南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (10): 2135-2145.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.10.10
• • 上一篇
缪祥卓1( ), 朱鹏宇1(
), 朱鹏宇1( ), 区活辉1,4, 朱庆1, 于林源1, 郭柏棠1, 廖渭5, 黄毓2, 相乐阳3(
), 区活辉1,4, 朱庆1, 于林源1, 郭柏棠1, 廖渭5, 黄毓2, 相乐阳3( ), 杨定华1(
), 杨定华1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-25
出版日期:2025-10-20
发布日期:2025-10-24
通讯作者:
相乐阳,杨定华
E-mail:u201712361@163.com;zpy0511@126.com;xly1991@jnu.edu.cn;yangdinghua@smu.edu.cn
作者简介:缪祥卓,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: u201712361@163.com基金资助:
Xiangzhuo MIAO1( ), Pengyu ZHU1(
), Pengyu ZHU1( ), Huohui OU1,4, Qing ZHU1, Linyuan YU1, Baitang GUO1, Wei LIAO5, Yu HUANG2, Leyang XIANG3(
), Huohui OU1,4, Qing ZHU1, Linyuan YU1, Baitang GUO1, Wei LIAO5, Yu HUANG2, Leyang XIANG3( ), Dinghua YANG1(
), Dinghua YANG1( )
)
Received:2025-03-25
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-10-24
Contact:
Leyang XIANG, Dinghua YANG
E-mail:u201712361@163.com;zpy0511@126.com;xly1991@jnu.edu.cn;yangdinghua@smu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探究甲状旁腺激素样激素(PTHLH)在肝细胞癌(HCC)中的表达水平,分析其与患者临床预后的关系,并探究其对HCC细胞生物学行为的影响及可能的作用通路。 方法 基于癌症基因组图谱(TCGA)和基因表达综合数据库(GEO)的数据,结合本院收治的70例HCC患者的临床样本,分析PTHLH在HCC组织和癌旁组织中的表达水平差异及其与患者临床预后的关系。体外培养HCC细胞,通过敲低和过表达PTHLH,采用CCK-8实验、克隆形成实验、Transwell迁移和侵袭实验评估PTHLH对HCC细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭能力的影响;Western blotting分析PTHLH可能激活的信号通路。 