Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 799-809.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.04.15
Previous Articles Next Articles
Tianli SONG1,2( ), Yimin WANG1,2, Tong SUN3, Xu LIU1, Sheng HUANG1,2(
), Yimin WANG1,2, Tong SUN3, Xu LIU1, Sheng HUANG1,2( ), Yun RAN3(
), Yun RAN3( )
)
Received:2024-06-26
Online:2025-04-20
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
Sheng HUANG, Yun RAN
E-mail:boiler001@126.com;hs19870604@163.com;35540785@qq.com
Tianli SONG, Yimin WANG, Tong SUN, Xu LIU, Sheng HUANG, Yun RAN. Zheng Gan Decoction inhibits diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats by activating the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 799-809.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.04.15
| Name of medicine | Drug specification (g/bag) | Mass of corresponding tablets (g) | Mass of drinkable tablets of punch (g) | Drug lot number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huangqi | 4.00 | 10.0 | 2.5 | A2092661 |
| Danshen | 2.50 | 5.0 | 2.0 | A2080131 |
| Baihuasheshecao | 2.83 | 15.0 | 15.3 | A301B311 |
| Gouqizi | 4.17 | 5.0 | 1.2 | A2080181 |
| Biejia | 1.67 | 10.0 | 6.0 | A2120021 |
| Nvzhenzi | 2.31 | 6.0 | 2.6 | A2021132 |
| Sanlen | 0.56 | 5.0 | 9.0 | A209A321 |
| Ezhu | 0.63 | 5.0 | 8.0 | A210B515 |
| Chognlou | 1.43 | 5.0 | 3.5 | A2072911 |
