南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (10): 2126-2134.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.10.09
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2025-03-29
出版日期:2025-10-20
发布日期:2025-10-24
通讯作者:
曾瑾,王玉炯
E-mail:zhangsiyu1997@163.com;zengjin@nxu.edu.cn;wyj@nxu.edu.cn
作者简介:张思雨,博士,实验师,E-mail: zhangsiyu1997@163.com
基金资助:
Siyu ZHANG1,2( ), Linwu RAN2, Jin ZENG1(
), Linwu RAN2, Jin ZENG1( ), Yujiong WANG1(
), Yujiong WANG1( )
)
Received:2025-03-29
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-10-24
Contact:
Jin ZENG, Yujiong WANG
E-mail:zhangsiyu1997@163.com;zengjin@nxu.edu.cn;wyj@nxu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探索P2X7受体调控钙稳态失调介导的产气荚膜梭菌Beta1毒素毒理机制,为Beta1毒素致病机制的研究提供新思路。 方法 将20只10日龄BALB/c乳鼠随机分为对照组、rCPB1组、PD151746组、PD151746+rCPB1组,5只/组。对照组灌胃PBS,rCPB1组灌胃rCPB1,PD151746组灌胃抑制剂PD151746,PD151746+rCPB1组先灌胃PD151746,2 h后再灌胃rCPB1。采用抗体芯片技术检测空肠的炎性因子的表达,在体内水平揭示钙稳态失调在Beta1毒素导致机体炎性损伤中的调控作用;进一步使用si-RNA-P2X7并经rCPB1处理THP-1细胞后,分别检测细胞存活率,Ca2+、ROS和ATP水平,以及细胞焦亡和铁死亡的标志性检测指标,在体外水平揭示P2X7受体调控钙稳态失调介导的Beta1毒素的毒理机制。 结果 rCPB1灌胃乳鼠后,空肠组织中有多种炎性细胞因子表达升高(P<0.05),而用PD151746治疗后,其表达水平下降(P<0.05)。成功建立P2X7受体沉默细胞模型;P2X7受体沉默后,细胞存活率升高(P<0.05)、Ca2+、活性氧、三磷酸腺苷水平以及细胞焦亡和铁死亡的标志性检测指标均下降(P<0.01)。 结论 P2X7受体介导的Beta1毒素功能性孔形成,能够进一步导致钙稳态失调,从而触发活性氧过度积累,进而诱导细胞焦亡和铁死亡共同发生。
张思雨, 冉林武, 曾瑾, 王玉炯. 产气荚膜梭菌Beta1毒素通过P2X7-Ca2+轴诱导巨噬细胞焦亡和铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2126-2134.
Siyu ZHANG, Linwu RAN, Jin ZENG, Yujiong WANG. Clostridium perfringens Beta1 toxin induces macrophage pyroptosis and ferroptosis through the purinergic receptor P2X7-Ca2+ axis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(10): 2126-2134.
| siRNA | Sequence |
|---|---|
| siRNA-P2X7-1 | F: GGAUAGCAGAGGUGAAAGATT |
| R: UCUUUCACCUCUGCUAUCCTT | |
| siRNA-P2X7-2 | F: AGAUCUACUGGGACUGCAATT |
| R: UUGCAGUCCCAGUAGAUCUTT | |
| siRNA-P2X7-3 | F: GGAUGGACCCGCAGAGCAATT |
| R: UUGCUCUGCGGGUCCAUCCTT |
表1 siRNA引物序列
Tab.1 Sequences for interference of P2X7 receptor
| siRNA | Sequence |
|---|---|
| siRNA-P2X7-1 | F: GGAUAGCAGAGGUGAAAGATT |
| R: UCUUUCACCUCUGCUAUCCTT | |
| siRNA-P2X7-2 | F: AGAUCUACUGGGACUGCAATT |
| R: UUGCAGUCCCAGUAGAUCUTT | |
| siRNA-P2X7-3 | F: GGAUGGACCCGCAGAGCAATT |
| R: UUGCUCUGCGGGUCCAUCCTT |
| Protein ID | AveExp.R | AveExp.NC | logFC | P | Foldchange | Regulation | Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | 11.038471 | 9.952830 | 1.085640 | 0.014842 | 2.122318 | Up | True |
| IL-4 | 10.367004 | 8.840474 | 1.526530 | 0.012641 | 2.880921 | Up | True |