结果 TCGA和GEO数据库分析显示,PTHLH mRNA在HCC组织中显著高表达,且与患者不良预后相关(P<0.05),PTHLH mRNA高表达可能是Huh7和Hep3B患者的独立预后危险因素(P<0.05)。通过临床样本对数据库结果进行验证,HCC组织中PTHLH mRNA表达水平高于癌旁组织(P<0.001),免疫组织化学染色分析也显示PTHLH蛋白在HCC组织中的表达水平显著升高(P<0.01)。单因素和多因素Cox回归分析表明,PTHLH mRNA高表达可能是影响HCC患者术后无瘤生存时间的独立危险因素(P<0.05),且基于PTHLH mRNA表达水平构建的预后预测模型提高了HCC患者术后复发风险的预测准确性。进一步的体外细胞实验结果显示,PTHLH可促进Huh7和Hep3B细胞的增殖(P<0.01)和克隆形成(P<0.01);增强Huh7和Hep3B细胞的迁移和侵袭能力(P<0.01);Western blotting分析显示,PTHLH可能通过激活ERK/JNK信号通路发挥其促癌作用。 结论 高表达PTHLH促进肝细胞癌的进展与患者预后不良相关,其促癌效应可能是通过激活ERK/JNK信号通路实现的。
缪祥卓, 朱鹏宇, 区活辉, 朱庆, 于林源, 郭柏棠, 廖渭, 黄毓, 相乐阳, 杨定华. 高表达甲状旁腺激素样激素促进肝细胞癌的进展并与患者预后不良相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2135-2145.
Xiangzhuo MIAO, Pengyu ZHU, Huohui OU, Qing ZHU, Linyuan YU, Baitang GUO, Wei LIAO, Yu HUANG, Leyang XIANG, Dinghua YANG. Overexpression of parathyroid hormone-like hormone facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression and correlates with adverse outcomes[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(10): 2135-2145.
| R package name | Description and Function |
|---|---|
| survival | Used for survival analysis |
| survminer | Used for drawing survival curves |
| ggplot2 | Used for drawing graphs or data graphics |
| pheatmap | Used for drawing heatmaps |
| limma | Used for difference analysis between groups |
| ggpubr | Extension of the ggplot2 package |
| dplyr | Simplify data processing |
| stringr | String manipulation package |
| forestplot | Draw forest plots |
