南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 100-109.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.13
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-08-09
出版日期:2025-01-20
发布日期:2025-01-20
通讯作者:
薛鸿
E-mail:44177798@qq.com;xuehongfjsl@fjmu.edu.cn
作者简介:许怀文,本科,E-mail: 44177798@qq.com
基金资助:
Huaiwen XU1( ), Li WENG2, Hong XUE2(
), Li WENG2, Hong XUE2( )
)
Received:2024-08-09
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-01-20
Contact:
Hong XUE
E-mail:44177798@qq.com;xuehongfjsl@fjmu.edu.cn
摘要:
目的 探讨2型糖尿病与慢性阻塞性肺疾病(COPD)的关键基因与免疫学共同机制,并研究潜在的治疗靶点。 方法 利用基因表达综合数据库(GEO)获取COPD与T2DM的基因表达谱。筛选出共同差异表达基因,并对其进行富集分析和蛋白-蛋白相互网络构建后,综合4种拓扑算法与Friends分析得到候选基因。进行数据集和疾病验证集中候选基因的差异表达验证,得到最终靶点基因,通过受试者工作特征曲线(ROC)评估诊断特征的准确性,通过临床收集的共患病患者资料和血液标本验证靶基因的表达和肺功能相关性。基于CIBERSORT算法分析数据集样品中22种免疫细胞丰度,通过相关性分析靶点基因与22种免疫细胞的关系。使用DGIdb数据库筛选药物-基因互作关系信息和可药用的基因。