南方医科大学学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 219-230.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.24
卓俐1( ), 曾敏1, 谭顺谦1, 梁涛1, 肖巍魏2, 甄鑫1(
), 曾敏1, 谭顺谦1, 梁涛1, 肖巍魏2, 甄鑫1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-06-13
出版日期:2026-01-20
发布日期:2026-01-16
通讯作者:
甄鑫
E-mail:zhuoli0901@163.com;xinzhen@smu.edu.cn
作者简介:卓 俐,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: zhuoli0901@163.com
基金资助:
Li ZHUO1( ), Min ZENG1, Shunqian TAN1, Tao LIANG1, Weiwei XIAO2, Xin ZHEN1(
), Min ZENG1, Shunqian TAN1, Tao LIANG1, Weiwei XIAO2, Xin ZHEN1( )
)
Received:2025-06-13
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2026-01-16
Contact:
Xin ZHEN
E-mail:zhuoli0901@163.com;xinzhen@smu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 建立基于扩散循环一致性生成对抗网络的骨盆活跃骨髓(ABM)分割方法,突破传统解剖图谱方法个体化精度不足的技术瓶颈。 方法 收集253例患者骨盆PET-CT数据,构建三阶段级联跨模态学习框架实现从CT到个体化ABM精准识别。首先通过循环一致性生成对抗网络建立CT-PET双向映射,采用9个残差模块学习跨模态特征关系。设计条件扩散模块基于1000步马尔可夫链实现渐进去噪,融合双向交叉注意力机制动态整合解剖与功能信息。最后构建多尺度渐进式特征金字塔分割网络,在4个尺度层级累积多模态特征实现ABM区域分割。采用峰值信噪比(PSNR)、结构相似性指数(SSIM)、归一化均方误差(NMSE)评估图像合成质量,Dice相似系数(DSC)、平均对称表面距离(ASSD)评估分割性能。 结果 本方法均优于现有方法,PSNR达到26.42±0.63 dB,SSIM达到0.894±0.011,NMSE降至0.0235±0.0026。在ABM分割任务中,平均Dice系数达到0.777±0.023,ASSD降至3.52±0.41 mm。 结论 与传统方法相比,该方法显著提高了个体化分割精度,适用于直肠癌个体化骨髓保护放疗的临床应用。