| reshape | Functions for changing array shapes |
| data.table | Extended R's data frame objects |
表2 分析中使用的R包
Tab.2 R packages used in the analysis
| R package name | Description and Function |
|---|---|
| survival | Used for survival analysis |
| survminer | Used for drawing survival curves |
| ggplot2 | Used for drawing graphs or data graphics |
| pheatmap | Used for drawing heatmaps |
| limma | Used for difference analysis between groups |
| ggpubr | Extension of the ggplot2 package |
| dplyr | Simplify data processing |
| stringr | String manipulation package |
| forestplot | Draw forest plots |
| reshape | Functions for changing array shapes |
| data.table | Extended R's data frame objects |
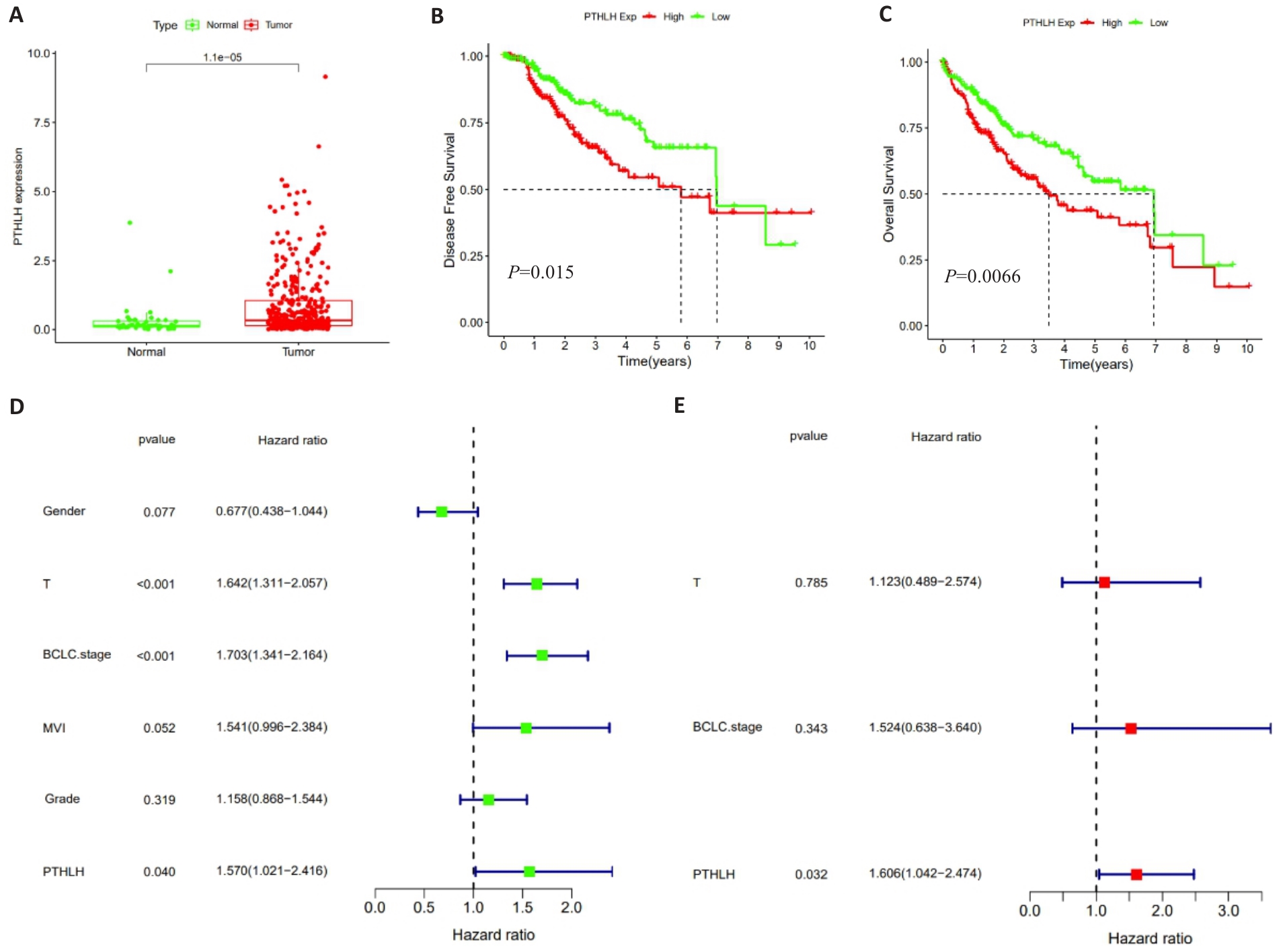
图1 TCGA数据库中PTHLH mRNA的表达水平及预后分析
Fig.1 Analysis of PTHLH mRNA expression levels and prognostic evaluation of HCC patients based on data from the TCGA database. A: Comparison of PTHLH mRNA expression levels between HCC and adjacent normal tissues. B: Kaplan-Meier curves for disease-free survival (DFS) stratified by the median expression level of PTHLH mRNA. C: Kaplan-Meier curves for overall survival (OS) stratified by the median expression level of PTHLH mRNA. D: Forest plot of univariate Cox regression analysis. E: Forest plot of multivariate Cox regression analysis.
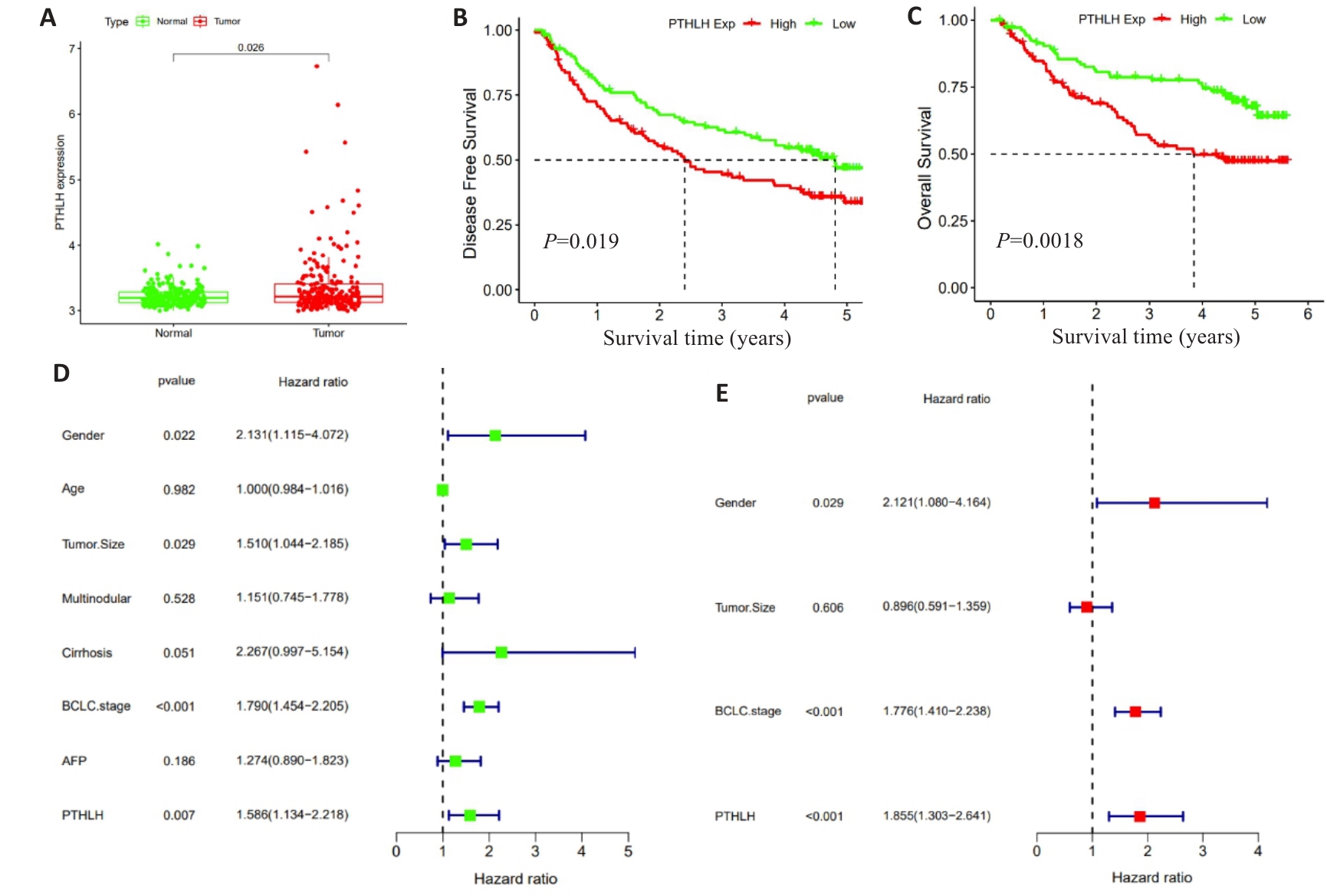
图2 GEO数据库中PTHLH mRNA的表达水平及预后分析