最后对进行基因集富集分析。 结果 选取两种疾病175个共同差异表达基因进分析,结果显示其主要富集于免疫与炎症相关通路,最终筛选趋化因子配体12(CXCL12)作为最终靶基因,其表达在两种疾病中均明显上升(P<0.05),且在ROC曲线中表现出较优异效能,并在COPD共患2型糖尿病患者的血液得到验证。CXCL12表达与肺功能的相关性也得到验证。免疫浸润分析结果显示,CXCL12与CD8+T细胞、γδT细胞和静息肥大细胞呈正相关,而与静息NK细胞和嗜酸性粒细胞呈负相关,差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.01)。GESA分析显示“细胞因子-细胞因子受体相互作用”为与CXCL12高表达密切相关的活化途径。药物-基因检测显示,与CXCL12相关的药物多为非靶向,有较大的细胞毒性,还有进一步改良的空间。 结论 CXCL12可能是COPD与T2DM共同的关键发病基因,靶向CXCL12药物可能是未来COPD和T2DM共病患者更为合理、有效的药物治疗新方向。
许怀文, 翁丽, 薛鸿. CXCL12可作为2型糖尿病合并慢性阻塞性肺疾病的潜在治疗靶点[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 100-109.
Huaiwen XU, Li WENG, Hong XUE. CXCL12 is a potential therapeutic target for type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 100-109.
| Database | Molecule | Tissue | Subgroup | Number | Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE76925 | mRNA | Lung tissue samples | COPD Non-COPD | 111 40 | GPL10558 |
