南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (8): 1697-1705.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.08.14
• • 上一篇
尚菲菲1,2( ), 师晓可1,2, 曾尧1,2, 陶循浅1, 李天真1, 梁艳1, 杨燕青1,2, 宋传旺1(
), 师晓可1,2, 曾尧1,2, 陶循浅1, 李天真1, 梁艳1, 杨燕青1,2, 宋传旺1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-18
出版日期:2025-08-20
发布日期:2025-09-05
通讯作者:
宋传旺
E-mail:2807601934@qq.com;bbmcscw@foxmail.com
作者简介:尚菲菲,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 2807601934@qq.com
基金资助:
Feifei SHANG1,2( ), Xiaoke SHI1,2, Yao ZENG1,2, Xunqian TAO1, Tianzhen LI1, Yan LIANG1, Yanqin YANG1,2, Chuanwang SONG1(
), Xiaoke SHI1,2, Yao ZENG1,2, Xunqian TAO1, Tianzhen LI1, Yan LIANG1, Yanqin YANG1,2, Chuanwang SONG1( )
)
Received:2025-04-18
Online:2025-08-20
Published:2025-09-05
Contact:
Chuanwang SONG
E-mail:2807601934@qq.com;bbmcscw@foxmail.com
摘要:
目的 探究Avitinib抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化并缓解感染性休克的作用及其机制。 方法 预先给药Avitinib作用小鼠骨髓来源巨噬细胞(BMDM)、人单核细胞白血病细胞系(THP-1)、健康志愿者外周血分离提取的单个核细胞(PBMC),后加入多种NLRP3炎症小体激动剂如尼日利亚菌素(Nigericin),单钠尿酸盐(MSU)结晶,三磷酸腺苷(ATP)活化经典NLRP3炎症小体,或在细胞内转染脂多糖(LPS)活化非经典形式NLRP3炎症小体(Western blotting)检测NLRP3炎症小体活化的分泌蛋白指征及细胞焦亡情况。利用酶联免疫吸附技术(ELISA)测定细胞上清中相关炎症因子的水平。构建小鼠感染性休克模型,采取随机分组的方法,将8周龄雄性C57BL/6J小鼠分为空白对照组(Control组),感染性休克模型组(LPS组),给药组(LPS+Avitinib组),6只/组。ELISA测定各组眼球血和腹腔灌洗液中的相关炎症因子水平,并记录小鼠的存活情况,采用Kaplan-Meier法进行生存分析。 结果 Avitinib在多种细胞类型中抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化,剂量依赖性地抑制IL-1β分泌和caspase-1剪切,同时抑制GSDMD介导的细胞焦亡(P<0.05),但对炎症早期预警因子白细胞介素-6(IL-6)、肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)的分泌并无影响(P>0.05)。动物实验结果表明,在LPS诱导的感染性休克模型中,给予Avitinib干预后小鼠血清和腹腔液中IL-1β的水平降低(P<0.05),并延长小鼠生存时间(P<0.05)。 结论 Avitinib可抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化并改善感染性休克。
尚菲菲, 师晓可, 曾尧, 陶循浅, 李天真, 梁艳, 杨燕青, 宋传旺. Avitinib抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化并改善小鼠感染性休克[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1697-1705.
Feifei SHANG, Xiaoke SHI, Yao ZENG, Xunqian TAO, Tianzhen LI, Yan LIANG, Yanqin YANG, Chuanwang SONG. Avitinib suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation and ameliorates septic shock in mice[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1697-1705.