Fig.2 Analysis of PTHLH mRNA expression levels and prognostic evaluation of HCC patients based on data from the GEO database. A: Comparison of PTHLH mRNA expression levels between HCC and adjacent normal tissues. B: Kaplan-Meier curves for DFS of HCC patients stratified by the median expression level of PTHLH mRNA. C: Kaplan-Meier curves for OS of HCC patients stratified by the median expression level of PTHLH mRNA. D: Forest plot of univariate Cox regression analysis. E: Forest plot of multivariate Cox regression analysis.
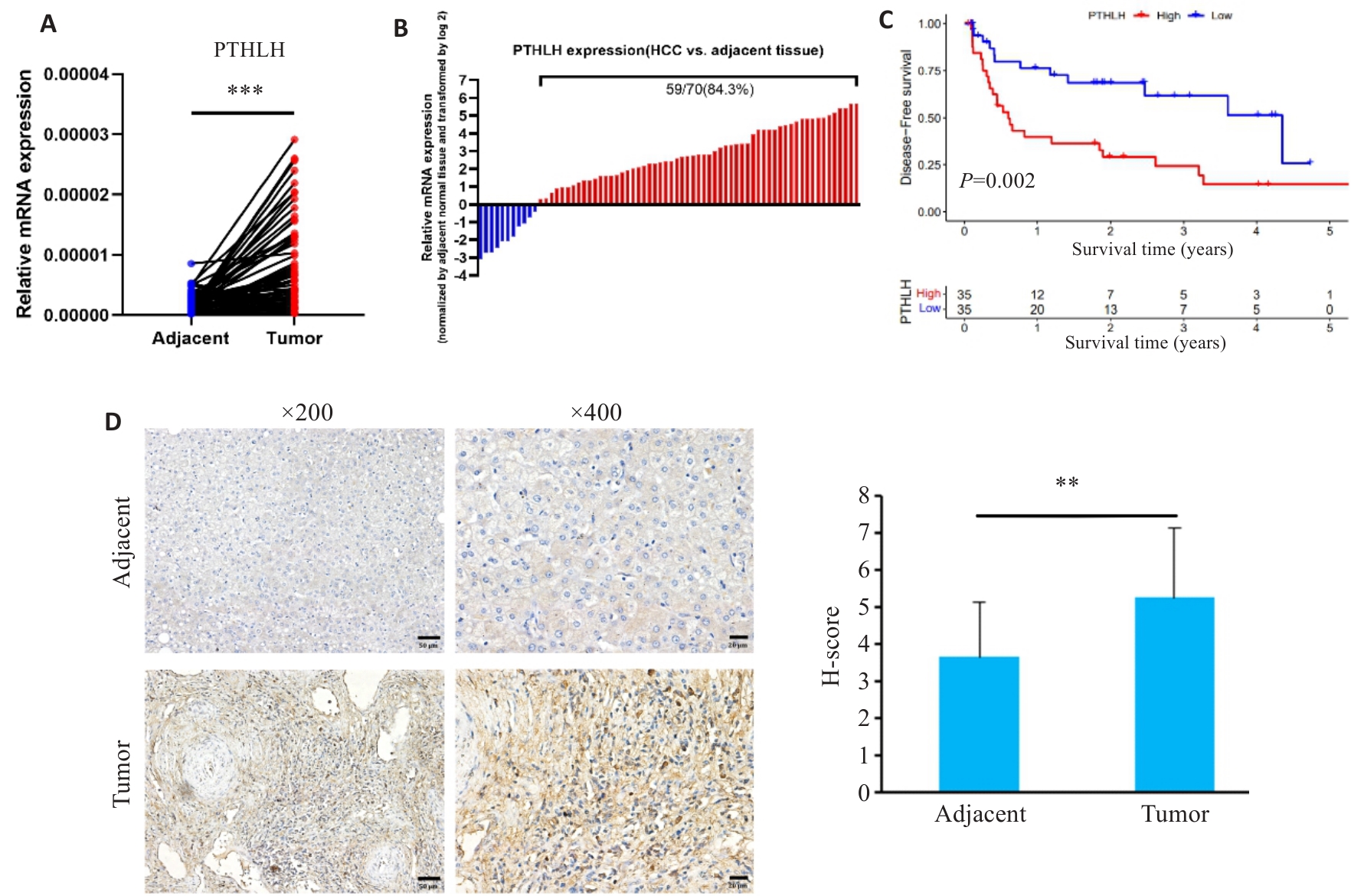
图3 HCC 临床组织样本中PTHLH的表达及预后分析
Fig.3 Expression and prognostic analysis of PTHLH in clinical HCC tissue samples. A, B: Relative PTHLH mRNA expression levels in 70 pairs of HCC and adjacent normal tissues. C: Kaplan-Meier curves for DFS of the patients stratified by the median expression level of PTHLH mRNA. D: Representative immunohistochemical staining of PTHLH in HCC and adjacent normal tissues (Scale bar=50 μm). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
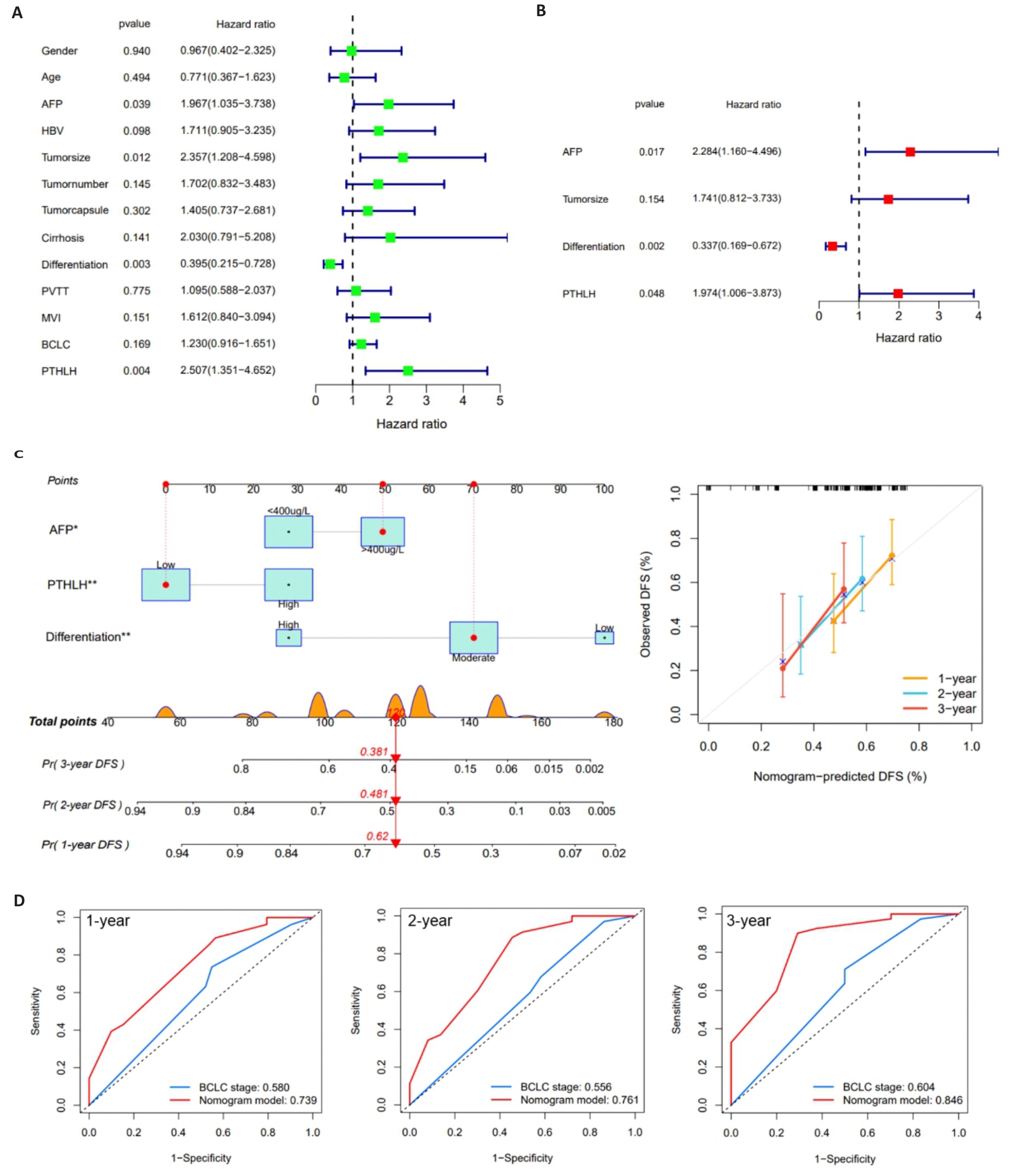
图4 PTHLH的临床预后价值
Fig.4 Clinical prognostic value of PTHLH in HCC patients. A: Forest plot of univariate Cox regression analysis. B: Forest plot of multivariate Cox regression analysis. C: Nomogram for predicting 1-year, 2-year, and 3-year DFS in HCC patients. D: ROC curves comparing the predictive performance of the PTHLH-based nomogram and BCLC staging system.