卓俐, 曾敏, 谭顺谦, 梁涛, 肖巍魏, 甄鑫. 基于扩散循环一致性生成对抗网络的骨盆活跃骨髓区域分割方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2026, 46(1): 219-230.
Li ZHUO, Min ZENG, Shunqian TAN, Tao LIANG, Weiwei XIAO, Xin ZHEN. Diffusion cycle-consistent generative adversarial networks for pelvic active bone marrow segmentation[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2026, 46(1): 219-230.
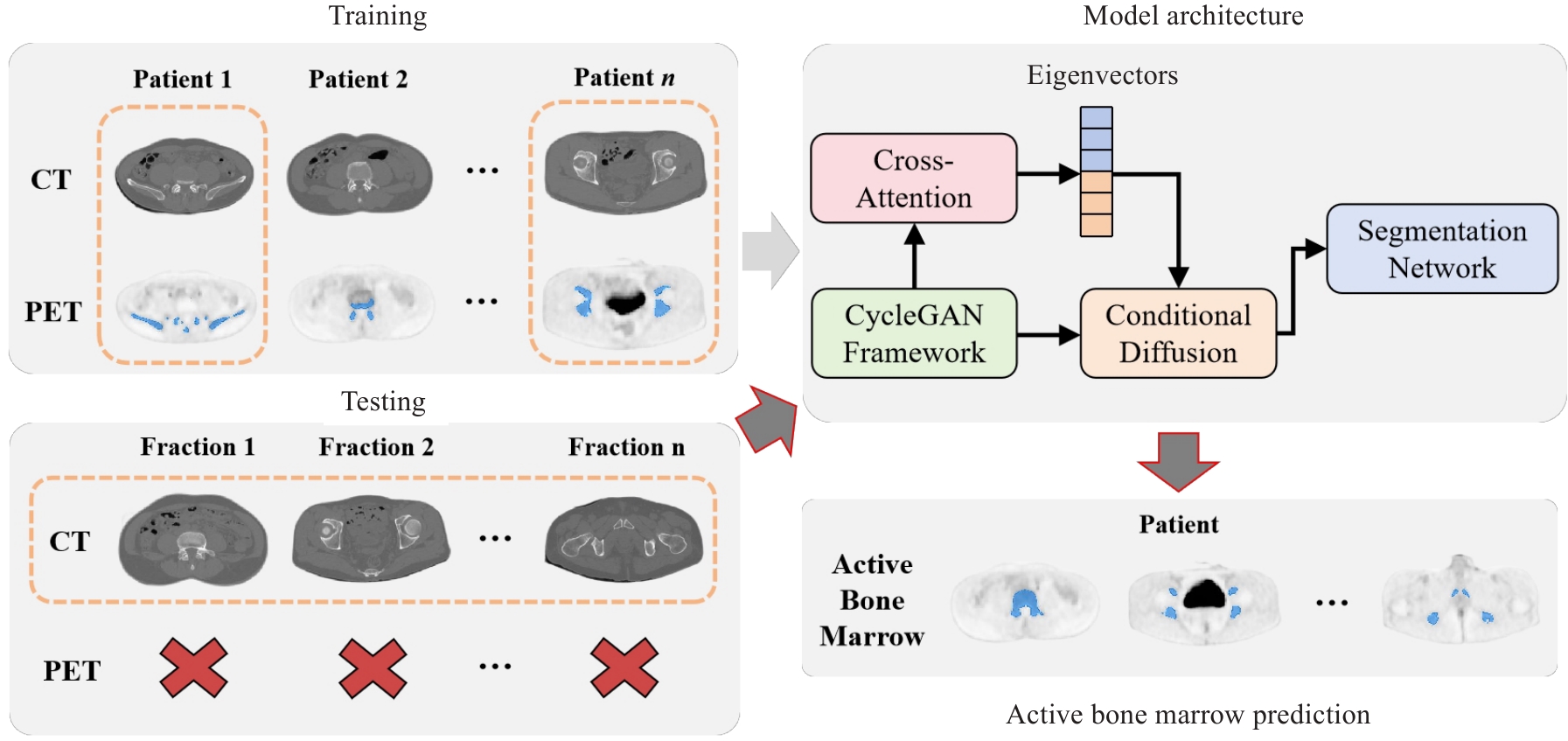
图1 基于扩散循环一致性生成对抗网络的骨盆活跃骨髓区分割方法整体架构图
Fig.1 Overall architecture of the pelvic active bone marrow segmentation method based on diffusion cycle-consistent generative adversarial network.
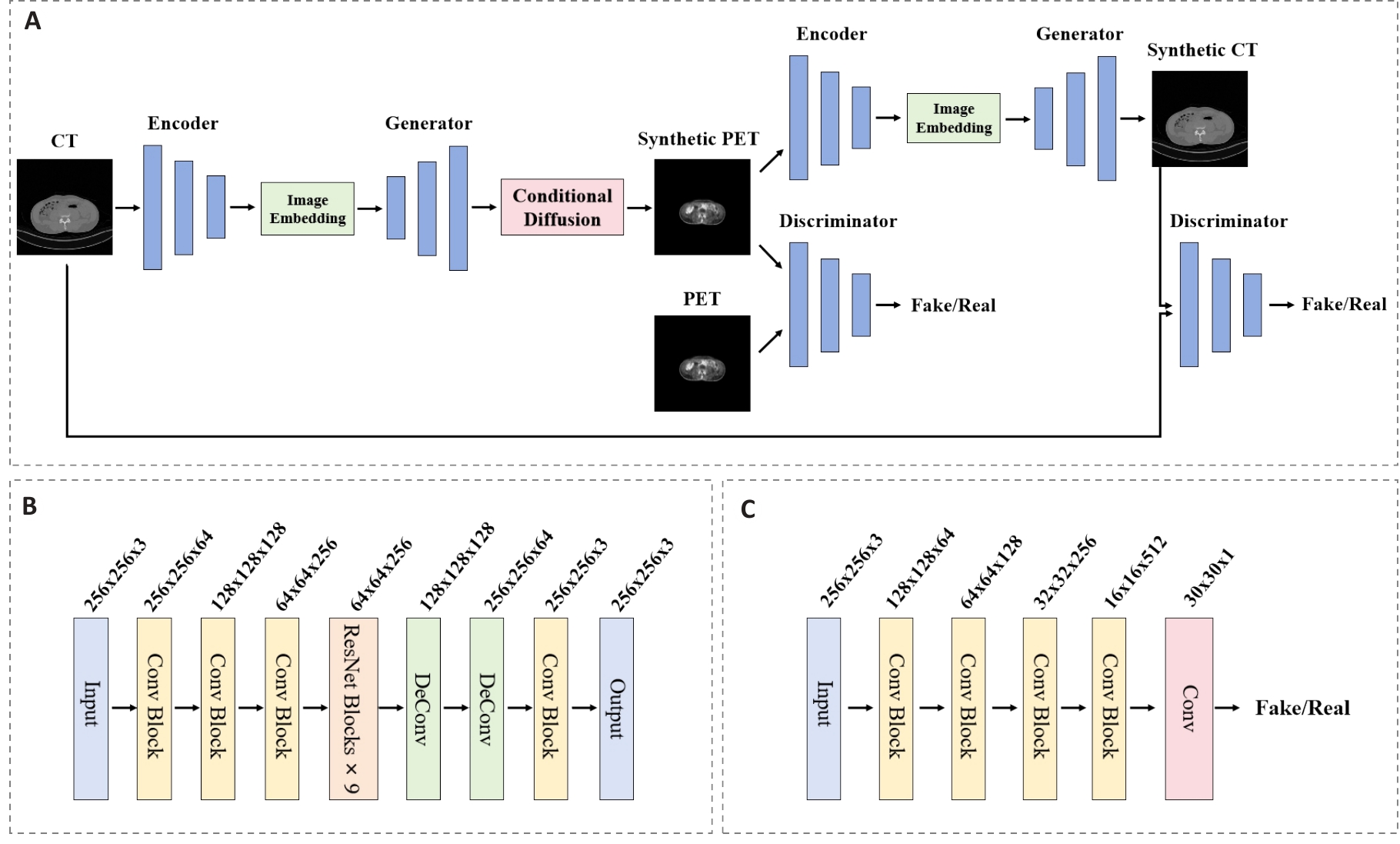
图2 循环一致性生成对抗网络模块架构图
Fig.2 Architecture diagram of the cycle-consistent generative adversarial network module. A: Overall architecture of the CycleGAN establishing bidirectional mapping. B: Generator network architecture containing 9 residual blocks. C: Discriminator network architecture employing spectral normalization.
