南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (11): 2192-2200.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.11.16
• • 上一篇
蔡祺晖1( ), 蓝海强2, 冼柏俊1, 刘连3, 王楠1, 黄晓蕾1, 牛晓璐1, 胡欣雨1, 李辰1, 谢俊毅1, 廖钊宏1,2(
), 蓝海强2, 冼柏俊1, 刘连3, 王楠1, 黄晓蕾1, 牛晓璐1, 胡欣雨1, 李辰1, 谢俊毅1, 廖钊宏1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-16
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2024-11-29
通讯作者:
廖钊宏
E-mail:m19802076244@163.com;liao1219315353@163.com
作者简介:蔡祺晖,在读本科生,E-mail: m19802076244@163.com
基金资助:
Qihui CAI1( ), Haiqiang LAN2, Bojun XIAN1, Lian LIU3, Nan WANG1, Xiaolei HUANG1, Xiaolu NIU1, Xinyu HU1, Chen LI1, Junyi XIE1, Zhaohong LIAO1,2(
), Haiqiang LAN2, Bojun XIAN1, Lian LIU3, Nan WANG1, Xiaolei HUANG1, Xiaolu NIU1, Xinyu HU1, Chen LI1, Junyi XIE1, Zhaohong LIAO1,2( )
)
Received:2024-05-16
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-11-29
Contact:
Zhaohong LIAO
E-mail:m19802076244@163.com;liao1219315353@163.com
摘要:
目的 探究骨骼肌E2信号对Cardiotoxin (CTX)诱导的小鼠急性损伤骨骼肌内巨噬细胞胞葬作用的影响。 方法 选择野生 C57BL/6雌鼠150只、C57BL/6雄鼠33只,对一部分雌鼠进行卵巢去势(OVX)操作。CTX胫骨前肌注射诱导小鼠急性肌损伤,后给予β-雌二醇(β-Estradiol)、4-他莫昔芬(4-OHT)等试剂肌注,分为Control(Female)组、Male组、Control+β-Estradiol组、Control+4-OHT组、OVX组、OVX+β-Estradiol组。采用ELISA法比较各组小鼠损伤肌内血清中E2表达。采用免疫荧光、流式细胞术等方法比较损伤肌内炎性渗出巨噬细胞数量、表型、胞葬作用与肌再生修复的差异。紫外照射法体外诱导细胞凋亡。体外分化培养C2C12细胞,分化为成熟肌管后,将之于炎性环境中与巨噬细胞、凋亡细胞共培养,且给予β-Estradiol、4-OHT等处理,主要分为Control(C2C12+HS+Mac+ACs)组、C2C12+HS+IFN-γ+Mac+ACs组、C2C12+HS+IFN-γ+β-Estradiol+Mac+ACs组、C2C12+HS+IFN-γ+4-OHT+Mac+ACs组、C2C12+HS+IFN-γ+β-Estradiol+4-OHT+Mac+ACs组。采用免疫荧光、流式细胞术等方法比较各组巨噬细胞胞葬作用的差异。 结果 较之于Control组,OVX鼠损伤肌内炎性单核巨噬细胞渗出增加,M1细胞比例增加(P<0.05),但M2细胞比例、胞葬作用下调(P<0.05),肌纤维再生修复延迟。体外炎性环境中,β-Estradiol共培养体系中的M2巨噬细胞数目、巨噬细胞胞葬较之于Control组均上调(P<0.05),而4-OHT组的趋势则相反(P<0.05)。 结论 骨骼肌纤维E2信号通过促使损伤肌内M1向M2的转变,以促进损伤肌内巨噬细胞胞葬作用,继而促进炎症撤退与肌再生修复。
蔡祺晖, 蓝海强, 冼柏俊, 刘连, 王楠, 黄晓蕾, 牛晓璐, 胡欣雨, 李辰, 谢俊毅, 廖钊宏. 肌纤维E2信号促进小鼠急性损伤骨骼肌内的巨噬细胞胞葬[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2192-2200.
