南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 179-186.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.21
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-07-15
出版日期:2025-01-20
发布日期:2025-01-20
通讯作者:
宋婷
E-mail:540651179@qq.com;tingsong2015@smu.edu.cn
作者简介:贺亚迪,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 540651179@qq.com
基金资助:
Yadi HE1,2( ), Xuanru ZHOU1, Jinhui JIN1, Ting SONG1(
), Xuanru ZHOU1, Jinhui JIN1, Ting SONG1( )
)
Received:2024-07-15
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-01-20
Contact:
Ting SONG
E-mail:540651179@qq.com;tingsong2015@smu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探索基于PE-CycleGAN方法从锥形束CT(CBCT)合成高质量CT(sCT),用于鼻咽癌自适应放疗(ART)。 方法 提出感知增强的CycleGAN模型(PE-CycleGAN),引入判别器双重对比度损失、生成器多感知损失和改进的U-Net结构。采用80例鼻咽癌患者的CBCT和CT作为训练集,7例为测试集。通过量化sCT与参考CT的平均绝对误差(MAE)、峰值信噪比(PSNR)、结构相似性指标(SSIM)以及sCT与参考CT剂量gamma通过率、靶区和危及器官(OAR)相对剂量偏差,评估sCT图像质量和剂量计算精度。 结果 PE-CycleGAN生成sCT与对应标准CT的MAE为56.89±13.84 HU,较CBCT的81.06±15.86 HU降低约30%(P<0.001)。PE-CycleGAN的PSNR和SSIM(26.69±2.41 dB,0.92±0.02)高于CBCT(21.54±2.37 dB,0.86±0.05)(P<0.001)。在与计划CT剂量gamma分析中,在2 mm/2%标准下,PE-CycleGAN的sCT剂量比对通过率(90.13±3.75)%高于CBCT的(81.65±3.92)% (P<0.001)和CycleGAN的(87.69±3.50)% (P<0.05)。在3 mm/3%标准下,PE-CycleGAN 的sCT通过率(97.20±2.52)%同样优于CBCT的(86.92±3.51)% (P<0.001)和CycleGAN的(94.58±2.23)% (P<0.01)。sCT相比计划CT的靶区和OAR相对剂量偏差均值除Lens Dmax(Gy)为3.38%(P=0.09)外都在±3%范围内(P>0.05),PTVnx HI、PTVnd HI、PTVnd CI、PTV1 HI、PRV_SC、PRV_BS、Parotid、Larynx、Oral、Mandible、PRV_ON相对剂量偏差均值都小于±1%(P>0.05)。 结论 PE-CycleGAN能从CBCT快速合成高质量sCT,可用于鼻咽癌的CBCT引导ART。
贺亚迪, 周炫汝, 金锦辉, 宋婷. 基于PE-CycleGAN网络的鼻咽癌自适应放疗CBCT-sCT生成研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 179-186.
Yadi HE, Xuanru ZHOU, Jinhui JIN, Ting SONG. PE-CycleGAN network based CBCT-sCT generation for nasopharyngeal carsinoma adaptive radiotherapy[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 179-186.
