Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 810-818.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.04.16
Linluo ZHANG1,2( ), Changqing LI2, Lingling HUANG3, Xueping ZHOU2, Yuanyuan LOU1
), Changqing LI2, Lingling HUANG3, Xueping ZHOU2, Yuanyuan LOU1
Received:2024-12-03
Online:2025-04-20
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
Linluo ZHANG
E-mail:13674991073@163.com
Linluo ZHANG, Changqing LI, Lingling HUANG, Xueping ZHOU, Yuanyuan LOU. Catalpol reduces liver toxicity of triptolide in mice by inhibiting hepatocyte ferroptosis through the SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway: testing the Fuzheng Zhidu theory for detoxification[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 810-818.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.04.16
| Gene | Forward primer (5'-3') | Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
SLC7A11 FTH1 GPX4 GAPDH | GGCAGTTGCTGGGCTGATTTA CATCAACCGCCAGATCAACCT TGAAGATCCAACCCAAGGGC GGAAGCTTGTCATCAATGGAAATC | GATGACGAAGCCAATCCCTGT GCAAAGTTCTTCAAAGCCACATC GACGGTGTCCAAACTTGGTG TGATGACCCTTTTGGCTCCC |
Tab.1 Primers used for qRT-PCR
| Gene | Forward primer (5'-3') | Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
SLC7A11 FTH1 GPX4 GAPDH | GGCAGTTGCTGGGCTGATTTA CATCAACCGCCAGATCAACCT TGAAGATCCAACCCAAGGGC GGAAGCTTGTCATCAATGGAAATC | GATGACGAAGCCAATCCCTGT GCAAAGTTCTTCAAAGCCACATC GACGGTGTCCAAACTTGGTG TGATGACCCTTTTGGCTCCC |
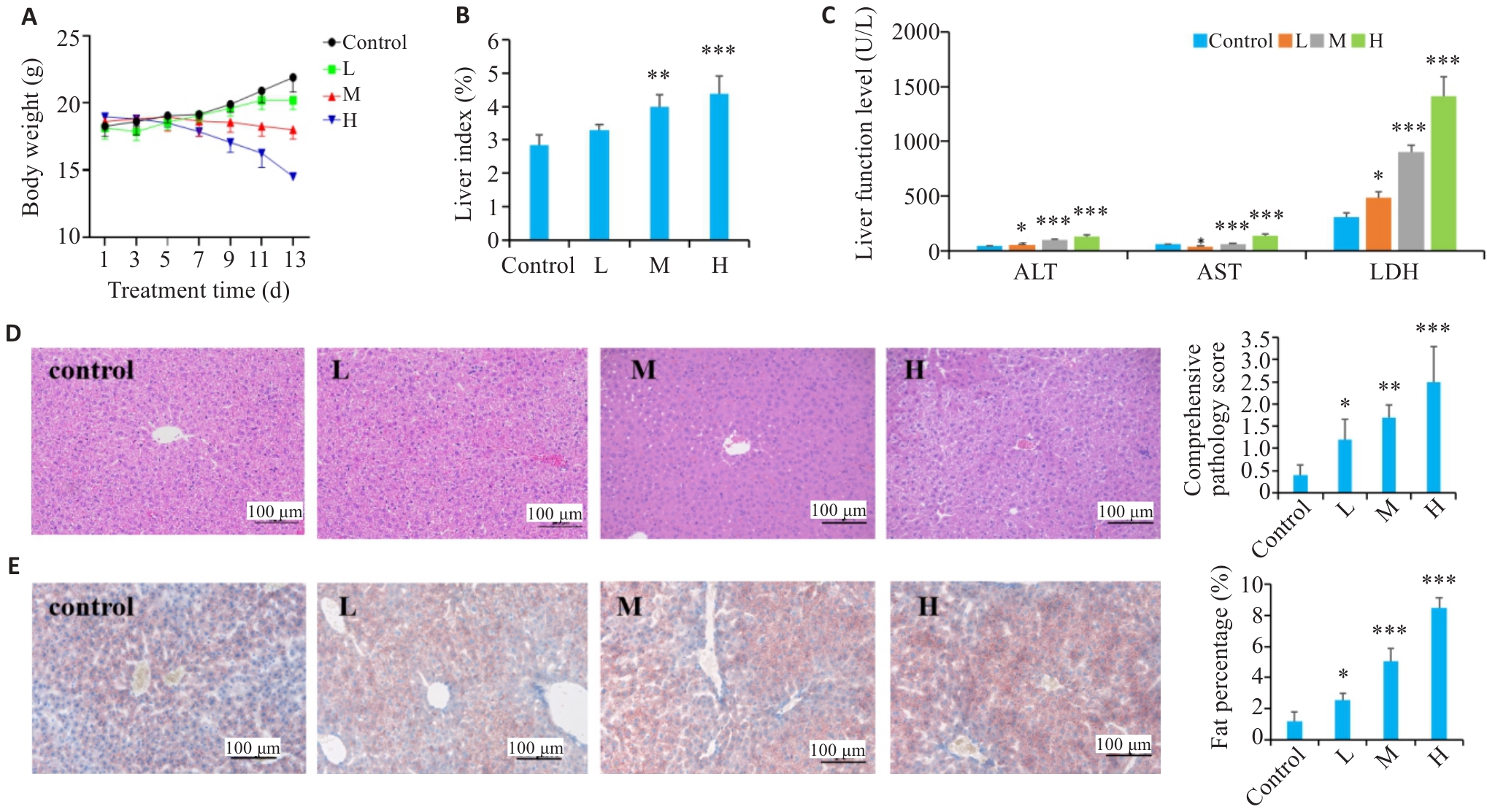
Fig.1 Triptolide-induced liver injury in C57BL/6J mice. A: Body weight changes of triptolide-treated mice. B: Liver index (%) changes. C: changes in ALT, AST and LDH levels. D: HE staining of the liver tissues. E: Oil Red O staining of the liver tissue. L, M and H: Low-, moderate-, and high-dose triptolide groups with daily dose of 0.3, 0.6 and 0.9 mg/kg, respectively. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=5). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Control group.
