南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (12): 2347-2358.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.12.10
收稿日期:2024-06-27
出版日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2024-12-26
通讯作者:
韩继明
E-mail:yadxzhh@yau.edu.cn;1909983949@qq.com;mthgh_jm@163.com
作者简介:张华华,硕士,E-mail: yadxzhh@yau.edu.cn基金资助:
Huahua ZHANG1( ), Qingyin TA1,2(
), Qingyin TA1,2( ), Yun FENG1, Jiming HAN1(
), Yun FENG1, Jiming HAN1( )
)
Received:2024-06-27
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2024-12-26
Contact:
Jiming HAN
E-mail:yadxzhh@yau.edu.cn;1909983949@qq.com;mthgh_jm@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨Holliday交叉识别蛋白(HJURP)在肿瘤发生、进展及免疫治疗中的作用。 方法 采用TCGA、GTEx、SangerBox和TIMER 2.0数据库等生物信息学方法分析HJURP在各类癌症中的表达水平及其与预后、临床分期和免疫细胞浸润的关联。利用LinkedOmics数据库分析肾透明细胞癌(KIRC)中HJURP的相关基因及其潜在功能。通过免疫组织化学分析、Western blotting和qRT-PCR实验验证HJURP在KIRC中的表达,并设计靶向HJURP的小干扰RNA,评估其对KIRC细胞增殖、迁移能力的影响。 结果 HJURP在包含KIRC的26种肿瘤组织中表达升高(P<0.05),且与包括KIRC的5种肿瘤患者的预后呈负相关(P<0.05)。HJURP的表达水平与肿瘤的临床分期及免疫细胞浸润密切相关。在KIRC中,HJURP表达升高(P<0.0001),且与TNM分期(P<0.05)、Stage分期(P<0.01)及免疫细胞浸润呈正相关。基因本体论功能分析结果显示:HJURP在生物学过程中主要富集于生物调节和代谢过程等;在细胞组分方面主要富集于细胞膜与细胞核等;在分子功能方面主要富集于蛋白质结合和离子结合等。组织和细胞水平实验显示,HJURP在KIRC中高表达(P<0.001),且沉默HJURP抑制KIRC细胞的增殖与迁移(P<0.01)。 结论 HJURP可作为KIRC预后和免疫治疗的预测因子,并在KIRC细胞的恶性行为中发挥促进作用。
