南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 901-910.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.05.02
田芷华( ), 杨青青, 陈欣, 张方方, 钟柏茂(
), 杨青青, 陈欣, 张方方, 钟柏茂( ), 曹虹(
), 曹虹( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-19
出版日期:2025-05-20
发布日期:2025-05-23
通讯作者:
钟柏茂,曹虹
E-mail:17837178813@163.com;zbm@dgp-institute.com;gzhcao@smu.edu.cn
作者简介:田芷华,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 17837178813@163.com
基金资助:
Zhihua TIAN( ), Qingqing YANG, Xin CHEN, Fangfang ZHANG, Baimao ZHONG(
), Qingqing YANG, Xin CHEN, Fangfang ZHANG, Baimao ZHONG( ), Hong CAO(
), Hong CAO( )
)
Received:2024-12-19
Online:2025-05-20
Published:2025-05-23
Contact:
Baimao ZHONG, Hong CAO
E-mail:17837178813@163.com;zbm@dgp-institute.com;gzhcao@smu.edu.cn
摘要:
目的 基于巨噬细胞中GBP5调控NLRP3炎症小体活化,探究精胺(Spm)治疗肠道病毒71型(EV71)感染引起的重症手足口病的机制。 方法 体内实验:将3~5 d龄的BALB/c乳鼠随机分为对照组(CON组)、感染组(EV71组)、治疗组(SPM组),感染组和治疗组每只腹腔注射浓度为1×106半数组织培养感染剂量(TCID50)病毒液50 μL,治疗组在注射病毒3 d后注射100 μmol/L 精胺50 μL,对照组腹腔注射无菌PBS 50 μL。观察小鼠状态1周,提取小鼠心、肝、肺及肾组织全蛋白、RNA及组织切片,Western blotting、qPCR检测小鼠组织GBP5、NLRP3、CXCL10、TNFSF10表达水平,HE染色观察小鼠组织损伤及炎症细胞浸润状况,免疫组化法观察组织巨噬细胞浸润情况及GBP5的表达水平。体外实验:分别设置对照组(CON组)、感染组(EV71组)、治疗组(SPM组)、多胺生物合成抑制剂组。提取THP-1及RAW细胞RNA,通过RT-PCR检测细胞GBP5、NLRP3、CXCL10、TNFSF10表达水平。 结果 与对照组相比,小鼠在感染EV71后心、肝、肺及肾组织出现明显损伤,其中心、肺组织中明显观察到巨噬细胞的浸润。心、肝、肺及肾组织中GBP5、NLRP3、CXCL10、TNFSF10表达水平明显升高(P<0.05);经精胺治疗后,与感染组相比治疗组小鼠组织损伤明显改善,心、肺组织中的巨噬细胞浸润减少。精胺治疗后小鼠心、肝、肺及肾组织中NLRP3、GBP5、CXCL10、TNFSF10表达水平降低(P<0.05)。在THP-1及RAW细胞中发现,感染EV71病毒后GBP5、NLRP3、CXCL10、TNFSF10表达升高(P<0.05),经精胺治疗后细胞中GBP5、NLRP3、CXCL10、TNFSF10表达降低(P<0.05)。在THP-1细胞中使用多胺生物合成抑制剂减少精胺合成可改善由GBP5 siRNA干扰引起的GBP5、NLRP3、CXCL10、TNFSF10表达降低(P<0.05)。 结论 精胺治疗可以降低EV71感染引起的巨噬细胞中GBP5介导的NLRP3炎症小体活化,减少炎症因子释放从而发挥治疗儿童重症手足口病的作用。
田芷华, 杨青青, 陈欣, 张方方, 钟柏茂, 曹虹. 精胺抑制巨噬细胞中GBP5介导的NLRP3炎性小体活化减轻感染肠道病毒71型的新生小鼠脏器损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 901-910.
Zhihua TIAN, Qingqing YANG, Xin CHEN, Fangfang ZHANG, Baimao ZHONG, Hong CAO. Spermine suppresses GBP5-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages to relieve vital organ injuries in neonatal mice with enterovirus 71 infection[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 901-910.
