南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 893-900.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.05.01
• • 下一篇
收稿日期:2024-11-01
出版日期:2025-05-20
发布日期:2025-05-23
通讯作者:
周礼华
E-mail:zhoulihuaby@sina.com
作者简介:周礼华,副教授,硕士生导师,E-mail:zhoulihuaby@sina.com
基金资助:
Lihua ZHOU( ), Xun ZHANG, Yingying YU, Panpan ZHANG
), Xun ZHANG, Yingying YU, Panpan ZHANG
Received:2024-11-01
Online:2025-05-20
Published:2025-05-23
Contact:
Lihua ZHOU
E-mail:zhoulihuaby@sina.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨Nrf2/HO-1抗氧化通路在氯氰菊酯(CYP)诱导的C57BL/6小鼠海马氧化损伤中的作用及其机制。 方法 将10周龄C57BL/6雄性小鼠随机分为对照组和CYP低剂量(5 mg/kg)、中剂量(10 mg/kg)、高剂量(20 mg/kg)组,连续3周经口灌胃染毒,检测海马组织丙二醛、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-PX)、总超氧化物歧化酶(T-SOD)及过氧化氢酶水平。HE染色观察海马组织细胞形态学变化。免疫荧光双标技术检测Nrf2/HO-1蛋白在海马锥体层神经元细胞中的表达。RT-qPCR及Western blotting检测Nrf2及其下游靶激酶HO-1的mRNA与蛋白表达。 结果 与对照组相比,CYP暴露组脂质过氧化产物丙二醛含量逐渐增加,GSH-PX、T-SOD、过氧化氢酶等抗氧化酶活性逐渐下降,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.01)。HE结果显示,海马CA1、CA3区锥体层神经元受损,且暴露剂量越高损伤越严重。免疫荧光结果显示,CYP暴露引起Nrf2细胞核易位,Nrf2/HO-1蛋白共表达增加。RT-qPCR与Western blotting结果显示,CYP暴露诱导Nrf2及其下游靶激酶HO-1 mRNA与蛋白表达上调(P<0.01)。 结论 抗氧化通路Nrf2/HO-1调控CYP诱导的C57BL/6小鼠海马氧化损伤,且损伤效应与暴露水平呈现剂量效应关系。
周礼华, 张汛, 郁瑛瑛, 张畔畔. Nrf2/HO-1抗氧化通路调控氯氰菊酯诱导的小鼠海马氧化损伤的机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 893-900.
Lihua ZHOU, Xun ZHANG, Yingying YU, Panpan ZHANG. Role of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in cypermethrin-induced oxidative injury of mice hippocampal neurons[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 893-900.