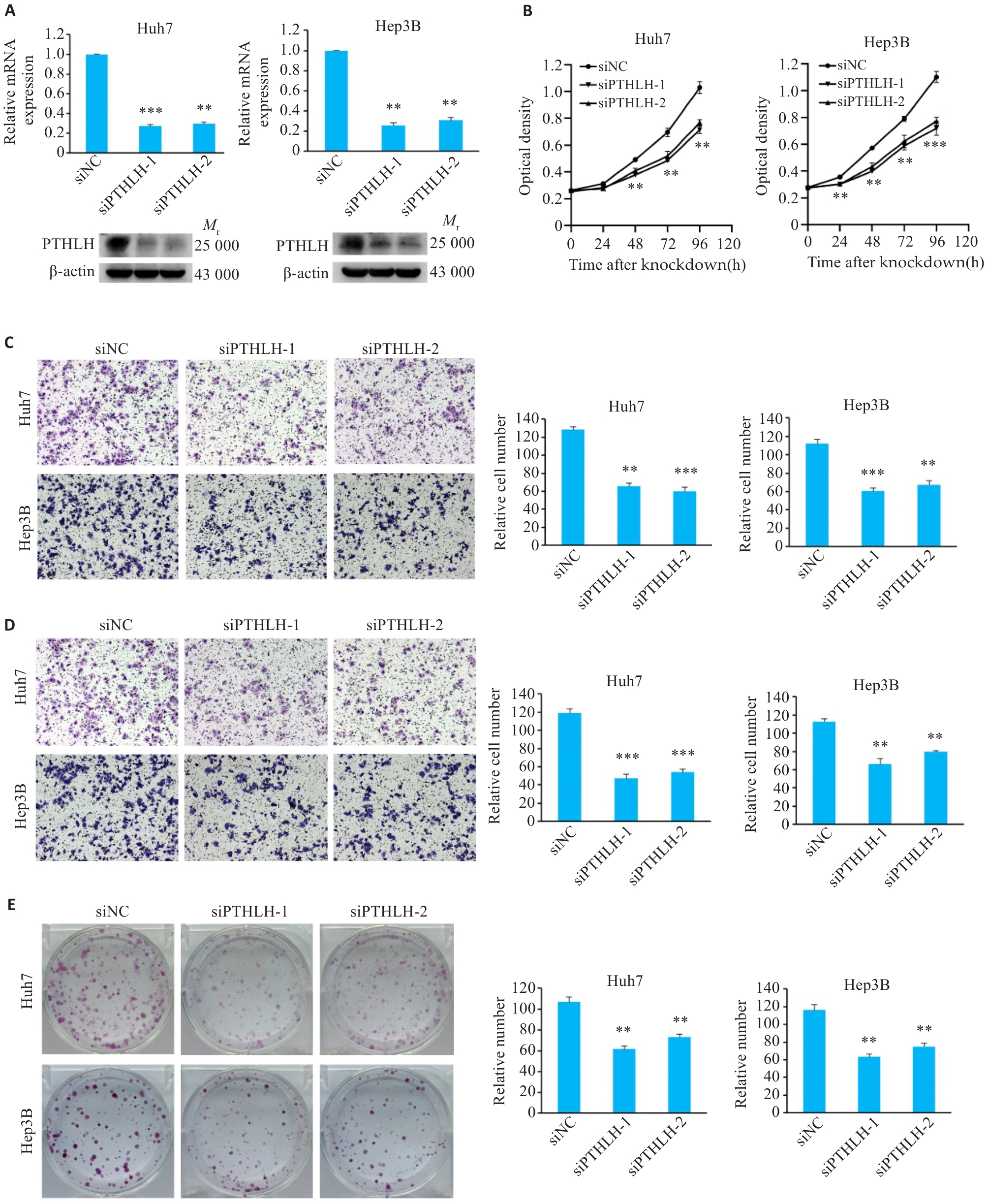
图5 敲低PTHLH可抑制HCC细胞的恶性表型
Fig.5 Knockdown of PTHLH suppresses malignant phenotypes of HCC cells. A: Validation of PTHLH knockdown efficiency by qRT-PCR and Western blotting. B: CCK-8 assay showing cell proliferation. C: Transwell migration assay results (Original magnification: ×100). D: Matrigel invasion assay results (×100). E: Colony formation assay results. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs control group (siNC).
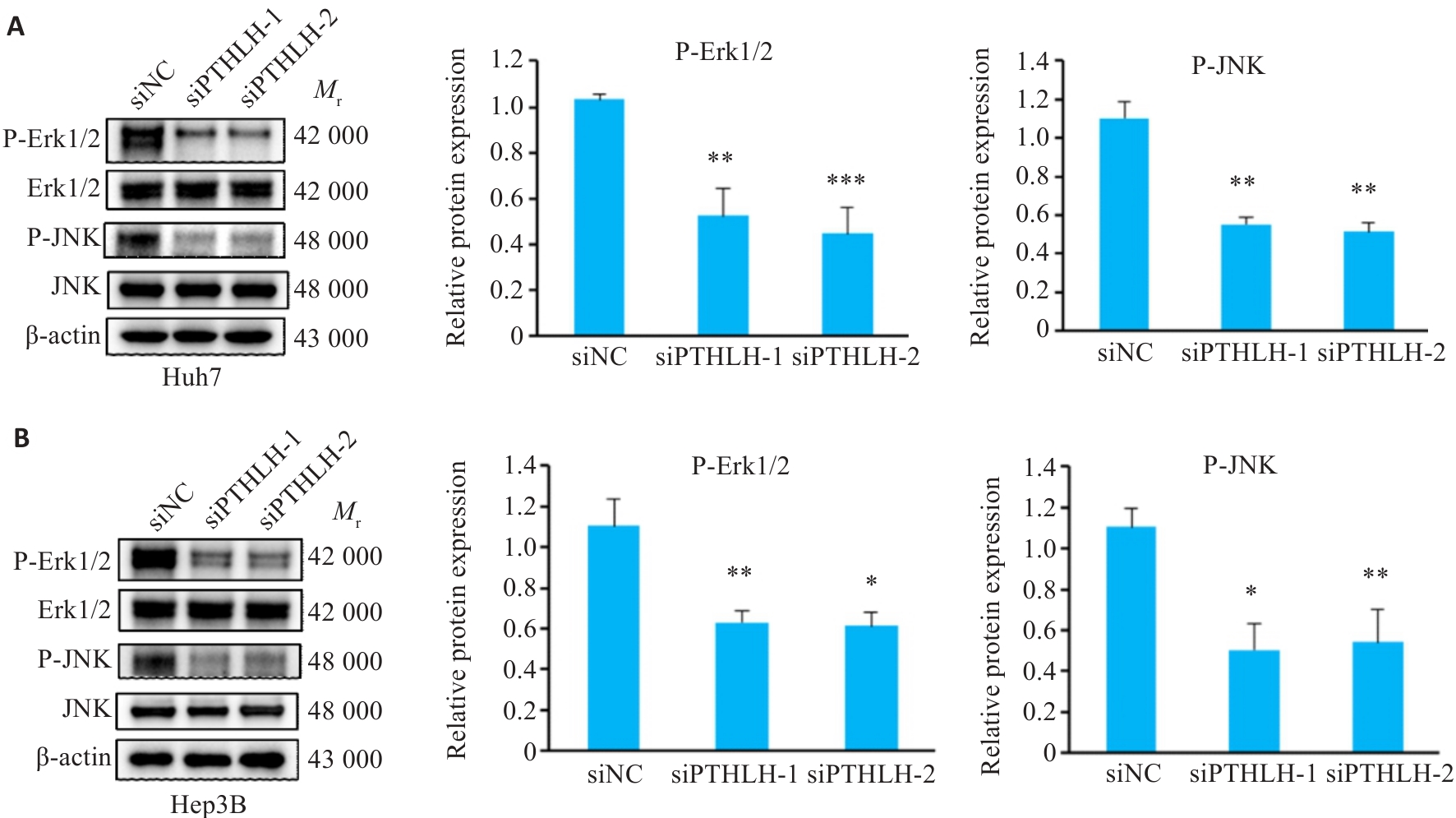
图6 敲低PTHLH后ERK/JNK信号通路的Western blotting分析
