Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1307-1316.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.20
Previous Articles Next Articles
Liping GUAN1( ), Yan YAN1, Xinyi LU1, Zhifeng LI1, Hui GAO2, Dong CAO1, Chenxi HOU1, Jingyu ZENG1, Xinyi LI1, Yang ZHAO2, Junjie WANG2, Huilong FANG1(
), Yan YAN1, Xinyi LU1, Zhifeng LI1, Hui GAO2, Dong CAO1, Chenxi HOU1, Jingyu ZENG1, Xinyi LI1, Yang ZHAO2, Junjie WANG2, Huilong FANG1( )
)
Received:2024-04-22
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-06-27
Contact:
Huilong FANG
E-mail:3078770751@qq.com;huilongfang@163.com
Liping GUAN, Yan YAN, Xinyi LU, Zhifeng LI, Hui GAO, Dong CAO, Chenxi HOU, Jingyu ZENG, Xinyi LI, Yang ZHAO, Junjie WANG, Huilong FANG. Compound Centella asiatica formula alleviates Schistosoma japonicum-induced liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting the inflammation-fibrosis cascade via regulating the TLR4/MyD88 pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.20
| Active ingredient | TNF | MMP9 | JUN | TP53 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| quercetin | -5.65 | -6.55 | -7.06 | -5.19 |
| Kaempferol | -5.62 | -7.87 | -5.39 | -5.15 |
| Stigmasterol | -9.52 | -8.75 | -7.88 | -7.02 |
Tab.1 Molecular docking score table (kcal/mol)
| Active ingredient | TNF | MMP9 | JUN | TP53 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| quercetin | -5.65 | -6.55 | -7.06 | -5.19 |
| Kaempferol | -5.62 | -7.87 | -5.39 | -5.15 |
| Stigmasterol | -9.52 | -8.75 | -7.88 | -7.02 |

Fig. 5 Molecular docking simulation of binding between the key components and core targets of compound Centella asiatica formula. A: quercetin-JUN. B: Kaempferol-MMP-9. C: Stigmasterol-TNF. D: Stigmasterol-TP53.
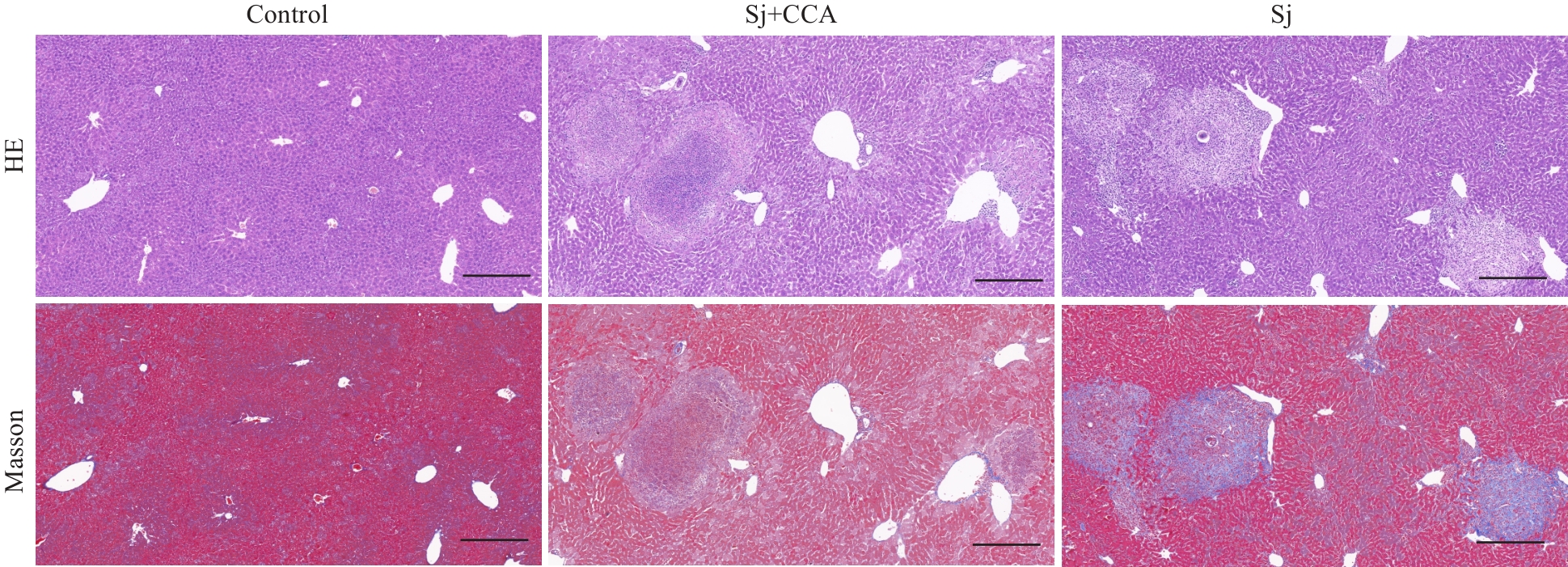
Fig.6 Pathological changes in liver tissue of mouse models with Schistosoma japonicum-induced liver fibrosis (HE and Masson staining, scale bar=200 µm).
