Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1185-1199.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.08
Previous Articles Next Articles
Guoyong LI1,2( ), Renling LI3, Yiting LIU1,2, Hongxia KE1,2, Jing LI1,2(
), Renling LI3, Yiting LIU1,2, Hongxia KE1,2, Jing LI1,2( ), Xinhua WANG1,2(
), Xinhua WANG1,2( )
)
Received:2025-01-06
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-06-27
Contact:
Jing LI, Xinhua WANG
E-mail:L15626421524@163.com;lijing82@gzhmu.edu.cn;xinhuaw@gzhmu.edu.cn
Supported by:Guoyong LI, Renling LI, Yiting LIU, Hongxia KE, Jing LI, Xinhua WANG. Therapeutic mechanism of Arctium lappa extract for post-viral pneumonia pulmonary fibrosis: a metabolomics, network pharmacology analysis and experimental verification[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.08
| No. | Retention time (min) | m/z | Adduct ion | Molecular formula | Compound | Fragment ion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical | Measured | Mass error/ppm | ||||||
| 1 | 1.574 | 138.055 | 138.0554 | 3.39 | [M+H]+ | C3H7NO2 | Aminobenzoic acid [ | 120.0449, 94.0657 |
| 2 | 2.228 | 268.104 | 268.1044 | 1.69 | [M+H]+ | C10H13N5O4 | Adenosine [ | 136.0608, 119.0346 |
| 3 | 2.494 | 132.1019 | 132.1023 | 2.93 | [M+H]+ | C6H13NO2 | L-Leucine [ | 86.0972, 69.0705 |
| 4 | 2.686 | 132.1019 | 132.1023 | 3.08 | [M+H]+ | C6H13NO2 | L-isoleucine [ | 86.0965, 77.0386 |
| 5 | 2.854 | 331.0671 | 331.0753 | 3.02 | [M-H]- | C13H16O10 | 1-O-Galloyl-glucose [ | 168.0063, 125.0242 |
| 6 | 3.237 | 345.0827 | 345.091 | 3.01 | [M-H]- | C14H18O10 | Methyl-6-O-galloyl-β-D-glucopyranoside [ | 137.0249, 93.0347 |
| 7 | 3.802 | 166.0863 | 166.0868 | 3.14 | [M+H]+ | C9H11NO2 | L-Phenylalanine [ | 120.0811, 103.0544 |
| 8 | 3.919 | 447.1508 | 447.1504 | 2.34 | [M-H]- | C19H28O12 | 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylalcohol-4-O-β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→6)-O-β-D-glucopyranoside [ | 293.0881, 149.0456 |
| 9 | 4.634 | 353.0878 | 353.0888 | 2.53 | [M-H]- | C16H18O9 | 5-caffeoylquinic acid[ | 135.0453, 191.0562 |
| 10 | 4.932 | 113.0597 | 113.0602 | 4.42 | [M+H]+ | C6H8O2 | Parasorbic acid[ | 95.0496, 59.0501 |
| 11 | 5.199 | 205.0972 | 205.0974 | 1.36 | [M+H]+ | C11H12N2O2 | Tryptophan[ | 146.0610, 118.0657 |
| 12 | 6.431 | 353.0878 | 353.0891 | 3.32 | [M-H]- | C16H18O9 | Chlorogenic acid(NBZ1)[ | 191.0569, 127.0402 |
| 13 | 6.681 | 353.0878 | 353.0890 | 3.24 | [M-H]- | C16H18O9 | Cryptochlorgenic acid[ | 191.0571, 85.0301 |
| 14 | 7.163 | 537.1978 | 537.1987 | 0.88 | [M-H]- | C26H34O12 | Terebinthacoside III(NBZ2)[ | 327.1251, 312.0999 |
| 15 | 7.496 | 179.035 | 179.0357 | 4.02 | [M-H]- | C9H8O4 | Caffeic acid(NBZ3)[ | 179.0351, 149.0611 |
| 16 | 7.579 | 161.0244 | 161.0246 | 4.97 | [M-H]- | C9H6O3 | Hydroxycoumarin(NBZ4)[ | 177.0562, 133.0660 |
| 17 | 8.061 | 337.0929 | 337.0941 | 3.26 | [M-H]- | C16H18O8 | 3-p-Coumaroylquinic acid [ | 191.0568, 93.0346 |
| 18 | 8.311 | 539.2134 | 539.2079 | 1.22 | [M-H]- | C26H36O12 | (7R,8R)-7,9,9'-trihydroxy-3,3'-dimethoxy-8-O-4'-neolignan-9'-O-β-D-glucopyranoside(NBZ5)[ | 377.1613, 195.0668 |
| 19 | 9.409 | 681.24 | 681.2461 | -1.69 | [M-H]- | C32H42O16 | Pinoresinol-4'4'-O-β-D-glucoside[ | 519.1874, 357.1347 |
| 20 | 10.326 | 417.1755 | 417.1865 | 1.41 | [M+H]+ | C19H28O10 | 2-phenethyl-β-primeveroside[ | 307.1153, 159.0806 |
| 21 | 10.907 | 567.2083 | 567.2092 | 0.85 | [M+HCOO]- | C26H34O11 | Lariciresinol-4-β-D-glucopyranoside[ | 151.0394, 314.1152 |
| 22 | 11.672 | 535.1821 | 535.1780 | 1 | [M-H]- | C26H32O12 | 4,4',9'-trihydroxy-3,3'-dimethoxy-7',9-epoxylignan-7-oxo-4-O-β-D-glucopyranoside[ | 387.1451, 151.0403 |
| 23 | 12.105 | 515.1195 | 515.1207 | 1.98 | [M-H]- | C25H24O12 | 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid(NBZ6)[ | 353.0881, 191.0562 |
| 24 | 12.347 | 749.2815 | 749.2821 | 0.79 | [M-H]- | C40H46O14 | Lappaol H(NBZ7)[ | 665.2400, 559.1979 |
| 25 | 12.720 | 549.1978 | 549.1972 | -1.55 | [M-H]- | C27H34O12 | 2-hydroxyarctiin [ | 387.1456, 151.0406 |
| 26 | 13.363 | 519.1872 | 519.1868 | -0.97 | [M-H]- | C26H32O11 | Pinoresinol‑O‑β‑D‑glucopyranoside(NBZ8)[ | 357.1348, 221.0817 |
| 27 | 14.334 | 515.1195 | 515.1205 | 1.7 | [M-H]- | C25H24O12 | 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid(NBZ9)[ | 353.0898, 173.0463 |
| 28 | 14.983 | 553.2079 | 553.2087 | 1.06 | [M-H]- | C30H34O10 | Lappaol C(NBZ10)[ | 505.1874, 411.1458 |
| 29 | 15.166 | 553.2079 | 553.2087 | 0.91 | [M-H]- | C30H34O10 | Isolappaol C(NBZ11)[ | 505.1874, 411.1458 |
| 30 | 15.796 | 552.2439 | 552.2442 | 2.1 | [M+NH4]+ | C27H34O11 | Arctiin(NBZ12)[ | 373.1655, 355.1547 |