Fig.6 Analysis of ERK/JNK signaling pathway in HCC cells by Western blotting following PTHLH knockdown. A: Western blotting of the ERK/JNK signaling pathway in Huh7 cells. B:Western blotting of the ERK/JNK signaling pathway in Hep3B cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs siNC.
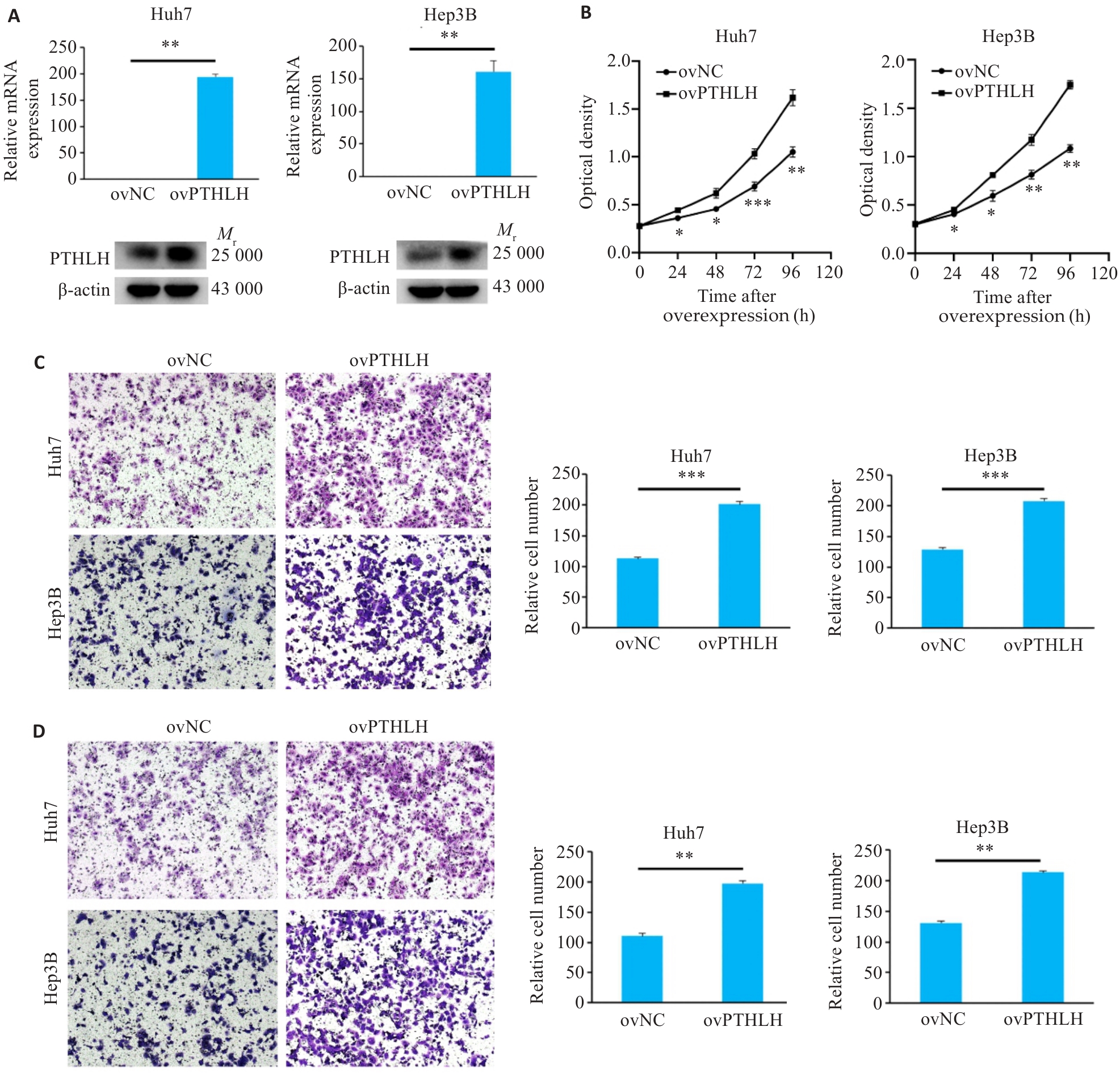
图7 过表达PTHLH增强HCC细胞的恶性表型
Fig.7 Overexpression of PTHLH enhances malignant phenotypes of HCC cells. A: Validation of PTHLH overexpression efficiency by qRT-PCR and Western blotting. B: CCK-8 assay showing cell proliferation. C: Transwell migration assay results (×100). D: Matrigel invasion assay results (×100). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs ovNC.