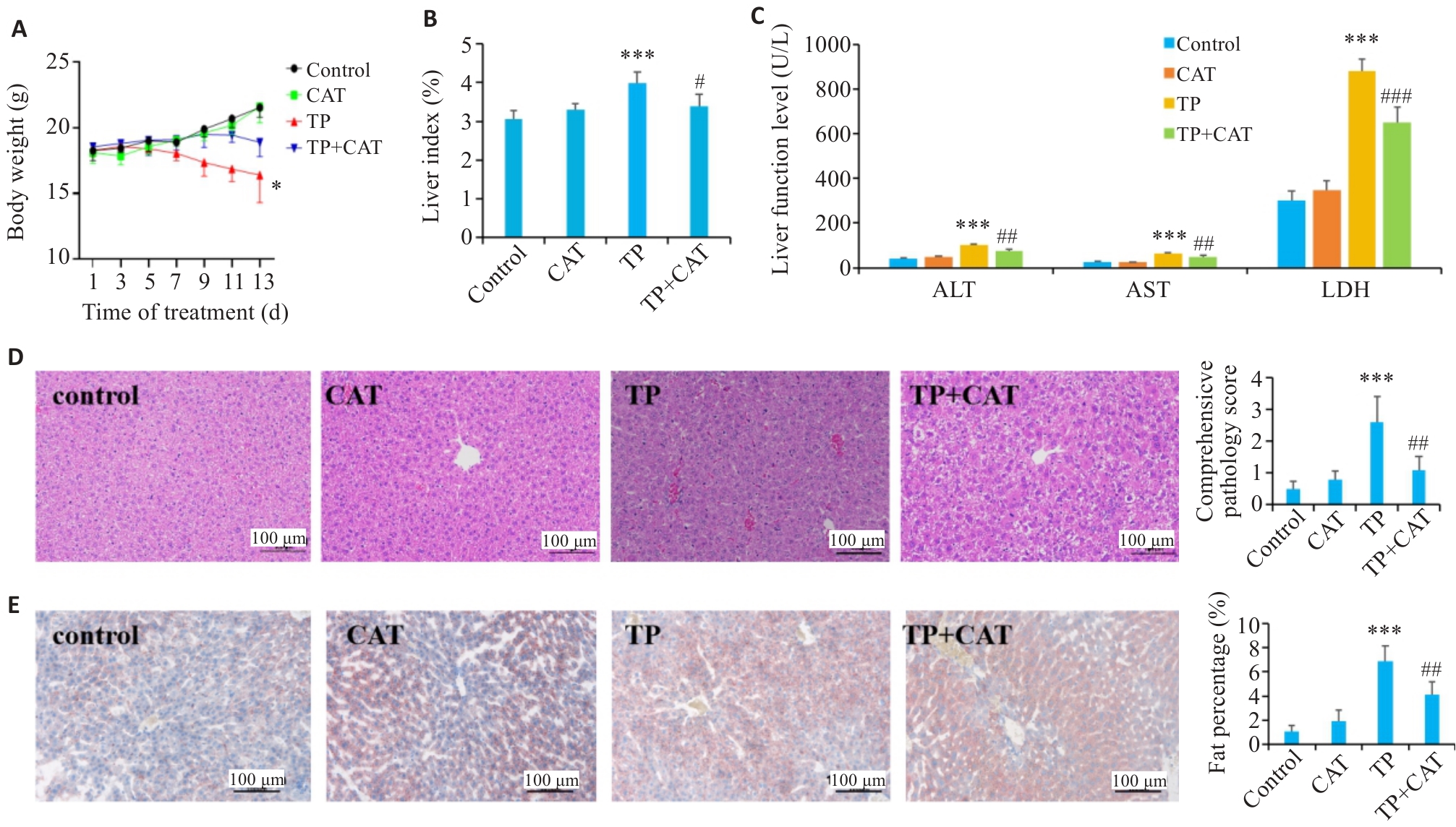
Fig.2 Catalpol alleviated triptolide-induced liver injury in C57BL/6J mice. A: Body weight changes. B: Liver function index (%). C: ALT, AST and LDH levels. D: HE staining results. E: Oil Red O staining results. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 vs Control group. #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs TP group.
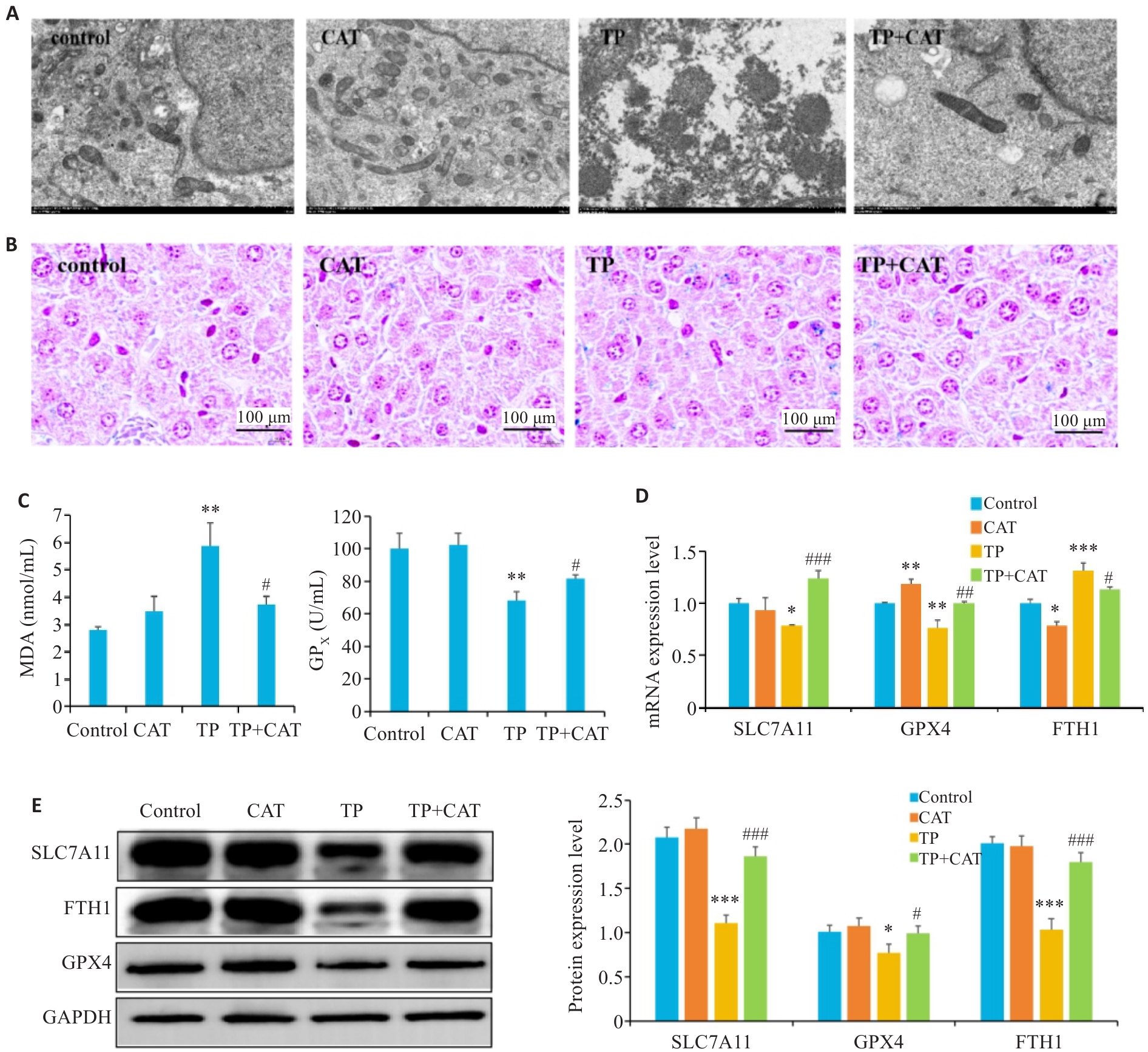
Fig.3 Catalpol alleviates triptolide-induced ferroptosis in C57BL/6J mice. A: Subcellular structure of mouse liver tissue (Original magnification: ×10000). B: PB staining (×100). C: MDA and GPX levels. D: mRNA levels of SLC7A11, FTH1 and GPX4 detected by qRT-PCR. E: Expressions of SLC7A11, FTH1 and GPX4 proteins detected by Western blotting. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Control group. #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs TP group.
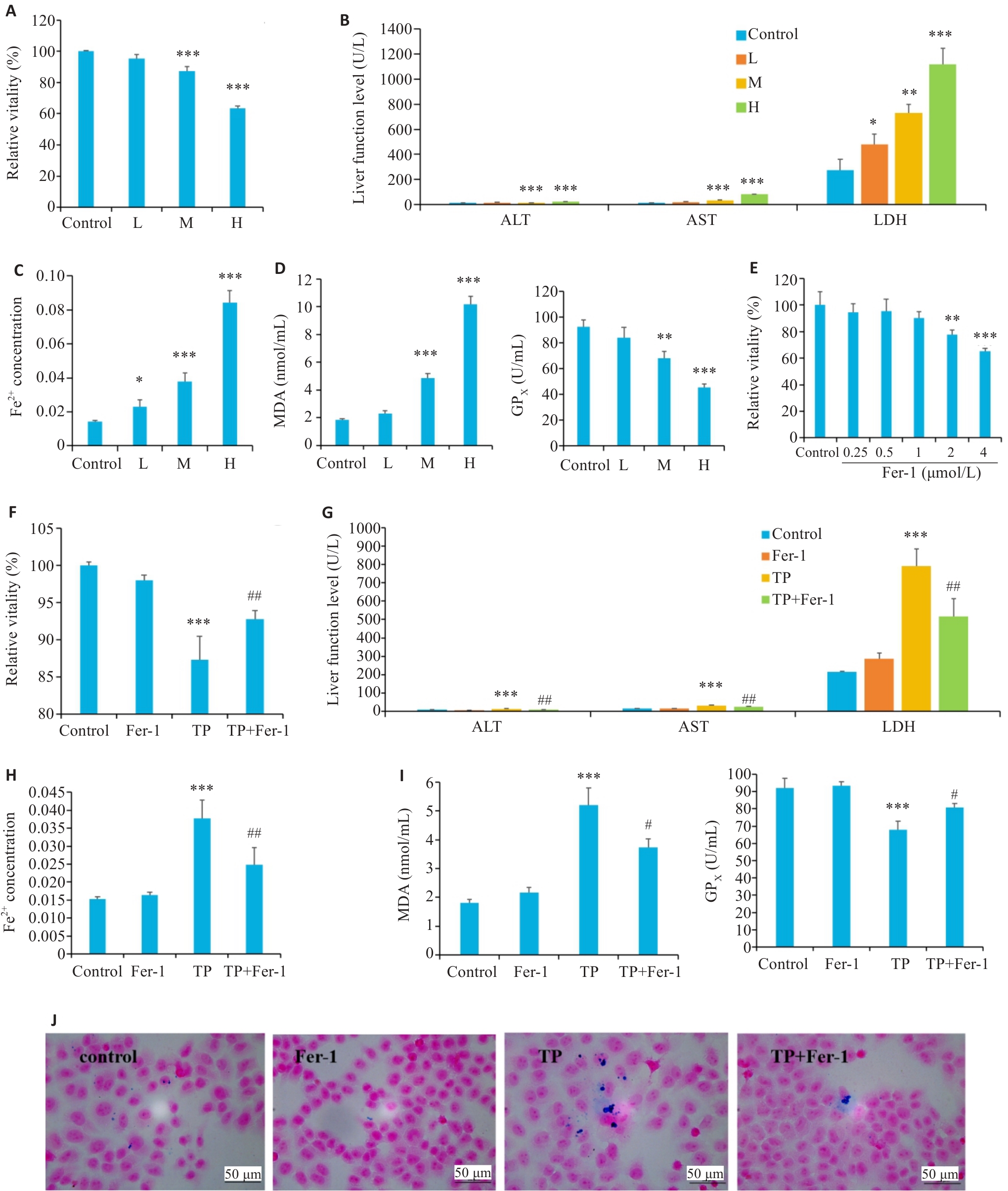
Fig.4 Inhibition of ferroptosis by Fer-1alleviates triptolide-induced injury in HL7702 cells. A: Cell viability changes (%). B: ALT, AST and LDH levels. C: Fe2+ concentration. D: MDA and GPX levels. E: Cell viability (%). F: Cell viability (%). G: ALT, AST and LDH indicators. H: Fe2+ concentration. I: MDA and GPX indicators. J: PB staining. L: Low-dose triptolide group (5 μg/L). M: Medium-dose triptolide group (20 μg/L). H: High-dose triptolide group (80 μg/L). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Control group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs TP group