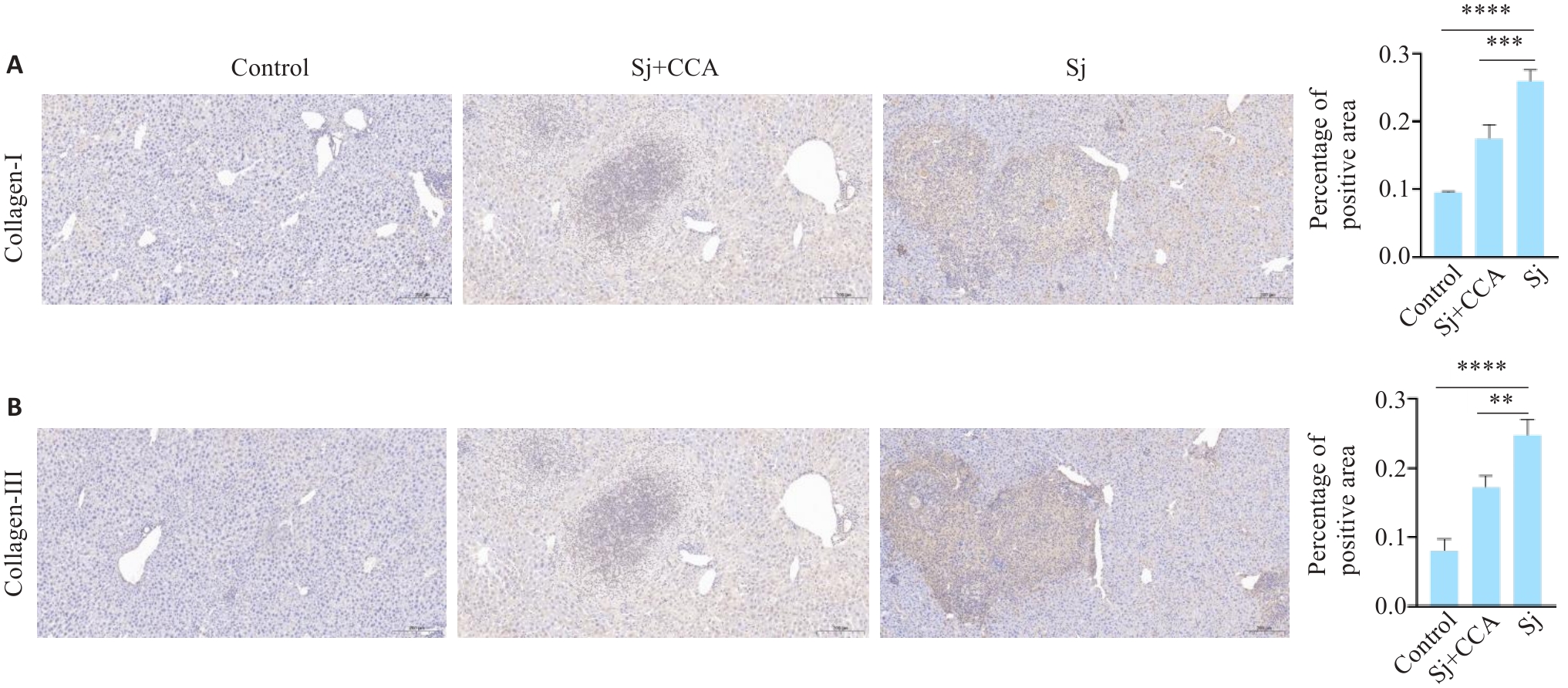
Fig.7 Immunohistochemical analysis of expression levels of type I and type III collagen mouse liver tissue (Scale bar=200 µm) and quantitative comparison among the 3 groups. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Sj, ****P<0.0001 vs control.
