Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (7): 1327-1335.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.07.12
Qianyi CHEN1,2( ), Shuhan SHANG1,2,3, Huan LU1,2, Sisi LI1,2,4, Zhimian SUN1,2,3, Xirui FAN1,2(
), Shuhan SHANG1,2,3, Huan LU1,2, Sisi LI1,2,4, Zhimian SUN1,2,3, Xirui FAN1,2( ), Zhilin QI1,2(
), Zhilin QI1,2( )
)
Received:2024-05-14
Online:2024-07-20
Published:2024-07-25
Contact:
Xirui FAN, Zhilin QI
E-mail:937441097@qq.com;20210006@wnmc.edu.cn;20010012@wnmc.edu.cn
Qianyi CHEN, Shuhan SHANG, Huan LU, Sisi LI, Zhimian SUN, Xirui FAN, Zhilin QI. Calenduloside E inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and migration by down-regulating GPX4 and SLC7A11 expression through the autophagy pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1327-1335.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.07.12
| Primers | Sequence of primer | |
|---|---|---|
| Forward (form 5′ to 3′) | Reverse (from 5′ to 3′) | |
| SLC7A11 | TCTCCAAAGGAGGTTACCTGC | AGACTCCCCTCAGTAAAGTGAC |
| GPX4 | GAGGCAAGACCGAAGTAAACTAC | CCGAACTGGTTACACGGGAA |
| GAPDH | AAAGCCTGCCGGTGACTAA | AGAGTTAAAAGCAGCCCTGG |
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR of SLC7A11, GPX4 and GAPDH
| Primers | Sequence of primer | |
|---|---|---|
| Forward (form 5′ to 3′) | Reverse (from 5′ to 3′) | |
| SLC7A11 | TCTCCAAAGGAGGTTACCTGC | AGACTCCCCTCAGTAAAGTGAC |
| GPX4 | GAGGCAAGACCGAAGTAAACTAC | CCGAACTGGTTACACGGGAA |
| GAPDH | AAAGCCTGCCGGTGACTAA | AGAGTTAAAAGCAGCCCTGG |
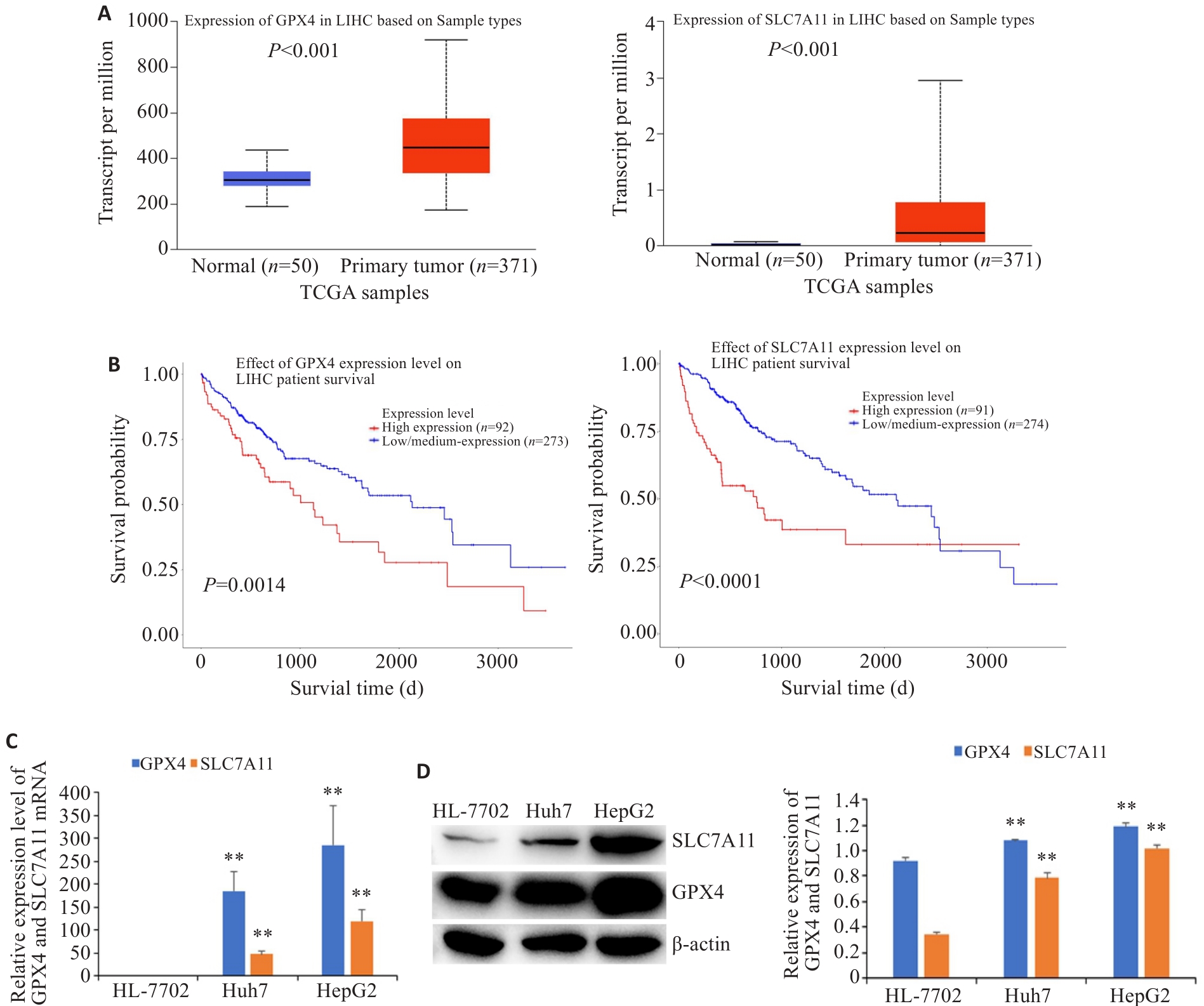
Fig.2 Expression levels of GPX4 and SLC7A11 in HCC tissues and cells and their correlation with the patients' survival (Mean±SD). A: Expression of GPX4 and SLC7A11 in HCC tissues and normal liver tissues. B: Correlation of GPX4 and SLC7A11 expressions with the patients' survival. The expressions of GPX4 and SLC7A11 mRNA (C) and protein (D) in HCC cells and normal liver cells. **P<0.01 vs HL-7702.