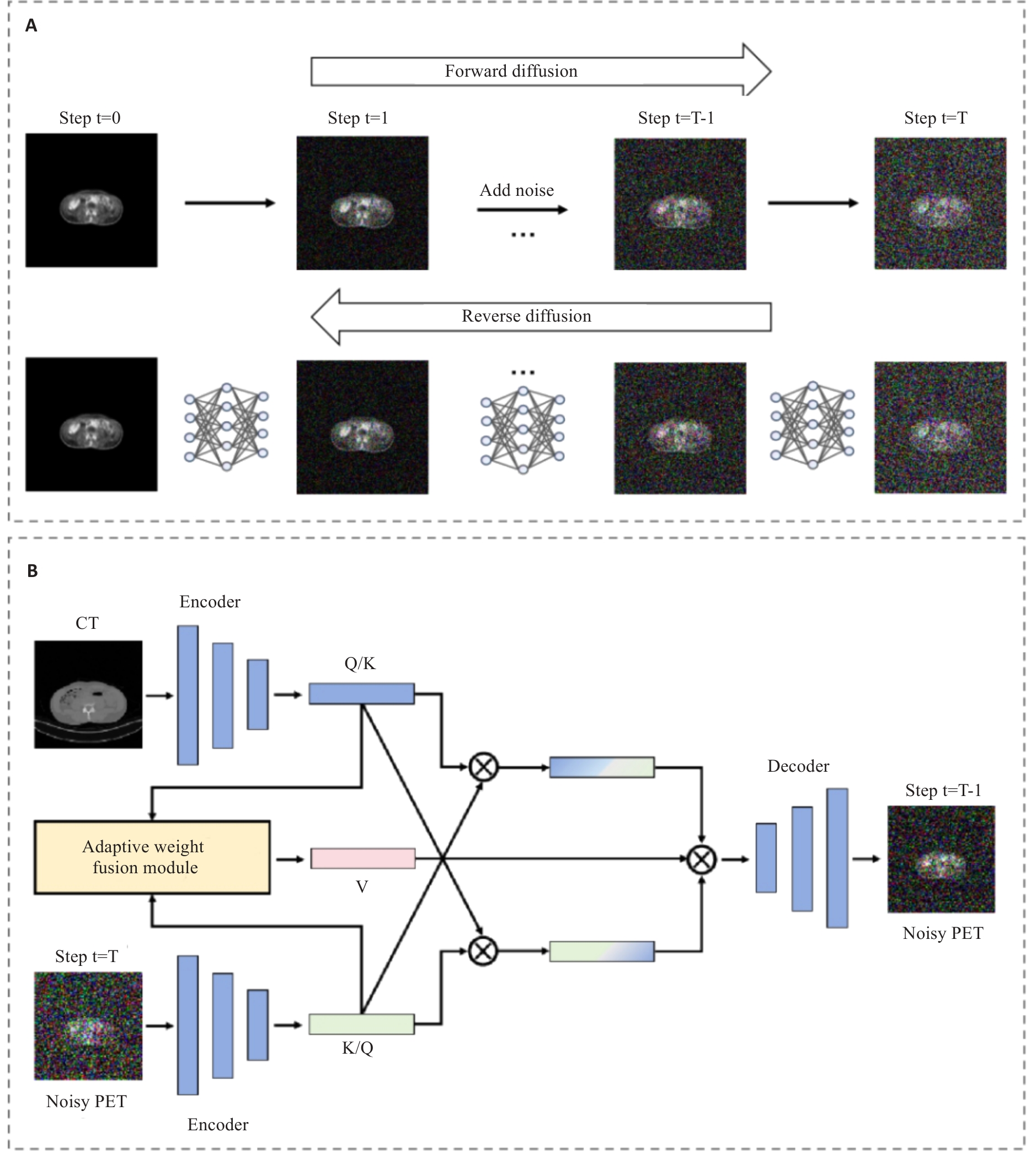
图3 条件扩散模块跨模态动态去噪方法
Fig.3 Cross-modal dynamic denoising method of the conditional diffusion module. A: Forward noise addition and reverse denoising reconstruction processes based on Markov chain. B: Structure of the cross-modal dynamic denoising network integrating Adaptive Weight Fusion Module and Bidirectional Cross-Attention
| Methods | PSNR | SSIM | NMSE | Average time (Epoch/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-net[ | 21.27±1.31 | 0.787±0.031 | 0.0438±0.0062 | 57.1 |
| Pix2pix[ | 22.61±1.04 | 0.815±0.026 | 0.0359±0.0045 | 48.9 |
| CycleGAN[ | 24.33±0.91 | 0.861±0.022 | 0.0297±0.0041 | 53.4 |
| WGAN[ | 20.42±1.52 | 0.771±0.035 | 0.0481±0.0073 | 65.3 |
| DCGAN[ | 19.08±1.89 | 0.738±0.044 | 0.0541±0.0095 | 44.8 |
| DDPM[ | 23.71±0.97 | 0.849±0.024 | 0.0324±0.0042 | 197.2 |
| Ours | 26.42±0.63 | 0.894±0.011 | 0.0235±0.0026 | 239.8 |
表1 各图像合成方法的性能比较
Tab.1 Quantitative comparison of different methods for image synthesis quality
| Methods | PSNR | SSIM | NMSE | Average time (Epoch/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-net[ | 21.27±1.31 | 0.787±0.031 | 0.0438±0.0062 | 57.1 |
| Pix2pix[ | 22.61±1.04 | 0.815±0.026 | 0.0359±0.0045 | 48.9 |