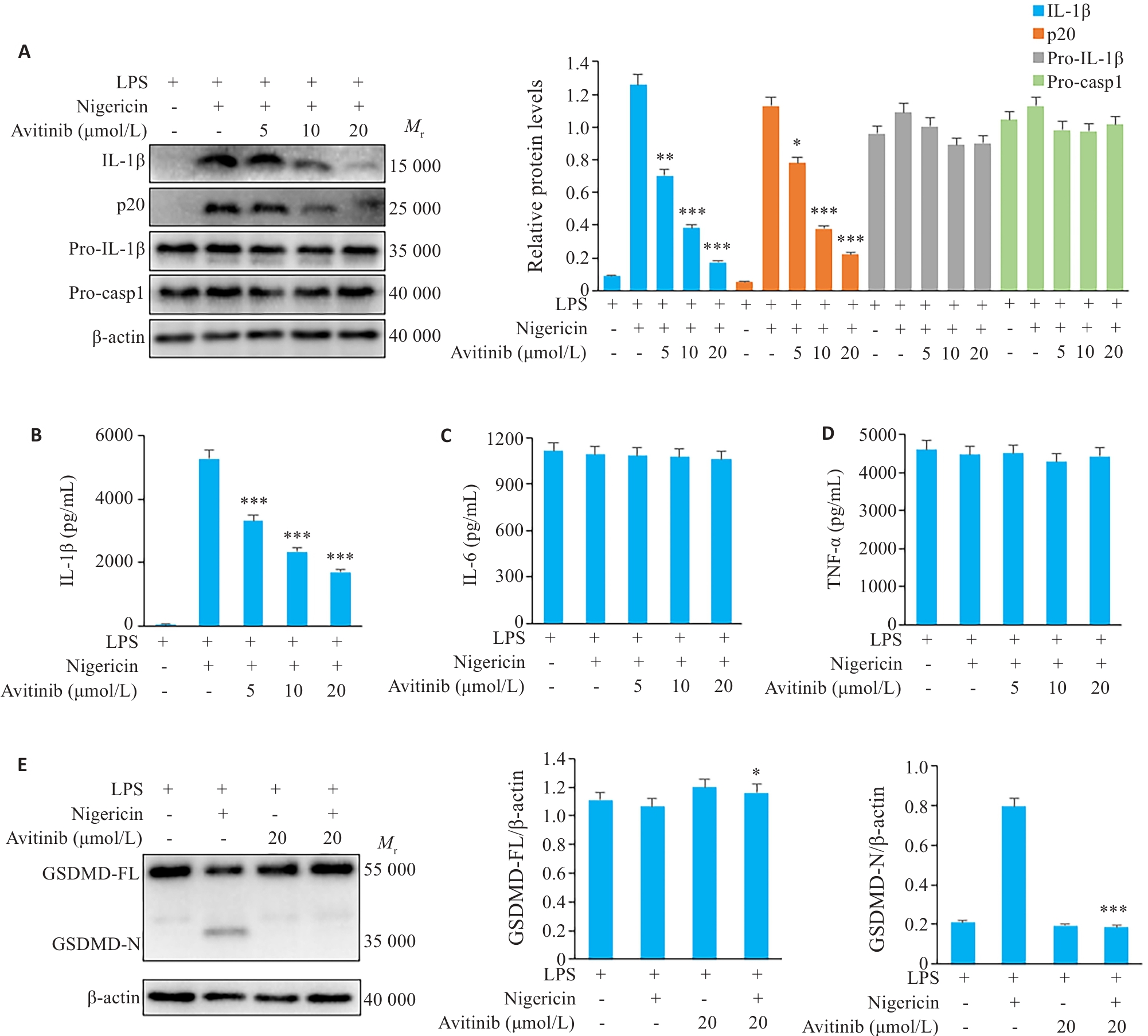
图1 Avitinib抑制鼠BMDM细胞Nigericin诱导的经典NLRP3炎症小体活化与焦亡
Fig.1 Avitinib inhibits nigericin-induced activation of the canonical NLRP3 inflammasome in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs). A: Western blotting for detecting cleaved IL-1β and caspase-1 (p20) in the culture supernatants and expressions of pro-IL-1β, pro-caspase-1 (Pro-casp1) and β-actin in the cell lysate of BMDMs. B-D: ELISA for detecting IL-1β (B), IL-6 (C), and TNF-α (D) levels in the culture supernatant. E: Western blotting of full-length and cleaved Gasdermin D (GSDMD) and β-actin in BMDM cell lysates. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs LPS+Nigericin group.
