南方医科大学学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 83-93.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.09
李钊泳1( ), 周凤华1, 孙晓敏1,2, 赵华杉1, 金瑶1, 何培坤1, 贾钰华1,2(
), 周凤华1, 孙晓敏1,2, 赵华杉1, 金瑶1, 何培坤1, 贾钰华1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-07-24
出版日期:2026-01-20
发布日期:2026-01-16
通讯作者:
贾钰华
E-mail:1425519001@qq.com;jyh@smu.edu.cn
作者简介:李钊泳,在读博士研究生,E-mail: 1425519001@qq.com
基金资助:
Zhaoyong LI1( ), Fenghua ZHOU1, Xiaomin SUN1,2, Huashan ZHAO1, Yao JIN1, Peikun HE1, Yuhua JIA1,2(
), Fenghua ZHOU1, Xiaomin SUN1,2, Huashan ZHAO1, Yao JIN1, Peikun HE1, Yuhua JIA1,2( )
)
Received:2025-07-24
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2026-01-16
Contact:
Yuhua JIA
E-mail:1425519001@qq.com;jyh@smu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 基于网络药理学探讨降脂祛斑方治疗2型糖尿病合并高脂血症的分子机制,并通过动物实验和临床对照试验验证其疗效与安全性。 方法 基于TCMSP和GeneCards数据库筛选降脂祛斑方活性成分和疾病靶点,构建网络图并进行PPI分析、GO功能和KEGG通路富集分析。动物实验用ApoE-/-小鼠高脂饲料造模24周,设空白组、模型组、中药低/高剂量组和辛伐他汀组(n=6),第9~24周给药,检测体质量、血糖、血脂、肝脏病理及炎症因子表达。临床研究纳入72例2型糖尿病合并高脂血症患者,随机分为观察组和对照组,36例/组,均给予二甲双胍联合恩格列净基础治疗,观察组加用降脂祛斑方,对照组加用辛伐他汀,治疗12周后观察相关指标变化。 结果 网络药理学筛得65个潜在靶点,核心成分包括槲皮素、山奈酚、木犀草素等,关键靶点为IL-6、IL-1β、TNF-α等。富集分析显示主要涉及炎症反应、糖尿病并发症等通路。动物实验显示,降脂祛斑方呈剂量依赖性改善体质量、血糖及血脂(P<0.05),高剂量组肝脂肪变性改善优于辛伐他汀组,炎症因子降低(P<0.05)。临床研究中,观察组29例、对照组31例完成试验。观察组治疗后体质量、空腹血糖、甘油三酯、糖化血红蛋白及肝酶水平改善(P<0.05),空腹血糖水平低于对照组(P<0.05),两组总有效率相近(P>0.05)。 结论 降脂祛斑方通过多成分协同作用,可能主要通过调控炎症-代谢网络发挥治疗2型糖尿病合并高脂血症的效果。
李钊泳, 周凤华, 孙晓敏, 赵华杉, 金瑶, 何培坤, 贾钰华. 降脂祛斑方多成分协同调控炎症-代谢网络改善2型糖尿病合并高脂血症:网络药理学与临床验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2026, 46(1): 83-93.
Zhaoyong LI, Fenghua ZHOU, Xiaomin SUN, Huashan ZHAO, Yao JIN, Peikun HE, Yuhua JIA. Jiangzhi Quban Recipe improves type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with hyperlipidemia by multi-target regulation of the inflammation-metabolism network: network pharmacology analysis and clinical validation[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2026, 46(1): 83-93.
