Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (9): 1919-1926.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.11
Zhihui FENG1( ), Wenyue LI2, Mingxiu ZHANG1, Peipei WANG3, Yangyang SHUAI3, Hong ZHANG1(
), Wenyue LI2, Mingxiu ZHANG1, Peipei WANG3, Yangyang SHUAI3, Hong ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2025-02-05
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Hong ZHANG
E-mail:feng18740536649@163.com;zhanghong@chnu.edu.cn
Supported by:Zhihui FENG, Wenyue LI, Mingxiu ZHANG, Peipei WANG, Yangyang SHUAI, Hong ZHANG. Long noncoding RNA HClnc1 promotes proliferation and migration of liver cancer cells by targeting RBBP5/KAT2B complex to enhance ODC1 transcription[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1919-1926.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.11
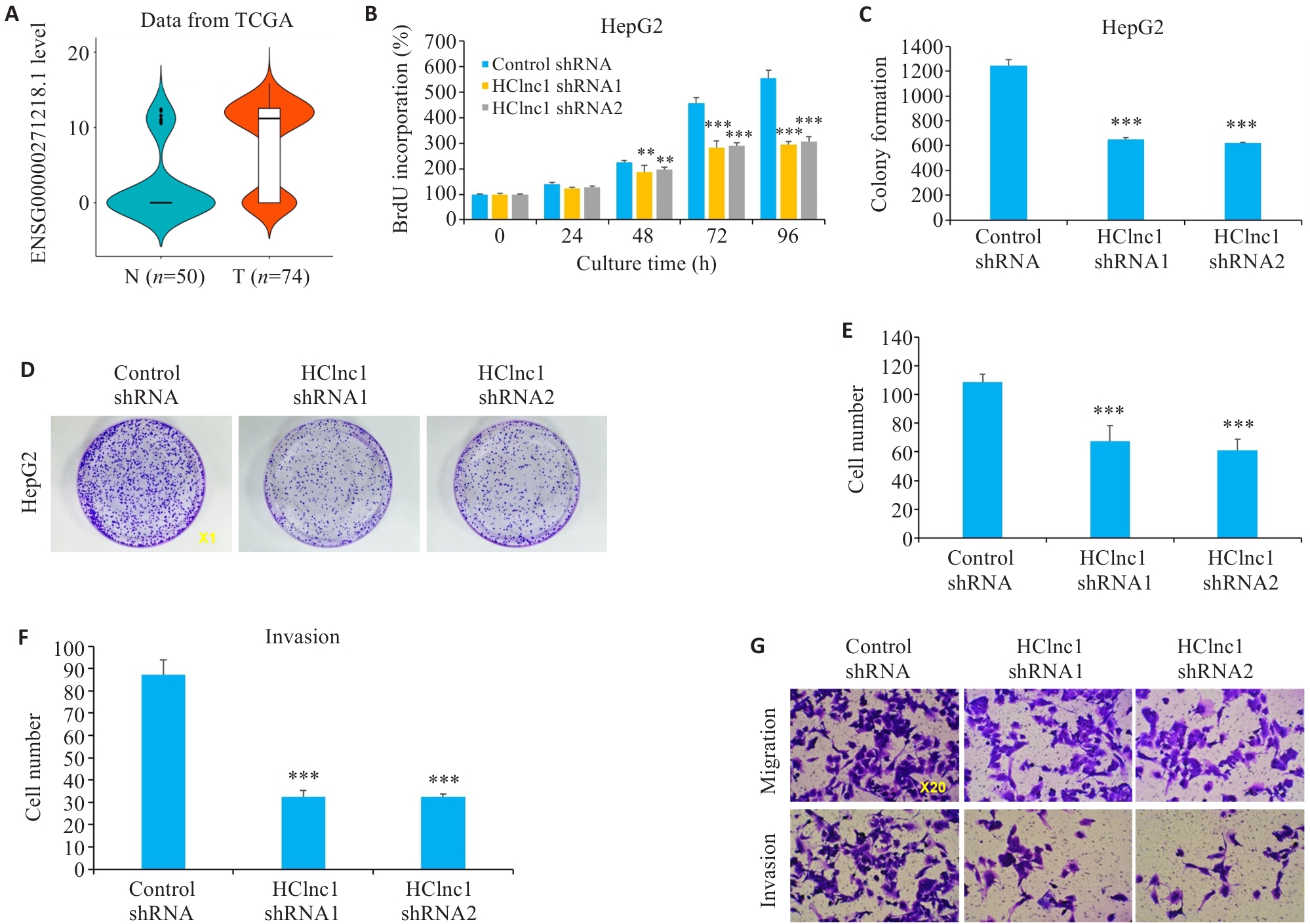
Fig.1 Effects of HClnc1 silencing on proliferation, invasion, and migration of liver cancer cells. A: Expression of HClnc1 in HCC (T) and adjacent regular tissues (N) from TCGA database. B: Proliferation of HepG2 cells assessed using BrdUrd assay. C, D: Colony formation of HepG2 cells (Original magnification:×1). E-G: Migration and invasion of HepG2 cells assessed using Transwell assay. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs control group.