Qihui CAI, Haiqiang LAN, Bojun XIAN, Lian LIU, Nan WANG, Xiaolei HUANG, Xiaolu NIU, Xinyu HU, Chen LI, Junyi XIE, Zhaohong LIAO. E2 signaling in myofibers promots macrophage efferocytosis in mouse skeletal muscles with cardiotoxin-induced acute injury[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2192-2200.
| Gene | Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| ERα | For:ACTGGCCAATCTTTCTCTGC Rev:CAATTCATCCCCAAAGACATGGAC |
| ERβ | For:TCACTTCTGCGCTGTCTGCAGCG Rev:CCTGGGTCGCTGTGCCAAG |
| GAPDH | For:CAATGTGTCCGTCGTGGATCT Rev:GTCCTCAGTGTAGCCCAAGATG |
表1 qRT-PCR的引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequence for qRT-PCR
| Gene | Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| ERα | For:ACTGGCCAATCTTTCTCTGC Rev:CAATTCATCCCCAAAGACATGGAC |
| ERβ | For:TCACTTCTGCGCTGTCTGCAGCG Rev:CCTGGGTCGCTGTGCCAAG |
| GAPDH | For:CAATGTGTCCGTCGTGGATCT Rev:GTCCTCAGTGTAGCCCAAGATG |
| Gene | Primer sequence(5'-3') |
|---|---|
| IL-1β | For:GCCCATCCTCTGTGACTC Rev:TGTGCCGTCTTTCATTAC |
| IL-10 | For:TTTCAAACAAAGGACCAG Rev:GGATCATTTCCGATAAGG |
| iNOS | For:CTTCCGGGCAGCCTGTGAGACG Rev:ATCCCCAGGTGTTCCCCAGGTAGG |
| TNF-α | For:GCTGTCTCCCCCGAAAGATG Rev:AGGCAGGTGTAGATGTTGTGG |
| Arg1 | For:CTCCAAGCCAAAGTCCTTAGAG Rev:AGGAGCTGTCATTAGGGACA |
| Mrc1 | For:CTCTGTTCAGCTATTGGACGC Rev:TGGCACTCCCAAACATAATTTGA |
| GAPDH | For:CAATGTGTCCGTCGTGGATCT Rev:GTCCTCAGTGTAGCCCAAGATG |
表2 qRT-PCR反应因子的引物序列
Tab.2 Primer sequence for qRT-PCR
| Gene | Primer sequence(5'-3') |
|---|---|
| IL-1β | For:GCCCATCCTCTGTGACTC Rev:TGTGCCGTCTTTCATTAC |
| IL-10 | For:TTTCAAACAAAGGACCAG Rev:GGATCATTTCCGATAAGG |
| iNOS | For:CTTCCGGGCAGCCTGTGAGACG Rev:ATCCCCAGGTGTTCCCCAGGTAGG |