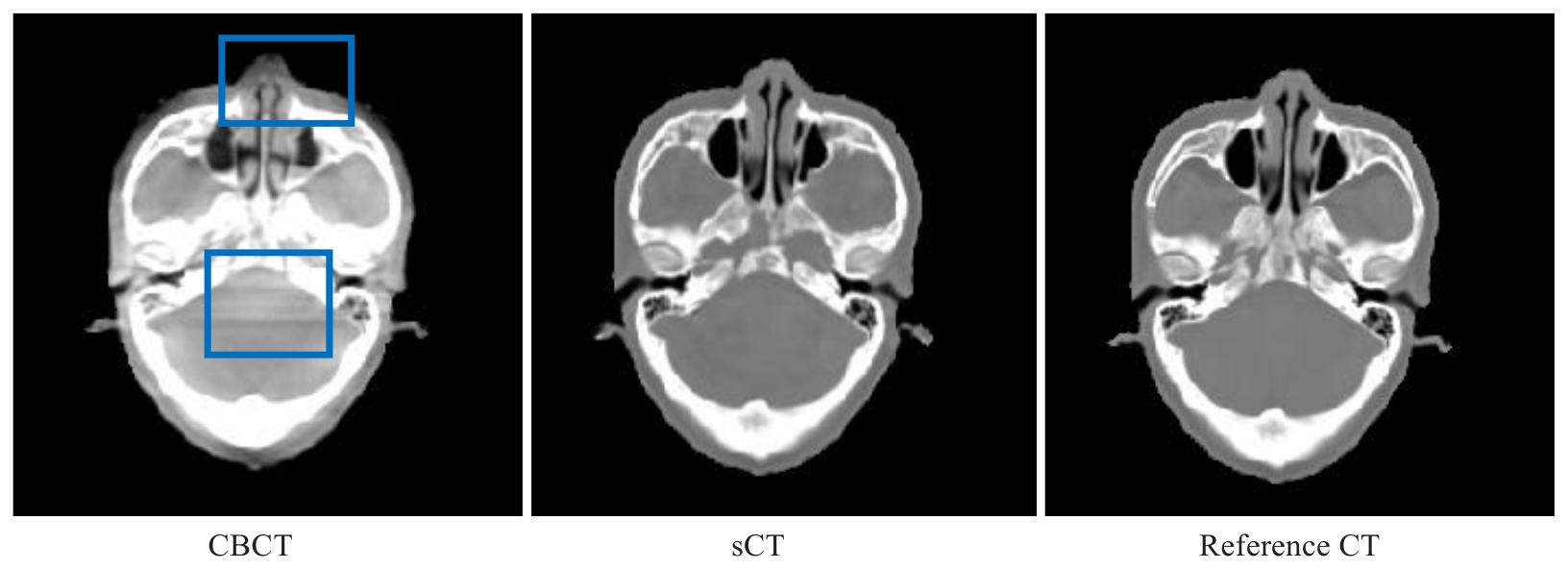
图2 一例鼻咽癌患者的CBCT、PE-CycleGAN合成sCT和参考CT图像
Fig.2 CBCT, PE-CycleGAN-generated synthetic CT (sCT) images and reference CT images of a patient with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. CBCT sCT Reference CT
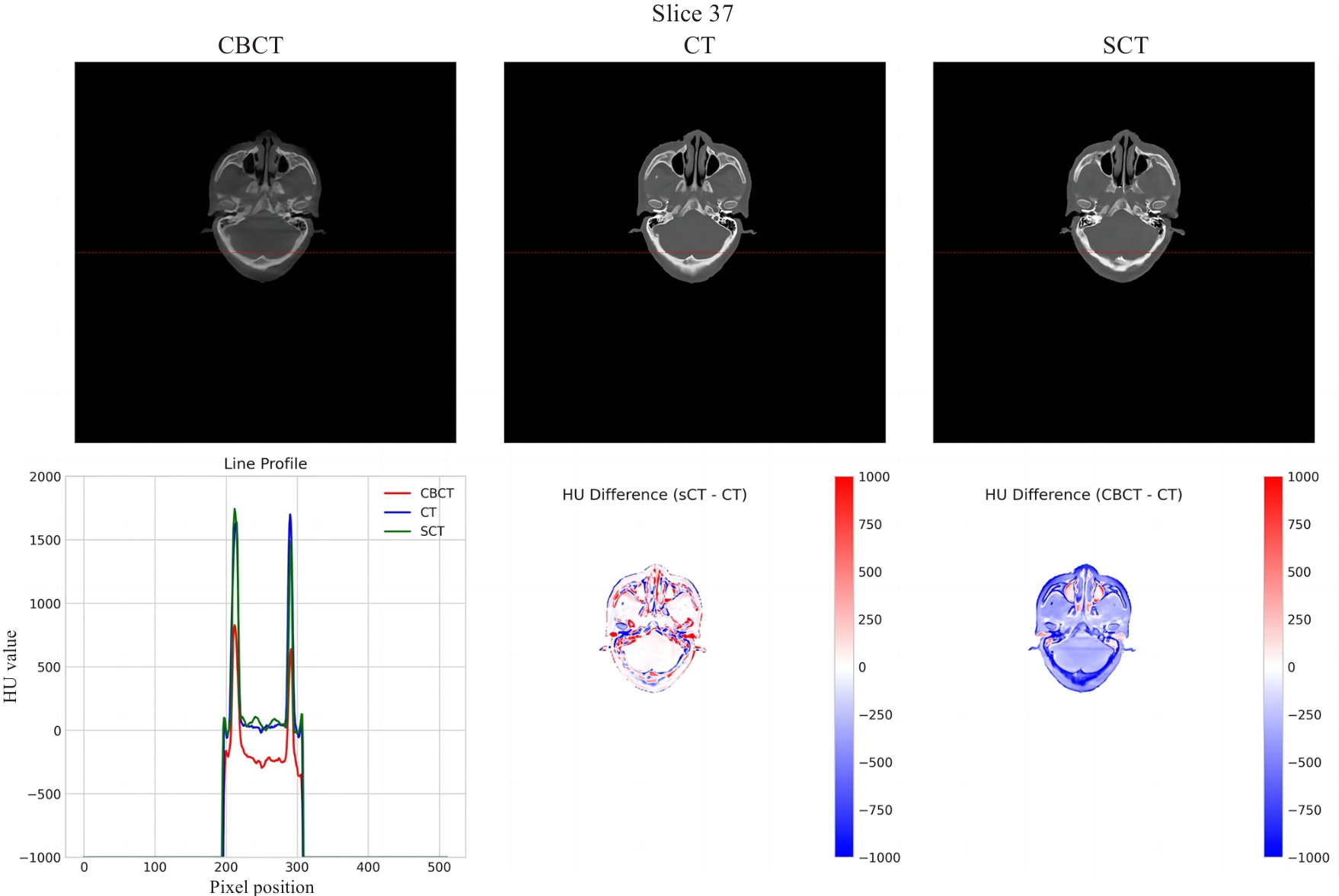
图3 一例鼻咽癌患者的原始参考CT图像和PE-CycleGAN合成sCT的Line Profile和HU Difference
Fig.3 Line profile and HU difference between original reference CT and PE-CycleGAN-generated sCT images for a NPC patient.