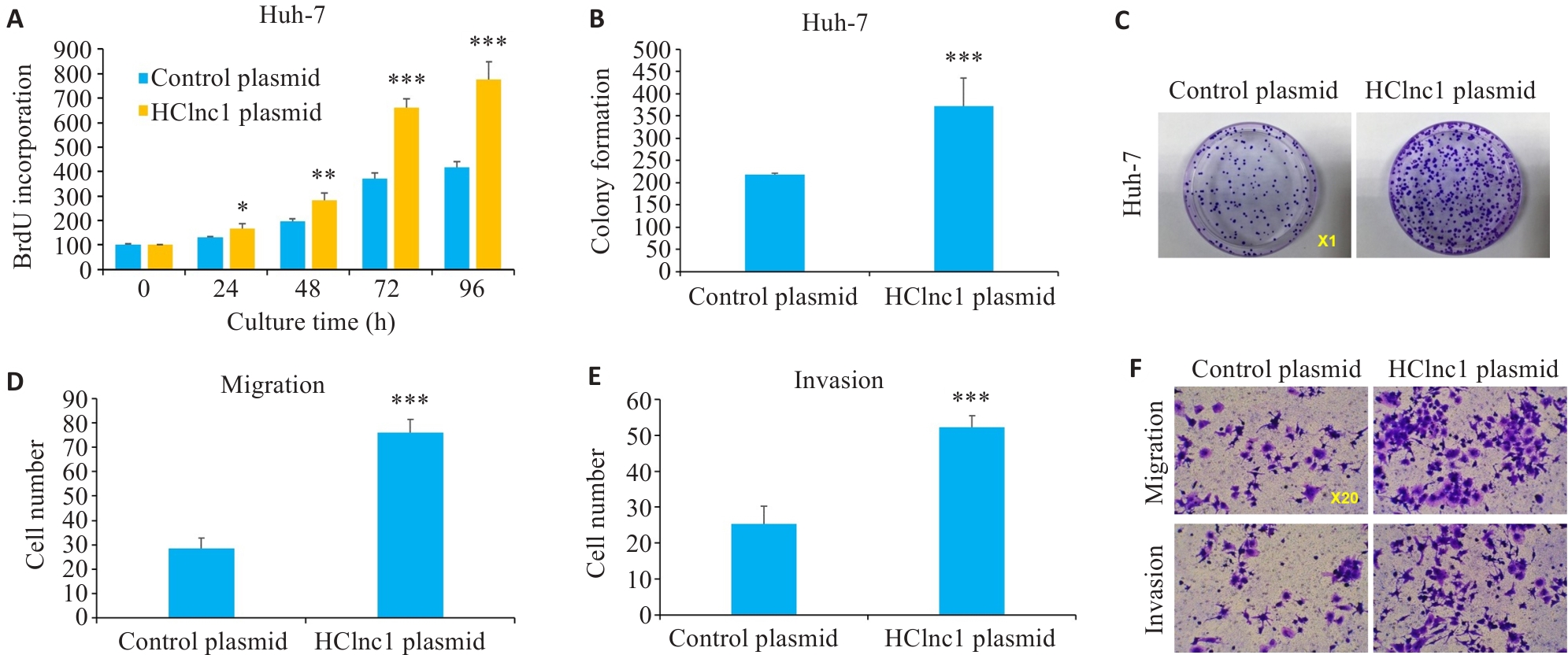
Fig.2 Effects of HClnc1 overexpression on proliferation, invasion, and migration of liver cancer cells. A: Proliferation of Huh7 cells assessed using BrdUrd assay. B, C: Colony formation of Huh7 cells. D-F: Migration and invasion of Huh7 cells assessed using Transwell assay. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs control group.
