南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (10): 2146-2159.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.10.11
• • 上一篇
梁晓涛1( ), 梁小珊2, 熊一凡1, 谢诗如1, 朱晓煜1, 谢炜1,2(
), 梁小珊2, 熊一凡1, 谢诗如1, 朱晓煜1, 谢炜1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-07-25
出版日期:2025-10-20
发布日期:2025-10-24
通讯作者:
谢炜
E-mail:1092296938@qq.com;xieweizn@126.com
作者简介:梁晓涛,医师,博士,E-mail: 1092296938@qq.com
基金资助:
Xiaotao LIANG1( ), Xiaoshan LIANG2, Yifan XIONG1, Shiru XIE1, Xiaoyu ZHU1, Wei XIE1,2(
), Xiaoshan LIANG2, Yifan XIONG1, Shiru XIE1, Xiaoyu ZHU1, Wei XIE1,2( )
)
Received:2025-07-25
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-10-24
Contact:
Wei XIE
E-mail:1092296938@qq.com;xieweizn@126.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨加味柴胡桂枝汤(MCGD)对慢性不可预见性温和应激模型(CUMS)小鼠焦虑抑郁的干预作用及机制。 方法 通过文献检索获取加味柴胡桂枝汤的主要化学成分,使用多重数据库分析预测药理机制。动物实验验证:选用雄性SPF C57BL/6J小鼠,每日给予小鼠2次随机应激刺激,共持续28 d,制备CUMS模型。以加味柴胡桂枝汤灌胃或氟西汀腹腔注射进行干预,根据干预方式的不同将小鼠分为对照组(Control)、慢性不可预见性温和应激模型组(CUMS)、氟西汀阳性对照组(FLX)、加味柴胡桂枝汤低剂量组(MCGD-L)、加味柴胡桂枝汤高剂量组(MCGD-H),15只/组。利用蔗糖偏好、强迫游泳实验评估小鼠抑郁状态,利用旷场、高架十字实验评估小鼠焦虑状态,RT-qPCR检测时钟基因、炎症因子,Western blotting检测JAK2/STAT3通路表达水平,免疫荧光检测小胶质细胞的活化水平。 结果 网络药理学结果显示,加味柴胡桂枝汤改善焦虑抑郁的主要活性成分为槲皮素、金合欢素、芒柄花素、川陈皮素、黄芩素等;GO功能富集分析共得到607条信号通路,其中生物过程447条,细胞组分61条,分子功能99条;KEGG富集分析显示,加味柴胡桂枝汤改善焦虑抑郁的通路主要涉及JAK2/STAT3和NF-κB信号通路。动物实验成功构建CUMS模型,氟西汀阳性对照组和加味柴胡桂枝汤治疗组小鼠焦虑、抑郁状态减轻。加味柴胡桂枝汤可降低Iba1的表达(P<0.01),改善炎症相关指标(P<0.01),逆转时钟基因昼夜节律紊乱(P<0.01);下调JAK2、p-STAT3、p-NF-κB、IL-1β、IL-6蛋白表达水平(P<0.01)。 结论 加味柴胡桂枝汤能有效调节炎症通路,抑制JAK2/STAT3信号转导和小胶质细胞过度活化,改善焦虑抑郁状态。
梁晓涛, 梁小珊, 熊一凡, 谢诗如, 朱晓煜, 谢炜. 加味柴胡桂枝汤通过抑制JAK2/STAT3信号通路改善慢性不可预见性温和应激模型小鼠的焦虑和抑郁状态[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2146-2159.
Xiaotao LIANG, Xiaoshan LIANG, Yifan XIONG, Shiru XIE, Xiaoyu ZHU, Wei XIE. Modified Chaihu Guizhi Decoction alleviates anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in mice with chronic unpredictable mild stress by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(10): 2146-2159.
| Primer name | Sequence |
|---|---|
| IFN-γ Forward | AGCAACAACATAAGCGTCATTGA |
| IFN-γ Reverse | TGACCTCAAACTTGGCAATACTC |
| TNF-α Forward | GCCTCCCTCTCATCAGTTCTATG |
| TNF-α Reverse | ACCTGGGAGTAGACAAGGTACAA |
| IL-1β Forward | GCAACTGTTCCTGAACTCAACT |
| IL-1β Reverse | ATCTTTTGGGGTCCGTCAACT |
| IL-4 Forward | TCCTCACAGCAACGAAGAACA |
| IL-4 Reverse | AGGCATCGAAAAGCCCGAAA |
| IL-6 Forward | ACAACCACGGCCTTCCCTACTT |
| IL-6 Reverse | CACGATTTCCCAGAGAACATGTG |
| IL-10 Forward | GGTTGCCAAGCCTTATCGGA |
| IL-10 Reverse | AGACACCTTGGTCTTGGAGCTTA |
| Bmal1 Forward | CTCCAGGAGGCAAGAAGATTC |
| Bmal1 Reverse | ATAGTCCAGTGGAAGGAATG |
| Clock Forward | TTCCTTCCTTAGAGACGAGACT |
| Clock Reverse | CTAAATGCTACCCTGAGGATAGAG |
| Cry1 Forward | GATCCACCATTTAGCCAGACAC |
| Cry1 Reverse | ACAGCCACATCCAACTTCCA |
| Cry2 Forward | CAAGCACTTGGAACGGAAGG |
| Cry2 Reverse | GAAGAGGCGGCAGGAGAG |