| Target gene | Forward primer (5' to 3') | Reverse primer (5' to 3') |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG | CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT |
| IL-6 | TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC | TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC |
| IL-1β | TTCAGGCAGGCAGTATCACTC | GAAGGTCCACGGGAAAGACAC |
| TNF-α | TGGAACTGGCAGAAGAGGCAC | AGGGTCTGGGCCATAGAACTGA |
表1 引物序列
Tab.1 Sequences of primers for RT-qPCR
| Target gene | Forward primer (5' to 3') | Reverse primer (5' to 3') |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG | CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT |
| IL-6 | TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC | TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC |
| IL-1β | TTCAGGCAGGCAGTATCACTC | GAAGGTCCACGGGAAAGACAC |
| TNF-α | TGGAACTGGCAGAAGAGGCAC | AGGGTCTGGGCCATAGAACTGA |
| MOL ID | Molecule name | TCM | OB (%) | DL | Degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOL000098 | Quercetin | Zhizi;Huanglian;Sanqi;Huzhang | 46.43 | 0.28 | 56 |
| MOL000422 | Kaempferol | Zhizi | 41.88 | 0.24 | 18 |
| MOL000006 | Luteolin | Danshen;Huzhang | 36.16 | 0.25 | 17 |
| MOL007154 | Tanshinone IIA | Danshen | 49.89 | 0.4 | 11 |
| MOL000449 | stigmasterol | Zhizi;Chishao;jmz;Sanqi | 43.83 | 0.76 | 11 |
| MOL000785 | palmatine | Huanglian | 64.6 | 0.65 | 10 |
| MOL007093 | dan-shexinkum d | Danshen | 38.88 | 0.55 | 10 |
| MOL000358 | beta-sitosterol | Zhizi;Chishao;Sanqi;Huzhang | 36.91 | 0.75 | 9 |
| MOL003095 | 5-hydroxy-7-methoxy-2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl) chromone | Zhizi | 51.96 | 0.41 | 9 |
| MOL002904 | Berlambine | Huanglian | 36.68 | 0.82 | 8 |
表2 降脂祛斑方部分有效活性成分列表
Tab.2 Effective active ingredients in Jiangzhi Quban Recipe
| MOL ID | Molecule name | TCM | OB (%) | DL | Degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOL000098 | Quercetin | Zhizi;Huanglian;Sanqi;Huzhang | 46.43 | 0.28 | 56 |
| MOL000422 | Kaempferol | Zhizi | 41.88 | 0.24 | 18 |
| MOL000006 | Luteolin | Danshen;Huzhang | 36.16 | 0.25 | 17 |
| MOL007154 | Tanshinone IIA | Danshen | 49.89 | 0.4 | 11 |
| MOL000449 | stigmasterol | Zhizi;Chishao;jmz;Sanqi | 43.83 | 0.76 | 11 |
| MOL000785 | palmatine | Huanglian | 64.6 | 0.65 | 10 |