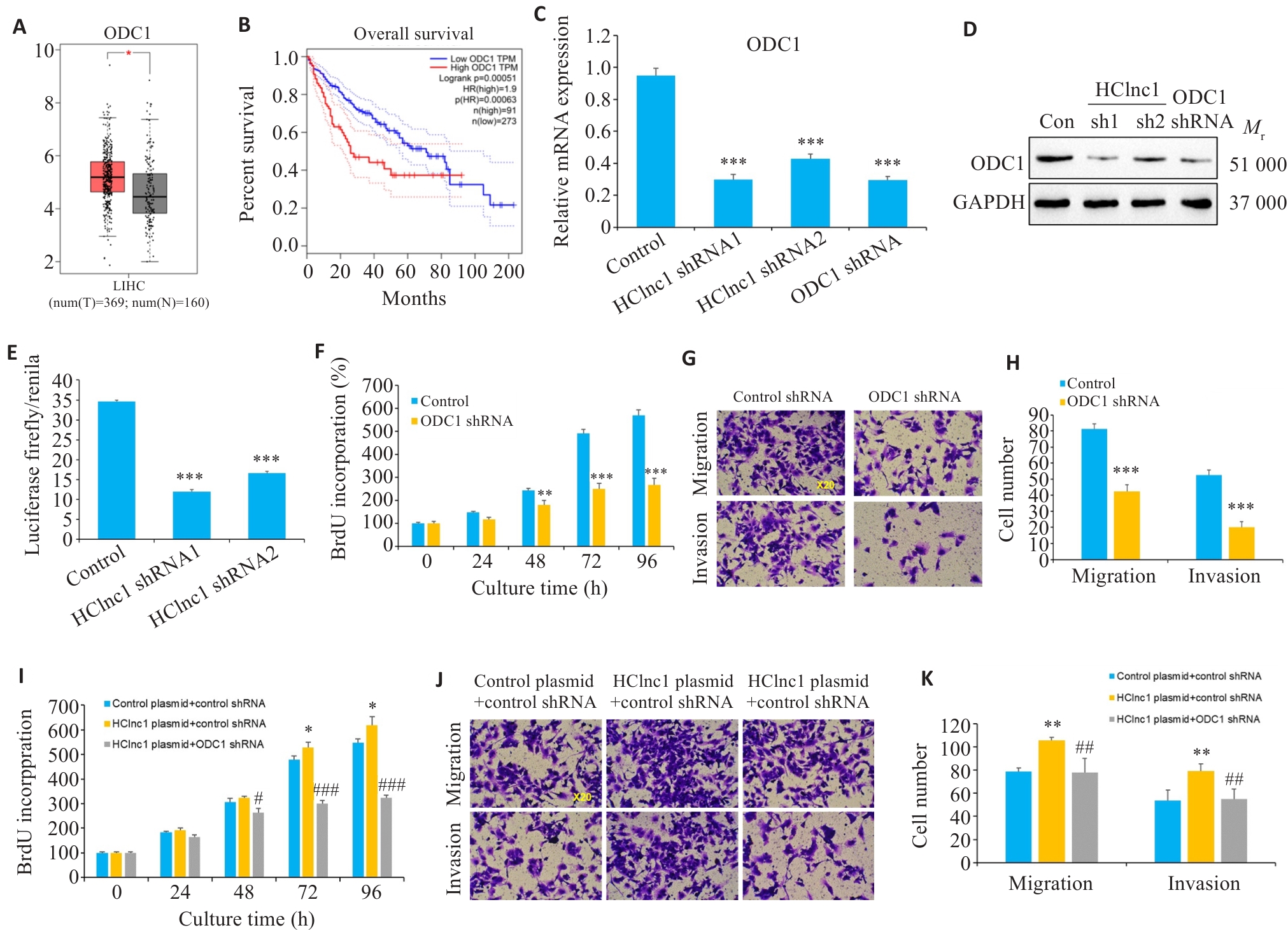
Fig.3 ODC1 knockdown reverses HClnc1-induced proliferation, invasion, and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. A, B: Gene expression levels of ODC1 in HCC and normal tissues from TCGA clinical samples and their correlation with survival. C, D: Relative mRNA and protein expression levels of ODC1 in HepG2 cells transfected with control, HClnc1 shRNA1/2, or ODC1 shRNA. E: ODC1 promoter activity assessed by luciferase activity assay. F: Proliferation of HepG2 cells assessed using BrdUrd assay. G-H: Migration and invasion of HepG2 cells assessed using Transwell assay (×20). I-K: HepG2 cells were co-transfected with control or HClnc1 plasmid plus control or ODC1 shRNA. I: Proliferation of HepG2 cells assessed using BrdUrd assay. J-K: Migration and invasion of HepG2 cells assessed using Transwell assay (×20). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs control or control plasmid +control shRNA. #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs HClnc1 plasmid+control shRNA.
