南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (9): 1989-1996.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.18
• • 上一篇
饶璐1,2( ), 丁家和1,2, 魏江平1,2, 阳勇1,2, 张小梅1,2(
), 丁家和1,2, 魏江平1,2, 阳勇1,2, 张小梅1,2( ), 王计瑞1,2(
), 王计瑞1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-07
出版日期:2025-09-20
发布日期:2025-09-28
通讯作者:
张小梅,王计瑞
E-mail:2473601792@qq.com;ZXM761@163.com;wangjiruizyy@163.com
作者简介:饶 璐,硕士,E-mail: 2473601792@qq.com
基金资助:
Lu RAO1,2( ), Jiahe DING1,2, Jiangping WEI1,2, Yong YANG1,2, Xiaomei ZHANG1,2(
), Jiahe DING1,2, Jiangping WEI1,2, Yong YANG1,2, Xiaomei ZHANG1,2( ), Jirui WANG1,2(
), Jirui WANG1,2( )
)
Received:2025-03-07
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Xiaomei ZHANG, Jirui WANG
E-mail:2473601792@qq.com;ZXM761@163.com;wangjiruizyy@163.com
摘要:
目的 采用网络药理学、分子对接技术及实验验证,探讨槐花治疗银屑病的作用机制。 方法 通过TCMSP、GeneCards、OMIM、DisGeNET以及String数据库获得槐花活性成分、作用靶点以及银屑病相关疾病靶点,采用Cytoscape 3.8.0软件绘制“药物—有效成分—关键靶点—信号通路—疾病”网络图以及GO、KEGG通路富集分析;使用Discovery Studio 2019软件进行分子对接。体外实验采用咪喹莫特(IMQ)诱导的银屑病BALB/c小鼠模型,分为正常组、模型组、槐花高剂量组(3.00 g/kg)、中剂量组(1.50 g/kg)、低剂量组(0.75 g/kg)和阳性药组,6只/组。提前给药1周并于造模期间给药物干预。通过体质量变化、脾脏系数、银屑病皮损面积及严重程度指数(PASI)评分和皮肤病理变化进行效果评价;运用免疫组化和Western blotting技术检测p-PI3K、p-AKT蛋白水平。 结果 共筛选出10个活性成分和110个关键靶点,GO和KEGG通路富集分析显示槐花可能通过调控PI3K/AKT信号通路、TNF信号通路、IL-17信号通路等改善银屑病。分子对接结果显示,槲皮素和山奈酚均与AKT1、TNF等位点结合紧密。动物实验结果显示,槐花低剂量组小鼠体质量增加,PASI评分下降,改善银屑病病理症状(P<0.05),降低PI3K、AKT蛋白的磷酸化水平(P<0.05)。 结论 槐花能够通过多成分、多靶点、多通路治疗银屑病,其作用机制可能与下调p-PI3K、p-AKT蛋白的表达,进而影响PI3K/AKT信号通路有关。
饶璐, 丁家和, 魏江平, 阳勇, 张小梅, 王计瑞. 槐花通过抑制PI3K/AKT通路减轻炎症反应治疗银屑病[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1989-1996.
Lu RAO, Jiahe DING, Jiangping WEI, Yong YANG, Xiaomei ZHANG, Jirui WANG. Flos Sophorae improves psoriasis in mice by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1989-1996.
