Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (7): 1471-1478.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.07.13
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mengying ZHANG( ), Chenling ZHAO, Liwei TIAN, Guofang YU, Wenming YANG, Ting DONG(
), Chenling ZHAO, Liwei TIAN, Guofang YU, Wenming YANG, Ting DONG( )
)
Received:2025-01-24
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-07-17
Contact:
Ting DONG
E-mail:1649392726@qq.com;876786557@qq.com
Mengying ZHANG, Chenling ZHAO, Liwei TIAN, Guofang YU, Wenming YANG, Ting DONG. Gandou Fumu Decoction improves liver steatosis by inhibiting hepatocyte ferroptosis in mice with Wilson's disease through the GPX4/ACSL4/ALOX15 signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1471-1478.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.07.13
| Gene | Sequence (5'to3') | |
|---|---|---|
| GPX4 | CGCCAAAGTCCTAGGAAACG | |
| ATGCACACGAAACCCCTGTA | ||
| ACSL4 | GACAGGCCAGTGTGAACGTA | |
| TCAGCCCATATCCCTGACCA | ||
| ALOX15 | CGGCGACCAGTATCTCTGAC | |
| TTCCAGGAGTTTCGAACCCG | ||
| FTH1 | GGAGCATGCCGAGAAACTGA | |
| GTCATCACGGTCTGGTTTCTTT | ||
| FTL | GATCGGGATGACGTGGCTC | |
| TTGAGATGGCTTCTGCACAT | ||
| TFR1 | GTGGAGTCTCCCGAGGGTTA | |
| TGGGCATTTGCAACCTTTTCT | ||
| ACOX1 | TTTGTGGAACCTGTTGGCCT | |
| TCGAAGATGAGTTCCGTGGC | ||
| SCD1 | ACAGCCTGTTCGTTAGCACC | |
| TATCCATAGAGATGCGCGGC | ||
| FAS | GTCCTGCCTCTGGTGCTTG | |
| AGCAAAATGGGCCTCCTTGA | ||