| Method | MAE(HU) | PSNR(dB) | SSIM |
|---|---|---|---|
| CBCT | 81.06±15.86 | 21.54±2.37 | 0.86±0.05 |
| CycleGAN | 63.92±12.08 | 24.89±2.15 | 0.89±0.04 |
| PE-CycleGAN | 56.89±13.84 | 26.69±2.41 | 0.92±0.02 |
表1 sCT、CBCT相对CT的图像质量定量对比
Tab.1 Quantitative comparison of image quality between sCT,CBCT and reference CT images (Mean±SD)
| Method | MAE(HU) | PSNR(dB) | SSIM |
|---|---|---|---|
| CBCT | 81.06±15.86 | 21.54±2.37 | 0.86±0.05 |
| CycleGAN | 63.92±12.08 | 24.89±2.15 | 0.89±0.04 |
| PE-CycleGAN | 56.89±13.84 | 26.69±2.41 | 0.92±0.02 |
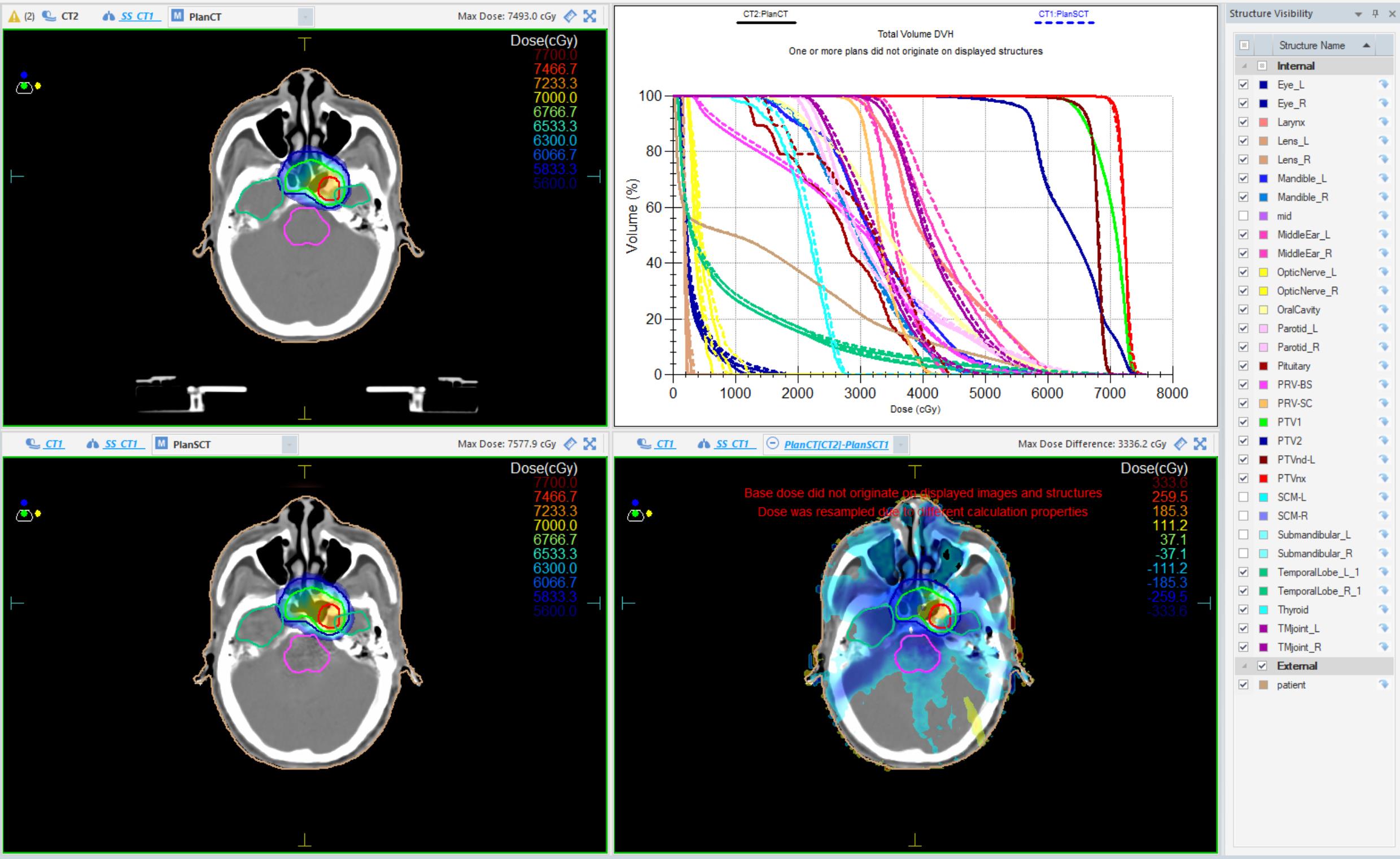
图4 一例患者在CT、PE-CycleGAN合成sCT图像上的剂量分布
Fig.4 Dose distribution on CT and PE-CycleGAN-generated sCT images for a patient. Top left: Dose distribution on planning CT; Top right: Dose-volume histogram (DVH) for planning CT and sCT; Bottom left: Dose distribution on sCT; Bottom right: Dose distribution difference between planning CT and sCT.