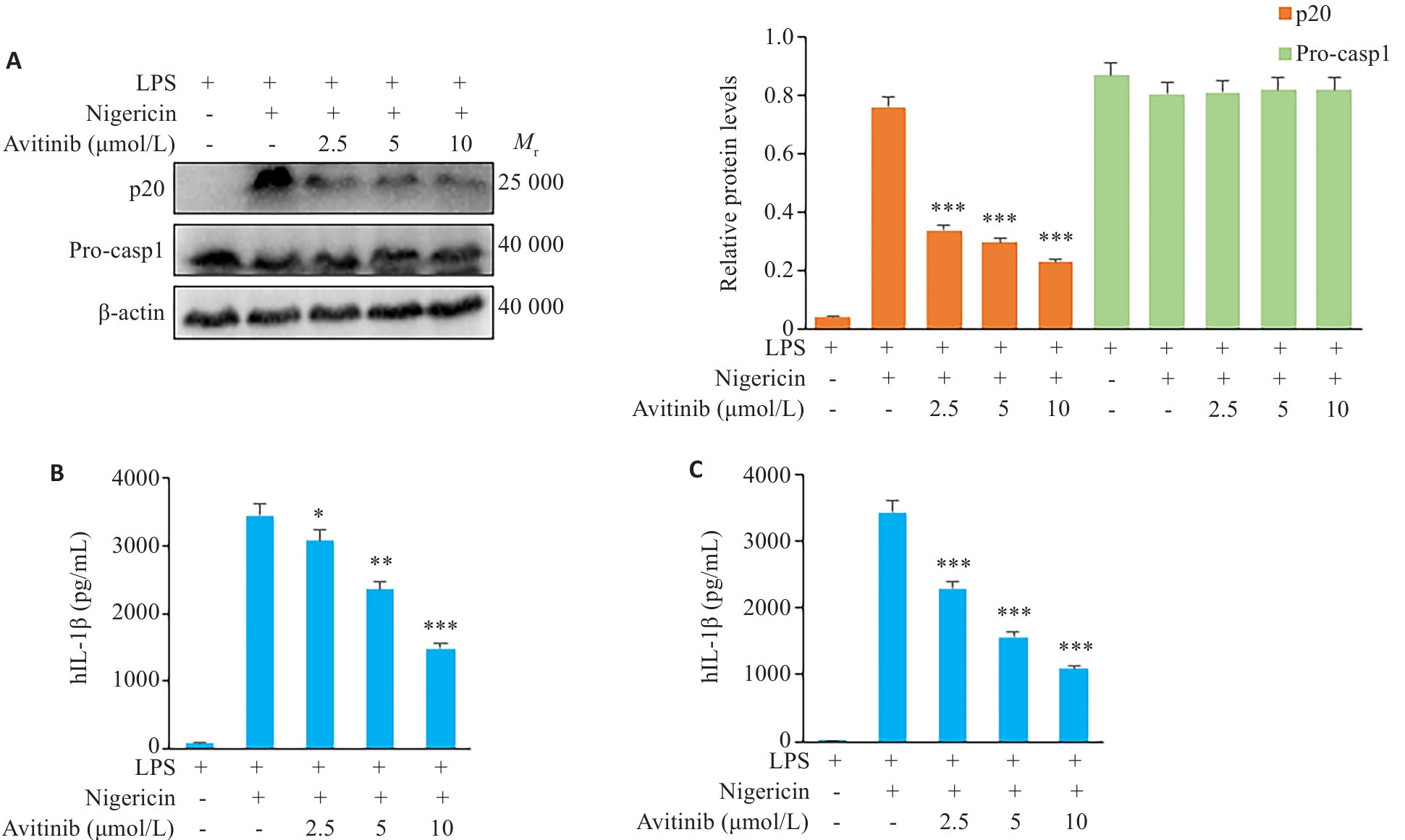
图2 Avitinib抑制THP-1细胞、人PBMC细胞中经典NLRP3炎症小体活化
Fig.2 Avitinib inhibits nigericin-induced activation of the canonical NLRP3 inflammasome in THP-1 cells and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). A: Western blotting of cleaved caspase-1 (p20) in the culture supernatants and expressions of pro-caspase-1 (Pro-casp1) and β-actin in THP-1 cell lysate. B: ELISA of IL-1β levels in the culture supernatant of THP-1 cells. C: ELISA of IL-1β levels in the culture supernatant of PBMCs. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs LPS+Nigericin group.
