南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (7): 1490-1497.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.07.15
韩瑞敏1( ), 赵曼可2, 袁俊芳3, 史振红3, 王珍2(
), 赵曼可2, 袁俊芳3, 史振红3, 王珍2( ), 王德峰3(
), 王德峰3( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-07
出版日期:2025-07-20
发布日期:2025-07-17
通讯作者:
王珍,王德峰
E-mail:hrm0201@163.com;wangzhen@hebeu.edu.cn;wdf991217@126.com
作者简介:韩瑞敏,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: hrm0201@163.com
基金资助:
Ruimin HAN1( ), Manke ZHAO2, Junfang YUAN3, Zhenhong SHI3, Zhen WANG2(
), Manke ZHAO2, Junfang YUAN3, Zhenhong SHI3, Zhen WANG2( ), Defeng WANG3(
), Defeng WANG3( )
)
Received:2025-03-07
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-07-17
Contact:
Zhen WANG, Defeng WANG
E-mail:hrm0201@163.com;wangzhen@hebeu.edu.cn;wdf991217@126.com
摘要:
目的 分析枯草杆菌二联活菌肠溶胶囊(LCBE)对2型糖尿病合并昼夜节律紊乱糖脂代谢的影响以及作用机制。 方法 将KM小鼠随机分为3组,正常组8只,给予正常饲料喂养,高脂组8只,给予高脂饲料喂养,节律干预组16只,给予节律干预和高脂喂养,8 周后给予链脲佐菌素100 mg/kg腹腔注射,将节律干预糖尿病造模成功的小鼠随机分为2组,灌胃干预的2型糖尿病合并昼夜节律紊乱组(n=8)和2型糖尿病合并昼夜节律紊乱对照组(n=8),给予灌胃干预组225 mg/kg的LCBE灌胃干预,其余3组给予等体积的生理盐水,持续8 周。使用鱼跃血糖仪测小鼠血糖,ELISA法检测Bmal 1、PER 2、胰岛素、C肽和血脂水平,HE染色观察小鼠结肠变化,油红O染色观察对肝脏脂代谢的影响,液相色谱-质谱法检测粪便短链脂肪酸的水平,qPCR和Western blotting法检测小鼠GPR43和GLP-1基因及蛋白表达情况。 结果 与CRD-DM组比较,LCBE-CRD-DM组体质量、周期节律调节因子2(PER2)、胰岛素、C肽、T-CHO、TC和LDL-C水平明显下降(P<0.001),Bmal 1和HDL-C水平明显升高(P<0.001);灌胃干预后,LCBE-CRD-DM组短链脂肪酸、GPR43和GLP-1基因和蛋白表达水平明显高于CRD-DM组(P<0.001)。 结论 LCBE能够降低节律紊乱2型糖尿病的体质量,改善小鼠的血脂水平,LCBE对节律紊乱2型糖尿病小鼠糖脂代谢的影响可能与SCFAs/GPR43/GLP-1通路有关。
韩瑞敏, 赵曼可, 袁俊芳, 史振红, 王珍, 王德峰. 枯草杆菌二联活菌肠溶胶囊调节2型糖尿病合并昼夜节律紊乱小鼠糖脂代谢的作用机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1490-1497.
Ruimin HAN, Manke ZHAO, Junfang YUAN, Zhenhong SHI, Zhen WANG, Defeng WANG. Live combined Bacillus subtilis and Enterococcus faecium improves glucose and lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetic mice with circadian rhythm disruption via the SCFAs/GPR43/GLP-1 pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1490-1497.