| Method | 2 mm/2% | 3 mm/3% | P value (vs CBCT) | P value (vs CycleGan) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBCT | (81.65±3.92) % | (86.92±3.51) % | - | - |
| CycleGAN | (87.69±3.50) % | (94.58±2.23) % | - | - |
| PE-CycleGAN | (90.13±3.75) % | (97.20±2.52) % | <0.001 (2 mm/2%), <0.001 (3 mm/3%) | <0.05 (2 mm/2%), <0.01 (3 mm/3%) |
表2 sCT、CBCT的gamma剂量通过率
Tab.2 Gamma pass rates for sCT and CBCT
| Method | 2 mm/2% | 3 mm/3% | P value (vs CBCT) | P value (vs CycleGan) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBCT | (81.65±3.92) % | (86.92±3.51) % | - | - |
| CycleGAN | (87.69±3.50) % | (94.58±2.23) % | - | - |
| PE-CycleGAN | (90.13±3.75) % | (97.20±2.52) % | <0.001 (2 mm/2%), <0.001 (3 mm/3%) | <0.05 (2 mm/2%), <0.01 (3 mm/3%) |
| Structure | Parameter | CT | sCT | Relative deviation (%) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTVnx | HI | 1.07±0.02 | 1.08±0.03 | 0.93±0.93 | 0.28 |
| CI | 0.58±0.13 | 0.59±0.12 | 1.72±1.72 | 0.36 | |
| PTVnd | HI | 1.11±0.07 | 1.11±0.06 | 0.00±0.90 | 0.95 |
| CI | 0.13±0.10 | 0.13±0.10 | 0.00±0.00 | 1.00 | |
| PTV1 | HI | 1.17±0.03 | 1.17±0.03 | 0.00±0.85 | 0.89 |
| CI | 0.46±0.14 | 0.47±0.14 | 2.17±2.17 | 0.42 | |
| PTV2 | HI | 1.41±0.09 | 1.39±0.06 | -1.42±1.42 | 0.18 |
| CI | 0.68±0.14 | 0.69±0.13 | 1.47±1.47 | 0.33 | |
| PRV_SC | Dmax (Gy) | 45.59±5.13 | 45.51±4.84 | -0.17±0.17 | 0.82 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 36.10±4.14 | 35.98±3.97 | -0.33±0.33 | 0.65 | |
| PRV_BS | Dmax (Gy) | 61.91±7.33 | 62.03±7.38 | 0.19±0.19 | 0.78 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 27.55±7.20 | 27.73±7.38 | 0.65±0.65 | 0.52 | |
| Parotid | V30 (%) | 49.91±8.82 | 49.41±8.64 | -1.00±1.00 | 0.31 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 33.67±3.83 | 33.55±3.89 | -0.36±0.36 | 0.64 | |
| Temp | Dmax (Gy) | 67.04±9.74 | 67.92±9.98 | 1.31±1.31 | 0.22 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 11.16±7.90 | 11.41±8.03 | 2.24±2.24 | 0.14 | |
| Larynx | Dmean (Gy) | 41.78±6.56 | 41.72±7.06 | -0.14±0.14 | 0.87 |
| Oral | Dmean (Gy) | 36.20±5.51 | 36.20±5.70 | 0.00±0.00 | 1.00 |
| Mandible | Dmax (Gy) | 63.50±7.06 | 63.66±6.97 | 0.25±0.25 | 0.73 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 35.59±6.73 | 35.53±6.65 | -0.17±0.17 | 0.82 | |
| Lens | Dmax (Gy) | 3.55±2.47 | 3.67±2.51 | 3.38±3.38 | 0.09 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 5.81±4.07 | 5.84±4.08 | 0.52±0.52 | 0.67 | |
| Eye | Dmax (Gy) | 24.95±27.58 | 25.28±27.22 | 1.32±1.32 | 0.25 |
| PRV_ON | Dmean (Gy) | 18.90±2.95 | 18.87±2.90 | -0.16±0.16 | 0.84 |
表3 PE-CycleGAN生成的sCT与CT在靶区和关键OAR剂量的对比
Tab.3 Comparison of target and key organ-at-risk doses between PE-CycleGAN-generated sCT and CT images (Mean±SD)
| Structure | Parameter | CT | sCT | Relative deviation (%) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTVnx | HI | 1.07±0.02 | 1.08±0.03 | 0.93±0.93 | 0.28 |
| CI | 0.58±0.13 | 0.59±0.12 | 1.72±1.72 | 0.36 | |
| PTVnd | HI | 1.11±0.07 | 1.11±0.06 | 0.00±0.90 | 0.95 |
| CI | 0.13±0.10 | 0.13±0.10 | 0.00±0.00 | 1.00 | |