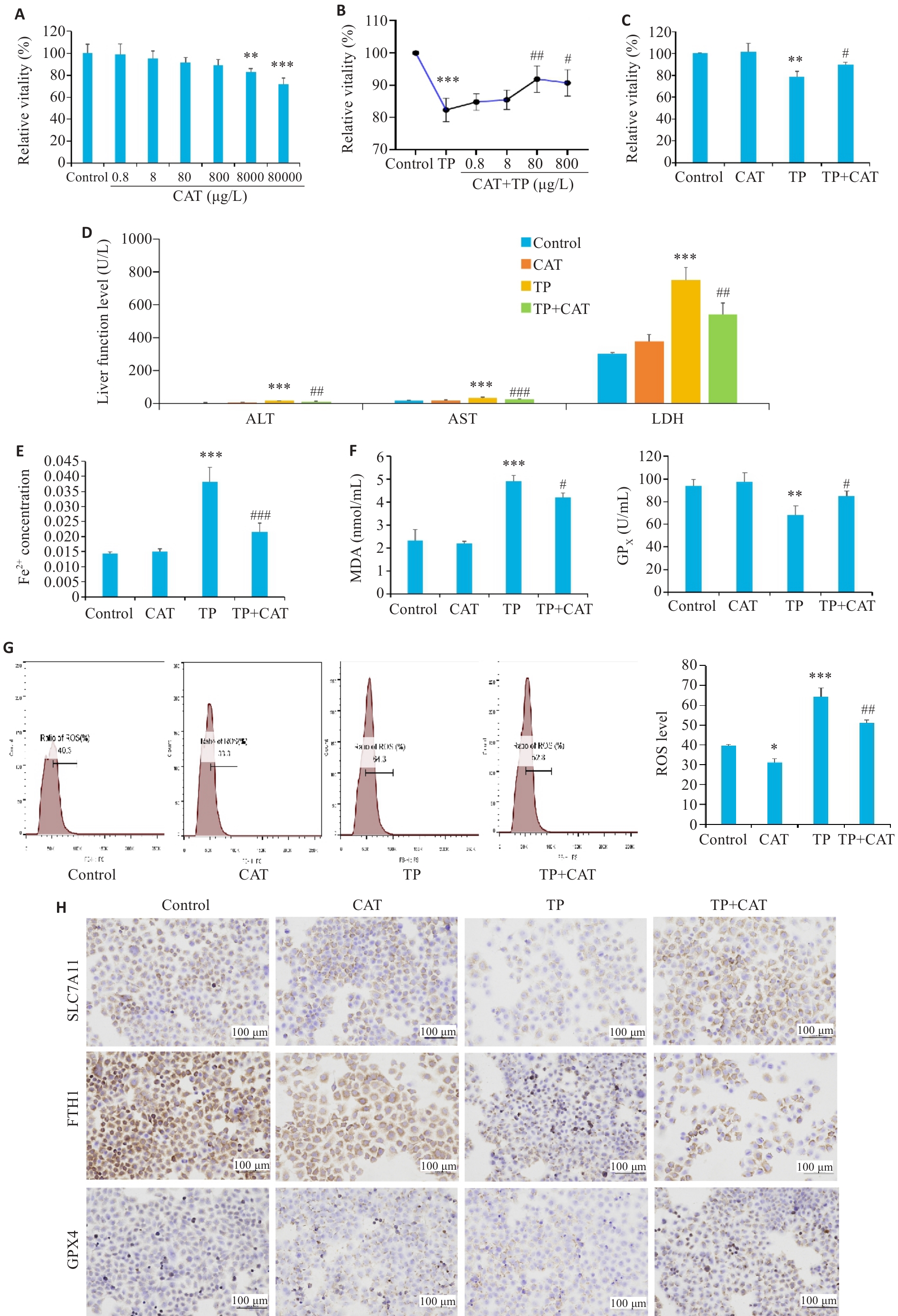
Fig.5 Catalpol reduces triptolide-induced HL7702 cell damage by inhibiting ferroptosis. A: Cell viability (%). B: Cell viability (%). C: Cell viability (%). D: ALT, AST and LDH indicators. E: Fe2+ concentration. F: MDA and GPX. G: The ratio of ROS (%). H: Immunohistochemistry of SLC7A11, FTH1 and GPX4. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Control group. #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs TP group.
| 1 | Gao J, Zhang Y, Liu X, et al. Triptolide: pharmacological spectrum, biosynthesis, chemical synthesis and derivatives[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(15): 7199-221. |
| 2 | Cui DX, Xu DQ, Yue SJ, et al. Recent advances in the pharmacological applications and liver toxicity of triptolide[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2023, 382: 110651. |
| 3 | Zhou X, Zhou Z, Jin M, et al. Clinical study of Qingluo Tongbi granules in treating 63 patients with rheumatoid arthritis of the type of Yin-deficiency and heat in collaterals[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2004, 24(2): 83-7. |
| 4 | 周学平, 周玲玲, 王 旭. 基于“异类相制” 理论探讨中药复方的配伍减毒作用[J]. 中医杂志, 2013, 54(4): 271-3. |
| 5 | Zhang L, Zhou J, Feng Z, et al. Qingluo Tongbi formula alleviates hepatotoxicity induced by Tripterygium wilfordii hook. F. by regulating excessive mitophagy through the PERK-ATF4 pathway[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 918466. |
| 6 | Capelletti MM, Manceau H, Puy H, et al. Ferroptosis in liver diseases: an overview[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(14): E4908. |