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5' to3') | |
|---|---|---|
| Forward primer | Reverse primer | |
| GPR43 | CTTCTTTCTTGGCAATTACTGGC | CCGAAATGGTCAGGTTTAGCAA |
| GCG | AAGAGGAACCGGAACAACATTG | GCCCTCCAAGTAAGAACTCACA |
| GAPDH | AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG | TGTAGACCATGTAGTTGAGGTCA |
表1 GPR43/GLP-1通路基因的引物序列
Tab. 1 Primer sequences for genes in the GPR43/GLP-1 pathway
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5' to3') | |
|---|---|---|
| Forward primer | Reverse primer | |
| GPR43 | CTTCTTTCTTGGCAATTACTGGC | CCGAAATGGTCAGGTTTAGCAA |
| GCG | AAGAGGAACCGGAACAACATTG | GCCCTCCAAGTAAGAACTCACA |
| GAPDH | AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG | TGTAGACCATGTAGTTGAGGTCA |
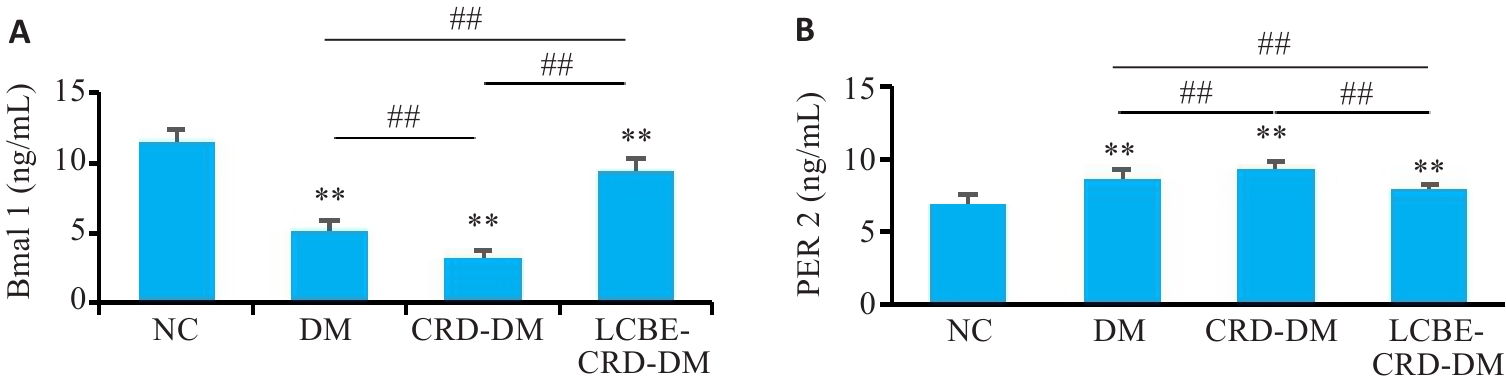
图4 各组小鼠节律因子水平
Fig. 4 Levels of rhythmic factors in the mice in each group. A: Level of Bmal 1 in the mice. B: Level of Per 2 in the mice. **P<0.001 vs NC group; ##P<0.001.
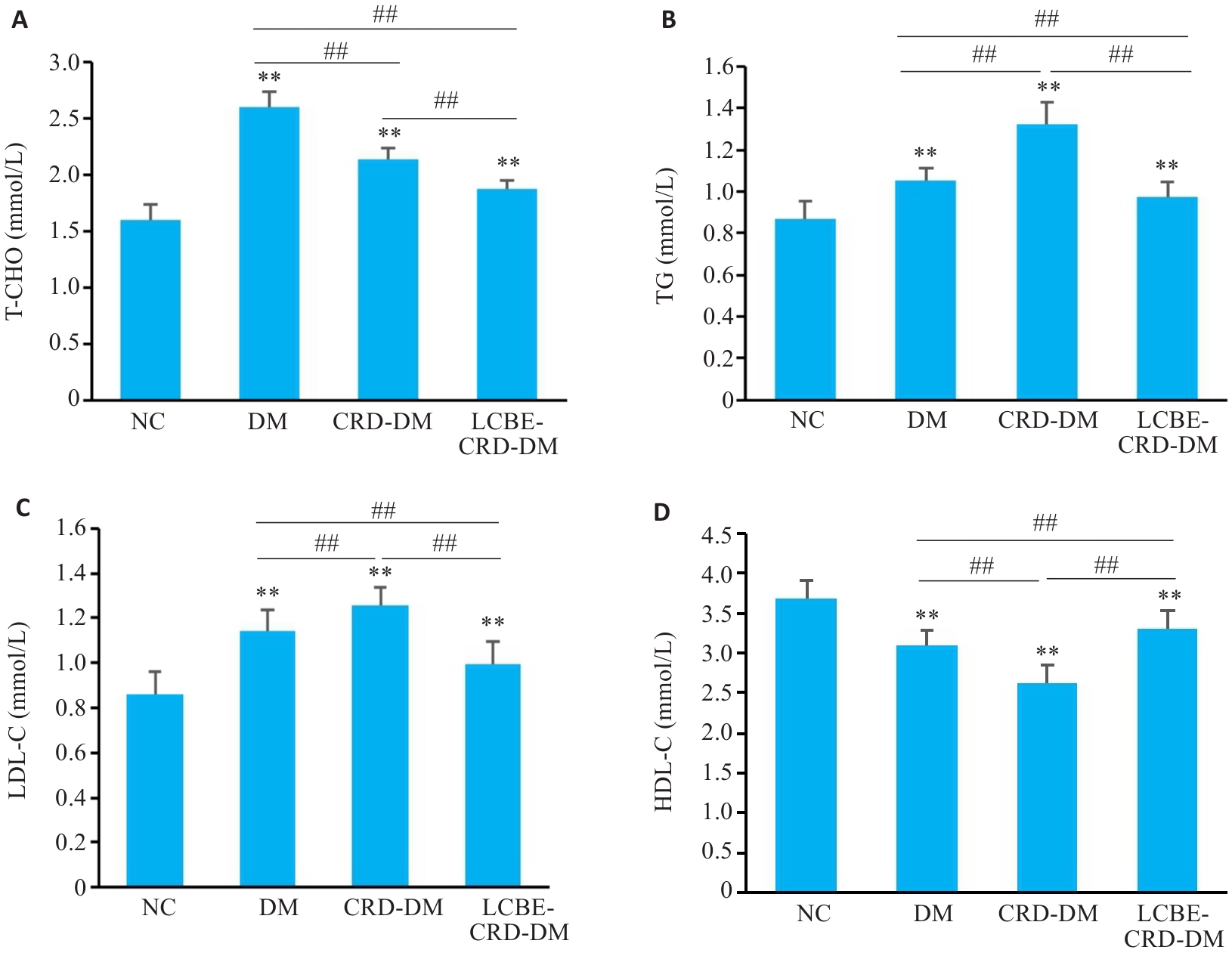
图6 各组小鼠血脂水平比较
Fig.6 Comparison of lipid levels among the groups. A: Total cholesterol levels of the mice in each group. B: Triglyceride levels of the mice in each group. C: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels of the mice in each group. D: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels of the mice in each group. **P<0.001 vs NC group; ##P<0.001.
