Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (9): 1805-1813.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.09.21
Previous Articles Next Articles
Kai CHEN1( ), Zhaofei MENG1,2, Jingting MIN3, Jiahui WANG3, Zhenghong LI3, Qin GAO3, Junfeng HU1,2(
), Zhaofei MENG1,2, Jingting MIN3, Jiahui WANG3, Zhenghong LI3, Qin GAO3, Junfeng HU1,2( )
)
Received:2024-05-15
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-10-31
Contact:
Junfeng HU
E-mail:1204784642@qq.com;bbmchjf@126.com
Kai CHEN, Zhaofei MENG, Jingting MIN, Jiahui WANG, Zhenghong LI, Qin GAO, Junfeng HU. Curcumin alleviates septic lung injury in mice by inhibiting TXNIP/TRX-1/GPX4-mediated ferroptosis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1805-1813.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.09.21
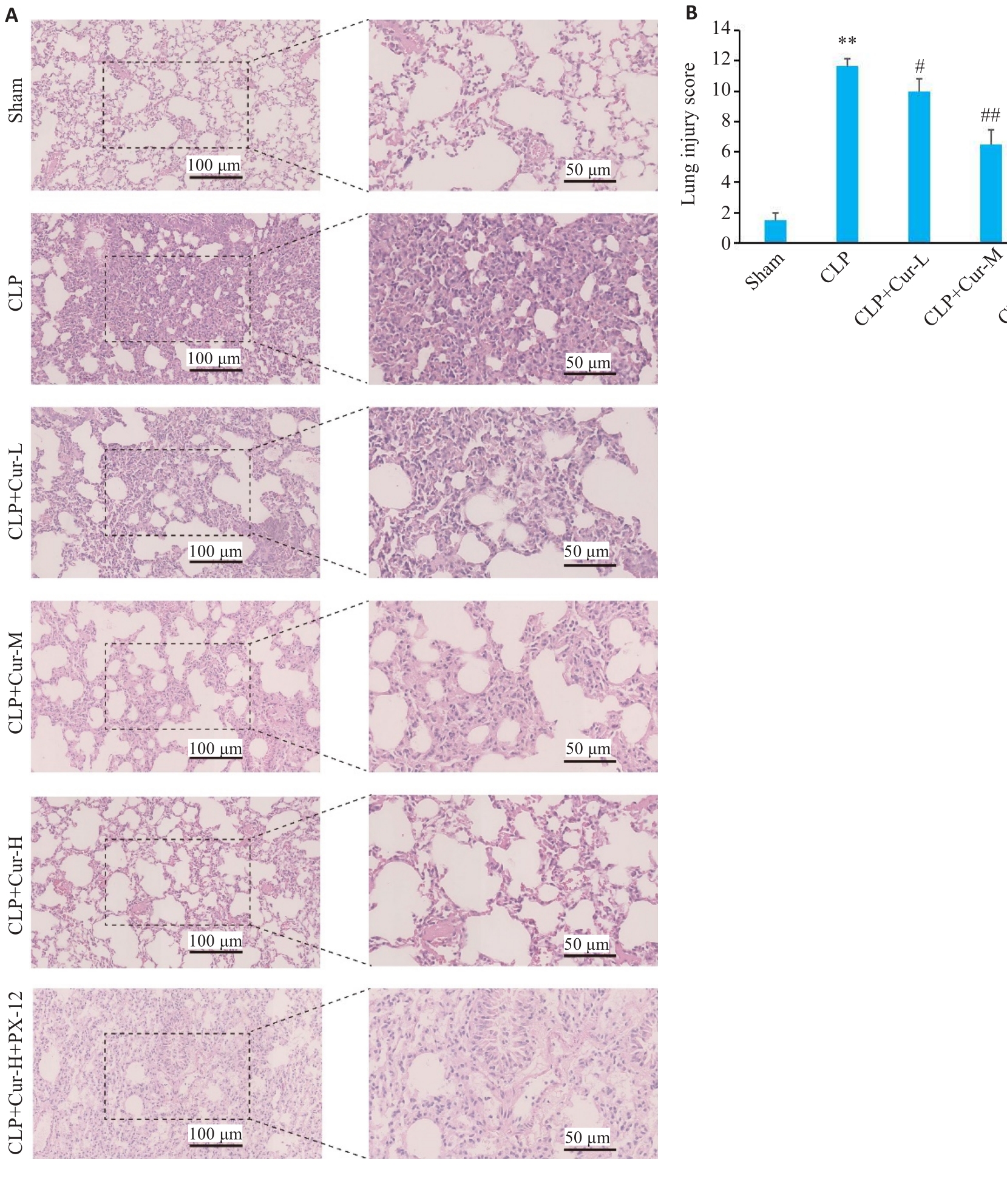
Fig.1 HE staining of lung tissue of the mice and lung injury scores in each group. A: HE staining of paraffin sections of the lung tissues. B: Comparison of lung injury scores among the groups. **P<0.01 vs Sham group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs CLP group; &&P<0.01 vs CLP+Cur-H group (Mean±SD, n=6).