| Per1 Forward | CAGGCTAACCAGGAATATTACCAGC |
| Per1 Reverse | CACAGCCACAGAGAAGGTGTCCTGG |
| Per2 Forward | CCACACTTGCCTCCGAAATA |
| Per2 Reverse | ACTGCCTCTGGACTGGAAGA |
| GAPDH Forward | CAACTACATGGTCTACATGTTC |
| GAPDH Reverse | CTCGCTCCTGGAAGATG |
表1 本研究涉及引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequences used for RT-qPCR in this study
| Primer name | Sequence |
|---|---|
| IFN-γ Forward | AGCAACAACATAAGCGTCATTGA |
| IFN-γ Reverse | TGACCTCAAACTTGGCAATACTC |
| TNF-α Forward | GCCTCCCTCTCATCAGTTCTATG |
| TNF-α Reverse | ACCTGGGAGTAGACAAGGTACAA |
| IL-1β Forward | GCAACTGTTCCTGAACTCAACT |
| IL-1β Reverse | ATCTTTTGGGGTCCGTCAACT |
| IL-4 Forward | TCCTCACAGCAACGAAGAACA |
| IL-4 Reverse | AGGCATCGAAAAGCCCGAAA |
| IL-6 Forward | ACAACCACGGCCTTCCCTACTT |
| IL-6 Reverse | CACGATTTCCCAGAGAACATGTG |
| IL-10 Forward | GGTTGCCAAGCCTTATCGGA |
| IL-10 Reverse | AGACACCTTGGTCTTGGAGCTTA |
| Bmal1 Forward | CTCCAGGAGGCAAGAAGATTC |
| Bmal1 Reverse | ATAGTCCAGTGGAAGGAATG |
| Clock Forward | TTCCTTCCTTAGAGACGAGACT |
| Clock Reverse | CTAAATGCTACCCTGAGGATAGAG |
| Cry1 Forward | GATCCACCATTTAGCCAGACAC |
| Cry1 Reverse | ACAGCCACATCCAACTTCCA |
| Cry2 Forward | CAAGCACTTGGAACGGAAGG |
| Cry2 Reverse | GAAGAGGCGGCAGGAGAG |
| Per1 Forward | CAGGCTAACCAGGAATATTACCAGC |
| Per1 Reverse | CACAGCCACAGAGAAGGTGTCCTGG |
| Per2 Forward | CCACACTTGCCTCCGAAATA |
| Per2 Reverse | ACTGCCTCTGGACTGGAAGA |
| GAPDH Forward | CAACTACATGGTCTACATGTTC |
| GAPDH Reverse | CTCGCTCCTGGAAGATG |
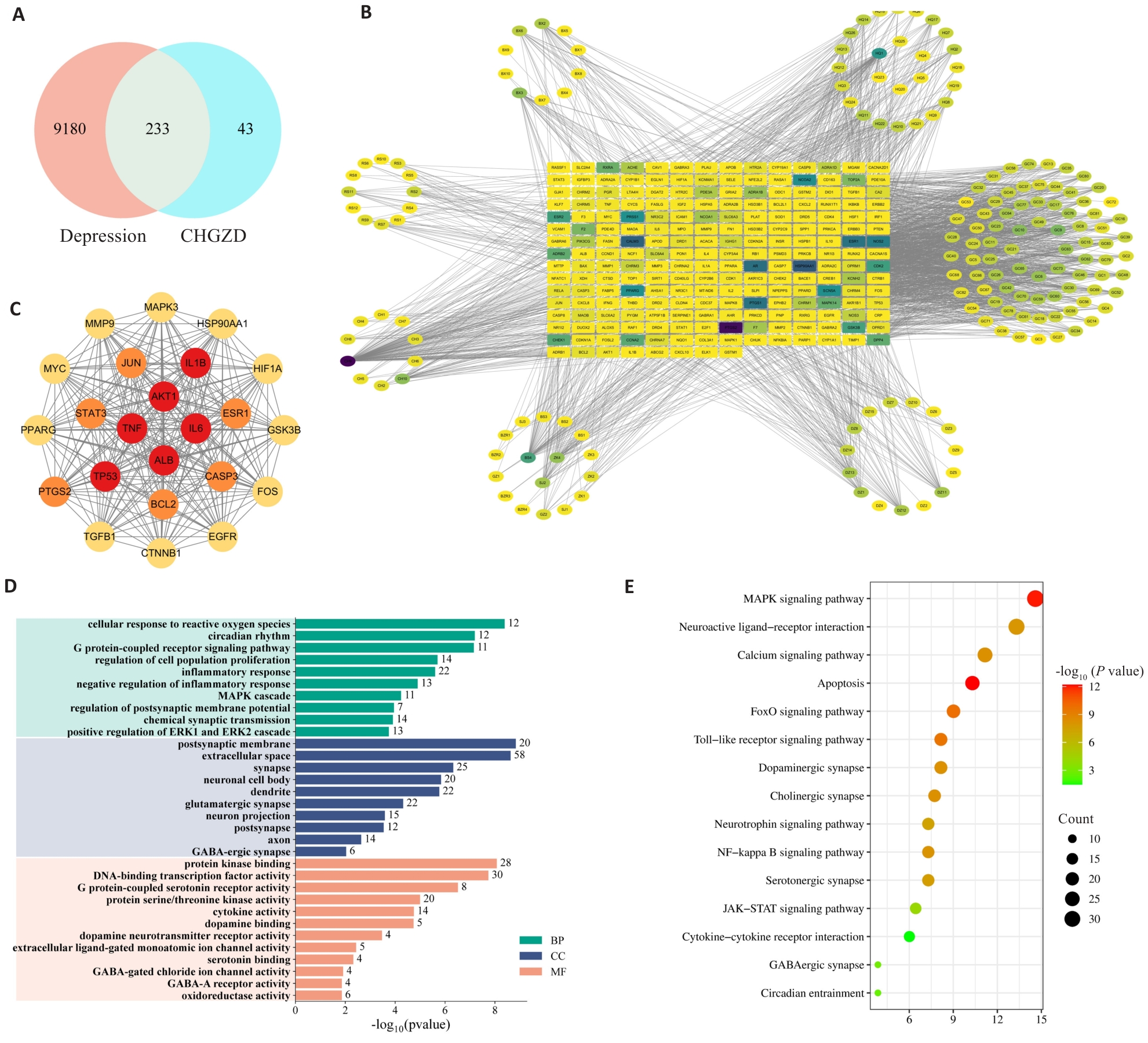
图1 网络药理学探讨加味柴胡桂枝汤(MCGD)减轻慢性不可预测性温和应激模型(CUMS)焦虑抑郁状态的作用机制
Fig.1 Network pharmacology analysis of the mechanisms by which Modified Chaihu Guizhi Decoction (MCGD) alleviates anxiety- and depression-like behavior in CUMS. A: Venn diagram of shared targets between MCGD and depression. B: Component-target-disease map. C: Core intersection targets. D: Gene Ontology (GO) analysis of the shared targets, categorized into Biological Processes (BP), Molecular Functions (MF), and Cellular Components (CC). E: Bubble chart of Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis for the shared targets.
| Code | ID | Name | Relevance | Soucre |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH9 | MOL000098 | Quercetin | 128 | Chinese thorawax root |
| HQ1 | MOL001689 | Acacetin | 62 | Baikal skullcap root |
| BS4 | MOL000422 | Kaempferol | 55 | White peony root |
| GC9 | MOL003896 | 7-Methoxy-2-methyl Isoflavone | 40 | Liquorice root |
| GC10 | MOL000392 | Formononetin | 36 | Liquorice root |
| ZK4 | MOL005828 | Nobiletin | 33 | Submature bitter orange |
| CH10 | MOL000354 | Isorhamnetin | 32 | Chinese thorawax root |
| GC6 | MOL002565 | Medicarpin | 32 | Liquorice root |
| BX3 | MOL002714 | Baicalein | 31 | Ternate pinellia |
| GC63 | MOL000497 | Licochalcone a | 30 | Liquorice root |
表2 加味柴胡桂枝汤治疗抑郁症的关键活性成分