| TNF-α | For:GCTGTCTCCCCCGAAAGATG Rev:AGGCAGGTGTAGATGTTGTGG |
| Arg1 | For:CTCCAAGCCAAAGTCCTTAGAG Rev:AGGAGCTGTCATTAGGGACA |
| Mrc1 | For:CTCTGTTCAGCTATTGGACGC Rev:TGGCACTCCCAAACATAATTTGA |
| GAPDH | For:CAATGTGTCCGTCGTGGATCT Rev:GTCCTCAGTGTAGCCCAAGATG |
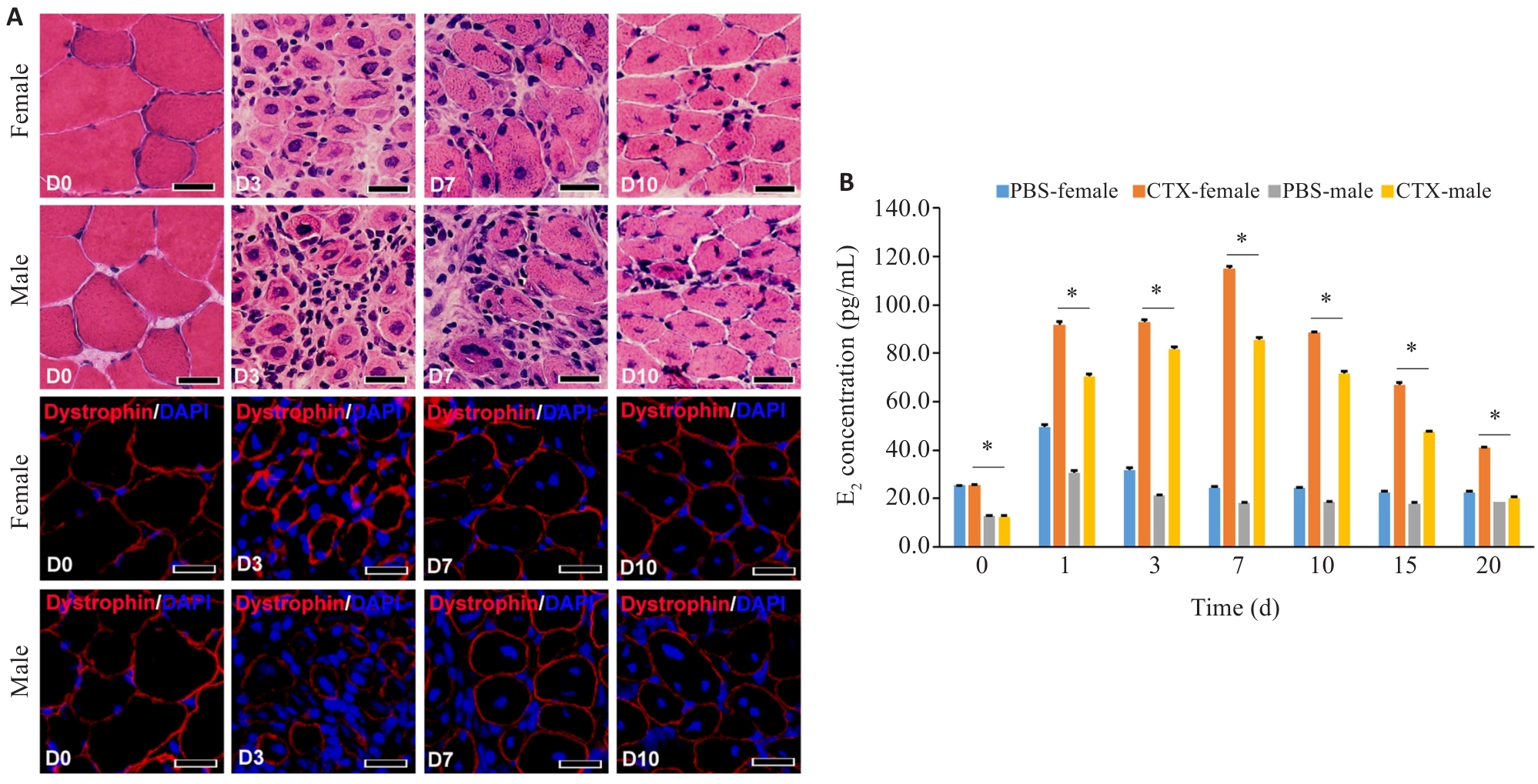
图1 肌纤维E2信号对急性骨骼肌炎症的影响
Fig.1 Effect of E2 in myofiber signaling on acute skeletal myositis in mice. A: HE and immunofluorescence staining for detecting inflammation in the tibialis anterior muscle (TA) after CTX injury (Scale bar=50 μm). B: ELISA for detection of serum E2 in male and female mice at different time points after muscle injury (*P<0.05).

图2 急性骨骼肌炎中雌激素的受体表达
Fig.2 Expression of estrogen receptors in acute skeletal myositis. A: Western blotting of ERα and ERβ expression level in mature myotubes derived from C2C12 cells. B: qRT-PCR analysis of ERα and ERβ mRNA levels in the damaged muscle of female mice. C: Immunofluorescence staining of ERβ expression level in injured mouse muscle (Scale bar=50 μm). *P<0.05, **P<0.01.

图3 肌纤维E2信号对急性骨骼肌炎症损伤肌内单核巨噬细胞渗出影响
Fig.3 Effect of E2 signaling in myofibers on exudation of intramuscular mononuclear macrophages after acute skeletal muscle injury. A: ELISA for detecting serum E2 level in female mice after different treatments. B: ELISA for detecting serum E2 levels in female mice at different time points after OVX treatment. C: HE staining for detecting muscular inflammation in female mice with different treatments after CTX injury. D: Immunofluorescence staining for detecting muscular inflammation in female mice after CTX injury with different treatments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01; Scale bar=50 μm.