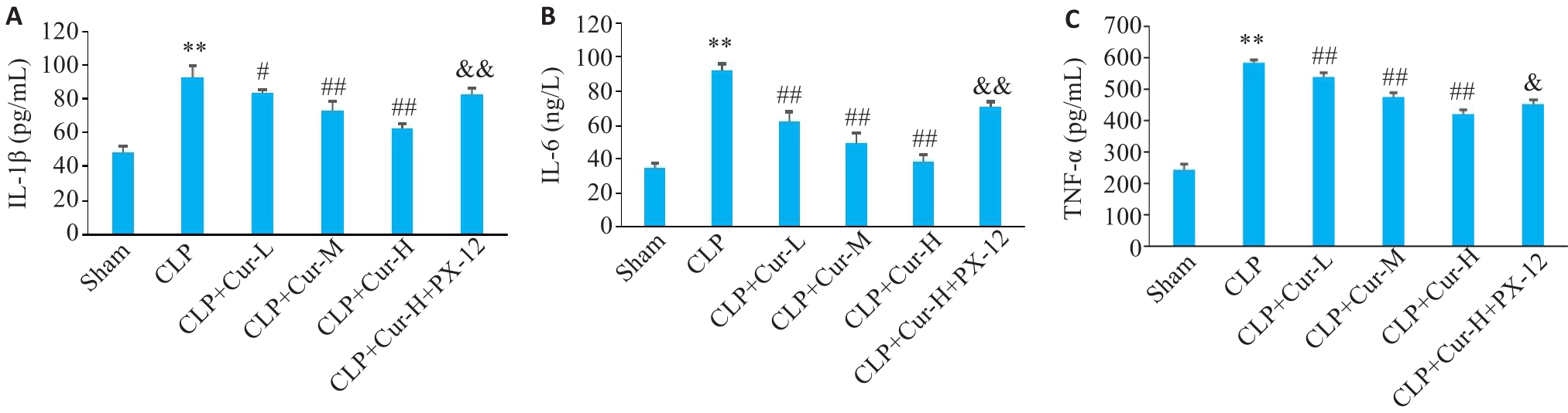
Fig.2 Expressions of IL-1β (A), IL-6 (B) and TNF-α (C) in the lung tissues of the mice in each group. **P<0.01 vs Sham group; #P< 0.05, ##P<0.01 vs CLP group; &P<0.05, &&P<0.01 vs CLP+Cur-H group (Mean±SD, n=6).
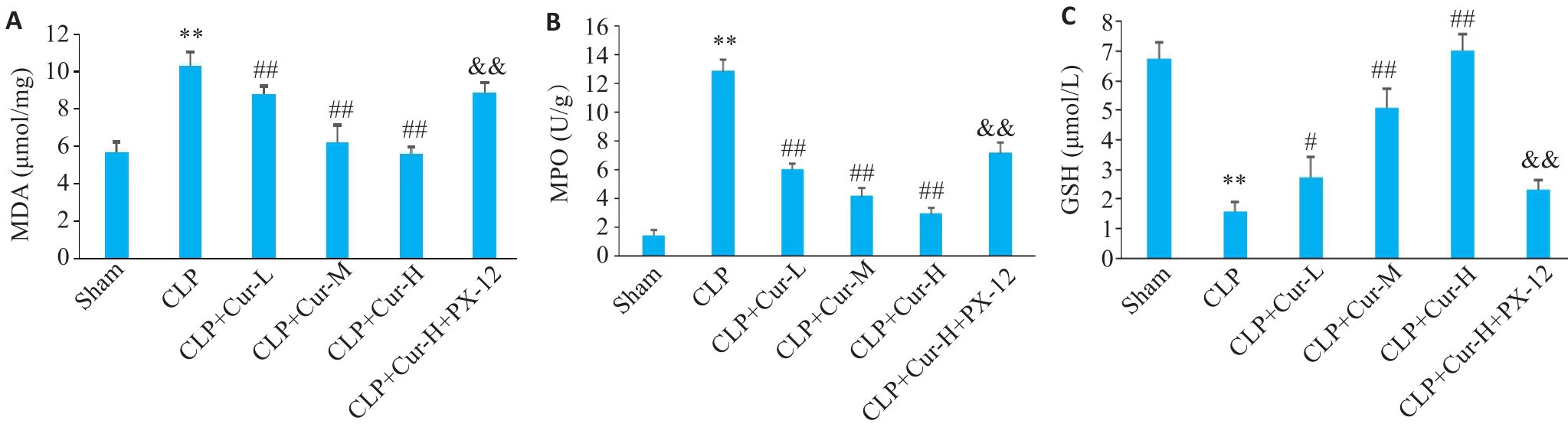
Fig.3 Determination of MDA (A), MPO (B) and GSH (C) levels in the lung tissues of the mice in each group. **P<0.01 vs Sham group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs CLP group; &&P<0.01 vs CLP+Cur-H group (Mean±SD, n=6).