| GAPDH | GTGTTCCTACCCCCAATGTG | |
| GTCATTGAGAGCAATGCCAG |
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Sequence (5'to3') | |
|---|---|---|
| GPX4 | CGCCAAAGTCCTAGGAAACG | |
| ATGCACACGAAACCCCTGTA | ||
| ACSL4 | GACAGGCCAGTGTGAACGTA | |
| TCAGCCCATATCCCTGACCA | ||
| ALOX15 | CGGCGACCAGTATCTCTGAC | |
| TTCCAGGAGTTTCGAACCCG | ||
| FTH1 | GGAGCATGCCGAGAAACTGA | |
| GTCATCACGGTCTGGTTTCTTT | ||
| FTL | GATCGGGATGACGTGGCTC | |
| TTGAGATGGCTTCTGCACAT | ||
| TFR1 | GTGGAGTCTCCCGAGGGTTA | |
| TGGGCATTTGCAACCTTTTCT | ||
| ACOX1 | TTTGTGGAACCTGTTGGCCT | |
| TCGAAGATGAGTTCCGTGGC | ||
| SCD1 | ACAGCCTGTTCGTTAGCACC | |
| TATCCATAGAGATGCGCGGC | ||
| FAS | GTCCTGCCTCTGGTGCTTG | |
| AGCAAAATGGGCCTCCTTGA | ||
| GAPDH | GTGTTCCTACCCCCAATGTG | |
| GTCATTGAGAGCAATGCCAG |
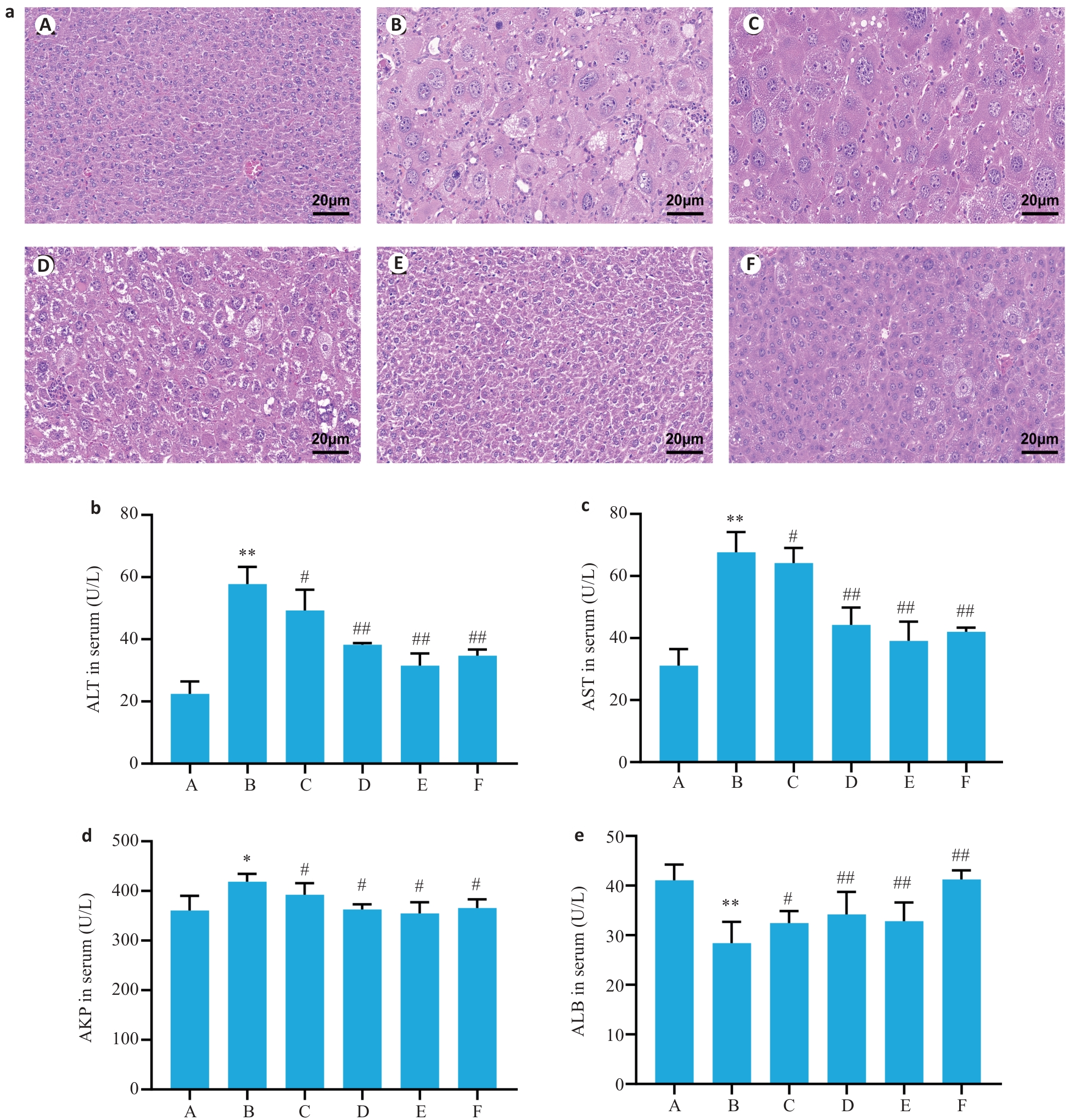
Fig.1 Effects of Gandou Fumu Decoction (GDFMD) on liver histopathology and serum biochemical indicators of liver function in tx-J mouse models of Wilson's disease (WD). a: HE staining showing histopathological changes in the liver of the mice. b-e: Comparison of serum levels of ALT, AST, AKP, and albumin (ALB) among the groups (Mean±SD, n=6). A: Blank group; B: Model group; C: Low-dose GDFMD group; D: Medium-dose GDFMD group; E: High-dose GDFMD group; F: Fer-1 group (the same group names are used consistently in all the following figures). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs group A; #P<0.05,##P<0.01 vs group B.