| Chuangxiong | 1.67 | 5.0 | 1.0 | A2039431 |
Tab.1 Formulation of Zheng Gan Decoction Granules
| Name of medicine | Drug specification (g/bag) | Mass of corresponding tablets (g) | Mass of drinkable tablets of punch (g) | Drug lot number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huangqi | 4.00 | 10.0 | 2.5 | A2092661 |
| Danshen | 2.50 | 5.0 | 2.0 | A2080131 |
| Baihuasheshecao | 2.83 | 15.0 | 15.3 | A301B311 |
| Gouqizi | 4.17 | 5.0 | 1.2 | A2080181 |
| Biejia | 1.67 | 10.0 | 6.0 | A2120021 |
| Nvzhenzi | 2.31 | 6.0 | 2.6 | A2021132 |
| Sanlen | 0.56 | 5.0 | 9.0 | A209A321 |
| Ezhu | 0.63 | 5.0 | 8.0 | A210B515 |
| Chognlou | 1.43 | 5.0 | 3.5 | A2072911 |
| Chuangxiong | 1.67 | 5.0 | 1.0 | A2039431 |
| Group | Liver index (%) | Spleen index (%) | Thymus index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal control | 2.34±0.14## | 0.16±0.02## | 0.05±0.01 |
| Model | 8.23±1.32** | 0.47±0.12** | 0.03±0.03* |
| Low dose | 7.95±0.96** | 0.53±0.18** | 0.05±0.02 |
| Middle dose | 5.97±0.55* | 0.42±0.07 | 0.06±0.02## |
| High dose | 5.45±0.55# | 0.31±0.08# | 0.05±0.02# |
| Active control | 6.27±0.55* | 0.44±0.05 | 0.05±0.01 |
Tab.2 Liver index, spleen index and thymus index of the rats in each group
| Group | Liver index (%) | Spleen index (%) | Thymus index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal control | 2.34±0.14## | 0.16±0.02## | 0.05±0.01 |