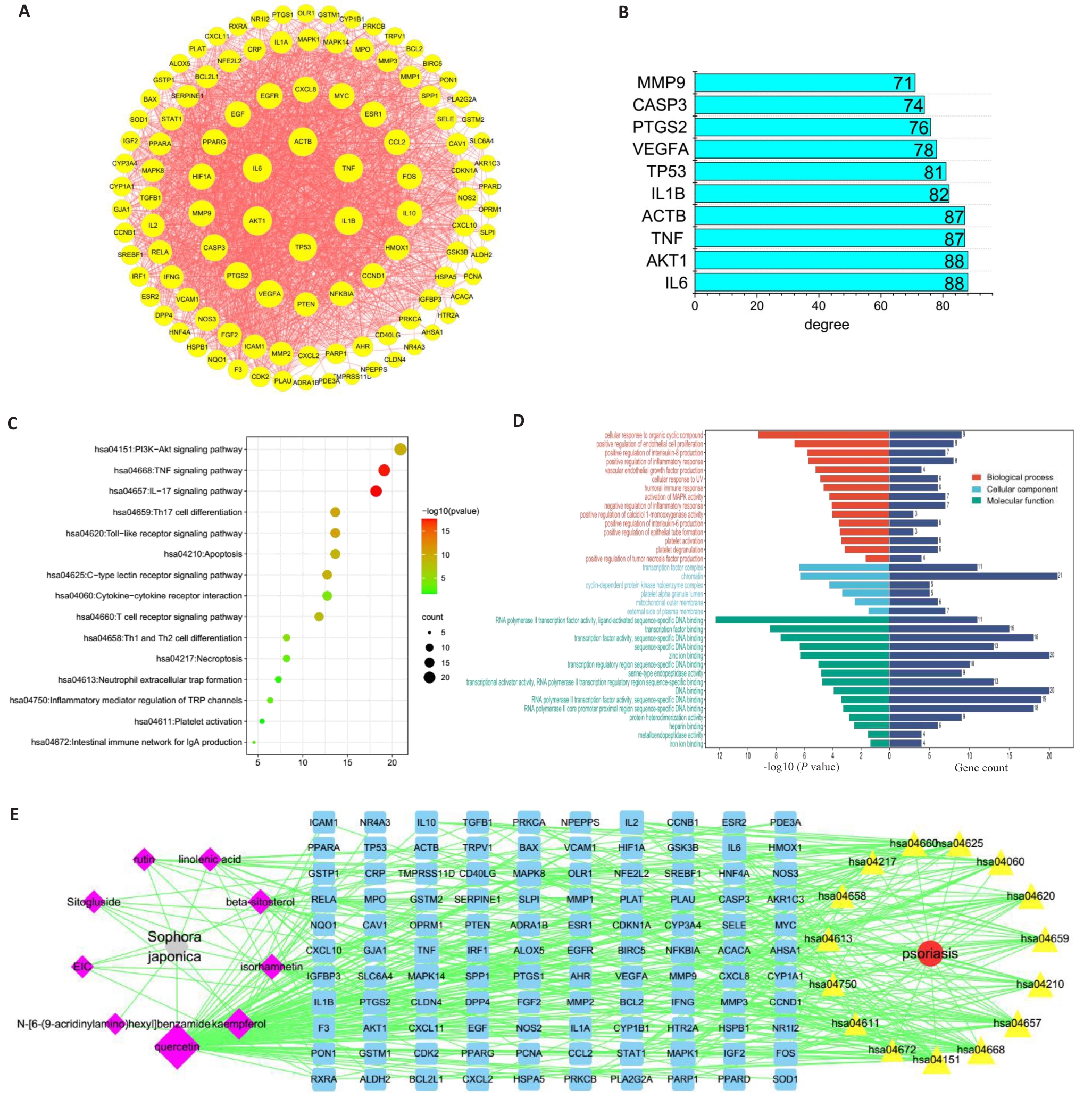
图1 槐花成分网络药理学分析
Fig.1 Network pharmacological analysis of the components of Flos Sophorae. A: PPI network diagram of the core targets of Flos Sophorae for treatment of psoriasis. B: Degree values of the targets in the PPI network. C: KEGG pathway enrichment analysis. D: GO enrichment analysis. E: Traditional Chinese Medicine-Active Ingredients-Key Targets-Signalling Pathways-Disease pathway network.