张华华, 拓庆银, 冯芸, 韩继明. Holliday交叉识别蛋白是肾透明细胞癌的潜在预测和预后生物标记物[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2347-2358.
Huahua ZHANG, Qingyin TA, Yun FENG, Jiming HAN. Holliday junction-recognizing protein is a potential predictive and prognostic biomarker for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2347-2358.
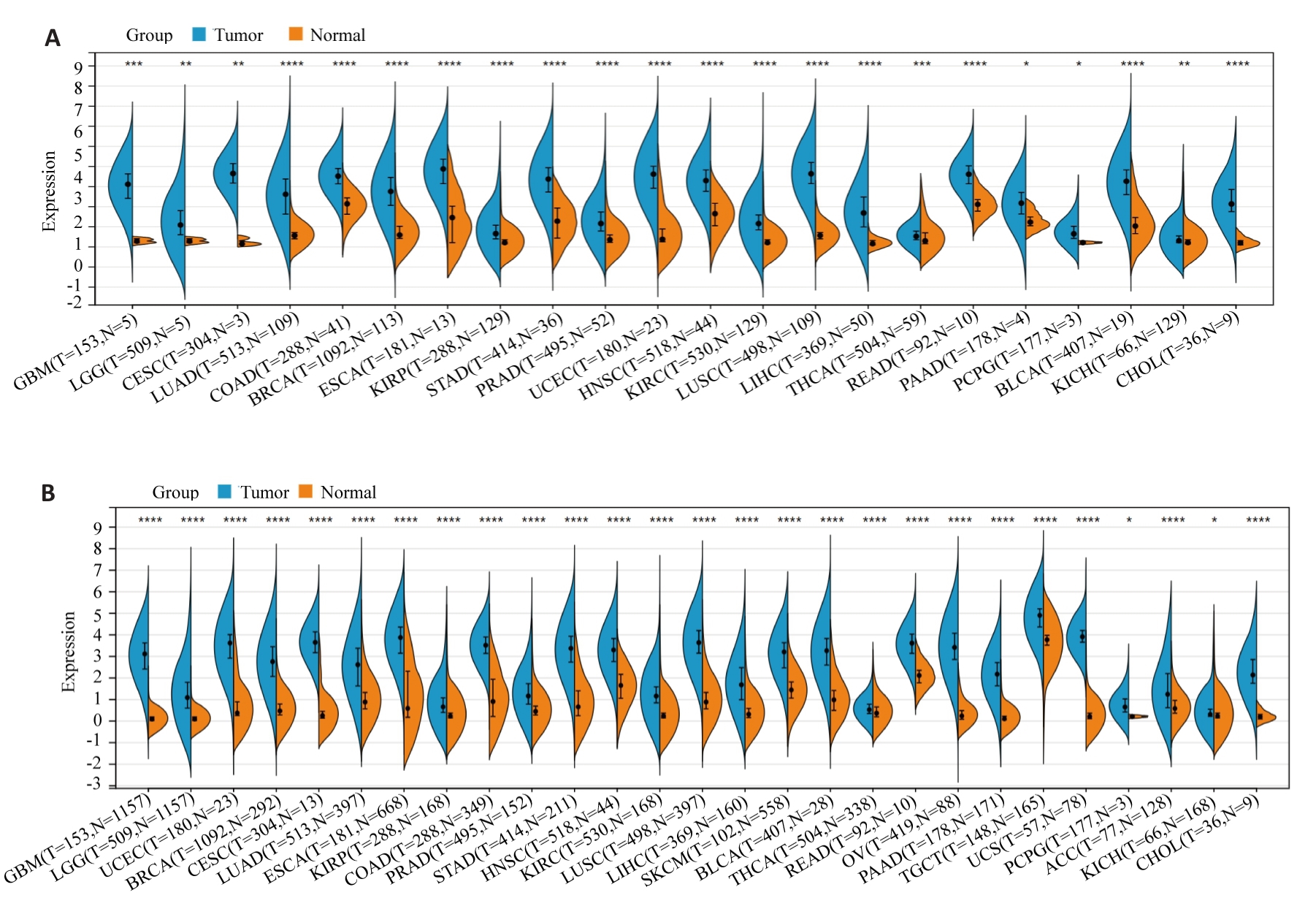
图1 HJURP在泛癌中的表达
Fig.1 Expression of Holliday junction-recognizing protein (HJURP) in pan-cancer. A: Expression of HJURP in different human tumors based on TCGA database. B: HJURP expression in 26 human tumors analyzed by integrating normal tissue data from GTEx database and TCGA tumor tissue. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs Normal group.
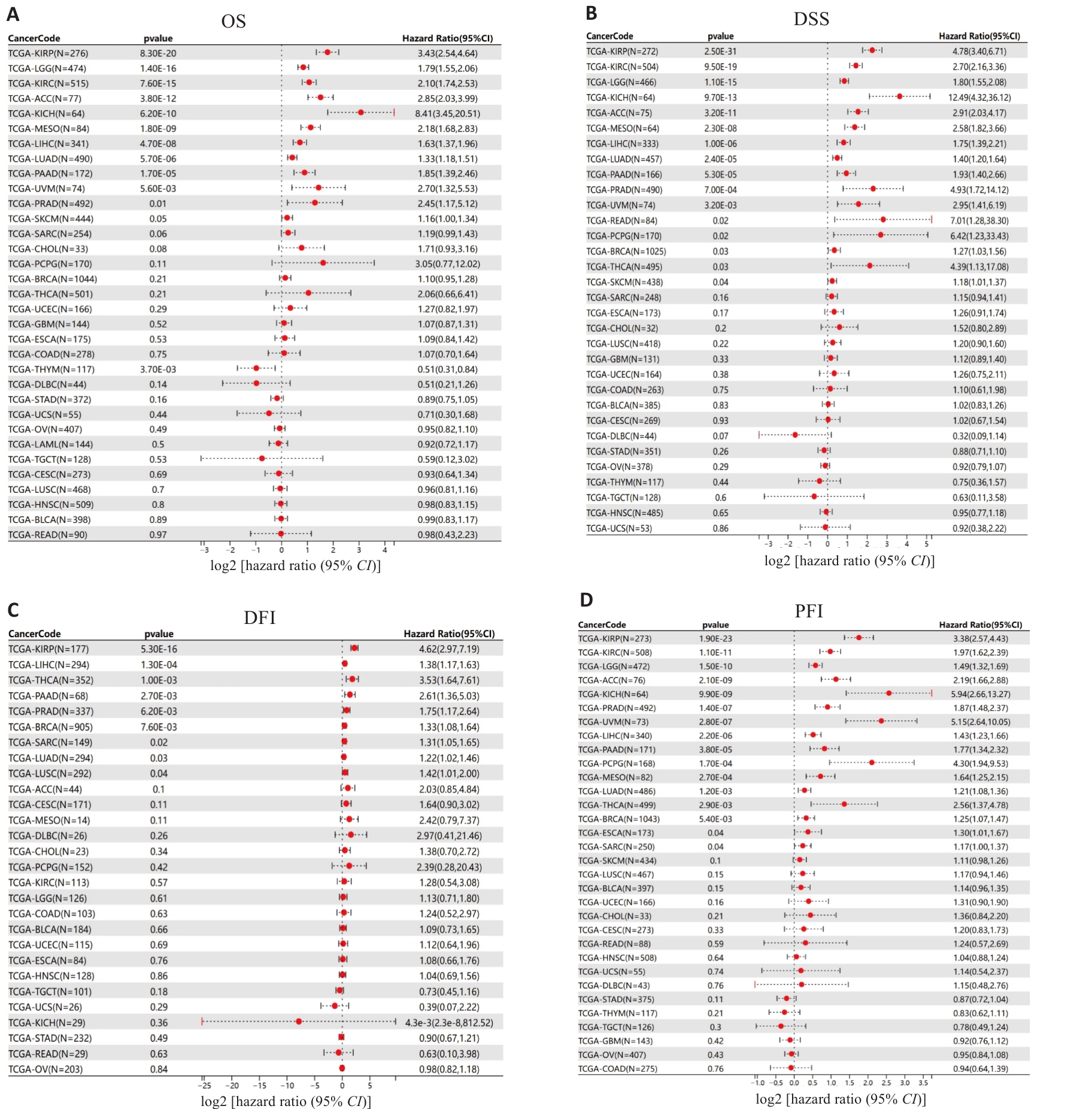
图2 HJURP的表达水平与泛癌预后关系的生存森林图
Fig.2 Survival forest map for prognostic analysis of HJURP expression in pan-cancer. OS: Overall survival; DSS: Disease-specific survival; DFI: Disease-free interval; PFI: Progression-free interval.