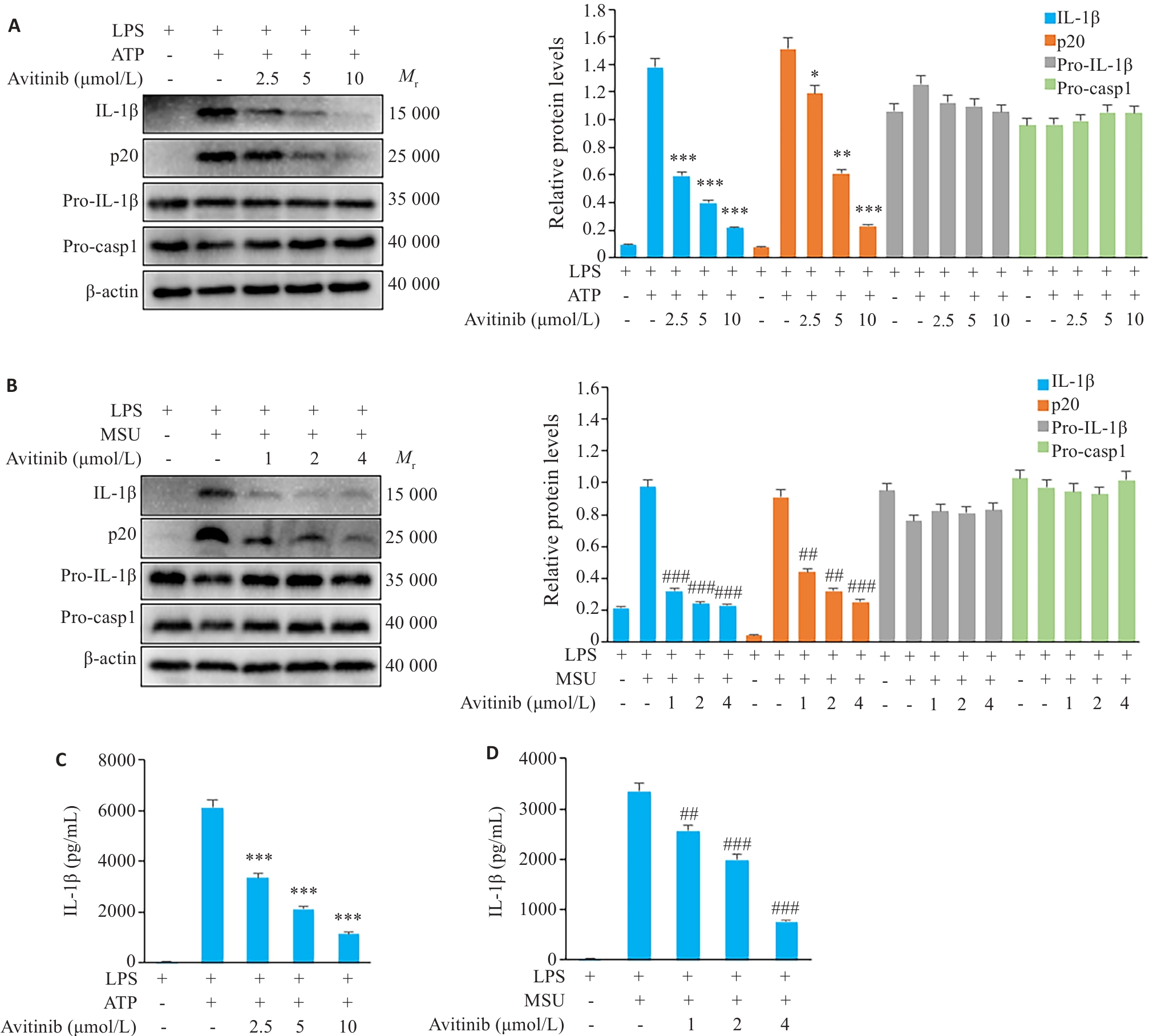
图3 Avitinib抑制鼠BMDM细胞ATP、MSU诱导的经典NLRP3炎症小体活化
Fig.3 Avitinib inhibits ATP- and MSU-induced activation of the canonical NLRP3 inflammasome in BMDMs. A,B: Western blotting of cleaved IL-1β and caspase-1 (p20) in culture supernatants and pro-IL-1β, Pro-caspase-1 (Pro-casp1), and β-actin in cell lysates of BMDMs stimulated with ATP (A) or MSU (B). C, D: ELISA of IL-1β in the culture supernatant of BMDMs stimulated with ATP (C) or MSU (D). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs LPS+ATP group; ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs LPS+MSU group.