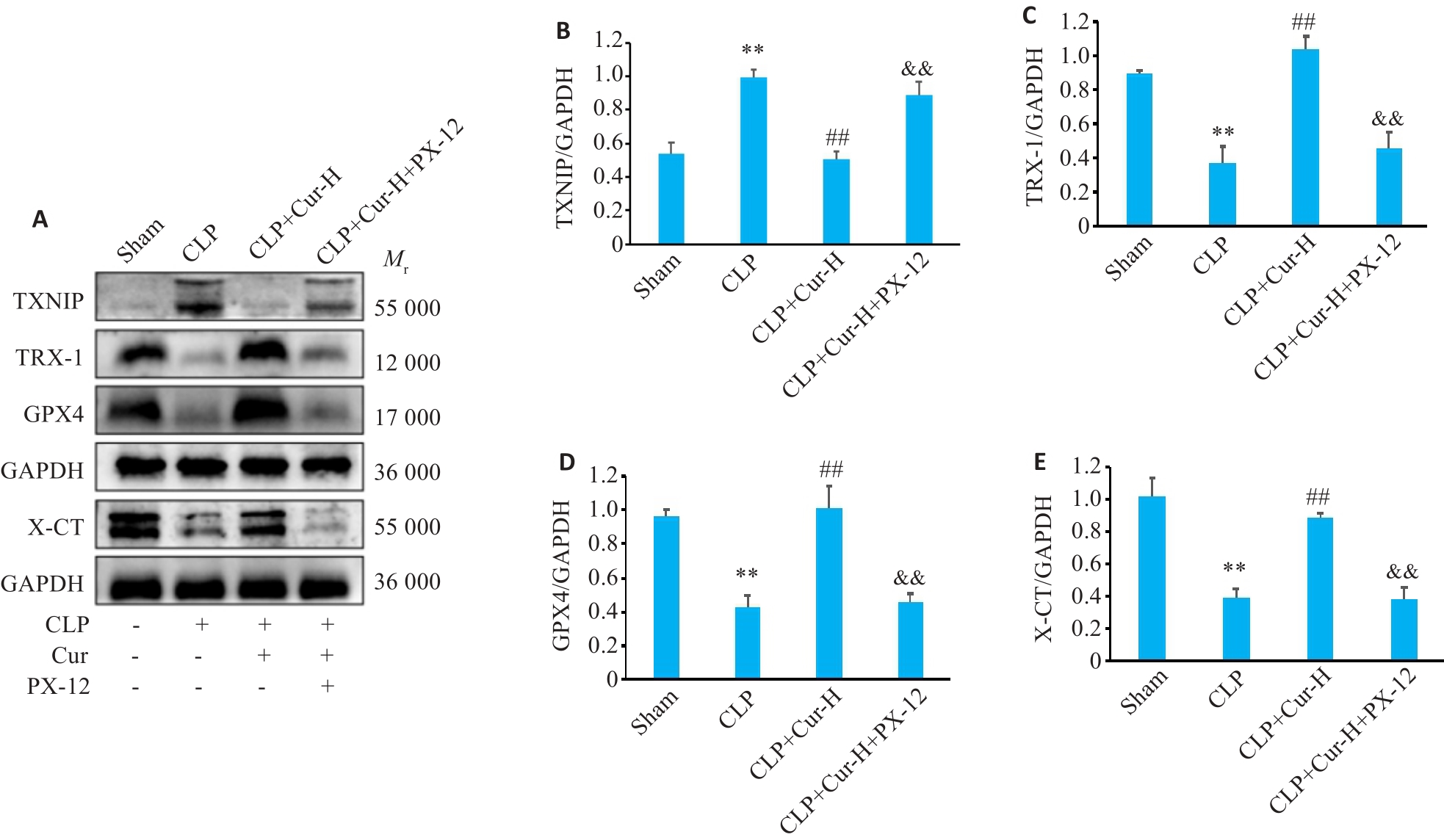
Fig.4 Results of Western blotting in each group. A: Western blots of TXNIP, TRX-1, GPX4 and X-CT proteins in the lung tissues of the mice in each group. B-E: Quantitative analysis of the protein levels. **P<0.01 vs Sham group; ##P<0.01 vs CLP group; &&P<0.01 vs CLP+Cur-H group (Mean±SD, n=3).