| 7 | Wu XH, Wang JM, Li BY, et al. Chlorogenic acid, rutin, and quercetin from Lysimachia christinae alleviate triptolide-induced multi-organ injury in vivo by modulating immunity and AKT/mTOR signal pathway to inhibit ferroptosis and apoptosis[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2023, 467: 116479. |
| 8 | Jaeschke H, Ramachandran A. Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: paradigm for understanding mechanisms of drug-induced liver injury[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2024, 19: 453-78. |
| 9 | 曹志文.甘草酸调控肝细胞线粒体稳态改善雷公藤甲素肝毒性的配伍解毒机制[D].中国中医科学院, 2024. |
| 10 | 刘春彤. 铁死亡在雷公藤甲素所致肝损伤中的作用[D]. 石家庄: 河北医科大学, 2021. |
| 11 | 杨 艳.雷公藤甲素诱导铁死亡致肝损伤的机制研究[D].长沙: 中南大学, 2023. |
| 12 | Guo L, Yang Y, Ma JT, et al. Triptolide induces hepatotoxicity by promoting ferroptosis through Nrf2 degradation[J]. Cell Biol Toxicol, 2024, 40(1): 94. |
| 13 | Zhang L, Li C, Fu L, et al. Protection of catalpol against triptolide-induced hepatotoxicity by inhibiting excessive autophagy via the PERK-ATF4-CHOP pathway[J]. PeerJ, 2022, 10: e12759. |
| 14 | Nie W, Zhu H, Sun X, et al. Catalpol attenuates hepatic glucose metabolism disorder and oxidative stress in triptolide-induced liver injury by regulating the SIRT1/HIF-1α pathway[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2024, 20(10): 4077-97. |
| 15 | Brunt EM. Grading and staging the histopathological lesions of chronic hepatitis: the Knodell histology activity index and beyond[J]. Hepatology, 2000, 31(1): 241-6. |
| 16 | 刘成海. 中草药相关肝损伤的研究进展与挑战[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40(8): 1505-11. |
| 17 | 马世武,刘成海,刘晓琰,等.中国药物性肝损伤诊治指南(2023年版)[J].胃肠病学, 2023, 28(07): 397-431. |
| 18 | Weaver RJ, Blomme EA, Chadwick AE, et al. Managing the challenge of drug-induced liver injury: a roadmap for the development and deployment of preclinical predictive models[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2020, 19(2): 131-48. |