图4 Avitinib抑制鼠BMDM细胞非经典NLRP3炎症小体活化
Fig.4 Avitinib inhibits activation of the non-canonical NLRP3 inflammasome in BMDMs. A: Western blotting of cleaved IL-1β and caspase-1 (p20) in the culture supernatants and pro-IL-1β, Pro-caspase-1 (Pro-casp1) and β-actin in the cell lysate of BMDM cells. B: ELISA of IL-1β in the culture supernatant. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Pam3+cLPS group.
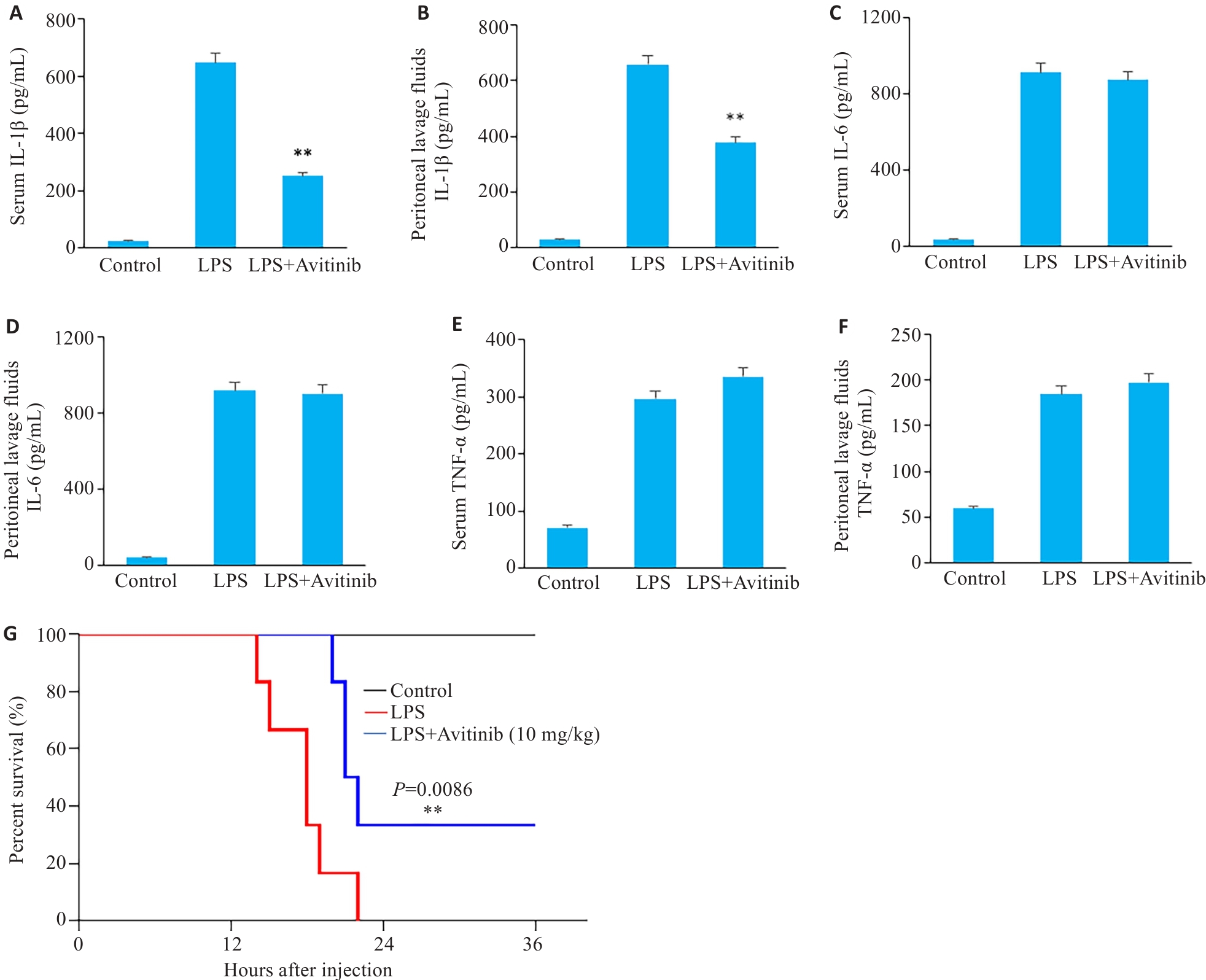
图5 Avitinib缓解小鼠感染性休克
Fig.5 Avitinib relieves septic shock in mice. A, B: ELISA for detecting IL-1β levels in serum (A) and peritoneal lavage fluid (B). C,D: ELISA for detecting IL-6 levels in serum (C)and peritoneal lavage fluid (D). E, F: ELISA for detecting TNF‑α levels in serum (E) and peritoneal lavage fluid (F). G: Survive curves of the mice within 36 h after LPS injection. n=6. **P<0.01 vs LPS group.