| Gene | Forward (5' to 3') | Reverse (5' to 3') |
|---|---|---|
| NLRP3 | ATTACCCGCCCGAGAAAGG | CATGAGTGTGGCTAGATCCAAG |
| M-NLRP3 | ATTACCCGCCCGAGAAAGG | CATGAGTGTGGCTAGATCCAAG |
| GBP5 | CCATGTGCCTCATCGAGAACT | ACAGGTTGCGTAATGGCAGAC |
| M-GBP5 | CAGACCTATTTGAACGCCAAAGA | TGCCTTGATTCTATCAGCCTCT |
| CXCL10 | GTGGCATTCAAGGAGTACCTC | TGATGGCCTTCGATTCTGGATT |
| M-CXCL10 | CCAAGTGCTGCCGTCATTTTC | GGCTCGCAGGGATGATTTCAA |
| TNFSF10 | TGCGTGCTGATCGTGATCTTC | GCTCGTTGGTAAAGTACACGTA |
| M-TNFSF10 | ATGGTGATTTGCATAGTGCTCC | GCAAGCAGGGTCTGTTCAAGA |
| ACTIN | CATGTACGTTGCTATCCAGGC | CTCCTTAATGTCACGCACGAT |
| M-ACTIN | ATGACCCAAGCCGAGAAGG | CGGCCAAGTCTTAGAGTTGTTG |
表1 qPCR引物序列
Tab.1 Primers used for qPCR
| Gene | Forward (5' to 3') | Reverse (5' to 3') |
|---|---|---|
| NLRP3 | ATTACCCGCCCGAGAAAGG | CATGAGTGTGGCTAGATCCAAG |
| M-NLRP3 | ATTACCCGCCCGAGAAAGG | CATGAGTGTGGCTAGATCCAAG |
| GBP5 | CCATGTGCCTCATCGAGAACT | ACAGGTTGCGTAATGGCAGAC |
| M-GBP5 | CAGACCTATTTGAACGCCAAAGA | TGCCTTGATTCTATCAGCCTCT |
| CXCL10 | GTGGCATTCAAGGAGTACCTC | TGATGGCCTTCGATTCTGGATT |
| M-CXCL10 | CCAAGTGCTGCCGTCATTTTC | GGCTCGCAGGGATGATTTCAA |
| TNFSF10 | TGCGTGCTGATCGTGATCTTC | GCTCGTTGGTAAAGTACACGTA |
| M-TNFSF10 | ATGGTGATTTGCATAGTGCTCC | GCAAGCAGGGTCTGTTCAAGA |
| ACTIN | CATGTACGTTGCTATCCAGGC | CTCCTTAATGTCACGCACGAT |
| M-ACTIN | ATGACCCAAGCCGAGAAGG | CGGCCAAGTCTTAGAGTTGTTG |
| siRNA | Sense (5'-3') | Antisense (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| NC | UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT | ACGUGACACGUCGGAGAATT |