| PTV1 | HI | 1.17±0.03 | 1.17±0.03 | 0.00±0.85 | 0.89 |
| CI | 0.46±0.14 | 0.47±0.14 | 2.17±2.17 | 0.42 | |
| PTV2 | HI | 1.41±0.09 | 1.39±0.06 | -1.42±1.42 | 0.18 |
| CI | 0.68±0.14 | 0.69±0.13 | 1.47±1.47 | 0.33 | |
| PRV_SC | Dmax (Gy) | 45.59±5.13 | 45.51±4.84 | -0.17±0.17 | 0.82 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 36.10±4.14 | 35.98±3.97 | -0.33±0.33 | 0.65 | |
| PRV_BS | Dmax (Gy) | 61.91±7.33 | 62.03±7.38 | 0.19±0.19 | 0.78 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 27.55±7.20 | 27.73±7.38 | 0.65±0.65 | 0.52 | |
| Parotid | V30 (%) | 49.91±8.82 | 49.41±8.64 | -1.00±1.00 | 0.31 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 33.67±3.83 | 33.55±3.89 | -0.36±0.36 | 0.64 | |
| Temp | Dmax (Gy) | 67.04±9.74 | 67.92±9.98 | 1.31±1.31 | 0.22 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 11.16±7.90 | 11.41±8.03 | 2.24±2.24 | 0.14 | |
| Larynx | Dmean (Gy) | 41.78±6.56 | 41.72±7.06 | -0.14±0.14 | 0.87 |
| Oral | Dmean (Gy) | 36.20±5.51 | 36.20±5.70 | 0.00±0.00 | 1.00 |
| Mandible | Dmax (Gy) | 63.50±7.06 | 63.66±6.97 | 0.25±0.25 | 0.73 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 35.59±6.73 | 35.53±6.65 | -0.17±0.17 | 0.82 | |
| Lens | Dmax (Gy) | 3.55±2.47 | 3.67±2.51 | 3.38±3.38 | 0.09 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 5.81±4.07 | 5.84±4.08 | 0.52±0.52 | 0.67 | |
| Eye | Dmax (Gy) | 24.95±27.58 | 25.28±27.22 | 1.32±1.32 | 0.25 |
| PRV_ON | Dmean (Gy) | 18.90±2.95 | 18.87±2.90 | -0.16±0.16 | 0.84 |
| 1 | 吴伟伟, 李韶今, 尹 慧, 等. 局部晚期鼻咽癌调强放疗中解剖结构改变及剂量分布变化研究[J]. 中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2017, 37(11): 826-31. |
| 2 | Zhao SH, Han J, Yang ZY, et al. Anatomical and dosimetric variations during volumetric modulated arc therapy in patients with locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma after induction therapy: implications for adaptive radiation therapy[J]. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol, 2024, 49: 100861. |
| 3 | Liu YZ, Lei Y, Wang TH, et al. CBCT-based synthetic CT generation using deep-attention cycleGAN for pancreatic adaptive radiotherapy[J]. Med Phys, 2020, 47(6): 2472-83. |
| 4 | Liang X, Chen LY, Nguyen D, et al. Generating synthesized computed tomography (CT) from cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) using CycleGAN for adaptive radiation therapy[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2019, 64(12): 125002. |
| 5 | Chen LY, Liang X, Shen CY, et al. Synthetic CT generation from CBCT images via deep learning[J]. Med Phys, 2020, 47(3): 1115-25. |
| 6 | 全科润, 程品晶, 陈榕钦, 等. 基于循环生成对抗网络的鼻咽癌CBCT图像修正[J]. 中国医学物理学杂志, 2021, 38(5): 582-6. |
| 7 | 亓孟科, 李永宝, 吴艾茜, 等. 基于生成对抗网络的鼻咽癌患者伪CT合成方法研究[J]. 中华放射肿瘤学杂志, 2020, 29(4): 267-72. |
| 8 | Hansen DC, Landry G, Kamp F, et al. ScatterNet: a convolutional neural network for cone-beam CT intensity correction[J]. Med Phys, 2018, 45(11): 4916-26. |
| 9 | 周 琼, 李永武, 王 奇, 等. 基于形变配准和伪CT的鼻咽癌自适应放疗剂量评估[J]. 中国医学物理学杂志, 2019, 36(8): 892-7. |