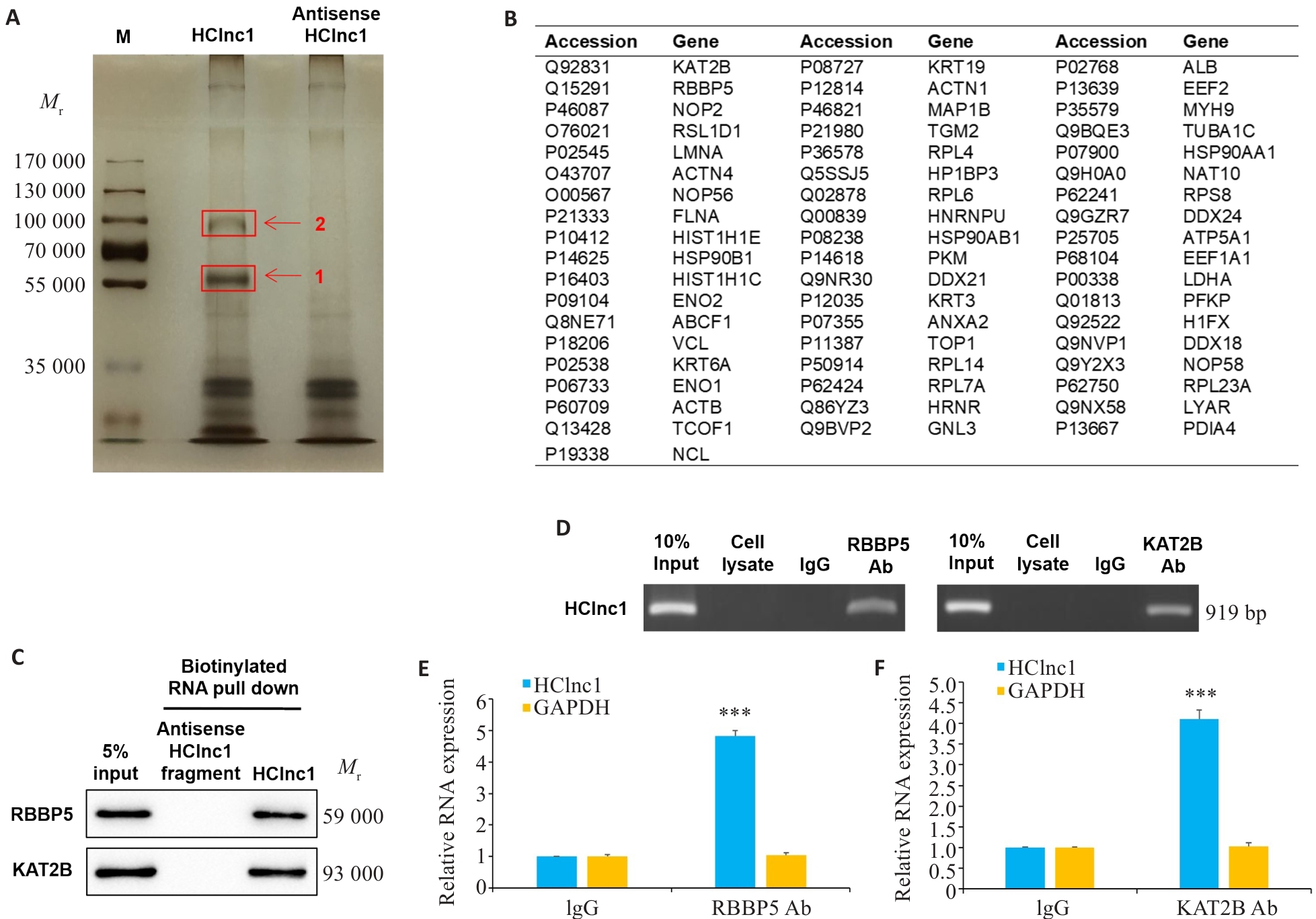
Fig.4 HClin1 binds to RBBP5 and KAT2B proteins. A: Silver staining of biotinylated HClnc1-associated proteins. The proteins were excised from the two HClnc1-specific bands (red arrows) for mass spectrometry analysis. B: 55 identified proteins. C: Western blotting of proteins from antisense HClnc1 and HClnc1 pull-down assay. D: RNA immunoprecipitation with anti-RBBP5 or anti-KAT2B antibody. E, F: Relative RNA levels of HClnc1 and GAPDH detected using real-time PCR assay. The nuclear fraction of HepG2 cells was immunoprecipitated with anti-RBBP5, anti-KAT2B, or IgG control antibodies. ***P<0.001 vs IgG.