| S1 | GCCAAAUCACACAUTT | AACUAAUGUGUGAUUUGGCTT |
| S2 | GGAAAUAGAUGGGCAACUUTT | AAGUUGCCCAUCUAUUUCCTT |
| S3 | CCAGCAAAUGGGCCAGAAATT | UUUCUGGCCCAUUUGCUGGTT |
表2 GBP5 siRNA序列
Tab.2 GBP5 siRNA sequences
| siRNA | Sense (5'-3') | Antisense (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| NC | UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT | ACGUGACACGUCGGAGAATT |
| S1 | GCCAAAUCACACAUTT | AACUAAUGUGUGAUUUGGCTT |
| S2 | GGAAAUAGAUGGGCAACUUTT | AAGUUGCCCAUCUAUUUCCTT |
| S3 | CCAGCAAAUGGGCCAGAAATT | UUUCUGGCCCAUUUGCUGGTT |
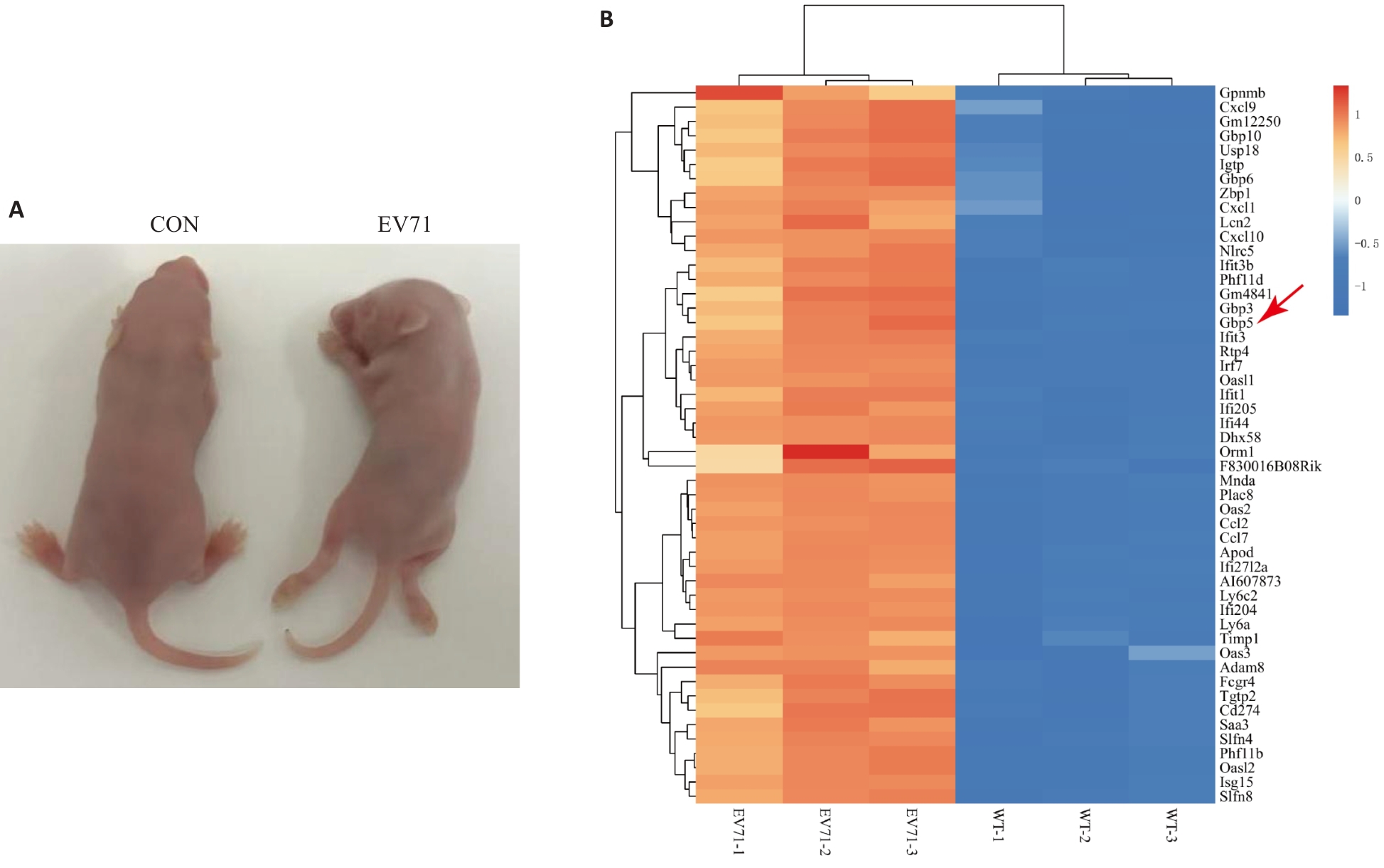
图1 建立EV71感染的重症手足口病小鼠模型
Fig.1 Establishment of a mouse model of severe hand, foot and mouth disease induced by EV71 infection. A: Observation of mice on the third day following intraperitoneal EV71 injection (Left: Control group; Right: EV71 infection group). B: TOP50 differential genes with increased expression by transcriptome sequencing of the muscular tissues.
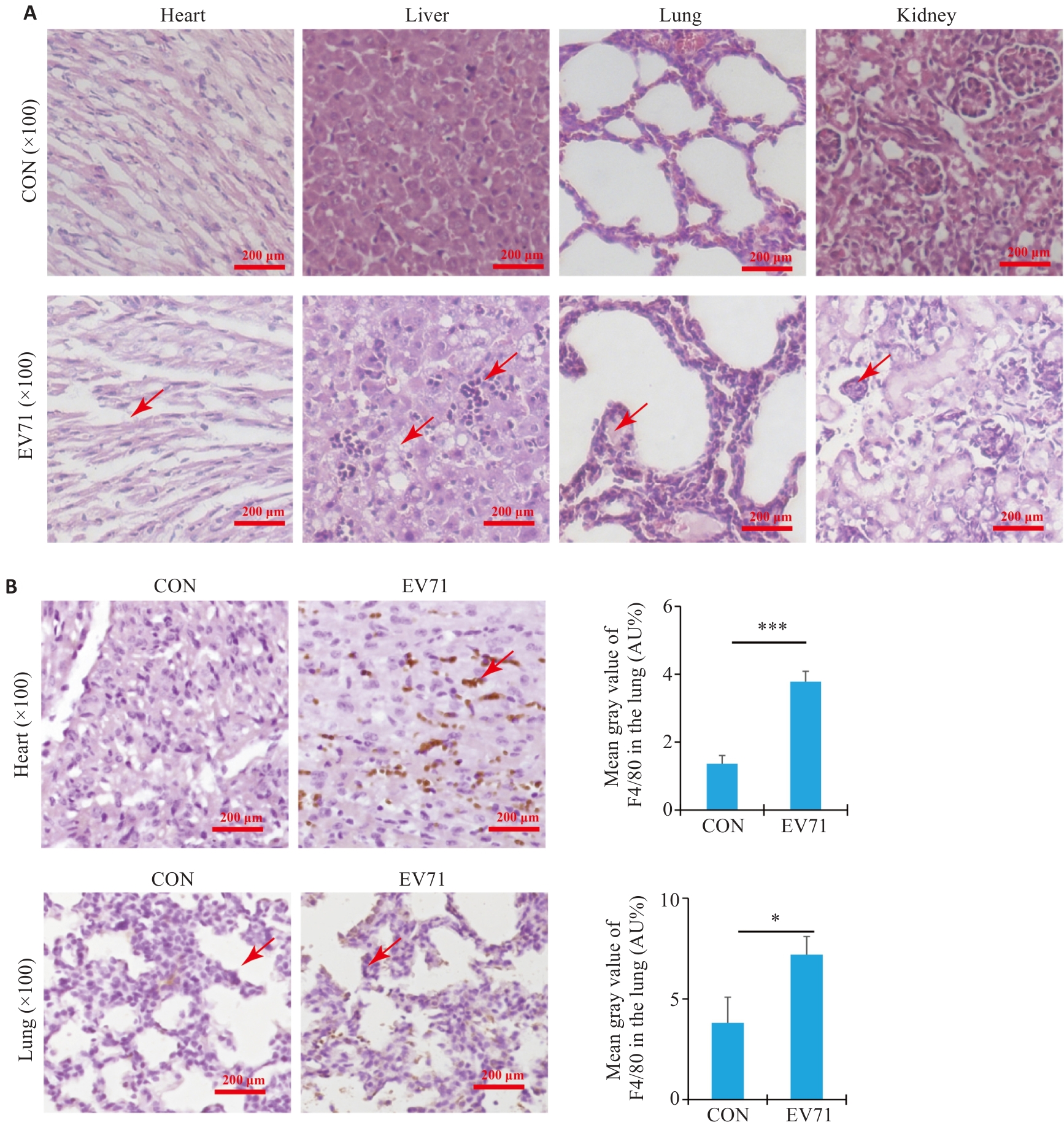
图2 感染EV71对小鼠组织的影响
Fig.2 Pathologies in the heart, liver, lung and kidney tissue of the mice with EV71 infection. A: Histopathological examination with HE staining for assessing tissue damages. Arrows indicate the area of pathological change. B: Immunohistochemical staining for detecting the expression of F4/80 in the heart and lungs of the mice. Arrows indicate IHC positive cells for F4/80 (*P<0.05, ***P<0.0001).