| [1] | Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-49. doi:10.3322/caac.21660 |
| [2] | Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2021, 7: 6. doi:10.1038/s41572-020-00240-3 |
| [3] | Villanueva A. Hepatocellular carcinoma. reply[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 381(1): e2. doi:10.1056/nejmc1906565 |
| [4] | Zeng HM, Chen WQ, Zheng RS, et al. Changing cancer survival in China during 2003-15: a pooled analysis of 17 population-based cancer registries[J]. Lancet Glob Health, 2018, 6(5): e555-67. doi:10.1016/s2214-109x(18)30127-x |
| [5] | Clemens TL, Cormier S, Eichinger A, et al. Parathyroid hormone-related protein and its receptors: nuclear functions and roles in the renal and cardiovascular systems, the placental trophoblasts and the pancreatic islets[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2001, 134(6): 1113-36. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0704378 |
| [6] | Srisuwarn P, Disthabanchong S. Role of parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related protein in protein-energy malnutrition[J]. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed), 2023, 28(8): 167. doi:10.31083/j.fbl2808167 |
| [7] | Strid H, Care A, Jansson T, et al. Parathyroid hormone-related peptide (38-94) amide stimulates ATP-dependent calcium transport in the Basal plasma membrane of the human syncytiotrophoblast[J]. J Endocrinol, 2002, 175(2): 517-24. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1750517 |
| [8] | Grinman DY, Boras-Granic K, Takyar FM, et al. PTHrP induces STAT5 activation, secretory differentiation and accelerates mammary tumor development[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2022, 24(1): 30. doi:10.1186/s13058-022-01523-1 |
| [9] | Pitarresi JR, Norgard RJ, Chiarella AM, et al. PTHrP drives pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis and reveals a new therapeutic vulnerability[J]. Cancer Discov, 2021, 11(7): 1774-91. |
| [10] | Urosevic J, Garcia-Albéniz X, Planet E, et al. Colon cancer cells colonize the lung from established liver metastases through p38 MAPK signalling and PTHLH[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2014, 16(7): 685-94. doi:10.1038/ncb2977 |
| [11] | Iddon J, Bundred NJ, Hoyland J, et al. Expression of parathyroid hormone-related protein and its receptor in bone metastases from prostate cancer[J]. J Pathol, 2000, 191(2): 170-4. doi:10.1002/(sici)1096-9896(200006)191:2<170::aid-path620>3.3.co;2-8 |
| [12] | Wang YF, Lei R, Zhuang XQ, et al. DLC1-dependent parathyroid hormone-like hormone inhibition suppresses breast cancer bone metastasis[J]. J Clin Invest, 2014, 124(4): 1646-59. doi:10.1172/jci71812 |
| [13] | Tang J, Liao Y, He SY, et al. Autocrine parathyroid hormone-like hormone promotes intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell proliferation via increased ERK/JNK-ATF2-cyclinD1 signaling[J]. J Transl Med, 2017, 15(1): 238. doi:10.1186/s12967-017-1342-1 |
| [14] | Fang YH, Xu YY, Liao W, et al. Multiomics analyses and machine learning of nuclear receptor coactivator 6 reveal its essential role in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Sci, 2023, 114(1): 75-90. doi:10.1111/cas.15577 |
| [15] | Yang Y, Xiao M, Song Y, et al. H-score of 11β-hydroxylase and aldosterone synthase in the histopathological diagnosis of adrenocortical tumors[J]. Endocrine, 2019, 65(3): 683-91. doi:10.1007/s12020-019-02022-8 |
| [16] | McCauley LK, Martin TJ. Twenty-five years of PTHrP progress: from cancer hormone to multifunctional cytokine[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 2012, 27(6): 1231-9. doi:10.1002/jbmr.1617 |
| [17] | Wysolmerski JJ. Parathyroid hormone-related protein: an update[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2012, 97(9): 2947-56. doi:10.1210/jc.2012-2142 |
| [18] | Maioli E, Fortino V. The complexity of parathyroid hormone-related proteinsignalling[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS, 2004, 61(3): 257-62. doi:10.1007/s00018-003-3233-2 |
| [19] | Mangin M, Webb AC, Dreyer BE, et al. Identification of a cDNA encoding a parathyroid hormone-like peptide from a human tumor associated with humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1988, 85(2): 597-601. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.2.597 |
| [20] | Assaker G, Camirand A, Abdulkarim B, et al. PTHrP, a biomarker for CNS metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer and selection for adjuvant chemotherapy in node-negative disease[J]. JNCI Cancer Spectr, 2019, 4(1): pkz063. doi:10.1093/jncics/pkz063 |
| [21] | Lv ZJ, Wu XB, Cao W, et al. Parathyroid hormone-related protein serves as a prognostic indicator in oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2014, 33(1): 100. doi:10.1186/s13046-014-0100-y |
| [22] | Li JR, Karaplis AC, Huang DC, et al. PTHrP drives breast tumor initiation, progression, and metastasis in mice and is a potential therapy target[J]. J Clin Invest, 2011, 121(12): 4655-69. doi:10.1172/jci46134 |