| MOL007093 | dan-shexinkum d | Danshen | 38.88 | 0.55 | 10 |
| MOL000358 | beta-sitosterol | Zhizi;Chishao;Sanqi;Huzhang | 36.91 | 0.75 | 9 |
| MOL003095 | 5-hydroxy-7-methoxy-2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl) chromone | Zhizi | 51.96 | 0.41 | 9 |
| MOL002904 | Berlambine | Huanglian | 36.68 | 0.82 | 8 |
| Group | Body weight (g) | FBG (mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|
| Blank control | 32.57±1.00 | 5.02±0.47 |
| Model | 48.85±3.35## | 7.45±0.65## |
| JZQBR-L | 45.17±3.22* | 7.00±0.61 |
| JZQBR-H | 42.00±2.14** | 6.52±0.42* |
| Simvastatin | 43.85±1.65** | 6.92±0.47 |
表3 降脂祛斑方对高脂饮食小鼠体质量及FBG的影响
Tab.3 Effects of Jiangzhi Quban Recipe on body weight and fasting blood glucose in high-fat diet mice (Mean±SD, n=6)
| Group | Body weight (g) | FBG (mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|
| Blank control | 32.57±1.00 | 5.02±0.47 |
| Model | 48.85±3.35## | 7.45±0.65## |
| JZQBR-L | 45.17±3.22* | 7.00±0.61 |
| JZQBR-H | 42.00±2.14** | 6.52±0.42* |
| Simvastatin | 43.85±1.65** | 6.92±0.47 |
| Group | TG (mmol/L) | TC (mmol/L) | LDL-C (mmol/L) | HDL-C (mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank control | 0.48±0.13 | 3.12±0.82 | 0.26±0.07 | 1.49±0.15 |
| Model | 2.87±0.62## | 21.28±2.51## | 15.65±1.39## | 1.60±0.14 |
| JZQBR-L | 2.33±0.27* | 19.77±1.76 | 15.10±1.27 | 1.72±0.55 |
| JZQBR-H | 2.13±0.31** | 18.70±1.41* | 13.68±1.44* | 1.81±0.16 |
| Simvastatin | 1.96±0.24** | 17.07±1.40** | 13.51±1.24* | 1.92±0.22 |
表4 降脂祛斑方对高脂饮食小鼠血脂的影响
Tab.4 Effects of Jiangzhi Quban Recipe on serum lipid profiles in high-fat diet mice (Mean±SD, n=6)
| Group | TG (mmol/L) | TC (mmol/L) | LDL-C (mmol/L) | HDL-C (mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank control | 0.48±0.13 | 3.12±0.82 | 0.26±0.07 | 1.49±0.15 |
| Model | 2.87±0.62## | 21.28±2.51## | 15.65±1.39## | 1.60±0.14 |
| JZQBR-L | 2.33±0.27* | 19.77±1.76 | 15.10±1.27 | 1.72±0.55 |
| JZQBR-H | 2.13±0.31** | 18.70±1.41* | 13.68±1.44* | 1.81±0.16 |
| Simvastatin | 1.96±0.24** | 17.07±1.40** | 13.51±1.24* | 1.92±0.22 |
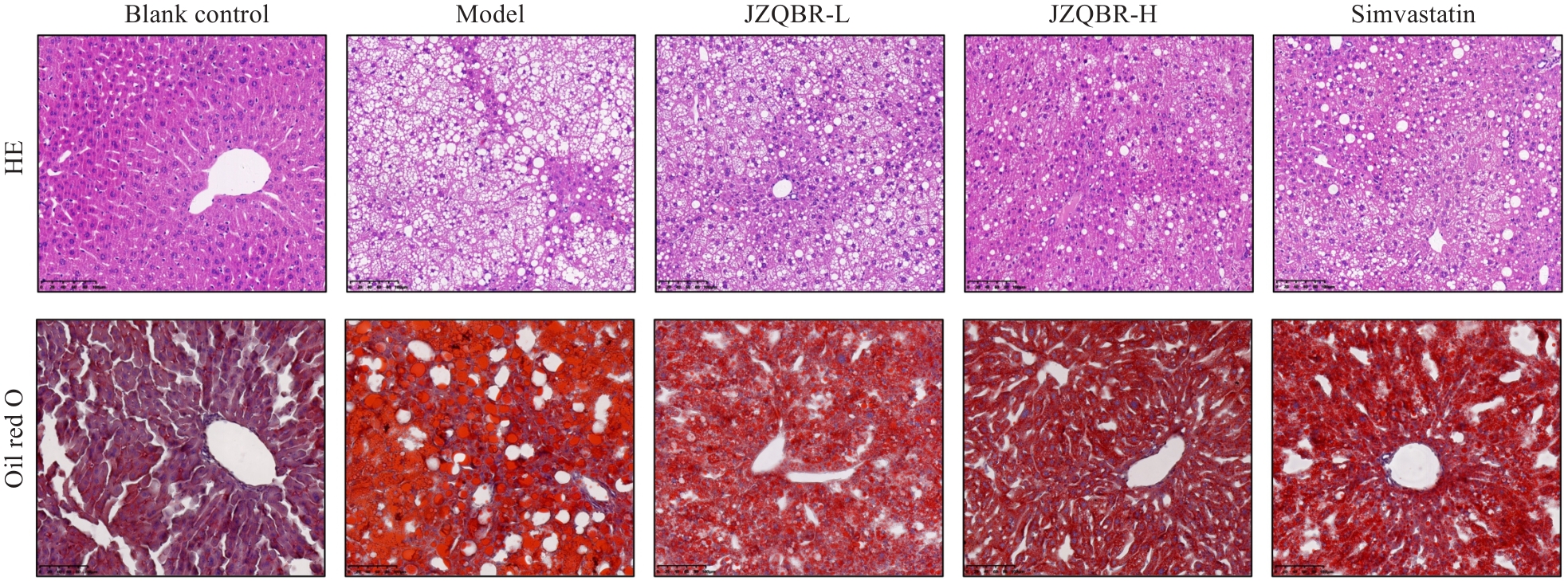
图6 降脂祛斑方对高脂饮食小鼠肝脏病理形态及脂质沉积的影响
Fig.6 Effects of Jiangzhi Quban Recipe on hepatic pathological morphology and lipid deposition in high-fat diet mice (Scale bar=100 µm).