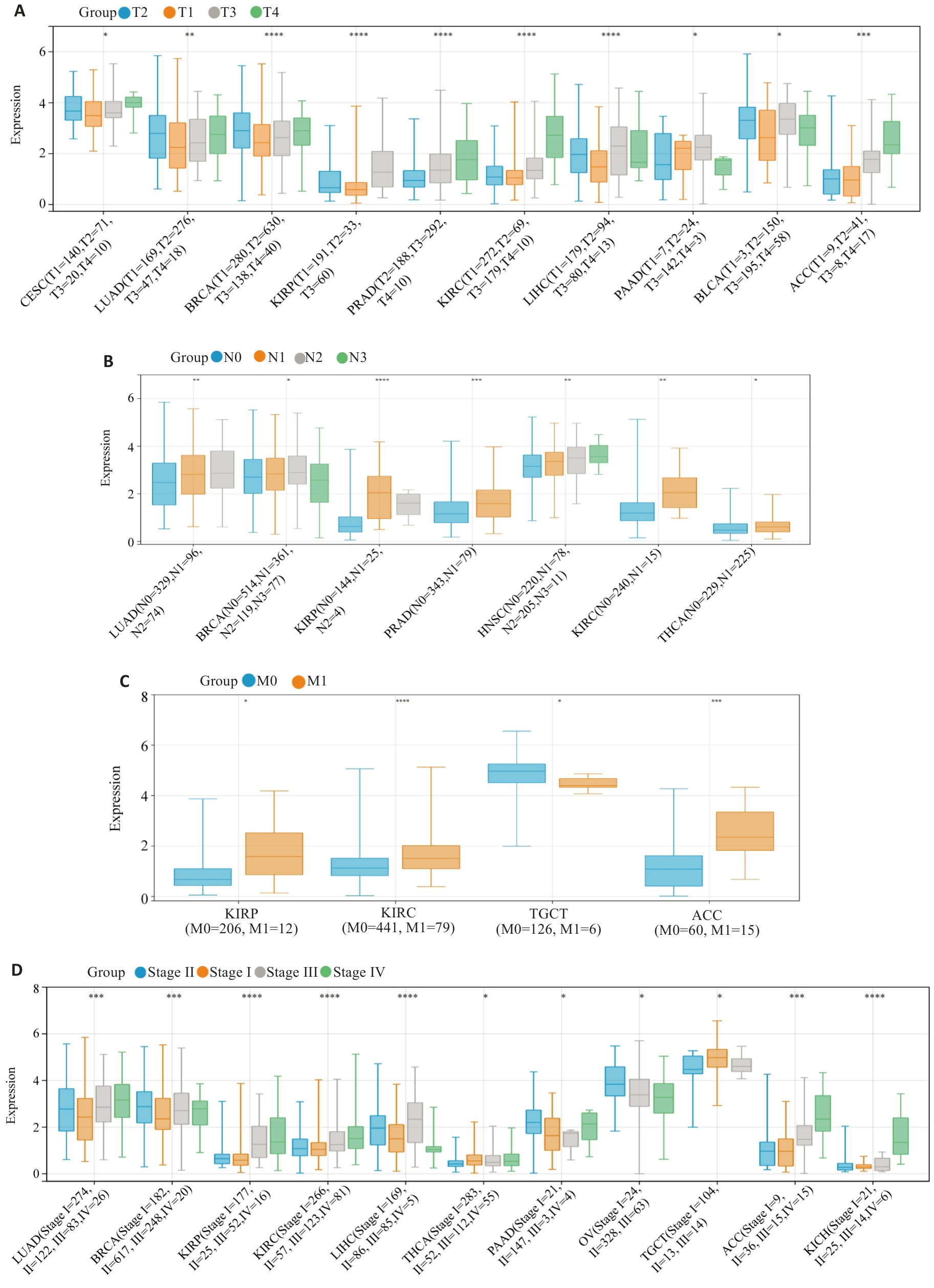
图3 HJURP表达与临床病理特征之间的相关性
Fig.3 Associations between HJURP expression and clinicopathological characteristics of pan-cancer. A: T grade. B: N grade. C: M status. D: clinical stage. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs T1, N0, M0 or Stage I.