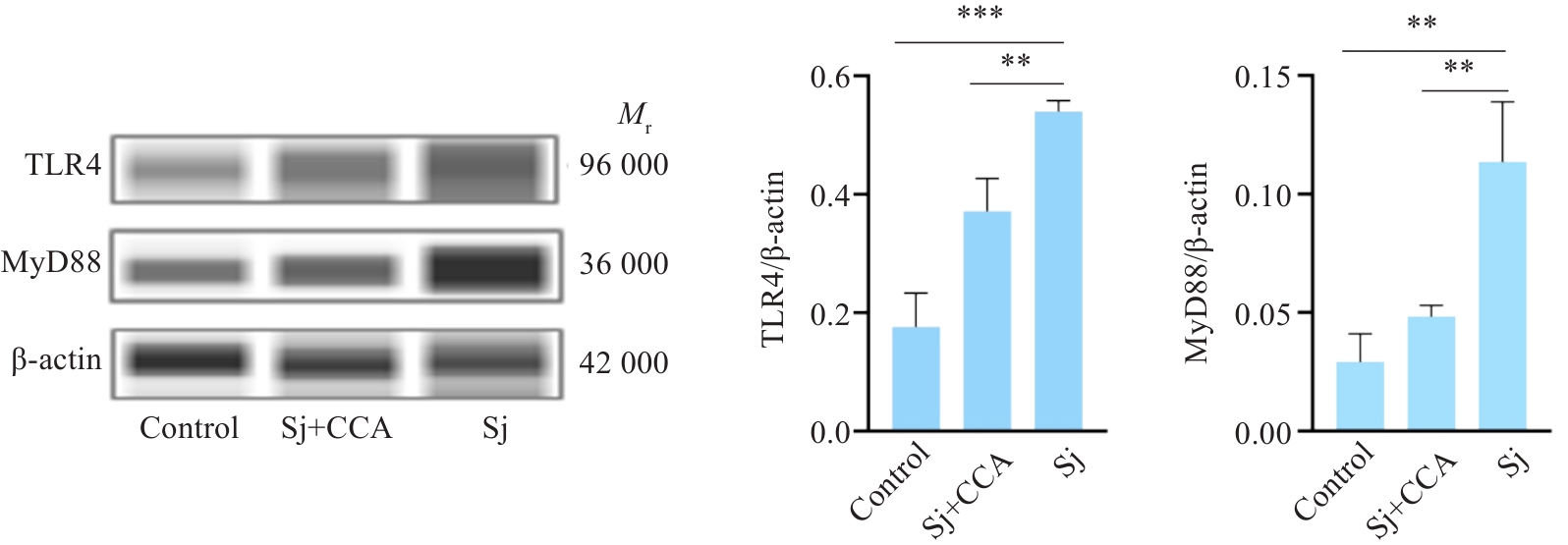
Fig.9 Effect of compound Centella asiatica formula on hepatic expressions of TLR4 and MyD88 proteins in mouse models of Schistosoma japonicum-induced liver fibrosis detected by Western blotting. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
| 1 | Wang YL, Gong WC, Zhou H, et al. A novel miRNA from egg-derived exosomes of Schistosoma japonicum promotes liver fibrosis in murine schistosomiasis[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 860807. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.860807 |
| 2 | McManus DP, Bergquist R, Cai P, et al. Schistosomiasis-from immunopathology to vaccines[J]. Semin Immunopathol, 2020, 42(3): 355-71. doi:10.1007/s00281-020-00789-x |
| 3 | Zhang Y, Li J, Li H, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing to dissect the immunological network of liver fibrosis in Schistosoma japonicum-infected mice[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 980872. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.980872 |
| 4 | Chen TT, Peng S, Wang Y, et al. Improvement of mitochondrial activity and fibrosis by resveratrol treatment in mice with Schistosoma japonicum infection[J]. Biomolecules, 2019, 9(11): E658. doi:10.3390/biom9110658 |
| 5 | Shao C, Xu H, Sun X, et al. New perspectives on Chinese medicine in treating hepatic fibrosis: lipid droplets in hepatic stellate cells[J]. Am J Chin Med, 2023, 51(6): 1413-29. doi:10.1142/s0192415x23500647 |
| 6 | 朱 勤, 陈洪宇, 曾佳丽, 等. 复方积雪草对糖尿病肾病大鼠肾脏保护作用及对血红素加氧酶-1、NADPH氧化酶4蛋白表达的影响[J]. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志, 2021, 22(2): 111-5, 190. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1009-587X.2021.02.005 |
| 7 | Zhu Q, Li XH, Chen HY, et al. The effects of compound Centella formula on OxInflammation and silent information regulator 1 in a high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic kidney disease rat model[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2021, 22(3): 962. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10394 |
| 8 | Polaris Observatory Collaborators. Global prevalence, treatment, and prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in 2016: a modelling study[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 3(6): 383-403. |
| 9 | Ginès P, Thiele M, Graupera I, et al. Screening for fibrosis to diagnose liver diseases early: the LIVERSCREEN project[J]. Nat Med, 2023, 29(4): 774-5. doi:10.1038/s41591-023-02265-z |
| 10 | Chen Y, Hu Y, Zhou H, et al. Induction of hepatic fibrosis in mice with schistosomiasis by extracellular microRNA-30 derived from Schistosoma japonicum eggs[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15: 1425384. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1425384 |
| 11 | Wang R, Zhang H, Wang YY, et al. Inhibitory effects of quercetin on the progression of liver fibrosis through the regulation of NF‑кB/IкBα, p38 MAPK, and Bcl-2/Bax signaling[J]. Int Immuno-pharmacol, 2017, 47: 126-33. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2017.03.029 |
| 12 | 徐 标, 韩春荣. 槲皮素对血吸虫肝纤维化小鼠肝组织c-fos、c-jun mRNA和转化生长因子β1表达的抑制作用[J]. 中草药, 2006, 37(3): 393-8. doi:10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2006.3.165 |
| 13 | Nam SY, Jeong HJ, Kim HM. Kaempferol impedes IL-32-induced monocyte-macrophage differentiation[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2017, 274: 107-15. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2017.07.010 |