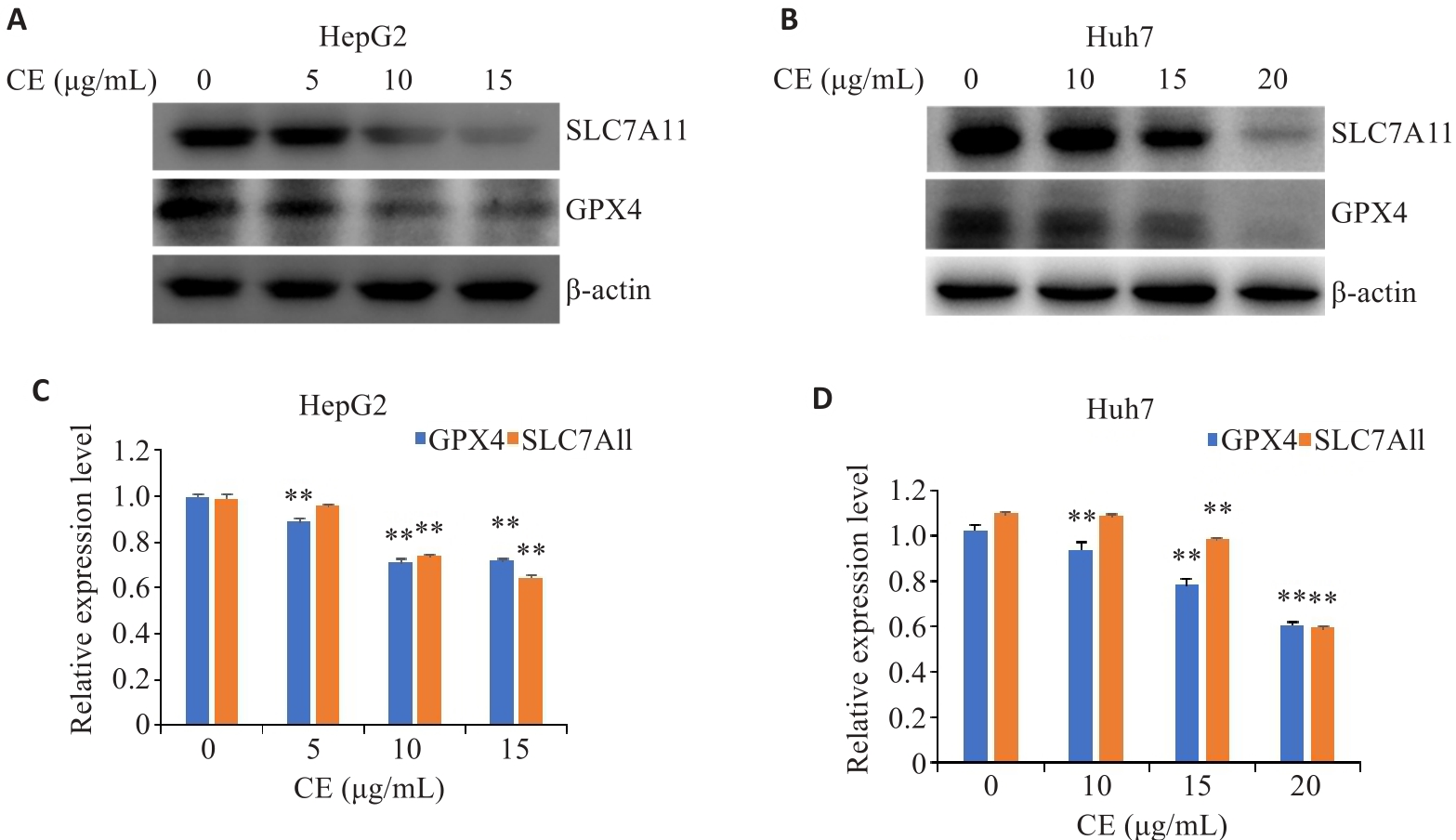
Fig.3 Effects of CE on GPX4 and SLC7A11 expressions in HepG2 (A, B) and Huh7 cells (C, D). Data are presented as Mean±SD. **P<0.01 vs 0 µg/mL. CE: Calenduloside E.
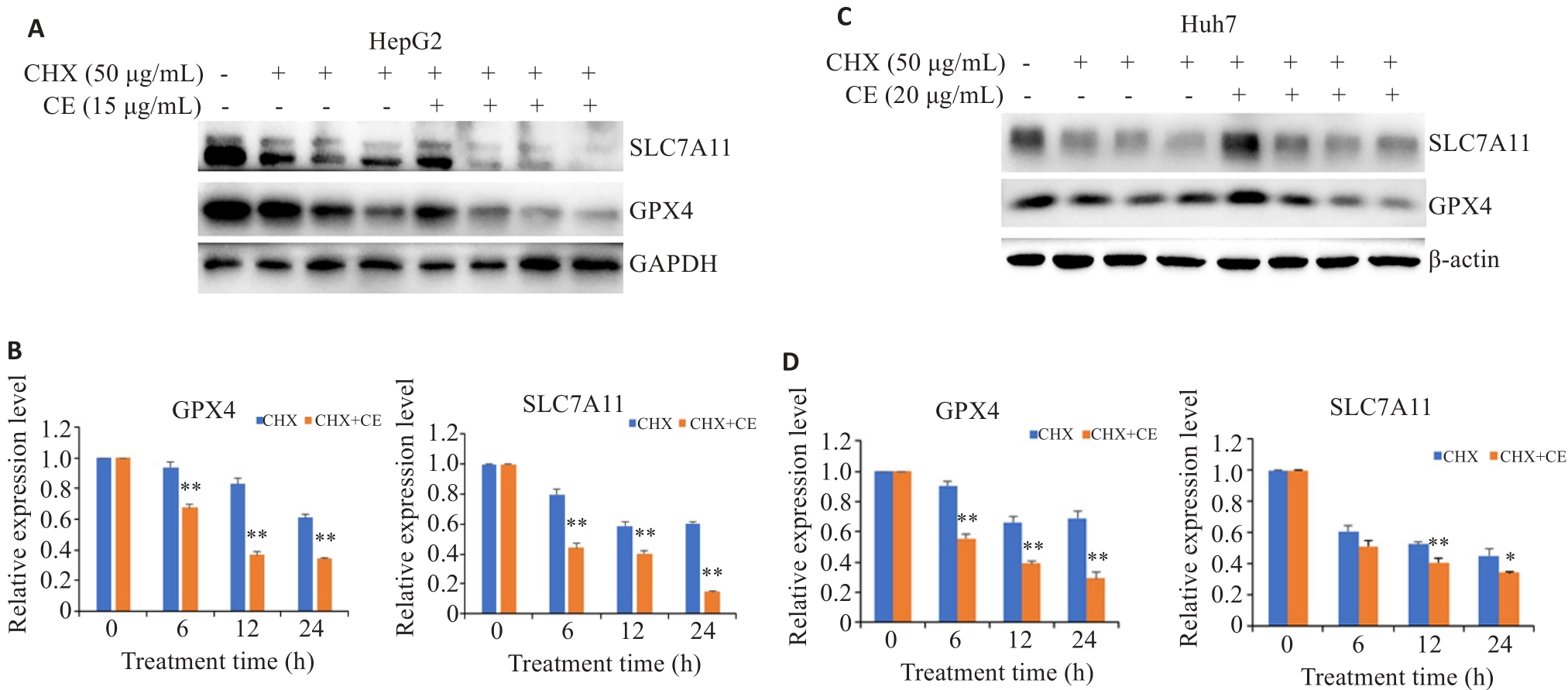
Fig.4 Effects of CE on GPX4 and SLC7A11 protein degradation in HepG2 (A, B) and Huh7 cells (C, D). Data are presented as Mean±SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs CHX group.
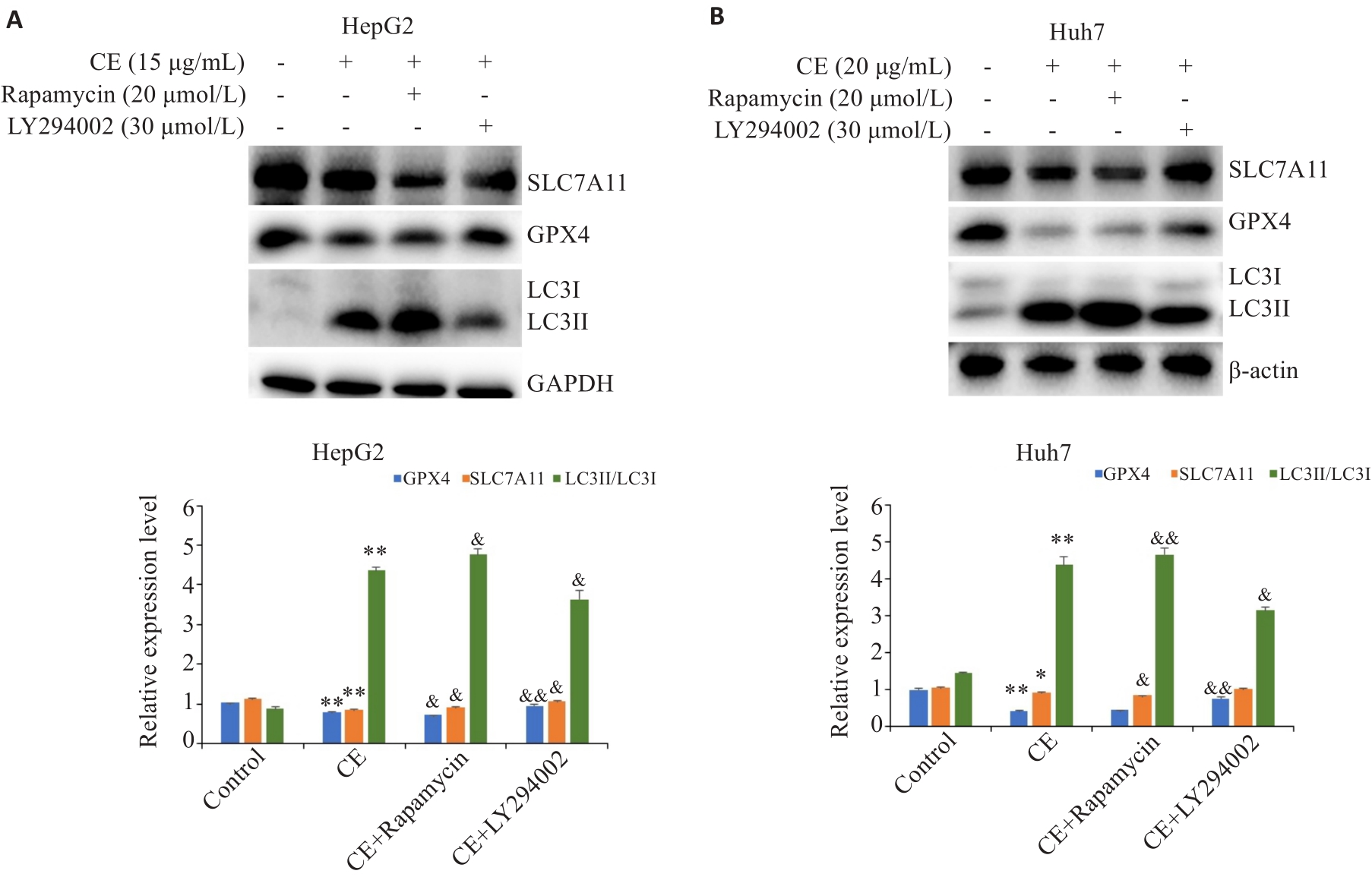
Fig.7 Effects of autophagy inhibitor or activator on CE-induced GPX4 and SLC7A11 down-regulation in HepG2 (A) and Huh7 (B) cells (Mean±SD). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Control; &P<0.05, &&P<0.01 vs CE.
| 1 | Xia CF, Dong XS, Li H, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants[J]. Chin Med J, 2022, 135(5): 584-90. |
| 2 | Wang SN, Wu XW, Wu XM, et al. Systematic analysis of the role of LDHs subtype in pan-cancer demonstrates the importance of LDHD in the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients[J]. BMC Cancer, 2024, 24(1): 156. |
| 3 | 谢思雨, 李淼生, 江峰乐, 等. EHHADH是肝细胞癌脂肪酸代谢通路的关键基因: 基于转录组分分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(5): 680-93. DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.05.02 |
| 4 | Metur SP, Lei YC, Zhang ZH, et al. Regulation of autophagy gene expression and its implications in cancer[J]. J Cell Sci, 2023, 136(10): jcs260631. |
| 5 | Jain V, Singh MP, Amaravadi RK. Recent advances in targeting autophagy in cancer[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2023, 44(5): 290-302. |
| 6 | Chow AK, Yau SW, Ng L. Novel molecular targets in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. World J Clin Oncol, 2020, 11(8): 589-605. |
| 7 | Wang Y, Deng BC. Hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular mechanism, targeted therapy, and biomarkers[J]. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2023, 42(3): 629-52. |