| Model | 8.23±1.32** | 0.47±0.12** | 0.03±0.03* |
| Low dose | 7.95±0.96** | 0.53±0.18** | 0.05±0.02 |
| Middle dose | 5.97±0.55* | 0.42±0.07 | 0.06±0.02## |
| High dose | 5.45±0.55# | 0.31±0.08# | 0.05±0.02# |
| Active control | 6.27±0.55* | 0.44±0.05 | 0.05±0.01 |
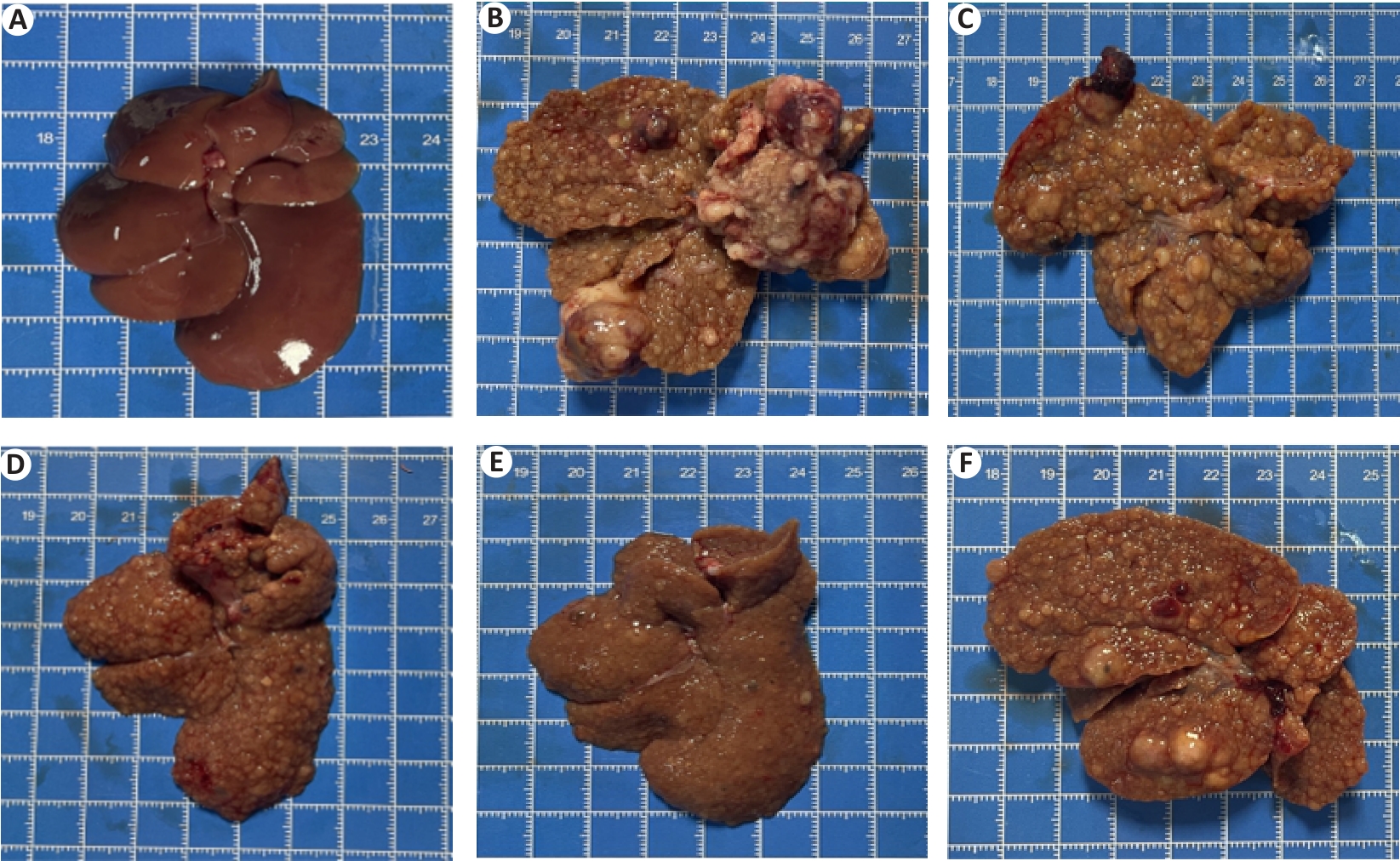
Fig.5 Histomorphologic changes of rat livers in each group. A: Normal control group. B: Model. C: Low dose group. D: Middle dose group. E: High dose group. F: Positive control group.
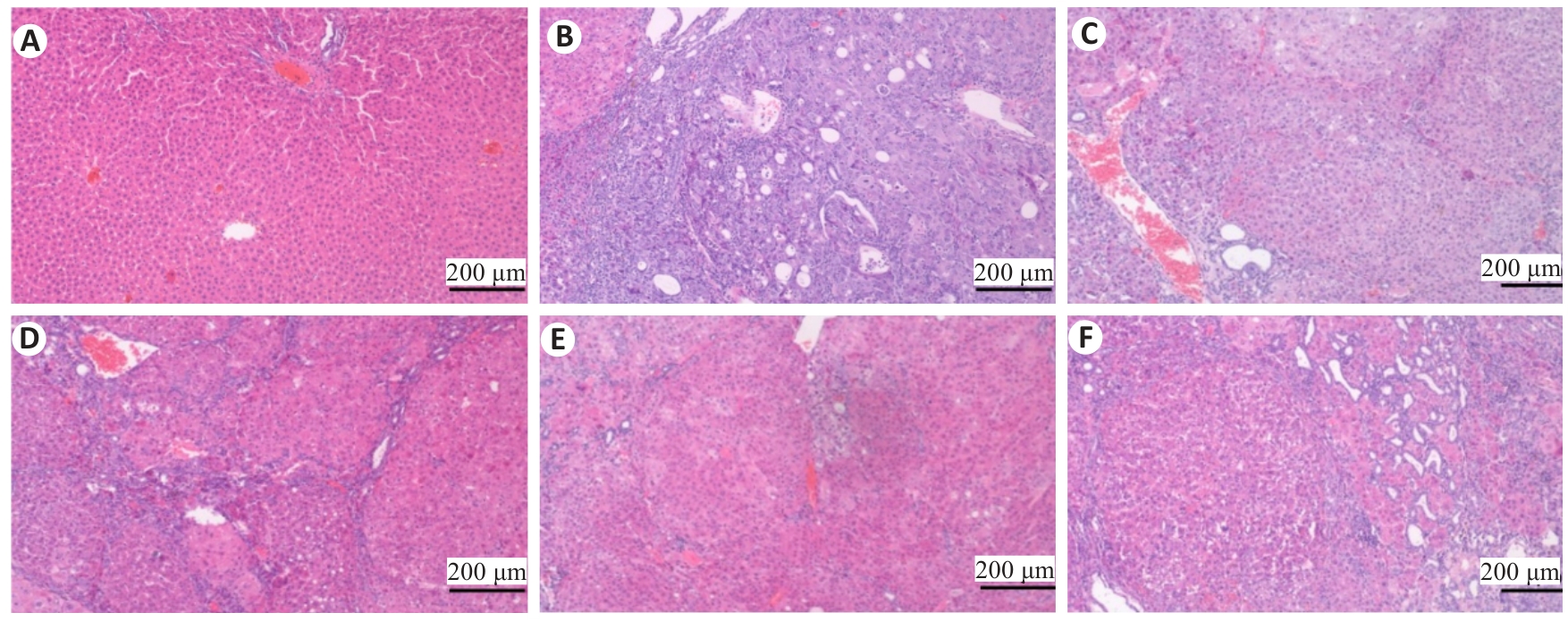
Fig.6 Effects of Zheng Gan Decoction on histopathological changes in the liver of the rats in each group (HE staining).A: Normal control group. B: Model. C: Low dose group. D: Middle dose group. E: High dose group. F: Positive control group.

Fig.7 Effect of Zheng Gan Decoction on YAP expression in liver tissues of rats with DEN-induced HCC (immunohistochemistry). A: Normal control group. B: Model. C: Low dose group. D: Middle dose group. E: High dose group. F: Positive control group.
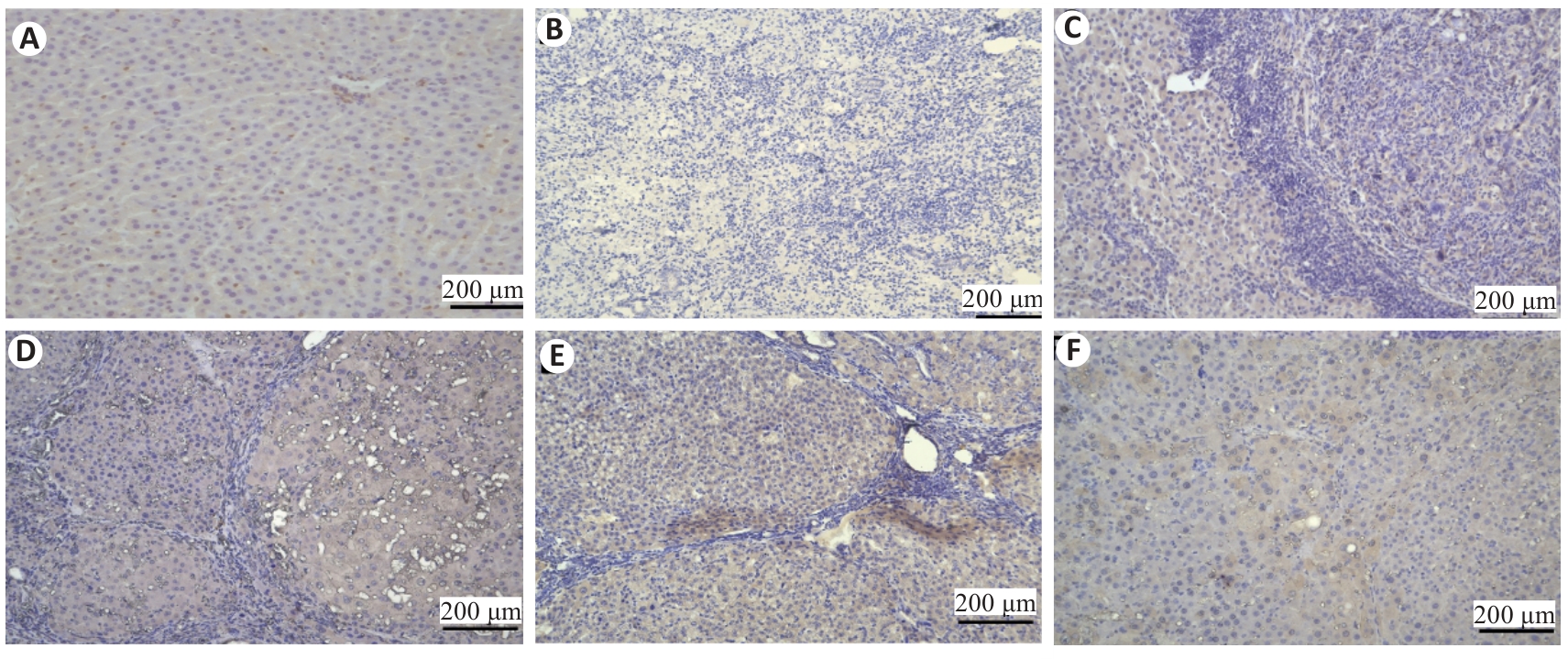
Fig.8 Effect of Zheng Gan Decoction on YAP expression in liver tissues of rats with DEN-induced HCC (immunohistochemistry0). A: Normal control group. B: Model. C: Low dose group. D: Middle dose group. E: High dose group. F: Positive control group.
