南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2679-2689.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.15
• • 上一篇
陈晶宇( ), 邹金虎, 周炳亮, 高雪锋, 黄鹏伟, 曹虹(
), 邹金虎, 周炳亮, 高雪锋, 黄鹏伟, 曹虹( )
)
收稿日期:2025-06-13
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-12-22
通讯作者:
曹虹
E-mail:2209661286@qq.com;gzhcao@smu.edu.cn
作者简介:陈晶宇,硕士,E-mail: 2209661286@qq.com
基金资助:
Jingyu CHEN( ), Jinhu ZOU, Bingliang ZHOU, Xuefeng GAO, Pengwei HUANG, Hong CAO(
), Jinhu ZOU, Bingliang ZHOU, Xuefeng GAO, Pengwei HUANG, Hong CAO( )
)
Received:2025-06-13
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Hong CAO
E-mail:2209661286@qq.com;gzhcao@smu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探究3-吲哚乙酸(IAA)通过调控应激颗粒(SGs)形成和炎症小体NLRP3激活来缓解新生隐球菌(Cn)诱导的脑微血管内皮细胞焦亡的作用机制。 方法 采用107/mL浓度的Cn处理脑微血管内皮细胞构建体外细胞模型,并使用IAA进行干预。通过Western blotting、细胞免疫荧光、ELISA和CCK-8活性检测评估G3BP1、DDX3X、NLRP3及焦亡相关蛋白、细胞因子、细胞活性的变化。在免疫抑制的C57BL/6小鼠中,尾静脉注射Cn,连续7 d给予IAA灌胃治疗,构建体内动物实验模型。小鼠随机分为对照组、模型组及IAA处理组(3只/组)。通过依文思蓝实验检测血脑屏障通透性,取小鼠大脑皮层组织检测相关蛋白表达情况。 结果 Cn感染可诱导脑微血管内皮细胞中G3BP1表达下调(P<0.05)、DDX3X和NLRP3表达上调(P<0.05)。IAA干预恢复了G3BP1、DDX3X和NLRP3的异常表达 (P<0.05),有效抑制焦亡相关蛋白NT-GSDMD/GSDMD(P<0.05)和P20/Caspase1(P<0.01)的活化,大幅减少炎性细胞因子IL-18(P<0.001)、IL-1β(P<0.01)的释放。IAA干预可逆转Cn引起的脑微血管内皮细胞DDX3X向NLRP3的转移(P<0.05), 促进DDX3X与G3BP1的结合(P<0.05)。体内实验结果显示:IAA治疗可缓解血脑屏障的损伤,减少依文思蓝的渗出量(2.64±0.32 vs 1.06±0.12,P<0.001),和大脑皮层中ZO-1的表达量(P<0.05)。同时有效抑制VEGFR2、G3BP1、DDX3X、NLRP3和焦亡相关蛋白NT-GSDMD/GSDMD、P20/Caspase1的异常表达(P<0.05)。 结论 IAA通过调控SGs的形成以及炎症小体NLRP3的活化,有效缓解Cn引起的脑微血管内皮细胞焦亡。