| 8 | Glaviano A, Foo ASC, Lam HY, et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies in cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2023, 22(1): 138. |
| 9 | He PZ, He Y, Ma JJ, et al. Thymoquinone induces apoptosis and protective autophagy in gastric cancer cells by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway[J]. Phytother Res, 2023, 37(8): 3467-80. |
| 10 | Lee J, Roh JL. SLC7A11 as a gateway of metabolic perturbation and ferroptosis vulnerability in cancer[J]. Antioxidants, 2022, 11(12): 2444. |
| 11 | Liu JY, Xia XJ, Huang P. xCT: a critical molecule that links cancer metabolism to redox signaling[J]. Mol Ther, 2020, 28(11): 2358-66. |
| 12 | Huang Y, Dai ZY, Barbacioru C, et al. Cystine-glutamate transporter SLC7A11 in cancer chemosensitivity and chemoresistance[J]. Cancer Res, 2005, 65(16): 7446-54. |
| 13 | Li SJ, Lu ZY, Sun RB, et al. The role of SLC7A11 in cancer: friend or foe[J]? Cancers, 2022, 14(13): 3059. |
| 14 | Zhang W, Liu Y, Liao Y, et al. GPX4, ferroptosis, and diseases[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2024, 174: 116512. |
| 15 | Jia CX, Zhang X, Qu TT, et al. Depletion of PSMD14 suppresses bladder cancer proliferation by regulating GPX4[J]. PeerJ, 2023, 11: e14654. |
| 16 | Tang X, Ding H, Liang ML, et al. Curcumin induces ferroptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer via activating autophagy[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2021, 12(8): 1219-30. |
| 17 | Le YF, Guo JN, Liu ZJ, et al. Calenduloside E ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via modulating a pyroptosis-dependent pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 319(Pt 2): 117239. |
| 18 | Li JX, Bu YJ, Li B, et al. Calenduloside E alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by preserving mitochondrial function[J]. J Mol Histol, 2022, 53(4): 713-27. |