| 31 | 17.079 | 553.2068 | 553.2077 | 1.63 | [M+H]+ | C30H32O10 | Arctignan C[ | 505.1858, 353.0384 |
| 32 | 17.379 | 551.1923 | 551.1930 | 1 | [M-H]- | C30H32O10 | Arctignan B[ | 521.1819, 397.1295 |
| 33 | 17.761 | 731.2709 | 731.2712 | 0.32 | [M-H]- | C40H44O13 | Arctignan D(NBZ13)[ | 665.2398, 559.1972 |
| 34 | 17.911 | 553.2079 | 553.2087 | 1.26 | [M-H]- | C30H34O10 | Arctignan A(NBZ14)[ | 505.1875, 357.1352 |
| 35 | 17.928 | 357.1344 | 357.1354 | 2.62 | [M-H]- | C20H22O6 | Matairesinol(NBZ15)[ | 342.1115, 221.0825 |
| 36 | 17.994 | 567.2236 | 567.2244 | 0.98 | [M-H]- | C31H36O10 | Lappaol D(NBZ16)[ | 415.1764, 519.2021 |
| 37 | 18.028 | 731.2709 | 731.2713 | 0.48 | [M-H]- | C40H44O13 | Arctignan E(NBZ17)[ | 559.1964, 665.2379 |
| 38 | 20.307 | 559.1939 | 559.1949 | 1.94 | [M+Na]+ | C30H32O9 | Lappaol A(NBZ18)[ | 460.0799, 137.0597 |
| 39 | 20.581 | 537.2119 | 537.2075 | 1.7 | [M+H]+ | C30H32O9 | Isolappaol A(NBZ19[ | 371.1481 137.0599 |
| 40 | 21.039 | 373.1646 | 373.1644 | 0.96 | [M+H]+ | C21H24O6 | Arctigenin(NBZ20)[ | 305.1175 137.0602 |
| 41 | 22.137 | 713.2604 | 713.2609 | 0.5 | [M-H]- | C40H42O12 | Lappaol F(NBZ21)[ | 665.2381, 653.2382 |
| 42 | 22.753 | 549.213 | 549.2134 | 0.5 | [M-H]- | C31H34O9 | Lappaol B(NBZ22)[ | 531.2001, 519.2020 |
| 43 | 34.532 | 313.2463 | 313.2392 | 2.81 | [M+CH3COO]- | C16H30O2 | Hexadecenoic acid [ | 183.1394, 129.0921 |
| 44 | 35.281 | 315.2541 | 315.2548 | 2.42 | [M+HCOO]- | C17H34O2 | Daturic acid [ | 112.9852, 127.1120 |
| 45 | 35.647 | 295.2279 | 295.2278 | 0.52 | [M-H]- | C18H32O3 | 9(10)-EpOME[ | 277.2171, 195.1386 |
| 46 | 36.795 | 297.2435 | 297.2444 | 2.47 | [M-H]- | C18H34O3 | 9-hydroxy-12-octadecenoic acid [ | 279.2327, 127.1117 |
| 47 | 37.66 | 277.2173 | 277.2181 | 2.69 | [M-H]- | C18H30O2 | Linolenic acid [ | 233.2273, 177.1655 |
| 48 | 37.712 | 353.2662 | 353.2673 | 2.68 | [M+Na]+ | C19H38O4 | Monopalmitin [ | 209.1541, 91.0553 |
| 49 | 38.093 | 279.233 | 279.2338 | 3.05 | [M-H]- | C18H32O2 | Linoleicacid(NBZ23)[ | 261.2213, 167.0723 |
| 50 | 38.675 | 255.233 | 255.2337 | 2.41 | [M-H]- | C16H32O2 | Methyl pentadecanoate [ | 209.0621, 108.0204 |
| 51 | 39.041 | 281.2486 | 281.2492 | 1.98 | [M-H]- | C18H34O2 | Oleic acid [ | 127.0748, 263.2380 |
| 52 | 39.061 | 376.3421 | 376.3403 | 2.12 | [M+NH4]+ | C21H42O4 | 2-monostearin [ | 260.2363, 95.0850 |
| 53 | 40.055 | 283.2643 | 283.2645 | 0.67 | [M-H]- | C18H36O2 | Octadecanoic acid [ | 96.0190, 161.0050 |
Tab.1 Identification of chemical compounds in Arctium lappa extract
| No. | Retention time (min) | m/z | Adduct ion | Molecular formula | Compound | Fragment ion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical | Measured | Mass error/ppm | ||||||
| 1 | 1.574 | 138.055 | 138.0554 | 3.39 | [M+H]+ | C3H7NO2 | Aminobenzoic acid [ | 120.0449, 94.0657 |
| 2 | 2.228 | 268.104 | 268.1044 | 1.69 | [M+H]+ | C10H13N5O4 | Adenosine [ | 136.0608, 119.0346 |
| 3 | 2.494 | 132.1019 | 132.1023 | 2.93 | [M+H]+ | C6H13NO2 | L-Leucine [ | 86.0972, 69.0705 |
| 4 | 2.686 | 132.1019 | 132.1023 | 3.08 | [M+H]+ | C6H13NO2 | L-isoleucine [ | 86.0965, 77.0386 |
| 5 | 2.854 | 331.0671 | 331.0753 | 3.02 | [M-H]- | C13H16O10 | 1-O-Galloyl-glucose [ | 168.0063, 125.0242 |
| 6 | 3.237 | 345.0827 | 345.091 | 3.01 | [M-H]- | C14H18O10 | Methyl-6-O-galloyl-β-D-glucopyranoside [ | 137.0249, 93.0347 |
| 7 | 3.802 | 166.0863 | 166.0868 | 3.14 | [M+H]+ | C9H11NO2 | L-Phenylalanine [ | 120.0811, 103.0544 |
| 8 | 3.919 | 447.1508 | 447.1504 | 2.34 | [M-H]- | C19H28O12 | 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylalcohol-4-O-β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→6)-O-β-D-glucopyranoside [ | 293.0881, 149.0456 |
| 9 | 4.634 | 353.0878 | 353.0888 | 2.53 | [M-H]- | C16H18O9 | 5-caffeoylquinic acid[ | 135.0453, 191.0562 |
| 10 | 4.932 | 113.0597 | 113.0602 | 4.42 | [M+H]+ | C6H8O2 | Parasorbic acid[ | 95.0496, 59.0501 |
| 11 | 5.199 | 205.0972 | 205.0974 | 1.36 | [M+H]+ | C11H12N2O2 | Tryptophan[ | 146.0610, 118.0657 |
| 12 | 6.431 | 353.0878 | 353.0891 | 3.32 | [M-H]- | C16H18O9 | Chlorogenic acid(NBZ1)[ | 191.0569, 127.0402 |
| 13 | 6.681 | 353.0878 | 353.0890 | 3.24 | [M-H]- | C16H18O9 | Cryptochlorgenic acid[ | 191.0571, 85.0301 |
| 14 | 7.163 | 537.1978 | 537.1987 | 0.88 | [M-H]- | C26H34O12 | Terebinthacoside III(NBZ2)[ | 327.1251, 312.0999 |
| 15 | 7.496 | 179.035 | 179.0357 | 4.02 | [M-H]- | C9H8O4 | Caffeic acid(NBZ3)[ | 179.0351, 149.0611 |
| 16 | 7.579 | 161.0244 | 161.0246 | 4.97 | [M-H]- | C9H6O3 | Hydroxycoumarin(NBZ4)[ | 177.0562, 133.0660 |
| 17 | 8.061 | 337.0929 | 337.0941 | 3.26 | [M-H]- | C16H18O8 | 3-p-Coumaroylquinic acid [ | 191.0568, 93.0346 |