| 14 | la Torre Fabiola VD, Ralf K, Gabriel B, et al. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of Critonia aromatisans leaves: Down-regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2016, 190: 174-82. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2016.06.006 |
| 15 | Liu C, Zhang YS, Chen F, et al. Immunopathology in schistosomiasis is regulated by TLR2, 4- and IFN-γ-activated MSC through modulating Th1/Th2 responses[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2020, 11(1): 217. doi:10.1186/s13287-020-01735-2 |
| 16 | Liu YF, Niu GC, Li CY, et al. Mechanism of ulcerative colitis-aggravated liver fibrosis: the activation of hepatic stellate cells and TLR4 signaling through gut-liver axis[J]. Front Physiol, 2021, 12: 695019. doi:10.3389/fphys.2021.695019 |
| 17 | Zhang D, Hao X, Xu L, et al. Intestinal flora imbalance promotes alcohol-induced liver fibrosis by the TGFβ/smad signaling pathway in mice[J]. Oncol Lett, 2017, 14(4): 4511-6. doi:10.3892/ol.2017.6762 |
| 18 | Yao D, Zhou Z, Wang P, et al. miR-125-5p/IL-6R axis regulates macrophage inflammatory response and intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis in ulcerative colitis through JAK1/STAT3 and NF‑κB pathway[J]. Cell Cycle, 2021, 20(23): 2547-64. doi:10.1080/15384101.2021.1995128 |
| 19 | Zhou LJ, Liu ZJ, Wang ZX, et al. Astragalus polysaccharides exerts immunomodulatory effects via TLR4-mediated MyD88-dependent signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo [J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 44822. doi:10.1038/srep44822 |
| 20 | Li XX, Zheng X, Liu Z, et al. Cryptotanshinone from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (Danshen) inhibited inflammatory responses via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway[J]. Chin Med, 2020, 15: 20. doi:10.1186/s13020-020-00303-3 |
| 21 | Yao H, Hu C, Yin L, et al. Dioscin reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory liver injury via regulating TLR4/MyD88 signal pathway[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2016, 36: 132-41. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2016.04.023 |
| 22 | Liu ZN, Wu X, Fang Q, et al. CD73 attenuates alcohol-induced liver injury and inflammation via blocking TLR4/MyD88/NF‑κB signaling pathway[J]. J Inflamm Res, 2022, 15: 53-70. doi:10.2147/jir.s341680 |
| 23 | Wang H, Gao M, Li J, et al. MMP-9-positive neutrophils are essential for establishing profibrotic microenvironment in the obstructed kidney of UUO mice[J]. Acta Physiol: Oxf, 2019, 227(2): e13317. doi:10.1111/apha.13317 |
| 24 | Li DD, Li N, Cai C, et al. A molecular network-based pharmacological study on the protective effect of Panax notoginseng rhizomes against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14: 1134408. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1134408 |
| 25 | Hassan HM, El-Kannishy SMH, Alattar A, et al. Therapeutic effects of blocking β‑catenin against hepatocellular carcinoma-induced activation of inflammation, fibrosis and tumor invasion[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, 135: 111216. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111216 |
| 26 | Chen L, Ji XF, Wang MN, et al. Involvement of TLR4 signaling regulated-COX2/PGE2 axis in liver fibrosis induced by Schistosoma japonicum infection[J]. Parasites Vectors, 2021, 14(1): 279. doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-139573/v1 |