| Gene | Serial number | Primer sequences (5'-3') | Product size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nrf2 | NM_010902.4 | F: AGTCGCTTGCCCTGGATATC R: GAACAGCGGTAGTATCAGCCA | 216 bp |
| HO-1 | NM_010442.2 | F: GCTAAGACCGCCTTCCTGCT R: ACGAAGTGACGCCATCTGTGA | 105 bp |
| β-actin | NM_007393.3 | F: GTGACGTTGACATCCGTAAAGA R: GTAACAGTCCGCCTAGAAGCAC | 287 bp |
表1 荧光定量PCR扩增基因引物
Tab.1 Primers for RT-qPCR amplification of the target genes
| Gene | Serial number | Primer sequences (5'-3') | Product size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nrf2 | NM_010902.4 | F: AGTCGCTTGCCCTGGATATC R: GAACAGCGGTAGTATCAGCCA | 216 bp |
| HO-1 | NM_010442.2 | F: GCTAAGACCGCCTTCCTGCT R: ACGAAGTGACGCCATCTGTGA | 105 bp |
| β-actin | NM_007393.3 | F: GTGACGTTGACATCCGTAAAGA R: GTAACAGTCCGCCTAGAAGCAC | 287 bp |
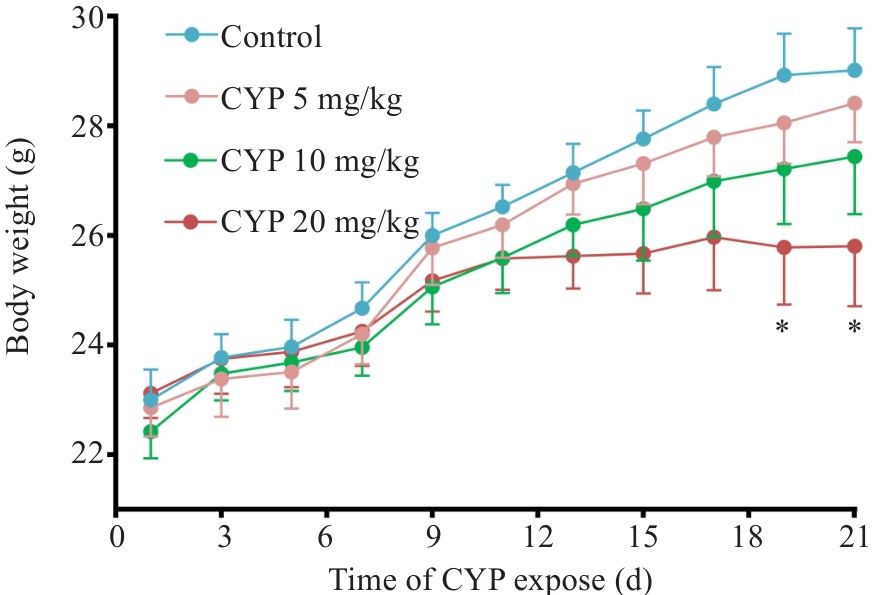
图1 CYP暴露对小鼠体质量的影响
Fig.1 Effects of oral cypermethrin (CYP) administration at 5, 10, or 20 mg/kg for 21 days on body weight of mice (Mean±SE, n=12). *P<0.05 vs Control.
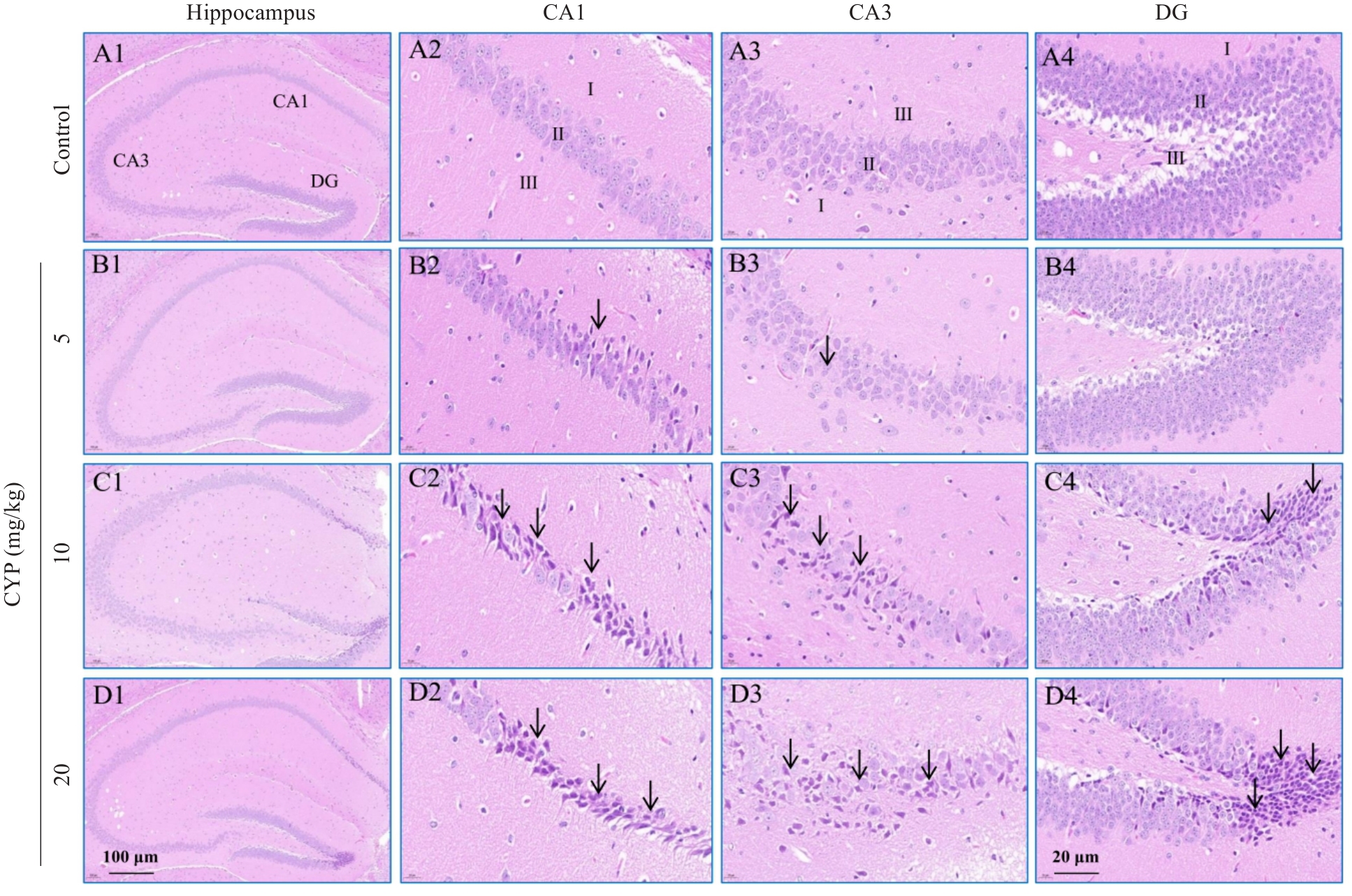
图3 HE染色观察海马区神经元细胞形态学变化
Fig.3 HE staining showing morphological alterations of the hippocampal neurons in control and CYP-treated mice. I: Molecular layer; II: Pyramidal layer in CA1 and CA3 regions (granular layer in DG); III: Polymorphic layer. black arrows: Chromatin condensation.