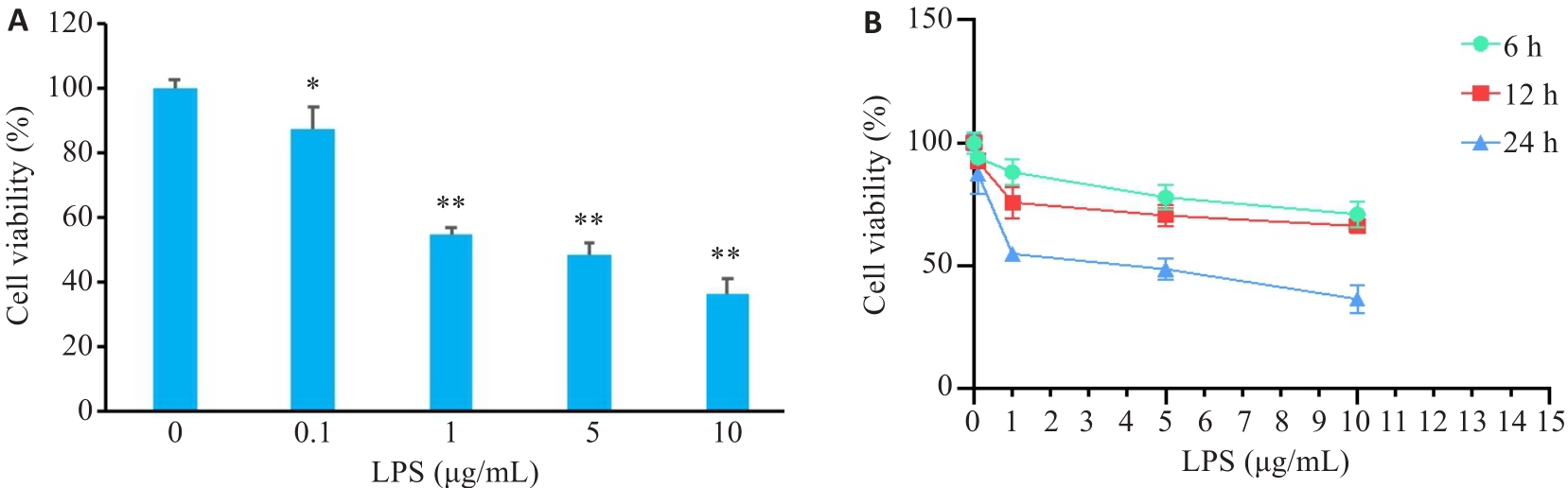
Fig.5 CCK8 assay for determining the optimal concentration and time of LPS for cell treatment. A: Cell viability assay after LPS treatment at 0, 0.1, 1, 5 and 10 μg/mL for 24 h. B: Cell viability assay after LPS treatment at 0, 0.1, 1, 5 and 10 μg/mL concentrations for 6, 12 and 24 h. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs 0 μg/mL group (Mean±SD, n=4).
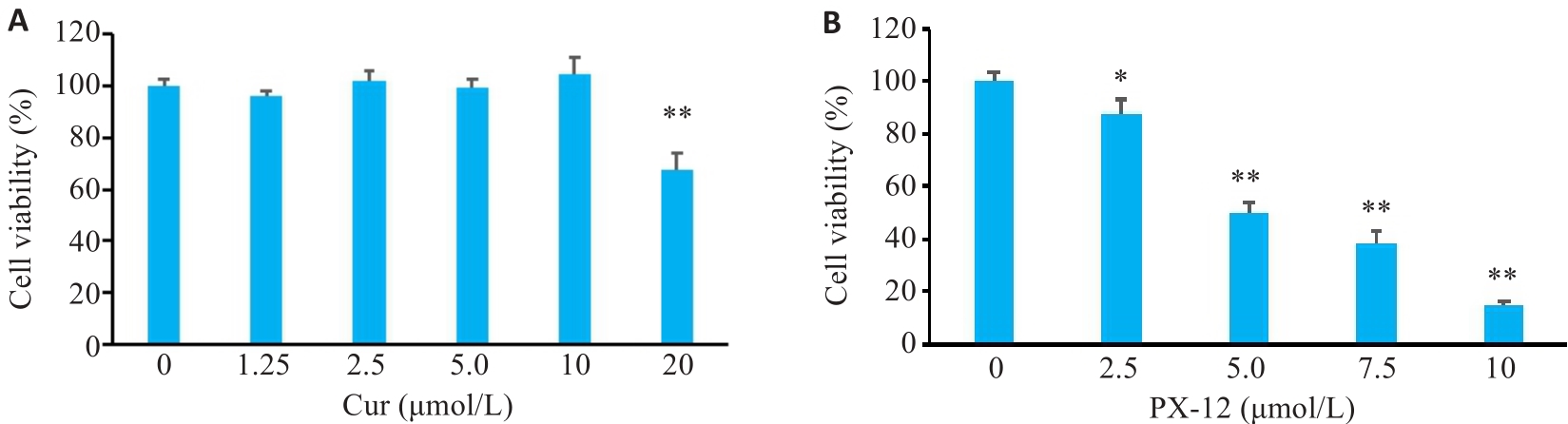
Fig.6 Effects of curcumin and PX-12 on cell viability. A: Effect of curcumin on cell viability; B: Effect of PX-12 on cell viability. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs 0 μg/mL group (Mean±SD, n=4)