| 27 | Huo LP, Bao MM, Lv ZM, et al. Identification, functional characterization and expression pattern of myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88) in Sepiella japonica [J]. Fish Shellfish Immunol, 2018, 79: 112-9. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2018.04.065 |
| 28 | Wen Z, Ji X, Tang J, et al. Positive feedback regulation between transglutaminase 2 and toll-like receptor 4 signaling in hepatic stellate cells correlates with liver fibrosis post Schistosoma japonicum infection[J]. Front Immunol, 2017, 8: 1808. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2017.01808 |
| 29 | Osawa Y, Hoshi M, Yasuda I, et al. Tumor necrosis factor‑α promotes cholestasis-induced liver fibrosis in the mouse through tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 production in hepatic stellate cells[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(6): e65251. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0065251 |
| 30 | Feng M, Ding J, Wang M, et al. Kupffer-derived matrix metalloproteinase-9 contributes to liver fibrosis resolution[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2018, 14(9): 1033-40. doi:10.7150/ijbs.25589 |
| 31 | Xia L, Xie H, Yu Y, et al. The effects of NF-κB and c-Jun/AP-1 on the expression of prothrombotic and proinflammatory molecules induced by anti-β2GPI in mouse[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(2): e0147958. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0147958 |
| 32 | Ma M, Hua S, Min X, et al. p53 positively regulates the proliferation of hepatic progenitor cells promoted by laminin-521[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2022, 7(1): 290. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01107-7 |
| 33 | Li Z, Qu B, Wu XW, et al. Methodology improvement for network pharmacology to correct the deviation of deduced medicinal constituents and mechanism: Xian-Ling-Gu-Bao as an example[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2022, 289: 115058. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115058 |
| 34 | Mei CJ, Yang YY, Dong PP, et al. Deficiency of PKCλ/ι alleviates the liver pathologic impairment of Schistosoma japonicum infection by thwarting Th2 response[J]. Parasites Vectors, 2022, 15(1): 154. doi:10.1186/s13071-022-05283-x |
| 35 | Zhang B, Li J, Zong X, et al. FXR deficiency in hepatocytes disrupts the bile acid homeostasis and inhibits autophagy to promote liver injury in Schistosoma japonicum-infected mice[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2022, 16(8): e0010651. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0010651 |
| 36 | Yu YR, Ni XQ, Huang J, et al. Taurine drinking ameliorates hepatic granuloma and fibrosis in mice infected with Schistosoma japonicum [J]. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist, 2016, 6(1): 35-43. doi:10.1016/j.ijpddr.2016.01.003 |
| [1] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | Liming WANG, Hongrui CHEN, Yan DU, Peng ZHAO, Yujie WANG, Yange TIAN, Xinguang LIU, Jiansheng LI. Yiqi Zishen Formula ameliorates inflammation in mice with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [3] | Yinfu ZHU, Yiran LI, Yi WANG, Yinger HUANG, Kunxiang GONG, Wenbo HAO, Lingling SUN. Therapeutic mechanism of hederagenin, an active component in Guizhi Fuling Pellets, against cervical cancer in nude mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [4] | Lijun HE, Xiaofei CHEN, Chenxin YAN, Lin SHI. Inhibitory effect of Fuzheng Huaji Decoction against non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and the possible molecular mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152. |