陈晶宇, 邹金虎, 周炳亮, 高雪锋, 黄鹏伟, 曹虹. 3-吲哚乙酸通过调控应激颗粒介导的NLRP3炎性小体激活减轻新生隐球菌诱导的脑微血管内皮细胞焦亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2679-2689.
Jingyu CHEN, Jinhu ZOU, Bingliang ZHOU, Xuefeng GAO, Pengwei HUANG, Hong CAO. Indole-3-acetic acid alleviates Cryptococcus neoformans-induced pyroptosis in cerebral microvascular endothelial cells by regulating stress granule-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2679-2689.
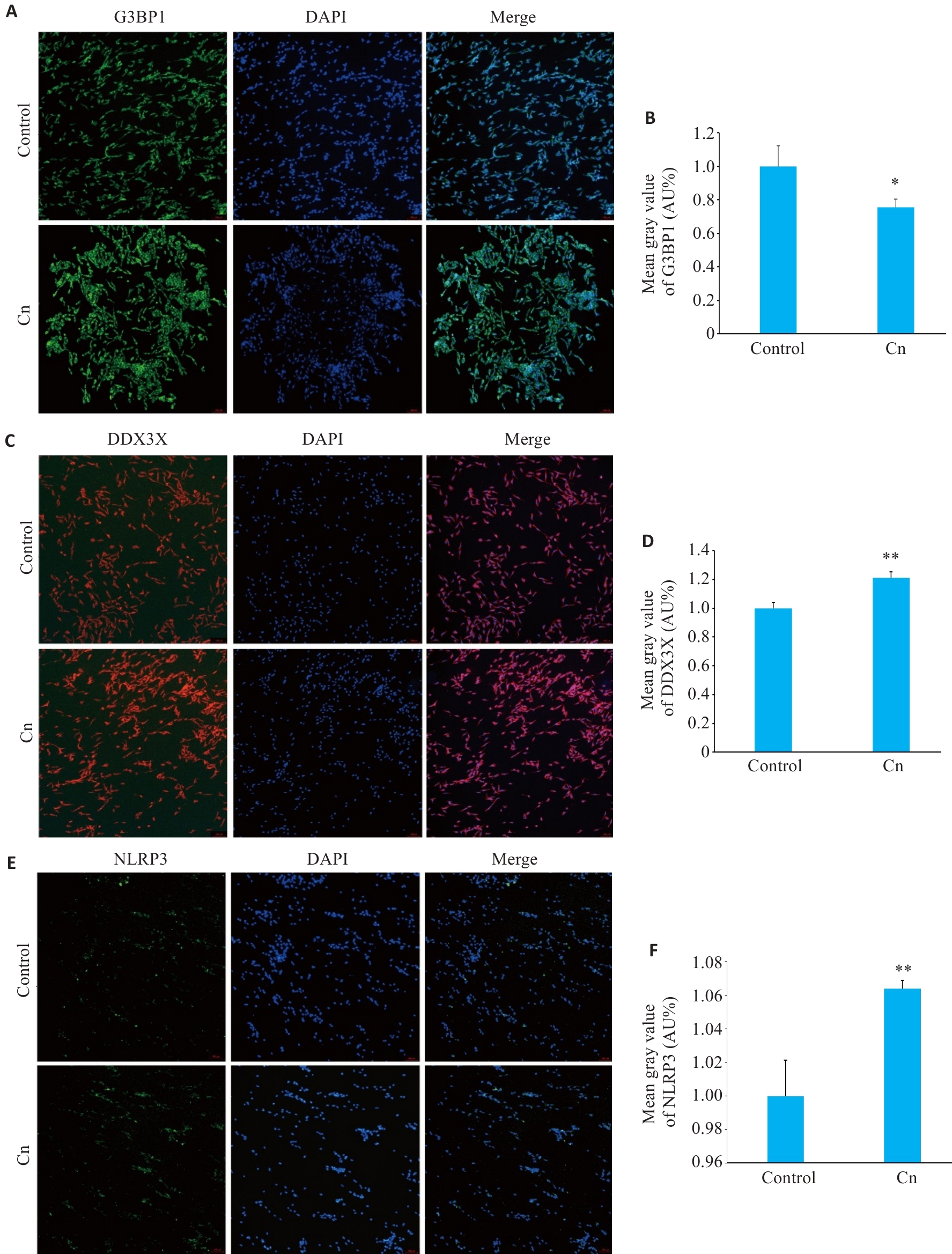
图1 细胞免疫荧光分析Cn感染后脑微血管内皮细胞中G3BP1、DDX3X和NLRP3蛋白表达水平变化
Fig.1 Immunofluorescence sataining for G3BP1 (A,B), DDX3X (C,D) and NLRP3 (E,F) in cerebral microvascular endothelial cells with Cn infection (Original magnification: ×100). *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
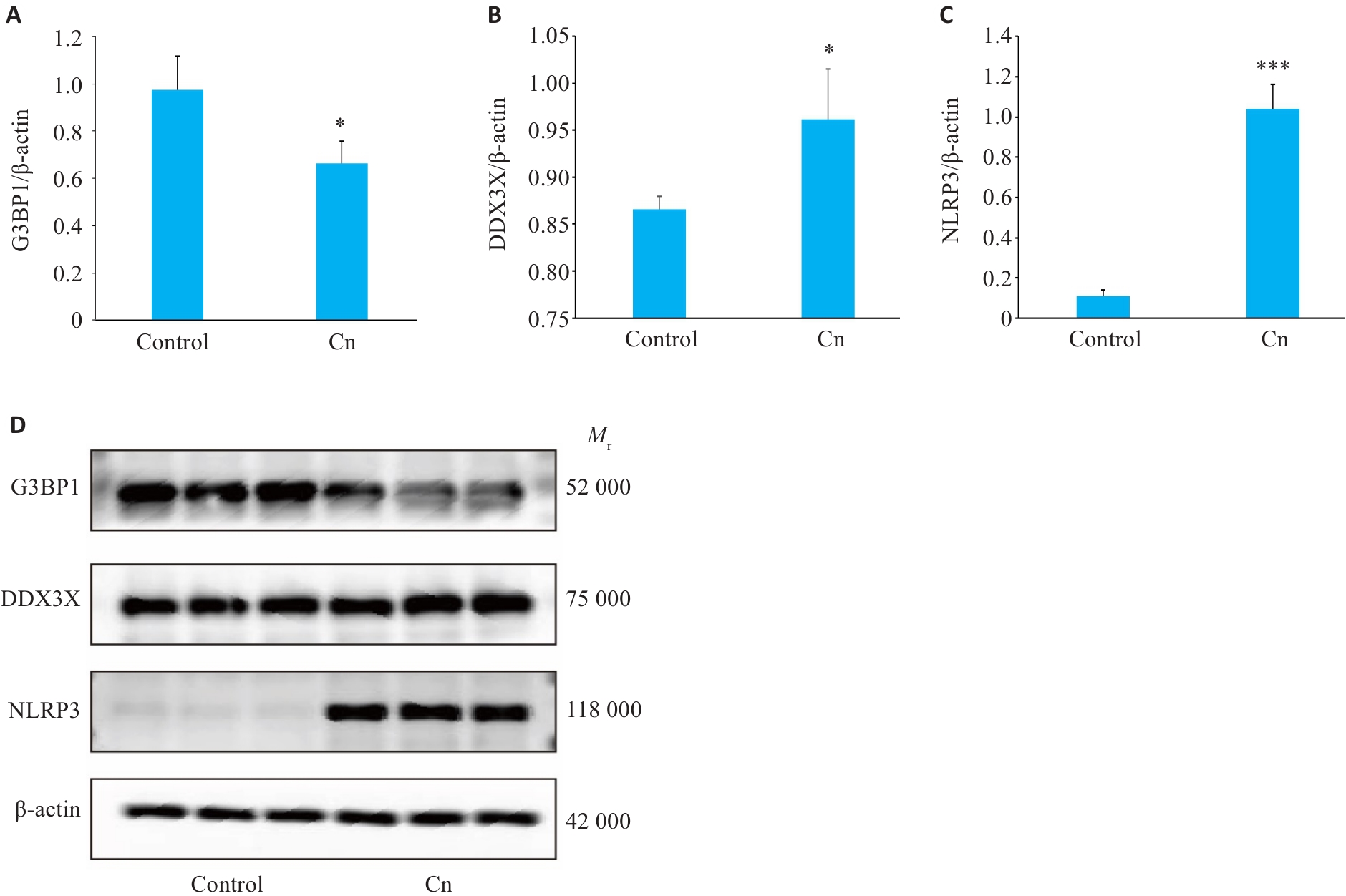
图2 Western blotting检测Cn处理脑微血管内皮细胞后细胞G3BP1, NLRP3, DDX3X表达情况
Fig.2 Western blotting for detecting G3BP1 (A), DDX3X(B) and NLRP3(C) protein expressions in cerebral microvascular endothelial cells following Cn infection. D: Protein bands in Western blotting. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001.