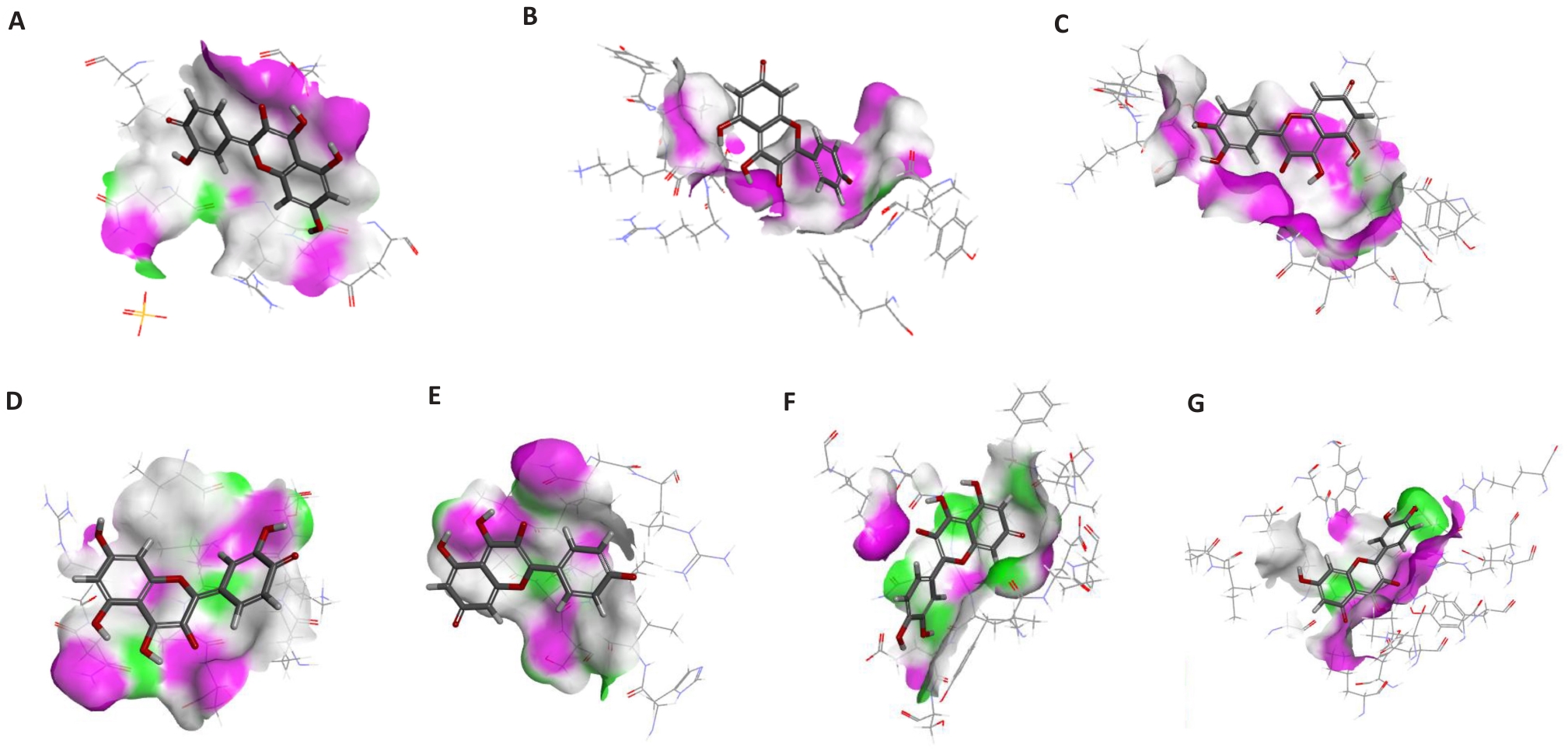
图2 槐花活性成分与蛋白分子的对接3D模型
Fig.2 3D modelling of docking of Flos Sophorae active ingredients with the protein molecules. A: Docking results of IL-6 with quercetin. B: Docking results of AKT1 with quercetin. C: Docking results of AKT1 with kaempferol. D: Docking results of TNF with quercetin. E: Docking results of TNF with kaempferol. F: Docking results of IL-1Β with quercetin. G: Docking results of TP53 with quercetin.
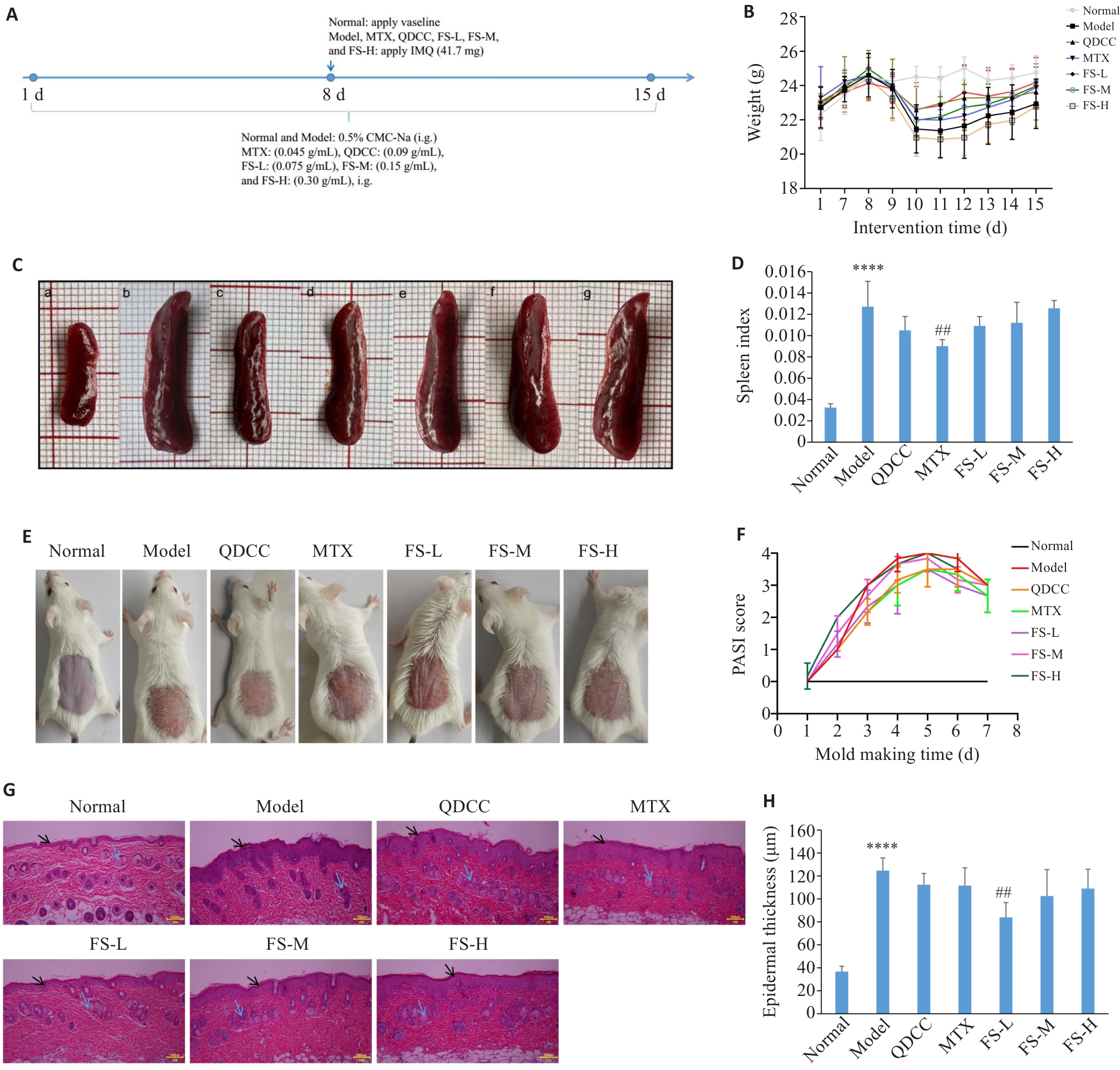
图3 槐花改善IMQ诱导的银屑病小鼠病症情况
Fig.3 Flos Sophorae ameliorates IMQ-induced psoriasis in mice. A: Schematic diagram of IMQ modeling in mice. B: Changes in body weight of the mice of each group. C: Morphological changes in the spleen. D: Spleen index. E: Morphological characteristics of dorsal skin lesions in each group on the 15th day of modelling. F: Skin PASI scores of the mice in each group. G: HE staining of the dorsal skin of the mice in each group (scale bar=100 μm). H: Skin thickness. ****P<0.05 vs Normal; ##P<0.01 vs Model group. The black arrow indicate the stratum corneum, and the blue arrow indicate the infiltrating inflammatory cells. FS-L/M/H: Flos Sophorae low/medium/high; QDCC: Qingdai compound capsule; MTX: Methotrexate.