| 18 | 8.311 | 539.2134 | 539.2079 | 1.22 | [M-H]- | C26H36O12 | (7R,8R)-7,9,9'-trihydroxy-3,3'-dimethoxy-8-O-4'-neolignan-9'-O-β-D-glucopyranoside(NBZ5)[ | 377.1613, 195.0668 |
| 19 | 9.409 | 681.24 | 681.2461 | -1.69 | [M-H]- | C32H42O16 | Pinoresinol-4'4'-O-β-D-glucoside[ | 519.1874, 357.1347 |
| 20 | 10.326 | 417.1755 | 417.1865 | 1.41 | [M+H]+ | C19H28O10 | 2-phenethyl-β-primeveroside[ | 307.1153, 159.0806 |
| 21 | 10.907 | 567.2083 | 567.2092 | 0.85 | [M+HCOO]- | C26H34O11 | Lariciresinol-4-β-D-glucopyranoside[ | 151.0394, 314.1152 |
| 22 | 11.672 | 535.1821 | 535.1780 | 1 | [M-H]- | C26H32O12 | 4,4',9'-trihydroxy-3,3'-dimethoxy-7',9-epoxylignan-7-oxo-4-O-β-D-glucopyranoside[ | 387.1451, 151.0403 |
| 23 | 12.105 | 515.1195 | 515.1207 | 1.98 | [M-H]- | C25H24O12 | 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid(NBZ6)[ | 353.0881, 191.0562 |
| 24 | 12.347 | 749.2815 | 749.2821 | 0.79 | [M-H]- | C40H46O14 | Lappaol H(NBZ7)[ | 665.2400, 559.1979 |
| 25 | 12.720 | 549.1978 | 549.1972 | -1.55 | [M-H]- | C27H34O12 | 2-hydroxyarctiin [ | 387.1456, 151.0406 |
| 26 | 13.363 | 519.1872 | 519.1868 | -0.97 | [M-H]- | C26H32O11 | Pinoresinol‑O‑β‑D‑glucopyranoside(NBZ8)[ | 357.1348, 221.0817 |
| 27 | 14.334 | 515.1195 | 515.1205 | 1.7 | [M-H]- | C25H24O12 | 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid(NBZ9)[ | 353.0898, 173.0463 |
| 28 | 14.983 | 553.2079 | 553.2087 | 1.06 | [M-H]- | C30H34O10 | Lappaol C(NBZ10)[ | 505.1874, 411.1458 |
| 29 | 15.166 | 553.2079 | 553.2087 | 0.91 | [M-H]- | C30H34O10 | Isolappaol C(NBZ11)[ | 505.1874, 411.1458 |
| 30 | 15.796 | 552.2439 | 552.2442 | 2.1 | [M+NH4]+ | C27H34O11 | Arctiin(NBZ12)[ | 373.1655, 355.1547 |
| 31 | 17.079 | 553.2068 | 553.2077 | 1.63 | [M+H]+ | C30H32O10 | Arctignan C[ | 505.1858, 353.0384 |
| 32 | 17.379 | 551.1923 | 551.1930 | 1 | [M-H]- | C30H32O10 | Arctignan B[ | 521.1819, 397.1295 |
| 33 | 17.761 | 731.2709 | 731.2712 | 0.32 | [M-H]- | C40H44O13 | Arctignan D(NBZ13)[ | 665.2398, 559.1972 |
| 34 | 17.911 | 553.2079 | 553.2087 | 1.26 | [M-H]- | C30H34O10 | Arctignan A(NBZ14)[ | 505.1875, 357.1352 |
| 35 | 17.928 | 357.1344 | 357.1354 | 2.62 | [M-H]- | C20H22O6 | Matairesinol(NBZ15)[ | 342.1115, 221.0825 |
| 36 | 17.994 | 567.2236 | 567.2244 | 0.98 | [M-H]- | C31H36O10 | Lappaol D(NBZ16)[ | 415.1764, 519.2021 |
| 37 | 18.028 | 731.2709 | 731.2713 | 0.48 | [M-H]- | C40H44O13 | Arctignan E(NBZ17)[ | 559.1964, 665.2379 |
| 38 | 20.307 | 559.1939 | 559.1949 | 1.94 | [M+Na]+ | C30H32O9 | Lappaol A(NBZ18)[ | 460.0799, 137.0597 |
| 39 | 20.581 | 537.2119 | 537.2075 | 1.7 | [M+H]+ | C30H32O9 | Isolappaol A(NBZ19[ | 371.1481 137.0599 |
| 40 | 21.039 | 373.1646 | 373.1644 | 0.96 | [M+H]+ | C21H24O6 | Arctigenin(NBZ20)[ | 305.1175 137.0602 |
| 41 | 22.137 | 713.2604 | 713.2609 | 0.5 | [M-H]- | C40H42O12 | Lappaol F(NBZ21)[ | 665.2381, 653.2382 |
| 42 | 22.753 | 549.213 | 549.2134 | 0.5 | [M-H]- | C31H34O9 | Lappaol B(NBZ22)[ | 531.2001, 519.2020 |
| 43 | 34.532 | 313.2463 | 313.2392 | 2.81 | [M+CH3COO]- | C16H30O2 | Hexadecenoic acid [ | 183.1394, 129.0921 |
| 44 | 35.281 | 315.2541 | 315.2548 | 2.42 | [M+HCOO]- | C17H34O2 | Daturic acid [ | 112.9852, 127.1120 |
| 45 | 35.647 | 295.2279 | 295.2278 | 0.52 | [M-H]- | C18H32O3 | 9(10)-EpOME[ | 277.2171, 195.1386 |
| 46 | 36.795 | 297.2435 | 297.2444 | 2.47 | [M-H]- | C18H34O3 | 9-hydroxy-12-octadecenoic acid [ | 279.2327, 127.1117 |
| 47 | 37.66 | 277.2173 | 277.2181 | 2.69 | [M-H]- | C18H30O2 | Linolenic acid [ | 233.2273, 177.1655 |
| 48 | 37.712 | 353.2662 | 353.2673 | 2.68 | [M+Na]+ | C19H38O4 | Monopalmitin [ | 209.1541, 91.0553 |
| 49 | 38.093 | 279.233 | 279.2338 | 3.05 | [M-H]- | C18H32O2 | Linoleicacid(NBZ23)[ | 261.2213, 167.0723 |
| 50 | 38.675 | 255.233 | 255.2337 | 2.41 | [M-H]- | C16H32O2 | Methyl pentadecanoate [ | 209.0621, 108.0204 |
| 51 | 39.041 | 281.2486 | 281.2492 | 1.98 | [M-H]- | C18H34O2 | Oleic acid [ | 127.0748, 263.2380 |
| 52 | 39.061 | 376.3421 | 376.3403 | 2.12 | [M+NH4]+ | C21H42O4 | 2-monostearin [ | 260.2363, 95.0850 |
| 53 | 40.055 | 283.2643 | 283.2645 | 0.67 | [M-H]- | C18H36O2 | Octadecanoic acid [ | 96.0190, 161.0050 |
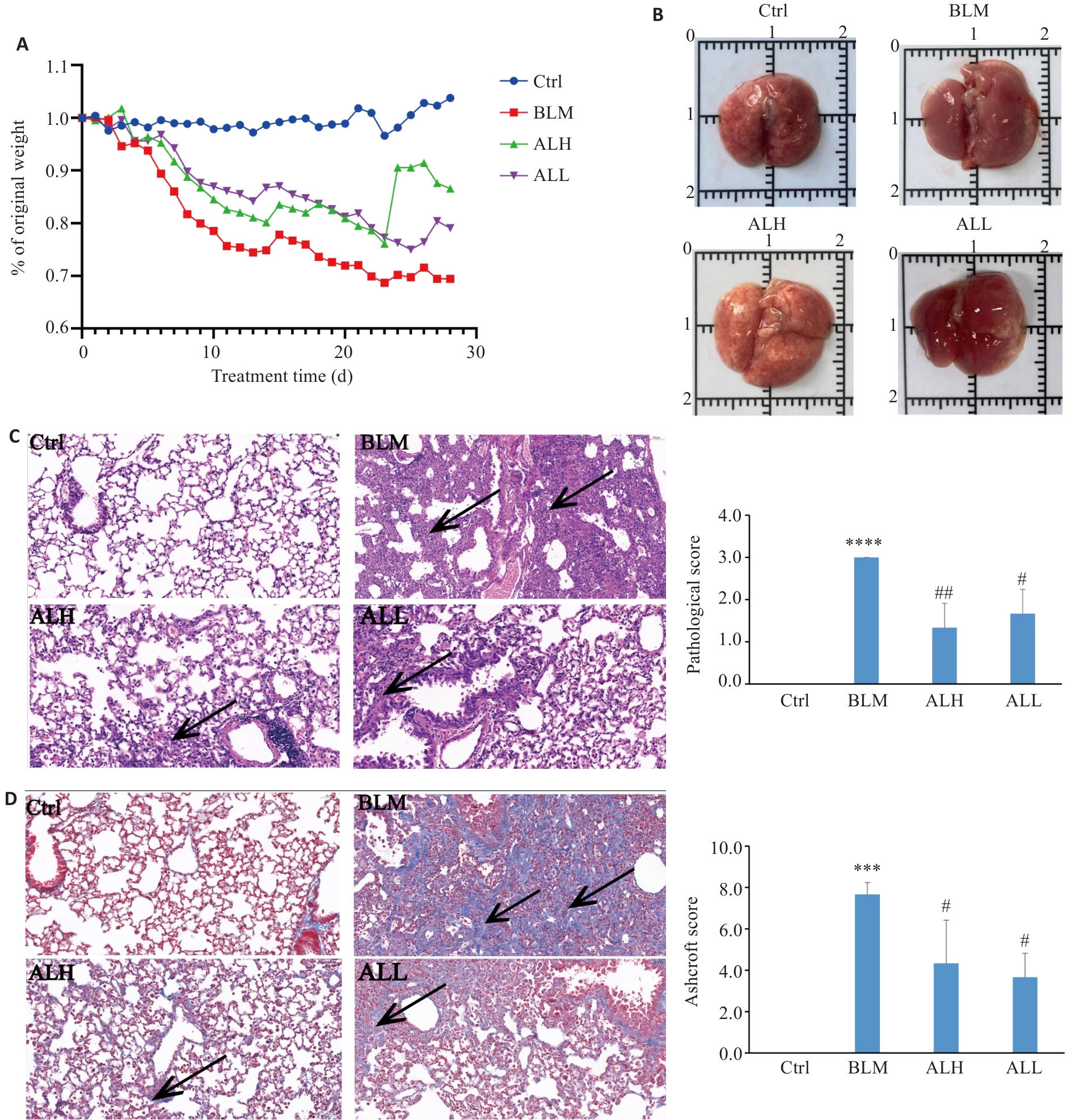
Fig.2 Effects of Arctium lappa extract on pulmonary fibrosis in mice. A: Body weight changes of the mice. B: Appearance of mouse lungs. C: HE staining of mouse lung tissue (Original magnification: ×200) and pathological scores (black arrow indicate typical areas of lung injury). D: Masson staining of mouse lung tissue (×200) and Ashcroft scores (black arrows indicate typical areas of fibrosis). ***P<0.00l, ****P<0.000l vs control group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.0l vs BLM group.