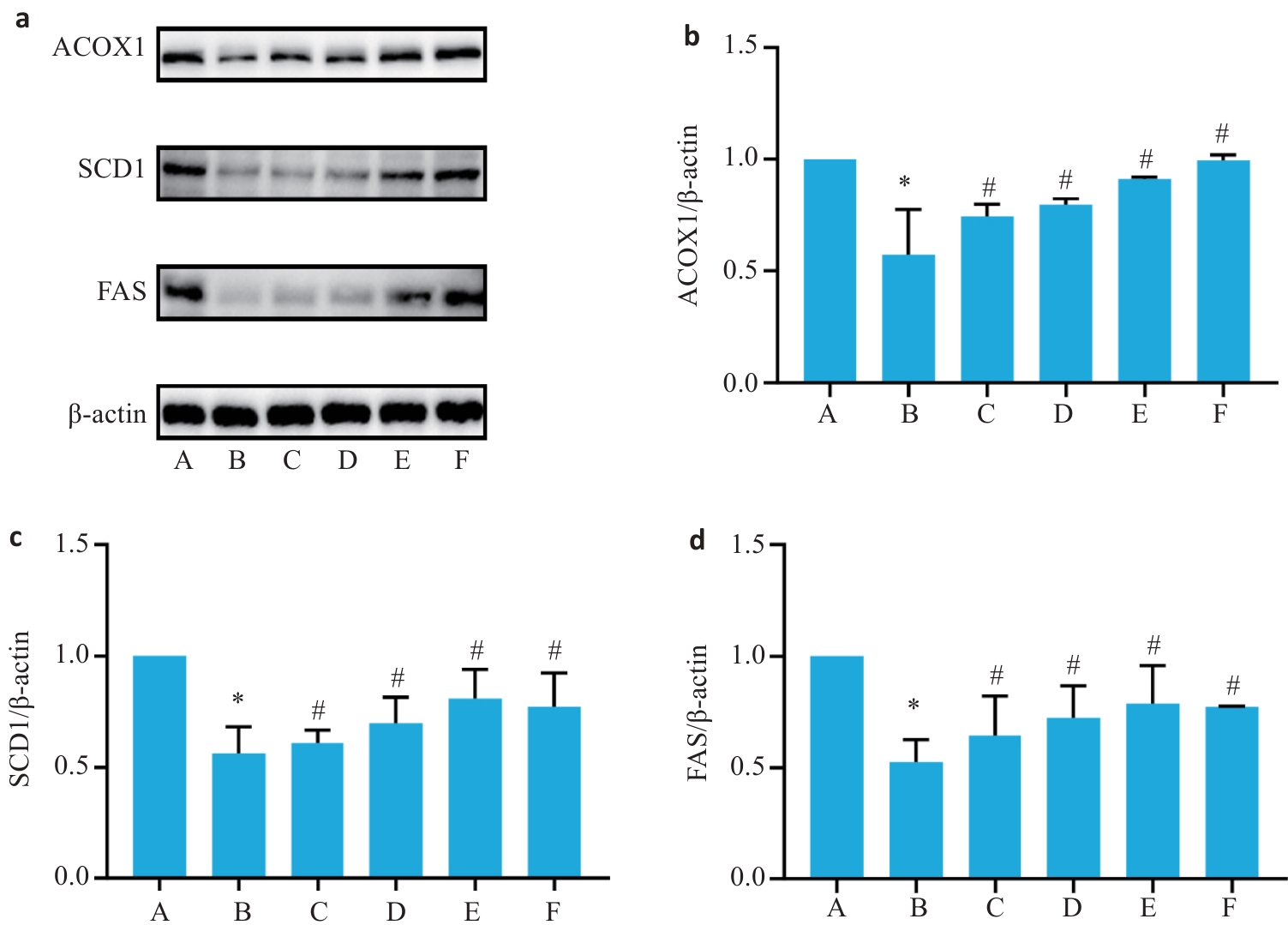
Fig.3 Expression levels of ACOX1, SCD1 and FAS protein in the liver tissue of the mice in each group (Mean±SD, n=6). a: Results of Western blotting of the proteins. b-d: Relative expressions of ACOX1, SCD1 and FAS proteins. *P<0.05 vs group A; #P<0.05 vs group B.
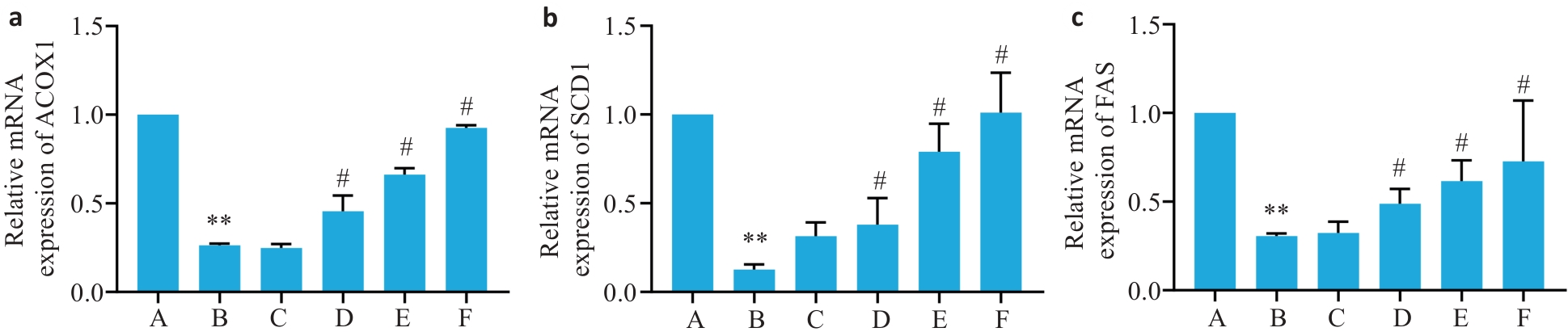
Fig.4 Expression levels of ACOX1 (a), SCD1 (b) and FAS (c) mRNA in the liver tissues of the mice (Mean±SD, n=6). **P<0.01 vs group A; #P<0.05 vs group B.
