南方医科大学学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 74-82.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.08
李楠1,2( ), 张亮3, 郭俏凤2, 周越2(
), 张亮3, 郭俏凤2, 周越2( ), 刘长江1
), 刘长江1
收稿日期:2025-09-11
出版日期:2026-01-20
发布日期:2026-01-16
通讯作者:
周越
E-mail:linan@xjtu.edu.cn;zhouy@bsu.edu.cn
作者简介:李 楠,助理教授,E-mail: linan@xjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Nan LI1,2( ), Liang ZHANG3, Qiaofeng GUO2, Yue ZHOU2(
), Liang ZHANG3, Qiaofeng GUO2, Yue ZHOU2( ), Changjiang LIU1
), Changjiang LIU1
Received:2025-09-11
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2026-01-16
Contact:
Yue ZHOU
E-mail:linan@xjtu.edu.cn;zhouy@bsu.edu.cn
摘要:
目的 探讨微RNA 221-3p(miR-221-3p)在有氧运动改善高脂饮食诱导的脂肪组织巨噬细胞极化及胰岛素抵抗(IR)中的作用及潜在生理机制。 方法 60只5周龄SPF级C57BL/6J雄性小鼠随机分为普通膳食组(20 只)和高脂膳食组(40 只)。在高脂膳食干预12周后,筛选出IR小鼠。经过造模和筛选,最终选取16只普通小鼠和16只IR小鼠进入后续实验。将小鼠随机分为4组(n=8):正常安静组(CS组),正常运动组(CE组),高脂安静组(HS组)和高脂运动组(HE组)。运动组进行为期8周的跑台运动(坡度0°,跑速15~20 m/min,1 h/d,5 d/周)。同时对小鼠单核巨噬细胞进行miR-221-3p转染,进一步验证miR-221-3p对巨噬细胞极化的作用。实验干预结束后,检测小鼠体质量、体成分;ELISA和生化试剂盒检测小鼠空腹血糖、胰岛素及血脂4项水平;采用荧光定量PCR(qPCR)检测miR-221-3p、Socs1、Tnf-α和Arg-1相对含量;双荧光素酶报告基因实验(Luciferase)验证miR-221-3p与细胞因子信号抑制蛋白1(SOCS1)的靶向关系Western blotting检测脂肪组织SOCS1、Janus激酶1(JAK1)、磷酸化信号转导子和转录激活子1和3(p-STAT1、p-STAT3)的蛋白表达水平。 结果 有氧运动显著降低小鼠体质量、脂肪质量和体脂率,空腹血糖、胰岛素水平胰岛素抵抗指数(HOMA-IR)、总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三酯(TG)水平显著降低(P<0.01),瘦体质量显著升高(P<0.01)。qPCR结果显示,与CS组相比,HS组小鼠血浆和脂肪组织miR-221-3p的相对表达量均显著升高(P<0.01);有氧运动显著降低小鼠血浆和脂肪组织miR-221-3p的相对表达量(P<0.01)。Western blotting结果显示,有氧运动显著降低了iNOS、JAK1和p-STAT1/STAT1的蛋白表达(P<0.01),Arg-1、SOCS1和p-STAT3/STAT3的蛋白表达显著提高(P<0.05,P<0.05,P<0.01)。体外实验结果显示过表达miR-221-3p可以显著降低Socs1、Arg-1的基因表达(P<0.01),miR-221-3p抑制剂显著促进了M2型巨噬细胞极化状态。 结论 有氧运动可能通过抑制miR-221-3p的表达,靶向激活SOCS1及下游JAK/STAT信号通路,抑制脂肪组织巨噬细胞M1极化,促进巨噬细胞M2极化,减轻脂肪组织炎症反应,从而提高组织胰岛素敏感性。
李楠, 张亮, 郭俏凤, 周越, 刘长江. 有氧运动通过调控miR-221-3p介导的脂肪组织巨噬细胞极化改善小鼠胰岛素抵抗[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2026, 46(1): 74-82.
Nan LI, Liang ZHANG, Qiaofeng GUO, Yue ZHOU, Changjiang LIU. Aerobic exercise regulates macrophage polarization and improves insulin resistance in mice: the mediating role of miR-221-3p[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2026, 46(1): 74-82.