| Score | Severity | Erythema | Epidermal flaking | Plaque thickness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Asymptomatic | None | None | Flush with normal skin |
| 1 | Mild symptom | Patch of pale red colour | Epidermal flaking | Slightly higher than normal skin |
| 2 | Moderate symptomatology | Red patch | Covered with flaky epidermal flakes | Moderate bulge |
| 3 | Severe symptoms | Dark red patches | Thick, stratified epidermal flakes | Bulge |
| 4 | Extremely severe symptoms | Very dark red patches | There is thick, stratified epidermal flaking | Marked thickening of the bulge |
表1 银屑病样小鼠PASI评分表
Tab.1 PASI scale for psoriasis-like mice
| Score | Severity | Erythema | Epidermal flaking | Plaque thickness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Asymptomatic | None | None | Flush with normal skin |
| 1 | Mild symptom | Patch of pale red colour | Epidermal flaking | Slightly higher than normal skin |
| 2 | Moderate symptomatology | Red patch | Covered with flaky epidermal flakes | Moderate bulge |
| 3 | Severe symptoms | Dark red patches | Thick, stratified epidermal flakes | Bulge |
| 4 | Extremely severe symptoms | Very dark red patches | There is thick, stratified epidermal flaking | Marked thickening of the bulge |
| Mol ID | Compound | OB (%) | DL |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOL000131 | Linoleic acid (EIC) | 41.90 | 0.14 |
| MOL000354 | isorhamnetin | 49.60 | 0.31 |
| MOL000357 | Sitogluside | 20.63 | 0.62 |
| MOL000358 | beta-sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| MOL000422 | kaempferol | 41.88 | 0.24 |
| MOL000432 | linolenic acid | 45.01 | 0.15 |
| MOL005935 | N-[6-(9-acridinylamino) hexyl]benzamide | 41.70 | 0.78 |
| MOL005940 | quercetin-3'-methyl ether | 46.44 | 0.3 |
| MOL000098 | quercetin | 46.43 | 0.28 |
| MOL000415 | rutin | 3.20153 | - |
表2 槐花中有效成分信息
Tab.2 General information of active ingredients of Flos Sophorae
| Mol ID | Compound | OB (%) | DL |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOL000131 | Linoleic acid (EIC) | 41.90 | 0.14 |
| MOL000354 | isorhamnetin | 49.60 | 0.31 |
| MOL000357 | Sitogluside | 20.63 | 0.62 |
| MOL000358 | beta-sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| MOL000422 | kaempferol | 41.88 | 0.24 |
| MOL000432 | linolenic acid | 45.01 | 0.15 |
| MOL005935 | N-[6-(9-acridinylamino) hexyl]benzamide | 41.70 | 0.78 |
| MOL005940 | quercetin-3'-methyl ether | 46.44 | 0.3 |
| MOL000098 | quercetin | 46.43 | 0.28 |
| MOL000415 | rutin | 3.20153 | - |
| Gene | Uniprot ID | PDB | Refinement resolution | Docking molecule | CDOCKER-ENERGY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | P05231 | 1ALU | 1.9A | quercetin | 35.587 4 |
| AKT1 | P31749 | 1UNQ | 0.98A | quercetin | 51.894 3 |
| kaempferol | 68.900 4 | ||||
| TNF | P01375 | 5UUI | 1.4A | quercetin | 26.816 3 |
| kaempferol | 34.701 2 | ||||
| IL-1β | P01584 | 5R8Q | 1.23A | quercetin | 47.096 9 |
| TP53 | P04637 | 5MHC | 1.2A | quercetin | 59.838 6 |
表3 靶点的筛选及对接结果