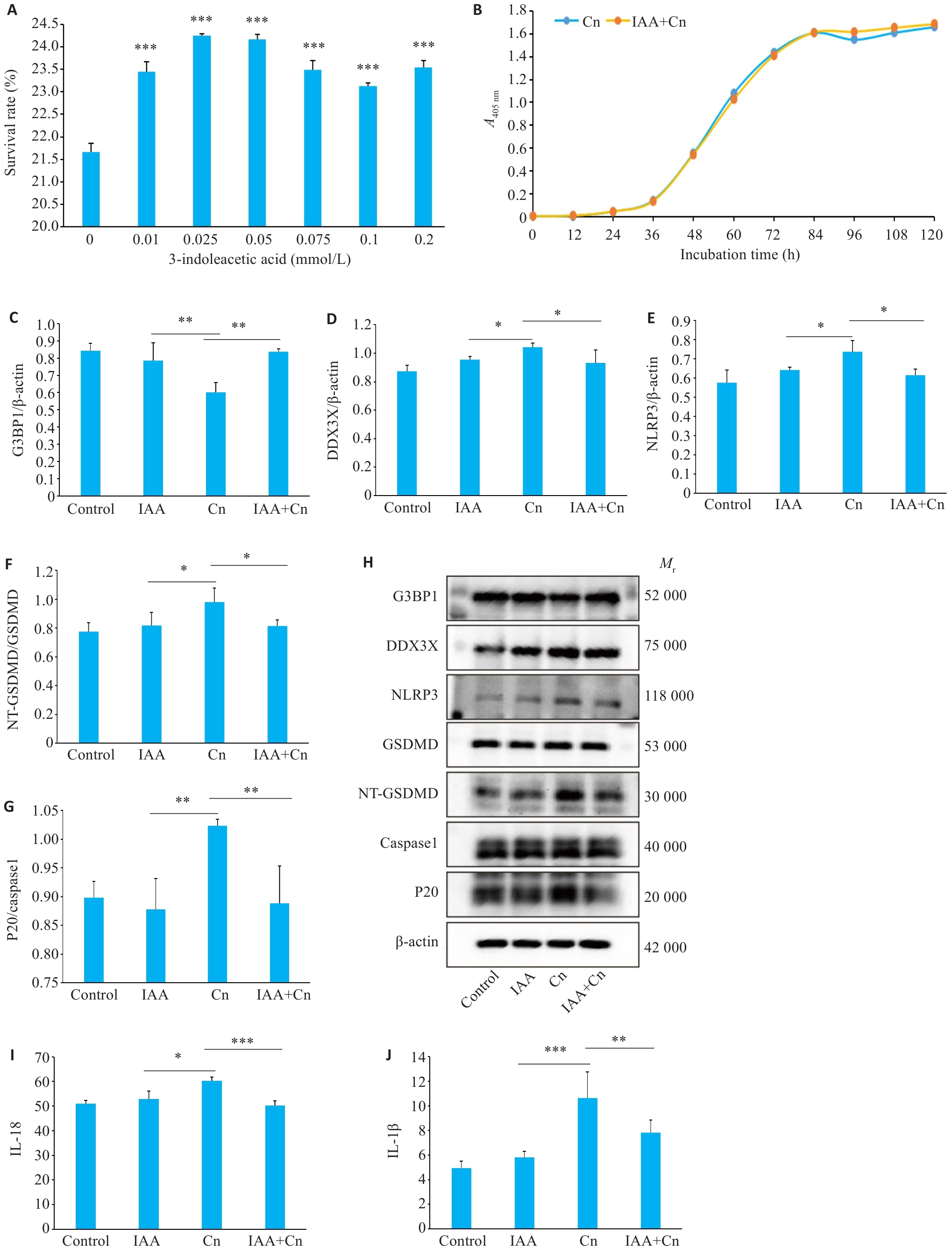
图3 IAA可缓解Cn引起的脑微血管内皮细胞焦亡
Fig.3 IAA alleviates Cn-induced pyroptosis of cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. A: Survival rates of Cn-infected cerebral microvascular endothelial cells treated with gradient concentrations of IAA. ***P<0.001 vs 0 mmol/L. B: The growth curve of Cn after IAA treatment. C-G: Expressions of G3BP1, DDX3X, NLRP3, NT-GSDMD /GSDMD, and P20/caspase-1 in Cn-infected cerebral microvascular endothelial cells with IAA treatment. H: Protein bands by Western blotting. I-J: IL-18 and IL-1β levels in the cell culture supernatant determined by ELISA. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
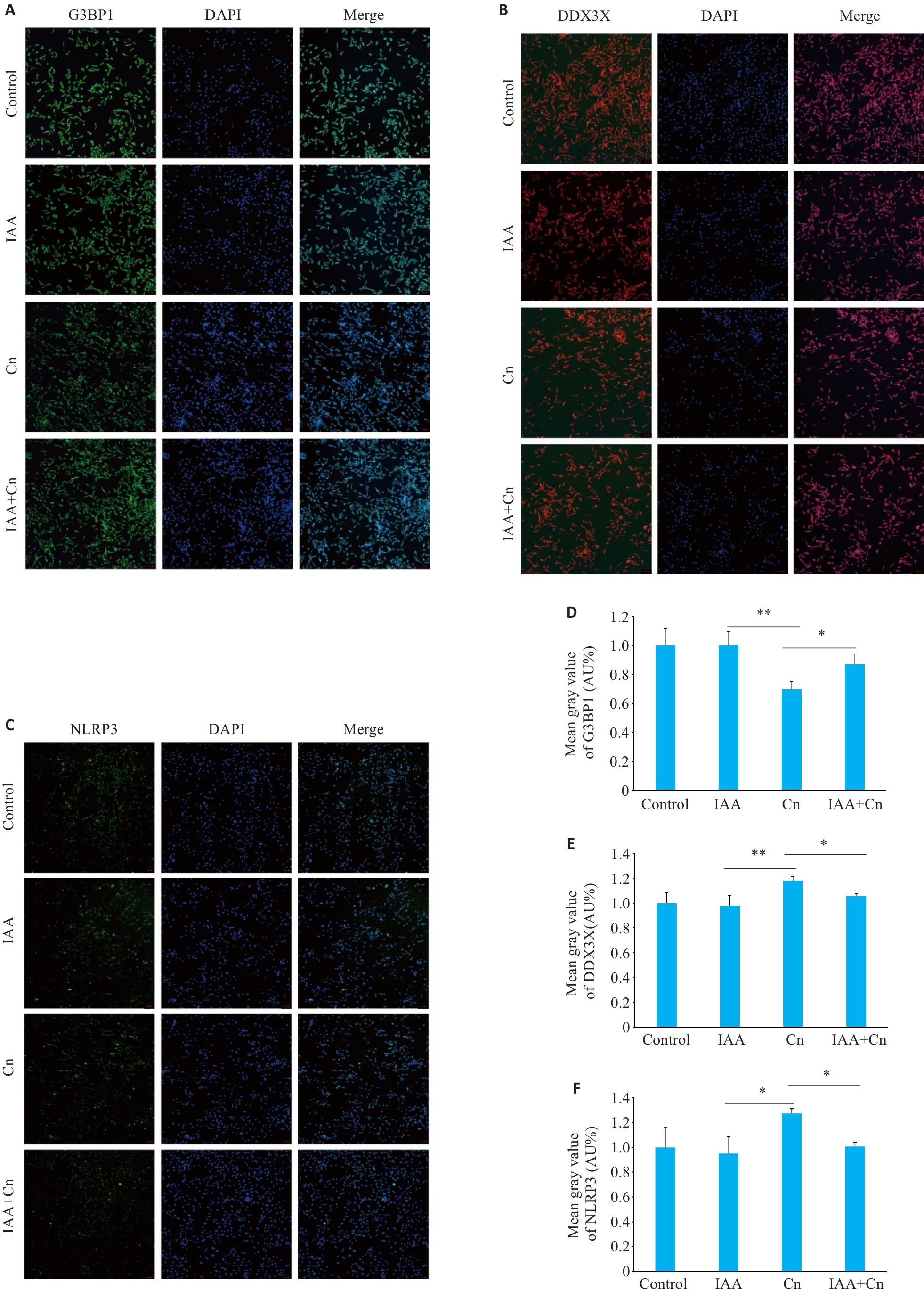
图4 细胞免疫荧光检测IAA可减轻Cn引起的G3BP1、DDX3X和NLRP3的变化
Fig.4 IAA alleviates Cn-induced changes in G3BP1, DDX3X and NLRP3 expressions in cerebral microvascular endothelial cells (Immunofluorescence staining, ×100). A, D: Effect of IAA on G3BP1 expression in Cn-infected cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. B,E: Effect of IAA on DDX3X expression in Cn-infected cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. C,F: Effect of IAA on NLRP3 expression in Cn-infected cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
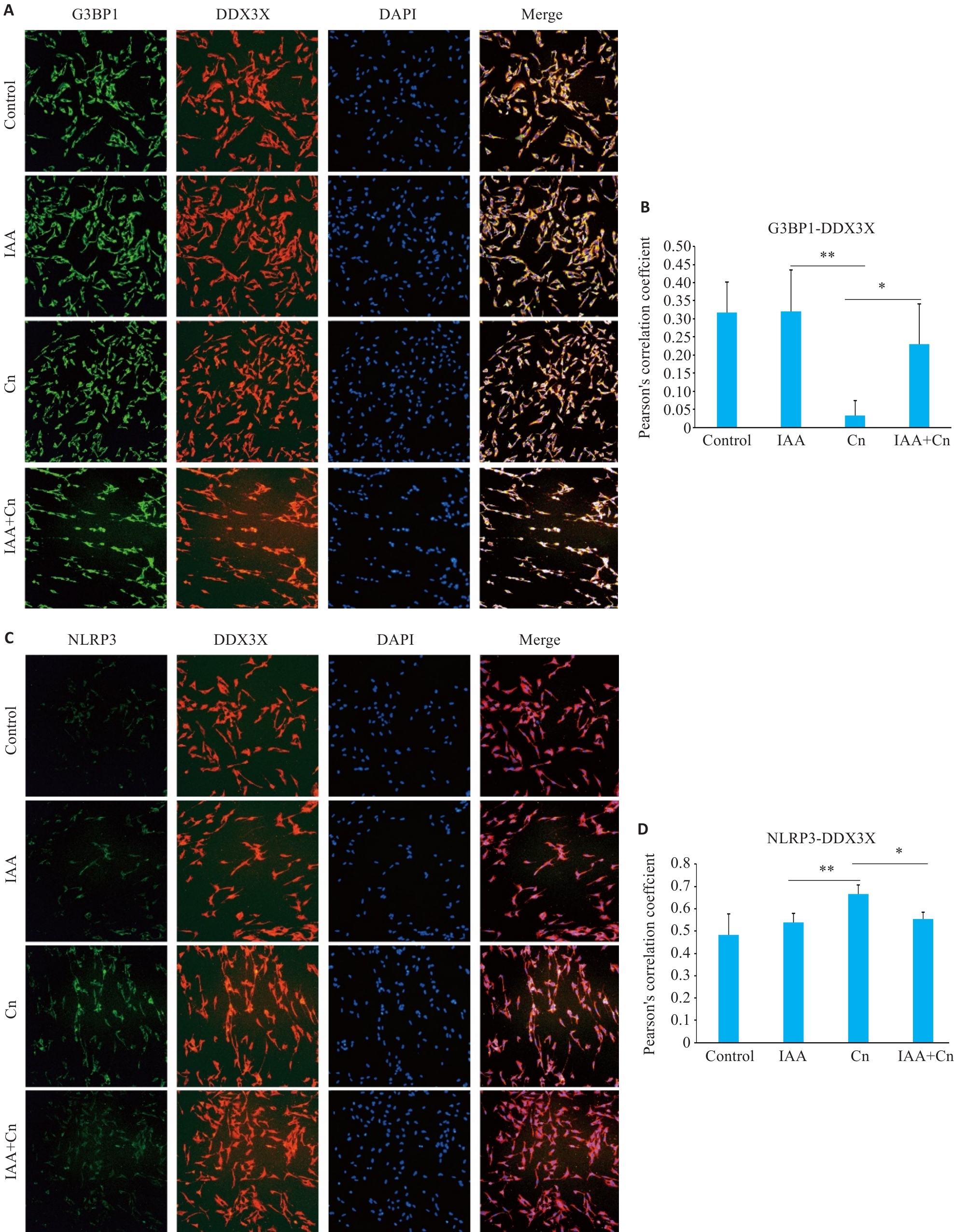
图5 IAA调控DDX3X对Cn诱导的脑微血管内皮细胞中SGs生成和NLRP3炎性小体活化
Fig.5 IAA regulates translocation of DDX3X in the formation of SGs and activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in Cn-infected cerebral microvascular endothelial cells (Immunofluorescence staining, ×200). A,B: Co-localization of G3BP1 and DDX3X in cells treated with Cn and IAA. C, D: Co-localization of NLRP3 and DDX3X in cells treated with Cn and IAA. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
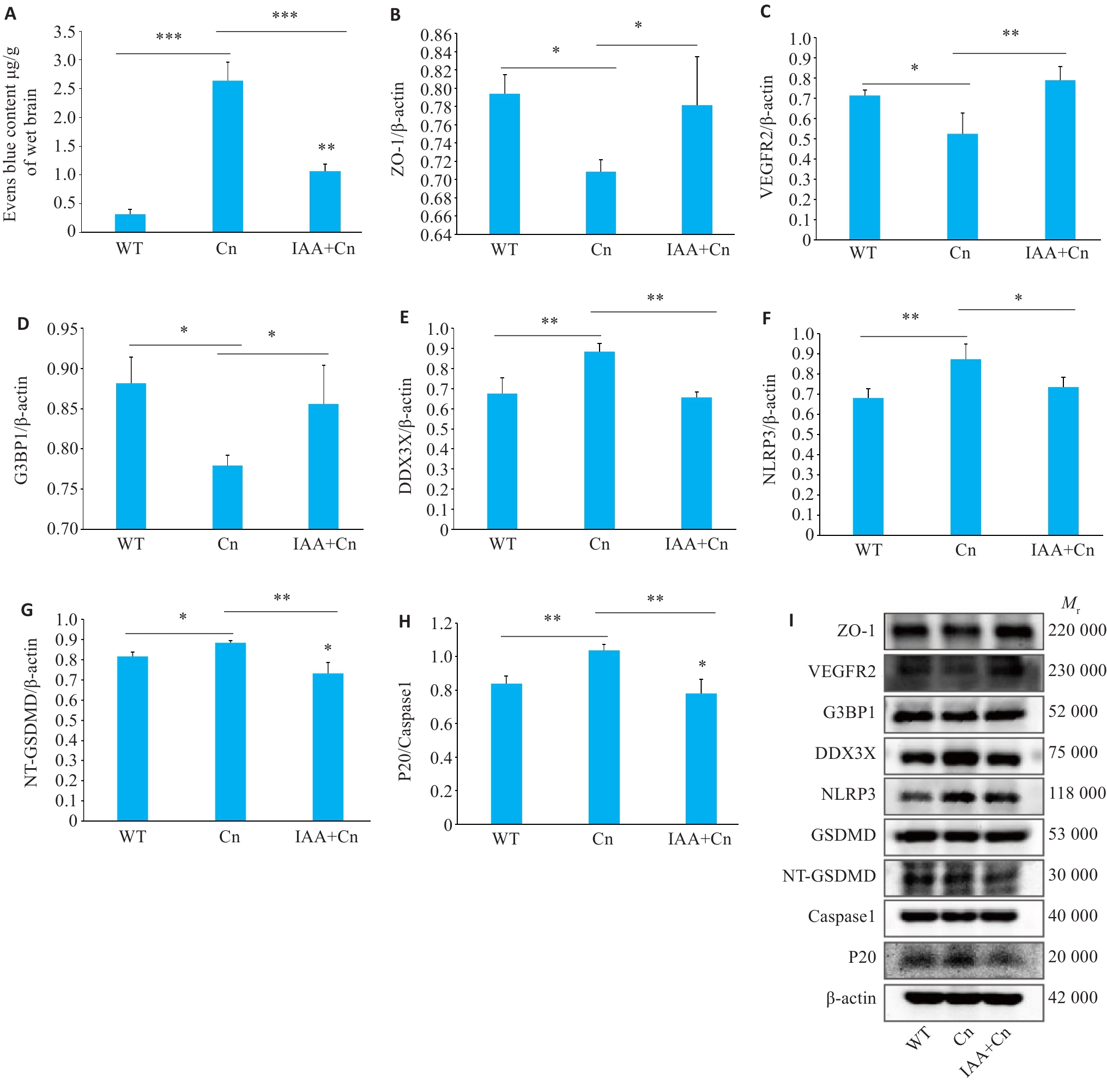
图6 体内实验验证IAA调控SGs的形成对Cn诱导的BBB焦亡的作用