Tab.2 Key active components in Modified Chaihu Guizhi Decoction (MCGD) for treatment of depression
| Code | ID | Name | Relevance | Soucre |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH9 | MOL000098 | Quercetin | 128 | Chinese thorawax root |
| HQ1 | MOL001689 | Acacetin | 62 | Baikal skullcap root |
| BS4 | MOL000422 | Kaempferol | 55 | White peony root |
| GC9 | MOL003896 | 7-Methoxy-2-methyl Isoflavone | 40 | Liquorice root |
| GC10 | MOL000392 | Formononetin | 36 | Liquorice root |
| ZK4 | MOL005828 | Nobiletin | 33 | Submature bitter orange |
| CH10 | MOL000354 | Isorhamnetin | 32 | Chinese thorawax root |
| GC6 | MOL002565 | Medicarpin | 32 | Liquorice root |
| BX3 | MOL002714 | Baicalein | 31 | Ternate pinellia |
| GC63 | MOL000497 | Licochalcone a | 30 | Liquorice root |
| Target | Sample | Estimated ΔG (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| JAK2 | CH9 | -6.45 |
| JAK2 | HQ1 | -6.48 |
| JAK2 | BS4 | -6.40 |
| JAK2 | GC9 | -5.53 |
| JAK2 | GC10 | -6.27 |
| JAK2 | ZK4 | -6.27 |
| JAK2 | CH10 | -6.7 |
| JAK2 | GC6 | -5.73 |
| JAK2 | BX3 | -5.43 |
| JAK2 | GC63 | -6.13 |
| STAT3 | CH9 | -5.48 |
| STAT3 | HQ1 | -5.16 |
| STAT3 | BS4 | -5.08 |
| STAT3 | GC9 | -5.9 |
| STAT3 | GC10 | -5.09 |
| STAT3 | ZK4 | -7.44 |
| STAT3 | CH10 | -5.64 |
| STAT3 | GC6 | -5.02 |
| STAT3 | BX3 | -4.78 |
| STAT3 | GC63 | -5.8 |
表3 加味柴胡桂枝汤治疗抑郁症核心活性成分与核心靶分子JAK2、STAT3对接结合能
Tab.3 Binding energies of the core active components of MCGD for depression treatment for docking with the core target molecules JAK2 and STAT3
| Target | Sample | Estimated ΔG (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| JAK2 | CH9 | -6.45 |
| JAK2 | HQ1 | -6.48 |
| JAK2 | BS4 | -6.40 |
| JAK2 | GC9 | -5.53 |
| JAK2 | GC10 | -6.27 |
| JAK2 | ZK4 | -6.27 |
| JAK2 | CH10 | -6.7 |
| JAK2 | GC6 | -5.73 |
| JAK2 | BX3 | -5.43 |
| JAK2 | GC63 | -6.13 |
| STAT3 | CH9 | -5.48 |
| STAT3 | HQ1 | -5.16 |
| STAT3 | BS4 | -5.08 |
| STAT3 | GC9 | -5.9 |
| STAT3 | GC10 | -5.09 |
| STAT3 | ZK4 | -7.44 |
| STAT3 | CH10 | -5.64 |
| STAT3 | GC6 | -5.02 |
| STAT3 | BX3 | -4.78 |
| STAT3 | GC63 | -5.8 |
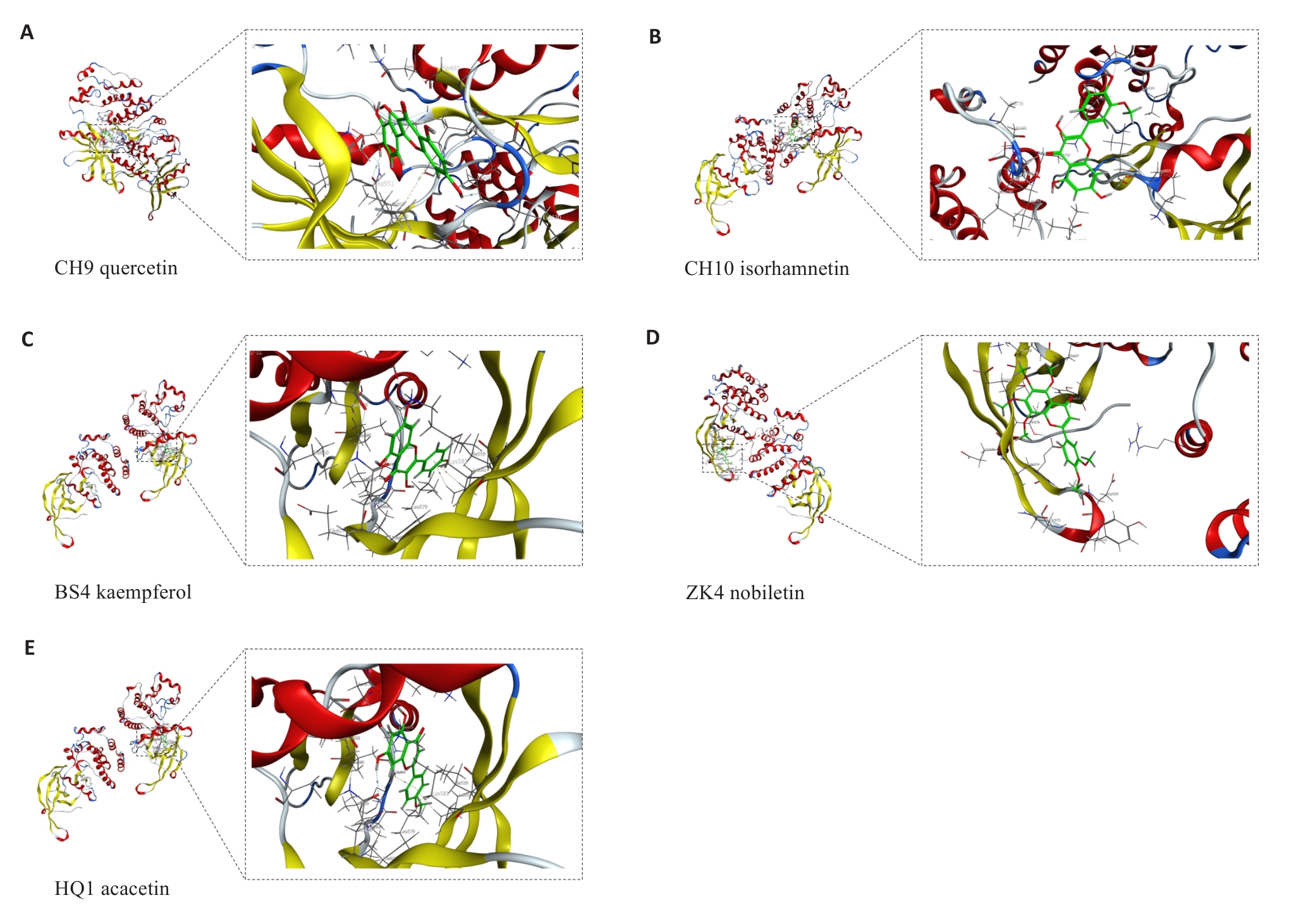
图2 分子对接结果可视化
Fig.2 Visualization of the results of molecular docking analysis. A: Docked molecular conformation of JAK2 with CH9. B: Molecular conformation of JAK2 docked with CH10. C: Molecular conformation of JAK2 docked with BS4. D: Molecular conformation of JAK2 docked with ZK4. E: Molecular conformation of JAK2 docked with HQ1.
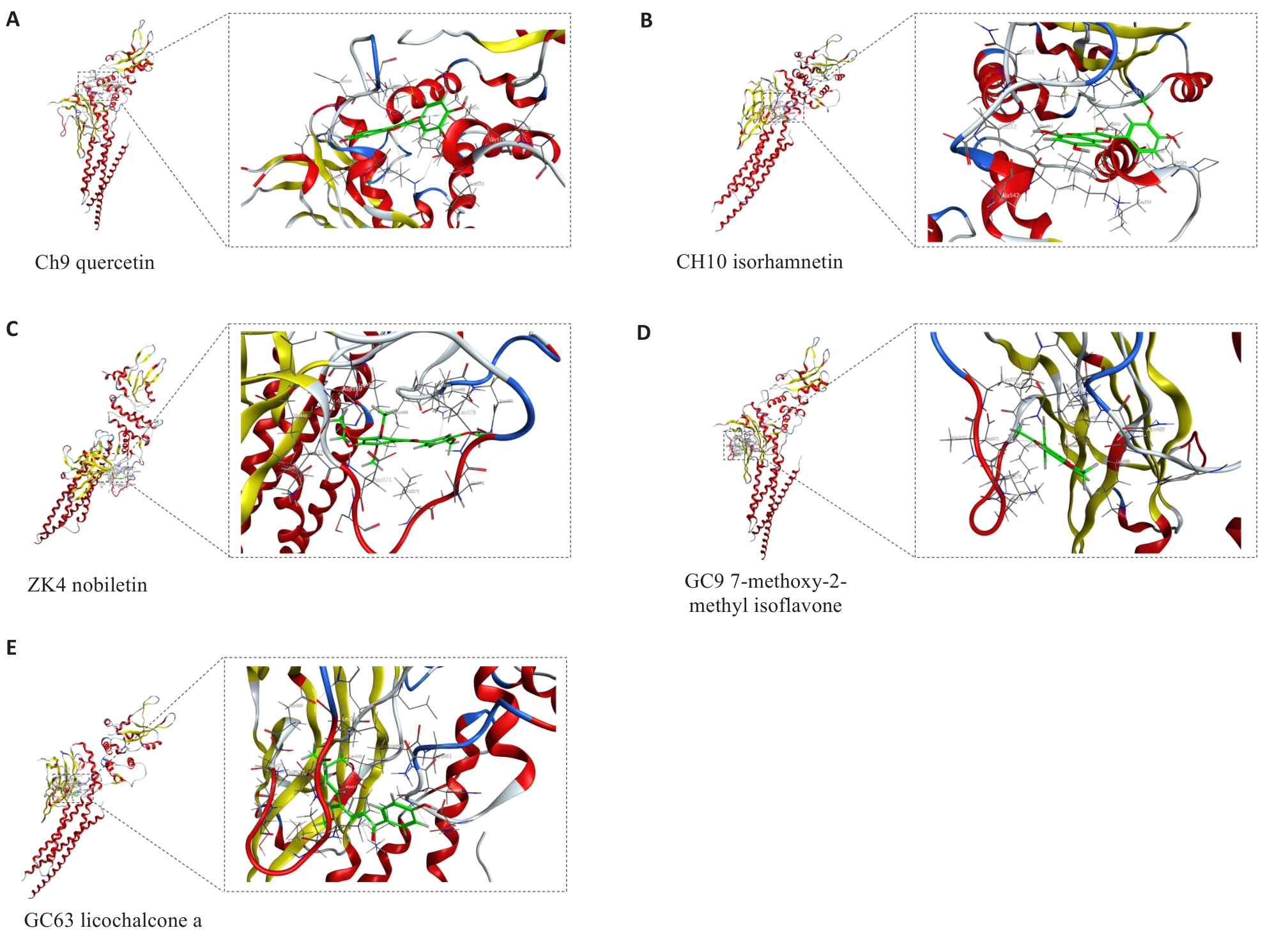
图3 分子对接结果可视化
Fig.3 Visualization of the results of molecular docking analysis. A: Docked molecular conformation of STAT3 with CH9. B: Molecular conformation of STAT3 docked with CH10. C: Molecular conformation of STAT3 docked with ZK4. D: Molecular conformation of STAT3 docked with GC9. E: Molecular conformation of STAT3 docked with GC63.