| [1] | Fu JN, Wu H. Structural mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and activation[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2023, 41: 301-16. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-081022-021207 |
| [2] | Oh S, Lee J, Oh J, et al. Integrated NLRP3, AIM2, NLRC4, Pyrin inflammasome activation and assembly drive PANoptosis[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2023, 20(12): 1513-26. doi:10.1038/s41423-023-01107-9 |
| [3] | Blevins HM, Xu YM, Biby S, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome pathway: a review of mechanisms and inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2022, 14: 879021. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2022.879021 |
| [4] | Sharma BR, Kanneganti TD. NLRP3 inflammasome in cancer and metabolic diseases[J]. Nat Immunol, 2021, 22(5): 550-9. doi:10.1038/s41590-021-00886-5 |
| [5] | Meier DT, de Paula Souza J, Donath MY. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome-IL-1β pathway in type 2 diabetes and obesity[J]. Diabetologia, 2025, 68(1): 3-16. doi:10.1007/s00125-024-06306-1 |
| [6] | McManus RM, Latz E. NLRP3 inflammasome signalling in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2024, 252: 109941. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2024.109941 |
| [7] | Zou J, Yang Y, Yang Y, et al. Polydatin suppresses proliferation and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation via NF‑κB pathway[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 108: 130-6. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.09.051 |
| [8] | Wu XX, Yang JH, Wu JJ, et al. Therapeutic potential of MCC950, a specific inhibitor of NLRP3 inflammasome in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2024, 172: 116261. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116261 |
| [9] | Jiang H, He HB, Chen Y, et al. Identification of a selective and direct NLRP3 inhibitor to treat inflammatory disorders[J]. J Exp Med, 2017, 214(11): 3219-38. doi:10.1084/jem.20171419 |
| [10] | Hurtado-Navarro L, Cuenca-Zamora EJ, Zamora L, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation and symptom burden in KRAS-mutated CMML patients is reverted by IL-1 blocking therapy[J]. Cell Rep Med, 2023, 4(12): 101329. doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101329 |
| [11] | Du XX, Amin N, Xu LH, et al. Pharmacological intervention of curcumin via the NLRP3 inflammasome in ischemic stroke[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14: 1249644. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1249644 |
| [12] | Xia CF, Dong XS, Li H, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2022, 135(5): 584-90. doi:10.1097/cm9.0000000000002108 |
| [13] | Wang TN, Nelson RA, Bogardus A, et al. Five-year lung cancer survival: which advanced stage nonsmall cell lung cancer patients attain long-term survival?[J]. Cancer, 2010, 116(6): 1518-25. doi:10.1002/cncr.24871 |
| [14] | Wang YH, Zhang HN, Xu YJ, et al. NLRP3 induces the autocrine secretion of IL-1β to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in breast cancer[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2021, 560: 72-9. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.04.122 |
| [15] | Lee HE, Lee JY, Yang G, et al. Inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome in tumor microenvironment leads to suppression of metastatic potential of cancer cells[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 12277. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-48794-x |
| [16] | Xu X. Parallel phase 1 clinical trials in the US and in China: accelerating the test of avitinib in lung cancer as a novel inhibitor selectively targeting mutated EGFR and overcoming T790M-induced resistance[J]. Chin J Cancer, 2015, 34(7): 285-7. doi:10.1186/s40880-015-0029-3 |