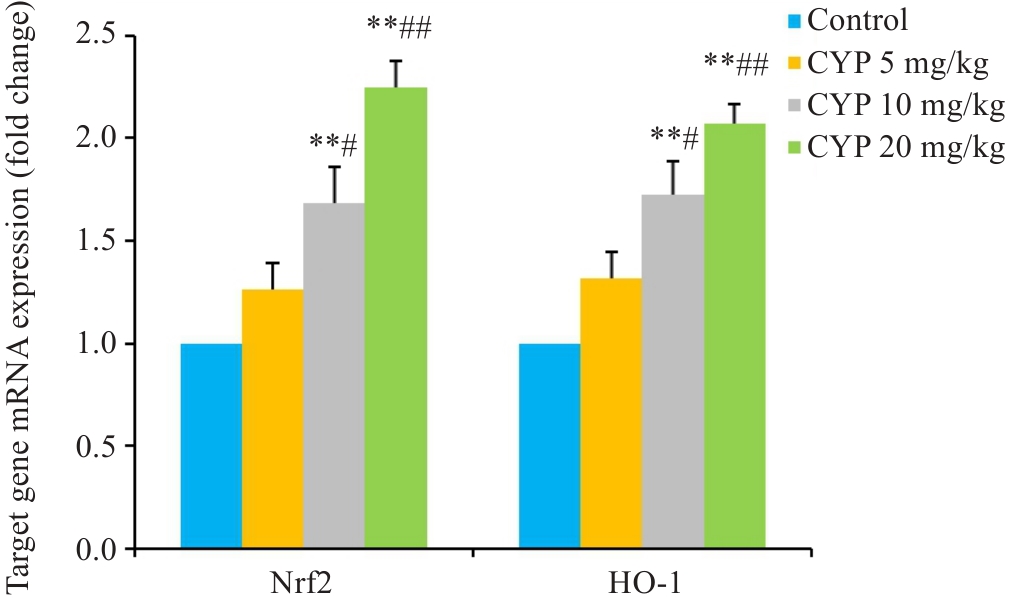
图5 RT-qPCR分析Nrf2和HO-1 mRNA表达
Fig.5 Transcription levels of Nrf2 and HO-1 in mice hippocampus analyzed using RT-qPCR. n=9. **P<0.01 vs Control; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs CYP 5 mg/kg.