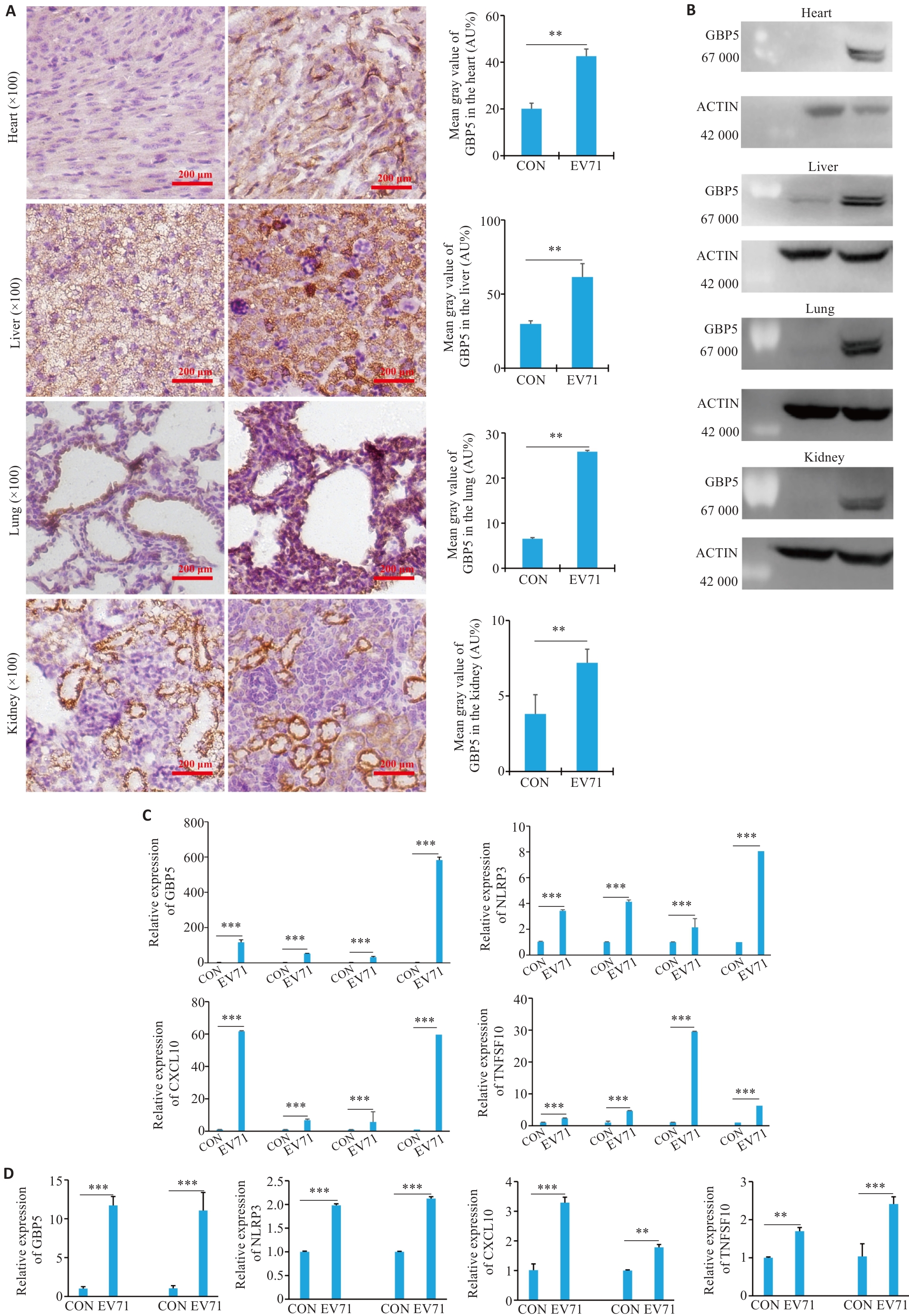
图3 感染EV71后小鼠及巨噬细胞中GBP5、NLRP3及CXCL10、TNFSF10的表达情况
Fig.3 Expressions of GBP5, NLRP, CXCL10 and TNFSF10 in neonatal mice and cultured macrophages with EV71 infection. A: Immunohistochemical staining for detecting the expression of GBP5 in the heart, liver, lung, and kidney of the mice. B-D: Western blotting and qPCR for detecting the expression of GBP5, NLRP, CXCL10 and TNFSF10 in EV71-infected mice (from left to right: heart, liver, lung and kidney) and cultured THP-1 (left) and RAW (right) cells. **P<0.001, ***P<0.0001.