| 19 | 汤 托, 王胜男, 蔡田雨, 等. 金盏花苷E通过ROS介导的JAK1-stat3信号途径抑制LPS诱发的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(8): 904-10. DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2019.08.05 |
| 20 | Wang SN, Chen XL, Cheng J, et al. Calunduloside E inhibits HepG2 cell proliferation and migration via p38/JNK-HMGB1 signalling axis[J]. J Pharmacol Sci, 2021, 147(1): 18-26. |
| 21 | Zhang W, Jiang BP, Liu YX, et al. Bufotalin induces ferroptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells by facilitating the ubiquitination and degradation of GPX4[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2022, 180: 75-84. |
| 22 | Li DB, Wang YH, Dong C, et al. CST1 inhibits ferroptosis and promotes gastric cancer metastasis by regulating GPX4 protein stability via OTUB1[J]. Oncogene, 2023, 42(2): 83-98. |
| 23 | Wang XB, Chen YQ, Wang XD, et al. Stem cell factor SOX2 confers ferroptosis resistance in lung cancer via upregulation of SLC7A11[J]. Cancer Res, 2021, 81(20): 5217-29. |
| 24 | Hanzl A, Winter GE. Targeted protein degradation: current and future challenges[J]. Curr Opin Chem Biol, 2020, 56: 35-41. |
| 25 | Wang Y, Le WD. Autophagy and ubiquitin-proteasome system[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2019, 1206: 527-50. |
| 26 | Xu ZR, Han X, Ou DM, et al. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy for tumor therapy[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2020, 104(2): 575-87. |
| 27 | Zhang M, Liu SH, Chua MS, et al. SOCS5 inhibition induces autophagy to impair metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10(8): 612. |
| 28 | Li H, Zhao SF, Shen LW, et al. E2F2 inhibition induces autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in gastric cancer[J]. Aging, 2021, 13(10): 13626-43. |