| GSE76894 | mRNA | Islet samples | T2DM Non-diabetic | 19 84 | GPL570 |
| GSE37768 | mRNA | Lung tissue samples | COPD Non-COPD | 20 18 | GPL570 |
| GSE25724 | mRNA | islet samples | T2DM Non-diabetic | 7 7 | GPL96 |
表1 研究所用数据集信息
Tab.1 Information of the datasets used in this study
| Database | Molecule | Tissue | Subgroup | Number | Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE76925 | mRNA | Lung tissue samples | COPD Non-COPD | 111 40 | GPL10558 |
| GSE76894 | mRNA | Islet samples | T2DM Non-diabetic | 19 84 | GPL570 |
| GSE37768 | mRNA | Lung tissue samples | COPD Non-COPD | 20 18 | GPL570 |
| GSE25724 | mRNA | islet samples | T2DM Non-diabetic | 7 7 | GPL96 |
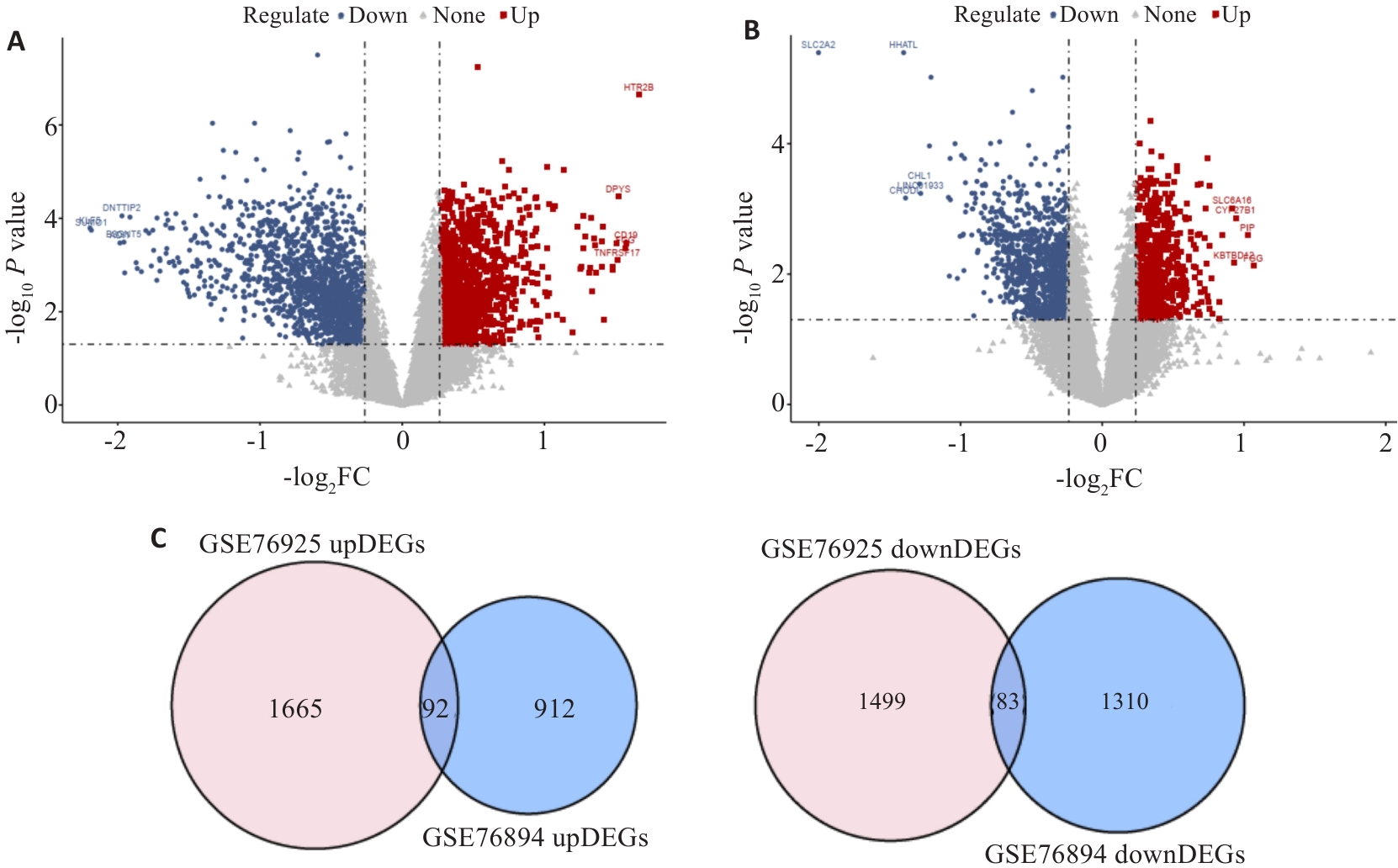
图 1 疾病相关共同易感基因的筛选