Tab.3 Target screening and docking results
| Gene | Uniprot ID | PDB | Refinement resolution | Docking molecule | CDOCKER-ENERGY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | P05231 | 1ALU | 1.9A | quercetin | 35.587 4 |
| AKT1 | P31749 | 1UNQ | 0.98A | quercetin | 51.894 3 |
| kaempferol | 68.900 4 | ||||
| TNF | P01375 | 5UUI | 1.4A | quercetin | 26.816 3 |
| kaempferol | 34.701 2 | ||||
| IL-1β | P01584 | 5R8Q | 1.23A | quercetin | 47.096 9 |
| TP53 | P04637 | 5MHC | 1.2A | quercetin | 59.838 6 |
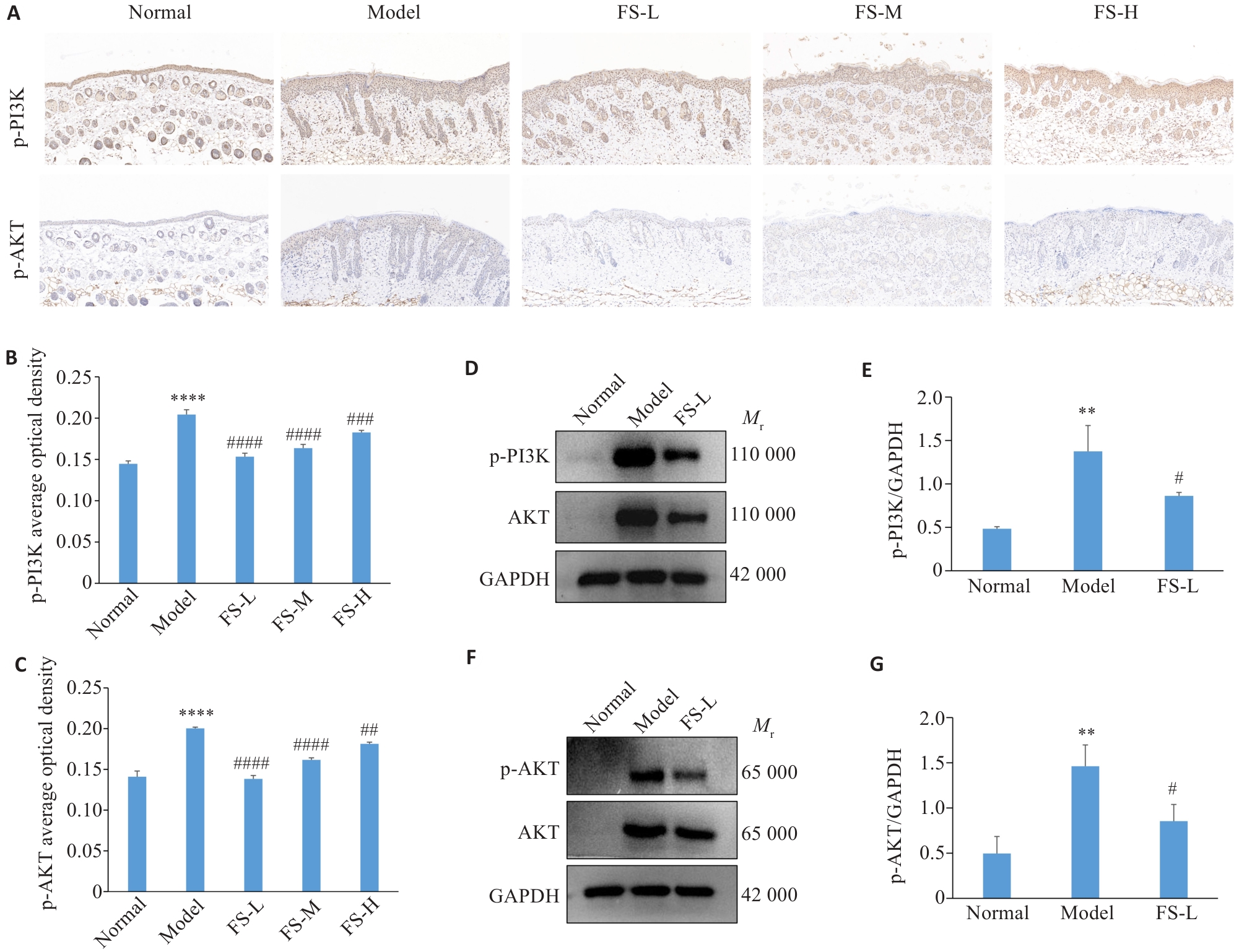
图4 银屑病小鼠皮肤组织PI3K/AKT的表达
Fig.4 Expression of PI3K and AKT in the skin tissue of psoriasis mice. A: results of immunohistochemistry (×20). B, C: AOD diagram. D, F: Results of Western blotting for p-PI3K, PI3K, p-AKT, and AKT. E, G: Quantitative analysis of the protein expressions. **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001 vs Normal; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001, ####P<0.0001 vs Model.
| [1] | Armstrong AW, Read C. Pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment of psoriasis: a review[J]. JAMA, 2020, 323(19): 1945-60. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.4006 |
| [2] | 胡安徽. 槐花入药的本草考证[J]. 中成药, 2018, 40(11): 2587-9. |
| [3] | Chen YT, Long PT, Xu HX, et al. The inhibitory activity of Flos Sophorae Immaturus extract and its major flavonoid components on pancreatic lipase[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2024, 277(Pt 1): 134092. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134092 |
| [4] | Zhang ZL, Zhang YR, Zhang AN, et al. Flos Sophorae Immaturus extracts: Effects of different extraction solvents on antioxidant, antimicrobial activities and active ingredients[J]. S Afr N J Bot, 2024, 170: 358-66. doi:10.1016/j.sajb.2024.05.045 |
| [5] | Peters RA, Shorthouse M. Identification of a volatile constituent formed by homogenates of Acacia georginae exposed to fluoride[J]. Nature, 1971, 231(5298): 123-4. doi:10.1038/231123a0 |
| [6] | Mou QQ, He JX, Yin RL, et al. Response surface optimized infrared-assisted extraction and UHPLC determination of flavonoid types from Flos sophorae[J]. Molecules, 2017, 22(6): 1000. doi:10.3390/molecules22061000 |
| [7] | 张 珩, 石晓琳. 槐米总黄酮的抗炎和镇痛作用[J]. 临床医学研究与实践, 2018, 3(31): 4-6. |
| [8] | Kim JM, Lee JH, Lee GS, et al. Sophorae Flos extract inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation by suppressing the NF-κB/NFATc1 pathway in mouse bone marrow cells[J]. BMC Complement Altern Med, 2017, 17(1): 164. doi:10.1186/s12906-017-1745-9 |
| [9] | 任晓莉, 杨 璐, 乔 鹏, 等. 复合酶法提取槐花多糖的工艺优化及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业科技, 2024, 45(7): 8-14. doi:10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2023070216 |
| [10] | 蒋 楠, 王富静, 封 亮, 等. 基于非酶糖基化反应的槐花抑制AGEs形成的活性组分筛选[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2019, 44(14): 3100-6. doi:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190424.201 |
| [11] | 强 燕, 王瑞平, 孙晓颖, 等. 银屑病血热证中药治疗用药规律及疗效分析[J]. 中国皮肤性病学杂志, 2020, 34(9): 1073-7. |