图4 精胺治疗对EV71感染的重症手足口病小鼠的影响
Fig.4 Therapeutic effect of spermine in neonatal mouse models of severe hand, foot and mouth disease induced by EV71 infection. A: Observation of the mice on the third day following intraperitoneal injection of spermine (from left to right: control group, EV71 infection group, and spermine treatment group). B: Histopathological examination for assessing heart, liver, lung, and kidney damage in the mice in different groups (HE staining). Arrows indicate the area of pathological change. C: Immunohistochemical staining for detecting the expression of F4/80 in the heart and lung tissues. Arrows indicate IHC positive cells for F4/80. **P<0.001, ***P<0.0001.
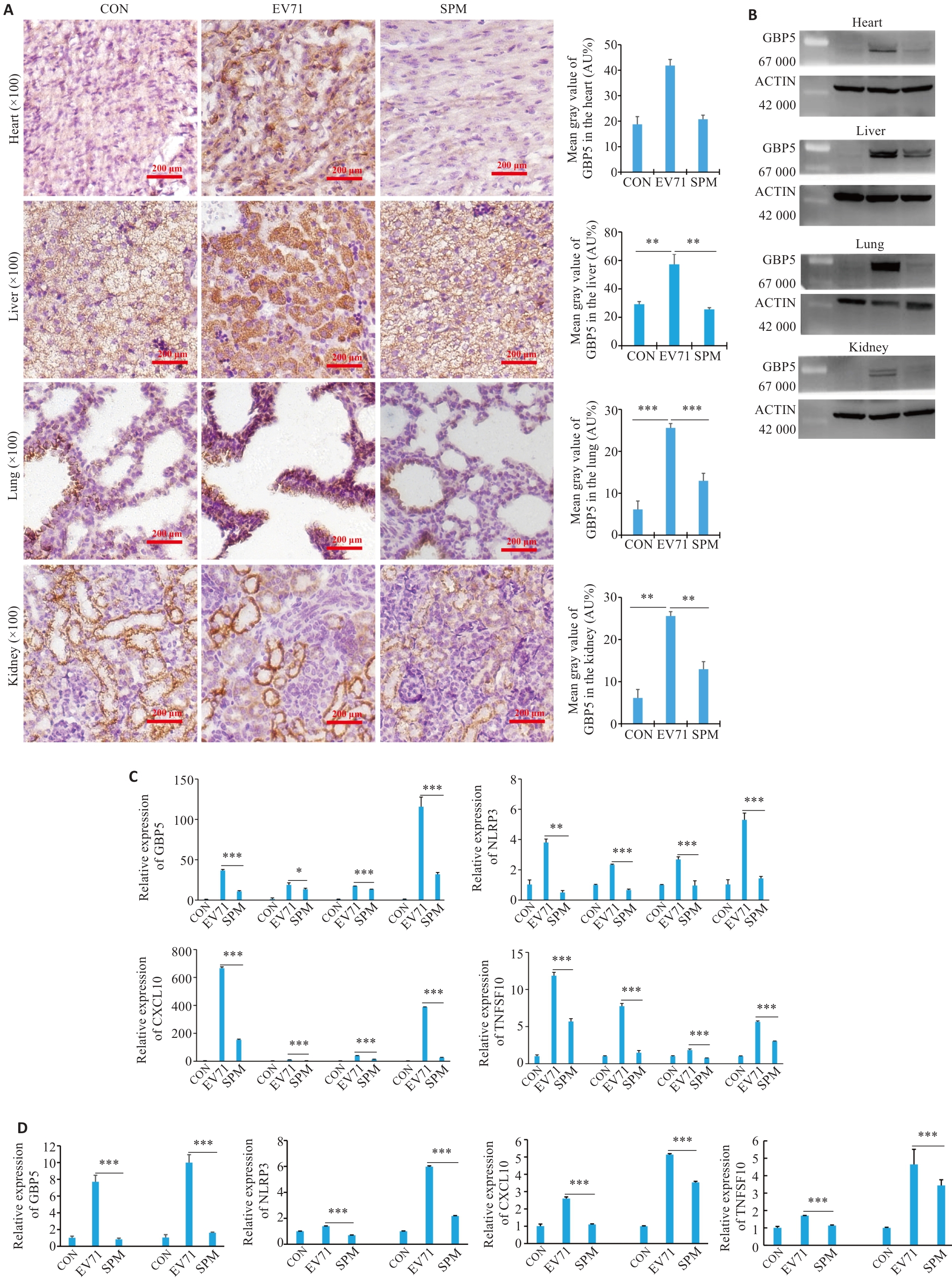
图5 精胺治疗后小鼠及巨噬细胞中GBP5、NLRP3及CXCL10、TNFSF10的表达情况