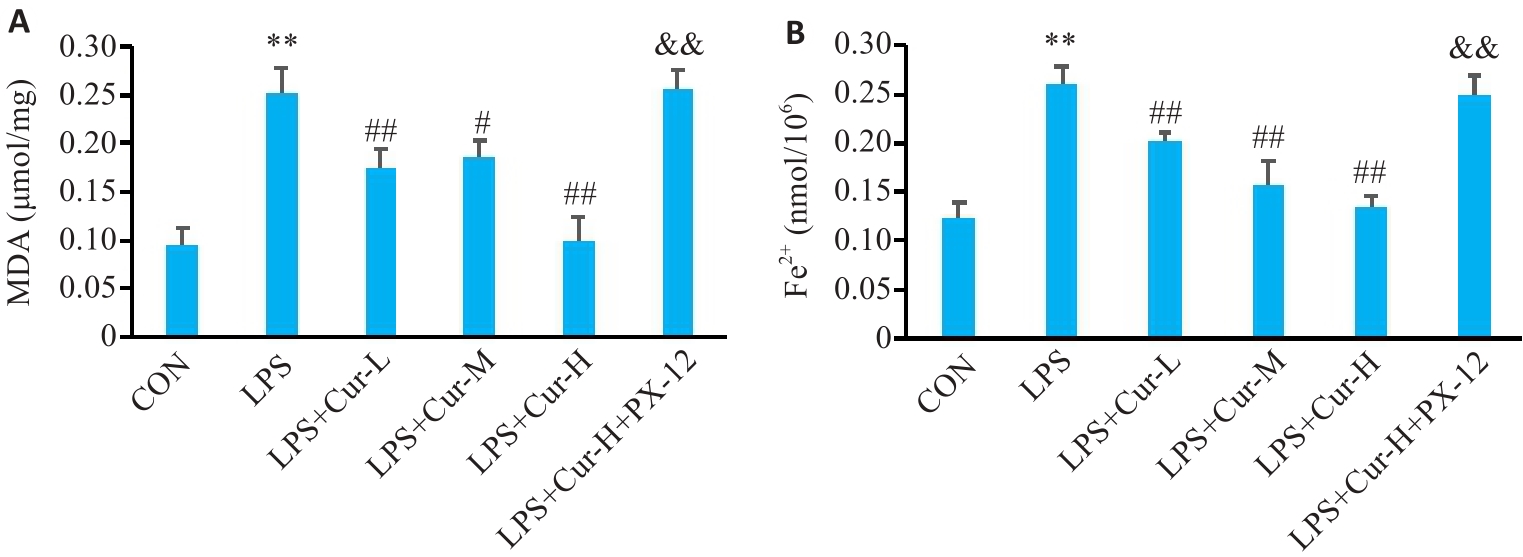
Fig.8 Changes in MDA (A) and Fe2+ (B) levels in the cells in each group. **P<0.01 vs control; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs LPS; &&P<0.01 vs LPS+Cur-H (Mean±SD, n=4).
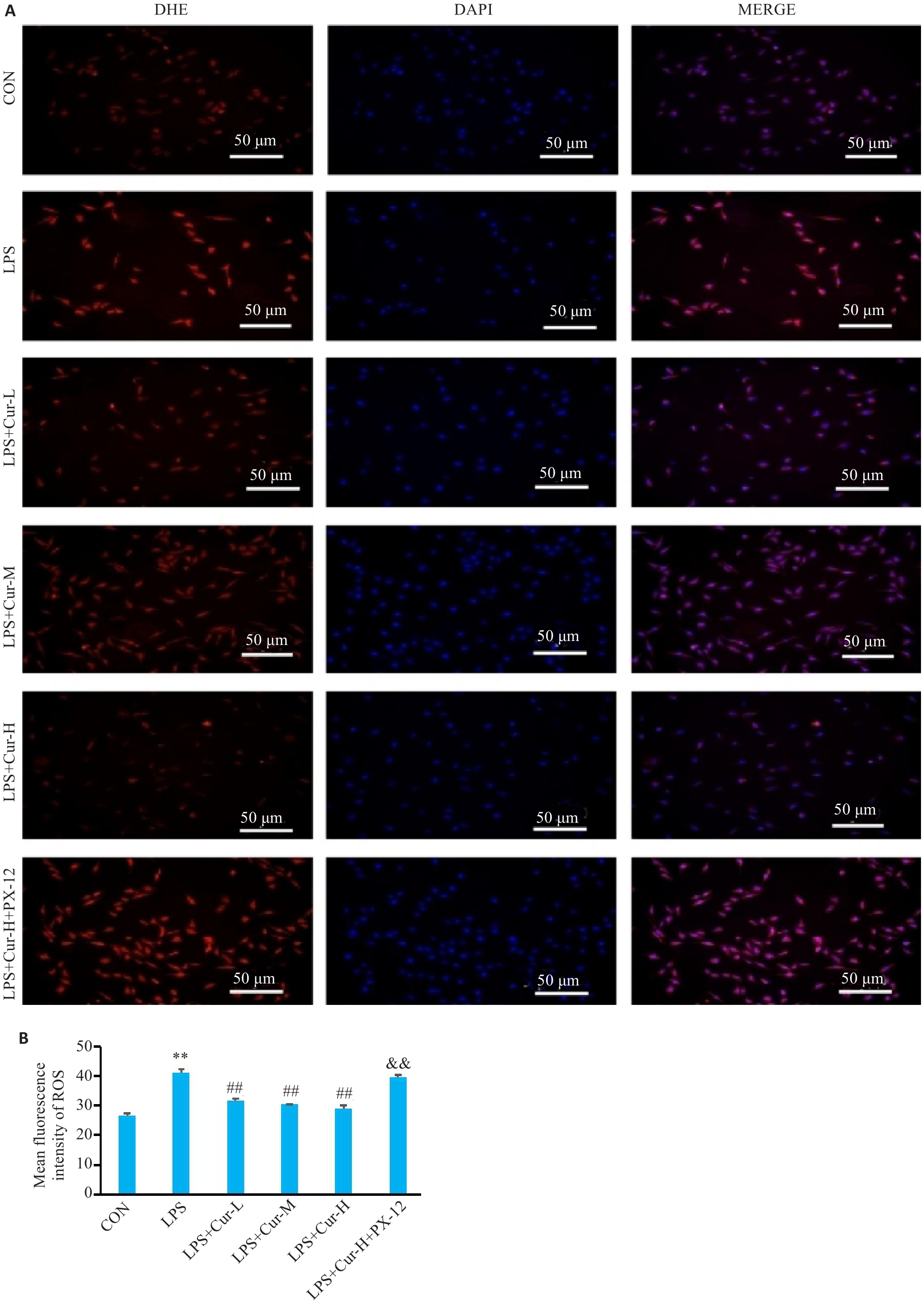
Fig.9 ROS immunofluorescence and fluorescence intensity in each group of cells. A: Immunofluorescence images of Beas-2B cells in each group. B: Comparison of ROS fluorescence intensity of the cells. **P<0.05 vs control group; ##P<0.01 vs LPS group; &&P<0.01 vs LPS+Cur-H group (Mean±SD, n=4).