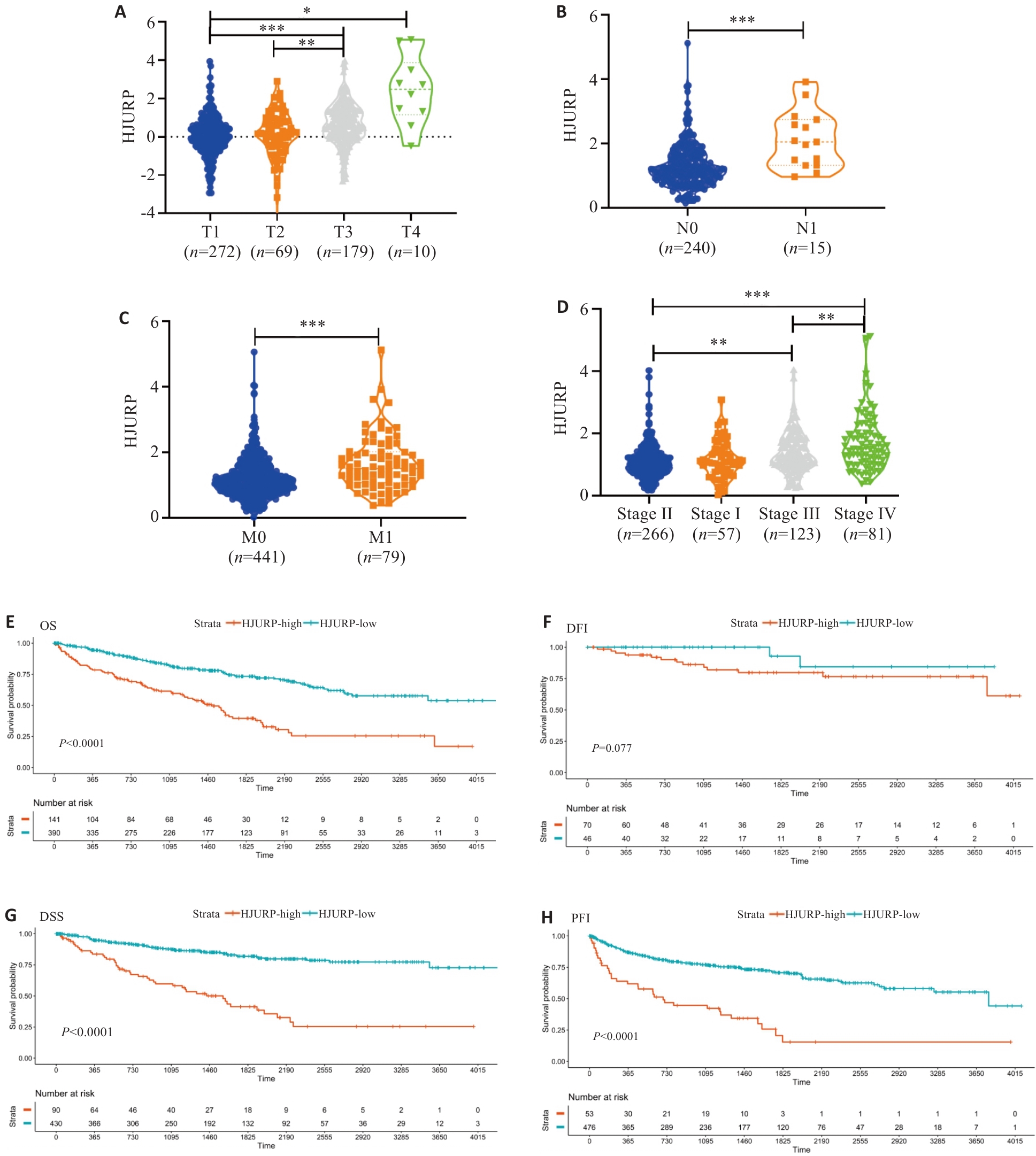
图5 HJURP表达与KIRC临床病理特征及预后的相关性
Fig.5 Correlation of HJURP expression with clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC). A: T grade. B: N grade. C: M status. D: clinical stage. E: HR (95% CI) for OS. F: HR (95% CI) for DSS. G: HR (95% CI) for DFI. H: HR (95% CI) for PFI. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs T1, N0, M0, or Stage I.