| 19 | 李长青, 周学平. 中药复方配伍扶正制毒法精微探要[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2021, 36(12): 7093-5. |
| 20 | 张伯礼, 王永炎. 方剂关键科学问题的基础研究: 以组分配伍研制现代中药[J]. 中国天然药物, 2005, 3(5): 258-61. |
| 21 | Jia J, Chen J, Wang G, et al. Progress of research into the pharmacological effect and clinical application of the traditional Chinese medicine Rehmanniae Radix [J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2023, 168: 115809. |
| 22 | Jiang X, Stockwell BR, Conrad M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2021, 22(4): 266-82. |
| 23 | Ryan F, Blex C, Ngo TD, et al. Ferroptosis inhibitor improves outcome after early and delayed treatment in mild spinal cord injury[J]. Acta Neuropathol, 2024, 147(1): 106. |
| 24 | 张林落,苏 奔, 谢允超, 等.扶阳消阴辨治癌病探要[J]. 北京中医药大学学报, 2024, 47(05): 704-8. |
| 25 | 魏惠芳, 张露芬. 从整体观念谈中医“正气” 的特点[J]. 北京中医药大学学报, 2009, 32(7): 440-2. |
| 26 | 袁子阳, 张 艳, 张 伟, 等. 基于“虚气留滞”探讨铁死亡对慢性心力衰竭的调控机制及中医药防治进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2025, 31(02): 248-55. |
| 27 | 管留丹, 韩 捷. 基于“正邪理论”探讨铁死亡在胃癌发展中的作用[J/OL]. 中医学报, 2024 [2024-08-26]. |
| 28 | 王羽嘉, 付 蔷, 朱雪莹, 等. 基于铁死亡从 “阴阳气不相顺接” 论治肺癌[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2024, 39(7): 3345-8. |
| 29 | Shui SF, Zhao ZL, Wang H, et al. Non-enzymatic lipid peroxidation initiated by photodynamic therapy drives a distinct ferroptosis-like cell death pathway[J]. Redox Biol, 2021, 45: 102056. |
| 30 | Liu J, Tang DL, Kang R. Targeting GPX4 in ferroptosis and cancer: chemical strategies and challenges[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2024, 45(8): 666-70. |
| 31 | Chen X, Li J, Kang R, et al. Ferroptosis: machinery and regulation[J]. Autophagy, 2021, 17(9): 2054-81. |