| [5] | Guoyong LI, Renling LI, Yiting LIU, Hongxia KE, Jing LI, Xinhua WANG. Therapeutic mechanism of Arctium lappa extract for post-viral pneumonia pulmonary fibrosis: a metabolomics, network pharmacology analysis and experimental verification [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [6] | Peipei TANG, Yong TAN, Yanyun YIN, Xiaowei NIE, Jingyu HUANG, Wenting ZUO, Yuling LI. Tiaozhou Ziyin recipe for treatment of premature ovarian insufficiency: efficacy, safety and mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| [7] | Xiaotao LIANG, Yifan XIONG, Xueqi LIU, Xiaoshan LIANG, Xiaoyu ZHU, Wei XIE. Huoxue Shufeng Granule alleviates central sensitization in chronic migraine mice via TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 986-994. |
| [8] | Niandong RAN, Jie LIU, Jian XU, Yongping ZHANG, Jiangtao GUO. n-butanol fraction of ethanol extract of Periploca forrestii Schltr.: its active components, targets and pathways for treating Alcheimer's disease in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 785-798. |
| [9] | Haonan¹ XU, Fang³ ZHANG, Yuying² HUANG, Qisheng⁴ YAO, Yueqin⁴ GUAN, Hao CHEN. Thesium chinense Turcz. alleviates antibiotic-associated diarrhea in mice by modulating gut microbiota structure and regulating the EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [10] | Junjie GAO, Kai YE, Jing WU. Quercetin inhibits proliferation and migration of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells by regulating TP53 gene [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 313-321. |
| [11] | Ying LIU, Borui LI, Yongcai LI, Lubo CHANG, Jiao WANG, Lin YANG, Yonggang YAN, Kai QV, Jiping LIU, Gang ZHANG, Xia SHEN. Jiawei Xiaoyao Pills improves depression-like behavior in rats by regulating neurotransmitters, inhibiting inflammation and oxidation and modulating intestinal flora [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 347-358. |
| [12] | Qiao CHU, Xiaona WANG, Jiaying XU, Huilin PENG, Yulin ZHAO, Jing ZHANG, Guoyu LU, Kai WANG. Pulsatilla saponin D inhibits invasion and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer cells through multiple targets and pathways [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [13] | Xiupeng LONG, Shun TAO, Shen YANG, Suyun LI, Libing RAO, Li LI, Zhe ZHANG. Quercetin improves heart failure by inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis via suppressing the MAPK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 187-196. |
| [14] | Meng XU, Lina CHEN, Jinyu WU, Lili LIU, Mei SHI, Hao ZHOU, Guoliang ZHANG. Mechanism of Hedyotis diffusa-Scutellaria barbata D. Don for treatment of primary liver cancer: analysis with network pharmacology, molecular docking and in vitro validation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 80-89. |
| [15] | Qing LIU, Jing LIU, Yihang ZHENG, Jin LEI, Jianhua HUANG, Siyu LIU, Fang LIU, Qunlong PENG, Yuanfang ZHANG, Junjie WANG, Yujuan LI. Quercetin mediates the therapeutic effect of Centella asiatica on psoriasis by regulating STAT3 phosphorylation to inhibit the IL-23/IL-17A axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 90-99. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||