Fig.5 Expressions of GBP5, NLRP, CXCL10 and TNFSF10 in vital organs of EV71-infected mice and in infected macrophages after spermidine treatment. A: Immunohistochemical staining for detecting the expression of GBP5 in the heart, liver, lung and kidney tissues. B-D: Western blotting and qPCR of the expressions of GBP5, NLRP, CXCL10 and TNFSF10 in EV71-infected mice and macrophages following spermine treatment. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
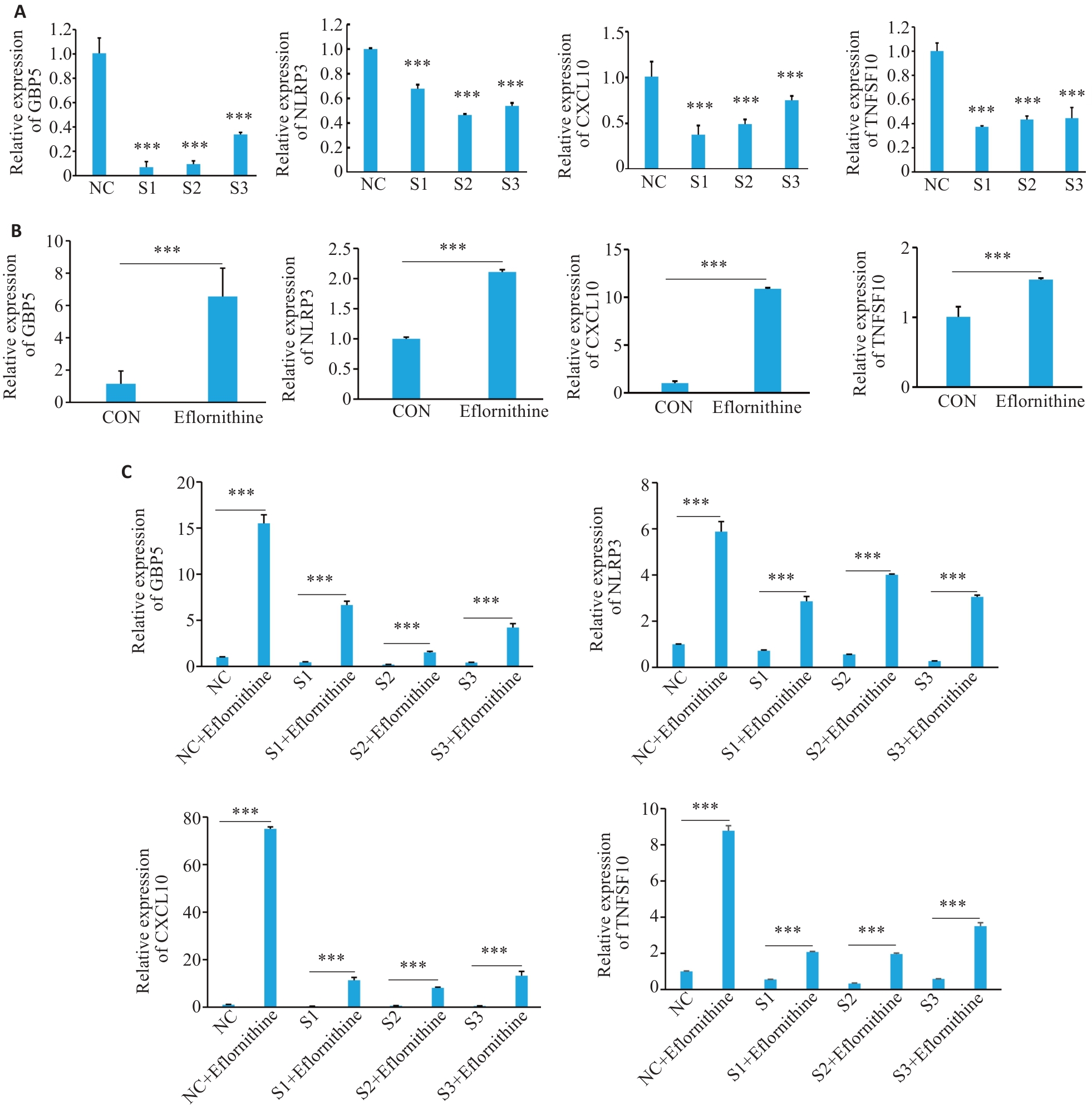
图6 在巨噬细胞中抑制精胺合成GBP5、NLRP3及CXCL10、TNFSF10的表达情况
Fig.6 Effect of spermine synthesis inhibition on GBP5, NLRP, CXCL10 and TNFSF10 expressions in macrophages. A: qPCR for detecting the mRNA expressions of GBP5, NLRP, CXCL10 and TNFSF10 after inhibiting GBP5 expression. ***P<0.001 vs NC. B: qPCR for examining the expressions of GBP5, NLRP, CXCL10 and TNFSF10 after inhibiting spermine synthesis. C: qPCR for examining the expressions of GBP5, NLRP, CXCL10 and TNFSF10 after inhibiting GBP5 and spermine synthesis simultaneously. ***P<0.001.