| IL-17 | 11.149417 | 9.917431 | 1.231985 | 0.011102 | 2.348900 | Up | True |
| IL-21 | 12.077335 | 11.492716 | 0.584619 | 0.016853 | 1.499643 | Up | True |
| IL-23 | 11.225443 | 9.751727 | 1.473716 | 0.020574 | 2.777363 | Up | True |
| TNF-α | 11.054078 | 7.873779 | 3.180298 | 0.024354 | 9.064948 | Up | True |
| IL-10 | 11.594167 | 10.449359 | 1.144807 | 0.032358 | 2.211166 | Up | True |
| IL-2 | 11.624989 | 8.212568 | 3.412420 | 0.039846 | 10.647333 | Up | True |
| IL-9 | 10.103333 | 7.685385 | 2.417947 | 0.053630 | 5.344102 | Up | False |
| IL-5 | 10.910604 | 9.888081 | 1.022522 | 0.072574 | 2.031467 | Up | False |
| IL-15 | 8.952885 | 6.671663 | 2.281222 | 0.076890 | 4.860896 | Up | False |
| IL-12p70 | 10.626989 | 9.659774 | 0.967215 | 0.093436 | 1.955062 | Up | False |
| IL-13 | 8.279287 | 5.954063 | 2.325224 | 0.190672 | 5.011438 | Up | False |
| GM-CSF | 11.105001 | 10.092616 | 1.012384 | 0.353971 | 2.017243 | Up | False |
| IL-6 | 10.714897 | 9.905783 | 0.809113 | 0.430292 | 1.752134 | Up | False |
| IFN-γ | 11.600352 | 11.329201 | 0.271151 | 0.441625 | 1.206770 | Up | False |
| IL-3 | 10.335866 | 9.441554 | 0.894311 | 0.495537 | 1.858723 | Up | False |
| G-CSF | 6.169542 | 4.829909 | 1.339633 | 0.575135 | 2.530870 | Up | False |
| IL-7 | 4.832278 | 4.495829 | 0.336449 | 0.857724 | 1.262645 | Up | False |
| IL-1α | 10.786292 | 10.839428 | -0.053135 | 0.954795 | 0.963839 | Down | False |
表2 空肠组织中rCPB1组与对照组差异表达的炎性因子
Tab.2 Differential expression of inflammatory factors in the jejunal tissue between Beta1 toxin group and blank control group
| Protein ID | AveExp.R | AveExp.NC | logFC | P | Foldchange | Regulation | Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | 11.038471 | 9.952830 | 1.085640 | 0.014842 | 2.122318 | Up | True |
| IL-4 | 10.367004 | 8.840474 | 1.526530 | 0.012641 | 2.880921 | Up | True |
| IL-17 | 11.149417 | 9.917431 | 1.231985 | 0.011102 | 2.348900 | Up | True |
| IL-21 | 12.077335 | 11.492716 | 0.584619 | 0.016853 | 1.499643 | Up | True |
| IL-23 | 11.225443 | 9.751727 | 1.473716 | 0.020574 | 2.777363 | Up | True |
| TNF-α | 11.054078 | 7.873779 | 3.180298 | 0.024354 | 9.064948 | Up | True |
| IL-10 | 11.594167 | 10.449359 | 1.144807 | 0.032358 | 2.211166 | Up | True |
| IL-2 | 11.624989 | 8.212568 | 3.412420 | 0.039846 | 10.647333 | Up | True |
| IL-9 | 10.103333 | 7.685385 | 2.417947 | 0.053630 | 5.344102 | Up | False |
| IL-5 | 10.910604 | 9.888081 | 1.022522 | 0.072574 | 2.031467 | Up | False |
| IL-15 | 8.952885 | 6.671663 | 2.281222 | 0.076890 | 4.860896 | Up | False |