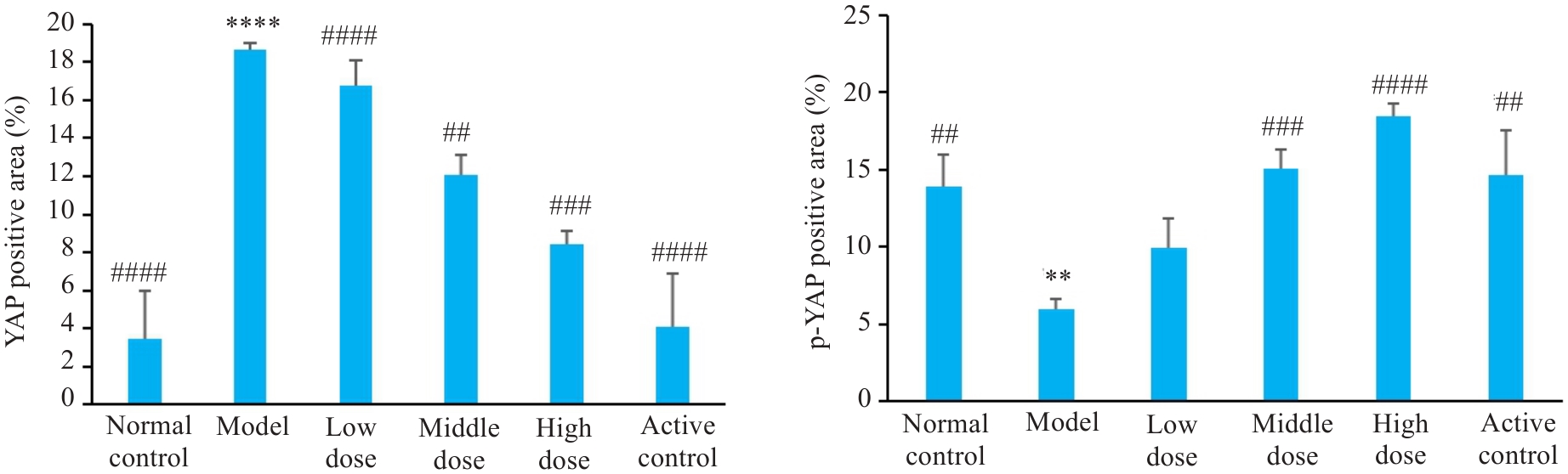
Fig. 9 Comparison of immunohistochemically detected YAP expression in rat liver tissue among the groups. **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001 vs control group; ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001, ####P<0.0001 vs model group.
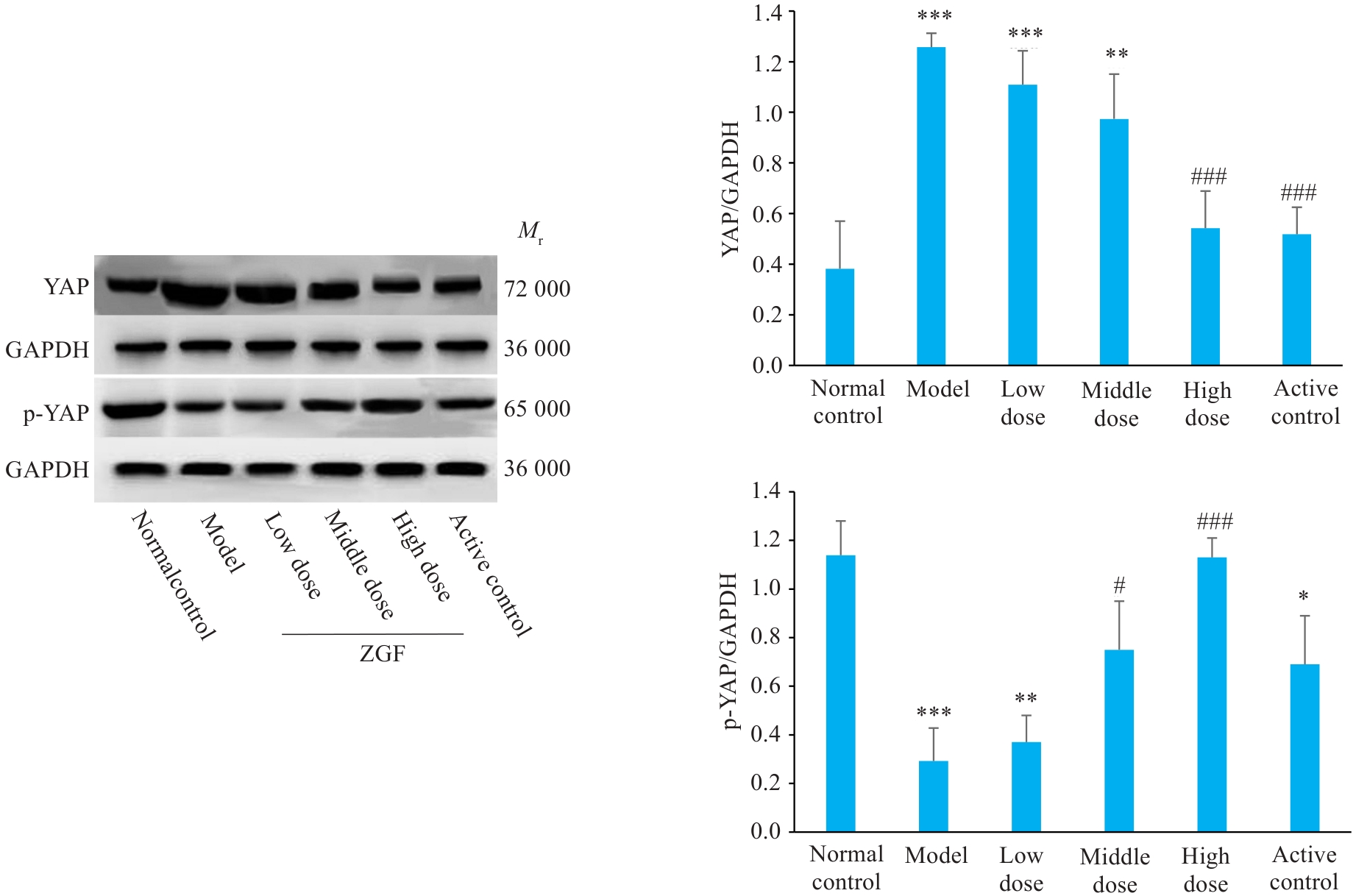