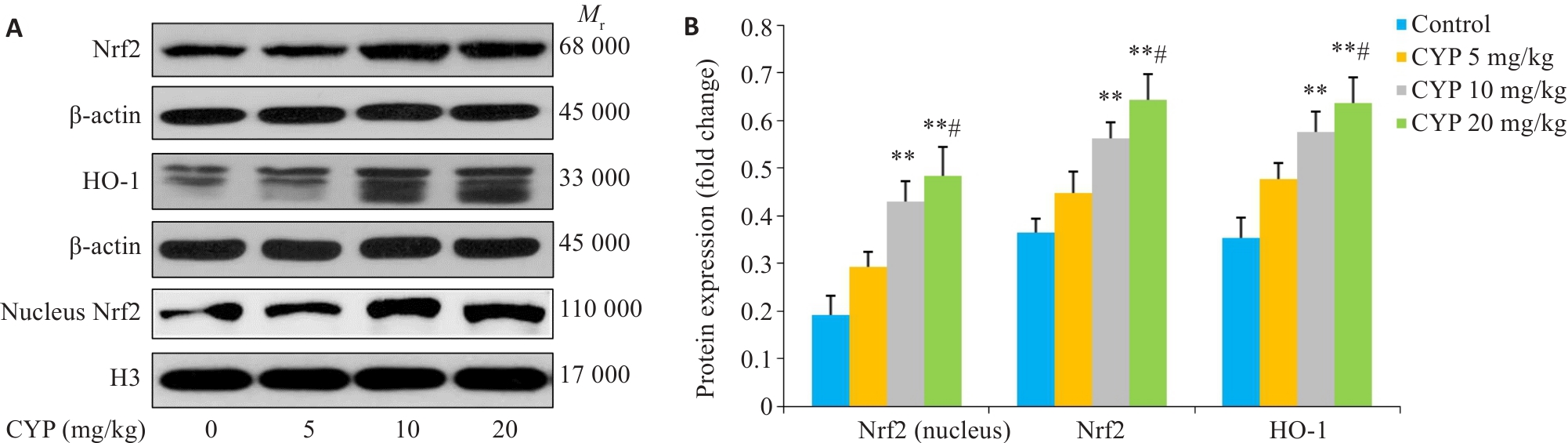
图6 Western blotting分析Nrf2和HO-1蛋白表达
Fig.6 Nrf2 and HO-1 protein expressions in mice hippocampus examined by Western blotting. A: Protein bands of Nrf2 and HO-1. B: Bar chart of gray values analyze of the protein bands (n=3). **P<0.01 vs Control; #P<0.05 vs CYP 5 mg/kg.
| 1 | Cassereau J, Ferré M, Chevrollier A, et al. Neurotoxicity of insecticides[J]. Curr Med Chem, 2017, 24(27): 2988-3001. |
| 2 | Stout DM, Bradham KD, Egeghy PP, et al. American healthy homes survey: a national study of residential pesticides measured from floor wipes[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2009, 43(12): 4294-300. |
| 3 | Pietrantonio PV, Junek TA, Parker R, et al. Detection and evolution of resistance to the pyrethroid cypermethrin in Helicoverpa zea (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) populations in Texas[J]. Environ Entomol, 2007, 36(5): 1174-88. |
| 4 | López O, Hernández AF, Rodrigo L, et al. Changes in antioxidant enzymes in humans with long-term exposure to pesticides[J]. Toxicol Lett, 2007, 171(3): 146-53. |
| 5 | Li Z, Jia B, Guo Z, et al. Therapeutic potential of salidroside in type I diabetic erectile dysfunction: Attenuation of oxidative stress and apoptosis via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway[J]. PLoS One, 2024, 19(7): e0306926. |
| 6 | Moratilla-Rivera I, Sánchez M, Valdés-González JA, et al. Natural products as modulators of Nrf2 signaling pathway in neuroprotection[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(4): 3748. |
| 7 | Barone E, Di Domenico F, Mancuso C, et al. The Janus face of the heme oxygenase/biliverdin reductase system in Alzheimer disease: It's time for reconciliation[J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2014, 62: 144-59. |
| 8 | Leal EC, Carvalho E. Heme oxygenase-1 as therapeutic target for diabetic foot ulcers[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(19): 12043. |
| 9 | Ndisang JF. Synergistic interaction between heme oxygenase (HO) and nuclear-factor E2-related factor-2 (Nrf2) against oxidative stress in cardiovascular related diseases[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2017, 23(10): 1465-70. |
| 10 | Srisook K, Kim C, Cha YN. Molecular mechanisms involved in enhancing HO-1 expression: de-repression by heme and activation by Nrf2, the "one-two" punch[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2005, 7(11/12): 1674-87. |
| 11 | Arsuffi-Marcon R, Souza LG, Santos-Miranda A, et al. Neurotoxicity of pyrethroids in neurodegenerative diseases: from animals' models to humans' studies[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2024, 391: 110911. |
| 12 | Parrón T, Requena M, Hernández AF, et al. Association between environmental exposure to pesticides and neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2011, 256(3): 379-85. |
| 13 | Costantini E, Masciarelli E, Casorri L, et al. Medicinal herbs and multiple sclerosis: overview on the hard balance between new therapeutic strategy and occupational health risk[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2022, 16: 985943. |
| 14 | Gargouri B, Yousif NM, Attaai A, et al. Pyrethroid bifenthrin induces oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and neuronal damage, associated with cognitive and memory impairment in murine hippocampus[J]. Neurochem Int, 2018, 120: 121-33. |
| 15 | Nasuti C, Fattoretti P, Carloni M, et al. Neonatal exposure to permethrin pesticide causes lifelong fear and spatial learning deficits and alters hippocampal morphology of synapses[J]. J Neurodev Disord, 2014, 6(1): 7. |