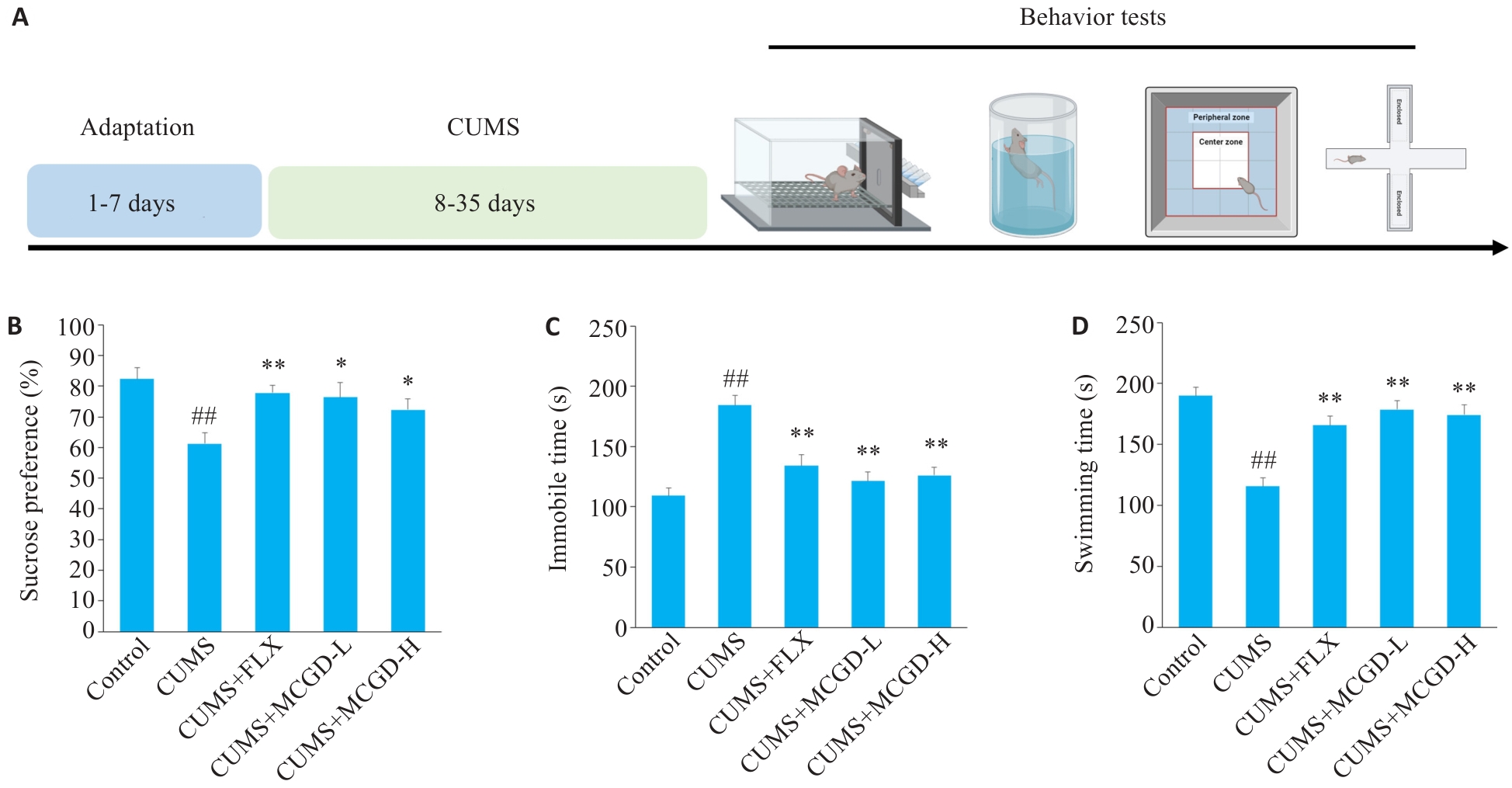
图4 加味柴胡桂枝汤显著改善CUMS小鼠的抑郁样行为
Fig.4 MCGD significantly improves depression-like behavior in CUMS mice. A: Experimental design. B: Sucrose preference percentage in the sucrose preference test (SPT). C: Immobility time in the forced swim test (FST). D: Swimming times in the FST. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=15). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. ##P<0.01 vs Control group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs CUMS group.
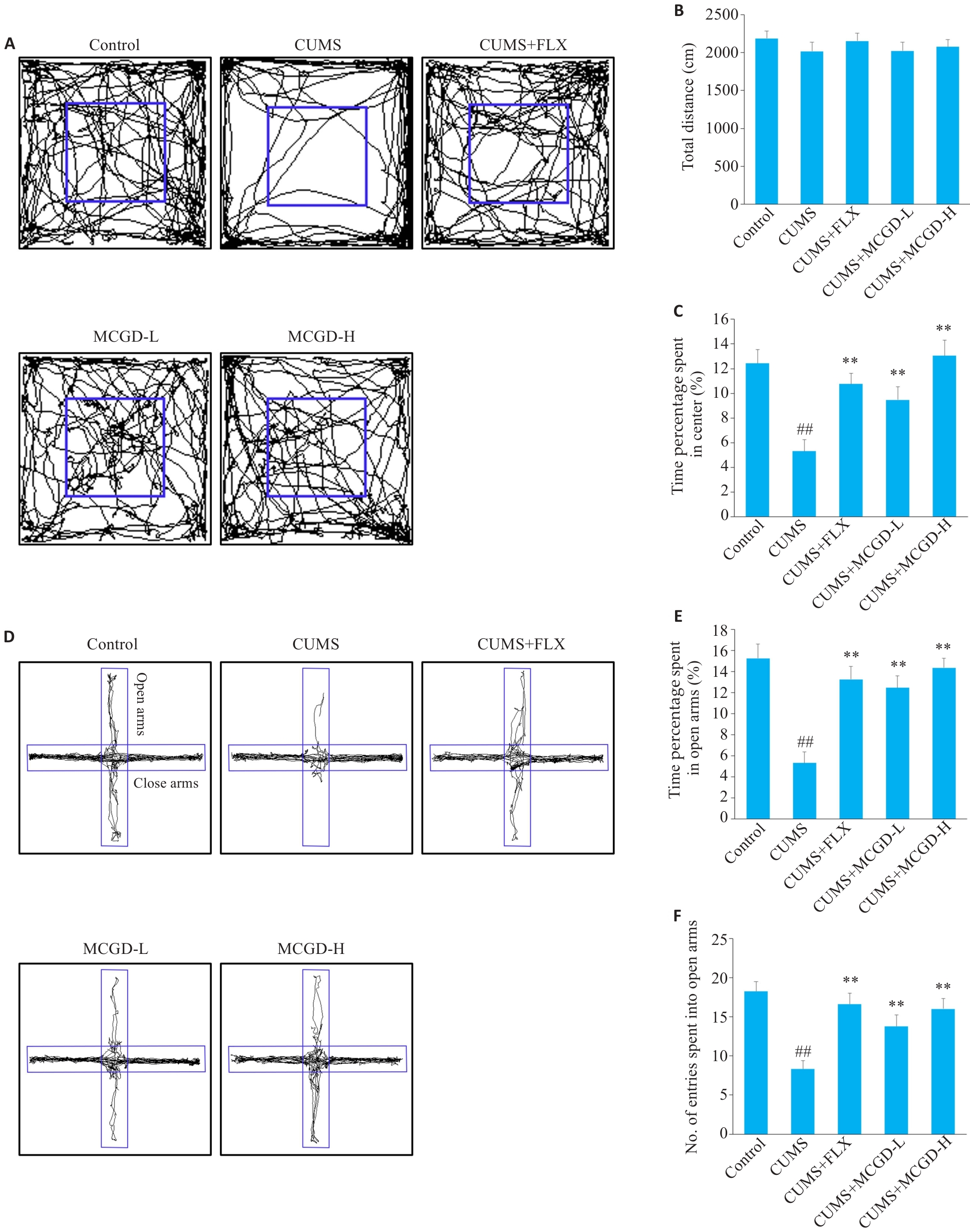
图5 加味柴胡桂枝汤显著改善CUMS小鼠的焦虑样行为
Fig.5 MCGD significantly improves anxiety-like behavior in CUMS mice. A: Trajectory map in the open field test (OFT). B: Total distance in OFT. C: Time percentage spent in center of OFT. D: Trajectory map in the elevated plus maze test (EPM). E: Time percentage spent in open arms of EPM. F: Number of entries spent into open arms of EPM. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=15). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. ##P<0.01 vs Control group; **P<0.01 vs CUMS group.