| [23] | Mula RV, Bhatia V, Falzon M. PTHrP promotes colon cancer cell migration and invasion in an integrin α6β4-dependent manner through activation of Rac1[J]. Cancer Lett, 2010, 298(1): 119-27. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2010.06.009 |
| [24] | Liao JH, Li X, Koh AJ, et al. Tumor expressed PTHrP facilitates prostate cancer-induced osteoblastic lesions[J]. Int J Cancer, 2008, 123(10): 2267-78. doi:10.1002/ijc.23602 |
| [25] | Sourbier C, Massfelder T. Parathyroid hormone-related protein in human renal cell carcinoma[J]. Cancer Lett, 2006, 240(2): 170-82. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2005.08.020 |
| [26] | Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation[J]. Cell, 2011, 144(5): 646-74. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013 |
| [27] | Henderson MA, Danks JA, Slavin JL, et al. Parathyroid hormone-related protein localization in breast cancers predict improved prognosis[J]. Cancer Res, 2006, 66(4): 2250-6. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-05-2814 |
| [28] | Hastings RH, Montgrain PR, Quintana R, et al. Cell cycle actions of parathyroid hormone-related protein in non-small cell lung carcinoma[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2009, 297(4): L578-85. doi:10.1152/ajplung.90560.2008 |
| [29] | He SY, Tang J, Diao N, et al. Parathyroid hormone-related protein activates HSCs via hedgehog signalling during liver fibrosis development[J]. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol, 2019, 47(1): 1984-94. doi:10.1080/21691401.2019.1615931 |
| [30] | Wang L, Huang JX, Jiang MH, et al. Inhibited PTHLH downstream leukocyte adhesion-mediated protein amino acid N-linked glyco-sylation coupling Notch and JAK-STAT cascade to iron-sulfur cluster assembly-induced aging network in no-tumor hepatitis/cirrhotic tissues (HBV or HCV infection) by systems-theoretical analysis[J]. Integr Biol (Camb), 2012, 4(10): 1256-62. doi:10.1039/c2ib20148h |
| [31] | Huang JX, Wang L, Jiang MH, et al. PTHLH coupling upstream negative regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis and Wnt receptor signal to downstream peptidase activity-induced apoptosis network in human hepatocellular carcinoma by systems-theoretical analysis[J]. J Recept Signal Transduct Res, 2012, 32(5): 250-6. doi:10.3109/10799893.2012.700717 |
| [32] | Kang N, Zhang XN, Liu K, et al. Roles of ERK/JNK in carbon black induced AP-1 cell signaling pathway changes[J]. J Hyg Res, 2021, 50(4): 533-8. |
| [33] | Zhang ZY, Yang ZH, Wang S, et al. Targeting MAPK-ERK/JNK pathway: a potential intervention mechanism of myocardial fibrosis in heart failure[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2024, 173: 116413. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116413 |
| [34] | Qiu QW, Yu XF, Chen QL, et al. Sema3A inactivates the ERK/JNK signalling pathways to alleviate inflammation and oxidative stress in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated rat endothelial cells and lung tissues[J]. Autoimmunity, 2023, 56(1): 2200908. doi:10.1080/08916934.2023.2200908 |
| [1] | 王康, 李海宾, 余靖, 孟源, 张虹丽. ELFN1高表达是结肠癌的预后生物标志物并促进结肠癌细胞的增殖转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1543-1553. |
| [2] | 高志, 吴傲, 胡仲翔, 孙培养. 类风湿性关节炎中氧化应激与免疫浸润的生物信息学分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 862-870. |
| [3] | 陈芊伊, 尚书涵, 鲁欢, 李思思, 孙志勉, 范喜瑞, 戚之琳. 金盏花苷E通过自噬途径下调GPX4和SLC7A11抑制肝癌细胞的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1327-1335. |
| [4] | 陈莉莉, 吴天宇, 张铭, 丁子夏, 张妍, 杨依清, 郑佳倩, 张小楠. 类风湿关节炎的潜在生物标志物及其免疫调控机制:基于GEO数据库[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1098-1108. |
| [5] | 何欣容, 熊斯丽, 朱真如, 孙景苑, 曹传辉, 王惠. UBE2T通过调节性T细胞诱导肝细胞癌的放疗抵抗[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1149-1158. |
| [6] | 刘鹏程, 娄丽娟, 刘霞, 王建, 姜颖. M2巨噬细胞特征基因风险评分能准确预测HBV相关肝细胞癌患者的预后[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 827-840. |
| [7] | 钟伟雄, 梁芳蓉, 杨蕊梦, 甄 鑫. 基于多期动态增强CT影像组学特征和多分类器分层融合模型预测肝细胞癌的微血管侵犯[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 260-269. |
| [8] | 胡嘉伟, 杜芳, 丁璐, 王路翔, 赵巍峰. 合并高血压病的乙型肝炎肝硬化患者发生肝细胞癌的风险评估:一项基于倾向性匹配评分的回顾性队列研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2243-2249. |
| [9] | 朱 权, 黄柏胜, 位磊艳, 罗奇志. 过表达LncRNA MEG3通过促进铁死亡增强肝癌细胞对顺铂的化疗敏感性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 17-24. |
| [10] | 于正涛, 李佳梦, 蒋俊文, 李 由, 林 珑, 夏 鹰, 王 磊. miRNA-128-3p通过下调KLHDC8A的表达抑制胶质瘤细胞的恶性生物学行为[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1447-1459. |
| [11] | 曹丹萍, 蔡 娟, 李艳娜, 董润雨, 王智雄, 左学良. TMEM64在肝癌组织中高表达并促进肝癌细胞的增殖和侵袭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1345-1355. |
| [12] | 黄 卓, 曾振宇, 李 佳, 蔡 蕊, 贺文霞, 胡淑婷. 心力衰竭患者Circ-PALLD的高表达受转录因子GATA4的转录调控[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1371-1378. |
| [13] | 兰 玉, 王凯风, 蓝智贤, 周何琪, 孙 剑. 脱醇红酒抑制肝细胞癌的发生和发展:基于诱导细胞周期的阻滞和凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1297-1305. |
| [14] | 巩 高, 曹 石, 肖 慧, 方威扬, 阙与清, 刘子蔚, 陈超敏. 深度注意力机制结合临床特征预测肝细胞癌微血管浸润[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(5): 839-851. |
| [15] | 程 阳, 何旭旭, 王 炼, 许轶博, 沈梦迪, 张文静, 夏勇生, 张 婕, 张 敏, 王宜君, 胡建国, 张 军. HSDL2高表达促进直肠癌细胞增殖:基于激活CDK6/cyclinD1信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(4): 544-551. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||