| Group | IL-6 | IL-1β | TNF-α |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blank control | 1.00±0.28 | 1.00±0.45 | 1.00±0.37 |
| Model | 14.06±3.32## | 7.44±1.39## | 7.59±1.29## |
| JZQBR-L | 12.41±3.12 | 6.60±0.80 | 6.21±0.77* |
| JZQBR-H | 9.87±2.74* | 5.59±0.91* | 4.73±0.74** |
| Simvastatin | 13.14±2.39 | 6.23±1.20 | 6.61±1.05 |
表5 降脂祛斑方对高脂饮食小鼠肝脏炎症因子转录水平的影响
Tab.5 Effects of Jiangzhi Quban Recipe on hepatic inflammatory factor transcription levels in high-fat diet mice (Mean±SD, n=6)
| Group | IL-6 | IL-1β | TNF-α |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blank control | 1.00±0.28 | 1.00±0.45 | 1.00±0.37 |
| Model | 14.06±3.32## | 7.44±1.39## | 7.59±1.29## |
| JZQBR-L | 12.41±3.12 | 6.60±0.80 | 6.21±0.77* |
| JZQBR-H | 9.87±2.74* | 5.59±0.91* | 4.73±0.74** |
| Simvastatin | 13.14±2.39 | 6.23±1.20 | 6.61±1.05 |
| Parameter | Observation group | Positive control group | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (kg) | 70.52±13.39 | 66.88±12.99 | 0.31 |
| BMI (kg/m²) | 25.40±3.47 | 24.73±4.11 | 0.55 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 3.48±3.47 | 2.45±1.21 | 0.10 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 5.16±1.07 | 5.72±1.08 | 0.06 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.08±0.26 | 1.07±0.22 | 0.85 |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 3.05±0.94 | 3.63±0.89 | 0.61 |
| FBG (mmol/L) | 8.79±2.37 | 9.13±3.36 | 0.62 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.85±1.73 | 8.92±2.72 | 0.08 |
表6 治疗前两组患者体质量、血脂及血糖水平比较
Tab.6 Comparison of body weight, blood lipid and blood glucose levels of the patients between the two groups before treatment (Mean±SD, n=36)
| Parameter | Observation group | Positive control group | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (kg) | 70.52±13.39 | 66.88±12.99 | 0.31 |
| BMI (kg/m²) | 25.40±3.47 | 24.73±4.11 | 0.55 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 3.48±3.47 | 2.45±1.21 | 0.10 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 5.16±1.07 | 5.72±1.08 | 0.06 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.08±0.26 | 1.07±0.22 | 0.85 |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 3.05±0.94 | 3.63±0.89 | 0.61 |
| FBG (mmol/L) | 8.79±2.37 | 9.13±3.36 | 0.62 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.85±1.73 | 8.92±2.72 | 0.08 |
| Parameter | Observation group | Positive control group | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| AST (U/L) | 24.08±12.16 | 23.84±14.10 | 0.92 |
| ALT (U/L) | 31.28±20.46 | 27.79±15.84 | 0.46 |
| SCr (μmol/L) | 72.35±16.32 | 68.78±19.89 | 0.47 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 5.23±1.66 | 5.36±1.57 | 0.56 |
| ALBU (mg/L) | 28.70±36.58 | 44.89±56.07 | 0.22 |
表7 治疗前两组患者肝、肾功能水平比较
Tab.7 Comparison of liver and kidney function levels of the patients between the two groups before treatment (Mean±SD, n=36)
| Parameter | Observation group | Positive control group | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| AST (U/L) | 24.08±12.16 | 23.84±14.10 | 0.92 |
| ALT (U/L) | 31.28±20.46 | 27.79±15.84 | 0.46 |
| SCr (μmol/L) | 72.35±16.32 | 68.78±19.89 | 0.47 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 5.23±1.66 | 5.36±1.57 | 0.56 |
| ALBU (mg/L) | 28.70±36.58 | 44.89±56.07 | 0.22 |
| Parameter | Observation group | Positive control group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before treatment | After 12 weeks treatment | Before treatment | After 12 weeks treatment | |
| Body weight (kg) | 72.24±12.99 | 69.58±13.06△△ | 66.86±13.21 | 65.68±12.97* |