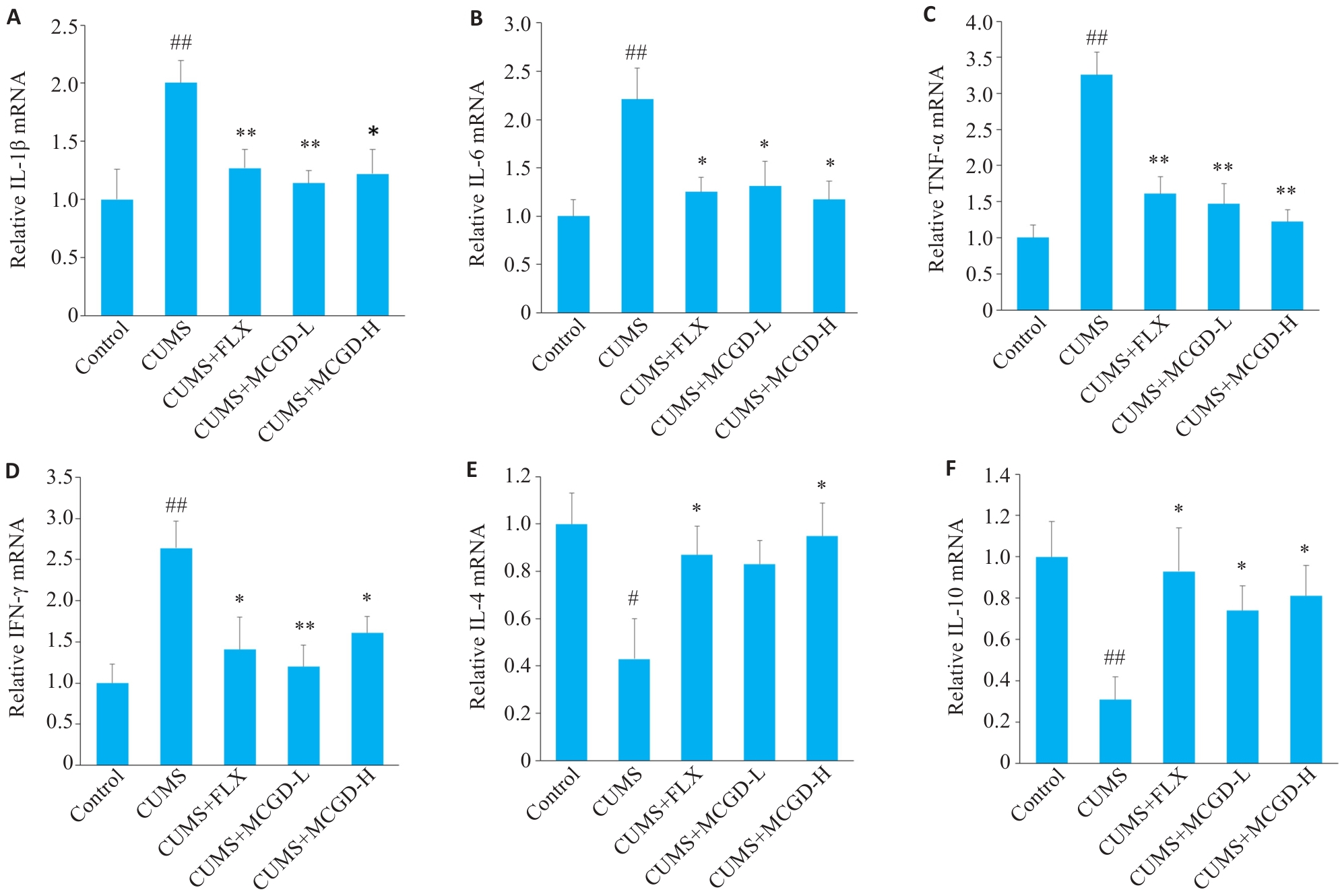
图6 加味柴胡桂枝汤对CUMS小鼠海马组织炎症因子表达水平的影响
Fig.6 Effects of MCGD on mRNA expression of inflammatory factors in the hippocampus of CUMS mice. A: Relative mRNA level of IL-1β. B: Relative mRNA level of IL-6. C: Relative mRNA level of TNF-α. D: Relative mRNA level of IFN-γ. E: Relative mRNA level of IL-4. F: Relative mRNA level of IL-10. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=6). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs Control group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs CUMS group.
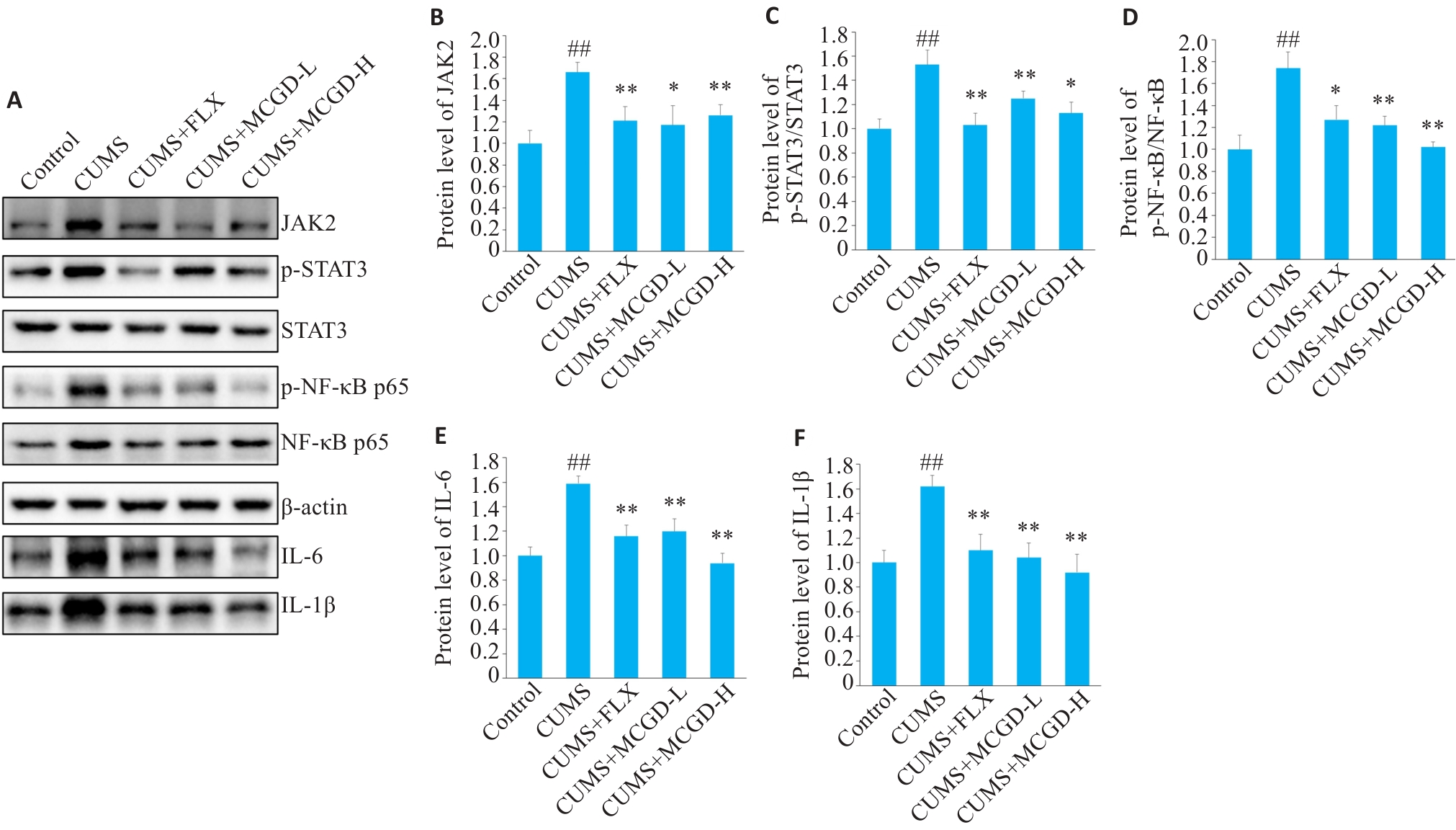
图7 加味柴胡桂枝汤对CUMS小鼠海马组织JAK2/STAT3信号通路的调控作用
Fig.7 Effects of MCGD on the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in the hippocampus of CUMS mice. A: Protein bands of JAK2, p-STAT3, STAT3, p-NF-κB, NF-κB, IL-1β, and IL-6 detected by Western blotting. B-F: Quantitative analysis of JAK2, p-STAT3, STAT3, p-NF-κB, NF-κB, IL-6, and IL-1β protein expression levels. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=3). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. ##P<0.01 vs Control group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs CUMS group.