| Gene | Primer sequences (5'-3') | |
|---|---|---|
| miR-221-3p | RT | CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGGAAACCCA |
| F | ACACTCCAGCTGGGAGCTACATTGTCTGC | |
| U6 | F | CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA |
| R | AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT | |
| Tnf-α | F | CCCTCACACTCAGATCATCTTCT |
| R | GCTACGACGTGGGCTACAG | |
| Arg-1 | F | ACAGCAGAGGAGGTGAAGAGTAC |
| R | AGTCAGTCCCTGGCTTATGGT | |
| Socs1 | F | CTGCGGCTTCTATTGGGGAC |
| R | AAAAGGCAGTCGAAGGTCTCG | |
| β-actin | F | GTGCTATGTTGCTCTAGACTTCG |
| R | ATGCCACAGGATTCCATACC | |
表1 qRT-PCR引物序列
Tab.1 Primers sequences for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Primer sequences (5'-3') | |
|---|---|---|
| miR-221-3p | RT | CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGGAAACCCA |
| F | ACACTCCAGCTGGGAGCTACATTGTCTGC | |
| U6 | F | CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA |
| R | AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT | |
| Tnf-α | F | CCCTCACACTCAGATCATCTTCT |
| R | GCTACGACGTGGGCTACAG | |
| Arg-1 | F | ACAGCAGAGGAGGTGAAGAGTAC |
| R | AGTCAGTCCCTGGCTTATGGT | |
| Socs1 | F | CTGCGGCTTCTATTGGGGAC |
| R | AAAAGGCAGTCGAAGGTCTCG | |
| β-actin | F | GTGCTATGTTGCTCTAGACTTCG |
| R | ATGCCACAGGATTCCATACC | |
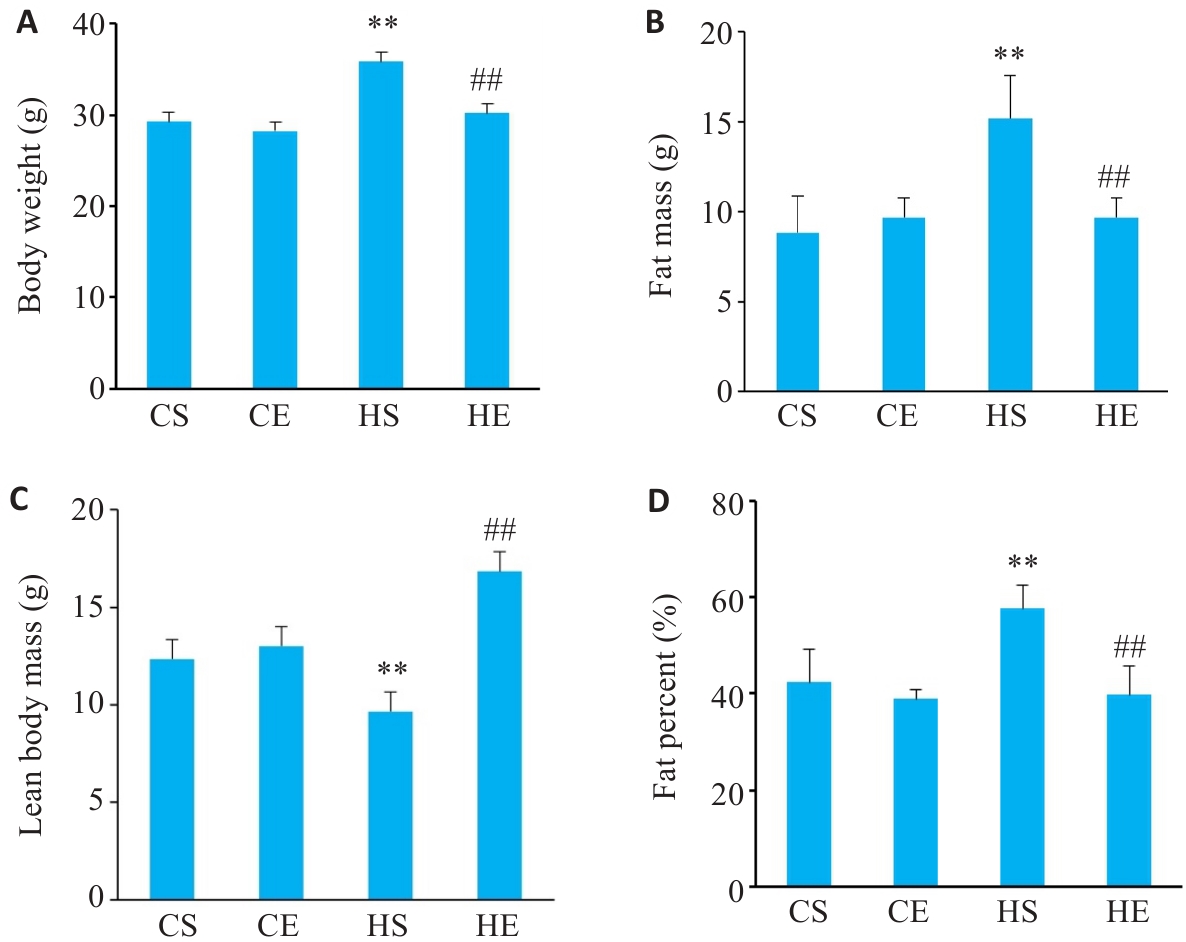
图1 有氧运动干预后各组小鼠体质量变化
Fig.1 Changes in body weight of the mice in each group (n=6). A: Changes in body weight. B: Changes in fat mass. C: Changes in lean body mass. D: Changes in fat percent. CS: Normally fed sedentary group without exercise; CE: Normally fed sedentary group with aerobic exercise; HS: High-fat diet sedentary group; HE: High-fat diet group with aerobic exercise. **P<0.01 vs CS group, ##P<0.01 vs HS group.