| BMI (kg/m²) | 25.99±3.18 | 25.29±3.49△△ | 24.73±4.11 | 24.23±3.47* |
| TG (mmol/L) | 3.84±3.77 | 2.78±2.18△ | 2.53±1.25 | 2.03±1.11** |
| TC (mmol/L) | 5.18±1.11 | 4.95±1.14 | 5.75±1.03 | 4.41±1.02** |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.08±0.27 | 1.14±0.26 | 1.05±0.23 | 1.17±0.31* |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 2.99±0.95 | 2.87±0.92 | 3.61±0.81 | 2.55±0.79** |
| FBG (mmol/L) | 8.91±2.52 | 6.92±2.02△△ | 9.09±3.46 | 7.92±2.33 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.70±1.46 | 6.51±0.94△△ | 8.87±2.89 | 6.75±1.12** |
表8 治疗12周前后患者体质量、血脂及血糖水平比较
Tab.8 Comparison of body weight, blood lipid, and blood glucose levels of the patients before and after 12 weeks of treatment (Mean±SD, n=36)
| Parameter | Observation group | Positive control group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before treatment | After 12 weeks treatment | Before treatment | After 12 weeks treatment | |
| Body weight (kg) | 72.24±12.99 | 69.58±13.06△△ | 66.86±13.21 | 65.68±12.97* |
| BMI (kg/m²) | 25.99±3.18 | 25.29±3.49△△ | 24.73±4.11 | 24.23±3.47* |
| TG (mmol/L) | 3.84±3.77 | 2.78±2.18△ | 2.53±1.25 | 2.03±1.11** |
| TC (mmol/L) | 5.18±1.11 | 4.95±1.14 | 5.75±1.03 | 4.41±1.02** |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.08±0.27 | 1.14±0.26 | 1.05±0.23 | 1.17±0.31* |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 2.99±0.95 | 2.87±0.92 | 3.61±0.81 | 2.55±0.79** |
| FBG (mmol/L) | 8.91±2.52 | 6.92±2.02△△ | 9.09±3.46 | 7.92±2.33 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.70±1.46 | 6.51±0.94△△ | 8.87±2.89 | 6.75±1.12** |
| Parameter | Observation group | Positive control group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before treatment | After 12 weeks treatment | Before treatment | After 12 weeks treatment | |
| AST (U/L) | 26.23±12.56 | 19.43±6.21△△ | 24.25±14.94 | 20.09±7.81 |
| ALT (U/L) | 34.84±21.25 | 22.04±10.28△△ | 27.84±16.19 | 21.66±10.91 |
| SCr (μmol/L) | 76.10±15.83 | 75.21±17.73 | 68.49±20.08 | 68.02±19.04 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 5.34±1.80 | 5.96±1.65 | 5.42±1.47 | 5.85±1.46 |
| ALBU (mg/L) | 33.55±40.87 | 35.19±49.16 | 47.29±59.81 | 76.26±189.12 |
表9 治疗12周前后患者肝肾功能指标比较
Tab.9 Comparison of liver and kidney function indicators of the patients before and after 12 weeks of treatment (Mean±SD, n=36)
| Parameter | Observation group | Positive control group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before treatment | After 12 weeks treatment | Before treatment | After 12 weeks treatment | |
| AST (U/L) | 26.23±12.56 | 19.43±6.21△△ | 24.25±14.94 | 20.09±7.81 |
| ALT (U/L) | 34.84±21.25 | 22.04±10.28△△ | 27.84±16.19 | 21.66±10.91 |
| SCr (μmol/L) | 76.10±15.83 | 75.21±17.73 | 68.49±20.08 | 68.02±19.04 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 5.34±1.80 | 5.96±1.65 | 5.42±1.47 | 5.85±1.46 |
| ALBU (mg/L) | 33.55±40.87 | 35.19±49.16 | 47.29±59.81 | 76.26±189.12 |
| Parameter | Observation group | Positive control group | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (kg) | 69.58±13.06 | 65.68±12.97 | 0.25 |
| BMI (kg/m²) | 25.29±3.49 | 24.23±3.47 | 0.24 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 4.95±1.14 | 4.41±1.02 | 0.06 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 2.78±2.18 | 2.03±1.11 | 0.10 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.14±0.26 | 1.17±0.31 | 0.73 |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 2.87±0.92 | 2.55±0.79 | 0.16 |