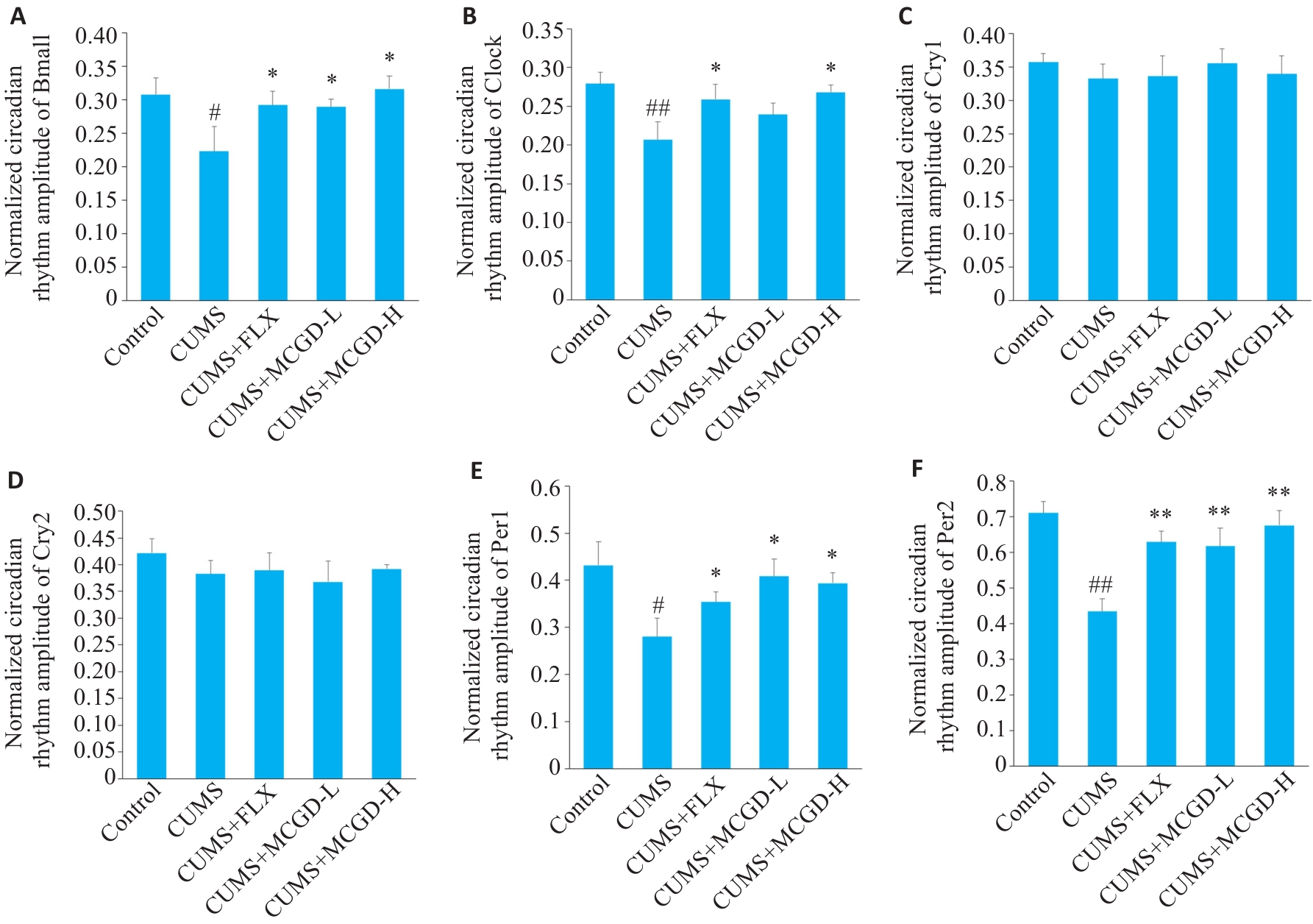
图8 加味柴胡桂枝汤对CUMS小鼠海马组织时钟蛋白基因表达水平的调控作用
Fig.8 Regulatory effect of MCGD on expression levels of clock protein genes in the hippocampus of CUMS mice. A: Normalized circadian rhythm amplitude of Bmal1. B: Normalized circadian rhythm amplitude of Clock1. C: Normalized circadian rhythm amplitude of Cry1. D: Normalized circadian rhythm amplitude of Cry2. E: Normalized circadian rhythm amplitude of Per1. F: Normalized circadian rhythm amplitude of Per2. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=3). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs Control group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs CUMS group.
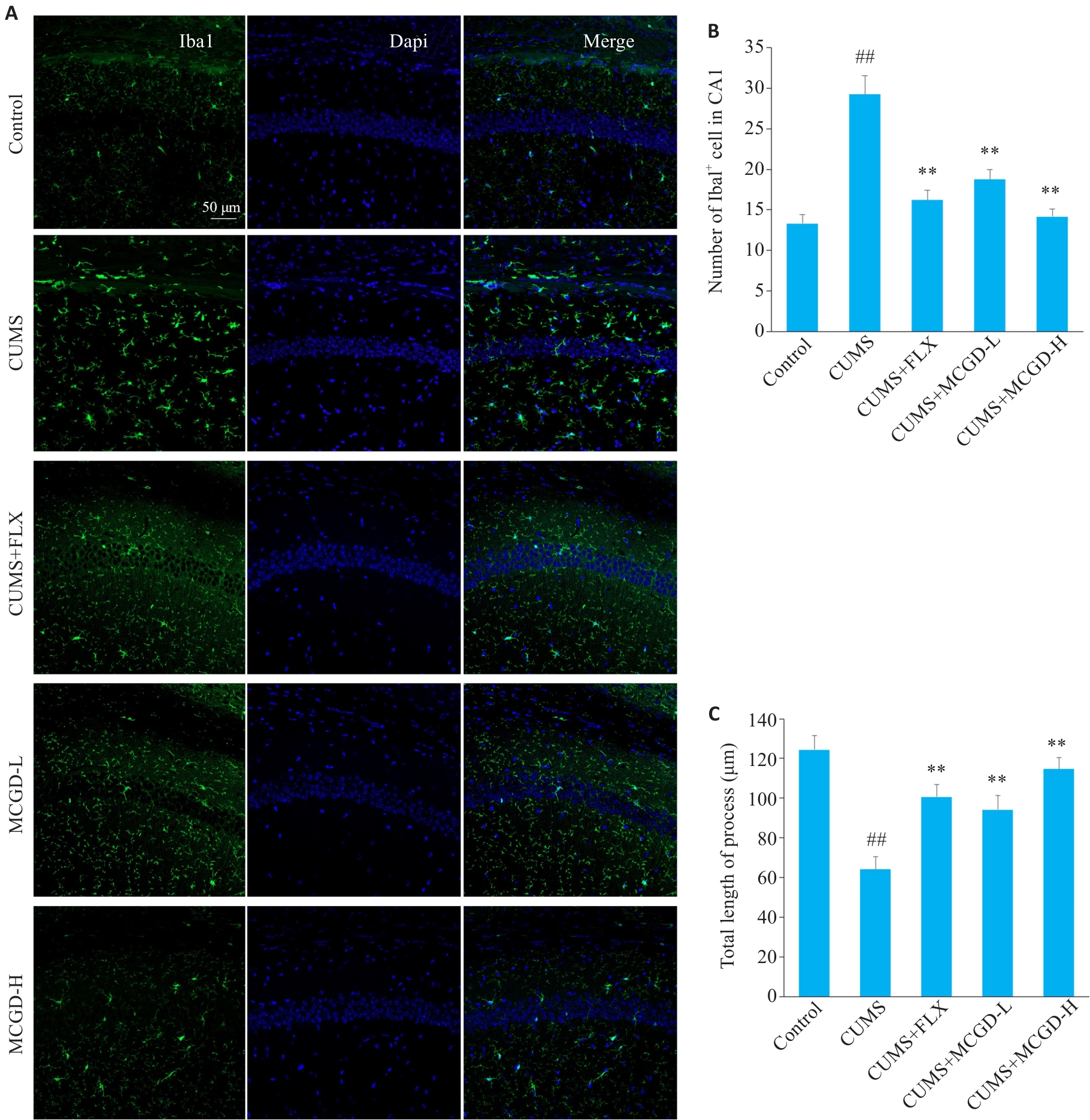
图9 加味柴胡桂枝汤对CUMS小鼠海马CA1区小胶质细胞活化水平的影响
Fig.9 Effects of MCGD on microglia activation level in the hippocampal CA1 region of CUMS mice. A: Immunofluorescence images of Iba1 expression (Original magnification: ×200). B: Statistics of Iba1+ cells in the hippocampal CA1 region. C: Statistics of microglia total length of process in the hippocampal CA1 region. Each group included 3 mice, and 4 slices were analyzed per mouse. Data are presented as Mean±SD. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. ##P<0.01 vs Control group; **P<0.01 vs CUMS group.