| Parameter | CS | CE | HS | HE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting blood glucose (mmol/L) | 6.70±0.38 | 6.13±0.44 | 13.10±0.99** | 7.56±0.69## |
| Insulin (μIU/mL) | 7.74±0.62 | 8.27±2.70 | 24.73±2.41** | 11.70±3.30**## |
| HOMA-IR | 2.32±0.22 | 2.24±0.72 | 14.46±2.27** | 3.87±0.84*## |
| TC (mmol/L) | 3.08±0.13 | 3.02±0.53 | 4.67±0.40** | 3.90±0.70**## |
| TG (mmol/L) | 0.59±0.07 | 0.60±0.09 | 0.88±0.19** | 0.72±0.07## |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 2.87±0.47 | 2.86±0.27 | 3.76±0.73** | 3.56±0.23 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 0.15±0.08 | 0.14±0.06 | 0.32±0.13 | 0.31±0.13 |
表2 有氧运动干预后各组小鼠基础指标的变化
Tab.2 Changes in the indicators of the mice in each group
| Parameter | CS | CE | HS | HE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting blood glucose (mmol/L) | 6.70±0.38 | 6.13±0.44 | 13.10±0.99** | 7.56±0.69## |
| Insulin (μIU/mL) | 7.74±0.62 | 8.27±2.70 | 24.73±2.41** | 11.70±3.30**## |
| HOMA-IR | 2.32±0.22 | 2.24±0.72 | 14.46±2.27** | 3.87±0.84*## |