| FBG (mmol/L) | 6.92±2.02 | 7.95±2.29 | 0.04 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.51±0.94 | 6.75±1.12 | 0.29 |
表10 治疗12周后两组患者体质量、血脂及血糖水平比较
Tab.10 Comparison of body weight, blood lipid, and blood glucose levels of the patients between two groups after 12 weeks of treatment (Mean±SD, n=36)
| Parameter | Observation group | Positive control group | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (kg) | 69.58±13.06 | 65.68±12.97 | 0.25 |
| BMI (kg/m²) | 25.29±3.49 | 24.23±3.47 | 0.24 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 4.95±1.14 | 4.41±1.02 | 0.06 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 2.78±2.18 | 2.03±1.11 | 0.10 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.14±0.26 | 1.17±0.31 | 0.73 |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 2.87±0.92 | 2.55±0.79 | 0.16 |
| FBG (mmol/L) | 6.92±2.02 | 7.95±2.29 | 0.04 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.51±0.94 | 6.75±1.12 | 0.29 |
| Parameter | Observation group | Positive control group | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| AST (U/L) | 19.26±6.17 | 20.09±7.81 | 0.65 |
| ALT (U/L) | 21.64±10.32 | 21.66±10.91 | 0.99 |
| SCr (μmol/L) | 74.57±17.36 | 68.02±19.04 | 0.17 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 5.93±1.62 | 5.85±1.46 | 0.83 |
| ALBU (mg/L) | 35.15±49.30 | 71.59±182.80 | 0.32 |
表11 治疗12周后两组患者肝、肾功能水平比较
Tab.11 Comparison of liver and kidney function levels between two groups after 12 weeks of treatment (Mean±SD, n=36)
| Parameter | Observation group | Positive control group | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| AST (U/L) | 19.26±6.17 | 20.09±7.81 | 0.65 |
| ALT (U/L) | 21.64±10.32 | 21.66±10.91 | 0.99 |
| SCr (μmol/L) | 74.57±17.36 | 68.02±19.04 | 0.17 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 5.93±1.62 | 5.85±1.46 | 0.83 |
| ALBU (mg/L) | 35.15±49.30 | 71.59±182.80 | 0.32 |
| Group | Total case | Markedly effective | Effective case | Ineffective case | Total effective rate | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observation | 29 | 11 | 11 | 7 | 75.86% | >0.05 |
| Positive control | 31 | 22 | 2 | 7 | 77.42% |
表12 治疗12周后两组患者疗效比较
Tab.12 Comparison of treatment efficacy between two groups after 12 weeks of treatment (n)
| Group | Total case | Markedly effective | Effective case | Ineffective case | Total effective rate | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observation | 29 | 11 | 11 | 7 | 75.86% | >0.05 |
| Positive control | 31 | 22 | 2 | 7 | 77.42% |
| [1] | Ji Q, Chai S, Zhang R, et al. Prevalence and co-prevalence of comorbidities among Chinese adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional, multicenter, retrospective, observational study based on 3B study database[J]. Front Endocrinol: Lausanne, 2024, 15: 1362433. doi:10.3389/fendo.2024.1362433 |
| [2] | Fan D, Li L, Li Z, et al. Effect of hyperlipidemia on the incidence of cardio-cerebrovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2018, 17(1): 102. doi:10.1186/s12944-018-0676-x |
| [3] | Li J, Shi L, Zhao G, et al. High triglyceride levels increase the risk of diabetic microvascular complications: a cross-sectional study[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2023, 22(1): 109. doi:10.1186/s12944-023-01873-5 |
| [4] | 中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志, 2021, 13(4): 315-409. |
| [5] | Bjornstad P, Eckel RH. Pathogenesis of lipid disorders in insulin resistance: a brief review[J]. Curr Diabetes Rep, 2018, 18(12): 127. doi:10.1007/s11892-018-1101-6 |