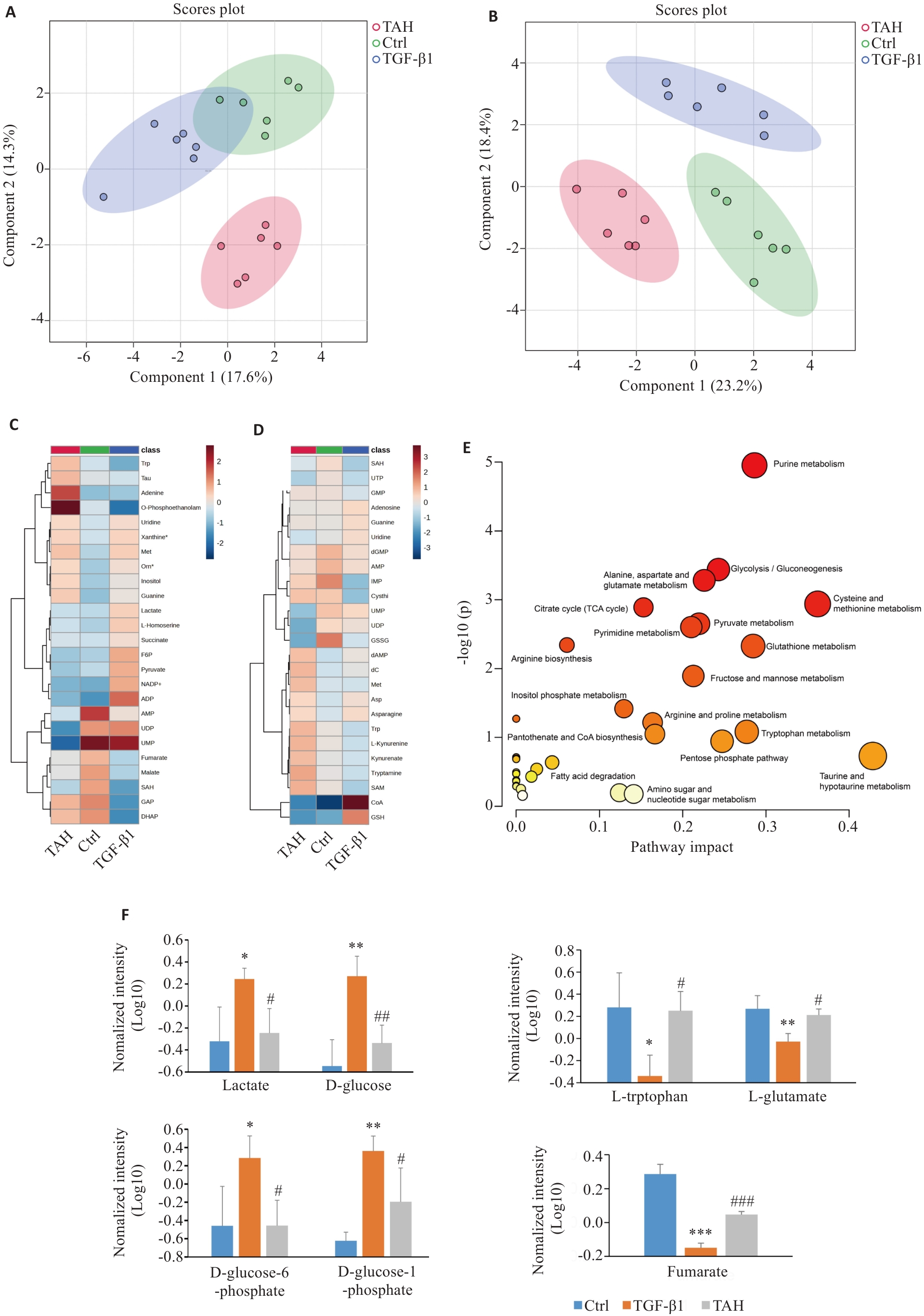
Fig.3 Metabolomics analysis of the differential metabolites in TGF β1-induced A549 cells with Arctium lappa extract treatment. A, B: OPLS-DA plots of different groups in negative (A) and positive (B) modes. C, D: Clustering heat map of the differential metabolites (Top 25) in negative mode (C) and positive mode (D). E: Differential metabolite-enriched metabolic pathways. F: Arctium lappa extract regulates the abundance of intermediate products in metabolic pathways. *P<0.05, **P<0.0l, ***P<0.00l vs control group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.0l, ###P<0.00l vs TGF-β1 group.
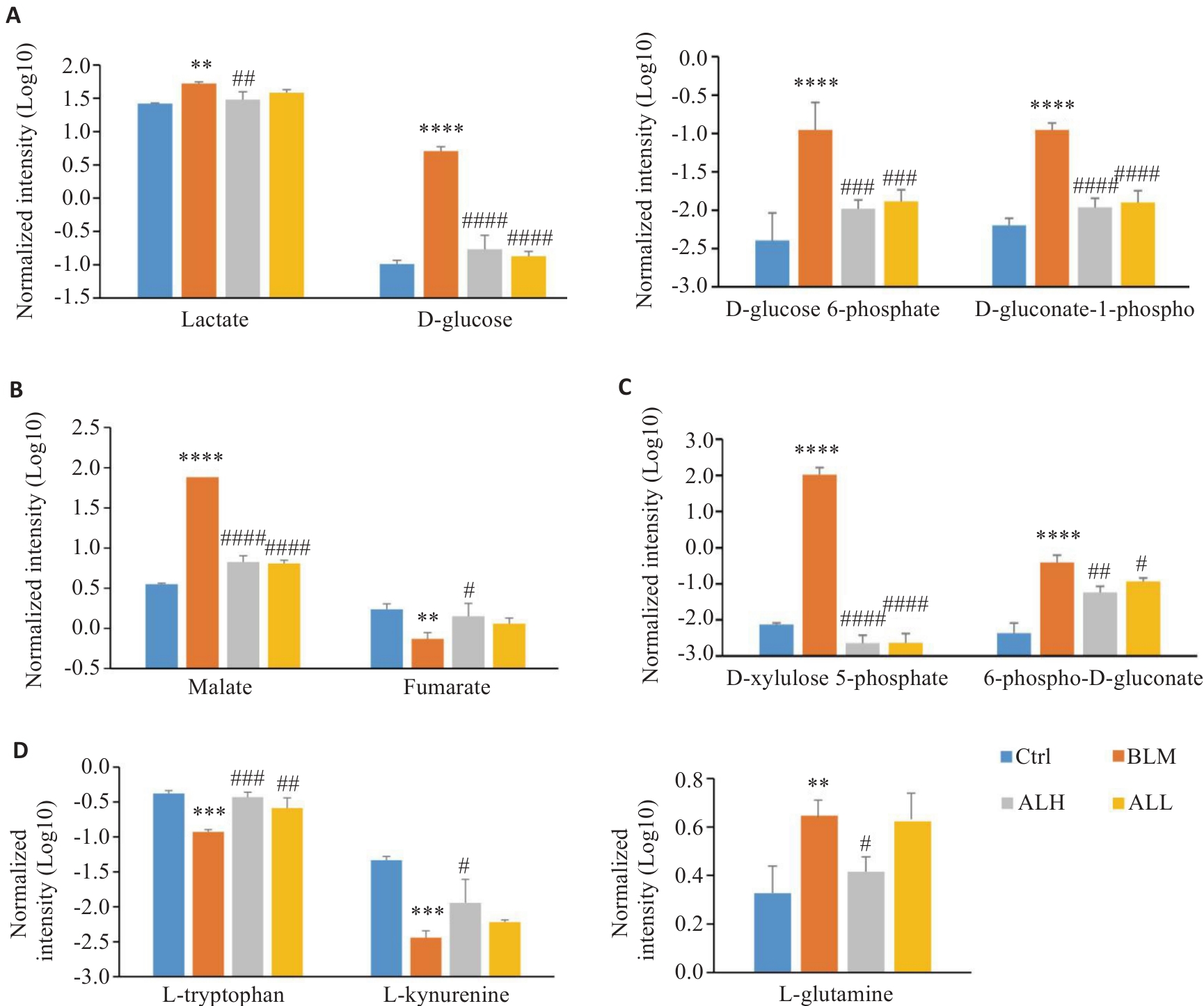
Fig.4 Effects of Arctium lappa extract on production of metabolites in mouse plasma. A: Metabolites from the glycolsis pathway. B: Metabolites from the citrate cycle pathway. C: Metabolites from the pentose phosphate pathway. D: Metabolites from the amino acid pathway. **P<0.0l, ***P<0.00l, ****P<0.000l vs control group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.0l, ###P<0.00l, ####P<0.000l vs BLM group.