| 32 | 郑明悦, 周红光, 庄育培, 等. 基于Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4信号通路探讨附芍地芩方抗结直肠癌作用机制[J]. 南京中医药大学学报, 2024, 40(5): 457-68. |
| 33 | Zhao X, Li X, Xu Y. Ferroptosis: a dual-edged sword in tumour growth[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14: 1330910. |
| 34 | Qiao YY, Su M, Zhao HF, et al. Targeting FTO induces colorectal cancer ferroptotic cell death by decreasing SLC7A11/GPX4 expression[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2024, 43(1): 108. |
| 35 | 钱婷婷, 邹 玲, 高 志, 等. 基于SLC 7A11/GPX4信号通路探讨“通督调神”针刺对抑郁症模型大鼠海马神经元铁死亡的影响[J/OL]. 中国针灸, 2024.[2024-12-16]. |
| 36 | 张榆雪, 蓝洁莹, 马昕怡, 等. 化橘红配方颗粒通过维持铁稳态并抑制脂质过氧化和铁死亡缓解斑马鱼脂肪性肝病[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12):2265-75. |
| 37 | Liu J, Kang R, Tang D. Signaling pathways and defense mechanisms of ferroptosis[J]. Febs J, 2022, 289(22): 7038-50. |
| 38 | 王伟艳, 刘 珊, 李会芳, 等. 基于谷胱甘肽/谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4轴探讨雷公藤甲素引起肝细胞铁死亡的作用机制[J]. 中草药, 2024, 55(9): 2967-75. |
| 39 | Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death[J]. Cell, 2012, 149(5): 1060-72. |
| 40 | 蔡华俊, 陈致岐, 胡文婷, 等. 鼠曲草总黄酮通过激活Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX-4信号通路抑制肝细胞铁死亡缓解对乙酰氨基酚诱导的小鼠急性肝损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2201-8. |
| [1] | Chunfei JI, Zongchao ZUO, Jun WANG, Miaonan LI. N-acetylneuraminic acid promotes ferroptosis of H9C2 cardiomyocytes with hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inhibiting the Nrf2 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 72-79. |
| [2] | Kai CHEN, Zhaofei MENG, Jingting MIN, Jiahui WANG, Zhenghong LI, Qin GAO, Junfeng HU. Curcumin alleviates septic lung injury in mice by inhibiting TXNIP/TRX-1/GPX4-mediated ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1805-1813. |