| [1] | McIntyre RS, Berk M, Brietzke E, et al. Bipolar disorders[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10265): 1841-56. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31544-0 |
| [2] | Malhi GS, Mann JJ. Depression[J]. Lancet, 2018, 392(10161): 2299-312. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(18)31948-2 |
| [3] | Otte C, Gold SM, Penninx BW, et al. Major depressive disorder[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2016, 2: 16065. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2016.65 |
| [4] | Hickie IB, Rogers NL. Novel melatonin-based therapies: potential advances in the treatment of major depression[J]. Lancet, 2011, 378(9791): 621-31. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(11)60095-0 |
| [5] | Marwaha S, Palmer E, Suppes T, et al. Novel and emerging treatm-ents for major depression[J]. Lancet, 2023, 401(10371): 141-53. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(22)02080-3 |
| [6] | Jha MK, Mathew SJ. Pharmacotherapies for treatment-resistant depression: how antipsychotics fit in the rapidly evolving therapeutic landscape[J]. Am J Psychiatry, 2023, 180(3): 190-9. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.20230025 |
| [7] | Crowell AL, Riva-Posse P, Holtzheimer PE, et al. Long-term outcomes of subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression[J]. Am J Psychiatry, 2019, 176(11): 949-56. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2019.18121427 |
| [8] | Lundberg J, Cars T, Lööv SÅ, et al. Association of treatment-resistant depression with patient outcomes and health care resource utilization in a population-wide study[J]. JAMA Psychiatry, 2023, 80(2): 167-75. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2022.3860 |
| [9] | 梁小珊, 熊一凡, 梁晓涛, 等. 谢炜教授基于“少阳为枢” 理论运用柴胡桂枝汤临床辨治经验[J]. 河北中医, 2020, 42(7): 977-80. |
| [10] | 梁晓涛, 梁小珊, 杨 路, 等. 谢炜教授“调肝安神,调和阴阳” 辨治失眠[J]. 环球中医药, 2021, 14(10): 1815-8. |
| [11] | 熊一凡, 梁小珊, 梁晓涛, 等. 柴胡皂甙a减轻戊四氮诱发的皮质酮抑郁模型小鼠的急性癫痫发作:基于小胶质细胞介导的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 515-22. |
| [12] | Zhu XY, Huang YY, Qiu J, et al. Chaihu Guizhi Decoction prevents cognitive, memory impairments and sensorimotor gating deficit induced by N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antibody in mice[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2025, 337(Pt 1): 118806. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118806 |
| [13] | Kanan MF, Sheehan PW, Haines JN, et al. Neuronal deletion of the circadian clock gene Bmal1 induces cell-autonomous dopaminergic neurodegeneration[J]. JCI Insight, 2024, 9(2): e162771. doi:10.1172/jci.insight.162771 |
| [14] | Guzmán-Ruiz MA, Guerrero-Vargas NN, Lagunes-Cruz A, et al. Circadian modulation of microglial physiological processes and immune responses[J]. Glia, 2023, 71(2): 155-67. doi:10.1002/glia.24261 |
| [15] | Brooks JF 2nd, Behrendt CL, Ruhn KA, et al. The microbiota coordinates diurnal rhythms in innate immunity with the circadian clock[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(16): 4154-67.e12. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.07.001 |
| [16] | Yang BQ, Han Y, Hu SQ, et al. Polystyrene microplastics induce depression-like behavior in zebrafish via neuroinflammation and circadian rhythm disruption[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2025, 959: 178085. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.178085 |
| [17] | Kou L, Chi XS, Sun YD, et al. The circadian clock protein Rev-erbα provides neuroprotection and attenuates neuroinflammation against Parkinson’s disease via the microglial NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2022, 19(1): 133. doi:10.1186/s12974-022-02494-y |
| [18] | Lananna BV, Nadarajah CJ, Izumo M, et al. Cell-autonomous regulation of astrocyte activation by the circadian clock protein BMAL1[J]. Cell Rep, 2018, 25(1): 1-9. e5. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2018.09.015 |
| [19] | Yao D, Li R, Hao JH, et al. Melatonin alleviates depression-like behaviors and cognitive dysfunction in mice by regulating the circadian rhythm of AQP4 polarization[J]. Transl Psychiatry, 2023, 13(1): 310. doi:10.1038/s41398-023-02614-z |
| [20] | Liang XT, Ding YW, Zhu XY, et al. Suprachiasmatic nucleus dysfunction induces anxiety- and depression-like behaviors via activating the BDNF-TrkB pathway of the striatum[J]. Transl Psychiatry, 2025, 15(1): 92. doi:10.1038/s41398-025-03313-7 |
| [21] | Chen X, Gan YT, Zhang KQ, et al. microRNA-204-5p deficiency within the vmPFC region contributes to neuroinflammation and behavioral disorders via the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in rats[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2025, 12(10): e2403080. doi:10.1002/advs.202403080 |
| [22] | Cavadini G, Petrzilka S, Kohler P, et al. TNF-alpha suppresses the expression of clock genes by interfering with E-box-mediated transcription[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2007, 104(31): 12843-8. doi:10.1073/pnas.0701466104 |
| [23] | Song N, Liu ZH, Gao Y, et al. NAc-DBS corrects depression-like behaviors in CUMS mouse model via disinhibition of DA neurons in the VTA[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2024, 29(5): 1550-66. doi:10.1038/s41380-024-02476-x |
| [24] | Liang XS, Liang XT, Zhao YY, et al. Dysregulation of the suprachiasmatic nucleus disturbs the circadian rhythm and aggravates epileptic seizures by inducing hippocampal GABAergic dysfunction in C57BL/6 mice[J]. J Pineal Res, 2024, 76(5): e12993. doi:10.1111/jpi.12993 |
| [25] | Pizzagalli DA, Roberts AC. Prefrontal cortex and depression[J]. Neuropsychopharmacology, 2022, 47(1): 225-46. doi:10.1038/s41386-021-01101-7 |
| [26] | Luo HR, Wang XQ, Zhang YL, et al. Can circadian rhythm predict changes in neurocognitive functioning in bipolar disorder: protocol of a 12-month longitudinal cohort study based on research domain criteria[J]. Ann Med, 2023, 55(2): 2240422. doi:10.1080/07853890.2023.2240422 |
| [27] | Mirchandaney R, Asarnow LD, Kaplan KA. Recent advances in sleep and depression[J]. Curr Opin Psychiatry, 2023, 36(1): 34-40. doi:10.1097/yco.0000000000000837 |
| [28] | Crouse JJ, Carpenter JS, Song YJC, et al. Circadian rhythm sleep-wake disturbances and depression in young people: implications for prevention and early intervention[J]. Lancet Psychiatry, 2021, 8(9): 813-23. doi:10.1016/s2215-0366(21)00034-1 |