Fig.6 Regulatory effect of IAA on formation of SGs and Cn-induced pyroptosis in the blood-brain barrier (BBB) in mice. A: Evans blue staining showing changes in permeability of the BBB after Cn infection and IAA treatment. B: Expression level of ZO-1 in the BBB of mice with Cn infection and IAA treatment detected by Western blotting. C-F: Expression levels of VEGFR2, G3BP1, DDX3X, and NLRP3 in the cerebral cortex of the mice detected by Western blotting. G: Expression levels of NT-GSDMD and GSDMD. H: Expression levels of P20 and caspase-1. I: Portein bands by Western blotting. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
| [1] | Tugume L, Ssebambulidde K, Kasibante J, et al. Cryptococcal meningitis[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2023, 9: 62. doi:10.1038/s41572-023-00472-z |
| [2] | Rajasingham R, Govender NP, Jordan A, et al. The global burden of HIV-associated cryptococcal infection in adults in 2020: a modelling analysis[J]. Lancet Infect Dis, 2022, 22(12): 1748-55. doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(22)00499-6 |
| [3] | Liu LJ, Tang YF, Zhang L, et al. The molecular mechanisms by which the NLRP3 inflammasome regulates blood-brain barrier permeability following cryptococcal meningitis[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(23): e39653. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39653 |
| [4] | Kim J, Lee KT, Lee JS, et al. Fungal brain infection modelled in a human-neurovascular-unit-on-a-chip with a functional blood-brain barrier[J]. Nat Biomed Eng, 2021, 5(8): 830-46. doi:10.1038/s41551-021-00743-8 |
| [5] | Zapata-Acevedo JF, Mantilla-Galindo A, Vargas-Sánchez K, et al. Chapter one blood-brain barrier biomarkers[J]. Adv Clin Chem, 2024, 121: 1-88. doi:10.1016/bs.acc.2024.04.004 |
| [6] | Zheng ZJ, Zhu LZ, Qiu H, et al. Neferine inhibits BMECs pyroptosis and maintains blood-brain barrier integrity in ischemic stroke by triggering a cascade reaction of PGC-1α[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 14438. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-64815-w |
| [7] | Han CY, Zhai LP, Shen HP, et al. Advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) promote endothelial cell pyroptosis under cerebral ischemia and hypoxia via HIF-1α-RAGE-NLRP3[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2023, 60(5): 2355-66. doi:10.1007/s12035-023-03228-8 |