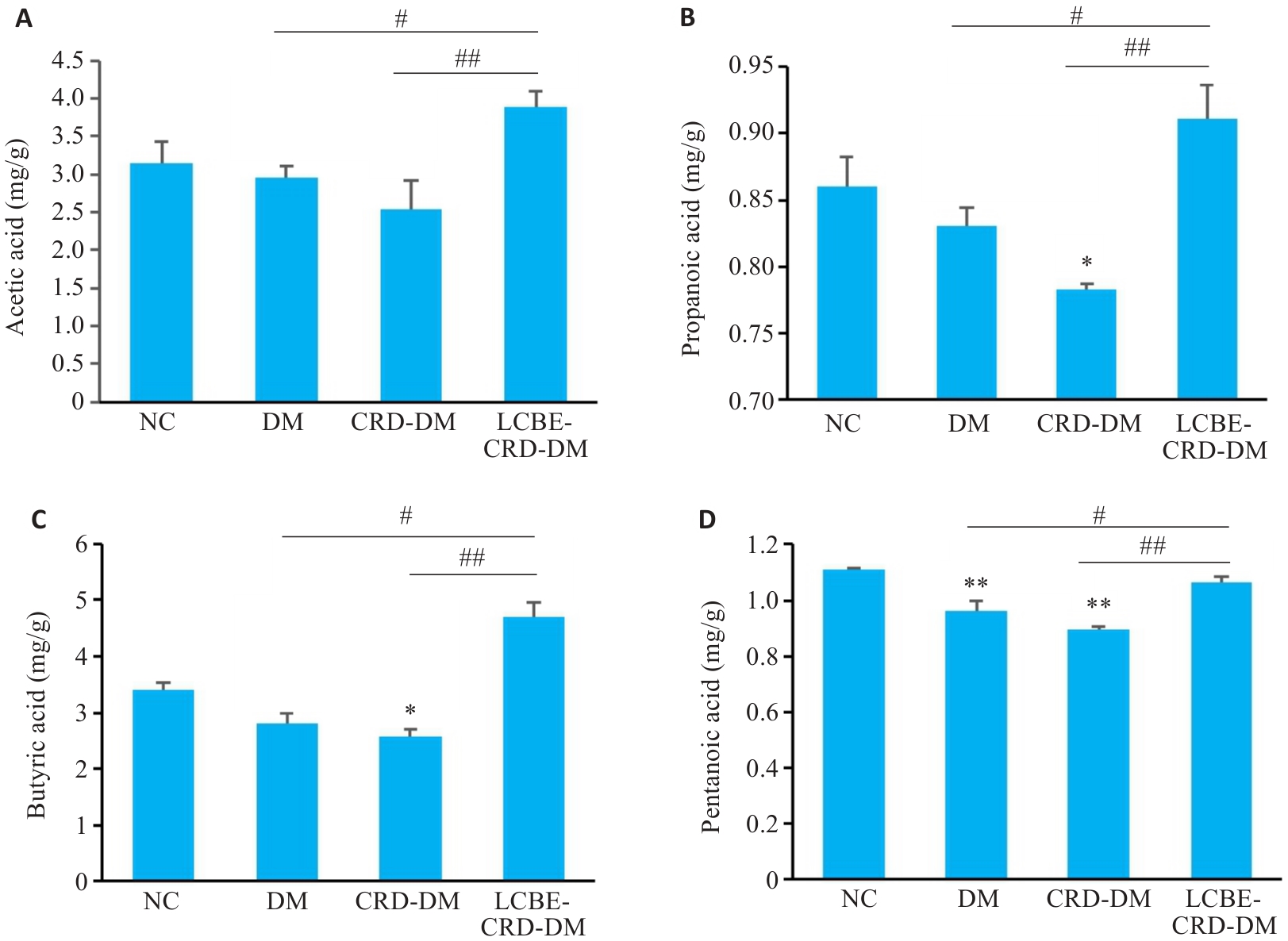
图9 各组短链脂肪酸结果比较
Fig. 9 Fecal levels of short-chain fatty acid in each group. A: Acetic acid level. B: Propanoic acid level. C: Butyric acid level. D: Pentanoic acid level. *P<0.05, **P<0.001 vs NC group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.001.