| IL-12p70 | 10.626989 | 9.659774 | 0.967215 | 0.093436 | 1.955062 | Up | False |
| IL-13 | 8.279287 | 5.954063 | 2.325224 | 0.190672 | 5.011438 | Up | False |
| GM-CSF | 11.105001 | 10.092616 | 1.012384 | 0.353971 | 2.017243 | Up | False |
| IL-6 | 10.714897 | 9.905783 | 0.809113 | 0.430292 | 1.752134 | Up | False |
| IFN-γ | 11.600352 | 11.329201 | 0.271151 | 0.441625 | 1.206770 | Up | False |
| IL-3 | 10.335866 | 9.441554 | 0.894311 | 0.495537 | 1.858723 | Up | False |
| G-CSF | 6.169542 | 4.829909 | 1.339633 | 0.575135 | 2.530870 | Up | False |
| IL-7 | 4.832278 | 4.495829 | 0.336449 | 0.857724 | 1.262645 | Up | False |
| IL-1α | 10.786292 | 10.839428 | -0.053135 | 0.954795 | 0.963839 | Down | False |
| Protein ID | AveExp.PR | AveExp.R | logFC | adj.P.Val | Foldchange | Regulation | Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | 9.017981 | 11.038472 | -2.020491 | 0.000628 | 0.246474 | Down | True |
| IL-4 | 7.738409 | 10.367005 | -2.628596 | 0.000628 | 0.161701 | Down | True |
| IL-10 | 9.194662 | 11.594168 | -2.399506 | 0.000628 | 0.189529 | Down | True |
| IFN-γ | 10.175170 | 11.600353 | -1.425182 | 0.001782 | 0.372372 | Down | True |
| GM-CSF | 6.999299 | 11.105001 | -4.105702 | 0.002697 | 0.058085 | Down | True |
| IL-3 | 5.430662 | 10.335866 | -4.905204 | 0.002697 | 0.033372 | Down | True |
| IL-23 | 9.085735 | 11.225443 | -2.139708 | 0.003959 | 0.226926 | Down | True |
| IL-5 | 9.121355 | 10.910604 | -1.789249 | 0.007069 | 0.289323 | Down | True |
| IL-17 | 9.684801 | 11.149417 | -1.464616 | 0.007069 | 0.362332 | Down | True |
| IL-2 | 7.235229 | 11.624989 | -4.389760 | 0.019791 | 0.047704 | Down | True |
| IL-12p70 | 9.127082 | 10.626990 | -1.499907 | 0.021880 | 0.353576 | Down | True |
| IL-21 | 11.530132 | 12.077336 | -0.547204 | 0.040580 | 0.684345 | Down | True |
| IL-7 | 0.713847 | 4.832278 | -4.118431 | 0.054878 | 0.057574 | Down | False |
| IL-6 | 8.623386 | 10.714897 | -2.091512 | 0.069235 | 0.234635 | Down | False |
| IL-9 | 8.054050 | 10.103334 | -2.049284 | 0.131383 | 0.241604 | Down | False |
| TNF-α | 8.907458 | 11.054079 | -2.146621 | 0.148291 | 0.225841 | Down | False |
| IL-13 | 5.552009 | 8.279288 | -2.727278 | 0.149572 | 0.151011 | Down | False |
| G-CSF | 3.761456 | 6.169543 | -2.408087 | 0.337903 | 0.188406 | Down | False |
| IL-15 | 7.700203 | 8.952886 | -1.252682 | 0.337903 | 0.419667 | Down | False |
| IL-1-α | 10.168991 | 10.786292 | -0.617301 | 0.511964 | 0.651889 | Down | False |