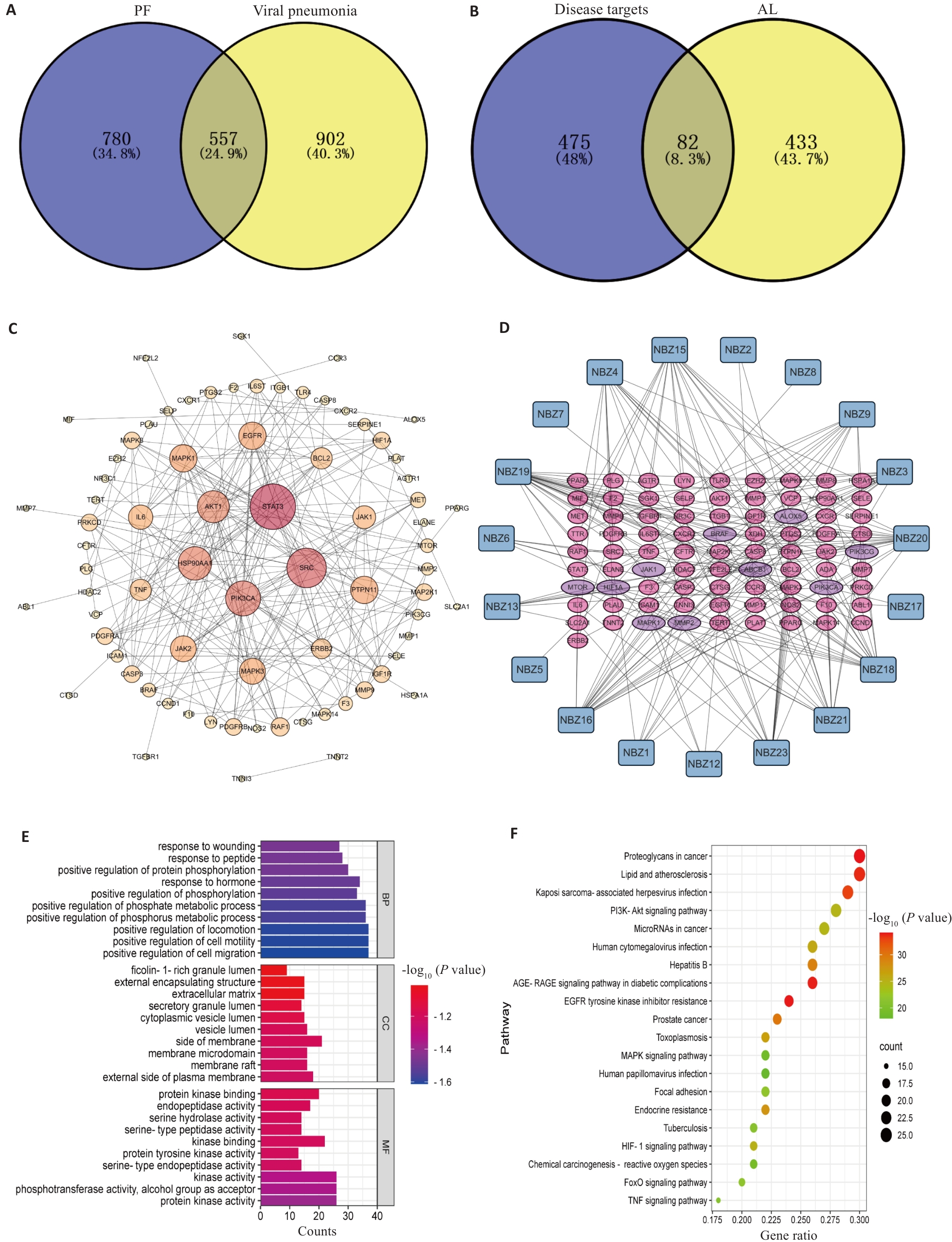
Fig.5 Prediction of the potential mechanism of Arctium lappa extract in treatment of PPF by network pharmacological analysis. A: Common targets of viral pneumonia and pulmonary fibrosis. B: Common targets of Arctium lappa extract and disease targets. C: Protein-protein interaction network of the key targets. D: Network of components-key targets interaction. E: Key targets of gene oncology biological process, cellular component and molecular function. F: Pathway enrichment analysis of the key targets.
| PDB ID | 4GV1 6NJS 1US0 6GR5 3HHM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AKT1 | STAT3 | SRC | HSP90AA1 | PIK3CA | |
| Arctigenin | -6.507 | -6.402 | -5.763 | -6.547 | -7.426 |
| Isolappaol A | -8.067 | -8.169 | -7.637 | -6.55 | -9.424 |
| Lappaol A | -6.757 | -8.544 | -7.251 | -6.45 | -9.126 |
| Lappaol D | -7.564 | -5.689 | -7.099 | -5.803 | -7.943 |
| Matairesinol | -6.829 | -5.633 | -6.700 | -6.764 | -6.998 |
Tab.2 Binding energy of active ingredients in Arctium lappa extract with the key targets
| PDB ID | 4GV1 6NJS 1US0 6GR5 3HHM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AKT1 | STAT3 | SRC | HSP90AA1 | PIK3CA | |
| Arctigenin | -6.507 | -6.402 | -5.763 | -6.547 | -7.426 |
| Isolappaol A | -8.067 | -8.169 | -7.637 | -6.55 | -9.424 |
| Lappaol A | -6.757 | -8.544 | -7.251 | -6.45 | -9.126 |
| Lappaol D | -7.564 | -5.689 | -7.099 | -5.803 | -7.943 |
| Matairesinol | -6.829 | -5.633 | -6.700 | -6.764 | -6.998 |
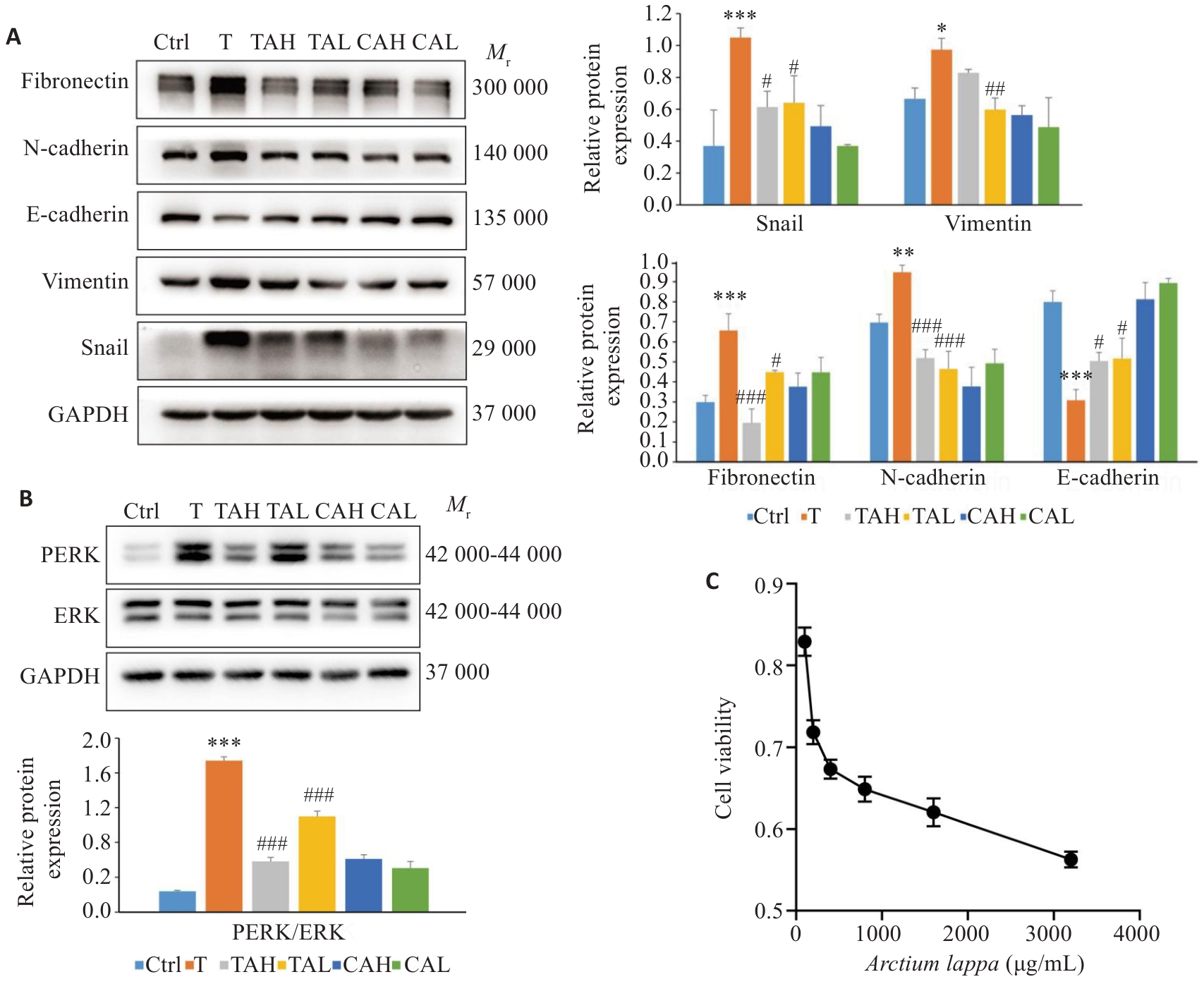
Fig.8 Arctium lappa (AL) extract regulates the expression of MAPK signaling pathway and EMT in vitro. A: Effect of Arctium lappa extract on expressions of EMT marker proteins in A549 cells detected by Western blotting. B: Arctium lappa extract inhibits MAPK signaling. C: Effect of Arctium lappa extract on A549 cell viability. *P<0.05, **P<0.0l, ***P<0.00l vs control group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.0l, ###P<0.00l vs T group.