| 29 | Zhang JH, Fan JJ, Zeng X, et al. Targeting the autophagy promoted antitumor effect of T-DM1 on HER2-positive gastric cancer[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(4): 288. |
| 30 | Yi H, Wang K, Du BY, et al. Aleuritolic acid impaired autophagic flux and induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells[J]. Molecules, 2018, 23(6): 1338. |
| 31 | Li JK, Zhu PL, Wang Y, et al. Gracillin exerts anti-melanoma effects in vitro and in vivo: role of DNA damage, apoptosis and autophagy[J]. Phytomedicine, 2023, 108: 154526. |
| 32 | Yu WX, Lu C, Wang B, et al. Effects of rapamycin on osteosarcoma cell proliferation and apoptosis by inducing autophagy[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2020, 24(2): 915-21. |
| 33 | Chen WS, Xian GY, Gu MH, et al. Autophagy inhibitors 3-MA and LY294002 repress osteoclastogenesis and titanium particle-stimulated osteolysis[J]. Biomater Sci, 2021, 9(14): 4922-35. |
| 34 | Ouyang SM, Li HX, Lou LL, et al. Inhibition of STAT3-ferroptosis negative regulatory axis suppresses tumor growth and alleviates chemoresistance in gastric cancer[J]. Redox Biol, 2022, 52: 102317. |
| 35 | Zeng C, Lin J, Zhang KT, et al. SHARPIN promotes cell proliferation of cholangiocarcinoma and inhibits ferroptosis via p53/SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling[J]. Cancer Sci, 2022, 113(11): 3766-75. |
| 36 | Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death[J]. Cell, 2012, 149(5): 1060-72. |
| 37 | Mou YH, Wang J, Wu JC, et al. Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death: opportunities and challenges in cancer[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2019, 12(1): 34. |
| [1] | Yao CHENG, Yuanying WANG, Feiyang YAO, Pan HU, Mingxian CHEN, Ning WU. Baicalin suppresses type 2 dengue virus-induced autophagy of human umbilical vein endothelial cells by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1272-1283. |