表3 空肠组织中PD151746+rCPB1组与rCPB1组差异表达的炎性因子
Tab.3 Differential expression of inflammatory factors in the jejunal tissue between PD151746 and Beta1 toxin co-treatment group and Beta1 toxin treatment group
| Protein ID | AveExp.PR | AveExp.R | logFC | adj.P.Val | Foldchange | Regulation | Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | 9.017981 | 11.038472 | -2.020491 | 0.000628 | 0.246474 | Down | True |
| IL-4 | 7.738409 | 10.367005 | -2.628596 | 0.000628 | 0.161701 | Down | True |
| IL-10 | 9.194662 | 11.594168 | -2.399506 | 0.000628 | 0.189529 | Down | True |
| IFN-γ | 10.175170 | 11.600353 | -1.425182 | 0.001782 | 0.372372 | Down | True |
| GM-CSF | 6.999299 | 11.105001 | -4.105702 | 0.002697 | 0.058085 | Down | True |
| IL-3 | 5.430662 | 10.335866 | -4.905204 | 0.002697 | 0.033372 | Down | True |
| IL-23 | 9.085735 | 11.225443 | -2.139708 | 0.003959 | 0.226926 | Down | True |
| IL-5 | 9.121355 | 10.910604 | -1.789249 | 0.007069 | 0.289323 | Down | True |
| IL-17 | 9.684801 | 11.149417 | -1.464616 | 0.007069 | 0.362332 | Down | True |
| IL-2 | 7.235229 | 11.624989 | -4.389760 | 0.019791 | 0.047704 | Down | True |
| IL-12p70 | 9.127082 | 10.626990 | -1.499907 | 0.021880 | 0.353576 | Down | True |
| IL-21 | 11.530132 | 12.077336 | -0.547204 | 0.040580 | 0.684345 | Down | True |
| IL-7 | 0.713847 | 4.832278 | -4.118431 | 0.054878 | 0.057574 | Down | False |
| IL-6 | 8.623386 | 10.714897 | -2.091512 | 0.069235 | 0.234635 | Down | False |
| IL-9 | 8.054050 | 10.103334 | -2.049284 | 0.131383 | 0.241604 | Down | False |
| TNF-α | 8.907458 | 11.054079 | -2.146621 | 0.148291 | 0.225841 | Down | False |
| IL-13 | 5.552009 | 8.279288 | -2.727278 | 0.149572 | 0.151011 | Down | False |
| G-CSF | 3.761456 | 6.169543 | -2.408087 | 0.337903 | 0.188406 | Down | False |
| IL-15 | 7.700203 | 8.952886 | -1.252682 | 0.337903 | 0.419667 | Down | False |
| IL-1-α | 10.168991 | 10.786292 | -0.617301 | 0.511964 | 0.651889 | Down | False |
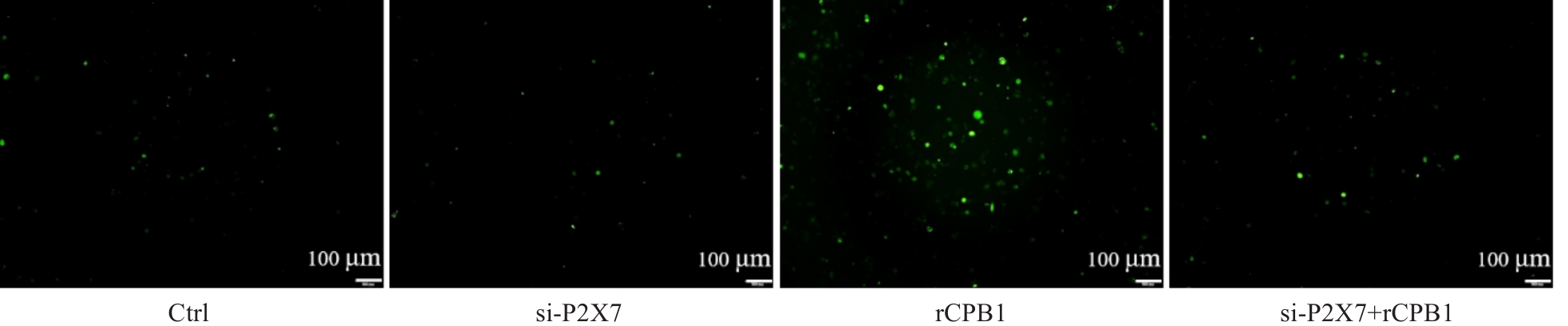
图4 THP-1细胞沉默P2X7受体后的Ca2+水平
Fig.4 P2X7 receptor knockdown decreases Ca2+ levels in rCPB1-treated THP-1 cells. Negative Ca2+ signal is seen in Ctrl group and si-P2X7 group, and positive Ca2+ signal (green) is shown in rCPB1 group and si-P2X7+ rCPB1group.
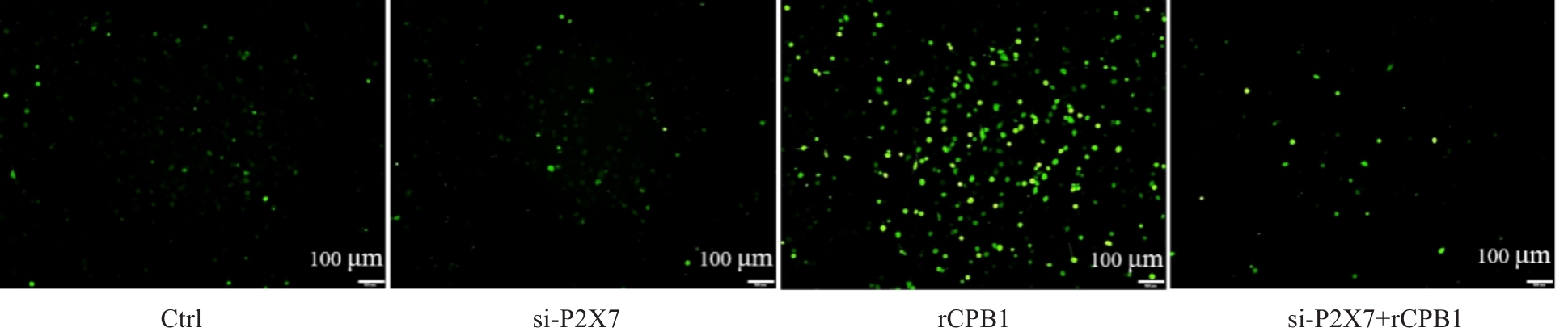
图5 THP-1细胞沉默P2X7受体后的ROS水平
Fig.5 P2X7 receptor knockdown decreases ROS levels in rCPB1-treated THP-1 cells. ROS signal is negative in Ctrl group and si-P2X7 group and positive (green) in rCPB1 group and si-P2X7+rCPB1 group.