| 10 | Rusanov B, Hassan GM, Reynolds M, et al. Deep learning methods for enhancing cone-beam CT image quality toward adaptive radiation therapy: a systematic review[J]. Med Phys, 2022, 49(9): 6019-54. |
| 11 | Kida S, Kaji, Nawa K, et al. Visual enhancement of Cone-beam CT by use of CycleGAN[J]. Med Phys, 2020, 47(3): 998-1010. |
| 12 | Liu JW, Yan H, Cheng HL, et al. CBCT-based synthetic CT generation using generative adversarial networks with disentangled representation[J]. Quant Imaging Med Surg, 2021, 11(12): 4820-34. |
| 13 | Wang TH, Lei Y, Fu YB, et al. Machine learning in quantitative PET: a review of attenuation correction and low-count image reconstruction methods[J]. Phys Med, 2020, 76: 294-306. |
| 14 | 潘 丹, 贾龙飞, 曾 安. 生成式对抗网络在医学图像处理中的应用[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2018, 35(6): 970-6. |
| 15 | Ronneberger O. Invited talk: U-net convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[M]//Informatik aktuell. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2017: 3. |
| 16 | He KM, Zhang XY, Ren SQ, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). June 27-30, 2016. Las Vegas, NV, USA. IEEE, 2016: 770-8. |
| 17 | Isola P, Zhu JY, Zhou T, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[J]. IEEE TPAMI, 2021, 43(12): 4254-67. |
| 18 | Wang R, Wu ZX, Weng ZJ, et al. Cross-domain contrastive learning for unsupervised domain adaptation[J]. IEEE Trans Multimedia, 2023, 25: 1665-73. |
| 19 | Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, et al. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2004, 13(4): 600-12. |
| 20 | Galić I, Habijan M, Leventić H, et al. Machine learning empowering personalized medicine: a comprehensive review of medical image analysis methods[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12(21): 4411. |
| 21 | Huynh E, Hosny A, Guthier C, et al. Artificial intelligence in radiation oncology[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2020, 17(12): 771-81. |
| 22 | Wendling M, Morrow A, Hoggarth M, et al. An efficient protocol for radiotherapy quality control with machine learning[J]. Med Phys, 2020, 47(4): 1526-34. |
| 23 | Lei Y, Tang XY, Higgins K, et al. Learning-based CBCT correction using alternating random forest based on auto-context model[J]. Med Phys, 2019, 46(2): 601-18. |
| 24 | Jiang J, Sharfo AWM, Mak RH, et al. Development and validation of an MRI‐only synthetic CT generation method using cycle‐consistent generative adversarial networks for prostate radiotherapy[J]. Med Phys, 2021, 48(1): 416-29. |
| 25 | Thummerer A, Zaffino P, Meijers A, et al. Comparison of CBCT based synthetic CT methods suitable for proton dose calculations in adaptive proton therapy[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2020, 65(9): 095002. |
| 26 | Pulliam KB, Huang JY, Howell RM, et al. Comparison of 2D and 3D gamma analyses[J]. Med Phys, 2014, 41(2): 021710. |
| 27 | 孙鸿飞, 倪昕晔, 杨建华. 基于深度学习方法的伪CT图像合成技术研究及在放疗中的应用进展[J]. 中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2021, 41(3): 222-8. |