| TC (mmol/L) | 3.08±0.13 | 3.02±0.53 | 4.67±0.40** | 3.90±0.70**## |
| TG (mmol/L) | 0.59±0.07 | 0.60±0.09 | 0.88±0.19** | 0.72±0.07## |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 2.87±0.47 | 2.86±0.27 | 3.76±0.73** | 3.56±0.23 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 0.15±0.08 | 0.14±0.06 | 0.32±0.13 | 0.31±0.13 |
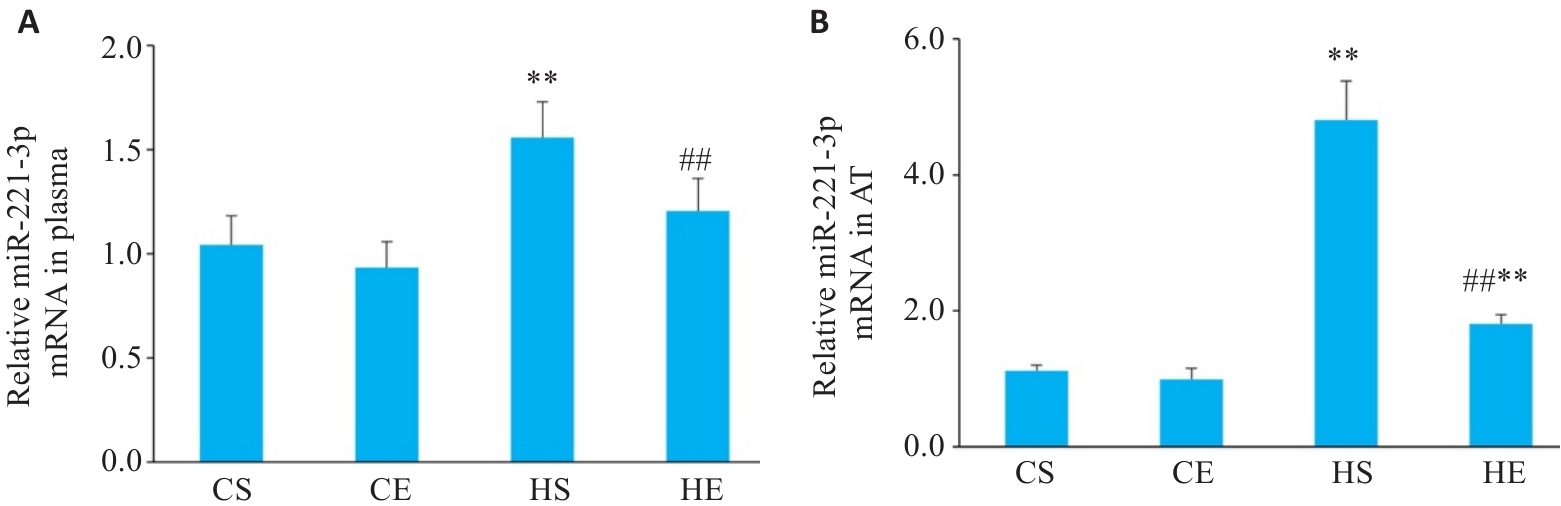
图2 有氧运动干预后小鼠血液与脂肪组织中miR-221-3p变化
Fig.2 Changes in miR-221-3p levels in each group. A: Expression levels of miR-221-3p in plasma (n=6). B: Expression levels of miR-221-3p in adipose tissue (AT). **P<0.01 vs CS group, ##P<0.01 vs HS group.
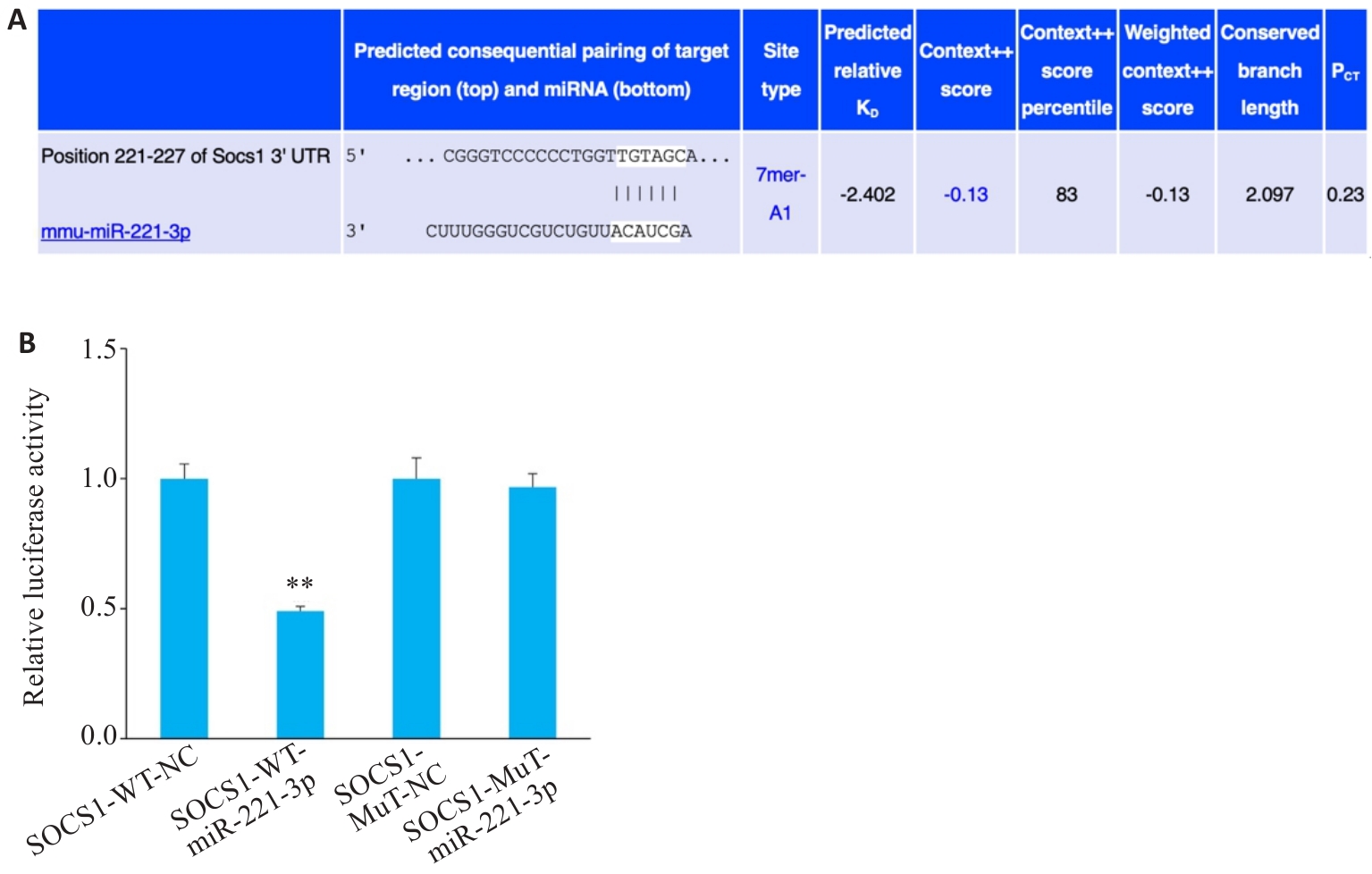
图3 miR-221-3p与Socs1的靶向关系
Fig.3 Targeting relationship between Socs1 and miR-221-3p (A) and dual-luciferase activity expression (B). n=3, **P<0.01 vs WT group.
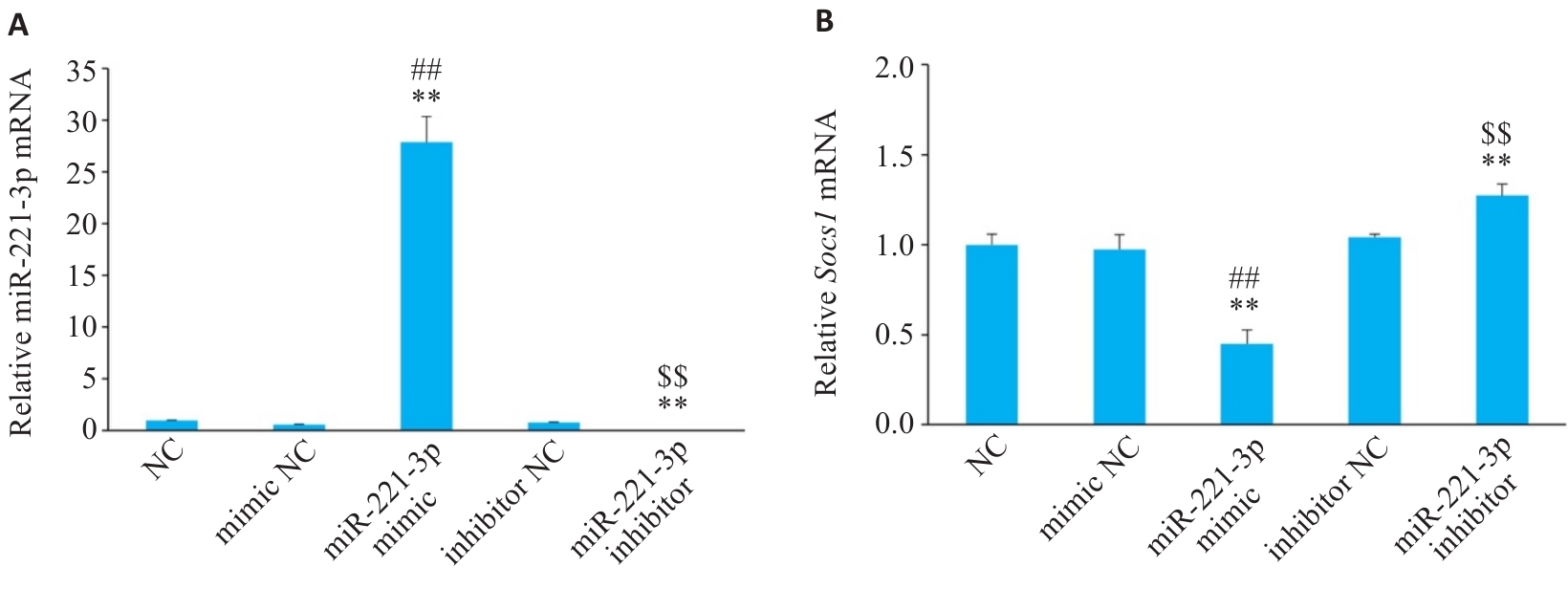
图4 细胞转染后各组miR-221-3p和Socs1的mRNA表达情况
Fig.4 Relative mRNA levels of miR-221-3p (A) and Socs1 (B) enriched in RAW 264.7 cells (n=3). **P<0.01 vs NC group, ##P<0.01 vs mimic NC group, $$P<0.01 vs inhibitor NC group.