| [6] | Elkanawati RY, Sumiwi SA, Levita J. Impact of lipids on insulin resistance: insights from human and animal studies[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2024, 18: 3337-60. doi:10.2147/dddt.s468147 |
| [7] | Galantini MPL, Ribeiro IS, Gonçalves CV, et al. The sweet fuel of inflammation: new perspectives on the complex web that interconnects diabetes[J]. Exp Gerontol, 2022, 167: 111905. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2022.111905 |
| [8] | Xiong PJ, Zhang F, Liu F, et al. Metaflammation in glucolipid metabolic disorders: Pathogenesis and treatment[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2023, 161: 114545. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114545 |
| [9] | 李琦文. HMG-CoA还原酶抑制剂-他汀类药物的作用及机制[J]. 中国现代药物应用, 2014, 8(17): 228-9. |
| [10] | 周凤华, 金 瑶, 刁慧玲, 等. 贾钰华教授论治冠心病临证经验精粹[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1786-93. |
| [11] | Zhai Y, Liu L, Zhang F, et al. Network pharmacology: a crucial approach in traditional Chinese medicine research[J]. Chin Med, 2025, 20(1): 8-15. doi:10.1186/s13020-024-01056-z |
| [12] | 王澄槟, 胡浩彬, 徐芷晴, 等. 基于网络药理学和分子对接探讨桃红四物汤治疗动脉粥样硬化的作用机制[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2025(18): 2760-9. |
| [13] | Bu Y, Li Z, Wang C, et al. Anemoside B4 targets RAGE to attenuate ferroptosis in sepsis-induced acute lung injury[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2025, 16: 1590797. doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1590797 |
| [14] | 李 楠, 陈 蕾, 张 琨. 基于网络药理学探讨人参调控铁死亡抗阿尔茨海默病的潜在作用机制[J]. 现代药物与临床, 2022, 37(2): 244-51. |
| [15] | 中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2017年版)[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2018, 38(4): 292-344. |
| [16] | 诸骏仁, 高润霖, 赵水平, 等. 中国成人血脂异常防治指南(2016年修订版)[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2016, 31(10): 937-53. |
| [17] | Huang X, Fang J, Lai W, et al. IL-6/STAT3 axis activates Glut5 to regulate fructose metabolism and tumorigenesis[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2022, 18(9): 3668-75. doi:10.7150/ijbs.68990 |
| [18] | Vida M, Gavito AL, Pavón FJ, et al. Chronic administration of recombinant IL-6 upregulates lipogenic enzyme expression and aggravates high-fat-diet-induced steatosis in IL-6-deficient mice[J]. Dis Model Mech, 2015, 8(7): 721-31. |
| [19] | Herder C, Dalmas E, Böni-Schnetzler M, et al. The IL-1 pathway in type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular complications[J]. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2015, 26(10): 551-63. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2015.08.001 |
| [20] | Meier DT, de Paula Souza J, Donath MY. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome-IL-1β pathway in type 2 diabetes and obesity[J]. Diabetologia, 2025, 68(1): 3-16. doi:10.1007/s00125-024-06306-1 |
| [21] | Cawthorn WP, Sethi JK. TNF‐α and adipocyte biology[J]. FEBS Letters, 2008, 582(1): 117-31. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2007.11.051 |
| [22] | Park JE, Han JS. Improving the effect of ferulic acid on inflammation and insulin resistance by regulating the JNK/ERK and NF-κB pathways in TNF‑α‑treated 3T3-L1 adipocytes[J]. Nutrients, 2024, 16(2): 294. doi:10.3390/nu16020294 |
| [23] | Dhanya R, Arya AD, Nisha P, et al. Quercetin, a lead compound against type 2 diabetes ameliorates glucose uptake via AMPK pathway in skeletal muscle cell line[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2017, 8: 336. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00336 |