Fig. 10 Effect of Zheng Gan Decoction on expression levels of YAP and its phosphorylated proteins in the liver tissues of rats with DEN-induced HCC. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs control group; #P<0.05, ###P<0.001 vs model group.
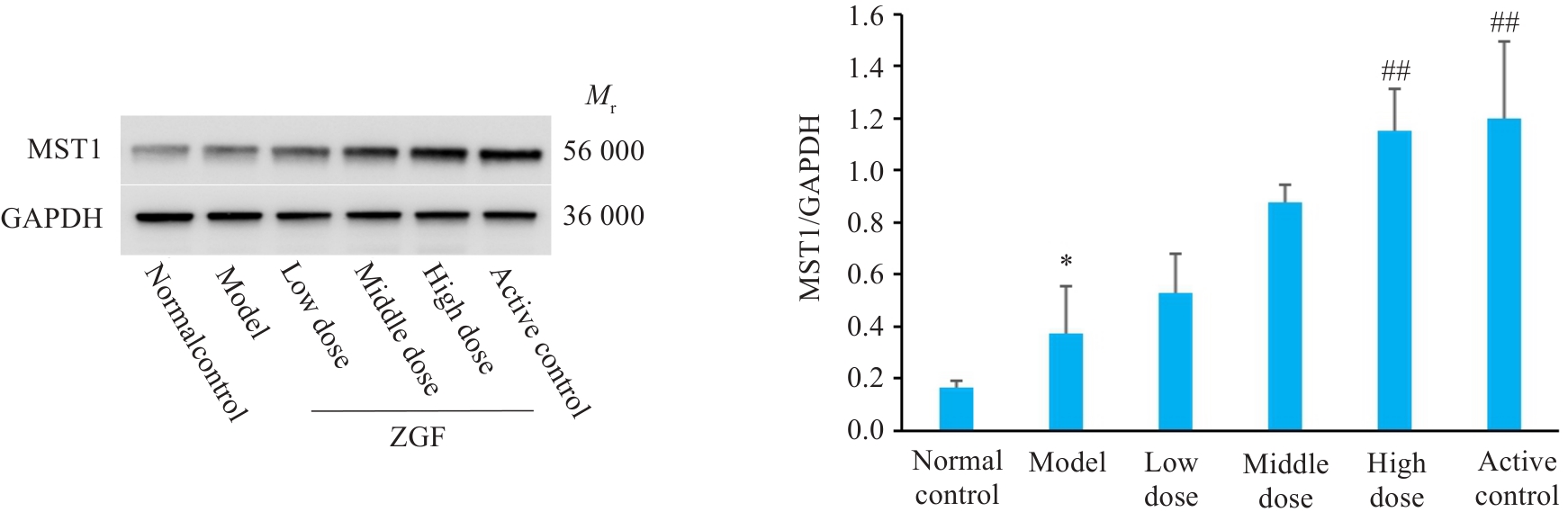
Fig.11 Effect of Zheng Gan Decoction on MST1 protein levels in liver tissues of rats with DEN-induced HCC. *P<0.05 vs control group; ##P<0.01 vs model group.