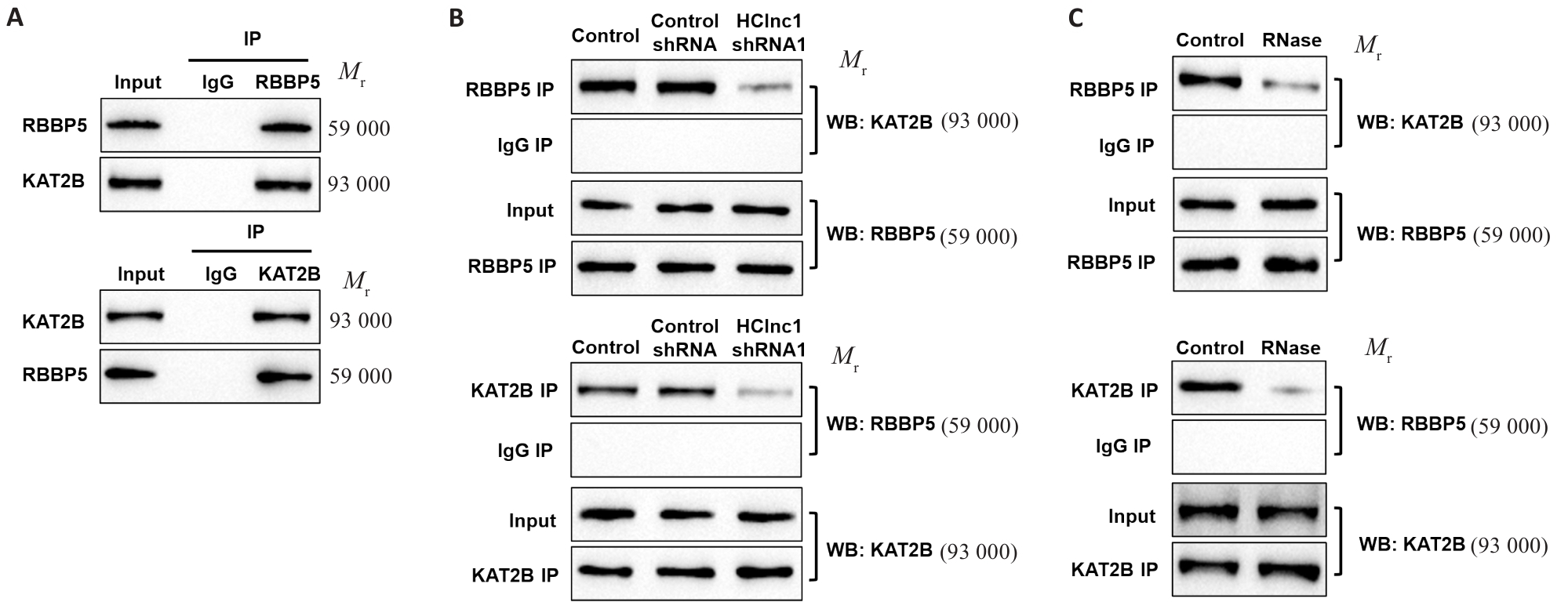
Fig.5 Knockdown of HClnc1 disrupts the protein-protein interaction between RBBP5 and KAT2B. A: Co-immunoprecipitation of RBBP5 and KAT2B in HepG2 cells. B, C: Interaction of RBBP5 and KAT2B after HClnc1 shRNA transfection (B) or RNase treatment (C).
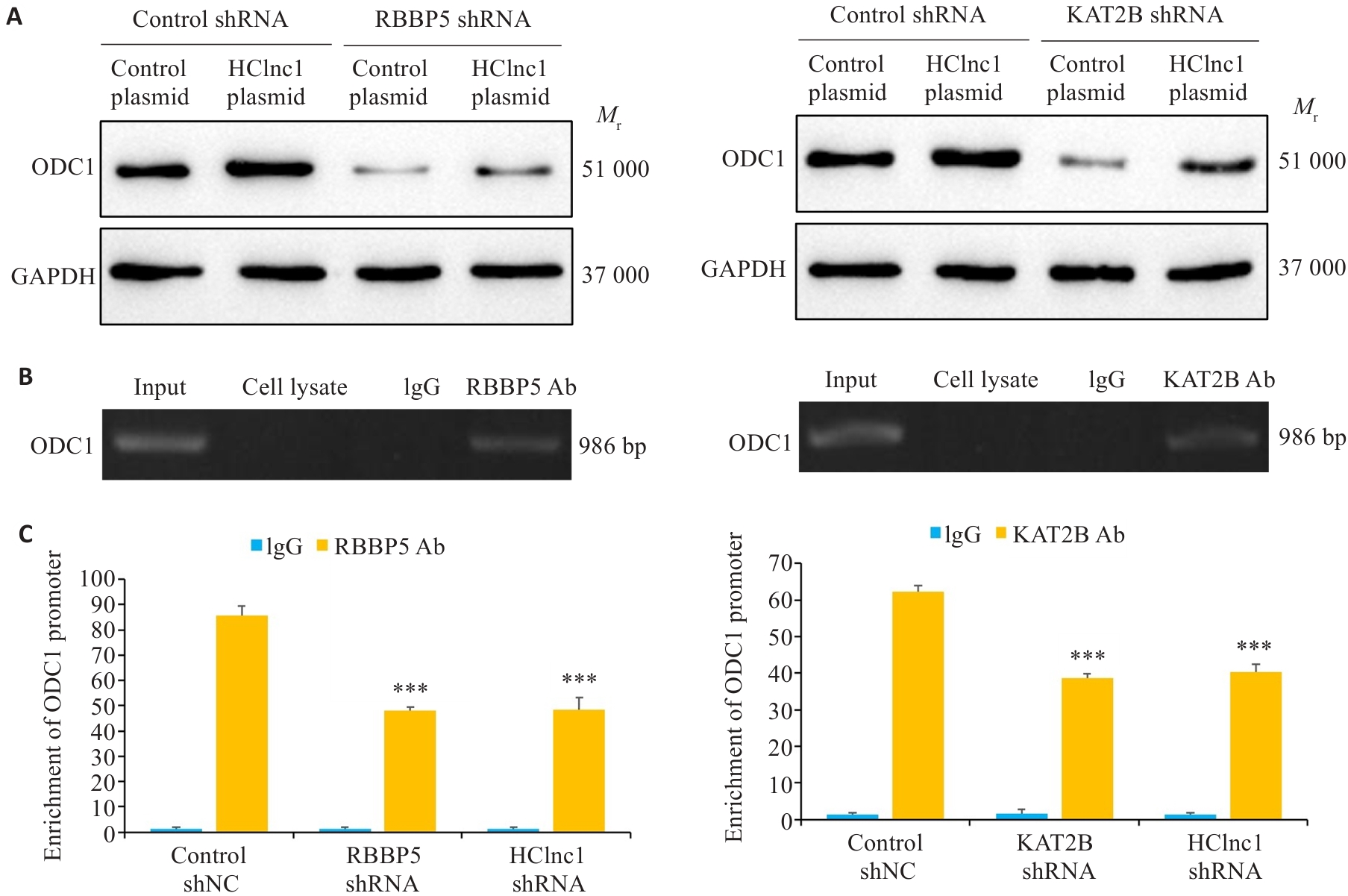
Fig.6 HClnc1 regulates the transcription of ODC1 by connecting RBBP5 and KAT2B. A: ODC1 protein levels in HepG2 cells transfected with control shRNA or RBBP5/KAT2B shRNA detected using Western blotting (with GAPDH as the internal control). B: Detection of ODC1 DNA in anti-RBBP5 or anti-KAT2B antibody-immunoprecipitated chromatin of HepG2 cells. C: ODC1 gene promoter levels in chromatin immunoprecipitation samples detected using real-time PCR analysis. ***P<0.001 vs control shNC or control plasmid.
| [1] | Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74(3): 229-63. doi:10.3322/caac.21834 |
| [2] | Han BF, Zheng RS, Zeng HM, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022[J]. J Natl Cancer Cent, 2024, 4(1): 47-53. doi:10.1016/j.jncc.2024.01.006 |
| [3] | Wen NY, Cai YL, Li FY, et al. The clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma worldwide: a concise review and comparison of current guidelines: 2022 update[J]. Biosci Trends, 2022, 16(1): 20-30. doi:10.5582/bst.2022.01061 |
| [4] | Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2021, 7: 6. doi:10.1038/s41572-020-00240-3 |
| [5] | Iyer MK, Niknafs YS, Malik R, et al. The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human transcriptome[J]. Nat Genet, 2015, 47(3): 199-208. doi:10.1038/ng.3192 |
| [6] | Schmitt AM, Chang HY. Long noncoding RNAs in cancer pathways[J]. Cancer Cell, 2016, 29(4): 452-63. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2016.03.010 |
| [7] | Kim MY. Long non-coding RNAs in cancer[J]. Non Coding RNA Res, 2019, 4(2): 45. doi:10.1016/j.ncrna.2019.02.003 |
| [8] | Coan M, Haefliger S, Ounzain S, et al. Targeting and engineering long non-coding RNAs for cancer therapy[J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2024, 25(8): 578-95. doi:10.1038/s41576-024-00693-2 |
| [9] | Huang Z, Zhou JK, Peng Y, et al. The role of long noncoding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Mol Cancer, 2020, 19(1): 77. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01188-4 |
| [10] | Peng L, Yuan XQ, Zhang CY, et al. The emergence of long non-coding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: an update[J]. J Cancer, 2018, 9(14): 2549-58. doi:10.7150/jca.24560 |
| [11] | Klingenberg M, Matsuda A, Diederichs S, et al. Non-coding RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma: mechanisms, biomarkers and therapeutic targets[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 67(3): 603-18. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2017.04.009 |
| [12] | 李菲凡, 向俊馨, 刘佳慧, 等. LncRNA FEZF1-AS1通过miR-130a-5p/CCND1轴促进非小细胞肺癌发展的分子机制研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 841-50. |
| [13] | 冯 雯, 赖跃兴, 王 静, 等. 长链非编码RNA ABHD11-AS1促进胃癌细胞糖酵解并加速肿瘤恶性进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1485-92. |
| [14] | Deng YQ, Gao M, Lu D, et al. Compound-composed Chinese medicine of Huachansu triggers apoptosis of gastric cancer cells through increase of reactive oxygen species levels and suppression of proteasome activities[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 123: 155169. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155169 |