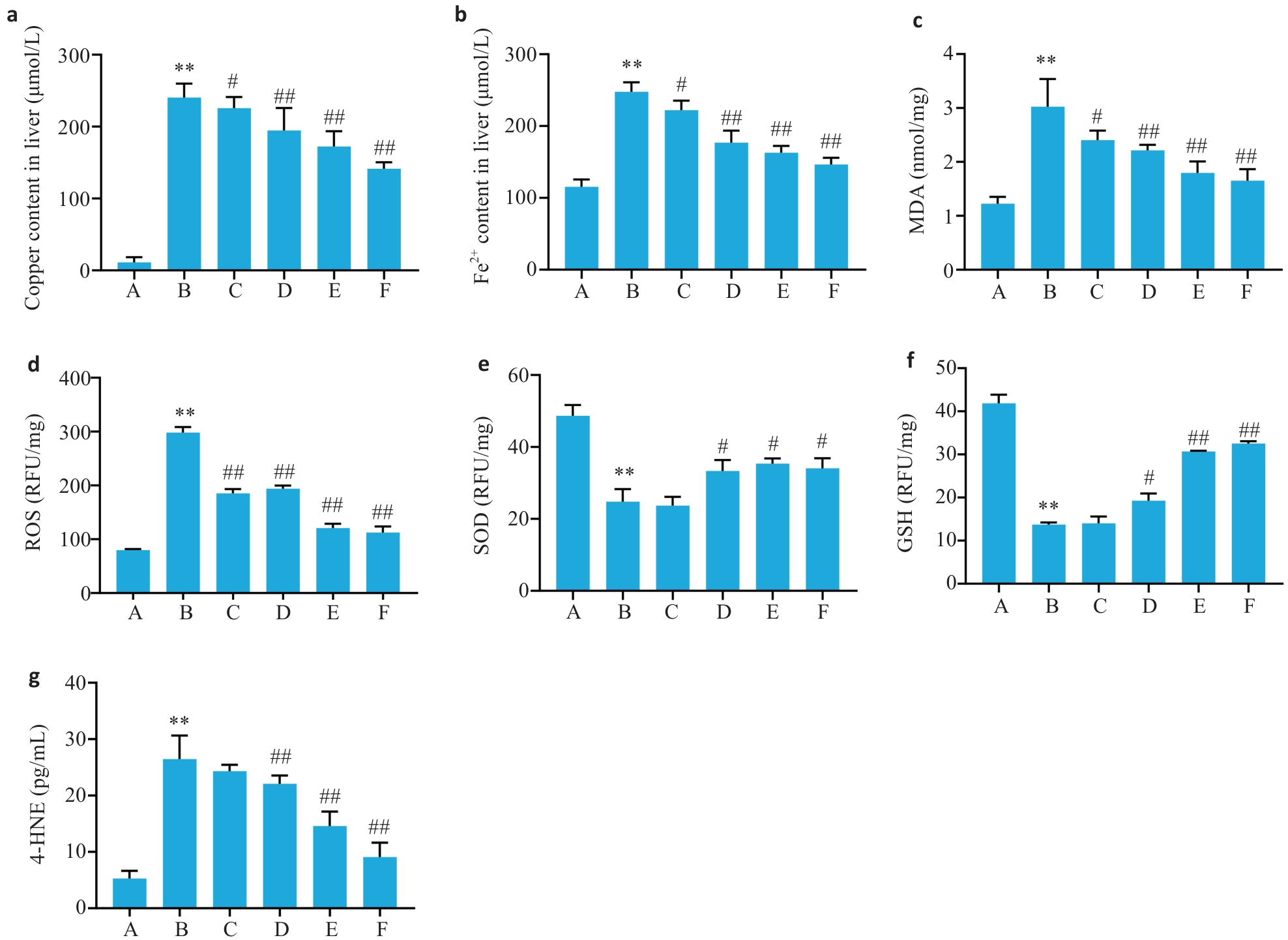
Fig.5 Levels of Fe2+ (a), Cu2+ (b), MDA (c), ROS (d), SOD (e), GSH (f) and 4-HNE (g) in the liver tissues of the tx-J mice (Mean±SD, n=6). **P<0.01 vs group A; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs group B.