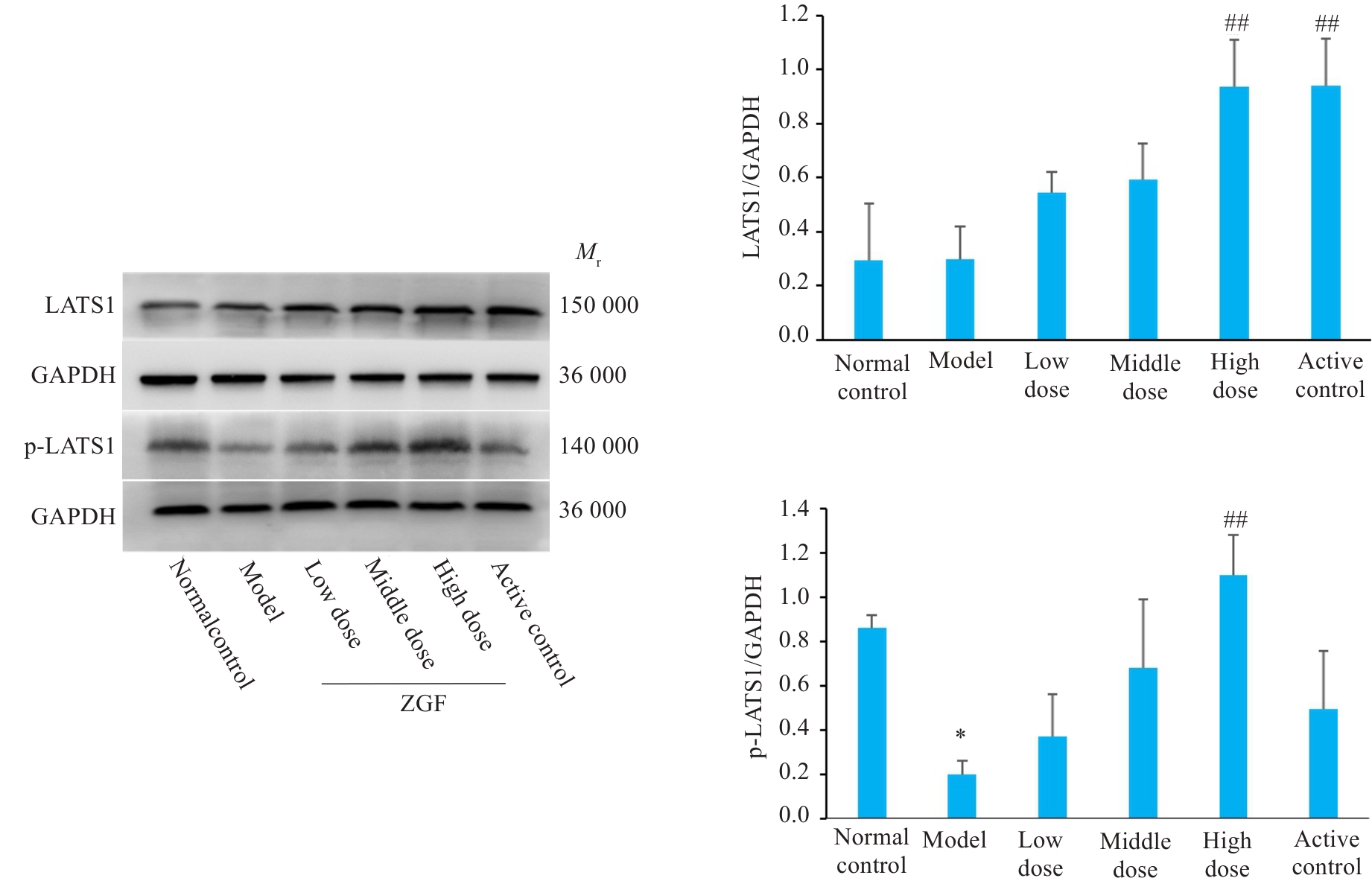
Fig.12 Effect of Zheng Gan Decoction on expression levels of LATS1 and its phosphorylated proteins in liver tissues of rats with DEN-induced HCC. *P<0.05 vs control group; ##P<0.01 vs model group.