| [17] | Ma YX, Zheng X, Zhao HY, et al. First-in-human phase I study of AC0010, a mutant-selective EGFR inhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer: safety, efficacy, and potential mechanism of resistance[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2018, 13(7): 968-77. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2018.03.025 |
| [18] | Karki R, Man SM, Malireddi RKS, et al. NLRC3 is an inhibitory sensor of PI3K-mTOR pathways in cancer[J]. Nature, 2016, 540(7634): 583-7. doi:10.1038/nature20597 |
| [19] | 陈秀会, 郑裕彤, 叶卫军, 等. NLRP3炎症小体在肿瘤中的作用及其抑制剂研究进展[J]. 中南药学, 2023, 21(7): 1897-906. |
| [20] | Kureshi CT, Dougan SK. Cytokines in cancer[J]. Cancer Cell, 2025, 43(1): 15-35. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2024.11.011 |
| [21] | Tengesdal IW, Dinarello CA, Marchetti C. NLRP3 and cancer: Pathogenesis and therapeutic opportunities[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2023, 251: 108545. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108545 |
| [22] | Huang SY, Li QX, Song YB. Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharide suppresses the progression of non-small cell lung cancer by triggering NLRP3/GSDMD-dependent pyroptosis[J]. Discov Oncol, 2024, 15(1): 510. doi:10.1007/s12672-024-01361-x |
| [23] | Miskiewicz A, Szparecki G, Durlik M, et al. The Q705K and F359L single-nucleotide polymorphisms of NOD-like receptor signaling pathway: association with chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, and periodontitis[J]. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz), 2015, 63(6): 485-94. doi:10.1007/s00005-015-0355-9 |
| [24] | Tengesdal IW, Menon DR, Osborne DG, et al. Targeting tumor-derived NLRP3 reduces melanoma progression by limiting MDSCs expansion[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2021, 118(10): e2000915118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2000915118 |
| [25] | Dupaul-Chicoine J, Arabzadeh A, Dagenais M, et al. The Nlrp3 inflammasome suppresses colorectal cancer metastatic growth in the liver by promoting natural killer cell tumoricidal activity[J]. Immunity, 2015, 43(4): 751-63. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2015.08.013 |
| [26] | Wei Q, Guo PB, Mu K, et al. Estrogen suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma cells through ERβ-mediated upregulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Lab Invest, 2015, 95(7): 804-16. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2015.63 |
| [27] | Shi JJ, Zhao Y, Wang K, et al. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death[J]. Nature, 2015, 526(7575): 660-5. doi:10.1038/nature15514 |
| [28] | Mangan MSJ, Olhava EJ, Roush WR, et al. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory diseases[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2018, 17(8): 588-606. doi:10.1038/nrd.2018.97 |
| [29] | Huang Y, Jiang H, Chen Y, et al. Tranilast directly targets NLRP3 to treat inflammasome-driven diseases[J]. EMBO Mol Med, 2018, 10(4): e8689. doi:10.15252/emmm.201708689 |
| [30] | Li XL, Wan A, Liu YM, et al. P2X7R mediates the synergistic effect of ATP and MSU crystals to induce acute gouty arthritis[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2023, 2023: 3317307. doi:10.1155/2023/3317307 |
| [31] | Kayagaki N, Warming S, Lamkanfi M, et al. Non-canonical inflammasome activation targets caspase-11[J]. Nature, 2011, 479(7371): 117-21. doi:10.1038/nature10558 |
| [32] | Shi XY, Sun QC, Hou YJ, et al. Recognition and maturation of IL-18 by caspase-4 noncanonical inflammasome[J]. Nature, 2023, 624(7991): 442-50. doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06742-w |
| [33] | 赵林林, 孔凡铭, 杨仕蕊, 等. 987例晚期非小细胞肺癌化疗患者的生存分析[J]. 中草药, 2024, 55(8): 2651-66. doi:10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2024.08.016 |