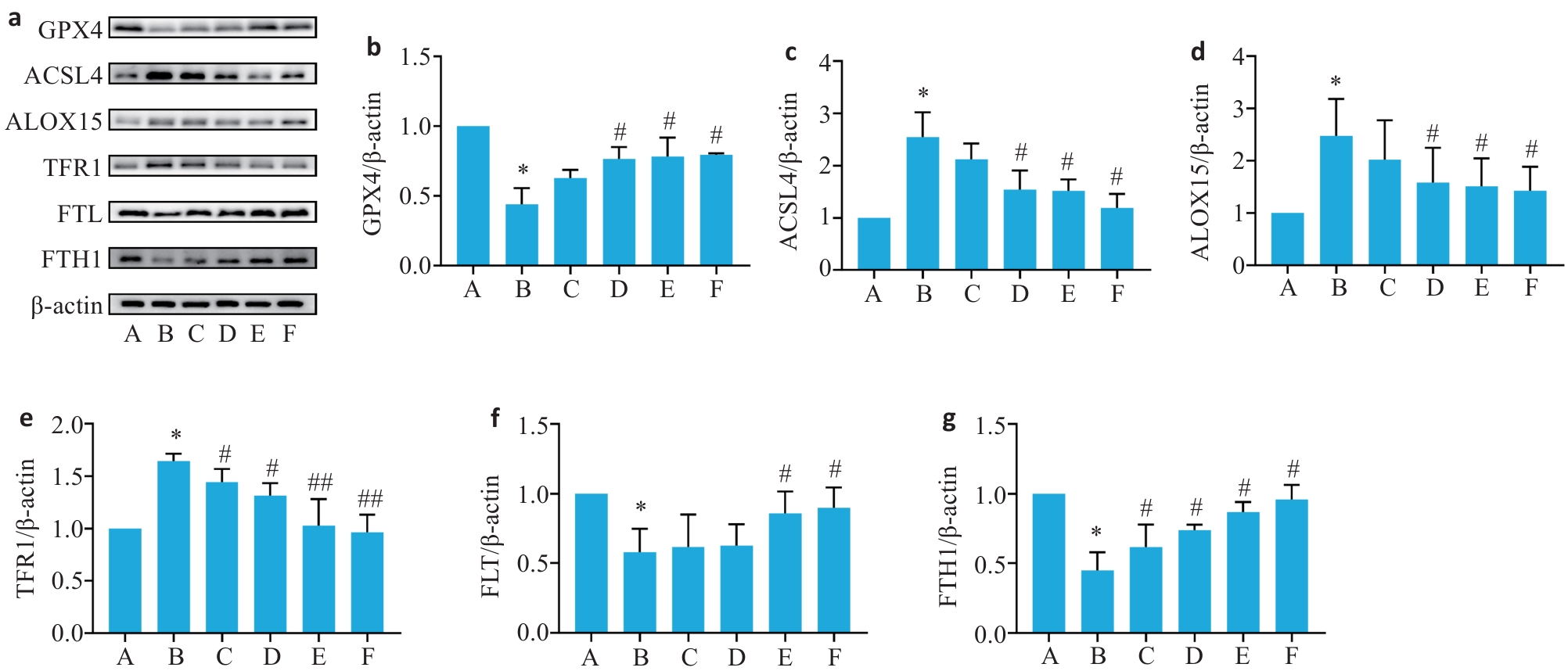
Fig.6 Relative expression levels of FTH1, FLT, TFR1, GPX4, ACSL4, and ALOX15 proteins in the liver tissues of the mice in each group. a: Protein bands detected by Western blotting. b-g: Relative expressions of GPX4, ACSL4, ALOX15, TFR1, FLT, and FTH1 proteins (Mean±SD, n=6) . *P<0.05 vs group A; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs group B.