Fig.1 Screening of the common differentially expressed genes in COPD and T2DM. A: Volcano plots of gene expression changes in GSE76925. B: Volcano plots of gene expression changes in GSE76894. C: Venn diagrams of the intersected DEGs.
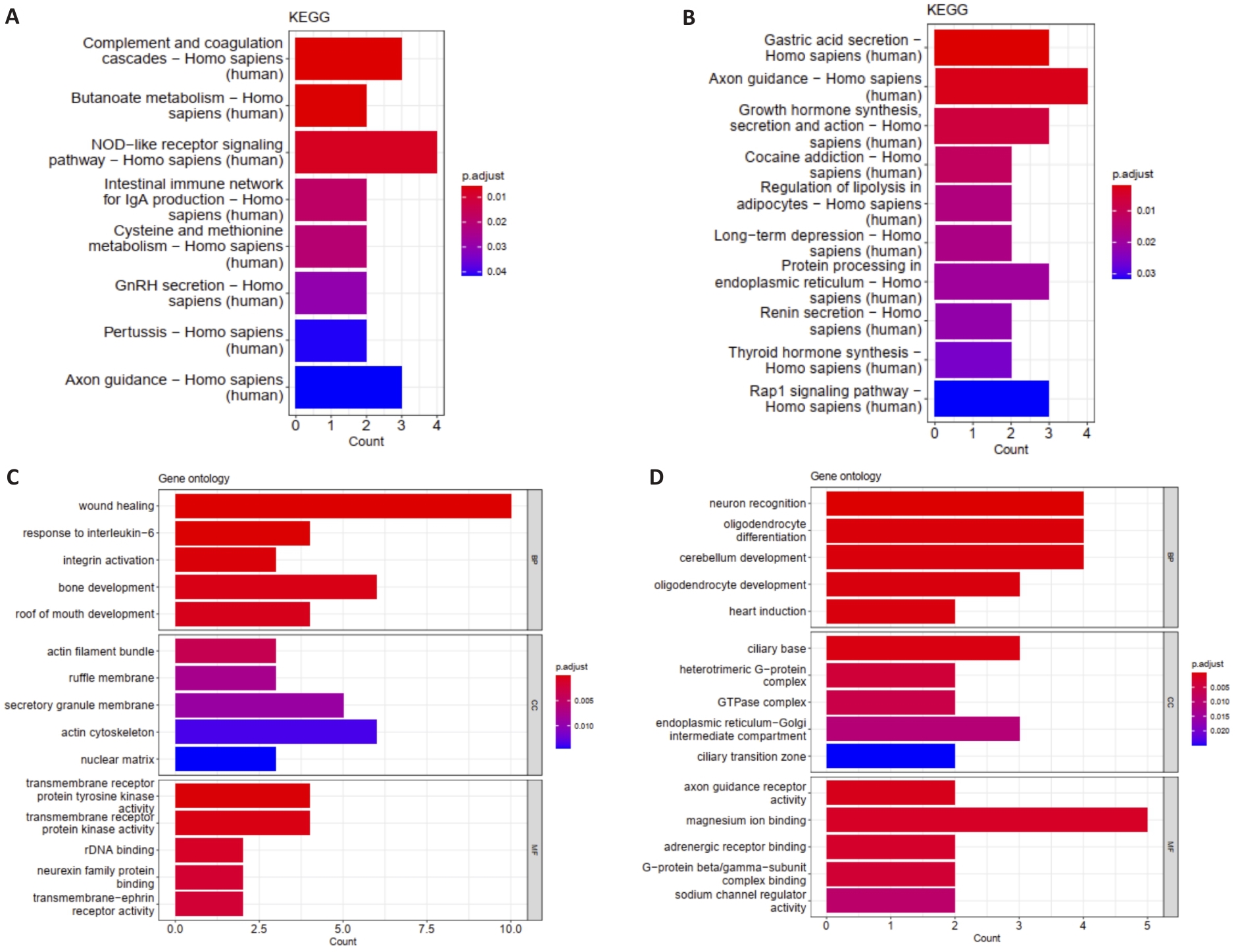
图2 共易感基因的GO和KEGG分析
Fig.2 Functional enrichment analyses of the common differentially expressed genes in COPD and T2DM using Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG). A: KEGG analysis of the upregulated genes. B: KEGG analysis of the downregulated genes. C: GO analysis of the upregulated genes. D: GO analysis of the downregulated genes.
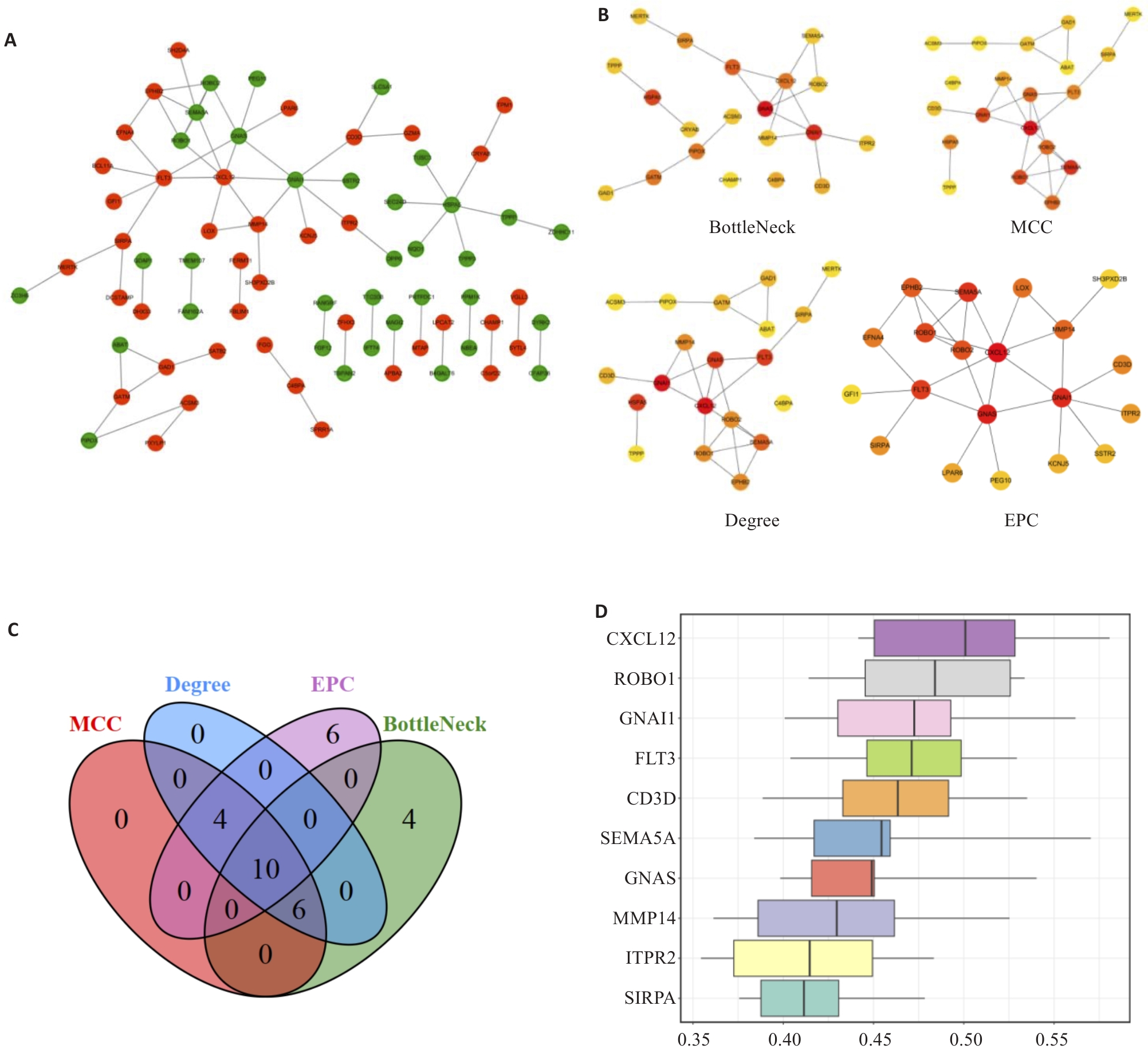
图3 PPI网络构建与候选hub基因鉴定
Fig.3 Protein-protein interaction network and identification of the candidate hub genes. A: PPI network diagram (Red: Upregulated genes; Green: downregulated genes). B: The top20 core gene networks predicted and explored