| [8] | Gong Z, Gao X, Li Y, et al. Alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonists prevent meningitic Escherichia coli-induced blood-brain barrier disruptions by targeting the CISH/JAK2/STAT5b axis[J]. Biomedicines, 2022, 10(10): 2358. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10102358 |
| [9] | Zhang ZL, Zou JH, Luo ZF, et al. NLRP3/caspase 1/gsdmd mediated pyroptosis exerts a crucial role in blood-brain barrier pathological injury induced by Cryptococcus neoformans [J]. Blood, 2023, 142: 5417. doi:10.1182/blood-2023-184554 |
| [10] | Marcelo A, Koppenol R, de Almeida LP, et al. Stress granules, RNA-binding proteins and polyglutamine diseases: too much aggregation?[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(6): 592. doi:10.1038/s41419-021-03873-8 |
| [11] | Zhang H, Mañán-Mejías PM, Miles HN, et al. DDX3X and stress granules: emerging players in cancer and drug resistance[J]. Cancers: Basel, 2024, 16(6): 1131. doi:10.3390/cancers16061131 |
| [12] | Feng D, Guo L, Liu J, et al. DDX3X deficiency alleviates LPS-induced H9c2 cardiomyocytes pyroptosis by suppressing activation of NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2021, 22(6): 1389. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10825 |
| [13] | Wang Q, Kohls W, Wills M, et al. A novel stroke rehabilitation strategy and underlying stress granule regulations through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2024, 30(1): e14405. doi:10.1111/cns.14405 |
| [14] | Su X, Gao Y, Yang R. Gut microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolites maintain gut and systemic homeostasis[J]. Cells, 2022, 11(15): 2296. doi:10.3390/cells11152296 |
| [15] | Krishnan S, Ding YF, Saedi N, et al. Gut microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolites modulate inflammatory response in hepatocytes and macrophages[J]. Cell Rep, 2018, 23(4): 1099-111. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.109 |
| [16] | Huang ZB, Zhang GP, Lu CX, et al. Gut microbiota-derived 3-indoleacetic acid confers a protection against sepsis-associated encephalopathy through microglial aryl hydrocarbon receptors[J]. Exp Neurol, 2025, 384: 115055. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.115055 |