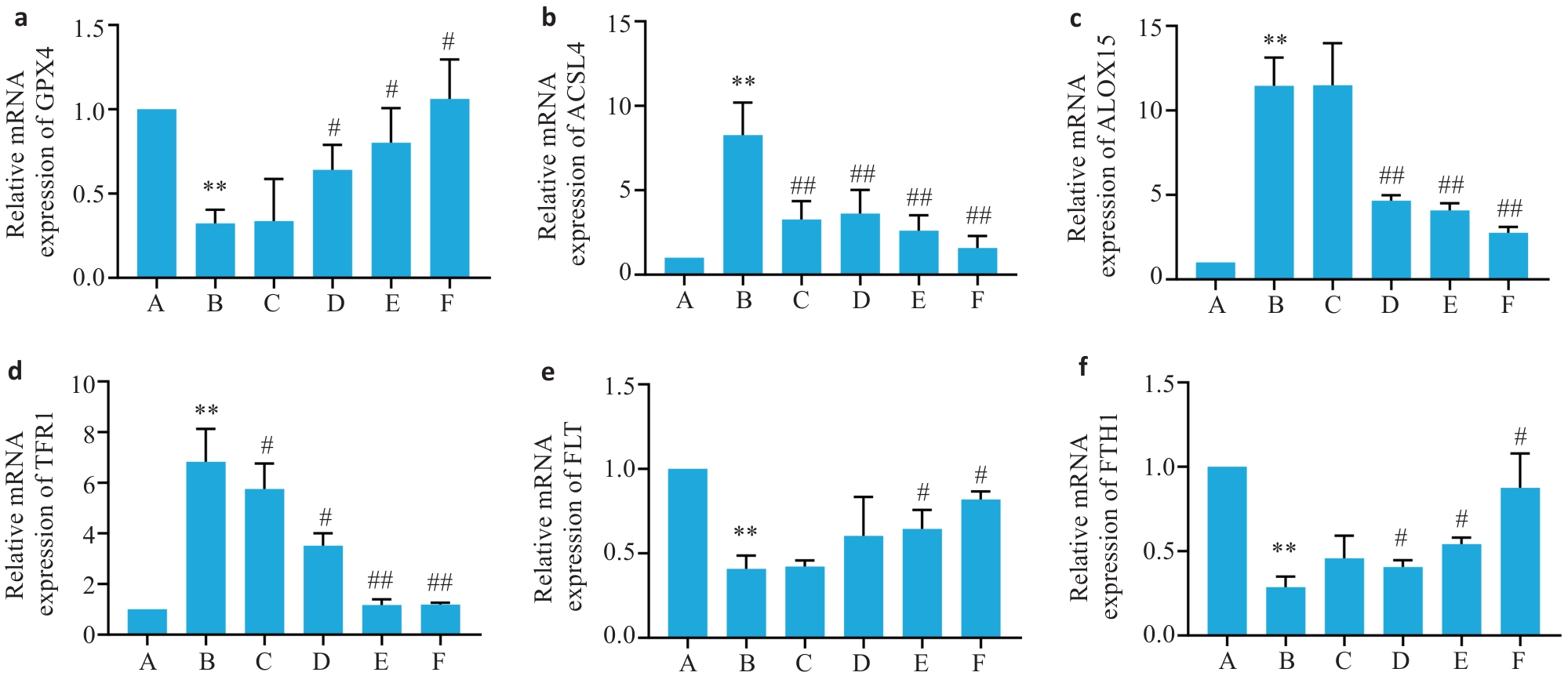
Fig.7 Relative mRNA expression levels of FTH1, FLT, TFR1, GPX4, ACSL4 and ALOX15 in the liver tissues of the mice in each group. a-f: Relative mRNA expression levels of GPX4, ACSL4, ALOX15, TFR1, FLT and FTH1 (Mean±SD, n=6). **P<0.01 vs group A; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs group B.
| [1] | Lucena-Valera A, Ruz-Zafra P, Ampuero J. Wilson's disease: overview[J]. Med Clin (Barc), 2023, 160(6): 261-7. doi:10.1016/j.medcle.2022.12.004 |
| [2] | Członkowska A, Litwin T, Dusek P, et al. Wilson disease[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2018, 4: 21. doi:10.1038/s41572-018-0018-3 |
| [3] | 文佩华, 汪世靖, 董健健, 等. 肝豆汤通过PPARγ-CD36通路调控Wilson病模型小鼠肝脏脂质代谢[J]. 安徽中医药大学学报, 2024, 43(6): 80-5. |
| [4] | Wu J, Wang Y, Jiang RT, et al. Ferroptosis in liver disease: new insights into disease mechanisms[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2021, 7(1): 276. doi:10.1038/s41420-021-00660-4 |
| [5] | 张榆雪, 蓝洁莹, 马昕怡, 等. 化橘红配方颗粒通过维持铁稳态并抑制脂质过氧化和铁死亡缓解斑马鱼脂肪性肝病[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2265-75. doi:10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.12.01 |
| [6] | Li Y, Du YH, Zhou YJ, et al. Iron and copper: critical executioners of ferroptosis, cuproptosis and other forms of cell death[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2023, 21(1): 327. doi:10.1186/s12964-023-01267-1 |
| [7] | 曾靖喻, 唐露露, 陈 洁, 等. 肝豆扶木汤对Wilson病小鼠肝纤维化和上皮-间质转化的干预作用[J]. 河北中医, 2024, 46(10): 1654-60. |
| [8] | 唐露露, 杨文明. 杨文明创肝豆扶木汤治疗肝豆状核变性肝纤维化经验[J]. 中医药临床杂志, 2021, 33(10): 1878-80. |
| [9] | Zhao CL, Chen J, Tian LW, et al. Gandouling ameliorates liver injury in Wilson’s disease through the inhibition of ferroptosis by regulating the HSF1/HSPB1 pathway[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2024, 28(17): e70018. doi:10.1111/jcmm.70018 |
| [10] | 郝文杰, 杨文明, 魏涛华, 等. 基于生物信息学和细胞实验探讨肝豆扶木汤调控铁死亡治疗肝豆状核变性的作用[J]. 中成药, 2023, 45(10): 3461-8. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2023.10.053 |
| [11] | Pang YL, Liu XJ, Wang X, et al. Edaravone modulates neuronal GPX4/ACSL4/5-LOX to promote recovery after spinal cord injury[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 10: 849854. doi:10.3389/fcell.2022.849854 |
| [12] | 杨 悦, 杨文明, 魏涛华, 等. 肝豆扶木汤通过JNK信号通路对Wilson病肝纤维化小鼠的干预作用[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2022, 28(12): 119-26. |
| [13] | 杨玉龙, 杨文明, 魏涛华, 等. 基于UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap-MS技术分析肝豆扶木汤中化学成分[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2024, 39(4): 2001-9. |
| [14] | 康 帅, 汪美霞, 陶 庄, 等. 基于网络药理学和临床研究探讨肝豆扶木颗粒调节肝豆状核变性肝纤维化的机制[J]. 中成药, 2024, 46(9): 3099-103. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2024.09.042 |
| [15] | 张孟莲, 张耀文, 唐林峰, 等. 天麻素通过调节SREBP1c信号通路抑制非酒精性脂肪肝[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2024, 30(11): 70-7. |
| [16] | Jackson SH, Devadas S, Kwon J, et al. T cells express a phagocyte-type NADPH oxidase that is activated after T cell receptor stimulation[J]. Nat Immunol, 2004, 5(8): 818-27. doi:10.1038/ni1096 |
| [17] | Liang DG, Minikes AM, Jiang XJ. Ferroptosis at the intersection of lipid metabolism and cellular signaling[J]. Mol Cell, 2022, 82(12): 2215-27. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2022.03.022 |
| [18] | Chen JR, Ding CF, Chen YH, et al. ACSL4 reprograms fatty acid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma via c-Myc/SREBP1 pathway[J]. Cancer Lett, 2021, 502: 154-65. doi:10.1038/s41389-020-0226-z |