| 1 | 张 翠. 手足口病患儿的病原体研究进展[J]. 中国城乡企业卫生, 2024, 39(9): 38-40. |
| 2 | 韦欢欢, 朱俊萍, 何秋水. 手足口病主要病原变迁及分子进化研究[J]. 病毒学报, 2020, 36(5): 936-45. DOI: 10.13242/j.cnki.bingduxuebao.003704 |
| 3 | Qi ZJ, Li Z, Hao D, et al. Association between angiopoietin-2 and enterovirus 71 induced pulmonary edema[J]. Indian J Pediatr, 2016, 83(5): 391-6. |
| 4 | Zhang WJ, Huang ZG, Huang MY, et al. Predicting severe enterovirus 71-infected hand, foot, and mouth disease: cytokines and chemokines[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2020, 2020: 9273241. |
| 5 | Hao JF, Wang H, Lu XF, et al. TLR4 signalling: the key to controlling EV71 replication and inflammatory response[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2024, 14: 1393680. |
| 6 | Lu MY, Lin YL, Kuo YL, et al. Muscle tissue damage and recovery after EV71 infection correspond to dynamic macrophage phenotypes[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 648184. |
| 7 | Zhao DR, Guo XY, Lin BB, et al. Magnolol against enterovirus 71 by targeting Nrf2-SLC7A11-GSH pathway[J]. Biomed Pharm-acother, 2024, 176: 116866. |
| 8 | Sheu KM, Hoffmann A. Functional hallmarks of healthy macrophage responses: their regulatory basis and disease relevance[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2022, 40:295-321. |
| 9 | Wang HB, Lei XB, Xiao X, et al. Reciprocal regulation between enterovirus 71 and the NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Cell Rep, 2015, 12(1): 42-8. |
| 10 | Cui J, Chen YJ, Wang HY, et al. Mechanisms and pathways of innate immune activation and regulation in health and cancer[J]. Hum Vaccin Immunother, 2014, 10(11): 3270-85. |
| 11 | Li JM, Deng HS, Yao YD, et al. Sinomenine ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by targeting GBP5 and regulating the P2X7 receptor to suppress NLRP3-related signaling pathways[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2023, 44(12): 2504-24. |
| 12 | Shenoy AR, Wellington DA, Kumar P, et al. GBP5 promotes NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and immunity in mammals[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6080): 481-5. |
| 13 | Schilperoort M, Ngai D, Sukka SR, et al. The role of efferocytosis-fueled macrophage metabolism in the resolution of inflammation[J]. Immunol Rev, 2023, 319(1):65-80. |
| 14 | Viola A, Munari F, Sánchez-Rodríguez R, et al. The metabolic sign-ature of macrophage responses[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 1462. |
| 15 | Zhang YZ, Yang QQ, Peng Q, et al. Impaired arginine/ornithine metabolism drives severe HFMD by promoting cytokine storm[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15: 1407035. |
| 16 | Bělíček J, Ľuptáková E, Kopečný D, et al. Biochemical and structural basis of polyamine, lysine and ornithine acetylation catalyzed by spermine/spermidine N-acetyl transferase in moss and maize[J]. Plant J, 2023, 114(3):482-98. |
| 17 | Suppola S, Heikkinen S, Parkkinen JJ, et al. Concurrent overex-pression of ornithine decarboxylase and spermidine/spermine N(1)-acetyltransferase further accelerates the catabolism of hepatic pol-yamines in transgenic mice[J]. Biochem J, 2001, 358(Pt 2): 343-8. |
| 18 | Gao YJ, Liu KY, Xiao WF, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor confers protection against macrophage pyroptosis and intestinal inflammation through regulating polyamine biosynthesis[J]. Theranostics, 2024, 14(11): 4218-39. |
| 19 | Makhoba XH, Makumire S. The capture of host cell's resources: The role of heat shock proteins and polyamines in SARS-COV-2 (COVID-19) pathway to viral infection[J]. Biomol Concepts, 2022, 13(1):220-29. |
| 20 | Chang CS, Liao CC, Liou AT, et al. Enterovirus 71 targets the cardiopulmonary system in a robust oral infection mouse model[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 11108. |
| 21 | Abplanalp WT, Cremer S, John D, et al. Clonal hematopoiesis-driver DNMT3A mutations alter immune cells in heart failure[J]. Circ Res, 2021, 128(2): 216-28. |
| 22 | Al-Qazazi R, Lima PDA, Prisco SZ, et al. Macrophage-NLRP3 Activation Promotes Right Ventricle Failure in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2022, 206(5):608-24. |