图4 肌纤维E2信号对急性骨骼肌炎症损伤肌内巨噬细胞表型影响
Fig.4 Effect of E2 signaling in myofibers on phenotype of intramuscular macrophages in mice after acute skeletal muscle injury. A: Flow cytometric analysis of mononuclear macrophages in the damaged muscle of female mice after OVX treatment. B: Flow cytometric analysis of the phenotype of macrophages in the injured muscles of female mice after OVX treatment. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.

图5 肌纤维E2信号对急性骨骼肌炎症损伤肌内炎症因子的影响
Fig.5 Effect of E2 signaling in myofibers on intramuscular inflammatory cytokines after acute skeletal muscle injury. A: qRT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines in female mice after OVX treatment. B: qRT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines in macrophages from the injured muscles isolated by flow cytometry in female mice after OVX treatment. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.

图6 肌纤维E2信号驱动急性骨骼肌炎症损伤肌内巨噬细胞胞葬作用
Fig.6 E2 signaling in myofibers drives intramuscular macrophage efferocytosis in acute skeletal myositis. A: Immunofluorescence detection of intramuscular macrophage efferocytosis in the damaged muscle. (scale bar=50 μm). B: Flow cytometry of intramuscular macrophage efferocytosis in the damaged muscle (*P<0.05).

图7 体外共培养体系中E2信号对巨噬细胞表型与胞葬作用的影响
Fig.7 Effect of E2 signaling on macrophage phenotypes and efferocytosis in an in vitro co-culture system. A: Immunofluorescence detection of macrophage phenotypes in the in vitro co-culture system. B: Immunofluorescence detection and flow cytometry analysis of macrophage efferocytosis in the in vitro co-culture system. *P<0.05; Scale bar=50 μm.

图8 肌纤维E2信号调控损伤骨骼肌内肌纤维再生修复
Fig.8 E2 signaling in myofibers regulates regeneration and repair of intramuscular myofibers in injured mouse skeletal muscles of female mice after different treatments (Immunofluorescence staining, scale bar=50 μm; *P<0.05).
| 1 | Zhong HH, Sian V, Johari M, et al. Revealing myopathy spectrum: integrating transcriptional and clinical features of human skeletal muscles with varying health conditions[J]. Commun Biol, 2024, 7(1): 438. |
| 2 | Zeller J, Peter K, Eisenhardt SU. Intravital imaging of leukocyte-endothelial interaction in hindlimb ischemia/reperfusion injury by intravital multiphoton microscopy[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2024, 2711: 89-104. |
| 3 | Zhang H, Qi G, Wang K, et al. Oxidative stress: Roles in skeletal muscle atrophy [J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2023, 214: 115664-77. |
| 4 | Al-Kharashi L, Attia H, Alsaffi A, et al. Pentoxifylline and thiamine ameliorate rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury in rats via suppressing TLR4/NF‑κB and NLRP-3/caspase-1/gasdermin mediated-pyroptosis[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2023, 461: 116387. |
| 5 | Boudhabhay I, Poillerat V, Grunenwald A, et al. Complement activation is a crucial driver of acute kidney injury in rhabdomyolysis[J]. Kidney Int, 2021, 99(3): 581-97. |
| 6 | Geraci A, Calvani R, Ferri E, et al. Sarcopenia and menopause: the role of estradiol[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2021, 12: 682012. |
| 7 | Ferreira J, Carneiro A, Vila I, et al. Inflammation and loss of skeletal muscle mass in chronic limb threatening ischemia[J]. Ann Vasc Surg, 2023, 88: 164-73. |
| 8 | Petrocelli JJ, McKenzie AI, de Hart NMMP, et al. Disuse-induced muscle fibrosis, cellular senescence, and senescence-associated secretory phenotype in older adults are alleviated during re-ambulation with metformin pre-treatment[J]. Aging Cell, 2023, 22(11): e13936. |