| [15] | Sun TT, He J, Liang Q, et al. LncRNA GClnc1 promotes gastric carcinogenesis and may act as a modular scaffold of WDR5 and KAT2A complexes to specify the histone modification pattern[J]. Cancer Discov, 2016, 6(7): 784-801. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.cd-15-0921 |
| [16] | Peng W, Fan H. Long noncoding RNA CCHE1 indicates a poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes carcinogenesis via activation of the ERK/MAPK pathway[J]. Biomed Pharm-acother, 2016, 83: 450-5. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2016.06.056 |
| [17] | Chen ZL, Yu C, Zhan L, et al. LncRNA CRNDE promotes hepatic carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion by suppressing miR-384[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2016, 6(10): 2299-309. |
| [18] | Huang RY, Wang XC, Zhang WJ, et al. Down-regulation of LncRNA DGCR5 correlates with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2016, 40(3/4): 707-15. doi:10.1159/000452582 |
| [19] | Xiao CH, Wang C, Cheng SJ, et al. The significance of low levels of LINC RP1130-1 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Biosci Trends, 2016, 10(5): 378-85. doi:10.5582/bst.2016.01123 |
| [20] | Fei MM, Li XY, Liang SH, et al. LncRNA PWRN1 inhibits the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by activating PKM2 activity[J]. Cancer Lett, 2024, 584: 216620. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2024.216620 |
| [21] | Zhang X, Li ZL, Nie HZ, et al. The IGF2BP2-lncRNA TRPC7-AS1 axis promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and invasion[J]. Cell Signal, 2024, 117: 111078. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111078 |
| [22] | Cha H, Kim M, Ahn N, et al. Role of UPF1 in lncRNA-HEIH regulation for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2024, 56(2): 344-54. doi:10.1038/s12276-024-01158-6 |
| [23] | Ma K, Chu JH, Liu YF, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma LINC01116 outcompetes T cells for linoleic acid and accelerates tumor progression[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2024, 11(21): e2400676. doi:10.1002/advs.202400676 |
| [24] | Li XY, Liang SH, Fei MM, et al. LncRNA CRNDE drives the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by inducing the immunosuppressive niche[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2024, 20(2): 718-32. doi:10.7150/ijbs.85471 |
| [25] | Casero RA, Murray Stewart T, Pegg AE. Polyamine metabolism and cancer: treatments, challenges and opportunities[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2018, 18(11): 681-95. doi:10.1038/s41568-018-0050-3 |
| [26] | Zhang XP, Zou WB, Li ZQ, et al. The heterogeneity of cellular metabolism in the tumour microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumour thrombus[J]. Cell Prolif, 2025, 58(1): e13738. doi:10.1111/cpr.13738 |
| [27] | Ji GY, Liu J, Zhao ZQ, et al. Polyamine anabolism promotes chemotherapy-induced breast cancer stem cell enrichment[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2024, 11(40): e2404853. doi:10.1002/advs.202470240 |
| [28] | Li YP, Huang ZJ, He QK, et al. Pirin promotes the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer by increasing ODC1 to suppress autophagy[J]. J Proteome Res, 2024, 23(5): 1713-24. doi:10.1021/acs.jproteome.3c00871 |