| 16 | 周礼华, 陈 冲, 张 朋, 等. 氯氰菊酯对小鼠小脑组织氧化损伤及核转录因子-E2相关因子2基因表达的影响[J]. 蚌埠医学院学报, 2016, 41(7): 845-8, 853. DOI: 10.13898/j.cnki.issn.1000-2200.2016.07.002 |
| 17 | 周礼华, 常见荣, 周梦晴, 等. 氯氰菊酯通过抑制Nrf2/ARE信号通路诱导原代C57BL/6小鼠大脑皮层神经元损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(12): 1469-75. DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2019.12.11 |
| 18 | Zhou LH, Zhou MQ, Tan HD, et al. Cypermethrin-induced cortical neurons apoptosis via the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway[J]. Pestic Biochem Physiol, 2020, 165: 104547. |
| 19 | Zhao HJ, Wang Y, Guo MH, et al. Environmentally relevant concentration of cypermethrin or/and sulfamethoxazole induce neurotoxicity of grass carp: Involvement of blood-brain barrier, oxidative stress and apoptosis[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2021, 762: 143054. |
| 20 | Aouey B, Derbali M, Chtourou Y, et al. Pyrethroid insecticide lambda-cyhalothrin and its metabolites induce liver injury through the activation of oxidative stress and proinflammatory gene expression in rats following acute and subchronic exposure[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 2017, 24(6): 5841-56. |
| 21 | Yang SS, Lian GJ. ROS and diseases: role in metabolism and energy supply[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2020, 467(1): 1-12. |
| 22 | Yang X, Fang Y, Hou J, et al. The heart as a target for deltamethrin toxicity: Inhibition of Nrf2/HO-1 pathway induces oxidative stress and results in inflammation and apoptosis[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 300: 134479. |
| 23 | Wang X, Michaelis EK. Selective neuronal vulnerability to oxidative stress in the brain[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2010, 2: 12. |
| 24 | Tayebati SK, Di Tullio MA, Ricci A, et al. Influence of dermal exposure to the pyrethroid insecticide deltamethrin on rat brain microanatomy and cholinergic/dopaminergic neurochemistry[J]. Brain Res, 2009, 1301: 180-8. |
| 25 | Chen NN, Luo DJ, Yao XQ, et al. Pesticides induce spatial memory deficits with synaptic impairments and an imbalanced tau phosphorylation in rats[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2012, 30(3): 585-94. |
| 26 | Sarkar A, Singh MP. A complex interplay of DJ-1, LRRK2, and Nrf2 in the regulation of mitochondrial function in cypermethrin-induced Parkinsonism[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2024, 61(2): 953-70. |
| 27 | Hermes-Lima M, Zenteno-Savı́n T. Animal response to drastic changes in oxygen availability and physiological oxidative stress[J]. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C Toxicol Pharmacol, 2002, 133(4): 537-56. |
| 28 | Chen XL, Kunsch C. Induction of cytoprotective genes through Nrf2/antioxidant response element pathway: a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of inflammatory diseases[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2004, 10(8): 879-91. |
| 29 | You L, Peng H, Liu J, et al. Catalpol protects ARPE-19 cells against oxidative stress via activation of the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(10): 2635. |
| 30 | Surh YJ, Kundu JK, Na HK, et al. Redox-sensitive transcription factors as prime targets for chemoprevention with anti-inflammatory and antioxidative phytochemicals 1-2 3[J]. J Nutr, 2005, 135(12): 2993S-3001S. |
| 31 | Edwards H, Mustfa W, Tehreem S, et al. Pharmacotherapeutic potential of malvidin to cure imidacloprid induced hepatotoxicity via regulating PI3K/AKT, Nrf-2/Keap-1 and NF‑κB pathway[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2024, 190: 114816. |