| 1 | 邱海波, 曹素梅, 徐瑞华. 基于2020年全球流行病学数据分析中国癌症发病率、死亡率和负担的时间趋势及与美国和英国数据的比较[J]. 癌症, 2022, 41(4): 165-77. |
| 2 | Cao MM, Li H, Sun DQ, et al. Current cancer burden in China: epidemiology, etiology, and prevention[J]. Cancer Biol Med, 2022, 19(8): 1121-38. |
| 3 | Anwanwan D, Singh SK, Singh S, et al. Challenges in liver cancer and possible treatment approaches[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2020, 1873(1): 188314. |
| 4 | Sia D, Villanueva A, Friedman SL, et al. Liver cancer cell of origin, molecular class, and effects on patient prognosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2017, 152(4): 745-61. |
| 5 | Hernández-Aquino E, Muriel P. Beneficial effects of naringenin in liver diseases: Molecular mechanisms[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2018, 24(16): 1679-707. |
| 6 | Li YT, Zhang RH, Xu Z, et al. Advances in nanoliposomes for the diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer[J]. Int J Nanomedicine, 2022, 17: 909-25. |
| 7 | Chen WQ, Chiang CL, Dawson LA. Efficacy and safety of radiotherapy for primary liver cancer[J]. Chin Clin Oncol, 2021, 10(1): 9. |
| 8 | Demir T, Lee SS, Kaseb AO. Systemic therapy of liver cancer[J]. Adv Cancer Res, 2021, 149: 257-94. |
| 9 | Han QH, Du LZ, Zhu LL, et al. Review of the application of dual drug delivery nanotheranostic agents in the diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(20): 7004. |
| 10 | Xiang Z, He CY, Lu D, et al. Editorial: liver transplantation for liver cancer in the era of transplant oncology: accurate diagnosis and treatment[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1276566. |
| 11 | He L, Peng XC, Chen N, et al. Automated treatment planning for liver cancer stereotactic body radiotherapy[J]. Clin Transl Oncol, 2023, 25(11): 3230-40. |
| 12 | Pérez-López A, Martín-Sabroso C, Gómez-Lázaro L, et al. Embolization therapy with microspheres for the treatment of liver cancer: State-of-the-art of clinical translation[J]. Acta Biomater, 2022, 149: 1-15. |
| 13 | Liu XF, Lu Y, Qin SK. Atezolizumab and bevacizumab for hepatocellular carcinoma: mechanism, pharmacokinetics and future treatment strategies[J]. Future Oncol, 2021, 17(17): 2243-56. |
| 14 | Chen JH, Jin HW, Zhou H, et al. Research into the characteristic molecules significantly affecting liver cancer immunotherapy[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1029427. |
| 15 | Johnston MP, Khakoo SI. Immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: current and future[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25(24): 2977-89. |
| 16 | Li K, Sun H, Wu CX. Research progress of compound injection of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of liver cancer[J]. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi, 2022, 30(9): 1007-11. |
| 17 | 钟晓丹, 文 彬, 孙海涛, 等. 鳖甲煎丸通过NF-κB信号通路抑制肝癌细胞上皮间质转化的作用机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2022, 28(1): 24-32. |
| 18 | 左 瑜, 刘永刚, 李京涛, 等. 常占杰教授重剂黄芪"固中焦" 治疗慢性肝病经验[J]. 中西医结合肝病杂志, 2022, 32(11): 1030-2. |
| 19 | 李志国. 抗纤抑癌方治疗肝癌前病变的疗效观察及作用机制研究[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2020. |
| 20 | 杨大国, 邓 欣, 李知玉, 等. 中药正肝方治疗肝炎后肝硬化伴高甲胎蛋白血症疗效观察[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2007, 15(6): 351-3. |
| 21 | 邓 欣, 杨大国, 吴其恺, 等. 正肝方对黄曲霉毒素B1诱发的肝癌前病变大鼠肝功能的影响[J]. 中西医结合肝病杂志, 2008, 18(6): 357-9. |
| 22 | 冉 云, 杨大国, 陈文林, 等. 正肝方药物血清对甲胎蛋白刺激的AFPsiRNA HepG2细胞系凋亡的影响[J]. 中西医结合肝病杂志, 2016, 26(3): 169-70. |
| 23 | 孙 童, 胡世平, 杨大国, 等. 正肝方对二乙基亚硝胺诱导的肝癌前病变模型大鼠肝组织PTEN/PI3K/AKT信号通路的影响[J]. 世界中西医结合杂志, 2023, 18(7): 1278-84, 1314. |
| 24 | 宋添力, 王一民, 刘 绪, 等. 运用生物信息学探讨正肝方治疗肝癌的作用机制及实验验证研究[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2024, 40(7): 1383-91. |
| 25 | 黄继汉, 黄晓晖, 陈志扬, 等. 药理试验中动物间和动物与人体间的等效剂量换算[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2004, 9(9): 1069-72. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2501.2004.09.026 |
| 26 | 刘见荣, 沈卫星, 程海波, 等. 参白解毒方显著抑制小鼠结直肠腺瘤的形成及癌变: 基于PTEN/PI3K/AKT通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(10): 1452-61. |