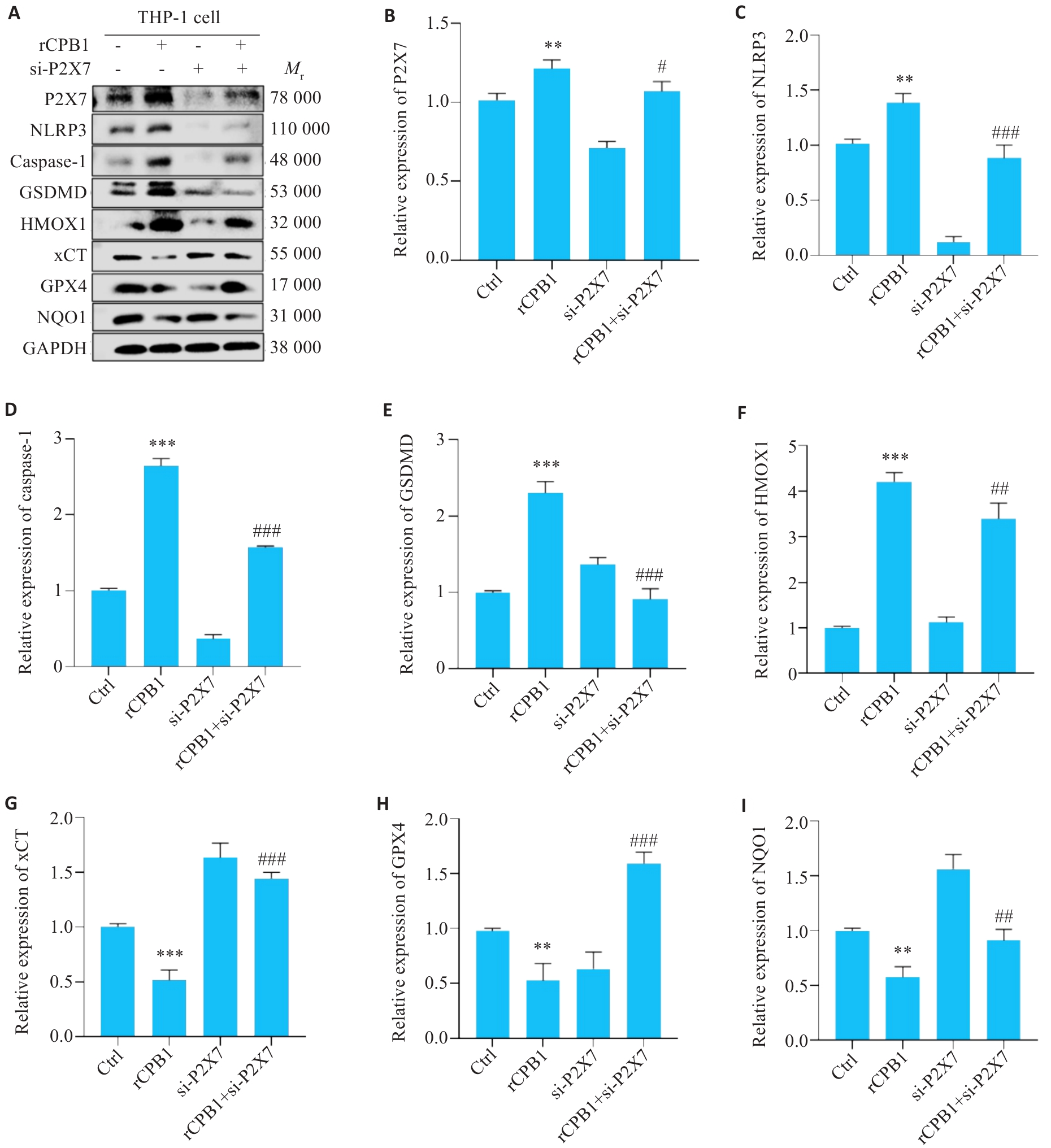
图7 THP-1细胞沉默P2X7受体后细胞焦亡、铁死亡相关蛋白的表达
Fig.7 Expressions of pyroptosis- and ferroptosis-related proteins in THP-1 cells with rCPB1 treatments, P2X7 receptor knockdown, or both. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Ctrl; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs rCPB1 (n=3).