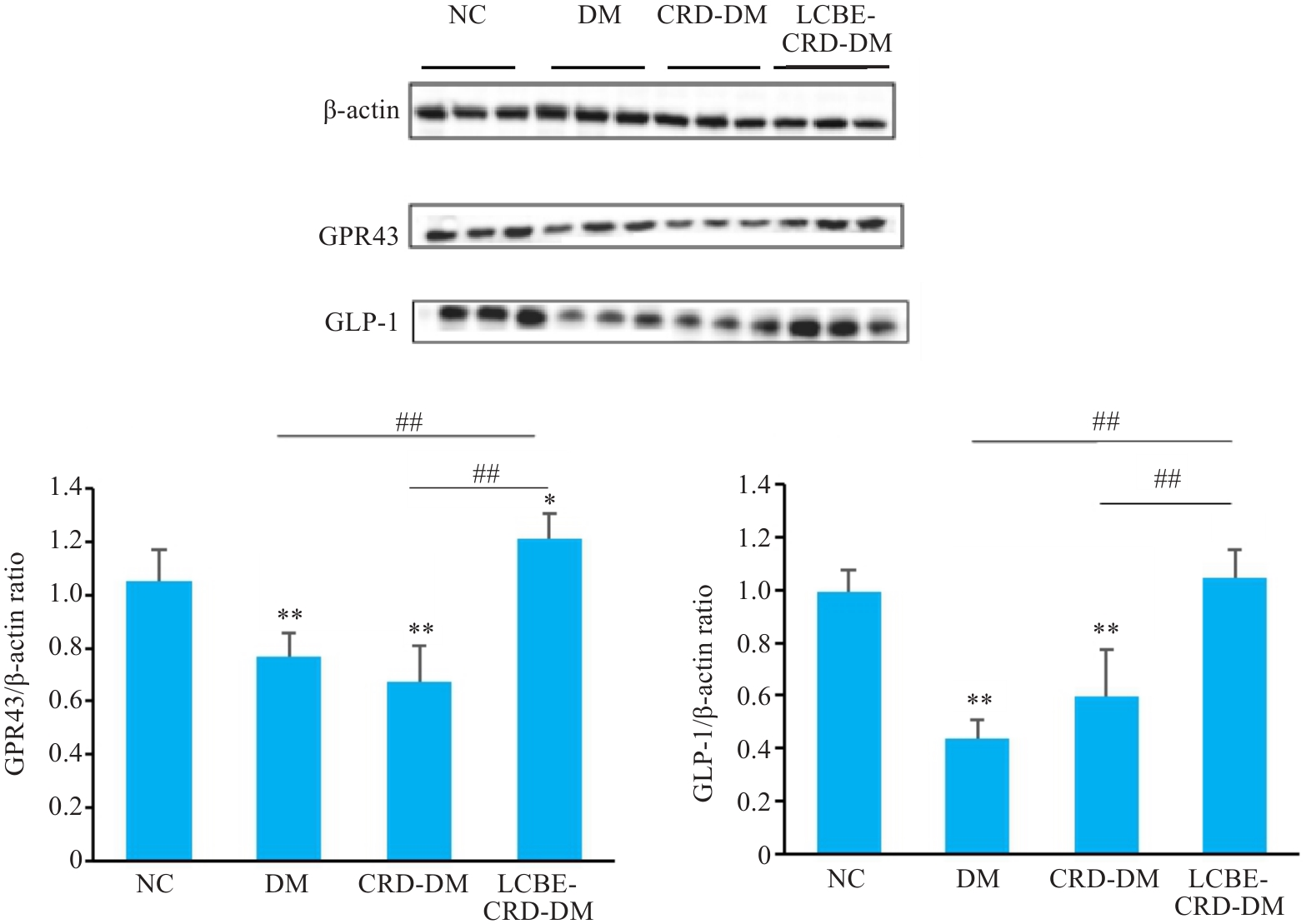
图11 各组小鼠结肠GPR43和GLP-1蛋白水平结果
Fig. 11 GPR43 and GLP-1 protein levels in the colon of the mice in each group detected by Western blotting. *P<0.05, **P<0.001 vs NC group; ##P<0.001.