| [12] | 翟永丽. 凉血活血汤治疗银屑病98例[J]. 实用中医药杂志, 2015, 31(3): 208. |
| [13] | 张 玲. 段行武治疗寻常型银屑病经验[J]. 中国民间疗法, 2017, 25(4): 4-5. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-5798.2017.04.005 |
| [14] | 明瑞蕊, 张彦琼, 徐 颖, 等. 基于网络药理学和实验验证探讨盘龙七片从PI3K/AKT信号通路干预大鼠椎动脉型颈椎病的机制[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2022, 47(16): 4454-61. |
| [15] | Tang ZL, Zhang K, Lv SC, et al. LncRNA MEG3 suppresses PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway to enhance autophagy and inhibit inflammation in TNF-α-treated keratinocytes and psoriatic mice[J]. Cytokine, 2021, 148: 155657. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155657 |
| [16] | Langley RG, Ellis CN. Evaluating psoriasis with psoriasis area and severity index, psoriasis global assessment, and lattice system physician's global assessment[J]. J Am Acad Dermatol, 2004, 51(4): 563-9. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.04.012 |
| [17] | 王胜利, 于 虹, 李超群, 等. 制备色谱法从槐米中同时精制芦丁和槲皮素[J]. 食品科技, 2022, 47(2): 245-50. |
| [18] | Ma J, Wang FF, Wang L, et al. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/GLUT1 signaling pathway by quercetin in the treatment of psoriasis[J]. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed), 2025, 30(2): 26884. doi:10.31083/fbl26884 |
| [19] | 贺凌宇. 从“血” 论治银屑病[J]. 中国临床医生杂志, 2025, 53(1): 116-9. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-8552.2025.01.030 |
| [20] | 叶晟桢, 凌桂华, 肖 敏, 等. 基于四川地域特色探讨寻常性银屑病的中医治疗[J]. 皮肤科学通报, 2024, 41(3): 348-51. doi:10.13735/j.cjdv.1001-7089.202208209 |
| [21] | Georgescu SR, Tampa M, Caruntu C, et al. Advances in understanding the immunological pathways in psoriasis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(3): 739. doi:10.3390/ijms20030739 |
| [22] | Boehncke WH, Brembilla NC. Unmet needs in the field of psoriasis: pathogenesis and treatment[J]. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol, 2018, 55(3): 295-311. doi:10.1007/s12016-017-8634-3 |
| [23] | Mercurio L, Albanesi C, Madonna S. Recent updates on the involvement of PI3K/AKT/mTOR molecular cascade in the pathogenesis of hyperproliferative skin disorders[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2021, 8: 665647. doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.665647 |
| [24] | Buerger C. Epidermal mTORC1 signaling contributes to the pathogenesis of psoriasis and could serve as a therapeutic target[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 2786. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.02786 |
| [25] | Liu JL, Li LY, He GH. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction conditions for five major bioactive compounds from Flos sophorae immaturus (cultivars of Sophora Japonica L.) using response surface methodology[J]. Molecules, 2016, 21(3): 296. doi:10.3390/molecules21030296 |
| [26] | Teng Y, Fan YB, Ma JW, et al. The PI3K/Akt pathway: emerging roles in skin homeostasis and a group of non-malignant skin disorders[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(5): 1219. doi:10.3390/cells10051219 |