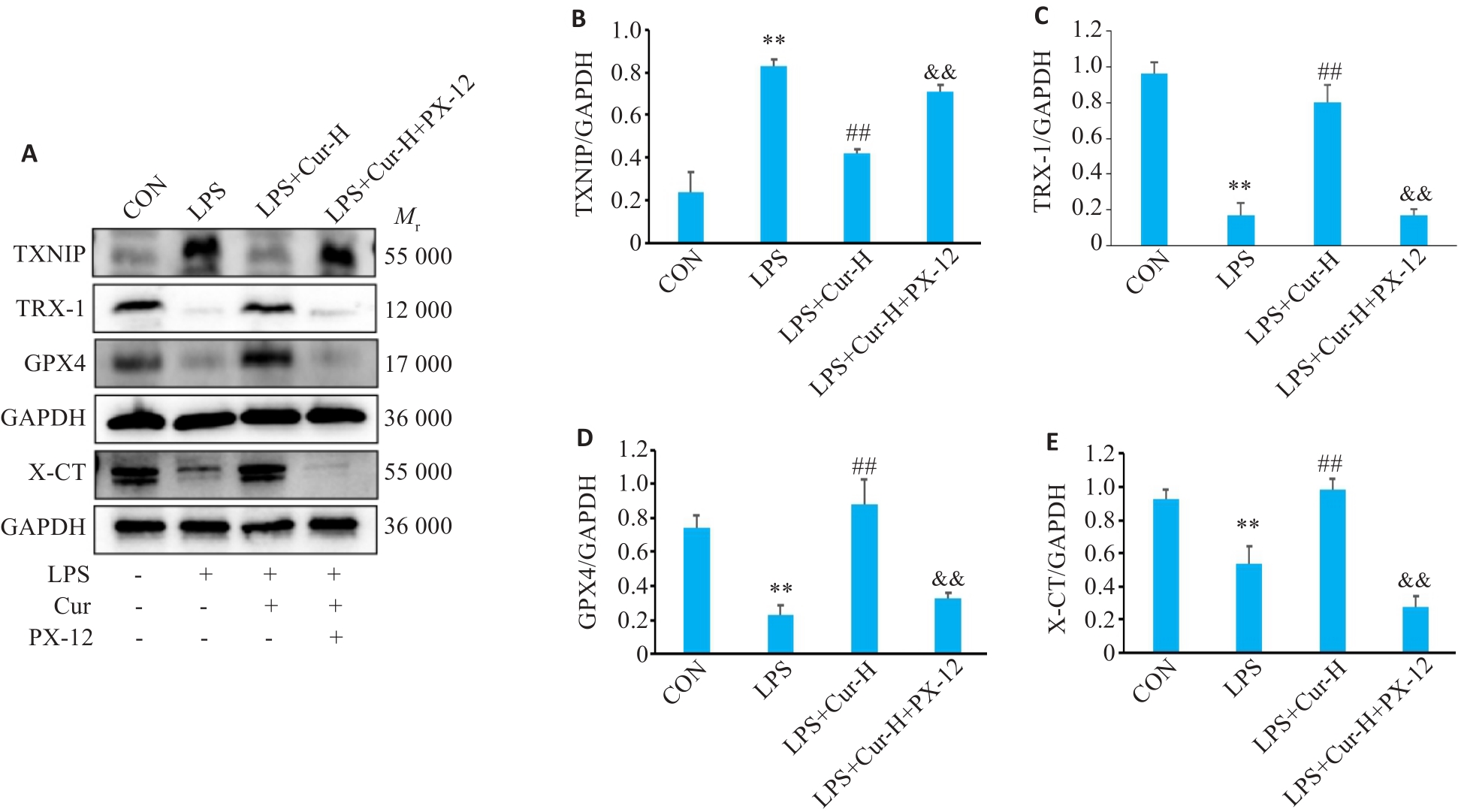
Fig.10 Western blotting for the proteins in the TXNIP/TRX-1/GPX4 pathways in each group of cells. A: Western blots of the proteins. B-E: Quantitative analysis of the protein expression levels. **P<0.01 vs control group; ##P<0.01 vs LPS group; &&P<0.01 vs LPS+Cur-H group (Mean±SD, n=3).