| [2] | Yeming ZHANG, Yuanxiang ZHANG, Xuebin SHEN, Guodong WANG, Lei ZHU. MiRNA-103-3p promotes neural cell autophagy by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling via targeting rab10 in a rat model of depression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1315-1326. |
| [3] | Pengcheng LIU, Lijuan LOU, Xia LIU, Jian WANG, Ying JIANG. A risk scoring model based on M2 macrophage-related genes for predicting prognosis of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 827-840. |
| [4] | ZHOU Fengmin, GUO Yanju, CHEN Ning. Exercise promotes irisin expression to ameliorate renal injury in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(4): 675-681. |
| [5] | CHEN Hao, LI Zhenhan, WANG Mingting, LU Linming, TANG Qianli, LUO Liangping. High expression of UBE2S promotes progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by increasing cancer cell stemness [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 455-464. |
| [6] | CHEN Junjie, HUANG Chuanbing, LI Ming. Jianpi Zishen granule inhibits podocyte autophagy in systemic lupus erythematosus: a network pharmacology and clinical study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 465-473. |
| [7] | XIAO Hongmin, HAN Baosong, GUO Jiacheng, WU Chao, WU Jingyi. HTD4010 attenuates myocardial injury in mice with septic cardiomyopathy by promoting autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 507-514. |
| [8] | ZHONG Weixiong, LIANG Fangrong, YANG Ruimeng, ZHEN Xin. Prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma based on multi-phase dynamic enhanced CT radiomics feature and multi-classifier hierarchical fusion model [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 260-269. |
| [9] | SUN Shuo, HUANG Xin, LI Guodong, ZHANG Chunyun, LU Zemei, ZHANG Weiwei, LI Zeyan, YANG Qingzhu. MACC1 knockdown enhances RSL3-induced ferroptosis in human colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting GPX4 expression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 173-178. |