| CycleGAN[ | 24.33±0.91 | 0.861±0.022 | 0.0297±0.0041 | 53.4 |
| WGAN[ | 20.42±1.52 | 0.771±0.035 | 0.0481±0.0073 | 65.3 |
| DCGAN[ | 19.08±1.89 | 0.738±0.044 | 0.0541±0.0095 | 44.8 |
| DDPM[ | 23.71±0.97 | 0.849±0.024 | 0.0324±0.0042 | 197.2 |
| Ours | 26.42±0.63 | 0.894±0.011 | 0.0235±0.0026 | 239.8 |
| Methods | Dice | ASSD | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lumbosacral spine | Ilium | Lower pelvis | Average | Lumbosacral spine | Ilium | Lower pelvis | Average | ||
| GAN+U-net[ | 0.696±0.031 | 0.652±0.039 | 0.638±0.035 | 0.662±0.035 | 4.21±0.48 | 5.08±0.63 | 5.61±0.71 | 4.97±0.61 | |
| SynSeg-Net[ | 0.718±0.027 | 0.675±0.034 | 0.661±0.032 | 0.685±0.031 | 3.89±0.44 | 4.68±0.58 | 5.15±0.64 | 4.57±0.55 | |
| Robust-Mseg[ | 0.731±0.024 | 0.693±0.030 | 0.675±0.028 | 0.700±0.027 | 3.67±0.40 | 4.35±0.52 | 4.83±0.58 | 4.28±0.50 | |
| SCM[ | 0.715±0.029 | 0.677±0.033 | 0.661±0.031 | 0.684±0.031 | 3.87±0.43 | 4.62±0.56 | 5.10±0.62 | 4.53±0.54 | |
| PEMMA[ | 0.748±0.022 | 0.709±0.026 | 0.688±0.027 | 0.715±0.025 | 3.45±0.38 | 4.12±0.49 | 4.56±0.55 | 4.04±0.47 | |
| Ours | 0.806±0.019 | 0.771±0.023 | 0.754±0.026 | 0.777±0.023 | 3.02±0.33 | 3.58±0.41 | 3.95±0.49 | 3.52±0.41 | |
表2 多种方法在不同ABM区域的分割性能比较