| 1 | Sun BS, Lei MX, Zhang JQ, et al. Acute lung injury caused by sepsis: how does it happen[J]? Front Med, 2023, 10: 1289194. |
| 2 | Li WL, Li D, Chen YS, et al. Classic signaling pathways in alveolar injury and repair involved in sepsis-induced ALI/ARDS: new research progress and prospect[J]. Dis Markers, 2022, 2022: 6362344. |
| 3 | Wang YF, Zhao ZJ, Xiao ZY. The emerging roles of ferroptosis in pathophysiology and treatment of acute lung injury[J]. J Inflamm Res, 2023, 16: 4073-85. |
| 4 | Chen Y, Fang ZM, Yi X, et al. The interaction between ferroptosis and inflammatory signaling pathways[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(3): 205. |
| 5 | Huo L, Liu CF, Yuan YJ, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of ferroptosis as a therapeutic target for sepsis-associated organ damage[J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2023, 257: 115438. |
| 6 | Zhang J, Zheng YP, Wang Y, et al. YAP1 alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 884362. |
| 7 | Zhang XY, Liu CM, Ma YH, et al. The TXNIP/Trx-1/GPX4 pathway promotes ferroptosis in hippocampal neurons after hypoxia-ischemia in neonatal rats[J]. Chin J Contemp Pediatr, 2022, 24(9): 1053-60. |
| 8 | Sadeghi M, Dehnavi S, Asadirad A, et al. Curcumin and chemokines: mechanism of action and therapeutic potential in inflammatory diseases[J]. Inflammopharmacology, 2023, 31(3): 1069-93. |
| 9 | Wang Y, Wang YJ, Cai N, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin in acute lung injury: in vivo and in vitro experimental model studies[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 96: 107600. |
| 10 | Yuan R, Li YQ, Han S, et al. Fe-curcumin nanozyme-mediated reactive oxygen species scavenging and anti-inflammation for acute lung injury[J]. ACS Cent Sci, 2022, 8(1): 10-21. |
| 11 | Zheng YX, Wang JP, Ling ZY, et al. A diagnostic model for sepsis-induced acute lung injury using a consensus machine learning approach and its therapeutic implications[J]. J Transl Med, 2023, 21(1): 620. |
| 12 | Tao HP, Shen LH. Research progress of curcumin in the treatment of sepsis[J]. Shock, 2024, 61(6): 805-16. |
| 13 | Liu RF, Fang XH, Meng C, et al. Lung inflation with hydrogen during the cold ischemia phase decreases lung graft injury in rats[J]. Exp Biol Med, 2015, 240(9): 1214-22. |
| 14 | Zhou X, Liao YX. Gut-lung crosstalk in sepsis-induced acute lung injury[J]. Front Microbiol, 2021, 12: 779620. |
| 15 | Zhang H, Liu JL, Zhou YL, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps mediate m6A modification and regulates sepsis-associated acute lung injury by activating ferroptosis in alveolar epithelial cells[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2022, 18(8): 3337-57. |
| 16 | Wang W, Xu RL, He P, et al. CircEXOC5 aggravates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by promoting ferroptosis through the IGF2BP2/ATF3 axis[J]. J Infect Dis, 2024, 229(2): 522-34. |
| 17 | Ahmad S, Zaki A, Manda K, et al. Vitamin-D ameliorates sepsis-induced acute lung injury via augmenting miR-149-5p and downregulating ER stress[J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2022, 110: 109130. |
| 18 | Jiang X, Stockwell BR, Conrad M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2021, 22(4):266-82. |
| 19 | Shi X, Han B, Zhang B, et al. Schisandra chinensis polysaccharides prevent cardiac hypertrophy by dissociating thioredoxin-interacting protein/thioredoxin-1 complex and inhibiting oxidative stress[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, 139:111688. |
| 20 | Lv HM, Zhu C, Wei W, et al. Enhanced Keap1-Nrf2/Trx-1 axis by daphnetin protects against oxidative stress-driven hepatotoxicity via inhibiting ASK1/JNK and Txnip/NLRP3 inflammasome activation[J]. Phytomedicine, 2020, 71: 153241. |
| 21 | Choi EH, Park SJ. TXNIP: A key protein in the cellular stress response pathway and a potential therapeutic target[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2023, 55(7): 1348-56. |
| 22 | Chen YF, Yin HW, Sun J, et al. TrxR/Trx inhibitor butaselen ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing NF‑κB/TGF‑β1/Smads signaling[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2023, 169: 115822. |
| 23 | 周 滟, 李晓茜, 汪思琴. 血清OSM、Trx-1及HBP与脓毒症严重程度相关性及对临床转归的预测研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志, 2024, 23(5): 473-7. |
| 24 | Shen K, Wang XJ, Wang YW, et al. MiR-125b-5p in adipose derived stem cells exosome alleviates pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells ferroptosis via Keap1/Nrf2/GPX4 in sepsis lung injury[J]. Redox Biol, 2023, 62: 102655. |
| 25 | Kumar A, Harsha C, Parama D, et al. Current clinical developments in curcumin-based therapeutics for cancer and chronic diseases[J]. Phytother Res, 2021, 35(12): 6768-801. |
| 26 | Shi Y, Wu Q, Lu Y, et al. Arginine-Glycine-aspartic acid-anchored curcumin-based nanotherapeutics inhibit pyroptosis-induced cytokine release syndrome for in vivo and in vitro sepsis applications[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2023, 29(4): 283-94. |