| 9 | Livshits G, Kalinkovich A. Restoration of epigenetic impairment in the skeletal muscle and chronic inflammation resolution as a therapeutic approach in sarcopenia[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2024, 96: 102267. |
| 10 | Aluganti Narasimhulu C, Singla DK. Amelioration of diabetes-induced inflammation mediated pyroptosis, sarcopenia, and adverse muscle remodelling by bone morphogenetic protein-7[J]. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2021, 12(2): 403-20. |
| 11 | Antuña E, Cachán-Vega C, Bermejo-Millo JC, et al. Inflammaging: implications in sarcopenia[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(23): 15039. |
| 12 | Ji Y, Lin J, Liu R, et al. Celecoxib attenuates hindlimb unloading-induced muscle atrophy via suppressing inflammation, oxidative stress and ER stress by inhibiting STAT3[J]. Inflammo-pharmacology, 2024, 32(2): 1633-46. |
| 13 | Fischer V, Ragipoglu D, Diedrich J, et al. Mast cells trigger disturbed bone healing in osteoporotic mice[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 2022, 37(1): 137-51. |
| 14 | Zhang Y, Chang YC, Han ZW, et al. Estrogen protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating Th17/treg cell immune balance[J]. Dis Markers, 2022, 2022: 7812099. |
| 15 | Kurmann L, Okoniewski M, Dubey RK. Estradiol inhibits human brain vascular pericyte migration activity: a functional and transcriptomic analysis[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(9): 2314. |
| 16 | Rodríguez-Benítez E, López-García K, Xelhuantzi N, et al. Shift from pro-to anti-inflammatory phase in pelvic floor muscles at postpartum matches histological signs of regeneration in multiparous rabbits[J]. Medicina, 2024, 60(4): 675. |
| 17 | Luo ZW, Qi BJ, Sun YY, et al. Engineering bioactive M2 macrophage-polarized, anti-inflammatory, miRNA-based liposomes for functional muscle repair: from exosomal mechanisms to biomaterials[J]. Small, 2022, 18(34): e2201957. |
| 18 | Guimarães-Pinto K, Maia EP, Ferreira JRM, et al. Efferocytosis in lung mucosae: implications for health and disease[J]. Immunol Lett, 2022, 248: 109-18. |
| 19 | Doran AC, Yurdagul A Jr, Tabas I. Efferocytosis in health and disease[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2020, 20(4): 254-67. |
| 20 | 吴泽锴, 黄 涛, 廖钊宏, 等. 肌纤维转化生长因子- β信号激活与急性肌损伤炎症反应的相关性研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2021, 23(3): 254-61. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115530-20210107-00010 |
| 21 | Xiao JW, Huang JW, Jian XT, et al. IRE1α arm of unfolded protein response in muscle-specific TGF-β signaling-mediated regulation of muscle cell immunological properties[J]. Cell Mol Biol Lett, 2023, 28(1): 15. |
| 22 | Hoffman DB, Raymond-Pope CJ, Sorensen JR, et al. Temporal changes in the muscle extracellular matrix due to volumetric muscle loss injury[J]. Connect Tissue Res, 2022, 63(2): 124-37. |
| 23 | Navi A, Patel H, Xu SW, et al. Role of toll-like receptor 4 in skeletal muscle damage in chronic limb-threatening ischemia[J]. JVS Vasc Sci, 2024, 5: 100194. |
| 24 | Hirtz A, Rech F, Dubois-Pot-Schneider H, et al. Estrogen signaling in healthy and tumor brain[J]. Steroids, 2023, 199: 109285. |
| 25 | Geraci A, Calvani R, Ferri E, et al. Sarcopenia and Menopause: The Role of Estradiol[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2021, 12: 682012-16. |
| 26 | Chaiyasing R, Sugiura A, Ishikawa T, et al. Estrogen modulates the skeletal muscle regeneration process and myotube morphogenesis: morphological analysis in mice with a low estrogen status[J]. J Vet Med Sci, 2021, 83(12): 1812-9. |