| 27 | 胡 光, 李 丹, 陈 阳, 等. 二乙基亚硝胺诱导斑马鱼肝癌模型的探索与优化[J]. 重庆理工大学学报: 自然科学, 2022, 36(4): 262-7. |
| 28 | Kurma K, Manches O, Chuffart F, et al. DEN-induced rat model reproduces key features of human hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancers, 2021, 13(19): 4981. |
| 29 | Malečková A, Tonar Z, Mik P, et al. Animal models of liver diseases and their application in experimental surgery[J]. Rozhl Chir, 2019, 98(3): 100-9. |
| 30 | 张舒曼, 王 源, 李淑莲. 间断低剂量二乙基亚硝胺诱导C57BL/6J小鼠肝癌模型[J]. 河南大学学报: 医学版, 2019, 38(2): 110-2. |
| 31 | Piccolo S, Dupont S, Cordenonsi M. The biology of YAP/TAZ: hippo signaling and beyond[J]. Physiol Rev, 2014, 94(4): 1287-312. |
| 32 | Sun T, Mao WH, Peng H, et al. YAP promotes sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by upregulating survivin[J]. Cell Oncol, 2021, 44(3): 689-99. |
| 33 | Luo J, Zou HL, Guo YB, et al. The oncogenic roles and clinical implications of YAP/TAZ in breast cancer[J]. Br J Cancer, 2023, 128(9): 1611-24. |
| 34 | 黄翠霞, 张雅倩, 杨爱萍, 等. 基于Hippo/YAP信号通路探讨穿心莲内酯抗三阴性乳腺癌的作用机制[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2023, 39(16): 2050-6. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2023.16.007 |
| 35 | 辛国松, 王毛毛, 侯妍秀, 等. 基于Hippo/YAP信号通路探究粉防己碱抗乳腺癌耐药机制[J]. 中草药, 2023, 54(18): 5960-7. |
| 36 | 周 铭. 紫草素对肝脏特异性Nf2基因敲除小鼠Hippo信号通路的影响[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2021. |
| 37 | Driskill JH, Pan DJ. The hippo pathway in liver homeostasis and pathophysiology[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2021, 16: 299-322. |
| 38 | Russell JO, Camargo FD. Hippo signalling in the liver: role in development, regeneration and disease[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 19(5): 297-312. |
| 39 | Chan EHY, Nousiainen M, Chalamalasetty RB, et al. The Ste20-like kinase Mst2 activates the human large tumor suppressor kinase Lats1[J]. Oncogene, 2005, 24(12): 2076-86. |
| 40 | Zheng AC, Chen QS, Zhang L. The Hippo-YAP pathway in various cardiovascular diseases: Focusing on the inflammatory response[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 971416. |
| 41 | Liu CY, Zha ZY, Zhou X, et al. The hippo tumor pathway promotes TAZ degradation by phosphorylating a phosphodegron and recruiting the SCF{beta}-TrCP E3 ligase[J]. J Biol Chem, 2010, 285(48): 37159-69. |
| 42 | Zhao B, Li L, Tumaneng K, et al. A coordinated phosphorylation by Lats and CK1 regulates YAP stability through SCF(beta-TRCP)[J]. Genes Dev, 2010, 24(1): 72-85. |
| 43 | Bai HB, Zhang NL, Xu Y, et al. Yes-associated protein regulates the hepatic response after bile duct ligation[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 56(3): 1097-107. |
| 44 | Rinschen MM, Grahammer F, Hoppe AK, et al. YAP-mediated mechanotransduction determines the podocyte's response to damage[J]. Sci Signal, 2017, 10(474): eaaf8165. |
| 45 | 彭 乐. 薯蓣皂苷元通过c-Src/Hippo信号通路发挥抗肝细胞癌作用的机制研究[D]. 宜春学院, 2023. |
| 46 | Michalopoulos GK. Hepatostat: Liver regeneration and normal liver tissue maintenance[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65(4): 1384-92. |
| 47 | Moroishi T, Hayashi T, Pan WW, et al. The hippo pathway kinases LATS1/2 suppress cancer immunity[J]. Cell, 2016, 167(6): 1525-39.e17. |
| 48 | Hong LX, Cai YB, Jiang MT, et al. The Hippo signaling pathway in liver regeneration and tumorigenesis[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin, 2015, 47(1): 46-52. |
| 49 | Li H, Wang SH, Wang GY, et al. Yes-associated protein expression is a predictive marker for recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation[J]. Dig Surg, 2014, 31(6): 468-78. |
| 50 | Lian I, Kim J, Okazawa H, et al. The role of YAP transcription coactivator in regulating stem cell self-renewal and differentiation[J]. Genes Dev, 2010, 24(11): 1106-18. |
| 51 | Koo JH, Guan KL. Interplay between YAP/TAZ and metabolism[J]. Cell Metab, 2018, 28(2): 196-206. |
| 52 | Elaimy AL, Mercurio AM. Convergence of VEGF and YAP/TAZ signaling: implications for angiogenesis and cancer biology[J]. Sci Signal, 2018, 11(552): eaau1165. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||