| [17] | Zhao Q, Chen T, Ni C, et al. Indole-3-propionic acid attenuates HI-related blood-brain barrier injury in neonatal rats by modulating the PXR signaling pathway[J]. ACS Chem Neurosci, 2022, 13(19): 2897-912. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00418 |
| [18] | Huang ZB, Hu Z, Lu CX, et al. Gut microbiota-derived indole 3-propionic acid partially activates aryl hydrocarbon receptor to promote macrophage phagocytosis and attenuate septic injury[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12: 1015386. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.1015386 |
| [19] | 李 猛, 左春月, 靳晓飞, 等. 补阳还五汤通过抑制脑微血管内皮细胞自噬减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2025,41(3):481-91. |
| [20] | 高加巍, 崔梦迪. 当归多糖调节Caspase-1/Gasdermin D通路促进脑缺血-再灌注损伤大鼠脑微血管内皮细胞血管新生[J]. 中药材, 2024,47(4):977-83. |
| [21] | 张晋卿, 刘 伟, 谭静文, 等. 烟曲霉在不同温度和营养条件下的生长特性初探[J]. 中国真菌学杂志, 2013, 8(1): 6-9. |
| [22] | Permpalung N, Chiang TP, Manothummetha K, et al. Invasive fungal infections in inpatient solid organ transplant recipients with COVID-19: a multicenter retrospective cohort[J]. Transplantation, 2024, 108(7): 1613-22. doi:10.1097/tp.0000000000004947 |
| [23] | Zhang B, Yu JY, Liu LQ, et al. Alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor is required for blood-brain barrier injury-related CNS disorders caused by Cryptococcus neoformans and HIV-1 associated comorbidity factors[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2015, 15: 352. doi:10.1186/s12879-015-1075-9 |
| [24] | Lun J, Li Y, Gao X, et al. Kynurenic acid blunts A1 astrocyte activation against neurodegeneration in HIV-associated neuroco-gnitive disorders[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2023, 20(1): 87. doi:10.1186/s12974-023-02771-4 |
| [25] | Tweedie A, Nissan T. Hiding in plain sight: formation and function of stress granules during microbial infection of mammalian cells[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2021, 8: 647884. doi:10.3389/fmolb.2021.647884 |