| [29] | Ye Z, Zeng ZR, Shen YY, et al. ODC1 promotes proliferation and mobility via the AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway and modulation of acidotic microenvironment in human hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2019, 12: 4081-92. doi:10.2147/ott.s198341 |
| [30] | Meng XQ, Peng JX, Xie XS, et al. Roles of lncRNA LVBU in regulating urea cycle/polyamine synthesis axis to promote colorectal carcinoma progression[J]. Oncogene, 2022, 41(36): 4231-43. doi:10.1038/s41388-022-02413-8 |
| [31] | Choi Y, Oh ST, Won MA, et al. Targeting ODC1 inhibits tumor growth through reduction of lipid metabolism in human hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2016, 478(4): 1674-81. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.09.002 |
| [32] | Zhang HX, Li XR, Liu ZY, et al. Elevated expression of HIGD1A drives hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating polyamine metabolism through c-Myc-ODC1 nexus[J]. Cancer Metab, 2024, 12(1): 7. doi:10.1186/s40170-024-00334-6 |
| [33] | Zhang GX, Lan YJ, Xie AM, et al. Comprehensive analysis of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA)-chromatin interactions reveals lncRNA functions dependent on binding diverse regulatory elements[J]. J Biol Chem, 2019, 294(43): 15613-22. doi:10.1074/jbc.ra119.008732 |
| [34] | Zhang P, Chaturvedi CP, Tremblay V, et al. A phosphorylation switch on RbBP5 regulates histone H3 Lys4 methylation[J]. Genes Dev, 2015, 29(2): 123-8. doi:10.1101/gad.254870.114 |
| [35] | Fournier M, Orpinell M, Grauffel C, et al. KAT2A/KAT2B-targeted acetylome reveals a role for PLK4 acetylation in preventing centrosome amplification[J]. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 13227. doi:10.1038/ncomms13227 |
| [36] | He BY, Pan HL, Zheng FQ, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00930 promotes PFKFB3-mediated tumor glycolysis and cell proliferation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2022, 41(1): 77. doi:10.1186/s13046-022-02282-9 |
| [37] | Fang M, Zhang MJ, Wang YQ, et al. Long noncoding RNA AFAP1-AS1 is a critical regulator of nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumo-rigenicity[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 601055. doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.601055 |
| [1] | Tianli SONG, Yimin WANG, Tong SUN, Xu LIU, Sheng HUANG, Yun RAN. Zheng Gan Decoction inhibits diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats by activating the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 799-809. |
| [2] | Jinhua ZOU, Hui WANG, Dongyan ZHANG. SLC1A5 overexpression accelerates progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting M2 polarization of macrophages [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 269-284. |
| [3] | Meng XU, Lina CHEN, Jinyu WU, Lili LIU, Mei SHI, Hao ZHOU, Guoliang ZHANG. Mechanism of Hedyotis diffusa-Scutellaria barbata D. Don for treatment of primary liver cancer: analysis with network pharmacology, molecular docking and in vitro validation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 80-89. |