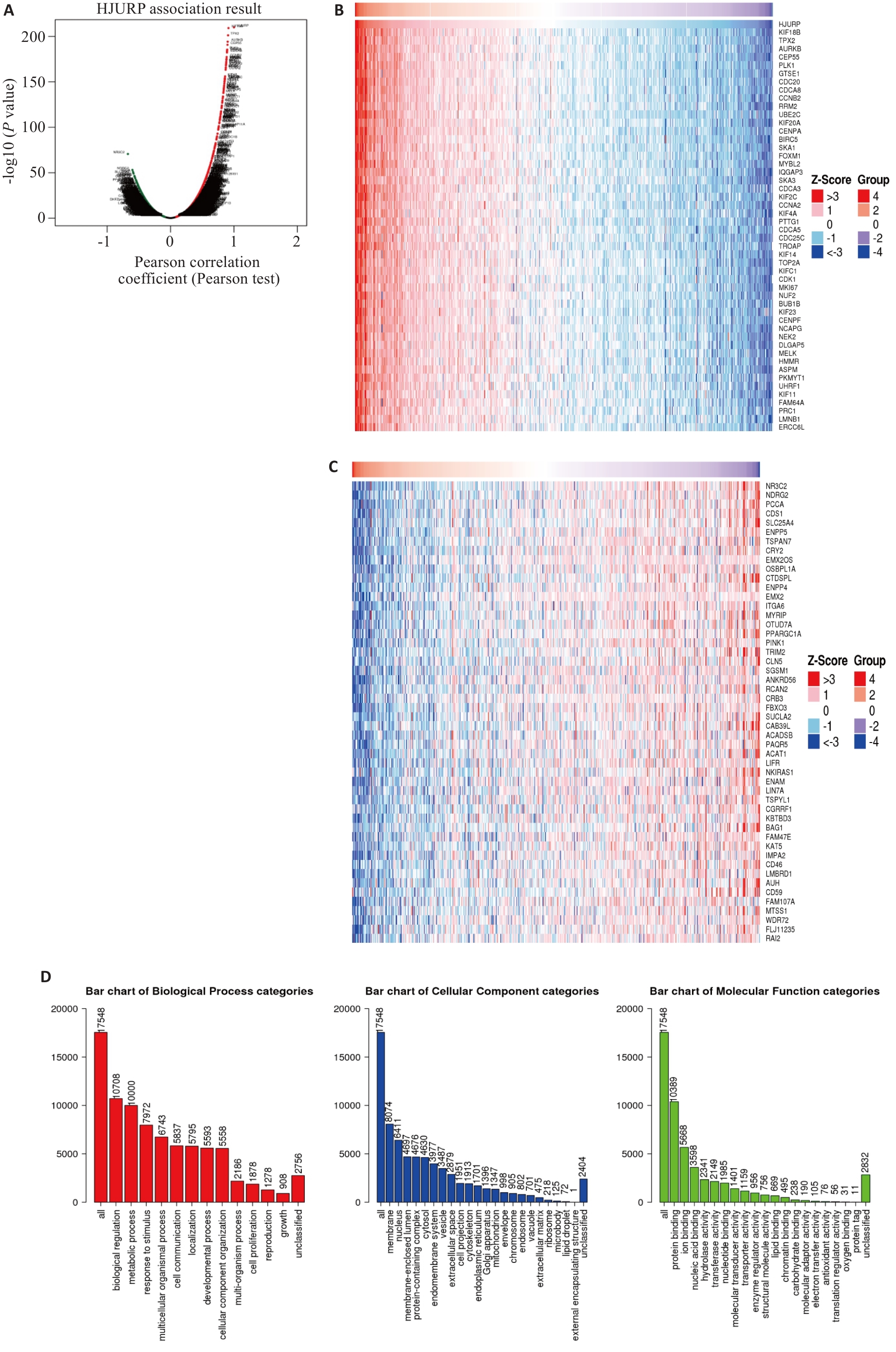
图6 KIRC中HJURP相关基因分析及其GO功能分析
Fig.6 Analysis of HJURP-related genes in KIRC and the GO function. A: Volcanic plot of HJURP-related genes in KIRC. B: Heat map of genes positively associated with HJURP in KIRC. C: Heat map of genes negatively associated with HJURP in KIRC. D: GO function analysis of HJURP in KIRC.
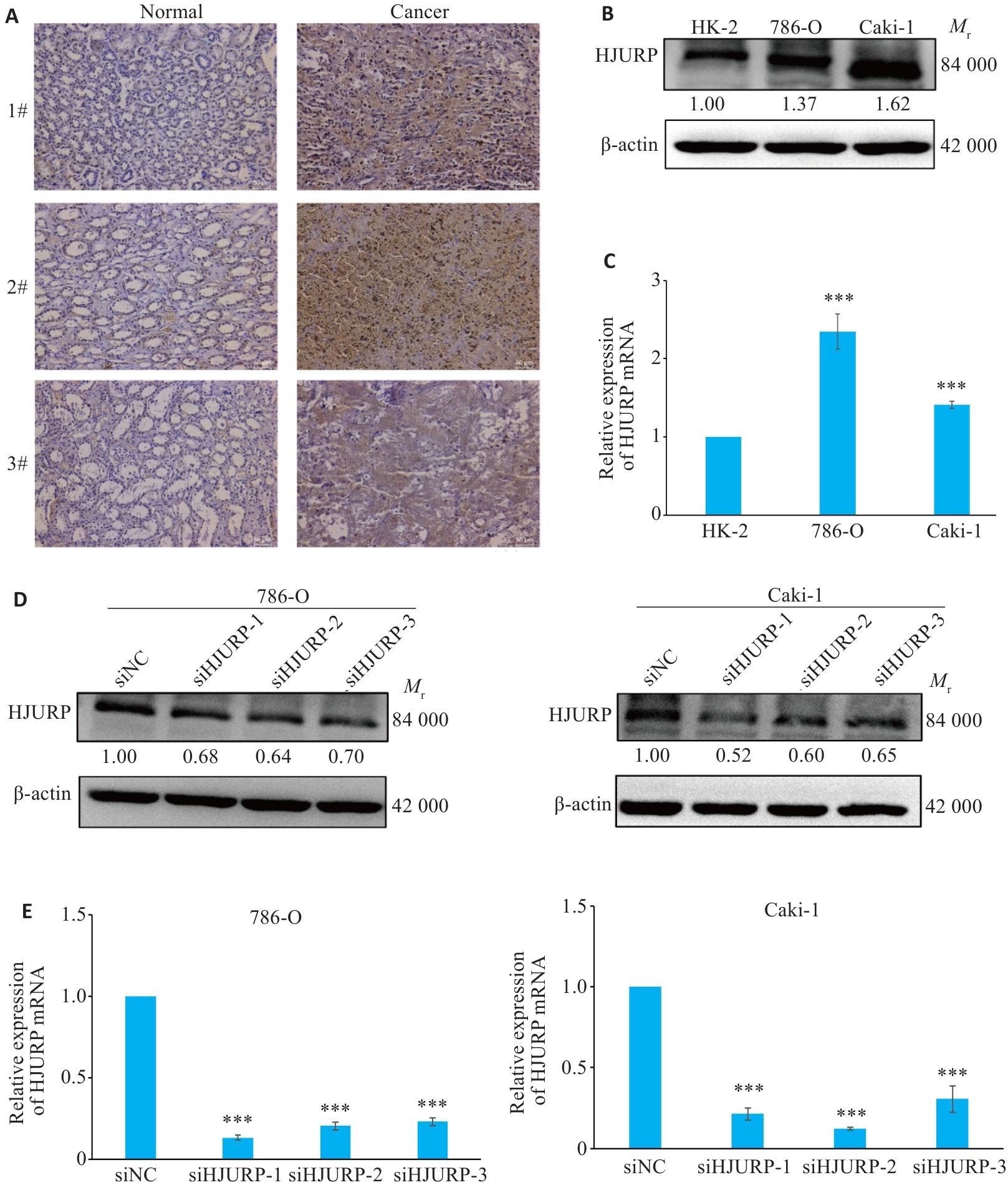
图7 HJURP在KIRC中的表达及HJURP的干扰片段的效率验证
Fig.7 Expression of HJURP in KIRC and validation of the efficiency of HJURP interference. A: HJURP in adjacent and KIRC tissues detected by immunohistochemistry (×100). B: Differential expression of HJURP in KIRC verified by Western blotting. C: Expression of HJURP mRNA in KIRC cell lines detected by qRT-PCR. D, E: Transfection efficiency of si-HJURP sequences assessed by Western blotting (D) and qRT-PCR (E). ***P<0.001 vs HK-2 or siNC group.