| [26] | Eiermann N, Haneke K, Sun Z, et al. Dance with the devil: stress granules and signaling in antiviral responses[J]. Viruses, 2020, 12(9): E984. doi:10.3390/v12090984 |
| [27] | Samir P, Kesavardhana S, Patmore DM, et al. DDX3X acts as a live-or-die checkpoint in stressed cells by regulating NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Nature, 2019, 573(7775): 590-4. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1551-2 |
| [28] | Matsuki H, Takahashi M, Higuchi M, et al. Both G3BP1 and G3BP2 contribute to stress granule formation[J]. Genes Cells, 2013, 18(2): 135-46. doi:10.1111/gtc.12023 |
| [29] | Tornavaca O, Chia M, Dufton N, et al. ZO-1 controls endothelial adherens junctions, cell-cell tension, angiogenesis, and barrier formation[J]. J Cell Biol, 2015, 208(6): 821-38. doi:10.1083/jcb.201404140 |
| [30] | Chen XY, Wan SF, Yao NN, et al. Inhibition of the immunoproteasome LMP2 ameliorates ischemia/hypoxia-induced blood-brain barrier injury through the Wnt/β‑catenin signalling pathway[J]. Mil Med Res, 2021, 8(1): 62. doi:10.1186/s40779-021-00356-x |
| [31] | Wang YJ, Guan X, Gao CL, et al. Medioresinol as a novel PGC-1α activator prevents pyroptosis of endothelial cells in ischemic stroke through PPARα-GOT1 axis[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2021, 169: 105640. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105640 |
| [32] | Lopez-Pastrana J, Ferrer LM, Li YF, et al. Inhibition of Caspase-1 Activation in Endothelial Cells Improves Angiogenesis a novel therapeutic potential for ischemia[J]. J Biol Chem, 2015, 290(28): 17485-94. doi:10.1074/jbc.m115.641191 |
| [33] | Li P, Hu Y, Liu J, et al. Naoluo Xintong Decoction activates caspase-1/Gasdermin D pathway to promote angiogenesis of rat brain microvascular endothelial cells after oxygen glucose deprivation/reperfusion injury[J]. Nan Fang Yi Ke da Xue Xue Bao, 2023, 43(7): 1093-101. |
| [1] | 罗善玉, 朱强, 闫玉翡, 纪宗红, 邹华杰, 张瑞霞, 巴应贵. 低氧环境下NLRP3信号通路促进非酒精性脂肪性肝炎小鼠的肝细胞焦亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 2026-2033. |