Tab.2 Comparison of segmentation performance of different methods in different ABM regions.
| Methods | Dice | ASSD | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lumbosacral spine | Ilium | Lower pelvis | Average | Lumbosacral spine | Ilium | Lower pelvis | Average | ||
| GAN+U-net[ | 0.696±0.031 | 0.652±0.039 | 0.638±0.035 | 0.662±0.035 | 4.21±0.48 | 5.08±0.63 | 5.61±0.71 | 4.97±0.61 | |
| SynSeg-Net[ | 0.718±0.027 | 0.675±0.034 | 0.661±0.032 | 0.685±0.031 | 3.89±0.44 | 4.68±0.58 | 5.15±0.64 | 4.57±0.55 | |
| Robust-Mseg[ | 0.731±0.024 | 0.693±0.030 | 0.675±0.028 | 0.700±0.027 | 3.67±0.40 | 4.35±0.52 | 4.83±0.58 | 4.28±0.50 | |
| SCM[ | 0.715±0.029 | 0.677±0.033 | 0.661±0.031 | 0.684±0.031 | 3.87±0.43 | 4.62±0.56 | 5.10±0.62 | 4.53±0.54 | |
| PEMMA[ | 0.748±0.022 | 0.709±0.026 | 0.688±0.027 | 0.715±0.025 | 3.45±0.38 | 4.12±0.49 | 4.56±0.55 | 4.04±0.47 | |
| Ours | 0.806±0.019 | 0.771±0.023 | 0.754±0.026 | 0.777±0.023 | 3.02±0.33 | 3.58±0.41 | 3.95±0.49 | 3.52±0.41 | |
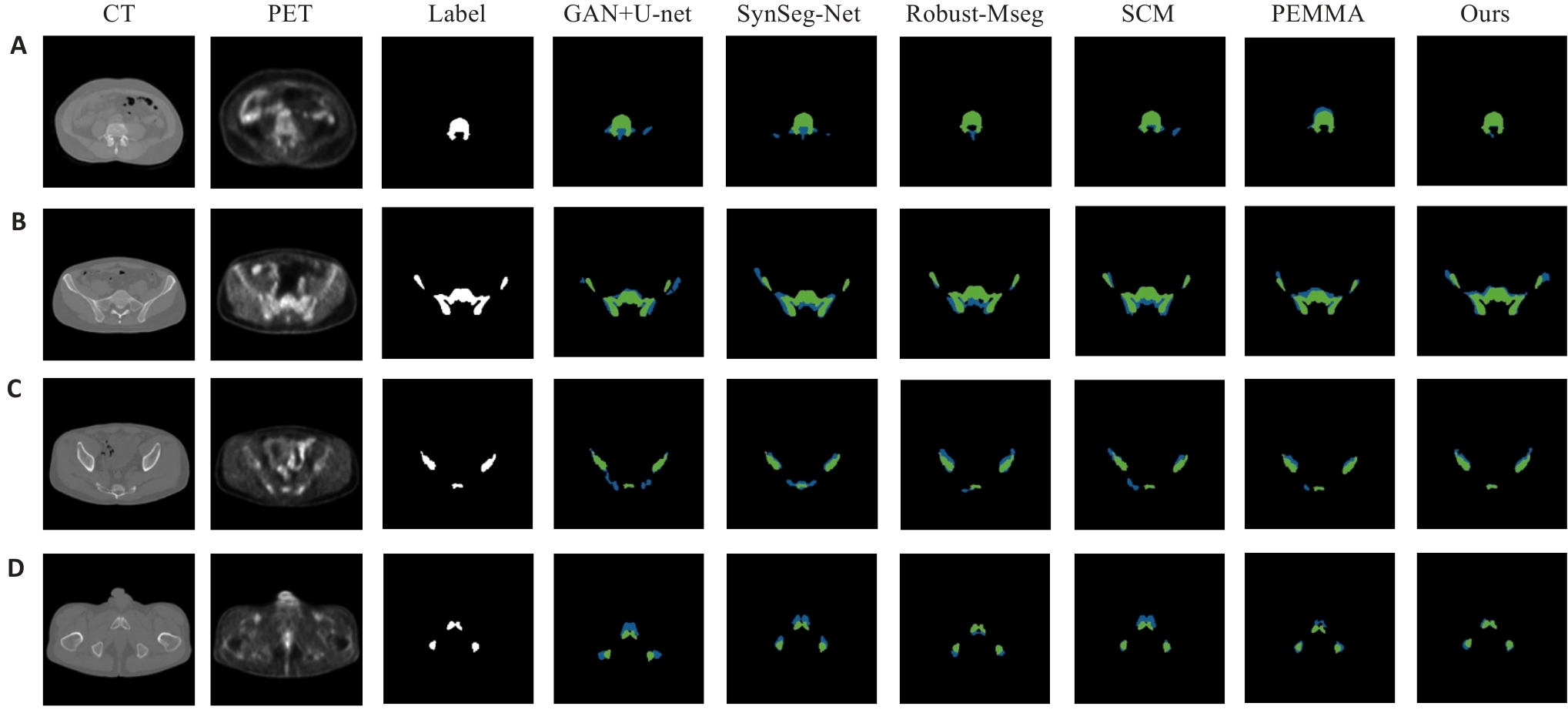
图7 ABM分割结果的可视化示例
Fig.7 Visual examples of ABM segmentation results. (A) Lumbosacral spine region; (B) Ilium region; (C) Lower pelvis region; (D) Representative case with ground truth (green) and predictions (blue).