| [27] | Guo J, Zhang HY, Lin WR, et al. Signaling pathways and targeted therapies for psoriasis[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 437. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01655-6 |
| [28] | 王 昊, 冉立伟, 惠 珂, 等. Survivin和PI3K、AKT在寻常型银屑病皮损角质形成细胞中的表达及其相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2017, 37(11): 1512-6. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2017.11.14 |
| [29] | 张梦欣, 高铭淑, 周宇航, 等. 基于MAPK/NF-κB通路研究丹参白疕消方联合甲氨蝶呤治疗银屑病的作用机制[J]. 中草药, 2025, 56(12): 4316-26. |
| [30] | Wang MX, Ma XX, Gao CJ, et al. Rutin attenuates inflammation by downregulating AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in psoriasis: Network pharmacology analysis and experimental evidence[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 125(Pt A): 111033. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111033 |
| [31] | 杨素清, 林 立, 王姗姗. 花类药治疗银屑病经验[J]. 吉林中医药, 2021, 41(11): 1450-3. |
| [1] | 呼琴, 金华. 清肾颗粒通过调控miR-23b及Nrf2通路改善慢性肾脏病湿热证患者的肾功能:基于网络药理学和临床试验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1867-1879. |
| [2] | 杨子为, 吕畅, 董柱, 计书磊, 毕生辉, 张雪花, 王晓武. 金樱子通过调控Src-AKT1轴抑制肺动脉高压平滑肌增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1889-1902. |
| [3] | 云琦, 杜若丽, 贺玉莹, 张贻欣, 王佳慧, 叶红伟, 李正红, 高琴. 肉桂酸通过抑制TLR4减轻阿霉素诱导的小鼠心肌损伤铁死亡的发生[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1946-1958. |
| [4] | 陈鑫源, 吴成挺, 李瑞迪, 潘雪芹, 张耀丹, 陶俊宇, 林才志. 双术汤通过P53/SLC7A11/GPX4通路诱导胃癌细胞铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [5] | 王立明, 陈宏睿, 杜燕, 赵鹏, 王玉洁, 田燕歌, 刘新光, 李建生. 益气滋肾方通过抑制PI3K/Akt/NF-κB通路改善小鼠慢性阻塞性肺疾病的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [6] | 朱胤福, 李怡燃, 王奕, 黄颖而, 龚昆翔, 郝文波, 孙玲玲. 桂枝茯苓丸活性成分常春藤皂苷元通过抑制JAK2/STAT3通路抑制宫颈癌细胞的生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [7] | 何丽君, 陈晓菲, 闫陈昕, 师林. 扶正化积汤治疗非小细胞肺癌的分子机制:基于网络药理学及体外实验验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152. |
| [8] | 李国永, 黎仁玲, 刘艺婷, 柯宏霞, 李菁, 王新华. 牛蒡子治疗小鼠病毒性肺炎后肺纤维化的机制:基于代谢组学、网络药理学和实验验证方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [9] | 管丽萍, 颜燕, 卢心怡, 李智峰, 高晖, 曹东, 侯晨曦, 曾靖宇, 李欣怡, 赵洋, 王俊杰, 方会龙. 复方积雪草减轻小鼠日本血吸虫引起的肝纤维化:通过调控TLR4/MyD88通路抑制炎症-纤维化级联反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [10] | 唐培培, 谈勇, 殷燕云, 聂晓伟, 黄菁宇, 左文婷, 李玉玲. 调周滋阴方治疗早发性卵巢功能不全的疗效、安全性及作用机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| [11] | 梁晓涛, 熊一凡, 刘雪琪, 梁小珊, 朱晓煜, 谢炜. 活血疏风颗粒通过抑制TLR4/NF-κB通路改善慢性偏头痛小鼠的中枢敏化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 986-994. |
| [12] | 冉念东, 刘杰, 徐剑, 张永萍, 郭江涛. 黑骨藤正丁醇萃取成分治疗大鼠阿尔茨海默病的药效学及作用机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 785-798. |
| [13] | 徐皓男, 张放, 黄钰莹, 姚其盛, 管悦琴, 陈浩. 百蕊草通过调节肠道菌群和调控EGFR/PI3K/Akt信号通路改善小鼠抗生素相关性腹泻[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [14] | 高俊杰, 叶开, 吴竞. 槲皮素通过调控TP53基因抑制肾透明细胞癌的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 313-321. |
| [15] | 裴月娇, 刘慧敏, 昕宇, 刘波. miR-124通过调控PI3K/AKT信号通路改善睡眠剥夺大鼠认知功能[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 340-346. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||