| 23 | Siebeler R, de Winther MPJ, Hoeksema MA. The regulatory landscape of macrophage interferon signaling in inflammation[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2023, 152(2):326-37. |
| 24 | Locati M, Curtale G, Mantovani A. Diversity, mechanisms, and significance of macrophage plasticity[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2020, 15: 123-47. |
| 25 | Shapouri-Moghaddam A, Mohammadian S, Vazini H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233(9): 6425-40. |
| 26 | Fujiwara Y, Hizukuri Y, Yamashiro K, et al. Guanylate-binding protein 5 is a marker of interferon-γ-induced classically activated macrophages[J]. Clin Transl Immunology, 2016, 5(11): e111. |
| 27 | Zhang J, Zhang YH, Chen Q, et al. The XPO1 inhibitor selinexor ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice via GBP5/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 130: 111734. |
| 28 | Yang L, Chu Z, Liu M, et al. Amino acid metabolism in immune cells: essential regulators of the effector functions, and promising opportunities to enhance cancer immunotherapy[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2023, 16(1):59. |
| 29 | Zhao HX, Raines LN, Huang SC. Carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism as hallmarks for innate immune cell activation and function[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(3): 562. |
| 30 | Cetin N, Dasdelen D, Mogulkoc R, et al. Role of exogenous putrescine in the status of energy, DNA damage, inflammation, and spermidine/spermine-n(1)‑acetyltransferase in brain ischemia-reperfusion in rats[J]. Iran J Basic Med Sci, 2022, 25(5):597-60. |
| 31 | Chen J, Rao JN, Zou TT, et al. Polyamines are required for expression of Toll-like receptor 2 modulating intestinal epithelial barrier integrity[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2007, 293(3): G568-76. |
| 32 | Jiang JT, Wang WW, Sun F, et al. Bacterial infection reinforces host metabolic flux from arginine to spermine for NLRP3 inflammasome evasion[J]. Cell Rep, 2021, 34(10): 108832. |
| [1] | 周海忆, 何斯怡, 韩瑞芳, 关永格, 董丽娟, 宋阳. 艾灸通过调控miR-223-3p/NLRP3焦亡通路修复薄型子宫内膜[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1380-1388. |
| [2] | 涂舒谕, 陈祥宇, 李程辉, 黄丹萍, 张莉. 补阳还五汤通过调控外泌体miR-590-5p介导的巨噬细胞极化延缓大鼠血管衰老[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1251-1259. |
| [3] | 牛民主, 殷丽霞, 乔通, 尹林, 张可妮, 胡建国, 宋传旺, 耿志军, 李静. 旱莲苷A通过调控JAK2/STAT3通路抑制M1型巨噬细胞极化改善葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1297-1306. |
| [4] | 卞芬兰, 倪诗垚, 赵鹏, 戚毛男星, 唐碧, 王洪巨, 康品方, 刘进军. 积雪草苷通过抑制NLRP3炎症体介导的细胞焦亡减轻大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 977-985. |
| [5] | 俞佳雯, 周薏, 钱春美, 穆蓝, 阙任烨. 铁过载诱导的小鼠肝纤维化过程影响巨噬细胞M2极化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 684-691. |
| [6] | 孙亚磊, 罗萌, 郭长胜, 高静, 苏凯奇, 陈立典, 冯晓东. 穗花杉双黄酮通过抑制细胞焦亡减轻小鼠急性肺损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 692-701. |
| [7] | 朱正望, 王琳琳, 赵静涵, 马瑞雪, 余雨春, 蔡庆春, 王兵, 朱平生, 苗明三. 退黄合剂通过调控法尼醇X受体抑制NLRP3炎症小体改善α-萘异硫氰酸酯诱导的大鼠胆汁淤积[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 718-724. |
| [8] | 邹金华, 王惠, 张冬艳. SLC1A5通过促进M2型巨噬细胞极化促进肝癌进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 269-284. |
| [9] | 罗维, 王宇航, 刘延松, 王媛媛, 艾磊. 高糖环境通过抑制免疫反应基因1的表达诱导巨噬细胞促炎性M1型极化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 1-9. |
| [10] | 李明远, 张玮, 华梦晴. 甲基巴多索龙通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化缓解小鼠急性肝损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1662-1669. |
| [11] | 陶怀祥, 骆金光, 闻志远, 虞亘明, 苏萧, 王鑫玮, 关翰, 陈志军. STING高表达通过调控TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3通路和影响炎症与凋亡水平促进小鼠肾脏缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1345-1354. |
| [12] | 张玮, 邓蒙蒙, 曾尧, 刘辰菲, 尚菲菲, 许文豪, 蒋昊轶, 王凤超, 杨燕青. 2,6-二甲氧基-1,4-苯醌通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化缓解小鼠的感染性休克[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1024-1032. |
| [13] | 刘鹏程, 娄丽娟, 刘霞, 王建, 姜颖. M2巨噬细胞特征基因风险评分能准确预测HBV相关肝细胞癌患者的预后[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 827-840. |
| [14] | 曹家樊, 孙 跃, 丁 鑫, 李盛文, 陈 博, 兰 天. 熊果苷通过抑制巨噬细胞募集并调控Akt/NF-κB和Smad信号通路改善小鼠肝纤维化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 652-659. |
| [15] | 范毅平, 罗梦琳, 黄东宗, 刘 琳, 傅 博, 王潇宇, 关淼升, 李鸿波. 缓释地塞米松改性丝胶蛋白水凝胶支架促进大鼠下颌骨缺损修复:基于调节巨噬细胞M2极化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 533-540. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||