| 28 | Lei Y, Harms J, Wang TH, et al. MRI-only based synthetic CT generation using dense cycle consistent generative adversarial networks[J]. Med Phys, 2019, 46(8): 3565-81. |
| 29 | Liu Y, Lei Y, Wang Y, et al. Evaluation of a deep learning-based synthetic CT generation method for MRI-only breast radiotherapy[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2020, 65(8): 085020. |
| 30 | Maspero M, Savenije MHF, Dinkla AM, et al. Dose evaluation of fast synthetic-CT generation using a generative adversarial network for general pelvis MR-only radiotherapy[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2018, 63(18): 185001. |
| 31 | Kim J, Park S, Yu H, et al. Deep learning-based synthetic CT generation from MR images for PET attenuation correction: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. IEEE T Radiat Plasma, 2022, 6(3): 273-287. |
| 32 | Sonke JJ, Aznar M, Rasch C. Adaptive radiotherapy for anatomical changes[J]. Semin Radiat Oncol, 2019, 29(3): 245-57. |
| 33 | Dona Lemus OM, Cao MS, Cai B, et al. Adaptive radiotherapy: next-generation radiotherapy[J]. Cancers, 2024, 16(6): 1206. |
| [1] | 方威扬, 肖慧, 王爽, 林晓明, 陈超敏. 基于MRI影像和临床参数特征融合的深度学习模型预测术前肝细胞癌的细胞角蛋白19状态[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1738-1751. |
| [2] | 欧嘉志, 詹长安, 杨丰. 一维卷积神经网络的自编码癫痫发作异常检测模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1796-1804. |
| [3] | 汪辰, 蒙铭强, 李明强, 王永波, 曾栋, 边兆英, 马建华. 基于双域Transformer耦合特征学习的CT截断数据重建模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 950-959. |
| [4] | 龙楷兴, 翁丹仪, 耿 舰, 路艳蒙, 周志涛, 曹 蕾. 基于多模态多示例学习的免疫介导性肾小球疾病自动分类方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 585-593. |
| [5] | 肖 慧, 方威扬, 林铭俊, 周振忠, 费洪文, 陈超敏. 基于两阶段分析的多尺度颈动脉斑块检测方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 387-396. |
| [6] | 刘操林, 邹青清, 王梦虹, 杨芹枚, 宋丽文, 陆紫箫, 冯前进, 赵英华. 鉴别原发性骨肿瘤骨样和软骨样基质矿化:基于CT和临床特征的深度学习融合模型的多中心回顾性研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2412-2420. |
| [7] | 弥 佳, 周宇佳, 冯前进. 基于正交视角X线图像重建的3D/2D配准方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1636-1643. |
| [8] | 楚智钦, 屈耀铭, 钟 涛, 梁淑君, 温志波, 张 煜. 磁共振酰胺质子转移模态的胶质瘤IDH基因分型识别:基于深度学习的Dual-Aware框架[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1379-1387. |
| [9] | 刘羽轩, 楚智钦, 张 煜. 基于物理模型的级联生成对抗网络加速定量多参数磁共振成像[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1402-1409. |
| [10] | 于佳弘, 张昆鹏, 靳 爽, 苏 哲, 徐晓桐, 张 华. 弦图插值结合UNIT网络图像转换的CT金属伪影校正[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1214-1223. |
| [11] | 滕 琳, 王 斌, 冯前进. 头颈癌放疗计划剂量分布的预测方法:基于深度学习的算法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 1010-1016. |
| [12] | 周 昊, 曾 栋, 边兆英, 马建华. 基于半监督网络的组织感知CT图像对比度的增强方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 985-993. |
| [13] | 吴雪扬, 张 煜, 张 华, 钟 涛. 基于注意力机制和多模态特征融合的猕猴脑磁共振图像全脑分割[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(12): 2118-2125. |
| [14] | 廖家慧, 李涵懿, 詹长安, 杨 丰. 癫痫发作预测模型:斯托克韦尔变换的生成对抗与长短时记忆网络半监督方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(1): 17-28. |
| [15] | 和法伟, 王永波, 陶 熙, 朱曼曼, 洪梓璇, 边兆英, 马建华. 基于噪声水平估计的低剂量螺旋CT投影数据恢复[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(6): 849-859. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||