| Diffusion steps T | PSNR (dB) | SSIM | NMSE | Dice | Average time (Epoch/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 22.28±1.29 | 0.797±0.043 | 0.0449±0.0076 | 0.548±0.049 | 113.5 |
| 250 | 23.94±1.05 | 0.827±0.036 | 0.0383±0.0063 | 0.625±0.041 | 142.6 |
| 500 | 25.58±0.86 | 0.861±0.029 | 0.0305±0.0050 | 0.715±0.020 | 184.0 |
| 1000 | 26.42±0.63 | 0.894±0.011 | 0.0235±0.0026 | 0.777±0.023 | 239.8 |
| 1500 | 26.21±0.70 | 0.888±0.025 | 0.0238±0.0039 | 0.768±0.030 | 337.1 |
| 2000 | 26.03±0.76 | 0.884±0.028 | 0.0245±0.0043 | 0.761±0.033 | 431.0 |
表3 不同扩散步数下的图像生成效果及分割预测对比
Tab.3 Comparison of image generation effects and segmentation prediction under different diffusion steps
| Diffusion steps T | PSNR (dB) | SSIM | NMSE | Dice | Average time (Epoch/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 22.28±1.29 | 0.797±0.043 | 0.0449±0.0076 | 0.548±0.049 | 113.5 |
| 250 | 23.94±1.05 | 0.827±0.036 | 0.0383±0.0063 | 0.625±0.041 | 142.6 |
| 500 | 25.58±0.86 | 0.861±0.029 | 0.0305±0.0050 | 0.715±0.020 | 184.0 |
| 1000 | 26.42±0.63 | 0.894±0.011 | 0.0235±0.0026 | 0.777±0.023 | 239.8 |
| 1500 | 26.21±0.70 | 0.888±0.025 | 0.0238±0.0039 | 0.768±0.030 | 337.1 |
| 2000 | 26.03±0.76 | 0.884±0.028 | 0.0245±0.0043 | 0.761±0.033 | 431.0 |
| Weight strategy | Weight function | PSNR (dB) | SSIM | NMSE | Dice |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed weight (0.3:0.7) | 24.91±0.92 | 0.851±0.026 | 0.0339±0.0048 | 0.728±0.037 | |
| Fixed weight (0.5:0.5) | 25.07±0.84 | 0.862±0.022 | 0.0323±0.0044 | 0.745±0.033 | |
| Fixed weight (0.7:0.3) | 24.73±0.99 | 0.845±0.029 | 0.0357±0.0055 | 0.719±0.040 | |
| Linear decay | 25.58±0.75 | 0.871±0.018 | 0.0287±0.0036 | 0.763±0.026 | |
| Cosine decay | 25.84±0.70 | 0.878±0.016 | 0.0271±0.0033 | 0.769±0.024 | |
| Exponential decay | 26.08±0.66 | 0.885±0.014 | 0.0253±0.0030 | 0.772±0.023 | |
| Exponential decay+error feedback | 26.42±0.63 | 0.894±0.011 | 0.0235±0.0026 | 0.777±0.023 |
表4 不同权重策略对模型性能的影响
Tab.4 Impact of different weighting strategies on model performance
| Weight strategy | Weight function | PSNR (dB) | SSIM | NMSE | Dice |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed weight (0.3:0.7) | 24.91±0.92 | 0.851±0.026 | 0.0339±0.0048 | 0.728±0.037 | |
| Fixed weight (0.5:0.5) | 25.07±0.84 | 0.862±0.022 | 0.0323±0.0044 | 0.745±0.033 | |
| Fixed weight (0.7:0.3) | 24.73±0.99 | 0.845±0.029 | 0.0357±0.0055 | 0.719±0.040 | |
| Linear decay | 25.58±0.75 | 0.871±0.018 | 0.0287±0.0036 | 0.763±0.026 | |
| Cosine decay | 25.84±0.70 | 0.878±0.016 | 0.0271±0.0033 | 0.769±0.024 | |
| Exponential decay | 26.08±0.66 | 0.885±0.014 | 0.0253±0.0030 | 0.772±0.023 | |
| Exponential decay+error feedback | 26.42±0.63 | 0.894±0.011 | 0.0235±0.0026 | 0.777±0.023 |
| Configuration | Input modality | Dice | ASSD | PSNR (dB) | SSIM | NMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | CT only | 0.664±0.036 | 4.97±0.62 | - | - | - |
| +CycleGAN | CT+pseudo-PET | 0.702±0.028 | 4.28±0.51 | 24.35±0.81 | 0.861±0.017 | 0.0281±0.0033 |
| +Conditional diffusion | CT+enhanced-PET | 0.726±0.031 | 4.11±0.55 | 26.42±0.63 | 0.894±0.011 | 0.0235±0.0026 |
| +Multi-scale fusion | CT+enhanced-PET+advanced fusion | 0.758±0.025 | 3.76±0.44 | 26.42±0.63 | 0.894±0.011 | 0.0235±0.0026 |
| Complete method | Full pipeline with joint optimization | 0.777±0.023 | 3.52±0.41 | 26.42±0.63 | 0.894±0.011 | 0.0235±0.0026 |
表5 消融实验结果
Tab.5 Ablation study results
| Configuration | Input modality | Dice | ASSD | PSNR (dB) | SSIM | NMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | CT only | 0.664±0.036 | 4.97±0.62 | - | - | - |
| +CycleGAN | CT+pseudo-PET | 0.702±0.028 | 4.28±0.51 | 24.35±0.81 | 0.861±0.017 | 0.0281±0.0033 |
| +Conditional diffusion | CT+enhanced-PET | 0.726±0.031 | 4.11±0.55 | 26.42±0.63 | 0.894±0.011 | 0.0235±0.0026 |
| +Multi-scale fusion | CT+enhanced-PET+advanced fusion | 0.758±0.025 | 3.76±0.44 | 26.42±0.63 | 0.894±0.011 | 0.0235±0.0026 |
| Complete method | Full pipeline with joint optimization | 0.777±0.023 | 3.52±0.41 | 26.42±0.63 | 0.894±0.011 | 0.0235±0.0026 |
| [1] | Siegel RL, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A, et al. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA A Cancer J Clinicians, 2020, 70(3): 145-64. doi:10.3322/caac.21601 |
| [2] | Conroy T, Bosset JF, Etienne PL, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy with FOLFIRINOX and preoperative chemoradiotherapy for patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (UNICANCER-PRODIGE 23): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2021, 22(5): 702-15. |