| [29] | Hao WZ, Ma QY, Wang L, et al. Gut dysbiosis induces the development of depression-like behavior through abnormal synapse pruning in microglia-mediated by complement C3[J]. Microbiome, 2024, 12(1): 34. doi:10.1186/s40168-024-01756-6 |
| [30] | Xian X, Cai LL, Li Y, et al. Neuron secrete exosomes containing miR-9-5p to promote polarization of M1 microglia in depression[J]. J Nanobiotechnology, 2022, 20(1): 122. doi:10.1186/s12951-022-01332-w |
| [31] | Shen SY, Liang LF, Shi TL, et al. Microglia-derived interleukin-6 triggers astrocyte apoptosis in the hippocampus and mediates depression-like behavior[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2025, 12(11): e2412556. doi:10.1002/advs.202412556 |
| [32] | Brécier A, Li VW, Smith CS, et al. Circadian rhythms and glial cells of the central nervous system[J]. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc, 2023, 98(2): 520-39. doi:10.1111/brv.12917 |
| [33] | 刘日群, 李字棋, 肖淑华, 等. 理气药抗抑郁作用及机制研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2024, 55(10): 3558-68. |
| [34] | 倪雨婷, 张欢欢, 赵丹丹, 等. 酸枣仁-柏子仁组分调控睡眠障碍中神经递质的研究[J]. 黑龙江医药, 2023, 36(05): 1000-4. |
| [35] | Agrawal K, Chakraborty P, Dewanjee S, et al. Neuropharm-acological interventions of quercetin and its derivatives in neurological and psychological disorders[J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2023, 144: 104955. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104955 |
| [36] | Wang MY, Wei X, Jia YG, et al. Quercetin alleviates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression-like behavior by inhibiting NMDAR1 with α2δ-1 in rats[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2024, 30(4): e14724. doi:10.1111/cns.14724 |
| [37] | Su P, Liu LM, Gong YH, et al. Kaempferol improves depression-like behaviors through shifting microglia polarization and suppressing NLRP3 via tilting the balance of PPARγ and STAT1 signaling[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 143(Pt 3): 113538. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113538 |
| [38] | Liu HT, Lin YN, Tsai MC, et al. Baicalein exerts therapeutic effects against endotoxin-induced depression-like behavior in mice by decreasing inflammatory cytokines and increasing brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels[J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2022, 11(5): 947. doi:10.3390/antiox11050947 |
| [39] | Zhang ML, Li XP, Gao LF, et al. Nobiletin, an activator of the pyruvate kinase isozyme M1/M2 protein, upregulated the glycolytic signalling pathway and alleviated depressive-like behaviour caused by artificial light exposure at night in zebrafish[J]. Food Chem, 2025, 463(Pt 2): 141328. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.141328 |
| [40] | Jin Y, Kang YL, Wang MH, et al. Targeting polarized phenotype of microglia via IL6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling to reduce NSCLC brain metastasis[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2022, 7(1): 52. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-00872-9 |
| [41] | Hao ZZ, Ji R, Su YJ, et al. Indole-3-propionic acid attenuates neuroinflammation and cognitive deficits by inhibiting the RAGE-JAK2-STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2025, 73(9): 5208-22. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.4c08548 |
| [42] | Liu PP, Liu XH, Ren MJ, et al. Neuronal cathepsin S increases neuroinflammation and causes cognitive decline via CX3CL1-CX3CR1 axis and JAK2-STAT3 pathway in aging and Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Aging Cell, 2025, 24(2): e14393. doi:10.1111/acel.14393 |
| [43] | 王 英, 巩子汉, 梁文青, 等. 基于JAK2/STAT3信号通路探讨温阳解郁方调节小鼠海马小胶质细胞激活的机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2025, 31(8): 88-96. |
| [44] | 杨晓珊, 王瑞瑞, 李 英, 等. IL-6介导JAK/STAT信号通路在胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠抑郁发生中的作用机制研究[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2021, 37(17): 2053-8. |
| [45] | Xu DD, Hou ZQ, Xu YY, et al. Potential role of Bmal1 in lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like behavior and its associated “inflammatory storm”[J]. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol, 2024, 19(1): 4. doi:10.1007/s11481-024-10103-3 |
| [1] | 呼琴, 金华. 清肾颗粒通过调控miR-23b及Nrf2通路改善慢性肾脏病湿热证患者的肾功能:基于网络药理学和临床试验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1867-1879. |
| [2] | 杨子为, 吕畅, 董柱, 计书磊, 毕生辉, 张雪花, 王晓武. 金樱子通过调控Src-AKT1轴抑制肺动脉高压平滑肌增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1889-1902. |
| [3] | 云琦, 杜若丽, 贺玉莹, 张贻欣, 王佳慧, 叶红伟, 李正红, 高琴. 肉桂酸通过抑制TLR4减轻阿霉素诱导的小鼠心肌损伤铁死亡的发生[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1946-1958. |
| [4] | 饶璐, 丁家和, 魏江平, 阳勇, 张小梅, 王计瑞. 槐花通过抑制PI3K/AKT通路减轻炎症反应治疗银屑病[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1989-1996. |
| [5] | 陈鑫源, 吴成挺, 李瑞迪, 潘雪芹, 张耀丹, 陶俊宇, 林才志. 双术汤通过P53/SLC7A11/GPX4通路诱导胃癌细胞铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [6] | 王立明, 陈宏睿, 杜燕, 赵鹏, 王玉洁, 田燕歌, 刘新光, 李建生. 益气滋肾方通过抑制PI3K/Akt/NF-κB通路改善小鼠慢性阻塞性肺疾病的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [7] | 朱胤福, 李怡燃, 王奕, 黄颖而, 龚昆翔, 郝文波, 孙玲玲. 桂枝茯苓丸活性成分常春藤皂苷元通过抑制JAK2/STAT3通路抑制宫颈癌细胞的生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [8] | 何丽君, 陈晓菲, 闫陈昕, 师林. 扶正化积汤治疗非小细胞肺癌的分子机制:基于网络药理学及体外实验验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152. |
| [9] | 李国永, 黎仁玲, 刘艺婷, 柯宏霞, 李菁, 王新华. 牛蒡子治疗小鼠病毒性肺炎后肺纤维化的机制:基于代谢组学、网络药理学和实验验证方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [10] | 吕夏, 肖蓉. 医学研究生物质主义及其与抑郁的关系:物质至上导致更高的抑郁风险[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1220-1225. |
| [11] | 牛民主, 殷丽霞, 乔通, 尹林, 张可妮, 胡建国, 宋传旺, 耿志军, 李静. 旱莲苷A通过调控JAK2/STAT3通路抑制M1型巨噬细胞极化改善葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1297-1306. |
| [12] | 管丽萍, 颜燕, 卢心怡, 李智峰, 高晖, 曹东, 侯晨曦, 曾靖宇, 李欣怡, 赵洋, 王俊杰, 方会龙. 复方积雪草减轻小鼠日本血吸虫引起的肝纤维化:通过调控TLR4/MyD88通路抑制炎症-纤维化级联反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [13] | 唐培培, 谈勇, 殷燕云, 聂晓伟, 黄菁宇, 左文婷, 李玉玲. 调周滋阴方治疗早发性卵巢功能不全的疗效、安全性及作用机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| [14] | 陈昌锋, 方勤, 高银环, 王烈成, 陈磊. 丰富环境通过调控前扣带回皮层锥体神经元兴奋性缓解束缚应激诱导的小鼠焦虑样行为[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 962-968. |
| [15] | 梁晓涛, 熊一凡, 刘雪琪, 梁小珊, 朱晓煜, 谢炜. 活血疏风颗粒通过抑制TLR4/NF-κB通路改善慢性偏头痛小鼠的中枢敏化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 986-994. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||