| [10] | XIN Chen, WANG Xiaoying, LI Xiang, CHEN Yu, WANG Xue, NING Jiaxi, YANG Shi, WANG Zhongqiong. LncRNA SOX2OT enhances 5-fluorouracil resistance of cholangiocarcinoma cells by promoting autophagy via up-regulating SIRT1 expression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 187-193. |
| [11] | ZHU Quan, HUANG Baisheng, WEI Leiyan, LUO Qizhi. Overexpression of LncRNA MEG3 promotes ferroptosis and enhances chemotherapy sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to cisplatin [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 17-24. |
| [12] | CAO Danping, CAI Juan, LI Yanna, DONG Runyu, WANG Zhixiong, ZUO Xueliang. TMEM64 is highly expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes tumor cell proliferation and invasion [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(8): 1345-1355. |
| [13] | LAN Yu, WANG Kaifeng, LAN Zhixian, ZHOU Heqi, SUN Jian. Dealcoholized red wine inhibits occurrence and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma possibly by inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(8): 1297-1305. |
| [14] | ZHANG Meng, ZHANG Yuanyuan, NIU Mengzhu, ZHU Yue, TONG Shiyi, KOU Xianjuan. Dihydromyricetin alleviates pyroptosis and necroptosis in mice with MPTP-induced chronic Parkinson's disease by inducing autophagy [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(8): 1268-1278. |
| [15] | FAN Yifan, FENG Zhiwei, FAN Kuohai, YIN wei, SUN Na, SUN Panpan, SUN Yaogui, LI Hongquan. Procine recombinant NK-lysin inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by downregulating FKBP3 and inhibiting oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis: a proteomic analysis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(7): 1116-1126. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||