| [2] | 刘辰菲, 张玮, 曾尧, 梁艳, 王梦婷, 张明芳, 李新元, 王凤超, 杨燕青. 2,6-二甲氧基-1,4-苯醌通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化改善葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1654-1662. |
| [3] | 尚菲菲, 师晓可, 曾尧, 陶循浅, 李天真, 梁艳, 杨燕青, 宋传旺. Avitinib抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化并改善小鼠感染性休克[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1697-1705. |
| [4] | 周海忆, 何斯怡, 韩瑞芳, 关永格, 董丽娟, 宋阳. 艾灸通过调控miR-223-3p/NLRP3焦亡通路修复薄型子宫内膜[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1380-1388. |
| [5] | 卞芬兰, 倪诗垚, 赵鹏, 戚毛男星, 唐碧, 王洪巨, 康品方, 刘进军. 积雪草苷通过抑制NLRP3炎症体介导的细胞焦亡减轻大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 977-985. |
| [6] | 孙亚磊, 罗萌, 郭长胜, 高静, 苏凯奇, 陈立典, 冯晓东. 穗花杉双黄酮通过抑制细胞焦亡减轻小鼠急性肺损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 692-701. |
| [7] | 朱正望, 王琳琳, 赵静涵, 马瑞雪, 余雨春, 蔡庆春, 王兵, 朱平生, 苗明三. 退黄合剂通过调控法尼醇X受体抑制NLRP3炎症小体改善α-萘异硫氰酸酯诱导的大鼠胆汁淤积[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 718-724. |
| [8] | 黄菊, 殷丽霞, 牛民主, 耿志军, 左芦根, 李静, 胡建国. 紫花前胡苷通过抑制肠上皮细胞焦亡改善2,4,6-三硝基苯磺酸诱导的小鼠实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 261-268. |
| [9] | 黄鹏伟, 陈洁, 邹金虎, 高雪锋, 曹虹. 槲皮素促进应激颗粒G3BP1解聚改善HIV-1 gp120诱导的星形胶质细胞神经毒性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 304-312. |
| [10] | 夏士程, 韦慧芳, 洪维灿, 张钰明, 尹菲玚, 张贻欣, 张淋淋, 高琴, 叶红伟. 金银花提取物对阿霉素诱导的小鼠心肌损伤的保护作用及其机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2527-2540. |
| [11] | 付长龙, 陈若岚, 徐诗淇, 游锦欣, 林晴, 黄艳峰. 巴戟天多糖通过靶向lncRNA XIST调控糖酵解-焦亡延缓小鼠骨关节炎软骨细胞退变[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2541-2550. |
| [12] | 张思雨, 冉林武, 曾瑾, 王玉炯. 产气荚膜梭菌Beta1毒素通过P2X7-Ca2+轴诱导巨噬细胞焦亡和铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2126-2134. |
| [13] | 李明远, 张玮, 华梦晴. 甲基巴多索龙通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化缓解小鼠急性肝损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1662-1669. |
| [14] | 张玮, 邓蒙蒙, 曾尧, 刘辰菲, 尚菲菲, 许文豪, 蒋昊轶, 王凤超, 杨燕青. 2,6-二甲氧基-1,4-苯醌通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化缓解小鼠的感染性休克[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1024-1032. |
| [15] | 孙一鸣, 张荣, 孟莹, 朱磊, 李明强, 刘哲. 辅酶Q10通过下调焦亡信号通路缓解抑郁小鼠的抑郁样行为[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 810-817. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||