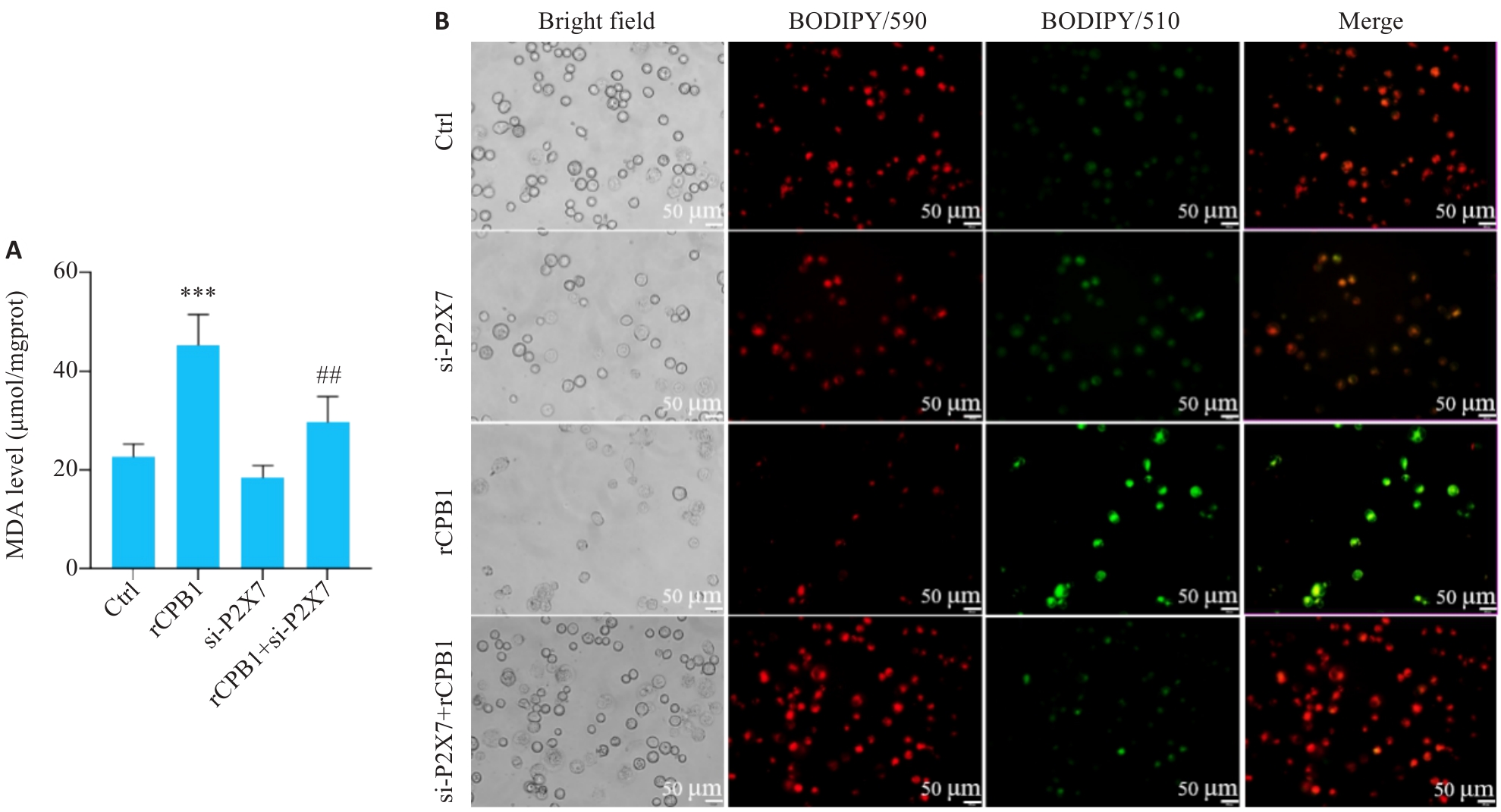
图8 THP-1细胞沉默P2X7受体后的脂质过氧化水平
Fig.8 P2X7 receptor knockdown lowers lipid peroxidation levels in rCPB1-treated THP-1 cells. A: The levels of MDA in Ctrl group, rCPB1 group, si-P2X7 group, and si-P2X7+rCPB1 group. B: Fluorescence images in the 4 groups of cells. ***P<0.001 vs Ctrl; ##P<0.01 vs rCPB1 (n=3).
| [1] | Kiu R, Hall LJ. An update on the human and animal enteric pathogen Clostridium perfringens [J]. Emerg Microbes Infect, 2018, 7(1): 141. doi:10.1038/s41426-018-0144-8 |
| [2] | Ba XL, Jin YS, Ning X, et al. Clostridium perfringens in the intestine: innocent bystander or serious threat [J]. Microorganisms, 2024, 12(8): 1610. doi:10.3390/microorganisms12081610 |
| [3] | Peterson LW, Artis D. Intestinal epithelial cells: regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2014, 14(3): 141-53. doi:10.1038/nri3608 |
| [4] | Nagahama M, Hayashi S, Morimitsu S, et al. Biological activities and pore formation of Clostridium perfringens beta toxin in HL 60 cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2003, 278(38): 36934-41. doi:10.1074/jbc.m306562200 |
| [5] | Nagahama M, Shibutani M, Seike S, et al. The p38 MAPK and JNK pathways protect host cells against Clostridium perfringens beta-toxin[J]. Infect Immun, 2013, 81(10): 3703-8. doi:10.1128/iai.00579-13 |
| [6] | Nagahama M, Seike S, Shirai H, et al. Role of P2X7 receptor in Clostridium perfringens beta-toxin-mediated cellular injury[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2015, 1850(11): 2159-67. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.08.011 |
| [7] | Zhang SY, Ma LL, Song FY, et al. Pyroptosis of macrophages induced by Clostridium perfringens beta-1 toxin[J]. Toxins (Basel), 2023, 15(6): 366. doi:10.3390/toxins15060366 |
| [8] | Zhang SY, Wang D, Ding YW, et al. Injury of macrophages induced by Clostridium perfringens type C exotoxins[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(7): 3718. doi:10.3390/ijms25073718 |
| [9] | Zhang SY, Wang D, Ding YW, et al. Inhibition of calpain reduces oxidative stress and attenuates pyroptosis and ferroptosis in Clostridium perfringens Beta-1 toxin-induced macrophages[J]. Microbiol Res, 2024, 289: 127916. doi:10.1016/j.micres.2024.127916 |
| [10] | Liu XX, Li MH, Chen ZW, et al. Mitochondrial calpain-1 activates NLRP3 inflammasome by cleaving ATP5A1 and inducing mitochondrial ROS in CVB3-induced myocarditis[J]. Basic Res Cardiol, 2022, 117(1): 40. doi:10.1007/s00395-022-00948-1 |
| [11] | Camargo A, Ramírez JD, Kiu R, et al. Unveiling the pathogenic mechanisms of Clostridium perfringens toxins and virulence factors[J]. Emerg Microbes Infect, 2024, 13(1): 2341968. doi:10.1080/22221751.2024.2341968 |
| [12] | Chakrabarti G, Zhou X, McClane BA. Death pathways activated in CaCo-2 cells by Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin[J]. Infect Immun, 2003, 71(8): 4260-70. doi:10.1128/iai.71.8.4260-4270.2003 |
| [13] | Nagahama M, Ochi S, Oda M, et al. Recent insights into Clostridium perfringens beta-toxin[J]. Toxins (Basel), 2015, 7(2): 396-406. doi:10.3390/toxins7020396 |