| [1] | Malone JI, Hansen BC. Does obesity cause type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM)? Or is it the opposite[J]? Pediatr Diabetes, 2019, 20(1): 5-9. doi:10.1111/pedi.12787 |
| [2] | Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2022, 183: 109119. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110945 |
| [3] | Snoek FJ, Bremmer MA, Hermanns N. Constructs of depression and distress in diabetes: time for an appraisal[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2015, 3(6): 450-60. doi:10.1016/s2213-8587(15)00135-7 |
| [4] | Perrin NE, Davies MJ, Robertson N, et al. The prevalence of diabetes-specific emotional distress in people with Type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Diabet Med, 2017, 34(11): 1508-20. doi:10.1111/dme.13448 |
| [5] | Cole JB, Florez JC. Genetics of diabetes mellitus and diabetes complications[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2020, 16(7): 377-90. doi:10.1038/s41581-020-0278-5 |
| [6] | Ding L, Xiao XH. Gut microbiota: closely tied to the regulation of circadian clock in the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Chin Med J: Engl, 2020, 133(7): 817-25. doi:10.1097/cm9.0000000000000702 |
| [7] | Butler TD, Gibbs JE. Circadian host-microbiome interactions in immunity[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 1783. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01783 |
| [8] | 赵国杰, 卢 悦, 崔 博, 等. 昼夜节律紊乱对大鼠肠道菌群及肠道屏障的影响[J]. 现代预防医学, 2022, 49(8): 1495-500. |
| [9] | Abildinova GZ, Benberin VV, Vochshenkova TA, et al. Global trends and collaborative networks in gut microbiota-insulin resistance research: a comprehensive bibliometric analysis (2000-2024)[J]. Front Med: Lausanne, 2024, 11: 1452227. doi:10.3389/fmed.2024.1452227 |
| [10] | Qin J, Li Y, Cai Z, et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes[J]. Nature, 2012, 490(7418): 55-60. doi:10.1038/nature11450 |
| [11] | Karlsson FH, Tremaroli V, Nookaew I, et al. Gut metagenome in European women with normal, impaired and diabetic glucose control[J]. Nature, 2013, 498(7452): 99-103. doi:10.1038/nature12198 |
| [12] | Sanders ME, Merenstein DJ, Reid G, et al. Author correction: probiotics and prebiotics in intestinal health and disease: from biology to the clinic[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 16(10): 642. doi:10.1038/s41575-019-0199-6 |
| [13] | Xie K, Tashkin DP, Luo MZ, et al. Pharmacokinetic study of thymol after intravenous injection and high-dose inhalation in mouse model[J]. Pharmacol Res Perspect, 2019, 7(5): e00515. doi:10.1002/prp2.515 |
| [14] | Altaha B, Heddes M, Pilorz V, et al. Genetic and environmental circadian disruption induce weight gain through changes in the gut microbiome[J]. Mol Metab, 2022, 66: 101628. doi:10.1016/j.molmet.2022.101628 |
| [15] | Hutchison AT, Wittert GA, Heilbronn LK. Matching meals to body clocks-impact on weight and glucose metabolism[J]. Nutrients, 2017, 9(3): E222. doi:10.3390/nu9030222 |
| [16] | Bhadra U, Thakkar N, Das P, et al. Evolution of circadian rhythms: from bacteria to human[J]. Sleep Med, 2017, 35: 49-61. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2017.04.008 |
| [17] | Shi SQ, Ansari TS, McGuinness OP, et al. Circadian disruption leads to insulin resistance and obesity[J]. Curr Biol, 2013, 23(5): 372-81. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2013.01.048 |