| [24] | Salehi B, Machin L, Monzote L, et al. Therapeutic potential of quercetin: new insights and perspectives for human health[J]. ACS Omega, 2020, 5(20): 11849-72. doi:10.1021/acsomega.0c01818 |
| [25] | Kadioglu O, Nass J, Saeed ME, et al. Kaempferol is an anti-inflammatory compound with activity towards NF‑κB pathway proteins[J]. Anticancer Res, 2015, 35(5): 2645-50. |
| [26] | Lee B, Kwon M, Choi JS, et al. Kaempferol isolated fromNelumbo nuciferaInhibits lipid accumulation and increases fatty acid oxidation signaling in adipocytes[J]. J Med Food, 2015, 18(12): 1363-70. doi:10.1089/jmf.2015.3457 |
| [27] | Kwon EY, Choi MS. Luteolin targets the toll-like receptor signaling pathway in prevention of hepatic and adipocyte fibrosis and insulin resistance in diet-induced obese mice[J]. Nutrients, 2018, 10(10): E1415. doi:10.3390/nu10101415 |
| [28] | Zhang L, Han YJ, Zhang X, et al. Luteolin reduces obesity-associated insulin resistance in mice by activating AMPKα1 signalling in adipose tissue macrophages[J]. Diabetologia, 2016, 59(10): 2219-28. doi:10.1007/s00125-016-4039-8 |
| [29] | Kwon EY, Jung UJ, Park T, et al. Luteolin attenuates hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance through the interplay between the liver and adipose tissue in mice with diet-induced obesity[J]. Diabetes, 2015, 64(5): 1658-69. doi:10.2337/db14-0631 |
| [30] | Kosmalski M, Ziółkowska S, Czarny P, et al. The coexistence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. J Clin Med, 2022, 11(5): 1375. doi:10.3390/jcm11051375 |
| [1] | 呼琴, 金华. 清肾颗粒通过调控miR-23b及Nrf2通路改善慢性肾脏病湿热证患者的肾功能:基于网络药理学和临床试验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1867-1879. |
| [2] | 杨子为, 吕畅, 董柱, 计书磊, 毕生辉, 张雪花, 王晓武. 金樱子通过调控Src-AKT1轴抑制肺动脉高压平滑肌增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1889-1902. |
| [3] | 云琦, 杜若丽, 贺玉莹, 张贻欣, 王佳慧, 叶红伟, 李正红, 高琴. 肉桂酸通过抑制TLR4减轻阿霉素诱导的小鼠心肌损伤铁死亡的发生[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1946-1958. |
| [4] | 饶璐, 丁家和, 魏江平, 阳勇, 张小梅, 王计瑞. 槐花通过抑制PI3K/AKT通路减轻炎症反应治疗银屑病[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1989-1996. |
| [5] | 邓楚玉, 王雪莹, 甘立祥, 王大禹, 郑晓燕, 唐纯志. 电针足三里改善高脂血症小鼠的血脂紊乱:基于肠道菌群结构的改善[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1633-1642. |
| [6] | 陈鑫源, 吴成挺, 李瑞迪, 潘雪芹, 张耀丹, 陶俊宇, 林才志. 双术汤通过P53/SLC7A11/GPX4通路诱导胃癌细胞铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [7] | 王立明, 陈宏睿, 杜燕, 赵鹏, 王玉洁, 田燕歌, 刘新光, 李建生. 益气滋肾方通过抑制PI3K/Akt/NF-κB通路改善小鼠慢性阻塞性肺疾病的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [8] | 朱胤福, 李怡燃, 王奕, 黄颖而, 龚昆翔, 郝文波, 孙玲玲. 桂枝茯苓丸活性成分常春藤皂苷元通过抑制JAK2/STAT3通路抑制宫颈癌细胞的生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [9] | 何丽君, 陈晓菲, 闫陈昕, 师林. 扶正化积汤治疗非小细胞肺癌的分子机制:基于网络药理学及体外实验验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152. |
| [10] | 李国永, 黎仁玲, 刘艺婷, 柯宏霞, 李菁, 王新华. 牛蒡子治疗小鼠病毒性肺炎后肺纤维化的机制:基于代谢组学、网络药理学和实验验证方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [11] | 管丽萍, 颜燕, 卢心怡, 李智峰, 高晖, 曹东, 侯晨曦, 曾靖宇, 李欣怡, 赵洋, 王俊杰, 方会龙. 复方积雪草减轻小鼠日本血吸虫引起的肝纤维化:通过调控TLR4/MyD88通路抑制炎症-纤维化级联反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [12] | 唐培培, 谈勇, 殷燕云, 聂晓伟, 黄菁宇, 左文婷, 李玉玲. 调周滋阴方治疗早发性卵巢功能不全的疗效、安全性及作用机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| [13] | 梁晓涛, 熊一凡, 刘雪琪, 梁小珊, 朱晓煜, 谢炜. 活血疏风颗粒通过抑制TLR4/NF-κB通路改善慢性偏头痛小鼠的中枢敏化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 986-994. |
| [14] | 冉念东, 刘杰, 徐剑, 张永萍, 郭江涛. 黑骨藤正丁醇萃取成分治疗大鼠阿尔茨海默病的药效学及作用机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 785-798. |
| [15] | 徐皓男, 张放, 黄钰莹, 姚其盛, 管悦琴, 陈浩. 百蕊草通过调节肠道菌群和调控EGFR/PI3K/Akt信号通路改善小鼠抗生素相关性腹泻[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||