| [34] | He WF, Dong HY, Wu CF, et al. The role of NLRP3 inflammasome in sepsis: a potential therapeutic target[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 115: 109697. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.109697 |
| [35] | Xu X, Mao L, Xu WH, et al. AC0010, an irreversible EGFR inhibitor selectively targeting mutated EGFR and overcoming T790M-induced resistance in animal models and lung cancer patients[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2016, 15(11): 2586-97. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.mct-16-0281 |
| [36] | Cai L, Gong QY, Qi L, et al. ACT001 attenuates microglia-mediated neuroinflammation after traumatic brain injury via inhibiting AKT/NFκB/NLRP3 pathway[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2022, 20(1): 56. doi:10.1186/s12964-022-00862-y |
| [37] | Kim Y, Jung KY, Kim YH, et al. Inhibition of SIRT7 overcomes sorafenib acquired resistance by suppressing ERK1/2 phosphorylation via the DDX3X-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Drug Resist Updat, 2024, 73: 101054. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2024.101054 |
| [38] | Huang SH, Wu BB, He YZ, et al. Canagliflozin ameliorates the development of NAFLD by preventing NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis through FGF21-ERK1/2 pathway[J]. Hepatol Commun, 2023, 7(3): e0045. doi:10.1097/hc9.0000000000000045 |
| [39] | Xie SJ, Liang JF, Zhao YY, et al. The second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor afatinib inhibits IL-1β secretion via blocking assembly of NLRP3 inflammasome independent of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in macrophage[J]. Mol Immunol, 2023, 153: 135-45. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2022.11.009 |
| [1] | 刘辰菲, 张玮, 曾尧, 梁艳, 王梦婷, 张明芳, 李新元, 王凤超, 杨燕青. 2,6-二甲氧基-1,4-苯醌通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化改善葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1654-1662. |
| [2] | 朱正望, 王琳琳, 赵静涵, 马瑞雪, 余雨春, 蔡庆春, 王兵, 朱平生, 苗明三. 退黄合剂通过调控法尼醇X受体抑制NLRP3炎症小体改善α-萘异硫氰酸酯诱导的大鼠胆汁淤积[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 718-724. |
| [3] | 李明远, 张玮, 华梦晴. 甲基巴多索龙通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化缓解小鼠急性肝损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1662-1669. |
| [4] | 张玮, 邓蒙蒙, 曾尧, 刘辰菲, 尚菲菲, 许文豪, 蒋昊轶, 王凤超, 杨燕青. 2,6-二甲氧基-1,4-苯醌通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化缓解小鼠的感染性休克[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1024-1032. |
| [5] | 凌旭光, 徐雯雯, 庞观来, 洪旭星, 刘凤芹, 李 洋. 茶多酚通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体改善脓毒症小鼠的急性肺损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 381-386. |
| [6] | 曹海若, 张 玮, 李明远, 杨燕青, 李玉云. 川藏香茶菜丙素抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化并缓解小鼠脓毒性休克[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1476-1484. |
| [7] | 陆 莉, 刘迪迪, 杨燕青, 王凤超. WP1130通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化缓解小鼠的感染性休克[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(12): 1747-1754. |
| [8] | 王佳慧, 梁 欢, 方 典, 黄毓慧, 苗雅琼, 于 影, 高 琴. 抑制线粒体活性氧自由基可减轻高糖诱导的心肌细胞焦亡和铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(7): 980-987. |
| [9] | 黄河灵, 高玉元, 聂 坤, 王丽娟. 巨噬细胞移动抑制因子介导MPP+/MPTP诱导的小胶质细胞NLRP3炎症小体的激活[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(7): 972-979. |
| [10] | 谭乐明,杨成,杨旭凯,王养民,蔡高平,曹志刚,黄创,徐东波. 尿源性脓毒血症严重程度的相关因素分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(01): 93-. |
| [11] | 高伟,张勇,倪海滨,张家留,周丹丹,殷丽萍,张丰,陈浩,张蓓蓓,李伟. 外周静脉-动脉血二氧化碳分压差可预测感染性休克患者预后:62例前瞻性研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(11): 1312-. |
| [12] | 杨仁强,黄玲,马晓欣,金思一,王丹,李旭. NLRP3炎症小体介导血管紧张素Ⅱ诱导的人脐静脉血管内皮细胞炎症因子IL-1β的表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(06): 790-. |
| [13] | 胡坚,杨闰平,汶春苗,李恒进,赵华. NLRP3 炎症小体在咪喹莫特诱导小鼠银屑病样模型中的表达及芥菜籽对其的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2013, 33(09): 1394-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||