| [14] | Theoret JR, Uzal FA, McClane BA. Identification and characterization of Clostridium perfringens beta toxin variants with differing trypsin sensitivity and in vitro cytotoxicity activity[J]. Infect Immun, 2015, 83(4): 1477-86. doi:10.1128/iai.02864-14 |
| [15] | 张思雨, 王玉炯, 曾 瑾. C型产气荚膜梭菌外毒素致小鼠肠道损伤的转录组分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2022, 53(10): 3570-81. |
| [16] | 赵 祎, 徐冰蕊, 叶紫梦玮, 等. 基于肠道炎症反应研究降糖3号方抗糖尿病的作用机制[J]. 世界中医药, 2024, 19(8): 1085-91. |
| [17] | 李柳杨, 韩小红, 钱文洁, 等. miR-23a对脂多糖诱导的奶牛乳腺上皮细胞炎症的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2025, 61(4): 235-8, 243. |
| [18] | 李明远, 张 玮, 华梦晴. 甲基巴多索龙通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化缓解小鼠急性肝损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1662-9. |
| [19] | 赵 娜, 沈梦迪, 赵 睿, 等. 血根碱通过调控Nrf2/NF-κB通路缓解小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1467-75. |
| [20] | Amaral EP, Ribeiro SCM, Lanes VR, et al. Pulmonary infection with hypervirulent Mycobacteria reveals a crucial role for the P2X7 receptor in aggressive forms of tuberculosis[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2014, 10(7): e1004188. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004188 |
| [21] | Fialho S, Trieu-Cuot P, Ferreira P, et al. Could P2X7 receptor be a potencial target in neonatal sepsis [J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 142(Pt A): 112969. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112969 |
| [22] | Di Virgilio F, Ben DD, Sarti AC, et al. The P2X7 receptor in infection and inflammation[J]. Immunity, 2017, 47(1): 15-31. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2017.06.020 |
| [23] | Engelhardt J, Klawonn A, Dobbelstein AK, et al. Lipopo-lysaccharide-neutralizing peptide modulates P2X7 receptor-mediated interleukin-1β release[J]. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci, 2024, 8(1): 136-45. doi:10.1021/acsptsci.4c00496 |
| [24] | Navarro MA, McClane BA, Uzal FA. Mechanisms of action and cell death associated with Clostridium perfringens toxins[J]. Toxins (Basel), 2018, 10(5): 212. doi:10.3390/toxins10050212 |
| [25] | Amini M, Frisch J, Jost P, et al. Purinergic receptor P2X7 regulates interleukin-1α mediated inflammation in chronic kidney disease in a reactive oxygen species-dependent manner[J]. Kidney Int, 2025, 107(3): 457-75. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2024.10.024 |
| [26] | Feng HY, Wu TC, Chin J, et al. Tangzu granule alleviate neuroinflammation in diabetic peripheral neuropathy by suppressing pyroptosis through P2X7R/NLRP3 signaling pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2025, 337(Pt 1): 118792. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118792 |
| [27] | Yang DH, He Y, Muñoz-Planillo R, et al. Caspase-11 requires the pannexin-1 channel and the purinergic P2X7 pore to mediate pyroptosis and endotoxic shock[J]. Immunity, 2015, 43(5): 923-32. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2015.10.009 |