| [19] | Zhang M, Zhou WH, Cao Y, et al. O-GlcNAcylation regulates long-chain fatty acid metabolism by inhibiting ACOX1 ubiquitination-dependent degradation[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2024, 266(Pt 2): 131151. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131151 |
| [20] | Ru Q, Li YS, Chen L, et al. Iron homeostasis and ferroptosis in human diseases: mechanisms and therapeutic prospects[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2024, 9(1): 271. doi:10.1038/s41392-024-01969-z |
| [21] | Xiao MQ, Zhong HQ, Xia L, et al. Pathophysiology of mitochondrial lipid oxidation: role of 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) and other bioactive lipids in mitochondria[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2017, 111: 316-27. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.04.363 |
| [22] | Kwiecien S, Jasnos K, Magierowski M, et al. Lipid peroxidation, reactive oxygen species and antioxidative factors in the pathogenesis of gastric mucosal lesions and mechanism of protection against oxidative stress-induced gastric injury[J]. J Physiol Pharmacol, 2014, 65(5): 613-22. |
| [23] | Fang YY, Chen XC, Tan QY, et al. Inhibiting ferroptosis through disrupting the NCOA4-FTH1 interaction: a new mechanism of action[J]. ACS Cent Sci, 2021, 7(6): 980-9. doi:10.1021/acscentsci.0c01592 |
| [24] | Feng HZ, Schorpp K, Jin J, et al. Transferrin receptor is a specific ferroptosis marker[J]. Cell Rep, 2020, 30(10): 3411-23. e7. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2020.02.049 |
| [25] | Dijkstra M, Vonk RJ, Kuipers F. How does copper get into bile? New insights into the mechanism(s) of hepatobiliary copper transport[J]. J Hepatol, 1996, 24(): 109-20. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(96)00447-x |
| [26] | Wang B, Wang XP. Does ceruloplasmin defend against neuro-degenerative diseases[J]? Curr Neuropharmacol, 2019, 17(6): 539-49. doi:10.2174/1570159x16666180508113025 |
| [27] | Cai HX, Cheng X, Wang XP. ATP7B gene therapy of autologous reprogrammed hepatocytes alleviates copper accumulation in a mouse model of Wilson's disease[J]. Hepatology, 2022, 76(4): 1046-57. doi:10.1002/hep.32484 |
| [28] | Xue Q, Yan D, Chen X, et al. Copper-dependent autophagic degradation of GPX4 drives ferroptosis[J]. Autophagy, 2023, 19(7): 1982-96. doi:10.1080/15548627.2023.2165323 |
| [29] | Wang SD, Liu ZJ, Geng JF, et al. An overview of ferroptosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2022, 153: 113374. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113374 |
| [30] | Gaschler MM, Stockwell BR. Lipid peroxidation in cell death[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2017, 482(3): 419-25. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.10.086 |
| [31] | Song SJ, Su ZY, Kon N, et al. ALOX5-mediated ferroptosis acts as a distinct cell death pathway upon oxidative stress in Huntington's disease[J]. Genes Dev, 2023, 37(5/6): 204-17. doi:10.1101/gad.350211.122 |
| [1] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | Anbang ZHANG, Xiuqi SUN, Bo PANG, Yuanhua WU, Jingyu SHI, Ning ZHANG, Tao YE. Electroacupuncture pretreatment alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting ferroptosis through the gut-brain axis and the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 911-920. |