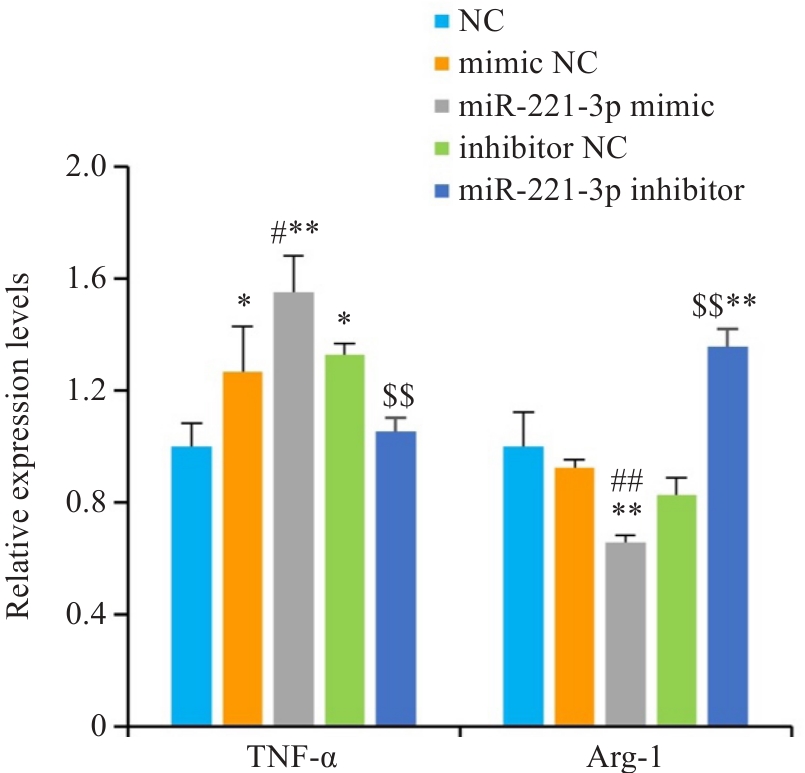
图5 细胞转染后各组炎症因子的mRNA表达
Fig.5 Relative mRNA levels of Tnf-α and Arg-1 enriched in RAW 264.7 cells (n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs NC group, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs mimic NC group, $$P<0.01 vs inhibitor NC group.
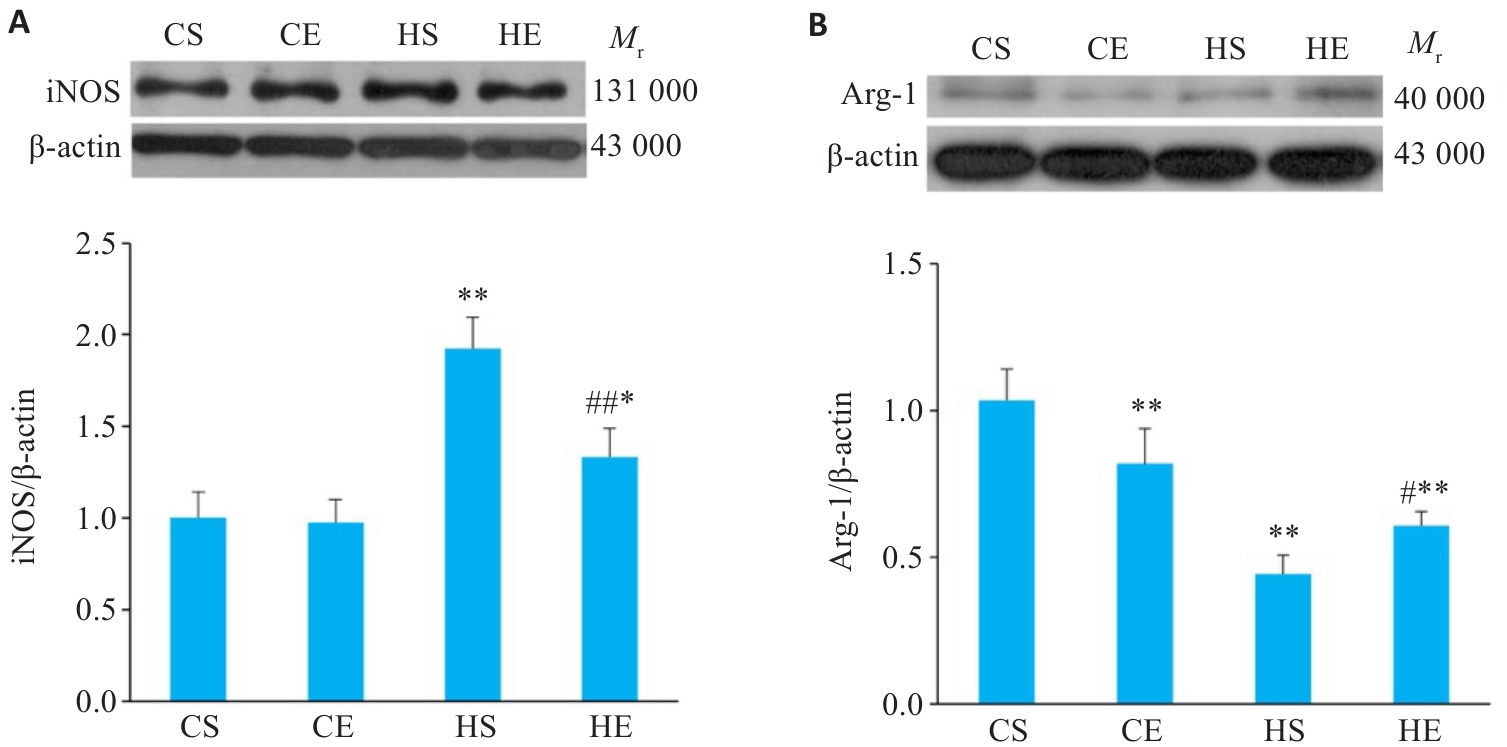
图6 有氧运动干预后小鼠脂肪组织巨噬细胞极化相关蛋白变化
Fig.6 Changes of macrophage polarization-related proteins in the adipose tissue of mice after aerobic exercise intervention. A: Expression of iNOS proteins in adipose tissue. B: Expression of Arg-1 proteins in adipose tissue. n=6. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs CS group, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs HS group.