| [28] | Kim JE, Lee DS, Wang SH, et al. P2X7 receptor augments kainic acid-induced nitrosative stress by abrogating GS-HSP25-mediated iNOS inhibition and GSH synthesis in the mouse hippocampus[J]. Mol Cell Neurosci, 2025, 133: 103995. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2025.103995 |
| [29] | Zhong X, Wang KW, Wang YH, et al. Angiotension II directly bind P2X7 receptor to induce myocardial ferroptosis and remodeling by activating human antigen R[J]. Redox Biol, 2024, 72: 103154. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2024.103154 |
| [30] | Pandolfi JB, Ferraro AA, Sananez I, et al. ATP-induced inflammation drives tissue-resident Th17 cells in metabolically unhealthy obesity[J]. J Immunol, 2016, 196(8): 3287-96. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1502506 |
| [1] | 何榕茂, 方泽扬, 张芸芸, 吴友谅, 梁世秀, 计涛, 陈科全, 王斯琪. 铁死亡相关基因对溃疡性结肠炎具有诊断预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1927-1937. |
| [2] | 云琦, 杜若丽, 贺玉莹, 张贻欣, 王佳慧, 叶红伟, 李正红, 高琴. 肉桂酸通过抑制TLR4减轻阿霉素诱导的小鼠心肌损伤铁死亡的发生[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1946-1958. |
| [3] | 罗善玉, 朱强, 闫玉翡, 纪宗红, 邹华杰, 张瑞霞, 巴应贵. 低氧环境下NLRP3信号通路促进非酒精性脂肪性肝炎小鼠的肝细胞焦亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 2026-2033. |
| [4] | 欧泽金, 李瀛, 陈诗, 王梓译, 何美仪, 陈志成, 唐侍豪, 孟晓静, 王致. 抑制铁死亡减轻敌草快引起的斑马鱼急性肾损伤的机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1743-1750. |
| [5] | 李军仪, 陈思源, 谢力遥, 王劲, 程奥, 张绍伟, 林继瑜, 方志涵, 潘一锐, 崔翀鹤, 陈庚鑫, 张超, 李栎. 益智仁提取物谷甾醇通过抑制铁死亡中的ETS-5基因表达延长秀丽隐杆线虫的寿命[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1751-1757. |
| [6] | 陈鑫源, 吴成挺, 李瑞迪, 潘雪芹, 张耀丹, 陶俊宇, 林才志. 双术汤通过P53/SLC7A11/GPX4通路诱导胃癌细胞铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [7] | 周海忆, 何斯怡, 韩瑞芳, 关永格, 董丽娟, 宋阳. 艾灸通过调控miR-223-3p/NLRP3焦亡通路修复薄型子宫内膜[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1380-1388. |
| [8] | 张梦影, 赵晨玲, 田丽伟, 余郭芳, 杨文明, 董婷. 肝豆扶木汤通过GPX4/ACSL4/ALOX15通路抑制铁死亡改善Wilson病小鼠的肝脏脂肪变性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1471-1478. |
| [9] | 张安邦, 孙秀颀, 庞博, 吴远华, 时靖宇, 张宁, 叶涛. 电针预处理通过调节肠道-大脑轴及Nrf2/HO-1信号通路抑制铁死亡减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 911-920. |
| [10] | 卞芬兰, 倪诗垚, 赵鹏, 戚毛男星, 唐碧, 王洪巨, 康品方, 刘进军. 积雪草苷通过抑制NLRP3炎症体介导的细胞焦亡减轻大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 977-985. |
| [11] | 孙亚磊, 罗萌, 郭长胜, 高静, 苏凯奇, 陈立典, 冯晓东. 穗花杉双黄酮通过抑制细胞焦亡减轻小鼠急性肺损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 692-701. |
| [12] | 朱正望, 王琳琳, 赵静涵, 马瑞雪, 余雨春, 蔡庆春, 王兵, 朱平生, 苗明三. 退黄合剂通过调控法尼醇X受体抑制NLRP3炎症小体改善α-萘异硫氰酸酯诱导的大鼠胆汁淤积[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 718-724. |
| [13] | 张林落, 李长青, 皇玲玲, 周学平, 娄媛媛. 梓醇扶正制毒配伍从SLC7A11/GPX4通路抑制铁死亡减轻雷公藤甲素肝毒性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 810-818. |
| [14] | 黄菊, 殷丽霞, 牛民主, 耿志军, 左芦根, 李静, 胡建国. 紫花前胡苷通过抑制肠上皮细胞焦亡改善2,4,6-三硝基苯磺酸诱导的小鼠实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 261-268. |
| [15] | 郭涛, 陈柏霖, 石金沙, 匡显锋, 余腾跃, 魏嵩, 刘雄, 肖蓉, 李娟娟. 天麻素通过激活GPX4/SLC7A11/FTH1信号抑制铁死亡减轻新生小鼠缺氧缺血性脑损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2071-2081. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||