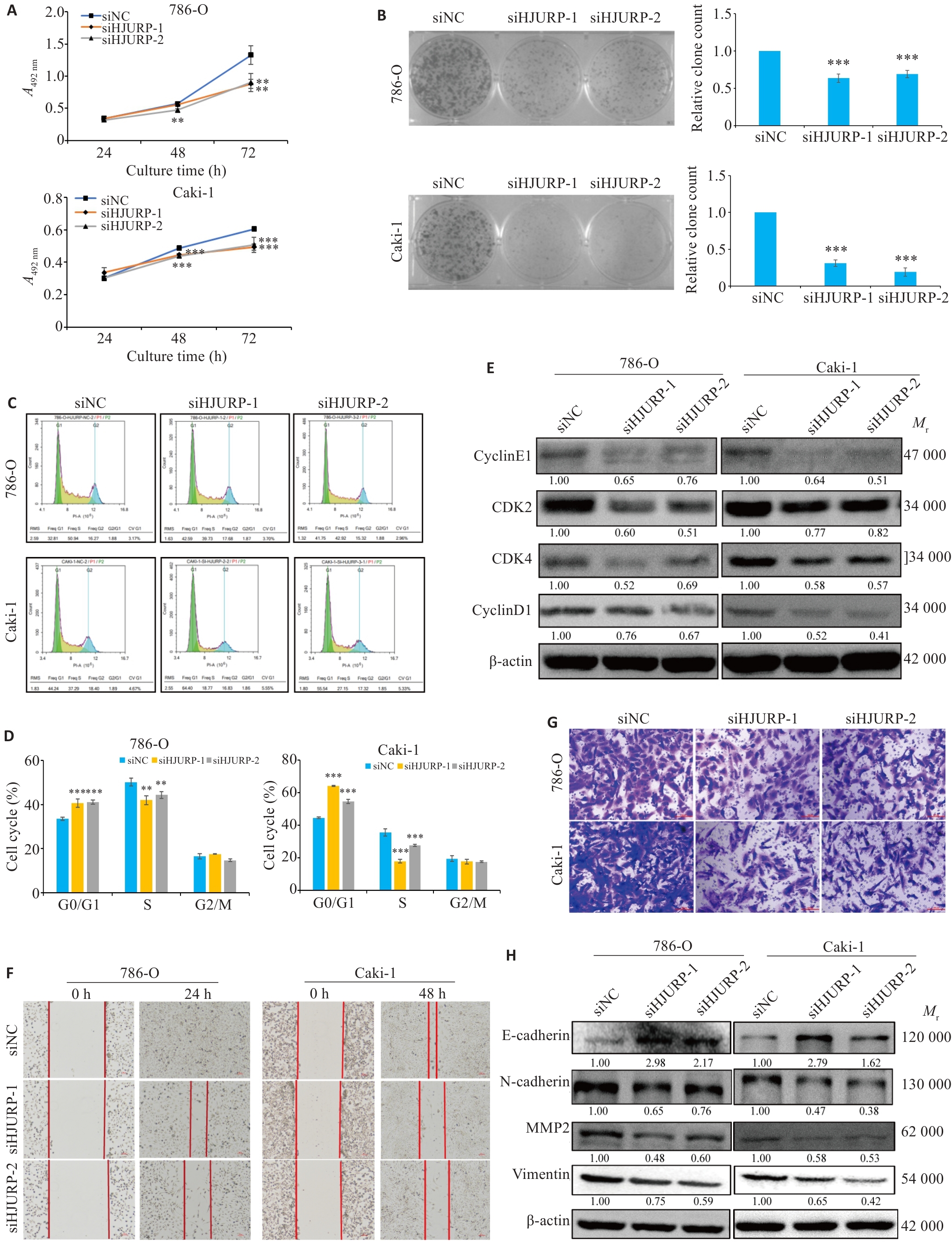
图8 沉默HJURP体外抑制KIRC细胞的增殖和迁移
Fig.8 Silencing of HJURP suppresses proliferation and migration of KIRC cells in vitro. A:CCK-8 assays for cell viability. B: Clone formation test to detect the changes of cell clone formation ability. C, D: Flow cytometry for analyzing cell cycle distribution in 786-O and Caki-1 cells (Mean±SD, n=3). E: Changes in cell cycle-related proteins after silencing HJURP. F: Scratch test for assessing cell migration ability (×100). G: Transwell assays for assessing cell migration (×200). H: Western blotting for detecting cell migration-related protein expressions including E-cadherin, N-cadherin, MMP2 and vimentin. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs siNC group.