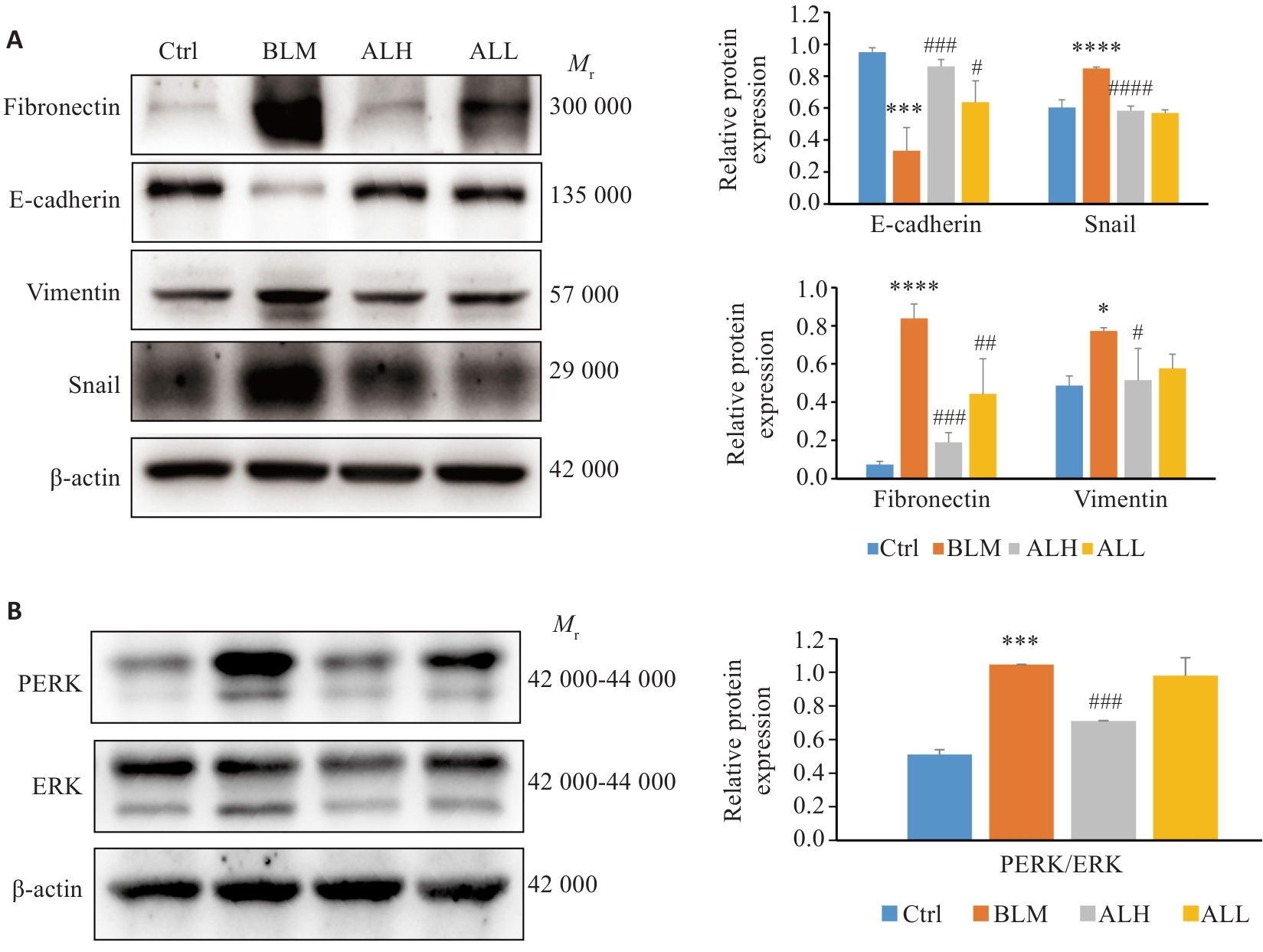
Fig.9 Arctium lappa extract regulates BLM-induced EMT and MAPK signaling pathway. *P<0.05, ***P<0.00l, ****P<0.000l vs control group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.0l, ###P<0.00l, ####P<0.000l vs BLM group.