using 4 topology algorithms. C: Venn diagram of the core genes identified by the 4 topology algorithms. D: Friend analysis of 10 common genes.
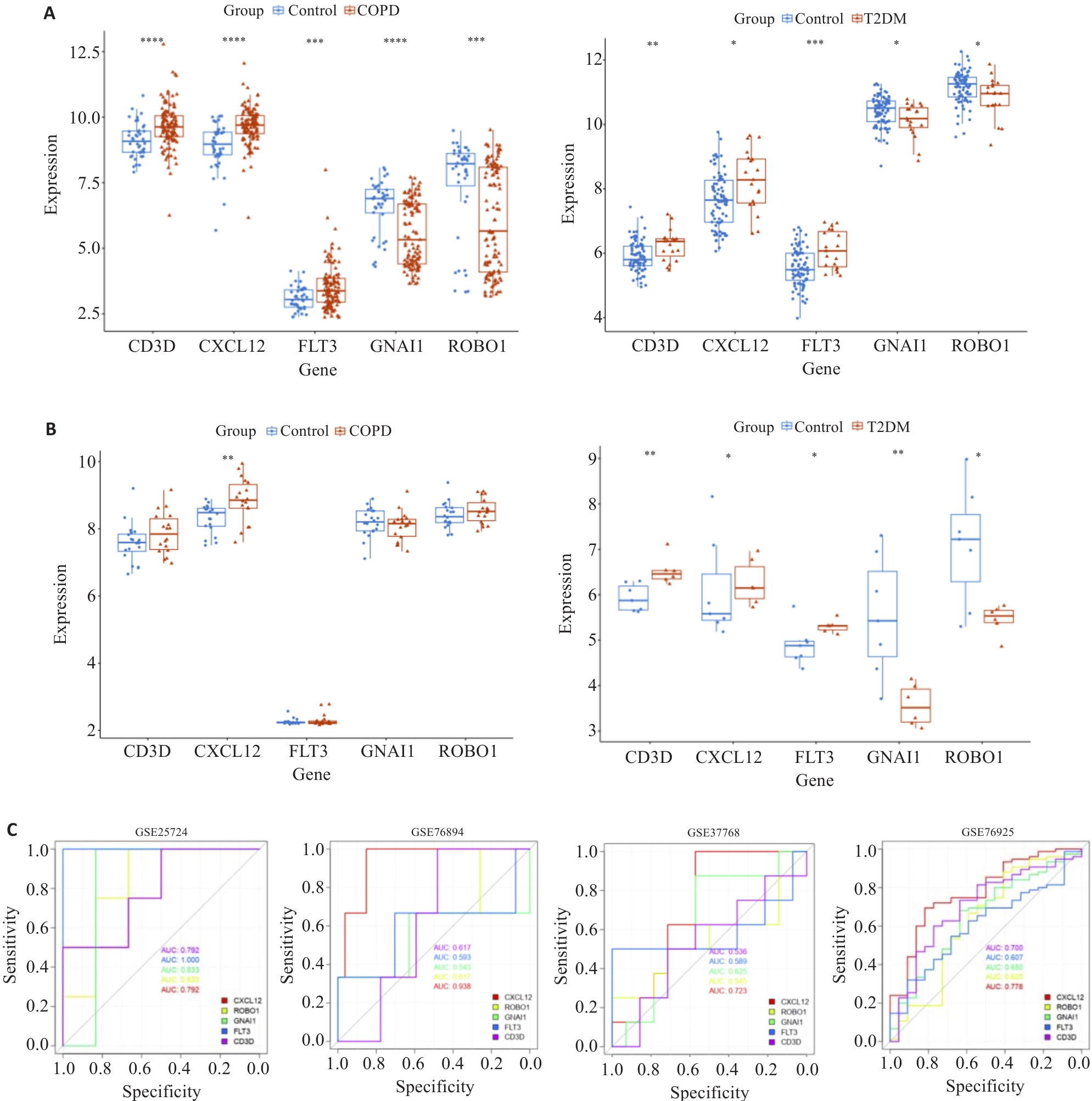
图4 候选hub基因的验证和诊断效能评价
Fig.4 Validation of the candidate hub genes and evaluation of their diagnostic effectiveness. A: Hub-gene expression in the analyzing datasets. B: Hub-gene expression in the validating datasets. C: Hub-gene ROC curves and AUC statistics in the analyzing datasets and validating datasets. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
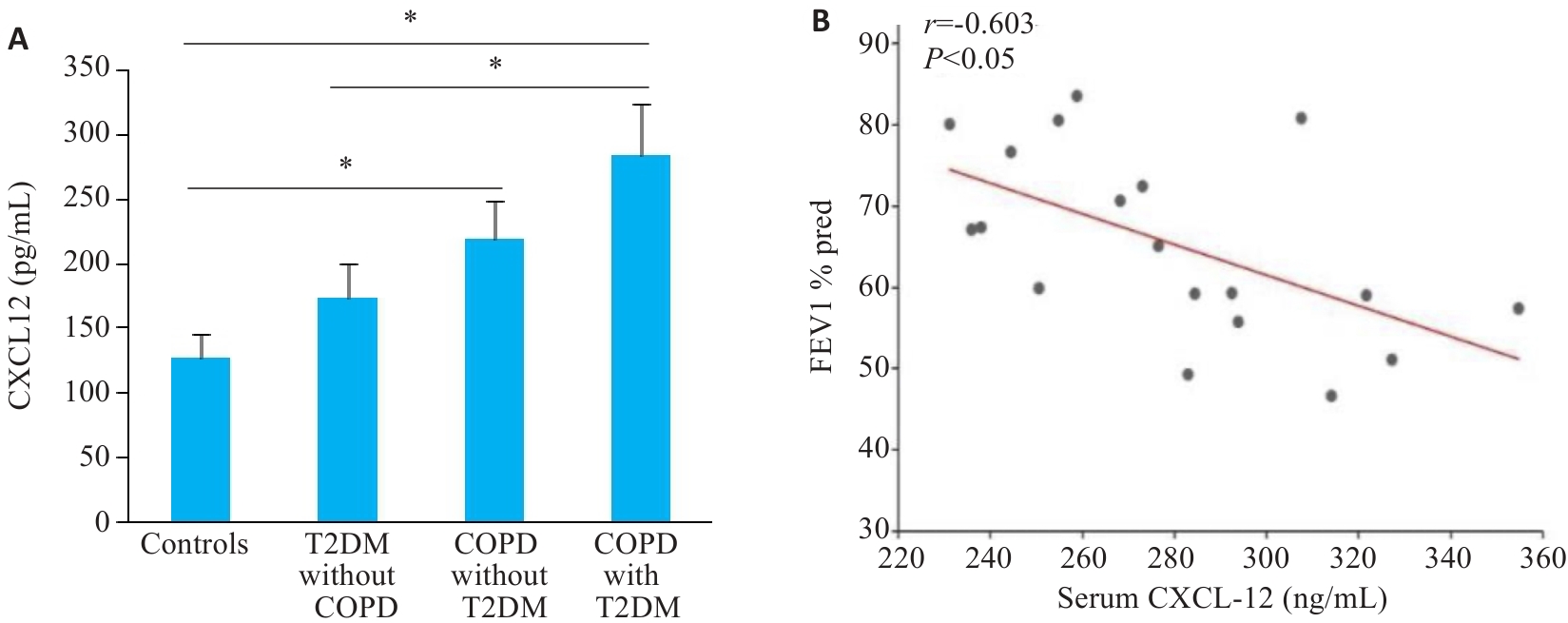
图5 CXCL12表达水平的临床血液标本检测及分析
Fig.5 Validation of CXCL12 expressions in clinical blood samples. A: Elevated CXCL12 in patients with T2DM complicated by COPD (n=12,*P<0.05). B: Correlation between CXCL12 and FEV1pred% in patients with T2DM complicated by COPD (n=20).