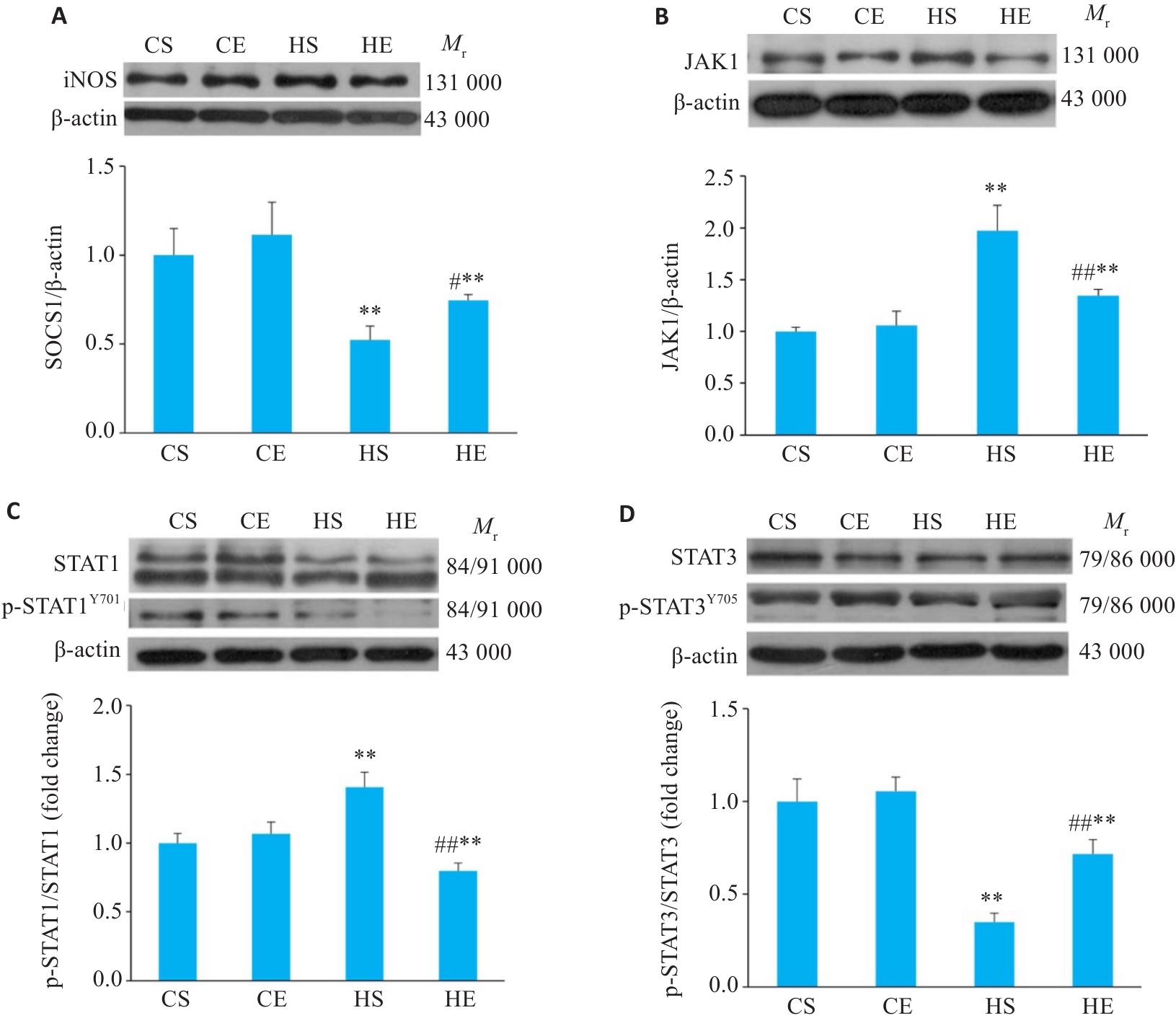
图7 各组小鼠脂肪组织JAK/STAT通路相关蛋白的表达
Fig.7 Comparison of the expression levels of JAK/STAT pathway proteins SOCS1 (A), JAK1 (B), p-STAT1/STAT1 (C), and p-STAT3/STAT3 (D) in the adipose tissue of the mice. n=6. **P<0.01 vs CS group, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs HS group.