| 32 | Park YH, Park HP, Kim E, et al. The antioxidant effect of preischemic dexmedetomidine in a rat model: increased expression of Nrf2/HO-1 via the PKC pathway[J]. Braz J Anesthesiol Engl Ed, 2023, 73(2): 177-85. |
| 33 | Pamplona A, Ferreira A, Ferreira A, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 and carbon monoxide suppress the pathogenesis of experimental cerebral malaria[J]. Nat Med, 2007, 13(6): 703-10. |
| 34 | Minj E, Yadav RK, Mehan S. Targeting abnormal Nrf2/HO-1 signaling in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: current insights on drug targets and influences on neurological disorders[J]. Curr Mol Med, 2021, 21(8): 630-44. |
| 35 | Zhou LH, Chang JR, Zhao WH, et al. Proanthocyanidins regulate the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway and protect neurons from cypermethrin-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis[J]. Pestic Biochem Physiol, 2021, 177: 104898. |
| 36 | Pickering AM, Vojtovich L, Tower J, et al. Oxidative stress adaptation with acute, chronic, and repeated stress[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2013, 55: 109-18. |
| 37 | Rabhi KK, Esancy K, Voisin A, et al. Unexpected effects of low doses of a neonicotinoid insecticide on behavioral responses to sex pheromone in a pest insect[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(12): e114411. |
| [1] | 唐令苇, 李佳松, 徐海兵. 海马CA1区与眶额叶皮质的神经节律同步活动参与大鼠空间目标导向任务中的学习与记忆巩固[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 479-487. |
| [2] | 刘洋, 贾亿卿, 李程程, 毛汉丁, 刘树元, 单毅. 右美托咪定通过激活Nrf2/HO-1通路减轻热应激诱导的人骨骼肌细胞胀亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 603-613. |
| [3] | 张方圆, 刘刚. 右美托咪定通过激活Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4通路抑制肾小管上皮细胞的铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1135-1140. |
| [4] | 王丽娅, 田美惠, 李 蓉, 吴 越, 王莎莎, 吕 恒, 刘忠义, 于 影. 乙醛脱氢酶2改善急性肺损伤小鼠的肺内皮屏障及维持线粒体动力学平衡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1388-1395. |
| [5] | 周礼华, 常见荣, 高扬丽, 王朝凯. 原花青素B2通过调控P13K/Akt/Nrf2信号通路减轻氯氰菊酯所致神经元损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(8): 1158-1164. |
| [6] | 任 陈,李旋子,杜莎莎. 维生素E通过抑制铁坏死减少放射性神经损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(08): 1097-1102. |
| [7] | 李 洋,李秀娟,谢明丹,程 莉,陈恒胜,孙 红,蒋 莉. 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯对原代培养海马神经元的毒性及机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(02): 225-232. |
| [8] | 曾善美,刘 恺,张竞予,吴玉兰,徐一华,孙学刚,文 戈. 抑郁倾向Itpr2-/-小鼠海马3D-ASL灌注成像改变[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(01): 56-60. |
| [9] | 周礼华,常见荣,周梦晴,肖梦曦,谭涵丹. 氯氰菊酯通过抑制Nrf2/ARE信号通路诱导原代C57BL/6小鼠大脑皮层神经元损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(12): 1469-1475. |
| [10] | 郭远波,王研,张登文,崔灿,李涛,王晟. 乌司他丁对异氟烷介导的大鼠海马神经元凋亡的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(07): 850-. |
| [11] | 方舒,蔡迎迎,李萍,吴春艳,邹少洲,张雨丹,林晓纯,关美萍. Exendin-4通过激活Nrf2/HO-1通路减轻糖尿病小鼠的肝脏氧化应激及纤维化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(04): 464-. |
| [12] | 张玉荣,王瑞忠,陈蕊,王莉. 产前应激子代大鼠海马Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的改变诱导抑郁和焦虑样行为[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(02): 222-. |
| [13] | 郑超,黄艳,张环环,查盈盈,汪萌芽. β2-nAChR促进小鼠海马CA1和CA3锥体神经元GABAA受体的功能成熟[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(09): 1045-. |
| [14] | 黄玲玥,杜浩,向露,刘琴,吕丽辉,陈璐璐,徐国政. 难治性颞叶内侧癫痫的手术疗效及其影响因素分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(07): 773-. |
| [15] | 韦倩,冯洁,何春梅,华子瑜. Caspase-1活化在胆红素诱导的大鼠海马神经元损伤中的作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(05): 567-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||