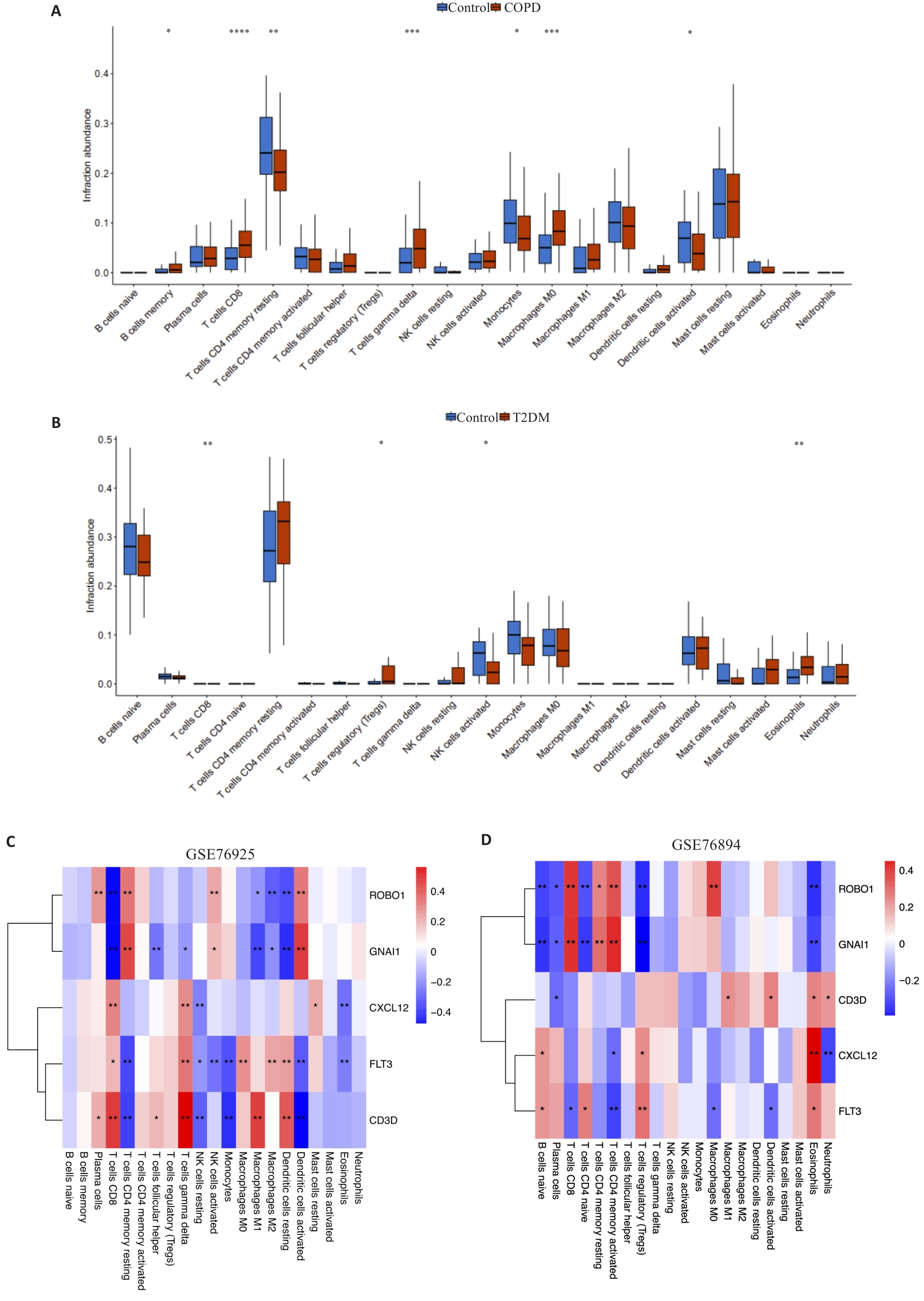
图6 候选Hub基因与免疫细胞浸润关联分析
Fig.6 Correlation analysis of the candidate hub genes and immune cells in COPD and T2DM. A: Violin plot of the distribution of immune cells in GSE76925. B: Violin plot of the distribution of immune cells in GSE76894. C: Heat map of the hub genes and immune infiltration in GSE76925. D: Heat map of the hub genes and immune infiltration in GSE76894. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
| 1 | Agustí A, Celli BR, Criner GJ, et al. Global initiative for chronic obstructive lung disease 2023 report: gold executive summary[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2023, 207(7): 819-37. |
| 2 | Rana JS, Khan SS, Lloyd-Jones DM, et al. Changes in mortality in top 10 causes of death from 2011 to 2018[J]. J Gen Intern Med, 2021, 36(8): 2517-8. |
| 3 | López-Campos JL, Tan W, Soriano JB. Global burden of COPD[J]. Respirology, 2016, 21(1): 14-23. |
| 4 | Castañ-Abad MT, Montserrat-Capdevila J, Godoy P, et al. Diabetes as a risk factor for severe exacerbation and death in patients with COPD: a prospective cohort study[J]. Eur J Public Health, 2020, 30(4): 822-7. |
| 5 | Stolz D, Mkorombindo T, Schumann DM, et al. Towards the elimination of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a Lancet Commission[J]. Lancet, 2022, 400(10356): 921-72. |
| 6 | Gayle A, Dickinson S, Poole C, et al. Incidence of type II diabetes in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a nested case-control study[J]. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med, 2019, 29(1): 28. |
| 7 | Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P, et al. NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets: update[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2013, 41(Database issue): D991-5. |
| 8 | Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, et al. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2015, 43(7): e47. |
| 9 | Langfelder P, Horvath S. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2008, 9: 559. |
| 10 | Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Nastou KC, et al. The STRING database in 2021: customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2021, 49(D1): D605-12. |
| 11 | Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, et al. cytoHubba: identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome[J]. BMC Syst Biol, 2014, 8(): S11. |
| 12 | Yu GC, Li F, Qin YD, et al. GOSemSim: an R package for measuring semantic similarity among GO terms and gene products[J]. Bioinformatics, 2010, 26(7): 976-8. |
| 13 | Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A, et al. pROC: an open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2011, 12: 77. |
| 14 | Chen BB, Khodadoust MS, Liu CL, et al. Profiling tumor infiltrating immune cells with CIBERSORT[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2018, 1711: 243-59. |
| 15 | Cotto KC, Wagner AH, Feng YY, et al. DGIdb 3.0: a redesign and expansion of the drug-gene interaction database[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2018, 46(D1): D1068-73. |