| [3] | Linluo ZHANG, Changqing LI, Lingling HUANG, Xueping ZHOU, Yuanyuan LOU. Catalpol reduces liver toxicity of triptolide in mice by inhibiting hepatocyte ferroptosis through the SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway: testing the Fuzheng Zhidu theory for detoxification [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 810-818. |
| [4] | Chunfei JI, Zongchao ZUO, Jun WANG, Miaonan LI. N-acetylneuraminic acid promotes ferroptosis of H9C2 cardiomyocytes with hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inhibiting the Nrf2 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 72-79. |
| [5] | Kai CHEN, Zhaofei MENG, Jingting MIN, Jiahui WANG, Zhenghong LI, Qin GAO, Junfeng HU. Curcumin alleviates septic lung injury in mice by inhibiting TXNIP/TRX-1/GPX4-mediated ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1805-1813. |
| [6] | Mingzi OUYANG, Jiaqi CUI, Hui WANG, Zheng LIANG, Dajin PI, Liguo CHEN, Qianjun CHEN, Yingchao WU. Kaixinsan alleviates adriamycin-induced depression-like behaviors in mice by reducing ferroptosis in the prefrontal cortex [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1441-1449. |
| [7] | Yinliang ZHANG, Zetan LUO, Rui ZHAO, Na ZHAO, Zhidong XU, Di AO, Guyi CONG, Xinyu LIU, Hailun ZHENG. Sanguinarine induces ferroptosis of colorectal cancer cells by upregulating STUB1 and downregulating GPX4 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1537-1544. |
| [8] | Yuanguo WANG, Peng ZHANG. Ferroptosis suppressor genes are highly expressed in esophageal cancer to inhibit tumor cell ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1389-1396. |
| [9] | Huaxing HE, Lulin LIU, Yingyin LIU, Nachuan CHEN, Suxia SUN. Sodium butyrate and sorafenib synergistically inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma cells possibly by inducing ferroptosis through inhibiting YAP [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1425-1430. |
| [10] | Zhixian REN, Beixian ZHOU, Linxin WANG, Jing LI, Rongping ZHANG, Xiping PAN. Inhibitory effect of 5-hydroxy-6,7-dimethoxyflavone on H1N1 influenza virus-induced ferroptosis and inflammation in A549 cells and its possible mechanisms [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1070-1078. |
| [11] | Fangyuan ZHANG, Gang LIU. Dexmedetomidine inhibits ferroptosis of human renal tubular epithelial cells by activating the Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1135-1140. |
| [12] | Nan WANG, Bin SHI, Xiaolan MAN, Weichao WU, Jia CAO. High expression of fragile X mental retardation protein inhibits ferroptosis of colorectal tumor cells by activating the RAS/MAPK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 885-893. |
| [13] | LI Shuxian, YU Shuping, MU Yaming, WANG Kai, LIU Yu, ZHANG Meihua. Metformin ameliorates PM2.5- induced functional impairment of placental trophoblasts by inhibiting ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 437-446. |
| [14] | Hong KUANG, Wenhan CAI, Yiming LIU, Jiaxin WEN, Shuo TIAN, Zhiqiang XUE. High expression of SLC2A1 inhibits ferroptosis and promotes proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2404-2411. |
| [15] | Qi ZHANG, Zezhao JI, Abai JIASHAER∙, Youda WANG, ABUDUXUKUER∙Abulimiti. FER-1 inhibits methylglyoxal-induced ferroptosis in mouse alveolar macrophages in vitro [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2443-2448. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||