| [3] | Mingzi OUYANG, Jiaqi CUI, Hui WANG, Zheng LIANG, Dajin PI, Liguo CHEN, Qianjun CHEN, Yingchao WU. Kaixinsan alleviates adriamycin-induced depression-like behaviors in mice by reducing ferroptosis in the prefrontal cortex [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1441-1449. |
| [4] | Yinliang ZHANG, Zetan LUO, Rui ZHAO, Na ZHAO, Zhidong XU, Di AO, Guyi CONG, Xinyu LIU, Hailun ZHENG. Sanguinarine induces ferroptosis of colorectal cancer cells by upregulating STUB1 and downregulating GPX4 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1537-1544. |
| [5] | Yuanguo WANG, Peng ZHANG. Ferroptosis suppressor genes are highly expressed in esophageal cancer to inhibit tumor cell ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1389-1396. |
| [6] | Huaxing HE, Lulin LIU, Yingyin LIU, Nachuan CHEN, Suxia SUN. Sodium butyrate and sorafenib synergistically inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma cells possibly by inducing ferroptosis through inhibiting YAP [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1425-1430. |
| [7] | Zhixian REN, Beixian ZHOU, Linxin WANG, Jing LI, Rongping ZHANG, Xiping PAN. Inhibitory effect of 5-hydroxy-6,7-dimethoxyflavone on H1N1 influenza virus-induced ferroptosis and inflammation in A549 cells and its possible mechanisms [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1070-1078. |
| [8] | Fangyuan ZHANG, Gang LIU. Dexmedetomidine inhibits ferroptosis of human renal tubular epithelial cells by activating the Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1135-1140. |
| [9] | Nan WANG, Bin SHI, Xiaolan MAN, Weichao WU, Jia CAO. High expression of fragile X mental retardation protein inhibits ferroptosis of colorectal tumor cells by activating the RAS/MAPK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 885-893. |