| 16 | Katsiki N, Steiropoulos P, Papanas N, et al. Diabetes mellitus and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an overview[J]. and, 2021, 129(10): 699-704. |
| 17 | Mannino DM, Thorn D, Swensen A, et al. Prevalence and outcomes of diabetes, hypertension and cardiovascular disease in COPD[J]. Eur Respir J, 2008, 32(4): 962-9. |
| 18 | Dupin I, Thumerel M, Maurat E, et al. Fibrocyte accumulation in the airway walls of COPD patients[J]. Eur Respir J, 2019, 54(3): 1802173. |
| 19 | Murdoch C, Thornhill MH, Fang HY, et al. CXCL12/CXCR4 axis mediates recruitment of monocytes to oral cancer spheroids [J]. Oral Dis, 2012, 18(6): 8-18. |
| 20 | Elena T, James O, Ann H, et al. Caveolin-1 regulates CXCR4/CXCL12-dependent monocyte recruitment in scleroderma patients and in a murine model of interstitial lung disease[J]. Clin Experim Rheumatol, 2010, 28(5): S79-80. |
| 21 | Hao WD, Li MX, Pang YM, et al. Increased chemokines levels in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: correlation with quantitative computed tomography metrics[J]. Br J Radiol, 2021, 94(1118): 20201030. |
| 22 | Aydin Ozgur B, Coskunpinar E, Bilgic Gazioglu S, et al. Effects of complement regulators and chemokine receptors in type 2 diabetes[J]. Immunol Invest, 2021, 50(5): 478-91. |
| 23 | Alagpulinsa DA, Cao JJL, Sobell D, et al. Harnessing CXCL12 signaling to protect and preserve functional β-cell mass and for cell replacement in type 1 diabetes[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2019, 193: 63-74. |
| 24 | Yin QZ, Sun KX, Xiang X, et al. Identification of novel CXCL12 genetic polymorphisms associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a Chinese sib-pair study[J]. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers, 2019, 23(7): 435-41. |
| 25 | Gredic M, Sharma V, Hadzic S, et al. iNOS deletion in alveolar epithelium cannot reverse the elastase-induced emphysema in mice[J]. Cells, 2022, 12(1): 125. |
| 26 | Choy JC, Yi T, Rao DA, et al. CXCL12 induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase in human CD8 T cells[J]. J Heart Lung Transplant, 2008, 27(12): 1333-9. |
| 27 | Teicher BA, Fricker SP. CXCL12 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 pathway in cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2010, 16(11): 2927-31. |
| 28 | Pallett LJ, Swadling L, Diniz M, et al. Tissue CD14+CD8+ T cells reprogrammed by myeloid cells and modulated by LPS[J]. Nature, 2023, 614(7947): 334-42. |
| 29 | Lim K, Hyun YM, Lambert-Emo K, et al. Neutrophil trails guide influenza-specific CD8⁺ T cells in the airways[J]. Science, 2015, 349(6252): aaa4352. |
| 30 | Zhong T, Li XY, Lei K, et al. CXCL12-CXCR4 mediates CD57+ CD8+ T cell responses in the progression of type 1 diabetes[J]. J Autoimmun, 2024, 143: 103171. |
| 31 | Barwinska D, Oueini H, Poirier C, et al. AMD3100 ameliorates cigarette smoke-induced emphysema-like manifestations in mice[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2018, 315(3): L382-6. |
| 32 | Cazzola M, Rogliani P, Ora J, et al. Hyperglycaemia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Diagnostics, 2023, 13(21): 3362. |