| 1 | Huang WJ, Tang XX. Virus infection induced pulmonary fibrosis[J]. J Transl Med, 2021, 19(1): 496. doi:10.1186/s12967-021-03159-9 |
| 2 | Herold S, Becker C, Ridge KM, et al. Influenza virus-induced lung injury: pathogenesis and implications for treatment[J]. Eur Respir J, 2015, 45(5): 1463-78. doi:10.1183/09031936.00186214 |
| 3 | Daş TE, Sargan A, Yağmur G, et al. Viral pneumonias in forensic autopsies: evaluation and classification of histopathologic changes with microbiologic correlation[J]. Am J Forensic Med Pathol, 2016, 37(4): 255-63. doi:10.1097/paf.0000000000000261 |
| 4 | Han XY, Fan YQ, Alwalid O, et al. Six-month follow-up chest CT findings after severe COVID-19 pneumonia[J]. Radiology, 2021, 299(1): E177-86. doi:10.1148/radiol.2021203153 |
| 5 | Chen C, Chen J, Huang JN. Persistence of lymphocytopenia with CT abnormalities among patients with critical H7N9 swine-origin influenza A virus infection[J]. Jpn J Radiol, 2015, 33(10): 657-62. doi:10.1007/s11604-015-0476-4 |
| 6 | Mineo G, Ciccarese F, Modolon C, et al. Post-ARDS pulmonary fibrosis in patients with H1N1 pneumonia: role of follow-up CT[J]. Radiol Med, 2012, 117(2): 185-200. doi:10.1007/s11547-011-0740-3 |
| 7 | Pociask DA, Robinson KM, Chen K, et al. Epigenetic and transcriptomic regulation of lung repair during recovery from influenza infection[J]. Am J Pathol, 2017, 187(4): 851-63. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.12.012 |
| 8 | Vaz de Paula CB, Nagashima S, Liberalesso V, et al. COVID-19: immunohistochemical analysis of TGF-β signaling pathways in pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 23(1): 168. doi:10.3390/ijms23010168 |
| 9 | Schäfer SC, Funke-Chambour M, Berezowska S. Idiopathische lungenfibrose-epidemiologie, ursachen und klinischer verlauf[J]. Der Pathol, 2020, 41(1): 46-51. doi:10.1007/s00292-019-00747-x |
| 10 | Saito S, Alkhatib A, Kolls JK, et al. Pharmacotherapy and adjunctive treatment for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF)[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2019, 11(): S1740-54. doi:10.21037/jtd.2019.04.62 |
| 11 | Zhang YK, Lu P, Qin H, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine combined with pulmonary drug delivery system and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Rationale and therapeutic potential[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, 133: 111072. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111072 |
| 12 | 刘晓明, 张 伟. 张伟教授从痰、瘀、虚、毒论治间质性肺疾病的经验[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2015, 26(3): 706-7. doi:10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2015.01.024 |
| 13 | 蔡恩博, 王瑞卿, 刘德民, 等. 牛蒡子苷元现代药理作用研究进展[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2016, 18(1): 130-4. doi:10.11842/wst.2016.01.022 |
| 14 | 范红江, 王克林. 银翘散的抗病毒作用研究进展[J]. 世界中医药, 2016, 11(7): 1378-80. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2016.07.059 |
| 15 | 王琬玥, 濮宇豪, 夏睿笛, 等. FeAl-LDH@FeS x -NBC光催化降解水中的对氨基苯甲酸[J]. 吉林大学学报: 理学版, 2025, 63(2): 647-54. |
| 16 | Shen SD, Zhuang JJ, Chen YJ, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of arctigenin ester and ether derivatives as activators of AMPK[J]. Bioorg Med Chem, 2013, 21(13): 3882-93. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2013.04.010 |
| 17 | 王清华. UHPLC-MS/MS法同时测定六合氨基酸注射液中6个有效成分的含量[J]. 药物分析杂志, 2019, 39(2): 257-62. |
| 18 | Li LF, Chang KC, Zhou YM, et al. Design of an amide N-glycoside derivative of β-glucogallin: a stable, potent, and specific inhibitor of aldose reductase[J]. J Med Chem, 2014, 57(1): 71-7. doi:10.1021/jm401311d |
| 19 | Chyba A, Mastihubová M, Mastihuba V. Regioselective galloylation of methyl β-d-glucopyranoside by a lipase[J]. Monatsh Für Chem Chem Mon, 2016, 147(6): 1137-42. doi:10.1007/s00706-016-1696-8 |
| 20 | 胡小勤, 蒙 丹, 曾学文, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS和HPLC的广东产广地龙鲜、干品主要化学成分分析[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2024, 36(12): 2051-63. |
| 21 | 杨桠楠, 黄小英, 王 尉, 等. 牛蒡子中一个新木脂素类化合物[J]. 药学学报, 2017, 52(5): 779-84. doi:10.16438/j.0513-4870.2017-0139 |
| 22 | Li J, Wang SP, Wang YQ, et al. Comparative metabolism study on chlorogenic acid, cryptochlorogenic acid and neochlorogenic acid using UHPLC-Q-TOF MS coupled with network pharmacology[J]. Chin J Nat Med, 2021, 19(3): 212-24. doi:10.1016/s1875-5364(21)60023-7 |
| 23 | Cardellina I, Meinwald J. Isolation of parasorbic acid from the cranberry plant, Vaccinium macrocarpon [J]. Phytochemistry, 1980, 19(10): 2199-200. doi:10.1016/s0031-9422(00)82223-2 |
| 24 | Morikawa T, Matsuda H, Nishida N, et al. Structures of new aromatics glycosides from a Japanese folk medicine, the roots of Angelica furcijuga [J]. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo), 2004, 52(11): 1387-90. doi:10.1248/cpb.52.1387 |
| 25 | 宋瑞睿, 洪占梅, 李杨杨, 等. HPLC多指标成分定量结合化学模式识别评价龙脷叶质量[J]. 现代药物与临床, 2025, 40(3): 611-7. |
| 26 | Di Lella S, Porta NL, Tognetti R, et al. White rot fungal impact on the evolution of simple phenols during decay of silver fir wood by UHPLC-HQOMS[J]. Phytochem Anal, 2022, 33(2): 170-83. doi:10.1002/pca.3077 |
| 27 | Kiselova-Kaneva Y, Galunska B, Nikolova M, et al. High resolution LC-MS/MS characterization of polyphenolic composition and evaluation of antioxidant activity of Sambucus ebulus fruit tea traditionally used in Bulgaria as a functional food[J]. Food Chem, 2022, 367: 130759. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130759 |
| 28 | Zhou BX, Li J, Liang XL, et al. Transcriptome profiling of influenza A virus-infected lung epithelial (A549) cells with lariciresinol-4-β-D-glucopyranoside treatment[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(3): e0173058. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0173058 |
| 29 | 王 珏, 王乃利, 姚新生, 等. 小花鬼针草中咖啡酰奎宁酸类成分及其抑制组胺释放活性[J]. 中草药, 2006, 37(7): 966-70. doi:10.3321/j.issn:0253-2670.2006.07.002 |
| 30 | Su S, Cheng XL, Wink M. Natural lignans from Arctium lappa modulate P-glycoprotein efflux function in multidrug resistant cancer cells[J]. Phytomedicine, 2015, 22(2): 301-7. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2014.12.009 |
| 31 | 孔 铭, 张 健, 姚 楠, 等. HPLC同时测定络石藤中5个化学成分的含量[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2013, 19(3): 93-6. |
| 32 | Li J, Liang XL, Zhou BX, et al. (+)-pinoresinol-O-β-D-glucopyranoside from Eucommia ulmoides Oliver and its anti-inflammatory and antiviral effects against influenza A (H1N1) virus infection[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2019, 19(1): 563-72. doi:10.3892/mmr.2018.9696 |
| 33 | 冉小库, 窦德强. 牛蒡子化学成分研究[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2013, 15(7): 71-2. |
| 34 | 刘抗伦. 牛蒡子的化学成分研究与抗肿瘤作用初步研究[D]. 广州: 广州中医药大学, 2008. |
| 35 | 邓寒霜, 李筱玲, 王 欣, 等. 基于HPLC指纹图谱和一测多评多成分定量分析的连翘质量评价研究[J]. 中国药学杂志, 2024, 59(15): 1429-37. |
| 36 | Umehara K, Nakamura M, Miyase T, et al. Studies on differentiation inducers. VI. Lignan derivatives from Arctium fructus. (2)[J]. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo), 1996, 44(12): 2300-4. doi:10.1248/cpb.44.2300 |
| 37 | Yang BC, Xin HX, Wang FE, et al. Purification of lignans from Fructus Arctii using off-line two-dimensional supercritical fluid chromatography/reversed-phase liquid chromatography[J]. J Sep Sci, 2017, 40(16): 3231-8. doi:10.1002/jssc.201700139 |
| 38 | Zhang JY, Mei JW, Wang HY, et al. Chromatographic fingerprint combined with quantitative analysis of multi-components by single-marker for quality control of total lignans from Fructus arctii by high-performance liquid chromatography[J]. Phytochem Anal, 2022, 33(8): 1214-24. doi:10.1002/pca.3172 |
| 39 | Park SY, Hong SS, Han XH, et al. Lignans from Arctium lappa and their inhibition of LPS-induced nitric oxide production[J]. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo), 2007, 55(1): 150-2. doi:10.1248/cpb.55.150 |
| 40 | 齐艳明. 牛蒡化学成分研究[D]. 齐齐哈尔: 齐齐哈尔大学, 2012. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-984X.2012.02.007 |
| 41 | 董 锋, 李子祥, 贾春媚, 等. 基于UPLC/Q-TOF MS/MS的芝麻油成分分析[J]. 中国油脂, 2022, 47(10): 130-6. |
| 42 | Nasr A, Yosuf I, Turki Z, et al. LC-MS metabolomics profiling of Salvia aegyptiaca L. and S. lanigera Poir. with the antimicrobial properties of their extracts[J]. BMC Plant Biol, 2023, 23(1): 340. doi:10.1186/s12870-023-04341-5 |
| 43 | Hildreth K, Kodani SD, Hammock BD, et al. Cytochrome P450-derived linoleic acid metabolites EpOMEs and DiHOMEs: a review of recent studies[J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2020, 86: 108484. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108484 |
| 44 | 胡珊珊. 牛蒡子的化学研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明医科大学, 2019. |
| 45 | Lutton ES, Jackson FL. The polymorphism of 1-monostearin and 1-monopalmitin[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 1948, 70(7): 2445-9. doi:10.1021/ja01187a043 |