| [10] | LI Shuxian, YU Shuping, MU Yaming, WANG Kai, LIU Yu, ZHANG Meihua. Metformin ameliorates PM2.5- induced functional impairment of placental trophoblasts by inhibiting ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 437-446. |
| [11] | Hong KUANG, Wenhan CAI, Yiming LIU, Jiaxin WEN, Shuo TIAN, Zhiqiang XUE. High expression of SLC2A1 inhibits ferroptosis and promotes proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2404-2411. |
| [12] | Qi ZHANG, Zezhao JI, Abai JIASHAER∙, Youda WANG, ABUDUXUKUER∙Abulimiti. FER-1 inhibits methylglyoxal-induced ferroptosis in mouse alveolar macrophages in vitro [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2443-2448. |
| [13] | Peipei ZHAO, Zhigang ZHOU, Yuanyuan YANG, Shusheng HUANG, Yixuan TU, Jian TU. Ferroptosis inducer Erastin inhibits proliferation of liver cancer cells in vitro by down-regulating ACSL4 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2131-2136. |
| [14] | Huajun CAI, Zhiqi CHEN, Wenting HU, Wei TAN, Hao WU, Chao WANG. Total flavonoids of Salvia miltiorrhiza alleviate acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in mice by suppressing hepatocyte ferroptosis via activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2201-2208. |
| [15] | Qinjun YANG, Hui WANG, Shuyu XU, Cheng YANG, Huanzhang DING, Di WU, Jie ZHU, Jiabing TONG, Zegeng LI. Shenqi Tiaoshen Formula alleviates airway inflammation in rats with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and kidney qi deficiency syndrome by inhibiting ferroptosis via regulating the Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(10): 1937-1946. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||