| [1] | Xu Y, Lu JL, Li M, et al. Diabetes in China part 1: epidemiology and risk factors[J]. Lancet Public Health, 2024, 9(12): e1089-97. doi:10.1016/s2468-2667(24)00250-0 |
| [2] | Wu H, Ballantyne CM. Metabolic inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity[J]. Circ Res, 2020, 126(11): 1549-64. doi:10.1161/circresaha.119.315896 |
| [3] | Feehan KT, Gilroy DW. Is resolution the end of inflammation[J]? Trends Mol Med, 2019, 25(3): 198-214. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2019.01.006 |
| [4] | Anderson E, Durstine JL. Physical activity, exercise, and chronic diseases: a brief review[J]. Sports Med Health Sci, 2019, 1(1): 3-10. doi:10.1016/j.smhs.2019.08.006 |
| [5] | Yaribeygi H, Atkin SL, Simental-Mendía LE, et al. Molecular mechanisms by which aerobic exercise induces insulin sensitivity[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(8): 12385-92. doi:10.1002/jcp.28066 |
| [6] | 王 平, 李佳欣, 陈小龙, 等. 转录因子EB在有氧运动改善高脂饮食诱导小鼠骨骼肌胰岛素抵抗中的作用 [J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2024, 43(3): 193-204. |
| [7] | 李 楠, 史海燕, 周 越. 运动介导microRNAs改善慢性炎症及骨骼肌胰岛素抵抗的研究进展 [J]. 生命科学, 2022, 34(3): 324-31. |
| [8] | Li N, Shi H, Guo Q, et al. Aerobic exercise prevents chronic inflammation and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of high-fat diet mice[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14(18): 3730. doi:10.3390/nu14183730 |
| [9] | Quah S, Subramanian G, Tan JSL, et al. microRNAs: a symphony orchestrating evolution and disease dynamics[J]. Trends Mol Med, 2025, 31(1): 21-35. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2024.07.004 |
| [10] | Agbu P, Carthew RW. microRNA-mediated regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2021, 22(6): 425-38. doi:10.1038/s41580-021-00354-w |
| [11] | Wang J, Li L, Zhang Z, et al. Extracellular vesicles mediate the communication of adipose tissue with brain and promote cognitive impairment associated with insulin resistance[J]. Cell Metab, 2022, 34(9): 1264-79.e8. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2022.08.004 |
| [12] | Huang F, Zhu P, Wang J, et al. Postnatal overfeeding induces hepatic microRNA-221 expression and impairs the PI3K/AKT pathway in adult male rats[J]. Pediatr Res, 2021, 89(1): 143-9. doi:10.1038/s41390-020-0877-7 |
| [13] | Wilson HM. SOCS proteins in macrophage polarization and function[J]. Front Immunol, 2014, 5: 357. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00357 |
| [14] | Cai MC, Shi Y, Zheng TH, et al. Mammary epithelial cell derived exosomal miR-221 mediates M1 macrophage polarization via SOCS1/STATs to promote inflammatory response[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2020, 83: 106493. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106493 |
| [15] | Li N, Zhang L, Guo Q, et al. Aerobic exercise improves inflammation and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle by regulating miR-221-3p via JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Front Physiol. 2025;16:1534911. doi:10.3389/fphys.2025.1534911 |
| [16] | Høydal MA, Wisløff U, Kemi OJ, et al. Running speed and maximal oxygen uptake in rats and mice: practical implications for exercise training[J]. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil, 2007, 14(6): 753-60. doi:10.1097/hjr.0b013e3281eacef1 |
| [17] | Hariri N, Thibault L. High-fat diet-induced obesity in animal models[J]. Nutr Res Rev, 2010, 23(2): 270-99. doi:10.1017/s0954422410000168 |
| [18] | Speakman JR. Use of high-fat diets to study rodent obesity as a model of human obesity[J]. Int J Obes: Lond, 2019, 43(8): 1491-2. doi:10.1038/s41366-019-0363-7 |
| [19] | Lichtenstein AH, Schwab US. Relationship of dietary fat to glucose metabolism[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2000, 150(2): 227-43. doi:10.1016/s0021-9150(99)00504-3 |
| [20] | Binwal M, Babu V, Israr KM, et al. Taxoids-rich extract from Taxus wallichiana alleviates high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance in C57BL/6 mice through inhibition of low-grade inflammation[J]. Inflammopharmacology, 2023, 31(1): 451-64. doi:10.1007/s10787-022-01119-3 |
| [21] | Villareal DT, Aguirre L, Gurney AB, et al. Aerobic or resistance exercise, or both, in dieting obese older adults[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 376(20): 1943-55. doi:10.1056/nejmoa1616338 |
| [22] | Brouwers B, Schrauwen-Hinderling VB, Jelenik T, et al. Exercise training reduces intrahepatic lipid content in people with and people without nonalcoholic fatty liver[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2018, 314(2): E165-73. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00266.2017 |
| [23] | Gopalan V, Yaligar J, Michael N, et al. A 12-week aerobic exercise intervention results in improved metabolic function and lower adipose tissue and ectopic fat in high-fat diet fed rats[J]. Biosci Rep, 2021, 41(1): BSR20201707. doi:10.1042/bsr20201707 |
| [24] | Yao F, Yu Y, Feng LJ, et al. Adipogenic miR-27a in adipose tissue upregulates macrophage activation via inhibiting PPARγ of insulin resistance induced by high-fat diet-associated obesity[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2017, 355(2): 105-12. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.03.060 |