| [3] | Garcia-Aguilar J, Patil S, Gollub MJ, et al. Organ preservation in patients with rectal adenocarcinoma treated with total neoadjuvant therapy[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2022, 40(23): 2546-56. |
| [4] | Jin J, Tang Y, Hu C, et al. Multicenter, randomized, phase III trial of short-term radiotherapy plus chemotherapy versus long-term chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer (STELLAR)[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2022, 40(15): 1681-92. doi:10.1200/jco.2021.39.15_suppl.3510 |
| [5] | Bahadoer RR, Dijkstra EA, van Etten B, et al. Short-course radiotherapy followed by chemotherapy before total mesorectal excision (TME) versus preoperative chemoradiotherapy, TME, and optional adjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer (RAPIDO): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2021, 22(1): 29-42. |
| [6] | Diefenhardt M, Ludmir EB, Hofheinz RD, et al. Association of treatment adherence with oncologic outcomes for patients with rectal cancer: a post hoc analysis of the CAO/ARO/AIO-04 phase 3 randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2020, 6(9): 1416-21. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.2394 |
| [7] | Hayman JA, Callahan JW, Herschtal A, et al. Distribution of proliferating bone marrow in adult cancer patients determined using FLT-PET imaging[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2011, 79(3): 847-52. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.11.040 |
| [8] | McGuire SM, Menda Y, Ponto LL, et al. A methodology for incorporating functional bone marrow sparing in IMRT planning for pelvic radiation therapy[J]. Radiother Oncol, 2011, 99(1): 49-54. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2011.01.025 |
| [9] | Li N, Noticewala SS, Williamson CW, et al. Feasibility of atlas-based active bone marrow sparing intensity modulated radiation therapy for cervical cancer[J]. Radiother Oncol, 2017, 123(2): 325-30. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2017.02.017 |
| [10] | Yusufaly T, Miller A, Medina-Palomo A, et al. A multi-atlas approach for active bone marrow sparing radiation therapy: implementation in the NRG-GY006 trial[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2020, 108(5): 1240-7. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.06.071 |
| [11] | Czernin J, Allen-Auerbach M, Nathanson D, et al. PET/CT in oncology: current status and perspectives[J]. Curr Radiol Rep, 2013, 1(3): 177-90. doi:10.1007/s40134-013-0016-x |
| [12] | Yang TJ, Oh JH, Apte A, et al. Clinical and dosimetric predictors of acute hematologic toxicity in rectal cancer patients undergoing chemoradiotherapy[J]. Radiother Oncol, 2014, 113(1): 29-34. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2014.09.002 |
| [13] | Zhu JD, Wu H, Chen YL, et al. The correlation between the change of Hounsfield units value and Modic changes in the lumbar vertebral endplate[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2021, 22(1): 509. doi:10.1186/s12891-021-04330-5 |
| [14] | Meyer HJ, Pönisch W, Monecke A, et al. Can diagnostic low-dose whole-body CT reflect bone marrow findings in systemic mastocytosis [J]. Anticancer Res, 2020, 40(2): 1015-22. doi:10.21873/anticanres.14036 |
| [15] | Goodsitt MM, Shenoy A, Shen JC, et al. Evaluation of dual energy quantitative CT for determining the spatial distributions of red marrow and bone for dosimetry in internal emitter radiation therapy[J]. Med Phys, 2014, 41(5): 051901. doi:10.1118/1.4870378 |
| [16] | Isola P, Zhu JY, Zhou TH, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). July 21-26, 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA. IEEE, 2017: 5967-76. doi:10.1109/cvpr.2017.632 |
| [17] | Salehjahromi M, Karpinets TV, Sujit SJ, et al. Synthetic PET from CT improves diagnosis and prognosis for lung cancer: Proof of concept[J]. Cell Rep Med, 2024, 5(3): 101463. doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101463 |
| [18] | Kazerouni A, Aghdam EK, Heidari M, et al. Diffusion models in medical imaging: a comprehensive survey[J]. Med Image Anal, 2023, 88: 102846. doi:10.1016/j.media.2023.102846 |
| [19] | DhariwalPrafulla, NicholAlex. Diffusion models beat GANs on image synthesis[C]. Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021: 8780-94. |
| [20] | Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[M]//Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention-MICCAI 2015. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2015: 234-41. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28 |