| [18] | Reitmeier S, Kiessling S, Clavel T, et al. Arrhythmic gut microbiome signatures predict risk of type 2 diabetes[J]. Cell Host Microbe, 2020, 28(2): 258-72. e6. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2020.06.004 |
| [19] | Bishehsari F, Voigt RM, Keshavarzian A. Circadian rhythms and the gut microbiota: from the metabolic syndrome to cancer[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2020, 16(12): 731-9. doi:10.1038/s41574-020-00427-4 |
| [20] | Gan Y, Yang C, Tong X, et al. Shift work and diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of observational studies[J]. Occup Environ Med, 2015, 72(1): 72-8. doi:10.1136/oemed-2014-102150 |
| [21] | Xie F, Hu K, Fu R, et al. Association between night shift work and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cohort-based meta-analysis[J]. BMC Endocr Disord, 2024, 24(1): 268. doi:10.1186/s12902-024-01808-w |
| [22] | Leung GKW, Huggins CE, Ware RS, et al. Time of day difference in postprandial glucose and insulin responses: Systematic review and meta-analysis of acute postprandial studies[J]. Chronobiol Int, 2020, 37(3): 311-26. doi:10.1080/07420528.2019.1683856 |
| [23] | Viklund A, Andersson T, Selander J, et al. Night and shift work patterns and incidence of type 2 diabetes and hypertension in a prospective cohort study of healthcare employees[J]. Scand J Work Environ Health, 2023, 49(6): 439-48. doi:10.5271/sjweh.4104 |
| [24] | Mokhlesi B, Temple KA, Tjaden AH, et al. Association of self-reported sleep and circadian measures with glycemia in adults with prediabetes or recently diagnosed untreated type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes Care, 2019, 42(7): 1326-32. doi:10.2337/dc19-0298 |
| [25] | Gao Y, Gan T, Jiang L, et al. Association between shift work and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of observational studies[J]. Chronobiol Int, 2020, 37(1): 29-46. doi:10.1080/07420528.2019.1683570 |
| [26] | Voigt RM, Forsyth CB, Green SJ, et al. Circadian disorganization alters intestinal microbiota[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(5): e97500. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0097500 |
| [27] | Thaiss CA, Levy M, Elinav E. Chronobiomics: the biological clock as a new principle in host-microbial interactions[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2015, 11(10): e1005113. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1005113 |
| [28] | Fatima N, Rana S. Metabolic implications of circadian disruption[J]. Pflügers Arch Eur J Physiol, 2020, 472(5): 513-26. doi:10.1007/s00424-020-02381-6 |
| [29] | Fan Y, Pedersen O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2021, 19(1): 55-71. doi:10.1038/s41579-020-0433-9 |
| [30] | Jayedi A, Aletaha A, Zeraattalab-Motlagh S, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics for type 2 diabetes management: a systematic review and network meta-analysis[J]. Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev, 2024, 18(1): 102923. doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2023.102923 |
| [31] | 李宜航. 四君子汤改善CKD小鼠肠道微生态的作用机制研究[D]. 沈阳: 辽宁中医药大学, 2023. |
| [32] | Everard A, Belzer C, Geurts L, et al. Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2013, 110(22): 9066-71. doi:10.1073/pnas.1219451110 |