| [4] | Liping ZHANG, Xijuan LIU, Xiao HU, Jiali WANG, Xihe YU, Guoliang LI, Haimin YOU, Qizhou ZHANG, Haibo ZHANG. Efficacy and safety of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization followed by hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy combined with TKI and PD-1 inhibitors as first-line treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1831-1838. |
| [5] | Qianyi CHEN, Shuhan SHANG, Huan LU, Sisi LI, Zhimian SUN, Xirui FAN, Zhilin QI. Calenduloside E inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and migration by down-regulating GPX4 and SLC7A11 expression through the autophagy pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1327-1335. |
| [6] | Huaxing HE, Lulin LIU, Yingyin LIU, Nachuan CHEN, Suxia SUN. Sodium butyrate and sorafenib synergistically inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma cells possibly by inducing ferroptosis through inhibiting YAP [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1425-1430. |
| [7] | Pengcheng LIU, Lijuan LOU, Xia LIU, Jian WANG, Ying JIANG. A risk scoring model based on M2 macrophage-related genes for predicting prognosis of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 827-840. |
| [8] | CHEN Hao, LI Zhenhan, WANG Mingting, LU Linming, TANG Qianli, LUO Liangping. High expression of UBE2S promotes progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by increasing cancer cell stemness [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 455-464. |
| [9] | ZHONG Weixiong, LIANG Fangrong, YANG Ruimeng, ZHEN Xin. Prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma based on multi-phase dynamic enhanced CT radiomics feature and multi-classifier hierarchical fusion model [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 260-269. |
| [10] | Jiawei HU, Fang DU, Lu DING, Luxiang WANG, Weifeng ZHAO. Risk assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis B-related cirrhosis and hypertension: a propensity score matching-based retrospective cohort study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2243-2249. |
| [11] | Cuiyuan HUANG, Yunping SUN, Wenqiang LI, Li LIU, Wei WANG, Jing ZHANG. Nlrp6 overexpression inhibits lipid synthesis to suppress proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by regulating the AMPK-Srebp1c axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(10): 1910-1917. |
| [12] | Xirui FAN, Zhilin QI, Yuanjie DENG, Zihan YANG, Li SUN, Guohao LI, Juanjuan LIANG, Fei WU, Liwen YUAN. LncRNA MAGI2-AS3 enhances cisplatin sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating the miR-1269a/PTEN/AKT pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(10): 2033-2043. |
| [13] | ZHU Quan, HUANG Baisheng, WEI Leiyan, LUO Qizhi. Overexpression of LncRNA MEG3 promotes ferroptosis and enhances chemotherapy sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to cisplatin [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 17-24. |
| [14] | CHEN Weiren, DU Hui, SHA Yuan, ZHOU Yujie, LIANG Jing, CHEN Yundai, MA Qian, WU Xueping, QIAN Geng. Long noncoding RNA H19 promotes vascular calcification by repressing the Bax inhibitor 1/optic atrophy 1 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(9): 1469-1475. |
| [15] | CAO Danping, CAI Juan, LI Yanna, DONG Runyu, WANG Zhixiong, ZUO Xueliang. TMEM64 is highly expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes tumor cell proliferation and invasion [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(8): 1345-1355. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||