| [25] | Kiran S, Kumar V, Kumar S, et al. Adipocyte, immune cells, and miRNA crosstalk: a novel regulator of metabolic dysfunction and obesity[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(5): 1004. doi:10.3390/cells10051004 |
| [26] | Ying W, Gao H, Dos Reis FCG, et al. miR-690, an exosomal-derived miRNA from M2-polarized macrophages, improves insulin sensitivity in obese mice[J]. Cell Metab, 2021, 33(4): 781-90.e5. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.12.019 |
| [27] | Galardi S, Mercatelli N, Giorda E, et al. miR-221 and miR-222 expression affects the proliferation potential of human prostate carcinoma cell lines by targeting p27Kip1[J]. J Biol Chem, 2007, 282(32): 23716-24. doi:10.1074/jbc.m701805200 |
| [28] | Wang T, Jiang L, Wei X, et al. Inhibition of miR-221 alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury via inactivation of SOCS1/NF‑κB signaling pathway[J]. Cell Cycle, 2019, 18(16): 1893-907. doi:10.1080/15384101.2019.1632136 |
| [29] | Li YY, Yan CH, Fan JH, et al. miR-221-3p targets Hif-1α to inhibit angiogenesis in heart failure[J]. Lab Investig, 2021, 101(1): 104-15. doi:10.1038/s41374-020-0450-3 |
| [30] | Wang N, Liang H, Zen K. Molecular mechanisms that influence the macrophage m1-m2 polarization balance[J]. Front Immunol, 2014, 5: 614. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00614 |
| [31] | Liu W, Long Q, Zhang W, et al. miRNA-221-3p derived from M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophage exosomes aggravates the growth and metastasis of osteosarcoma through SOCS3/JAK2/STAT3 axis[J]. Aging: Albany NY, 2021, 13(15): 19760-75. doi:10.18632/aging.203388 |
| [32] | Meerson A, Traurig M, Ossowski V, et al. Human adipose microRNA-221 is upregulated in obesity and affects fat metabolism downstream of leptin and TNF‑α[J]. Diabetologia, 2013, 56(9): 1971-9. doi:10.1007/s00125-013-2950-9 |
| [33] | Olefsky JM, Glass CK. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance[J]. Annu Rev Physiol, 2010, 72: 219-46. doi:10.1146/annurev-physiol-021909-135846 |
| [34] | Yan B, Ma H, Jiang S, et al. microRNA-221 restricts human cytomegalovirus replication via promoting type I IFN production by targeting SOCS1/NF-κB pathway[J]. Cell Cycle, 2019, 18(22): 3072-84. doi:10.1080/15384101.2019.1667706 |
| [35] | Liau NPD, Laktyushin A, Lucet IS, et al. The molecular basis of JAK/STAT inhibition by SOCS1[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 1558. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-04013-1 |
| [36] | Dodington DW, Desai HR, Woo M. JAK/STAT-emerging players in metabolism[J]. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2018, 29(1): 55-65. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2017.11.001 |
| [1] | 张兆君, 吴琼, 谢苗苗, 叶洳吟, 耿晨晨, 石纪雯, 杨清玲, 王文锐, 石玉荣. 层状双氢氧化物负载si-NEAT1通过miR-133b/PD-L1轴调控乳腺癌紫杉醇耐药及巨噬细胞极化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1718-1731. |
| [2] | 涂舒谕, 陈祥宇, 李程辉, 黄丹萍, 张莉. 补阳还五汤通过调控外泌体miR-590-5p介导的巨噬细胞极化延缓大鼠血管衰老[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1251-1259. |
| [3] | 牛民主, 殷丽霞, 乔通, 尹林, 张可妮, 胡建国, 宋传旺, 耿志军, 李静. 旱莲苷A通过调控JAK2/STAT3通路抑制M1型巨噬细胞极化改善葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1297-1306. |
| [4] | 俞佳雯, 周薏, 钱春美, 穆蓝, 阙任烨. 铁过载诱导的小鼠肝纤维化过程影响巨噬细胞M2极化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 684-691. |
| [5] | 张芡, 刘博文, 雷丽, 王晔, 张馨月, 毛樟坤, 唐鹏, 张金梅, 杨佳宜, 彭彦茜, 刘泽. 丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂E1过表达通过诱导M2型巨噬细胞极化促进三阴性乳腺癌细胞增殖与紫杉醇耐药[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2551-2560. |
| [6] | 刘新新, 徐迎芮, 盛红娜, 刘昊. 人源脐带间充质干细胞移植通过Chi3l1抑制M1型巨噬细胞极化减轻1型糖尿病小鼠的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2738-2746. |
| [7] | 陈志亮, 杨永刚, 黄霞, 成彦, 瞿媛, 衡琪琪, 符羽佳, 李可薇, 顾宁. 外泌体miRNA差异表达可作为诊断慢性心力衰竭合并高尿酸血症患者新型分子标志物及靶基因功能分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 43-51. |
| [8] | 周雪利, 李华, 陈青宇, 靳美娜, 李海波, 白炜, 贾楚璇, 魏翠英. 慢性间歇低氧和复氧对大鼠胰岛素抵抗及骨骼肌miR-27a-3p/PPARγ/IRS1/PI3K/AKT表达的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1729-1737. |
| [9] | 肖静, 李盈, 方敏, 巩红, 李文, 张春艳, 陈方尧, 张岩, 韩拓. 甘油三酯-葡萄糖指数与非肥胖型非酒精性脂肪性肝病的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1266-1271. |
| [10] | 梁国新, 唐红悦, 郭畅, 张明明. miR-224-5p调控PI3K/Akt/FoxO1轴抑制氧化应激减轻缺氧/复氧诱导的心肌细胞损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1173-1181. |
| [11] | 胡司淦, 程增为, 李敏, 高世毅, 高大胜, 康品方. 冠状动脉慢性完全闭塞病变侧支循环的建立与胰岛素抵抗的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 780-786. |
| [12] | 李粉霞, 林浩生, 黎一琳, 朱雯倩, 孙元洁, 黄源, 裘毓雯, 秦霞, 常清贤. 孤立性侧脑室扩张胎儿孕妇羊水外泌体miRNA差异表达谱[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2256-2264. |
| [13] | 方福生, 王 宁, 刘星宇, 王 薇, 孙 菁, 李 红, 孙般若, 谷昭艳, 傅晓敏, 闫双通. 基于C肽的胰岛素抵抗指数可准确评估健康体检者的胰岛素抵抗与血尿酸水平的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1509-1514. |
| [14] | 李敬怡, 杨思圆, 韩 振, 江天乐, 朱 耀, 周子航, 周静萍. Akt2抑制剂促进大鼠根尖周炎症微环境中巨噬细胞的极化:基于降低miR-155-5p的表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(4): 568-576. |
| [15] | 张梦莹, 李 志, 裴纬亚, 李雪琴, 杨 辉, 朱小龙, 吕 坤. M2型巨噬细胞来源的外泌体lncRNA NR_028113.1通过激活JAK2/STAT3通路促进巨噬细胞的极化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 393-399. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||