 右美托咪定通过激活Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4通路抑制肾小管上皮细胞的铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1135-1140. |
| [12] | 王南, 石斌, 马小兰, 吴伟超, 曹佳. FMRP通过激活RAS/MAPK信号通路抑制结直肠肿瘤细胞的铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 885-893. |
| [13] | 李淑贤, 于淑平, 穆亚铭, 王 凯, 刘 玉, 张美华. 二甲双胍通过抑制铁死亡改善PM2.5导致的胎盘滋养细胞功能损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 437-446. |
| [14] | 张笑颜, 王 谢, 王 杰, 邵 楠, 蔡 标, 谢道俊. 黄蒲通窍胶囊改善Wilson病铜负荷大鼠的认知损害:基于抑制内质网应激介导的凋亡途径[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 447-454. |
| [15] | 张榆雪, 蓝洁莹, 马昕怡, 周琼, 秦梦晨, 高磊. 化橘红配方颗粒通过维持铁稳态并抑制脂质过氧化和铁死亡缓解斑马鱼脂肪性肝病[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2265-2275. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||