| 27 | Ahmadabady S, Beheshti F, Shahidpour F, et al. A protective effect of curcumin on cardiovascular oxidative stress indicators in systemic inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats[J]. Biochem Biophys Rep, 2021, 25: 100908. |
| 28 | Zhou Y, Gao LP, Xia P, et al. Glycyrrhetinic acid protects renal tubular cells against oxidative injury via reciprocal regulation of JNK-connexin 43-thioredoxin 1 signaling[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 619567. |
| 29 | Li WC, Xu XT, Dong DD, et al. Up-regulation of thioredoxin system by puerarin inhibits lipid uptake in macrophages[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2021, 162: 542-54. |
| 30 | 林全德, 闫 艳, 刘 晴, 等. PX-12促进硼替佐米诱导多发性骨髓瘤细胞H929凋亡的实验研究[J]. 中国实验血液学杂志, 2021, 29(2): 515-9. |
| 31 | Lin Y, Chen XW, Yu CC, et al. Radiotherapy-mediated redox homeostasis-controllable nanomedicine for enhanced ferroptosis sensitivity in tumor therapy[J]. Acta Biomater, 2023, 159: 300-11. |
| [1] | Mingzi OUYANG, Jiaqi CUI, Hui WANG, Zheng LIANG, Dajin PI, Liguo CHEN, Qianjun CHEN, Yingchao WU. Kaixinsan alleviates adriamycin-induced depression-like behaviors in mice by reducing ferroptosis in the prefrontal cortex [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1441-1449. |
| [2] | Yinliang ZHANG, Zetan LUO, Rui ZHAO, Na ZHAO, Zhidong XU, Di AO, Guyi CONG, Xinyu LIU, Hailun ZHENG. Sanguinarine induces ferroptosis of colorectal cancer cells by upregulating STUB1 and downregulating GPX4 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1537-1544. |
| [3] | Yuanguo WANG, Peng ZHANG. Ferroptosis suppressor genes are highly expressed in esophageal cancer to inhibit tumor cell ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1389-1396. |
| [4] | Huaxing HE, Lulin LIU, Yingyin LIU, Nachuan CHEN, Suxia SUN. Sodium butyrate and sorafenib synergistically inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma cells possibly by inducing ferroptosis through inhibiting YAP [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1425-1430. |
| [5] | Zhixian REN, Beixian ZHOU, Linxin WANG, Jing LI, Rongping ZHANG, Xiping PAN. Inhibitory effect of 5-hydroxy-6,7-dimethoxyflavone on H1N1 influenza virus-induced ferroptosis and inflammation in A549 cells and its possible mechanisms [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1070-1078. |
| [6] | Fangyuan ZHANG, Gang LIU. Dexmedetomidine inhibits ferroptosis of human renal tubular epithelial cells by activating the Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1135-1140. |
| [7] | Nan WANG, Bin SHI, Xiaolan MAN, Weichao WU, Jia CAO. High expression of fragile X mental retardation protein inhibits ferroptosis of colorectal tumor cells by activating the RAS/MAPK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 885-893. |
| [8] | LI Shuxian, YU Shuping, MU Yaming, WANG Kai, LIU Yu, ZHANG Meihua. Metformin ameliorates PM2.5- induced functional impairment of placental trophoblasts by inhibiting ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 437-446. |
| [9] | SUN Shuo, HUANG Xin, LI Guodong, ZHANG Chunyun, LU Zemei, ZHANG Weiwei, LI Zeyan, YANG Qingzhu. MACC1 knockdown enhances RSL3-induced ferroptosis in human colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting GPX4 expression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 173-178. |
| [10] | ZHANG Xiaohong, ZHAO Pin, KUAI Jianke, CHANG Chao, YUAN Qing. Spermidine alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial injury in mice by suppressing apoptosis, ROS production and ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 166-172. |
| [11] | ZHU Quan, HUANG Baisheng, WEI Leiyan, LUO Qizhi. Overexpression of LncRNA MEG3 promotes ferroptosis and enhances chemotherapy sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to cisplatin [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 17-24. |
| [12] | HUANG Yi, Lin Lishan, HUANG Haohua, DONG Hangming. VDAC1 participates in house dust mite- induced asthmatic airway inflammation in mice by inducing ferroptosis of airway epithelial cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(8): 1333-1338. |
| [13] | REN Li, ZOU Mingyuan, ZHU Xingchun, XU Wenjun, LIU Gang, SUN Junjie, FAN Fangtian, ZHANG Congli. Curcumin suppresses proliferation, migration and invasion of papillary thyriod cancer B-CPAP cells through the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(8): 1356-1362. |
| [14] | XIE Siyu, LI Miaosheng, JIANG Fengle, YI Qian, YANG Wei. EHHADH is a key gene in fatty acid metabolism pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma: a transcriptomic analysis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(5): 680-693. |
| [15] | LI Shai, LI Li, MIN Simin, LIU Saisai, QIN Zhiwen, XIONG Zhishang, XU Jianguo, WANG Bowen, DING Dushan, ZHAO Shidi. Soybean isoflavones alleviate cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting ferroptosis and inflammatory cascade reaction [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(2): 323-330. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||