| 46 | Suastes-Rivas JK, Hernández-Altamirano R, Mena-Cervantes VY, et al. Efficient production of fatty acid methyl esters by a wastewater-isolated microalgae-yeast co-culture[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 2020, 27(23): 28490-9. doi:10.1007/s11356-019-07286-1 |
| 47 | Hama Amin BJ, Kakamad FH, Ahmed GS, et al. Post COVID-19 pulmonary fibrosis; a meta-analysis study[J]. Ann Med Surg (Lond), 2022, 77: 103590. doi:10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103590 |
| 48 | Zhang PX, Li J, Liu HX, et al. Long-term bone and lung consequences associated with hospital-acquired severe acute respiratory syndrome: a 15-year follow-up from a prospective cohort study[J]. Bone Res, 2020, 8: 8. doi:10.1038/s41413-020-00113-1 |
| 49 | Ung CY, Onoufriadis A, Parsons M, et al. Metabolic perturbations in fibrosis disease[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2021, 139: 106073. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2021.106109 |
| 50 | Liberti MV, Locasale JW. The Warburg effect: how does it benefit cancer cells[J]? Trends Biochem Sci, 2016, 41(3): 211-8. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2016.01.004 |
| 51 | Cui HC, Xie N, Banerjee S, et al. Lung myofibroblasts promote macrophage profibrotic activity through lactate-induced histone lactylation[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2021, 64(1): 115-25. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2020-0360oc |
| 52 | 段 然, 李青原, 冯 同. 代谢重编程在特发性肺纤维化发病中的作用[J]. 基础医学与临床, 2024, 44(6): 882-6. doi:10.16352/j.issn.1001-6325.2024.06.0882 |
| 53 | Hu XT, Xu QY, Wan HX, et al. PI3K-Akt-mTOR/PFKFB3 pathway mediated lung fibroblast aerobic glycolysis and collagen synthesis in lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Lab Invest, 2020, 100(6): 801-11. doi:10.1038/s41374-020-0404-9 |
| 54 | Coward WR, Watts K, Feghali-Bostwick CA, et al. Defective histone acetylation is responsible for the diminished expression of cyclooxygenase 2 in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2009, 29(15): 4325-39. doi:10.1128/mcb.01776-08 |
| 55 | 冯金龙, 罗 培, 袁业现, 等. 三羧酸循环中间产物调控炎症和免疫的研究进展[J]. 生命科学, 2022, 34(5): 532-42. |
| 56 | Kato K, Papageorgiou I, Shin YJ, et al. Lung-targeted delivery of dimethyl fumarate promotes the reversal of age-dependent established lung fibrosis[J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2022, 11(3): 492. doi:10.3390/antiox11030492 |
| 57 | Wang Y, Wu GR, Yue HH, et al. Kynurenine acts as a signaling molecule to attenuate pulmonary fibrosis by enhancing the AHR-PTEN axis[J]. J Adv Res, 2025, 71: 521-32. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2024.06.017 |
| 58 | Fang L, Chen HT, Kong RY, et al. Endogenous tryptophan metabolite 5-Methoxytryptophan inhibits pulmonary fibrosis by downregulating the TGF‑β/SMAD3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 260: 118399. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118399 |
| 59 | Hamanaka RB, O'Leary EM, Witt LJ, et al. Glutamine metabolism is required for collagen protein synthesis in lung fibroblasts[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2019, 61(5): 597-606. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2019-0008oc |
| 60 | Wang JC, Hu KL, Cai XY, et al. Targeting PI3K/AKT signaling for treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2022, 12(1): 18-32. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2021.07.023 |
| 61 | 刘 玲, 何振华. PI3K/Akt信号通路与肺纤维化[J]. 微生物学免疫学进展, 2017, 45(6): 80-4. doi:10.13309/j.cnki.pmi.2017.06.014 |
| 62 | Nie YJ, Sun L, Wu YX, et al. AKT2 regulates pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis via modulating macrophage activation[J]. J Immunol, 2017, 198(11): 4470-80. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1601503 |
| 63 | Guo LF, Wang QH, Zhang DQ. microRNA-4485 ameliorates severe influenza pneumonia via inhibition of the STAT3/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Oncol Lett, 2020, 20(5): 215. doi:10.3892/ol.2020.12078 |
| 64 | Goda C, Balli D, Black M, et al. Loss of FOXM1 in macrophages promotes pulmonary fibrosis by activating p38 MAPK signaling pathway[J]. PLoS Genet, 2020, 16(4): e1008692. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1008692 |
| 65 | Zhang XL, Zhang XY, Huang WM, et al. The role of heat shock proteins in the regulation of fibrotic diseases[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, 135: 111067. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111067 |
| 66 | Rajesh R, Atallah R, Bärnthaler T. Dysregulation of metabolic pathways in pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2023, 246: 108436. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108436 |
| 67 | 王 搏, 宋庆华, 唐会猛, 等. 博来霉素诱导的肺纤维化动物模型研究进展[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2023, 31(12): 1617-28. |
| [1] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | Liming WANG, Hongrui CHEN, Yan DU, Peng ZHAO, Yujie WANG, Yange TIAN, Xinguang LIU, Jiansheng LI. Yiqi Zishen Formula ameliorates inflammation in mice with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [3] | Yinfu ZHU, Yiran LI, Yi WANG, Yinger HUANG, Kunxiang GONG, Wenbo HAO, Lingling SUN. Therapeutic mechanism of hederagenin, an active component in Guizhi Fuling Pellets, against cervical cancer in nude mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [4] | Lijun HE, Xiaofei CHEN, Chenxin YAN, Lin SHI. Inhibitory effect of Fuzheng Huaji Decoction against non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and the possible molecular mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152. |
| [5] | Liping GUAN, Yan YAN, Xinyi LU, Zhifeng LI, Hui GAO, Dong CAO, Chenxi HOU, Jingyu ZENG, Xinyi LI, Yang ZHAO, Junjie WANG, Huilong FANG. Compound Centella asiatica formula alleviates Schistosoma japonicum-induced liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting the inflammation-fibrosis cascade via regulating the TLR4/MyD88 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [6] | Peipei TANG, Yong TAN, Yanyun YIN, Xiaowei NIE, Jingyu HUANG, Wenting ZUO, Yuling LI. Tiaozhou Ziyin recipe for treatment of premature ovarian insufficiency: efficacy, safety and mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| [7] | Xiaotao LIANG, Yifan XIONG, Xueqi LIU, Xiaoshan LIANG, Xiaoyu ZHU, Wei XIE. Huoxue Shufeng Granule alleviates central sensitization in chronic migraine mice via TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 986-994. |
| [8] | Niandong RAN, Jie LIU, Jian XU, Yongping ZHANG, Jiangtao GUO. n-butanol fraction of ethanol extract of Periploca forrestii Schltr.: its active components, targets and pathways for treating Alcheimer's disease in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 785-798. |
| [9] | Lixia YIN, Minzhu NIU, Keni ZHANG, Zhijun GENG, Jianguo HU, Jiangyan LI, Jing LI. Cimifugin ameliorates Crohn's disease-like colitis in mice by modulating Th-cell immune balance via inhibiting the MAPK pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 595-602. |
| [10] | Haonan¹ XU, Fang³ ZHANG, Yuying² HUANG, Qisheng⁴ YAO, Yueqin⁴ GUAN, Hao CHEN. Thesium chinense Turcz. alleviates antibiotic-associated diarrhea in mice by modulating gut microbiota structure and regulating the EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [11] | Junjie GAO, Kai YE, Jing WU. Quercetin inhibits proliferation and migration of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells by regulating TP53 gene [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 313-321. |
| [12] | Ying LIU, Borui LI, Yongcai LI, Lubo CHANG, Jiao WANG, Lin YANG, Yonggang YAN, Kai QV, Jiping LIU, Gang ZHANG, Xia SHEN. Jiawei Xiaoyao Pills improves depression-like behavior in rats by regulating neurotransmitters, inhibiting inflammation and oxidation and modulating intestinal flora [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 347-358. |
| [13] | Qiao CHU, Xiaona WANG, Jiaying XU, Huilin PENG, Yulin ZHAO, Jing ZHANG, Guoyu LU, Kai WANG. Pulsatilla saponin D inhibits invasion and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer cells through multiple targets and pathways [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [14] | Xiupeng LONG, Shun TAO, Shen YANG, Suyun LI, Libing RAO, Li LI, Zhe ZHANG. Quercetin improves heart failure by inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis via suppressing the MAPK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 187-196. |
| [15] | Meng XU, Lina CHEN, Jinyu WU, Lili LIU, Mei SHI, Hao ZHOU, Guoliang ZHANG. Mechanism of Hedyotis diffusa-Scutellaria barbata D. Don for treatment of primary liver cancer: analysis with network pharmacology, molecular docking and in vitro validation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 80-89. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||