| 33 | Au PCM, Tan KCB, Lam DCL, et al. Association of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor vs dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor use with risk of incident obstructive airway disease and exacerbation events among patients with type 2 diabetes in Hong Kong [J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2023, 6(1): e2251177. |
| 34 | Pradhan R, Lu S, Yin H, et al. Novel antihyperglycaemic drugs and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations among patients with type 2 diabetes: population based cohort study[J]. BMJ, 2022, 379: e071380. |
| 35 | Janssens R, Struyf S, Proost P. The unique structural and functional features of CXCL12[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2018, 15(4): 299-311. |
| [1] | 周凤敏, 郭艳菊, 陈 宁. 运动诱导的Irisin表达改善2型糖尿病大鼠的肾脏损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 675-681. |
| [2] | 梁一豪, 赖颖君, 袁燕文, 袁 炜, 张锡波, 张拔山, 卢志锋. 基于GEO数据库筛选胃癌差异表达基因及其功能和通路富集分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 605-616. |
| [3] | 任自敬, 周佩洋, 田静. 基于ceRNA芯片研究帕金森病患者血浆长链非编码RNA表达谱并验证lnc-CTSD-5∶1在PD细胞模型中的作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2146-2155. |
| [4] | 梅莉, 张璐, 吴迪, 丁焕章, 王新汝, 张西安, 卫宇航, 李泽庚, 童佳兵. 六味补气方通过调控NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD焦亡通路延缓大鼠慢性阻塞性肺疾病的发展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2156-2162. |
| [5] | 杨勤军, 王卉, 徐淑钰, 杨程, 丁焕章, 吴迪, 朱洁, 童佳兵, 李泽庚. 参芪调肾方减轻慢阻肺肺肾气虚证大鼠气道炎症的机制:基于铁死亡途径[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(10): 1937-1946. |
| [6] | 程蒙蒙, 刘新光, 魏焱鑫, 邢小香, 刘览, 辛楠, 赵鹏. 通塞颗粒阻抑巨噬细胞炎症反应改善大鼠慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(10): 1995-2003. |
| [7] | 徐桂铃, 龚钊乾, 王珺娆, 马妍妍, 许懋升, 陈美佳, 胡大鹏, 梁健鹏, 赵文驱, 赵海金. 2型炎症对慢阻肺大、小气道支气管舒张反应性的不同影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 93-99. |
| [8] | 方福生, 王 宁, 刘星宇, 王 薇, 孙 菁, 李 红, 孙般若, 谷昭艳, 傅晓敏, 闫双通. 基于C肽的胰岛素抵抗指数可准确评估健康体检者的胰岛素抵抗与血尿酸水平的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1509-1514. |
| [9] | 刘 泽, 何汶霞, 房睿哲, 肖 钢, 言 芳, 邱祁广, 方会龙, 王俊杰. 生命潮生物反馈技术干预2型糖尿病的先导观察[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1622-1628. |
| [10] | 吴 迪, 王小乐, 高雅婷, 童佳兵, 杨勤军, 丁焕章, 张 璐, 李泽庚. 参芪温肺方减轻慢性阻塞性肺疾病大鼠的肺气虚证:基于调节NLRP3/GSDMD细胞焦亡通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1500-1508. |
| [11] | 王 敏, 张 茜, 徐桂铃, 黄淑榆, 赵文驱, 梁健鹏, 黄俊文, 蔡绍曦, 赵海金. 健康人群和慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者的血清维生素D与血嗜酸性粒细胞计数的关系[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(5): 727-732. |
| [12] | 徐 晨, 李春颖, 王 胜. 益肺健脾方降低香烟烟雾诱导的人支气管上皮细胞的炎性损伤和黏液高分泌:基于抑制TLR4/NF-κB信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(4): 507-515. |
| [13] | 周 蓓, 李 静, 方晨圆, 黄亚楠, 桑贵蕊, 陶少平, 何春玲. 二甲双胍/维格列汀和利拉鲁肽对肥胖合并2型糖尿病患者的临床疗效比较[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 436-442. |
| [14] | 刘思妤, 刘 青, 彭群龙, 张远芳, 王俊杰. 二氢杨梅素通过抑制HMGB1改善糖尿病大鼠心功能不全[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(5): 641-648. |
| [15] | 谭漫琳, 简文星, 梁秋菊, 李树钧, 崔海燕. 不同评价系统对慢阻肺患者病情及治疗疗效的评估价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(7): 1119-1124. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||