| 1 | Zheng RS, Chen R, Han BF, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2024, 46(3): 221-31. |
| 2 | Ansell SM, Lesokhin AM, Borrello I, et al. PD-1 blockade with nivolumab in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2015, 372(4): 311-9. |
| 3 | Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, et al. Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab or monotherapy in untreated melanoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2015, 373(1): 23-34. |
| 4 | Robert C, Ribas A, Wolchok JD, et al. Anti-programmed-death-receptor-1 treatment with pembrolizumab in ipilimumab-refractory advanced melanoma: a randomised dose-comparison cohort of a phase 1 trial[J]. Lancet, 2014, 384(9948): 1109-17. |
| 5 | Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LQ, et al. Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with advanced cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2012, 366(26): 2455-65. |
| 6 | Weinstein JN, Collisson EA, Mills GB, et al. The Cancer Genome Atlas Pan-Cancer analysis project[J]. Nat Genet, 2013, 45(10): 1113-20. |
| 7 | Kato T, Sato N, Hayama S, et al. Activation of Holliday junction recognizing protein involved in the chromosomal stability and immortality of cancer cells[J]. Cancer Res, 2007, 67(18): 8544-53. |
| 8 | Barnhart MC, Kuich PH, Stellfox ME, et al. HJURP is a CENP-a chromatin assembly factor sufficient to form a functional de novo kinetochore[J]. J Cell Biol, 2011, 194(2): 229-43. |
| 9 | Wei Y, Ouyang GL, Yao WX, et al. Knockdown of HJURP inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by repressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2019, 23(9): 3847-56. |
| 10 | Kang DH, Woo J, Kim H, et al. Prognostic relevance of HJURP expression in patients with surgically resected colorectal cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(21): 7928. |
| 11 | Wang CJ, Li X, Shi P, et al. Holliday junction recognition protein promotes pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis via modulation of the MDM2/p53 signaling[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(5): 386. |
| 12 | Cao R, Wang G, Qian KY, et al. Silencing of HJURP induces dysregulation of cell cycle and ROS metabolism in bladder cancer cells via PPARγ-SIRT1 feedback loop[J]. J Cancer, 2017, 8(12): 2282-95. |
| 13 | Wang L, Qu JL, Liang Y, et al. Identification and validation of key genes with prognostic value in non-small-cell lung cancer via integrated bioinformatics analysis[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2020, 11(4): 851-66. |
| 14 | Gu Y, Li J, Guo DL, et al. Identification of 13 key genes correlated with progression and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by weighted gene co-expression network analysis[J]. Front Genet, 2020, 11: 153. |
| 15 | Hu Z, Huang G, Sadanandam A, et al. The expression level of HJURP has an independent prognostic impact and predicts the sensitivity to radiotherapy in breast cancer[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2010, 12(2): R18. |
| 16 | Fu FQ, Zhang Y, Gao ZD, et al. Development and validation of a five-gene model to predict postoperative brain metastasis in operable lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Int J Cancer, 2020, 147(2): 584-92. |
| 17 | Shen WT, Song ZG, Zhong X, et al. Sangerbox: a comprehensive, interaction-friendly clinical bioinformatics analysis platform[J]. Imeta, 2022, 1(3): e36. |
| 18 | Li TW, Fan JY, Wang BB, et al. TIMER: a web server for comprehensive analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells[J]. Cancer Res, 2017, 77(21): e108-10. |
| 19 | Yoshihara K, Shahmoradgoli M, Martínez E, et al. Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data[J]. Nat Commun, 2013, 4: 2612. |
| 20 | Telloni SM. Tumor staging and grading: a primer[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2017, 1606: 1-17. |
| 21 | Vasaikar SV, Straub P, Wang J, et al. LinkedOmics: analyzing multi-omics data within and across 32 cancer types[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2018, 46(D1): D956-63. |