| [21] | Zhu JY, Park T, Isola P, et al. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). October 22-29, 2017, Venice, Italy. IEEE, 2017: 2242-51. doi:10.1109/iccv.2017.244 |
| [22] | Arjovsky M, Chintala S, Bottou L. Wasserstein generative adversarial networks[C]. Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2017: 214-23. |
| [23] | Radford A, Metz L, Chintala S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:, 2015. |
| [24] | Huo YK, Xu ZB, Moon H, et al. SynSeg-net: synthetic segmentation without target modality ground truth[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2018: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2876633. doi:10.1109/tmi.2018.2876633 |
| [25] | Chen C, Dou Q, Jin YM, et al. Robust multimodal brain tumor segmentation via feature disentanglement and gated fusion[M]//Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2019. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2019: 447-56. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-32248-9_50 |
| [26] | Diao ZS, Jiang HY, Shi TY, et al. Siamese semi-disentanglement network for robust PET-CT segmentation[J]. Expert Syst Appl, 2023, 223: 119855. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2023.119855 |
| [27] | Saadi N, Saeed N, Yaqub M, et al. PEMMA: parameter-efficient multi-modal adaptation for medical image segmentation[M]//Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention- MICCAI 2024. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2024: 262-71. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-72390-2_43 |
| [28] | Ponnusamy R, Zhang M, Wang Y, et al. Automatic segmentation of bone marrow lesions on MRI using a deep learning method[J]. Bioengineering (Basel), 2024, 11(4): 374. doi:10.3390/bioengineering11040374 |
| [29] | Sizikova E, Badal A, Delfino JG, et al. Synthetic data in radiological imaging: current state and future outlook[J]. Bjr|artificial Intell, 2024, 1: ubae007. doi:10.1093/bjrai/ubae007 |
| [30] | Hu C, Cao N, Li XH, et al. CBCT-to-CT synthesis using a hybrid U-Net diffusion model based on transformers and information bottleneck theory[J]. Sci Rep, 2025, 15: 10816. doi:10.1038/s41598-025-92094-6 |
| [31] | Shi YQ, Abulizi A, Wang H, et al. Diffusion models for medical image computing: a survey[J]. Tsinghua Sci Technol, 2025, 30(1): 357-83. doi:10.26599/tst.2024.9010047 |
| [1] | 计寰宇, 王蕊, 高盛祥, 车文刚. SG-UNet:基于全局注意力和自校准卷积增强的黑色素瘤分割模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1317-1326. |
| [2] | 翁诺舟, 谭彬, 曾文涛, 古家宇, 翁炼基, 郑克鸿. 过表达RGL1通过激活CDC42/RAC1复合体上调运动型黏着斑组装促进结直肠癌转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 1031-1038. |
| [3] | 马振南, 刘福全, 赵雪峰, 张晓微. DTX2促进奥沙利铂耐药的结直肠癌细胞增殖、侵袭和上皮间质转化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 829-836. |
| [4] | 庆顺杰, 沈智勇. 过表达己糖激酶2通过激活JAK/STAT途径促进结直肠癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭并调节肿瘤免疫微环境[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 542-553. |
| [5] | 喻珍妮, 高竟哲, 孙惠, 冯芹, 那效旗, 张宁, 沈昆双, 王媛媛, 王喜军. 肠道菌群、T细胞在结直肠癌发病中的因果关联:孟德尔随机化分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2756-2766. |
| [6] | 贺亚迪, 周炫汝, 金锦辉, 宋婷. 基于PE-CycleGAN网络的鼻咽癌自适应放疗CBCT-sCT生成研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 179-186. |
| [7] | 纪凯, 于冠宇, 周乐其, 张天帅, 凌潜龙, 满文江, 朱冰, 张卫. HNRNPA1基因在结直肠癌组织中高表达及其潜在的诊断和治疗价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1685-1695. |
| [8] | 张银亮, 骆泽谭, 赵睿, 赵娜, 徐志东, 奥迪, 丛古一, 刘新宇, 郑海伦. 血根碱通过调控STUB1/GPX4诱导直肠癌细胞发生铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1537-1544. |
| [9] | 李和平, 李高桦, 张学华, 王亚楠. 直肠癌炎症蛋白因子的遗传驱动:孟德尔随机化方法在临床预后研究中的应用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1361-1370. |
| [10] | 武若杰, 刘 睿, 张一粟, 李晓红. 帕瑞昔布钠改善腹腔镜下直肠癌根治术患者的炎症微环境并促进患者恢复:基于下调CXCL8-CXCR1/2表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 363-369. |
| [11] | 郗雪艳, 邓婷, 杜伯雨. 结直肠成纤维细胞通过激活ERK信号通路促进结直肠癌细胞的恶性生物学行为[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(10): 1866-1873. |
| [12] | 刘羽轩, 楚智钦, 张 煜. 基于物理模型的级联生成对抗网络加速定量多参数磁共振成像[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1402-1409. |
| [13] | 颜 畅, 刘 爽, 宋庆志, 胡艺冰. 二甲双胍通过抑制线粒体氧化磷酸化降低结直肠癌干细胞的自我更新能力[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1279-1286. |
| [14] | 魏 可, 石纪雯, 肖雨寒, 王文锐, 杨清玲, 陈昌杰. miR-30e-5p过表达促进结直肠癌细胞的增殖和迁移:基于下调PTEN激活CXCL12轴[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1081-1092. |
| [15] | 张雪芳, 陈延华, 李宗恒, 尚 靖, 袁泽婷, 邓皖利, 骆 莺, 韩 娜, 殷佩浩, 殷 军. 六神丸治疗小鼠结肠炎相关性结直肠癌的作用机制:基于网络药理学和体内验证方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1051-1062. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||