| [33] | Reutrakul S, Van Cauter E. Sleep influences on obesity, insulin resistance, and risk of type 2 diabetes[J]. Metabolism, 2018, 84: 56-66. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2018.02.010 |
| [34] | Zarrinpar A, Chaix A, Yooseph S, et al. Diet and feeding pattern affect the diurnal dynamics of the gut microbiome[J]. Cell Metab, 2014, 20(6): 1006-17. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2014.11.008 |
| [35] | Jiang J, Xiong J, Ni JB, et al. Live combined B. subtilis and E. faecium alleviate liver inflammation, improve intestinal barrier function, and modulate gut microbiota in mice with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2021, 27: 931143-1 -931143-12. doi:10.12659/msm.931143 |
| [36] | Pi X, Teng W, Fei D, et al. Effects of live combined Bacillus subtilis and Enterococcus faecium on gut microbiota composition in C57BL/6 mice and in humans[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12: 821662. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.821662 |
| [37] | Huang JL, Xu YF, Wang MH, et al. Enterococcus faecium R-026 combined with Bacillus subtilis R-179 alleviate hypercho-lesterolemia and modulate the gut microbiota in C57BL/6 mice[J]. FEMS Microbiol Lett, 2023, 37010.1093: femsle. doi:10.1093/femsle/fnad118 |
| [1] | 许欣筑, 郭丽娜, 郑康帝, 马燕, 林淑娴, 何盈犀, 盛雯, 许素哗, 邱峰. 副干酪乳酪杆菌E6通过其代谢物改善长春瑞滨诱导的斑马鱼免疫抑制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 331-339. |
| [2] | 许怀文, 翁丽, 薛鸿. CXCL12可作为2型糖尿病合并慢性阻塞性肺疾病的潜在治疗靶点[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 100-109. |
| [3] | 周凤敏, 郭艳菊, 陈 宁. 运动诱导的Irisin表达改善2型糖尿病大鼠的肾脏损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 675-681. |
| [4] | 方福生, 王 宁, 刘星宇, 王 薇, 孙 菁, 李 红, 孙般若, 谷昭艳, 傅晓敏, 闫双通. 基于C肽的胰岛素抵抗指数可准确评估健康体检者的胰岛素抵抗与血尿酸水平的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1509-1514. |
| [5] | 刘 泽, 何汶霞, 房睿哲, 肖 钢, 言 芳, 邱祁广, 方会龙, 王俊杰. 生命潮生物反馈技术干预2型糖尿病的先导观察[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1622-1628. |
| [6] | 周 蓓, 李 静, 方晨圆, 黄亚楠, 桑贵蕊, 陶少平, 何春玲. 二甲双胍/维格列汀和利拉鲁肽对肥胖合并2型糖尿病患者的临床疗效比较[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 436-442. |
| [7] | 刘思妤, 刘 青, 彭群龙, 张远芳, 王俊杰. 二氢杨梅素通过抑制HMGB1改善糖尿病大鼠心功能不全[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(5): 641-648. |
| [8] | 高俊凤, 刘曼曼, 郭召平, 胡春平, 冯珍凤, 严 军. 葛根素通过Fetuin B-AMPK/ACC信号通路减轻2型糖尿病小鼠肝脏胰岛素抵抗[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(6): 839-846. |
| [9] | 苏 姗, 汤旭磊, 车红霞, 甄洁玉, 刘丽娟, 赵 楠, 刘进进, 关聪会, 傅松波, 王丽婷, 李红利, 张 迪, 王强梅, 甄东户. 基线25(OH)D水平与2型糖尿病发病风险无相关性:基于5044例人群的前瞻性队列研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(6): 811-819. |
| [10] | 唐淬蓉, 胡承光, 周宇辰, 宋杨达, 李 孟, 廖敏君, 孙家润, 钟春秀, 周 琳, 林志昭, 周元平. 乙型肝炎肝硬化合并糖尿病时发生肝细胞癌的风险:一项随访5年的前瞻性队列研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(3): 313-318. |
| [11] | 肖 瑶, 牛 玥, 毛明慧, 林 涵, 汪佰丽, 乌恩奇, 赵焕虎, 李树春. 2型糖尿病与肠道核心菌群的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(3): 358-369. |
| [12] | 邱倩琪, 宋兴荣, 孙昌志, 谭永红, 徐颖怡, 黄桂亮, 张 娜, 李峥科, 魏 伟. 全身麻醉影响4~6岁鼾症儿童术后首夜褪黑素的分泌但不造成抑制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(1): 128-134. |
| [13] | 吴壮炜, 吴良平, 戴晓江, 赵为国, 余 翔, 宋志高, 杨宝琳, 黄宗海. 腹腔镜胃旁路术治疗非肥胖2型糖尿病患者的疗效分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(07): 1044-1048. |
| [14] | 颜俊锋,郑开元,林 川,刘 春. 2型糖尿病患者肌肉减少症与并发白蛋白尿的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(03): 407-412. |
| [15] | 王 珊,张 健,张卫欢,汪海涛,侯婧悦,张瑞秀,刘红芬,吴寿岭. 体质量指数联合腰围对 2型糖尿病患者新发非酒精性脂肪肝的预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(11): 1293-1297. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||