| 22 | Li L, Yuan Q, Chu YM, et al. Advances in holliday junction recognition protein (HJURP): structure, molecular functions, and roles in cancer[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2023, 11: 1106638. |
| 23 | Chen TC, Zhou LF, Zhou Y, et al. HJURP promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via upregulating SPHK1 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2019, 15(6): 1139-47. |
| 24 | Yang Y, Yuan JY, Liu ZZ, et al. The expression, clinical relevance, and prognostic significance of HJURP in cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 972550. |
| 25 | Zhang F, Yuan DB, Song JK, et al. HJURP is a prognostic biomarker for clear cell renal cell carcinoma and is linked to immune infiltration[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 99: 107899. |
| 26 | Hinshaw DC, Shevde LA. The tumor microenvironment innately modulates cancer progression[J]. Cancer Res, 2019, 79(18): 4557-66. |
| 27 | Luo DC, Liao SN, Liu Y, et al. Holliday cross-recognition protein HJURP: association with the tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma and with patient prognosis[J]. Pathol Oncol Res, 2022, 28: 1610506. |
| 28 | Liu L, Zhang ZF, Xia XL, et al. KIF18B promotes breast cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting TRIP13 and activating the Wnt/β‑catenin signaling pathway[J]. Oncol Lett, 2022, 23(4): 112. |
| 29 | Xie JL, Wang B, Luo WJ, et al. Upregulation of KIF18B facilitates malignant phenotype of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by activating CDCA8/mTORC1 pathway[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2022, 36(10): e24633. |
| 30 | Koike Y, Yin CZ, Sato Y, et al. TPX2 is a prognostic marker and promotes cell proliferation in neuroblastoma[J]. Oncol Lett, 2022, 23(4): 136. |
| 31 | Li LZ, Jiang PC, Hu WM, et al. AURKB promotes bladder cancer progression by deregulating the p53 DNA damage response pathway via MAD2L2[J]. J Transl Med, 2024, 22(1): 295. |
| [1] | 谢婷, 王云云, 郭婷, 袁春华. 雷氏大疣蛛多肽毒素组分通过激活促凋亡通路和协同作用抑制癌细胞增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1460-1470. |
| [2] | 龚秀莹, 侯顺福, 赵苗苗, 王晓娜, 张致涵, 刘清华, 尹崇高, 李洪利. LncRNA SNHG15通过miR-30b-3p调控COX6B1轴促进肺腺癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的分子机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1498-1505. |
| [3] | 赵华轩, 张桂潮, 刘家荣, 莫富添, 李韬恩, 类成勇, 吕世栋. 肾透明细胞癌患者的免疫细胞浸润特征与临床病理参数具有相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1280-1288. |
| [4] | 曾玉梅, 李继科, 黄仲曦, 周毅波. 绒毛样蛋白VILL通过与LMO7蛋白相互作用抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 954-961. |
| [5] | 岳雅清, 牟召霞, 王希波, 刘艳. Aurora-A过表达通过激活NF-κBp65/ARPC4信号轴促进宫颈癌细胞的侵袭和转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 837-843. |
| [6] | 张毅, 沈昱, 万志强, 陶嵩, 柳亚魁, 王栓虎. CDKN3高表达促进胃癌细胞的迁移和侵袭:基于调控p53/NF-κB信号通路和抑制胃癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [7] | 庆顺杰, 沈智勇. 过表达己糖激酶2通过激活JAK/STAT途径促进结直肠癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭并调节肿瘤免疫微环境[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 542-553. |
| [8] | 陶露, 韦卓利, 王月月, 项平. CEACAM6通过调控上皮间质转化抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 566-576. |
| [9] | 黄晴晴, 张文静, 张小凤, 王炼, 宋雪, 耿志军, 左芦根, 王月月, 李静, 胡建国. 高表达MYO1B促进胃癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭并与患者的不良预后有关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 622-631. |
| [10] | 邹金华, 王惠, 张冬艳. SLC1A5通过促进M2型巨噬细胞极化促进肝癌进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 269-284. |
| [11] | 高俊杰, 叶开, 吴竞. 槲皮素通过调控TP53基因抑制肾透明细胞癌的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 313-321. |
| [12] | 宾禹, 李子雯, 左素微, 孙思诺, 李敏, 宋佳茵, 林旭, 薛刚, 吴靖芳. 载脂蛋白C1高表达通过激活JAK2/STAT3信号通路促进甲状腺乳头状癌细胞的增殖并抑制凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 359-370. |
| [13] | 曹周芳, 汪元, 王梦娜, 孙玥, 刘菲菲. LINC00837/miR-671-5p/SERPINE2功能轴促进类风湿关节炎成纤维细胞样滑膜细胞的恶性病理学过程[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 371-378. |
| [14] | 陈晓睿, 魏青政, 张宗亮, 原江水, 宋卫青. 过表达带电多泡体蛋白2B基因抑制肾透明细胞癌细胞的增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 126-136. |
| [15] | 王耀彬, 陈柳燕, 罗伊凌, 申继清, 周素芳. NUF2对泛癌的预后和免疫治疗效果的预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 137-149. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||