| 27 | Lou YY, Fu ZJ, Tian Y, et al. Estrogen-sensitive activation of SGK1 induces M2 macrophages with anti-inflammatory properties and a Th2 response at the maternal-fetal interface[J]. Reprod Biol Endocrinol, 2023, 21(1): 50. |
| 28 | Bauerschmitz G, Hüchel S, Gallwas J, et al. Inhibition of increased invasiveness of breast cancer cells with acquired tamoxifen resistance by suppression of CYR61[J]. Cancer Genomics Proteomics, 2023, 20(6): 531-8. |
| 29 | Valero-Breton M, Tacchi F, Abrigo J, et al. Angiotensin-(1-7) improves skeletal muscle regeneration[J]. Eur J Transl Myol, 2023, 33(4): 12037. |
| 30 | Landeros RV, Jobe SO, Aranda-Pino G, et al. Convergent ERK1/2, p38 and JNK mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPKs) signalling mediate catecholoestradiol-induced proliferation of ovine uterine artery endothelial cells[J]. J Physiol, 2017, 595(14): 4663-76. |
| 31 | Mitchnick KA, Mendell AL, Wideman CE, et al. Dissociable involvement of estrogen receptors in perirhinal cortex-mediated object-place memory in male rats[J]. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 2019, 107: 98-108. |
| [1] | 左涵珺, 段兆达, 王朝, 郭涛, 石金沙, 石浩龙, 李娟娟. 天麻素经PI3K/AKT通路改善新生大鼠缺氧缺血性脑损伤后小胶质细胞介导的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1712-1719. |
| [2] | 李明远, 张玮, 华梦晴. 甲基巴多索龙通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化缓解小鼠急性肝损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1662-1669. |
| [3] | 张先恒, 刘健, 韩琦, 陈一鸣, 丁香, 陈晓露. 黄芩清热除痹胶囊通过PTEN/PI3K/AKT信号通路改善痛风性关节炎大鼠的炎症反应及尿酸、脂质代谢失衡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1450-1458. |
| [4] | 张钰明, 夏士程, 张淋淋, 陈梦茜, 刘晓婧, 高琴, 叶红伟. 金银花提取物对小鼠阿霉素肝脏损伤的保护作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1571-1581. |
| [5] | 向珊, 张宗星, 江露, 刘道忠, 李玮怡, 包卓玛, 田瑞, 陈丹, 袁林. 三百棒通过调控PI3K/Akt信号通路改善胶原诱导性类风湿性关节炎大鼠的血管翳[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1582-1588. |
| [6] | 肖林雨, 段婷, 夏勇生, 陈悦, 孙洋, 许轶博, 徐磊, 闫兴洲, 胡建国. 蒙花苷通过抑制TLR4/NF-κB通路抑制小鼠脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞活化介导的神经炎症和神经元凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1589-1598. |
| [7] | 陶怀祥, 骆金光, 闻志远, 虞亘明, 苏萧, 王鑫玮, 关翰, 陈志军. STING高表达通过调控TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3通路和影响炎症与凋亡水平促进小鼠肾脏缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1345-1354. |
| [8] | 李和平, 李高桦, 张学华, 王亚楠. 直肠癌炎症蛋白因子的遗传驱动:孟德尔随机化方法在临床预后研究中的应用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1361-1370. |
| [9] | 张玮, 邓蒙蒙, 曾尧, 刘辰菲, 尚菲菲, 许文豪, 蒋昊轶, 王凤超, 杨燕青. 2,6-二甲氧基-1,4-苯醌通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化缓解小鼠的感染性休克[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1024-1032. |
| [10] | 鲁玲君, 杨小迪, 张华平, 梁媛, 石秀兰, 周鑫. 重组日本血吸虫半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂对急性肝损伤小鼠的保护作用及机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1126-1134. |
| [11] | 曹家樊, 孙 跃, 丁 鑫, 李盛文, 陈 博, 兰 天. 熊果苷通过抑制巨噬细胞募集并调控Akt/NF-κB和Smad信号通路改善小鼠肝纤维化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 652-659. |
| [12] | 何 程, 陈 炜, 张念志, 栾 军, 王三凤, 张 尤. 参七虫草方通过ASS1/src/STAT3信号通路改善肺纤维化大鼠的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 644-651. |
| [13] | 席 进, 张 敏, 张永玉, 张 晨, 张雨路, 王 锐, 申 林, 李 静, 宋 雪. 上调KLF11可改善结肠炎模型小鼠的肠道炎症:基于抑制JAK2/STAT3信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 765-772. |
| [14] | 包汉生, 王苏童, 吕穆杰, 王永成, 姜 萍, 李 晓. 激活α7nAchR促进肥胖小鼠的脂肪稳态和米色脂肪生成及产热作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 499-506. |
| [15] | 凌旭光, 徐雯雯, 庞观来, 洪旭星, 刘凤芹, 李 洋. 茶多酚通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体改善脓毒症小鼠的急性肺损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 381-386. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||